2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
|
|
|
- Conrad Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as used in physiology? 2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system? 3. What are the principal organs of the respiratory system? Describe the patterns of flow within the lungs and list the different segments. 4. What is the difference between the conducting division and the respiratory division of the respiratory system? What is the difference between the upper and lower respiratory tract? 5. What is the histology of the cells that line the nasal cavity? What is the function and structure of the olfactory mucosa? What accessory structures associated with the nasal cavity are found in the lamina propria? 6. What is the structure of the erectile tissue associated with inferior choncha and explain the function of this tissue? Why is it important? 7. What two structures define the superior and inferior margins of the pharynx? What are the three regions within the pharynx? Indicate prominent structures: 8. What happens to the larynx and epiglottis when you swallow? 9. What is the relative relationship between the vestibular folds and the vocal cords? What is the opening between the vocal cords called? 10. What is the name of the structure which separates the upper and lower respiratory system? 11. The common term used to describe the trachea is windpipe. a. How long is the trachea? b. What is the function of the hyaline C rings? c. What is the histology of the lining of the trachea? d. What is the mucociliary escalator? 12. You will study in detail the anatomy of the lung in lab. Note: a. What is the hilum? b. How many lobes are in the right and left lung? c. What is the cardiac impression? d. What is the inferior end of the trachea called?
2 13. List all the segments of the bronchial tree between the primary bronchi and the alveolus. 14. The bronchial tree: a. In which bronchi will aspirated foreign objects more likely to lodge? b. When do you see the absence of C-shaped hyaline cartilages? c. What is the difference between secondary and tertiary bronchi? d. How do pulmonary arteries make their way through the lungs spongy parenchyma? e. What artery provides nutrients to the bronchial tree? f. What is a pulmonary lobule? g. How does the histology change between the terminal bronchioles and the respiratory bronchioles? h. What is the relationship between an alveolar duct and alveolar sacs? 15. Each human lung is composed of 150 million alveoli which provide about 70 square meters of surface area for diffusion. a. What type of cell form the walls of the alveolus? b. What is pulmonary surfactant? c. Where do you find alveolar macrophages? d. How many alveolar macrophage die in a day and where do they end up? e. What is the respiratory membrane? 16. What is the difference between the parietal and visceral pleurae? a. What is the pleural cavity? b. What is the function of the pleural fluid? 17. What defines a respiratory cycle? a. What is the difference between quiet and forced respiration? b. What do you need for pulmonary ventilation? 18. What type of muscle do we have in the lungs? a. Where within the lungs do you find this muscle? b. What is the function of this muscle? 19 What type of muscle is responsible for pulmonary ventilation? a. What is the prime mover of pulmonary ventilation? Describe this muscle s position when at rest. b. What muscles are synergists to the prime mover of pulmonary ventilation? c. What is the function of an accessory muscle of respiration? d. What accessory muscles contract during deep inspiration? Explain their function. e. What accessory muscles contract during forced expiration? Explain their function.
3 19. What is the Valsalva maneuver? What functions does this maneuver aid? 20. How would you describe breathing? Is it voluntary or involuntary? 21. Where is the respiratory center located? 22. How much oxygen is required during periods of rest? During strenuous exercise? 23. What are the three main components of the respiratory control center? 24. What is the function of the dorsal respiratory group? What types of local neural circuits are found in the dorsal respiratory group? 25. How many seconds is the discharge by inspiratory neurons? 26. How long is the total respiratory cycle during quiet breathing? 27. What is the function of the ventral respiratory group? 28. What is the Botzinger complex? 29. What is the function of the pontine respiratory group? 30. What type of sensory information may influence the ventral respiratory group? 31. Where are inspiratory neurons located? How long do they discharge? 32. Where is the pontine respiratory center located? 33. What higher brain centers synapse in the pontine respiratory center? 34. Pain, anxiety and other emotions can influence the respiratory centers. The origin of these events are said to be of a higher order within the brain. Where do these events originate? 35. Central and peripheral receptors monitor different types of stimuli and send this information to the brainstem respiratory centers. List four different type of receptors and explain their mechanism of action. 25 Where is the voluntary control of breathing located? Can you hold your breath until you die? What role does the corticospinal tract play in voluntary breathing? 26 What factors influence respiratory airflow? What does one atmosphere measure? What happens when intrapulmonary pressure is greater or less than the atmospheric pressure?
4 27 To understand inspiration and expiration you need to review the anatomy of the pleural cavity. a. What is the relationship between the visceral and parietal pleura? b. What is between the two membranes? c. What is the space between the two membranes called? d. What is the space within the lung tissue called? e. How does body temperature influence inspiration? 28 Relaxed expiration is a passive process. What tissue type makes relaxed expiration passive? Where do you find this tissue? 29 What is pneumothorax? 30 What is atelectasis? 31 Explain how resistance influences airflow: a. How do epinephrine and the sympathetic neurotransmitter (norepinephrine) influence pulmonary resistance? b. How do histamine and parasympathetic nerves (acetylcholine) influence pulmonary resistance? c. How do tuberculosis and black lung disease influence pulmonary resistance? d. What role do hydrogen bonds play in pulmonary resistance? e. What is surfactant? 32 What are the four different respiratory volumes? 33 What is the difference between respiratory volumes and respiratory capacities? 34 What is the alveolar ventilation rate? How do you determine AVR? 35 What is the difference between anatomical and physiological dead space? 36 What is the difference between restrictive and obstructive disorders? 37 What is the difference between minute respiratory volume and maximum voluntary ventilation? 38 Under what condition would you experience maximum voluntary ventilation? 39 How is a cough different than a sneeze? 40 What are the four main gases in inspired air? 41 What does the partial pressure of a gas indicate?
5 42 What is the difference between external (pulmonary gas exchange) respiration and internal (systemic gas exchange) respiration? 43 What is alveolar gas exchange and where does it occur? 44 What variables affect gas exchange? 45 Ventilation-perfusion coupling is an important concept is respiratory physiology. When an area of the lung is well ventilated, what happens to the associated capillaries? 46 When mucous obstructs a bronchiole and prevents an area of the lung to be ventilated, what happens to the capillaries in this area? How does this compare to hypoxia and the local control of the capillary network in the systemic circulation? 47 We have already studied the role that RBCs and hemoglobin play in the transport of oxygen. What percent of oxygen is transported by hemoglobin? 48 How many oxygen molecules can one hemoglobin molecule carry? 49 What is the difference between oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin? 50 Why is carbon monoxide such a dangerous poison? 51 How is carbon dioxide transported? Be able to rank the three different transport methods. 52 How do the events associated with blood gasses differ during systemic gas exchange and alveolar gas exchange? Be able to associate these terms with your explanation: (carbonic anhydrase, chloride-bicarbonate exchanger, chloride shift, venous reserve) 53 Ultimately, pulmonary ventilation is adjusted to maintain the ph of the brain. If hydrogen ions can not cross the blood brain barrier, then where does the acid come from that drives the chemoreceptors in the medulla oblongata? 54 How is acidosis and alkalosis related to hypercapnia and hypocapnia? 55 What are the corrective homeostatic responses to acidosis and alkalosis? 56 Under normal conditions, the partial pressure of oxygen has little effect on respiration. What conditions would result in the partial pressure of oxygen becoming the main driver of respiration? What is this condition called? 57 What is hypoxia? What is an indicator of hypoxia? Define the following terms : (hypoxemic hypoxia, ischemic hypoxia, anemic hypoxia, histotoxic hypoxia)
6 46 What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? 47 What are the three most common COPDs?
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System
 Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Gas exchange Regulate blood ph Voice production Olfaction Innate immunity
 Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Control of Respiration
 Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1
 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Respiratory Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Respiratory Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Gas exchange Gas exchange in the lungs (to capillaries) occurs by diffusion across respiratory membrane due to differences in partial
Respiratory Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Gas exchange Gas exchange in the lungs (to capillaries) occurs by diffusion across respiratory membrane due to differences in partial
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Respiration. Functions Anatomy
 Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
otorhinolaryngology -the study of the structure, function, and disorders of the ears, nose, and throat
 89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
Unit 13: The Respiratory System
 Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
The Respiratory System PROGRAM STUDI S1 KEPERAWATAN FAKULTAS ILMU KESEHATAN UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH MALANG 2014
 The Respiratory System PROGRAM STUDI S1 KEPERAWATAN FAKULTAS ILMU KESEHATAN UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH MALANG 2014 5 Functions of the Respiratory System 1. Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between
The Respiratory System PROGRAM STUDI S1 KEPERAWATAN FAKULTAS ILMU KESEHATAN UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH MALANG 2014 5 Functions of the Respiratory System 1. Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
MASTERY TEST. 3. Carbon dioxide combines with water to form. An excess of COz will cause the blood ph to (increaseldecrease).
 MASTERY TEST Now take the mastery test. Do not guess. Some questions may have more than one correct answer. As soon as you complete the test, correct it. Note your successes and failures so that you can
MASTERY TEST Now take the mastery test. Do not guess. Some questions may have more than one correct answer. As soon as you complete the test, correct it. Note your successes and failures so that you can
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Chapter 14 Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 14 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 14 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATION. a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen. c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy
 RESPIRATION 01. The process of respiration is concerned with a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy 02. The narrowest and most numerous tubes
RESPIRATION 01. The process of respiration is concerned with a) In take of oxygen b) Liberation of oxygen c) Liberation of carbon dioxide d) Liberation of energy 02. The narrowest and most numerous tubes
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
The respiratory system
 Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE. Learning Objectives. Pronunciation Guide Click on the megaphone icon before each item to hear the pronunciation.
 ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
? Pulmonary Respiratory System
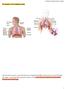 The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
3. Which of the following would be inconsistent with respiratory alkalosis? A. ph = 7.57 B. PaCO = 30 mm Hg C. ph = 7.63 D.
 Pilbeam: Mechanical Ventilation, 4 th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The diffusion of carbon dioxide across the alveolar capillary membrane is. A.
Pilbeam: Mechanical Ventilation, 4 th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The diffusion of carbon dioxide across the alveolar capillary membrane is. A.
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology
 Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
3. Which statement is false about anatomical dead space?
 Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Regulation of respiration
 Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
a. dissolved gases b. nutrients c. globulins d. surfactants e. hormones
 Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
The Respiratory System
 Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
The Respiratory System
 23 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Respiratory System Learning Outcomes 23-1 Describe the primary
23 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Respiratory System Learning Outcomes 23-1 Describe the primary
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure.
 B. 10 Applied Respiratory Physiology a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure. Intermittent positive pressure ventilation
B. 10 Applied Respiratory Physiology a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure. Intermittent positive pressure ventilation
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
