Page 1 L 58. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION
|
|
|
- Joan Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver Readings: Purves, 2012, 5 th edition. p 391 Upper motor neuron control; p 440 Horizontal movement of the eyes; p 464 Central control of visceral motor function; pp Autonomic regulation of cardiovascular and bladder function; pp Reticular activating system, circuits for sleep; pp Integration of emotional behavior Kiernan JA (2009) Barr's the Human Nervous System: an Anatomical Viewpoint, 9th ed., ISBN: Allen Brain Atlas, online Waxman SG (2003) Clinical Neuroanatomy, Lange Med Books SUMMARY The reticular formation is in the central part of the brainstem where the neurons and fibers present a netlike (reticular) appearance in transverse sections. All parts of the reticular formation share this property in their appearance. So, it suggests a general or even random organization without distinct nuclear structures or specialized neural circuits. However, this is only partly true. Many parts of the reticular formation form interconnections widely within the central nervous system. On the other hand, other parts of the reticular formation participate in specific neural circuits with specific function. The clinical significance of the reticular formation is that it is involved in many neural circuits including cranial nerve reflexes, autonomic control of heart rate, breathing, and micturition, gaze control, circuits for attention and sleep, and the general integration of motor and emotional responses. GENERAL FEATURES OF THE RETICULAR FORMATION Diffuse appearance usually identified as the area between the brainstem nuclei o Neuron groups are indistinct Cells at raphe Very large neurons (gigantocellular) tend to be at paramedian location in medulla and pons Smaller cells (parvocellular) tend to be lateral and involve in more local functions GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE RETICULAR FORMATION Everyone should be able to identify the location of: Mesencephalic RF Pontine RF Medullary RF Important Individual Nuclei in the Reticular Formation That You Should Know Raphe nuclei at the midline o Neurons use serotonin as a neurotransmitter
2 Page 2 L 58 Central reticular nuclei, gigantocellular nucleus of the central pons and medulla, not including the midline raphe o Includes paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) o Neurons use GABA and glutamate as neurotransmitters Parvocellular nuclei o Medulla, pons, and midbrain o Around nucleus ambiguus, facial, trigeminal nuclei, oculomotor nuclei o Neurons use GABA and glutamate as neurotransmitters Cholinergic nuclei o In dorsal and rostral pons o Neurons using acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter o Not motor neurons (that are also cholinergic) o Other important non motor cholinergic neurons are in the basal forebrain Locus coeruleus o Rostral pons o Catecholamine nuclei o Neurons using norepinephrine as neurotransmitter FUNCTIONS OF THE RETICULAR FORMATION Short local connections of the reticular formation o Cranial nerve reflexes o Central pattern generators o Cerebellum input & output o Gaze centers within brainstem Long connections of the reticular formation o Mescencephalic and rostral pontine RF modulates forebrain activity o Medullary and caudal pontine RF modulate somatic and visceral motor activity SHORT CONNECTIONS Short Local Connections between Cranial Nerves for Reflexes Lateral parvocellular reticular formation around cranial nerve nuclei Gag reflex RF connects sensory nerve 9 (spinal trigeminal and solitary tr) with motor 9 (nucleus ambiguous) Corneal blink reflex RF connects spinal trigeminal with facial motor. Acoustic startle reflex input via 8 th nerve from ear and output via reticular central pathway. (This one involves some longer pathways mentioned below.) Central Pattern Generators Central Pattern Generator for Chewing control the rhythm of chewing o Location in parvocellular RF Surrounds motor trigeminal nucleus Caudal to facial nuc. o Central Pattern Generator for Chewing Afferents Trigeminal (lips, oral cavity, muscle spindles in muscles that elevate mandible) Cortical masticatory area in M1
3 Page 3 L 58 Central pattern generator Trigeminal motor for jaw muscles Jaw closing rostral 2/3 of Motor V Jaw opening ventromedial middle 1/3 and caudal Motor V Central Pattern Generator for Respiration o Respiratory regions in parvocellular RF near nuc. Ambiguus o Pattern generator controls cycle of active inspiration o Inputs modulate breathing pattern o Outputs control diaphragm and other muscles Cerebellar Input and Output: Pre Cerebellar RF Nuclei Inputs to cerebellum from reticular formation o Lateral reticular nucleus o Paramedian reticular nucleus o Pontine reticulotegmental nucleus Output from cerebellum o To Spinocerebellar tract (Vermal cortex > Fastigial nucleus > RF) o Vestibulocerebellar (Flocculus Nodulus > Fastigial + Vestibular > RF Gaze Centers Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) o Gigantocellular reticular formation just lateral to midline raphe o Horizontal gaze center controlling abducens nucleus motor neurons and intranuclear neurons Rostral interstitial midbrain reticular formation (rimrf) o Lateral to oculomotor nucleus in rostral midbrain o Vertical gaze center controlling muscles of oculomotor nucleus via posterior commissure. LONG CONNECTIONS Long Connection Circuitry of RF Central Medial Nuclei including gigantocellular, central medullary, caudal pontine, and oral pontine Neurons o Large dendritic fields o Dendritic fields are heavily overlapping Inputs o Many sources o Highly overlapping (not topographic) Outputs o Axons may be ascending or descending or both o Axons make local and long connections o Many targets o Long distances Long connections of the reticular formation o Mescencephalic and rostral pontine RF modulates forebrain activity o Medullary and caudal pontine RF modulate somatic and visceral motor activity Whole Body Reactions and Reflexes: Central Group of Reticular Nuclei
4 Page 4 L 58 Large neurons in the central reticular nuclei in the pons and medulla. Cuneiform nucleus of the midbrain. Most neurons in the reticular formation use glutamate or GABA as a neurotransmitter. Precise identity not known in human and less known about primate. Inputs from all sensory systems, including auditory, somatosensory, superior colliculus Origin of the reticulospinal tract control of muscle tone and posture Origin of the reticulothalamic tract. Inputs to intralaminar nuclei and other thalamic nuclei. Important for o Startle o Posture o Muscle tone o Attention & consciousness Raphe Nuclei: Serotonergic Neurons Raphe nuclei use serotonin as a neurotransmitter. (Barr, Fig ) o Serotonin is synthesized from the amino acid L tryptophan. The metabolic pathway consists of two enzymes: tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) and amino acid decarboxylase (DDC). TPH2 is a brain specific isoform, and the TPH mediated reaction is the rate limiting step. o In the Allen brain atlas, see the P56 mouse brain, medulla section 58 and midbrain section 138: map.org/data/tph2/ /thumbnails.html Identify the raphe nuclei at the level of the pons and midbrain. Inputs from periaqueductal gray and limbic forebrain. Outputs o Descending outputs to the dorsal horn of spinal cord. This pathway is important for the conscious suppression of pain. o Descending modulation of the autonomic nervous system. o Ascending outputs of the raphe project to the forebrain and are active in deep sleep. This suggests that they suppress thalamic and cortical activity. Cholinergic Neurons Cholinergic neurons are located in the pedunculopontine nuclei and lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus. (Barr, Fig ). Acetylcholine is synthesized by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase, Chat. These neurons using acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter. In the Allen brain atlas, see the P56 mouse brain sections 85 or 93: o map.org/brain/chat/252/thumbnails.html o In the pons and midbrain find the Chat positive neurons. Distinguish the mesencephalic trigeminal neurons from the pedunculopontine nuclei. Inputs o Reticular formation (raphe and locus coeruleus) o Hypothalamus o Globus pallidus in basal ganglia Outputs o RF o Forebrain Basal ganglia system
5 Page 5 L 58 Intralaminar thalamic nuclei, Cholinergic basal forebrain These neurons are important for maintaining consciousness, but also active during REM sleep. Catecholaminergic Neurons Locus coeruleus is the main source of noradrenergic innervation (Barr, Fig ). Catecholamines are norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine. Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3 monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). DOPA is a precursor for dopamine, which, in turn, is a precursor for norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline). In humans, tyrosine hydroxylase is encoded by the TH gene. In the Allen brain atlas, see the P56 mouse brain, section 87 or section 95: o map.org/data/th/ /thumbnails.html o Find cells in the mouse brain that may synthesize DOPA at the level of the pons and midbrain. These will be in the locus coeruleus. Inputs from RF and hypothalamus. Locus coeruleus outputs are generally excitatory o Projects widely to the forebrain, including the hippocampus, amygdala, and frontal neocortex to modulate activity in the direction of increase excitability. o Projects to cerebellum. o Projects to brainstem and spinal cord. Motor Control and Emotion Reticular formation integrates voluntary movement with emotional expression Part of a whole body reaction or expression RF inputs from motor cortex o Proximal limbs and torso o Posture, muscle tone, and general excitability RF inputs from limbic cortex & basal forebrain o Viscera o Heart rate, breathing rate, bladder control, blood pressure, etc. Sleep and Wakefulness (See also Lecture 64, McNally for definitive details related to Sleep on the exam) Wakefulness o Neocortex must be stimulated by thalamus and brainstem for consciousness. o Cholinergic RF neurons activate hypothalamus, intralaminar nuclei, and cholinergic basal forebrain o Essential for wakefulness o Activation of locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons to activation of cortex important for consciousness o Lesions of locus coeruleus do not lead to unconsciousness o Central RF nuclei also activate thalamus and basal cholinergic forebrain
6 Page 6 L 58 o Orexin A and B from lateral hypothalamus activate brain and cholinergic RF during waking. Sleep o Preoptic GABAergic neurons inhibit locus coeruleus and cholinergic RF. o Serotonin and norepinephrine neurons are less active during deep sleep. o Cholinergic RF active during REM sleep Consciousness and Coma What is consciousness? o We have no idea o Christof Koch lists the following four definitions of consciousness in his latest book, [78] which can be summarized as follows: Consciousness is the inner mental life that we lose each night when we fall into dreamless sleep. Consciousness can be measured with the Glasgow Coma Scale that assesses the reactions of patients. An active cortico thalamic complex is necessary for consciousness in humans, and Put philosophically, consciousness is what it is like to feel something. From Wikipedia and Consciousness, Confessions of a Romantic Reductionist, Christof Koch, 2012, MIT Press Loss of consciousness can be caused by lesions In general, reticular formation is disconnected from the forebrain with lesions in o Midbrain or rostral pons o Caudal diencephalon o Mass lesions of forebrain Glasgow Coma Scale is used clinically to judge level of consciousness o Eye opening o Best motor response
7 Page 7 L 58 o Verbal response Waxman SG (2003) Clinical Neuroanatomy, Lange Med Books
Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the anatomical and functional organization of the brainstem reticular formation into three general regions: median (raphe), medial
Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the anatomical and functional organization of the brainstem reticular formation into three general regions: median (raphe), medial
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Non-cranial nerve nuclei
 Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Spinal Interneurons. Control of Movement
 Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons
 Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
Hindbrain, Midbrain, Forebrain. Lecture 3
 Hindbrain, Midbrain, Forebrain Lecture 3 1 Phrenology An Early View of Functional Specialization In Vienna F.J. Gall (1788-1828) J.K. Spurzheim (1776-1832) In Scotland G. Combe (1788-1858) In the United
Hindbrain, Midbrain, Forebrain Lecture 3 1 Phrenology An Early View of Functional Specialization In Vienna F.J. Gall (1788-1828) J.K. Spurzheim (1776-1832) In Scotland G. Combe (1788-1858) In the United
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges References... 3
 Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Organization of the nervous system 2
 Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle
 Chapter 1 OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle The
Chapter 1 OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle The
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Central Nervous System. January 7, 2016
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B
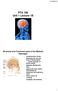 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Central Nervous System
 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Course Calendar - Neuroscience
 2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
California State University, Los Angeles School of Natural and Social Sciences Department of Biological Sciences WINTER, 2011
 1 California State University, Los Angeles School of Natural and Social Sciences Department of Biological Sciences WINTER, 2011 Course title, number and units: Neurobiology: Neuroanatomy, Biology 435 (4)
1 California State University, Los Angeles School of Natural and Social Sciences Department of Biological Sciences WINTER, 2011 Course title, number and units: Neurobiology: Neuroanatomy, Biology 435 (4)
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology
 1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6
 Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
