Key Knowledge. What is CONSCIOUSNESS? Consciousness is. Unit 3 ~ Chapter 2 ~ States of Consciousness. Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012
|
|
|
- Amber Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012 Key Knowledge Consciousness as described by Rene Descartes & William James Normal Waking Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness Comparison of Normal & Altered states of Consciousness Controlled and Automatic processes Perceptual and cognitive distortions Emotional awareness Self control Time orientation Methods used to study the level of alertness in normal waking consciousness: EEG, Heart rate, body temperature, GSR Research methods and ethical principals associated with the study of states of consciousness 2 What is CONSCIOUSNESS? CONSCIOUSNESS is the awareness of Objects and events in the external world Our own existence Mental experiences at any given time Consciousness is described as being Personal Selective Continuous Changing 3 Consciousness is PERSONAL It is your subjective understanding of both your private internal world & the environment. SELECTIVE You can select/choose to pay attention to certain things and to ignore others. CONTINUOUS The contents of your consciousness blend into one another. Your consciousness is never empty. CHANGING Your consciousness is never still, particularly while you are awake. 4
2 René Descartes 1800 s Descartes came up with the theory of DUALISM the mind and body are two different things MIND = non-physical spiritual entity (the soul) BODY = physical structure Descartes believed that the mind and body came into contact through the PINEAL GLAND in the brain This gland is close to the centre of the brain and was seen as the centre of consciousness Descartes also believed that the body could affect the mind and the mind could affect the body Eg: memory was a result of bodily functions It is now known that Descartes theory was incorrect 5 William James 1890 William James was the first to describe consciousness as: CONSTANTLY CHANGING There is continual movement of thoughts, feelings, perceptions, images, sensations, etc into and out of our minds James stated that consciousness is like a stream as it s contents are continuously moving and changing just like the water in a stream is continuously flowing. 6 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS State of consciousness = Level of awareness Our brain continually receives information about our internal & external world, however the amount of information that is taken in is determined by our level of awareness. There are no distinct boundaries to indicate where one state of consciousness ends and another begins. Consciousness ranges along a continuum or scale (see next slide) from total awareness to a complete lack of awareness. A Continuum of States of Consciousness ** TOTAL AWARENESS ** Focused attention ** Ordinary wakefulness ** Daydreaming Meditation Hypnosis Sleep Anaesthetised Unconscious/Coma COMPLETE LACK OF AWARENESS 7 8
3 Two Categories of Consciousness NORMAL WAKING CONSCIOUSNESS The states of consciousness when we are awake and aware of our thoughts, memories, feelings and the sensations we are experiencing from the outside world. ALTERED STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS A distinctly different level of mental awareness to normal waking consciousness Major changes occur in the qualities and characteristics of an individual s thoughts, feelings & perceptions. Cognitive processes or perception of your self or the world may change, and normal inhibitions or self-control may weaken. 9 Characteristics Of Normal Waking Consciousness Although the content of each individual s consciousness is unique, there are some characteristics that differentiate the different states of consciousness These characteristics are classed as: PSYCHOLOGICAL PHYSIOLOGICAL 10 Psychological Characteristics Level of attention Level of awareness Content of consciousness Perceptual experiences Cognitive abilities Emotional awareness Self control The experience of time Physiological Characteristics Changes in brain wave patterns Heart rate Body temperature Electrical conductivity in the skin 11 12
4 Normal Waking Consciousness Level of Awareness Attention involves focusing on specific stimuli & ignoring others. The states of consciousness that are at the top end of the continuum require more attention. In normal waking consciousness, attention can be focused on either internal thoughts or feelings or on external stimuli. You can change the focus of your attention freely. The change in focus of attention can be intentional or may occur without you being aware of it. Focused attention is a CONTROLLED PROCESS. 13 SELECTIVE ATTENTION At any given moment the focus of our awareness is on only a LIMITED range of all that we are capable of experiencing. It can be either internal or external. Study to demonstrate selective attention carried out by Neisser & Becklen (1975) video with the image of clapping hands superimposed over a basketball game. Cocktail Party Effect the ability to pay attention to one person s speech among competing conversations; your attention is attracted to a competing conversation when you hear your own name being mentioned. Our attention is also attracted by any CHANGES in stimulation, or the introduction of a NEW stimulus. Selective attention allows us to either allow information to enter into or be excluded from our consciousness. 14 Selective Attention Video DIVIDED ATTENTION The ability to distribute your attention and manage 2 or more tasks simultaneously. People are able to divide their attention among competing stimuli (eg: listening to radio & driving). Research findings have shown that our perceptual system can handle some divided attention tasks, as long as the tasks are not complex and there fore do not demand considerable mental effort. The ABILITY to divide our attention depends on how much conscious effort is required for the various tasks in which we are undertaking. A complex task requires selective attention and a higher level of consciousness than a familiar task
5 Normal Waking Consciousness Content Limitations Content is restricted and limited during normal waking consciousness. We are able to control what we allow into normal waking consciousness. The content of normal waking consciousness is generally organised & logical. Because a significant amount of information that enters our consciousness is within our control, we can block things which make us feel self-conscious, embarrassed, depressed, repulsed, sad, afraid, hurt etc. 17 Normal Waking Consciousness Controlled Processes Required for the activities that demand high levels of concentration during normal waking consciousness. Involves information processing requiring conscious, alert awareness and mental effort in which the individual actively focuses their attention on achieving a particular goal. Controlled processing is serial only one activity requiring controlled processes can usually be performed at a time. Usually require controlled processing when an activity is difficult or unfamiliar. Attention is focused exclusively on the task preventing attention being directed towards any other activities. 18 Normal Waking Consciousness Automatic Processes Require little conscious awareness and mental effort, minimal attention & do not interfere with the performance of other activities. Require LESS conscious effort than controlled processes. Automatic processing is PARALLEL we can handle two or more activities at the same time. Activities which require less concentration and therefore a lower level of consciousness involve automatic processes. Example of Automatic Processing: STROOP EFFECT, by J. Ridley Stroop (1935) this effect occurs because when we are presented with a word, our automatic response is to read the word. 19 The four conditions The Stroop Effect 1. words in black ink words are colours read out each word 2. words in coloured ink words are names of colours read out the colour of the ink (not the actual word) 3. coloured blocks name the colour of each block 4. words in coloured ink words are names of everyday objects read out the colour of the ink (not the actual word) 20
6 THE STROOP EFFECT What is your hypothesis? Equipment: stop watch, score sheet, stroop cards Work in pairs One person is the TIME KEEPER (experimenter) The other person reads out the words/colours (Participant) Time how long it takes for the participant to correctly identify each word/colour. Collate class results tabulate, analyse, graph Was your hypothesis supported/rejected?
7 ALTERED STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS 25 Any state of consciousness that is distinctly different from normal waking consciousness in terms of: Level of awareness & experience The quality or intensity of sensations Perceptions Thoughts Feelings Memories that are experienced Mental processing shows distinct changes unique to the particular altered state. Cognitive processes or perceptions of your self or the world may change Normal inhibitions or self control may weaken 26 Characteristics Of Altered States Of Consciousness Altered State of Consciousness (ASC) may occur naturally (eg, sleep) or may be purposely induced (through meditation, hypnosis, drugs). Although the psychological changes that occur as a result of an ASC will vary for each individual, there are some characteristics that are common to ASC. These include: Perceptual & Cognitive Distortions Disturbed sense of time Changes in emotional awareness Changes in self-control 27 Altered States of Consciousness Distortions of Perception & Cognition The way we experience sensations and perceptions in an ASC will be different than when in normal waking consciousness. Senses can either be heightened or dulled. For example, experiencing hallucinations under drug-induced states It may be possible to lose your own sense of identity by believing you are someone else or outside yourself. Experiencing a sense of losing touch with reality. 28
8 Distortions of Perception & Cognition (cont ) Cognitive functions (information processing) are also distorted during an ASC. Thoughts become disorganised. Thinking in an illogical manner and lacking in sequence Difficulties in problem solving Difficulty remembering what occurred during an ASC. Difficulty retrieving information stored in memory prior to the ASC, however, these memories can be accessed when returned to a state of normal waking consciousness. Altered States of Consciousness Disturbed Sense of Time Estimation of time is distorted during an ASC. Time may seem to pass more slowly or more quickly Altered States of Consciousness Changes in Emotional Awareness Emotions may be experienced differently. Feelings may appear to be in a state of turmoil. People in an ASC may respond to a situation uncharacteristically. People may be much more emotional or may feel emotionless. Emotional responses may be unpredictable during an ASC, eg. Crying for no real reason when drunk. 31 Altered States of Consciousness Changes in Self Control The ability to maintain self control can change during an ASC. Eg1: Inability to control emotions when drunk; Inability to co-ordinate & control movements when drunk Eg2: The use of hypnosis to help some people give up smoking, gambling, overeating, and for pain management. 32
9 Daydreaming Altered state of consciousness This is when we shift our attention from external stimuli to internal thoughts, feelings and imagined scenarios May occur naturally without being aware that it has happened More likely to occur when We are not moving Alone Waiting to fall asleep Travelling on public transport Doing boring/routine activities Purpose of Daydreaming Enables us to mentally try out a range of options for responding to a particular situation Allows us to solve problems Allows us to stay mentally alert in situations where there is insufficient external stimulation Meditative State Altered State of Consciousness Deliberately alter normal waking consciousness to induce a deep state of relaxation May also produce a heightened state of personal awareness and feelings of inner peace and tranquility Brain waves may resemble those of when a person is asleep The sense of pain is found to be less intense due to the senses being less receptive to the incoming internal & external messages that have been blocked to keep the mind clear 35 Alcohol-induced State Alcohol is considered to be a PSYCHOACTIVE DRUG chemicals that alter brain function by causing changes in conscious awareness, perception or moods The specific effects of alcohol on consciousness depend on a wide range of variables including: Concentration of alcohol Conditions under which the alcohol is consumed Rate of consumption Body weight Age, gender Physical wellbeing 36
10 Effects of Small Amounts of Alcohol Promotes relaxation Elevates mood Increases talkativeness Lowers inhibitions Impairs judgement Effects of High Amounts of Alcohol BAC = Brain becomes more depressed Thinking & concentration is slowed Muscular coordination is impaired BAC = Strong sedative effect Major impairment BAC = May become unconscious BAC 0.50 May cause death Alcohol and Memory Heavy drinking can prevent memories from being formed causing an alcoholic blackout loss of memory when drinking KORSAKOFF S SYNDROME (amnesia) can occur in alcoholics due to brain damage. Symptoms include problems with selective attention Limited attention maintenance leading to problems comprehending information Emotional flattening (reactions are flat or non-existent) 39 Effects of Alcohol on Consciousness Shortened attention span Impaired perception (senses not processed correctly) Impaired thinking Impaired memory Slower reaction times Reduced self-awareness Impaired emotional awareness and control Impaired perception of time Less self-control Difficulties with voluntary muscular control and fine movements Less able to perform complex tasks 40
11 Effects of Psychoactive Drugs - LSD LSD is an example of a psychoactive drug and has been extensively studied LSD works by influencing the serotonin in the brain The hallucinations experienced can include: Familiar objects becoming unrecognisable Inanimate objects appear to come to life The senses can intermingle Time is distorted Intense and rapid emotional changes Either a euphoric or a terrifying trip may be experienced Side effects include panic attacks requiring medical attention 41 Effects of Psychoactive Drugs - Marijuana Marijuana is also a hallucinogen Senses are heightened Time is distorted Mood is elevated Existing depression can be intensified Outside thoughts and ideas invade consciousness Users struggle to maintain focus on a goal Speech is slow The mind wanders and they experience frequent loss in the train of thought Marijuana also impairs the transfer of new information into long term memory Regular users have been observed to have poor school performance, apathetic attitude, low motivation and low self-esteem 42 Methods used to study level of alertness in Normal Waking Consciousness Consciousness cannot be directly measured or observed and is referred to as a psychological construct Psychological Construct: a concept that is constructed to describe specific psychological activity that is believed to exist but cannot be directly observed. Inferences are made from information that is provided by the individual, behaviour that is demonstrated or from physiological changes that can be measured. Psychologists focus on physiological measures as they are objective and less prone to bias. Measuring Physiological Responses States of consciousness cannot be observed or measured directly. Various devices exist that are used to measure the physiological responses during the various states of consciousness. Different patterns of physiological responses indicate different states of consciousness
12 Physiological Responses Different states of consciousness will show variations in the: Electrical activity of the brain Heart rate Body temperature Galvanic Skin Response/Electrical conductivity of the skin (ie: levels of perspiration) 45 Electrical Activity of the Brain Brain wave patterns are measured using EEG recordings. Brain waves can differ in: Frequency the number of brain waves per second Amplitude the intensity of the brain waves; judged by the size of the peaks & troughs of the pattern of brain waves. There are 4 different brain wave categories with different combinations of frequencies & amplitudes. BETA waves ALPHA waves THETA waves DELTA waves 46 Wave Type Beta Waves Alpha Waves Theta Waves Delta Waves Frequency & Amplitude High Frequency Low Amplitude High Frequency Slightly higher Amplitude than Beta waves Medium Frequency Irregular pattern of Amplitude Low Frequency High Amplitude Examples Normal Waking Consciousness Focused attention Relaxed or meditative state Early stages of sleep Deepest stages of sleep 47 Brain Wave Patterns Quick Quiz! Identify and describe each type of EEG brain wave A pattern in terms of: B Frequency Amplitude C In which state of consciousness they are likely to occur? D 48
13 Heart Rate Heart rate can either increase or decrease during an ASC as compared to the usual heart rate during the normal waking consciousness for that particular individual. DECREASES during: Sleep Unconsciousness Meditation INCREASES during: Intake of stimulant drugs, Periods of arousal 49 Body Temperature Body temperature is less variable than other physiological indicators of ASC. The most predictable change in temperature is during sleep when the body temperature decreases by more than 1 Celsius. 50 Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) GSR indicates a change in the resistance of the skin to an electrical current how much conductivity is there on the skin. As a person sweats more, the resistance to an electrical current decreases More sweat = more electrical current can pass = LESS resistance Electrodes are placed on the skin to measure the conductivity of the skin. High emotional arousal = more sweat = less resistance During an ASC there could be either an increased or decreased level of arousal, hence the GSR can be used as a comparison to the person s usual level during normal waking consciousness. 51 Usefulness of Physiological Indicators to Measure ASC Changes in physiological indicators can be due to a variety of factors, not just due to an ASC. Hence, psychologists are careful to use OTHER methods, in conjunction with physiological indicators to build up an accurate set of data. Other methods include observations of behaviour and selfreports. 52
14 Normal States of Consciousness vs Altered States of Consciousness QUICK QUIZ Question 1: Each different state of consciousness can be defined exactly and is experienced the same by everyone. True or false? Question 2: How can consciousness be measured? Question 3: Controlled and automatic processes occur during normal waking consciousness. True or false? Question 4: Altered states of consciousness enhance the experience of external stimuli. True or false? Question 5: Give an example of when you may use divided attention? Question 6: If you are experiencing time slower, what state of consciousness could you be in? Question 7: Give an example of an altered state of consciousness in which an individual might exhibit a reduction in self control
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
Chapter 6. Consciousness
 Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS. Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
Week 4 Psychology. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding that they and others think, feel, perceive, and have private experiences.
 Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
How Hypnosis Feels. P a g e 1 6
 How Hypnosis Feels Since everyone has experienced light levels of hypnosis at different times, don t be surprised if you don t feel hypnotized. All that is required to be hypnotized is a motivation to
How Hypnosis Feels Since everyone has experienced light levels of hypnosis at different times, don t be surprised if you don t feel hypnotized. All that is required to be hypnotized is a motivation to
ENGAGE: Level of awareness activity
 ENGAGE: Level of awareness activity ENGAGE: Meditation instructions Step 1: Explain how people meditate for religious and/or relaxation reasons. Step 2: Describe three major characteristics of an altered
ENGAGE: Level of awareness activity ENGAGE: Meditation instructions Step 1: Explain how people meditate for religious and/or relaxation reasons. Step 2: Describe three major characteristics of an altered
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity.
 Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis
 Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Sleep and Dreams. Sleep and Dreams. Brain Waves and Sleep Stages Typical Nightly Sleep Stages. Chapter 7 States of Consciousness
 Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
VCE Psychology Unit 4. Year 2017 Mark Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, By Alice (99.
 VCE Psychology Unit 4 Year 2017 Mark 50.00 Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, 2017 By Alice (99.45 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Alice. Alice
VCE Psychology Unit 4 Year 2017 Mark 50.00 Pages 45 Published Feb 10, 2018 COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 4 NOTES, 2017 By Alice (99.45 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Alice. Alice
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND
 Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
SELF HYPNOSIS. Contrary to popular belief, hypnosis is not a state of sleep or a state in which you are unconscious or not aware.
 SELF HYPNOSIS What is Hypnosis? Contrary to popular belief, hypnosis is not a state of sleep or a state in which you are unconscious or not aware. Hypnosis is actually a heightened state of mind in which
SELF HYPNOSIS What is Hypnosis? Contrary to popular belief, hypnosis is not a state of sleep or a state in which you are unconscious or not aware. Hypnosis is actually a heightened state of mind in which
Module Five: Review Questions
 1. Which of the following statements IS NOT true? a) Meditation affects brain activity b) All types of meditation lead to same kind of brain activity affection c) The brain travels through different patterns
1. Which of the following statements IS NOT true? a) Meditation affects brain activity b) All types of meditation lead to same kind of brain activity affection c) The brain travels through different patterns
AOS1 How do levels of consciousness affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview
 UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness
 AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness 1. What is an example of synesthesia? Following a car accident, someone has the ability to see sounds and hear touch. 2. What is the most basic distinction
AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness 1. What is an example of synesthesia? Following a car accident, someone has the ability to see sounds and hear touch. 2. What is the most basic distinction
States of Consciousness
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
States of Consciousness
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 States of Consciousness "We do imagery work and talk about having that innovative mindset of being special," Wilson says. "We talk about being in the moment and increasing chaos
Myers PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 States of Consciousness "We do imagery work and talk about having that innovative mindset of being special," Wilson says. "We talk about being in the moment and increasing chaos
Your body radiates energy, called an aura; just as a radio station radiates electromagnetic waves that carry a radio program.
 You can learn to use your aura to help you By Jose Silva Here's a short quiz: Why is your body like a radio? Because both are communications devices. Your body radiates energy, called an aura; just as
You can learn to use your aura to help you By Jose Silva Here's a short quiz: Why is your body like a radio? Because both are communications devices. Your body radiates energy, called an aura; just as
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
What is Consciousness?
 What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
Psychology study chapter 2
 Consciousness Psychology study chapter 2 Definition: Awareness of objects and events in the external world and of our own experiences at any given moment - Provides us with a sense of self Commonly described
Consciousness Psychology study chapter 2 Definition: Awareness of objects and events in the external world and of our own experiences at any given moment - Provides us with a sense of self Commonly described
Consciousness and Brainwaves Part 1.
 Consciousness and Brainwaves Part 1. January 4, 2015. The Arcturians advised me to present some information about brainwaves and consciousness in preparation for exploring Gamma Wave Consciousness. Gamma
Consciousness and Brainwaves Part 1. January 4, 2015. The Arcturians advised me to present some information about brainwaves and consciousness in preparation for exploring Gamma Wave Consciousness. Gamma
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams. Defined:
 Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS
 Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to
 How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
Video Clip: What is consciousness?
 Video Clip: What is consciousness? Importance of Sleep: Consciousness = state of awareness of feelings, ideas and perceptions Altered States of Consciousness Ex: Sleep Why do we sleep? Recharge the body
Video Clip: What is consciousness? Importance of Sleep: Consciousness = state of awareness of feelings, ideas and perceptions Altered States of Consciousness Ex: Sleep Why do we sleep? Recharge the body
States of Consciousness
 1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS
 Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Chapter 5/7. Variations in Consciousness
 Chapter 5/7 Variations in Consciousness -The Nature of Consciousness Consciousness is the awareness of internal and external stimuli. External: sound of my voice. Internal: heart beat Consciousness- it
Chapter 5/7 Variations in Consciousness -The Nature of Consciousness Consciousness is the awareness of internal and external stimuli. External: sound of my voice. Internal: heart beat Consciousness- it
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT.
 CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
States of Consciousness:
 States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
What is Stress? What Causes Stress?
 Stress Management What is Stress? Any situation can lead to stress too much to do, a conflict between people, disappointment, criticism, even compliments. These situations are not stress; they are stressors.
Stress Management What is Stress? Any situation can lead to stress too much to do, a conflict between people, disappointment, criticism, even compliments. These situations are not stress; they are stressors.
The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby
 The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby A Fully Integrated Platform for Observation, Daily Reporting, Communications and Assessment For Early Childhood Professionals and the Families that they Serve Alignment
The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby A Fully Integrated Platform for Observation, Daily Reporting, Communications and Assessment For Early Childhood Professionals and the Families that they Serve Alignment
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight Levels of Consciousness
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight Levels of Consciousness
Chapter 13 and 16. Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text
 Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
EXAM REVISION. Theories and Issues. Psychology Exam Review
 EXAM REVISION Theories and Issues The nature of psychology Psychology is the scientific study of behaviour and the mind The approach to psychology is systematic and therefore more accurate than everyday
EXAM REVISION Theories and Issues The nature of psychology Psychology is the scientific study of behaviour and the mind The approach to psychology is systematic and therefore more accurate than everyday
- copyright
 Relaxation Exercises Let s start with breathing! Your breathing is often the first thing to be affected by stress. When we are anxious we tend to hunch up the shoulders and breathe in a more rapid and
Relaxation Exercises Let s start with breathing! Your breathing is often the first thing to be affected by stress. When we are anxious we tend to hunch up the shoulders and breathe in a more rapid and
**Consciousness is generally defined as a state of awareness of ourselves and of the world around us; and that it shifts during the course of a day
 **Consciousness is generally defined as a state of awareness of ourselves and of the world around us; and that it shifts during the course of a day from periods of alert wakefulness to those of drifting
**Consciousness is generally defined as a state of awareness of ourselves and of the world around us; and that it shifts during the course of a day from periods of alert wakefulness to those of drifting
I. What Is Consciousness? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you. 3 Meanings of Consciousness
 I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
Healthier, greater sense of well being Less stress, more inner peace More focused, more easily access a flow state. Theta waves, 4 and 8 Hz
 SL #6 Wow. It s been 12 weeks since you started using Holosync. That s 3 months. What are you noticing? Please call us and have a chat with a support coach about what s happening. A month from the minimum
SL #6 Wow. It s been 12 weeks since you started using Holosync. That s 3 months. What are you noticing? Please call us and have a chat with a support coach about what s happening. A month from the minimum
Psychological preparation for natural disasters
 Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
Lectures I & II : Stimuli and Responses, Environment and Behavior: Where is the Mind? Overview of the Development of Mind and Consciousness.
 Willis F. Overton Department of Psychology Temple University September 12, 2004 Psych 60 Introductory Psychology Lectures I & II : Stimuli and Responses, Environment and Behavior: Where is the Mind? Overview
Willis F. Overton Department of Psychology Temple University September 12, 2004 Psych 60 Introductory Psychology Lectures I & II : Stimuli and Responses, Environment and Behavior: Where is the Mind? Overview
THE EFFECT OF STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS ON RECOVERY
 THE EFFECT OF STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS ON RECOVERY Lynne Couchara WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? Our experience of life is beyond the physical Significant mental portion, i.e. consciousness The state or quality
THE EFFECT OF STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS ON RECOVERY Lynne Couchara WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? Our experience of life is beyond the physical Significant mental portion, i.e. consciousness The state or quality
The Physiological Mechanism Underlying the Glo to Sleep Effect Technical Report No.GTS
 Line 49 Inc. The Physiological Mechanism Underlying the Glo to Sleep Effect Technical Report No.GTS02 10.21.2008 Introduction The Glo to Sleep effect, raising the eyes to alter the mind state, is based
Line 49 Inc. The Physiological Mechanism Underlying the Glo to Sleep Effect Technical Report No.GTS02 10.21.2008 Introduction The Glo to Sleep effect, raising the eyes to alter the mind state, is based
SLEEP THEORIES. Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed
 SLEEP THEORIES Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed about kept our ancestors out of harm s way. Sleep Recuperates: Sleep helps restore and repair brain tissue. Sleep Helps Remembering:
SLEEP THEORIES Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed about kept our ancestors out of harm s way. Sleep Recuperates: Sleep helps restore and repair brain tissue. Sleep Helps Remembering:
Improving Your Sleep Course. Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind
 Improving Your Sleep Course Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind This session will: Help you to learn ways of overcoming the mental alertness, repetitive thoughts and
Improving Your Sleep Course Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind Session 4 Dealing With a Racing Mind This session will: Help you to learn ways of overcoming the mental alertness, repetitive thoughts and
University Staff Counselling Service
 University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
ECTA Handouts Keynote Address. Affective Education. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy. Affective Education. Affective Education 19/06/2010
 ECTA Handouts Keynote Address ECTA: International Trends in Behavioural Guidance Approaches 26 th June 2010 Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Affective Development (maturity, vocabulary and repair). Cognitive
ECTA Handouts Keynote Address ECTA: International Trends in Behavioural Guidance Approaches 26 th June 2010 Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Affective Development (maturity, vocabulary and repair). Cognitive
Concussion & You. A Handbook for Parents and Kids DEVELOPED BY CONCUSSION EXPERTS AT HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL
 Concussion & You A Handbook for Parents and Kids DEVELOPED BY CONCUSSION EXPERTS AT HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL Trusted experts in youth concussion www.hollandbloorview.ca/concussion
Concussion & You A Handbook for Parents and Kids DEVELOPED BY CONCUSSION EXPERTS AT HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL Trusted experts in youth concussion www.hollandbloorview.ca/concussion
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Habits & Goals Discovery & Assessment. What kind of person do I want my child to grow up to be? How do I react to my child most often?
 Habits & Goals Discovery & Assessment How do I react to my child most often? What kind of person do I want my child to grow up to be? Focus on the Relationship Conscious Communication Practice Use these
Habits & Goals Discovery & Assessment How do I react to my child most often? What kind of person do I want my child to grow up to be? Focus on the Relationship Conscious Communication Practice Use these
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity.
 Sleep and Dreams What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity. A state we do not know we are in until we leave it. Characterized by
Sleep and Dreams What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity. A state we do not know we are in until we leave it. Characterized by
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind 1. When did the concept of consciousness begin to reemerge in the field of psychology? Explain why. Include all three explanations
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind 1. When did the concept of consciousness begin to reemerge in the field of psychology? Explain why. Include all three explanations
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
Do You Get Enough Sleep?
 LP 3A sleep deprivation 1 Do You Get Enough Sleep? Many college students do not get enough sleep. In a survey of more than 200,000 first year students, more than 80% say that stayed up all night at least
LP 3A sleep deprivation 1 Do You Get Enough Sleep? Many college students do not get enough sleep. In a survey of more than 200,000 first year students, more than 80% say that stayed up all night at least
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or ecstasy ) stimulates the release of dopamine at low doses. At higher doses it also stimulates serotonin
 Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or ecstasy ) stimulates the release of dopamine at low doses. At higher doses it also stimulates serotonin synapses, producing hallucinogenic effects similar to those
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or ecstasy ) stimulates the release of dopamine at low doses. At higher doses it also stimulates serotonin synapses, producing hallucinogenic effects similar to those
Subliminal Programming
 Subliminal Programming Directions for Use Common Questions Background Information Session Overview These sessions are a highly advanced blend of several mind development technologies. Your mind will be
Subliminal Programming Directions for Use Common Questions Background Information Session Overview These sessions are a highly advanced blend of several mind development technologies. Your mind will be
Understanding Hypnosis
 Understanding Hypnosis Are the Results of Hypnosis Permanent? Suggestions stay with some individuals indefinitely, while others need reinforcement. The effects of hypnosis are cumulative: The more the
Understanding Hypnosis Are the Results of Hypnosis Permanent? Suggestions stay with some individuals indefinitely, while others need reinforcement. The effects of hypnosis are cumulative: The more the
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
Module 04: Sleep. Module 04:
 Module 04: Sleep Module 04: Sleep Module 04: SLEEP This module includes the following sections: Key Messages Common Sleep Challenges Medications and Sleep Tips from Families for Getting a Good Night s
Module 04: Sleep Module 04: Sleep Module 04: SLEEP This module includes the following sections: Key Messages Common Sleep Challenges Medications and Sleep Tips from Families for Getting a Good Night s
Welcome to the ADHD group
 Welcome to the ADHD group Aims of this group 1. To help you make sense of your diagnosis and how ADHD has affected you 2. To learn strategies to cope with ADHD 3. To meet others with similar experiences
Welcome to the ADHD group Aims of this group 1. To help you make sense of your diagnosis and how ADHD has affected you 2. To learn strategies to cope with ADHD 3. To meet others with similar experiences
THINGS TO REMEMBER PSYCHOLOGY 2
 PREMIER CURRICULUM SERIES Based on the Sunshine State Standards for Secondary Education, established by the State of Florida, Department of Education THINGS TO REMEMBER PSYCHOLOGY 2 Copyright 2009 Revision
PREMIER CURRICULUM SERIES Based on the Sunshine State Standards for Secondary Education, established by the State of Florida, Department of Education THINGS TO REMEMBER PSYCHOLOGY 2 Copyright 2009 Revision
6/29/2009. Awareness of everything going on inside and outside of you CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS. Meaning of consciousness
 6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B
 Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Stress levels in people today are higher than ever. Our world is much faster paced than
 Jolie Frye Intrapersonal Communication Meditation and Self Talk: Dealing with Stress Stress levels in people today are higher than ever. Our world is much faster paced than ever before. People pile on
Jolie Frye Intrapersonal Communication Meditation and Self Talk: Dealing with Stress Stress levels in people today are higher than ever. Our world is much faster paced than ever before. People pile on
DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include:
 DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include: 1. Memory loss The individual may repeat questions or statements,
DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include: 1. Memory loss The individual may repeat questions or statements,
Sleep and Dreaming Notes December 14, 2015
 an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
Psych 120. General Psychology 7/12/2010. In the last lecture we learned about
 Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the last lecture we learned about How memory was first studied.
Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the last lecture we learned about How memory was first studied.
THE POWER OF SUGGESTION: HYPNOSIS
 UW MEDICINE TITLE OR EVENT THE POWER OF SUGGESTION: HYPNOSIS MINI MED SCHOOL SHELLEY WIECHMAN, PH.D., ABPP FEBRUARY 4, 2014 INTRODUCTION I. Definition II. History III. What exactly is hypnosis? IV. Theories
UW MEDICINE TITLE OR EVENT THE POWER OF SUGGESTION: HYPNOSIS MINI MED SCHOOL SHELLEY WIECHMAN, PH.D., ABPP FEBRUARY 4, 2014 INTRODUCTION I. Definition II. History III. What exactly is hypnosis? IV. Theories
Reprogramming. Your Subconscious Mind. A Step-By-Step Guide Bought to you by I m Allowed
 Reprogramming Your Subconscious Mind A Step-By-Step Guide Bought to you by I m Allowed Your subconscious mind has immense power in controlling your life experiences: from the types of food you eat to the
Reprogramming Your Subconscious Mind A Step-By-Step Guide Bought to you by I m Allowed Your subconscious mind has immense power in controlling your life experiences: from the types of food you eat to the
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme
 FACTS : Participants handouts Module 2 Mindfulness and Emotion Management Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme A short course for family members
FACTS : Participants handouts Module 2 Mindfulness and Emotion Management Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) FACTS Families and Carers Training and Support Programme A short course for family members
THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING
 THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING WRITTEN BY VALERIA CRUZ PUBLISHED 6 JUNE 2017 1 P a g e HISTORY Dreams are your subconscious creating a possible world. This, however, is not a new phenomenon. In fact,
THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING WRITTEN BY VALERIA CRUZ PUBLISHED 6 JUNE 2017 1 P a g e HISTORY Dreams are your subconscious creating a possible world. This, however, is not a new phenomenon. In fact,
 Module 2: Booklet 5 http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/intro-to-statesof-consciousness.html#lesson (3:55) Different levels of awareness that occur each day (I.e. sleeping, dreaming, thinking, etc)
Module 2: Booklet 5 http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/intro-to-statesof-consciousness.html#lesson (3:55) Different levels of awareness that occur each day (I.e. sleeping, dreaming, thinking, etc)
Unit 5. States of Consciousness
 Unit 5. States of Consciousness College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 2-4% And then suddenly, I saw this bright light at the end of the tunnel. Summary Outline A. Sleep and Dreaming B. Hypnosis
Unit 5. States of Consciousness College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 2-4% And then suddenly, I saw this bright light at the end of the tunnel. Summary Outline A. Sleep and Dreaming B. Hypnosis
Contents. Chapter. A Closer Look at You. Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude. Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You
 Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
PERMA Theory Engagement the E in PERMA
 PERMA Theory Engagement the E in PERMA Striving for the achievement of Flow States Engagement and Well Being Seligman sees Engagement as essential for happiness, it s one of the core elements of happiness.
PERMA Theory Engagement the E in PERMA Striving for the achievement of Flow States Engagement and Well Being Seligman sees Engagement as essential for happiness, it s one of the core elements of happiness.
Biopsychosocial Characteristics of Somatoform Disorders
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 19 Somatoform and Sleep Disorders Biopsychosocial Characteristics of Somatoform Disorders Unconscious transformation of emotions into physical symptoms
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 19 Somatoform and Sleep Disorders Biopsychosocial Characteristics of Somatoform Disorders Unconscious transformation of emotions into physical symptoms
How to Reduce Test Anxiety
 How to Reduce Test Anxiety To reduce math test anxiety, you need to understand both the relaxation response and how negative self-talk undermines your abilities. Relaxation Techniques The relaxation response
How to Reduce Test Anxiety To reduce math test anxiety, you need to understand both the relaxation response and how negative self-talk undermines your abilities. Relaxation Techniques The relaxation response
A Healthy Brain. An Injured Brain
 A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
Introduction to Neurofeedback. Penny Papanikolopoulos
 Introduction to Neurofeedback Penny Papanikolopoulos Our World is.. The Marvelous World of the Brain Senses, Perception, Cognitions, Images, Emotions, Executive functions etc. Are all regulated by the
Introduction to Neurofeedback Penny Papanikolopoulos Our World is.. The Marvelous World of the Brain Senses, Perception, Cognitions, Images, Emotions, Executive functions etc. Are all regulated by the
Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness
 Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness Complete the following: I tasted I smelled I saw I touched I heard I remembered I felt I thought DEFINING
Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness Complete the following: I tasted I smelled I saw I touched I heard I remembered I felt I thought DEFINING
Psychology. January 11, 2019.
 Psychology January 11, 2019. The Attendance Question: Do you have a habit or a ritual or something you do to clear your mind and focus before a big test, a big game or something important? Reminders:
Psychology January 11, 2019. The Attendance Question: Do you have a habit or a ritual or something you do to clear your mind and focus before a big test, a big game or something important? Reminders:
Sleep History Questionnaire. Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center. General Information. Age: Sex: F M (select one)
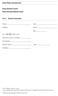 Sleep History Questionnaire Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center Part I: General Information Name: Address: Date: Phone: Age: Sex: F M (select one) Education (years of school): Occupation:
Sleep History Questionnaire Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center Part I: General Information Name: Address: Date: Phone: Age: Sex: F M (select one) Education (years of school): Occupation:
IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization. Visual Attention. Lyn Bartram
 IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization Visual Attention Lyn Bartram Why we care in an information-rich world, the wealth of information means a dearth of something else: a scarcity of whatever it is that information
IAT 814 Knowledge Visualization Visual Attention Lyn Bartram Why we care in an information-rich world, the wealth of information means a dearth of something else: a scarcity of whatever it is that information
CANNABIS. MARIJUANA. WEED.SKUNK. NPS. SPICE. MCAT. BALLOONS. COCAINE. COKE. GEAR. CHARLIE. ALCOHOL. BEVVY. BOOZE. JUICE.
 is the drug and alcohol service providing VISIONS support for young people in Hounslow. CANNABIS. MARIJUANA. WEED.SKUNK. NPS. SPICE. MCAT. BALLOONS. COCAINE. COKE. GEAR. CHARLIE. ALCOHOL. BEVVY. BOOZE.
is the drug and alcohol service providing VISIONS support for young people in Hounslow. CANNABIS. MARIJUANA. WEED.SKUNK. NPS. SPICE. MCAT. BALLOONS. COCAINE. COKE. GEAR. CHARLIE. ALCOHOL. BEVVY. BOOZE.
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness On the Nature of Consciousness Awareness of and Stimuli Variations on levels of stream of consciousness unconscious Sleep/dreaming research A family of practices that train to heighten
States of Consciousness On the Nature of Consciousness Awareness of and Stimuli Variations on levels of stream of consciousness unconscious Sleep/dreaming research A family of practices that train to heighten
Consciousness. Encounters. Alien Abductions 1/8/2012. Chapter Six. Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens)
 Chapter Six Consciousness Encounters Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens) Almost 1 in 10 claim to have experienced or met an alien Are people being visited and abducted
Chapter Six Consciousness Encounters Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens) Almost 1 in 10 claim to have experienced or met an alien Are people being visited and abducted
Using Guided Imagery for Surgical Support
 Using Guided Imagery for Surgical Support A Comprehensive Guide for Nurses, Massage Therapists, Doctors, Energy Workers, and Anyone Who Believes in Our Healing Potential Debra Basham and Joel P. Bowman
Using Guided Imagery for Surgical Support A Comprehensive Guide for Nurses, Massage Therapists, Doctors, Energy Workers, and Anyone Who Believes in Our Healing Potential Debra Basham and Joel P. Bowman
Optical Illusions 4/5. Optical Illusions 2/5. Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5. Reading. Reading. Fang Chen Spring 2004
 Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
(consciousness) (monitor) (control)
 : (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
: (2002) (consciousness) (monitor) (control) selective attention Stroop Stroop illusion hallucination (delusion) Altered states of consciousness In many cultures, inducing and altered state
