Level 5 Paramedic Primary Skills
|
|
|
- Prosper Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title: Paramedic Primary Assessment Sheets V-4 Page: 1 of 15 Owner: LD Approved by: Examination Quality Group Approval date: March 2017 PHECC National Qualification in Emergency Medical Technology (NQEMT) Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) Primary Assessment Sheets Level 5 Paramedic Primary Skills Primary stations The six (6) primary stations assessed in the NQEMT - Paramedic examination which are drawn from the skills objectives relating to PHECC s Education and Training Standards. Learning Outcome 1, Domain 1; and Learning Outcome 1, Domain 2 General notes OSCE assessment sheets for inclusion in an NQEMT examination will be available on for a minimum of sixty (60) days prior to the examination. White text on a black background indicates either an instruction to the examiner/candidate or separates two distinct skills on the assessment sheet. Successful completion of each OSCE requires the candidate to score 80% of each station s elements. Critical elements, which the candidate must successfully achieve to successfully complete the station, are marked with an asterisk (*) on the assessment sheet. There are no critical elements on secondary assessment sheets. 1 P a g e
2 Assessment Name: Cardiac Arrest Asystole Cease Resuscitation Unique Identifier: PARA_AA_P001 1 Assemble equipment (Connect O 2 and reservoir to BVM) 2 Check responsiveness 3 Turn on defibrillator (Early in sequence) 4 Open airway 5 Assess breathing & pulse (5-10 seconds) (Examiner note: no breathing, no pulse) 6 Request ALS and additional personnel 7 Prepare patient s chest (Appropriate checks) 8 Place left defibrillation pad in correct location 9 Place right defibrillation pad in correct location 10 Ascertain rhythm (Verbalise) Non Shockable rhythm 11 Provide CPR for 2 minutes 12 Consider OPA/advanced airway (Verbalise) 13 Minimise hands off time * 14 Ascertain rhythm (Verbalise) 15 Correct hand placement 16 CPR assist device Consider mechanical Non-Shockable rhythm 17 Immediately resume CPR for 2 minutes 18 Consider causes and treat as appropriate 19 Ascertain rhythm (Verbalise) Candidate is advised - you are on scene for 10 minutes, ALS is 40 minutes away 20 Consider cease resuscitation (Verbalise) 21 Confirms unwitnessed arrest (Verbalise) 22 Identifies unresponsiveness 23 Identifies absence of central pulse and respiration 24 Identifies asystole and 2 minutes CPR x 3 and no shock indicated x 3 25 Refer to CPG prior to ceasing resuscitation (Safe practice) 26 Inform control (Verbalise) 27 Record two rhythm strips (10 seconds) 28 Write required information on rhythm strip 29 If present inform next of kin and consider emotional support for relatives 30 Flag PCR for mandatory clinical audit 31 Identify the cease resuscitation and OHCAR section of PCR Rule: Line 13 = 1 2 P a g e
3 Assessment Name: Cardiac Arrest VF & VT Unique Identifier: PARA_VOPVA_P001 1 Assemble equipment (Connect O 2 and reservoir to BVM) 2 Check responsiveness 3 Turn on defibrillator (Early in sequence) 4 Open airway 5 Assess breathing & pulse (5-10 seconds) (Examiner note: no breathing, no pulse) 6 Request ALS and additional personnel 7 Prepare patient s chest (Appropriate checks) 8 Place left defibrillation pad in correct location 9 Place right defibrillation pad in correct location 10 Ascertain rhythm (Verbalise) Shockable rhythm 11 Analyse/charge 12 Ensure safety of personnel and others * 13 Continue CPR while charging (appropriate to the defibrillator) 14 Defibrillate (One shock) 15 Resume CPR immediately after shock delivered 16 Provide CPR for 2 minutes 17 Consider mechanical CPR device 18 Consider OPA /advanced airway (Verbalise) 19 Consider causes and treat as appropriate 20 Ensure adequate ventilations 21 Minimise hands off time * VF/VT has converted to non-shockable rhythm 22 Check pulse (if appropriate) 23 Assess and support ventilations 24 Document rhythm, pulse, BP, respiratory rate and S PO 2 (Verbalise) 25 Continue to monitor, consider post resuscitation care (Verbalise) Minimum one shock delivered per candidate Rule: Sum line 12 and 21 = 2 3 P a g e
4 Assessment Name: Adult FBAO and Recovery Position Unique Identifier: PARA_FBAOA_P001 1 Confirm airway obstruction * 2 Position and perform up to 5 back blows 3 Correct hand position during back blows 4 Perform up to 5 abdominal thrusts (or chest thrusts if obese/pregnant) 5 Correct hand position during thrusts 6 Continue until effective or patient collapse Candidate is advised - Patient becomes unresponsive 7 Patient lowered safely to the ground 8 Request ALS 9 Commence CPR with compressions 10 Inspect airway before ventilations Candidate is advised - The object has become visible (after one cycle approx.) 11 Perform finger sweep 12 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Patient is breathing adequately 13 Consider Oxygen 14 Check circulation Candidate is advised - Adequate pulse present 15 During performance of CPR compressions were effective Recovery position 16 Check responsiveness 17 Open airway * 18 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Patient is breathing adequately 19 Check pulse Candidate is advised - Pulse present 20 Inspect and prepare immediate area (Safety) 21 Physically assess patient for obscured objects that may cause harm 22 Remove unsafe objects for patient s safety 23 Roll patient laterally 24 Support the head as patient is turned 25 Ensure the uppermost arm rests at right angle to the body 26 Maintain an open airway 27 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Pulse present and patient is breathing adequately 28 Check pulse Candidate is advised - Pulse present STOP STATION Rule: Sum line 1 and 17 = 2 4 P a g e
5 Assessment Name: Paediatric FBAO and Adult Recovery Position Unique Identifier: PARA_FBAOP_P001 Current Version: Version 5 (December 2016) 1 Confirm airway obstruction * 2 Position and perform up to 5 back blows 3 Correct hand position during back blows 4 Perform up to 5 abdominal thrusts (or chest thrusts for infant) 5 Correct hand position during thrusts 6 Continue until effective or patient collapse Candidate is advised - Patient becomes unresponsive 7 Patient lowered safely to the ground/placed on flat surface 8 Request ALS 9 Inspect airway 10 If visible 1 attempt to remove object 11 Attempt 5 rescue breaths 12 Commence CPR with compressions 13 Inspect airway before ventilations (After one cycle approx. candidate is advised) - The object has become visible 14 Perform finger sweep 15 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Patient is breathing 16 Consider Oxygen 17 Check circulation Candidate is advised - Adequate pulse present 18 During performance of CPR compressions were effective Adult recovery position 19 Check responsiveness 20 Open airway * 21 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Patient is breathing adequately 22 Check pulse Candidate is advised - Pulse present 23 Inspect and prepare immediate area (Safety) 24 Physically assess patient for obscured objects that may cause harm 25 Remove unsafe objects for patient s safety 26 Roll patient laterally 27 Support the head as patient is turned 28 Ensure the uppermost arm rests at right angle to the body 29 Maintain an open airway 30 Check breathing Candidate is advised - Pulse present and patient is breathing adequately 31 Check pulse Candidate is advised - Pulse present STOP STATION Rule: Sum line 1 and 20 = 2 5 P a g e
6 Assessment Name: Airway Management Medical Patient Unique Identifier: PARA_AAMA_P002 Level / Section: Paramedic / Respiratory Emergencies Head tilt chin lift 1 Hand position 2 Correctly performs head tilt/chin lift * 3 Open mouth Oral suctioning 4 Gather and assemble necessary equipment 5 Test suction device to ensure suction is being provided 6 Appropriate measurement of catheter 7 Advance suction tip into mouth without applying suction 8 Suction is provided for 15 seconds maximum 9 Following suction, ensure ventilation or oxygenation (as appropriate) Oropharyngeal airway (OPA) 10 Select and measure appropriate size airway 11 Insert airway with inversion and rotation 12 Remove oropharyngeal airway (Following gagging) Nasopharyngeal airway (NPA) 13 Selects appropriate size airway (length and diameter) 14 Measure airway 15 Lubricate tube with appropriate lubricant 16 Fully insert airway with bevel facing septum Supraglottic Airway (SGA) 17 Ensure open airway 18 Pre-oxygenate patient 19 Select appropriate device 20 Apply lubricant (As appropriate) 21 Attach BVM 22 Insert airway using recognised technique 23 Ensure adequate ventilation * 24 Auscultate breath sounds (Examiner will operate BVM for candidate) 25 Secure airway 26 Attach CO 2 detector device 27 Attach SpO 2 device (Verbalise) Candidate is advised - Due to a complication with the device there is no longer chest rise 28 Remove airway 29 Correct technique to remove airway 30 Perform airway manoeuvre 31 Suction if necessary (Verbalise) 32 Insert OPA 33 Ventilate patient using BVM Rule: Sum line 2 & 23 = 2 6 P a g e
7 Assessment Name: CPR - Adult and Paediatric Unique Identifier: PARA_BLS_P001 Candidate is read an appropriate adult scenario 1 Assemble equipment (Connect O 2 and ensure reservoir on BVM) 2 Check responsiveness 3 Open airway 4 Check breathing & pulse for no longer than 10 seconds Candidate advised that there is no pulse 6 Commence chest compressions (30:2) 7 Request ALS and additional personnel 8 Provide two ventilations 9 Ensure chest rise 10 Provide CPR for 2 minutes 11 Correct hand placement 12 Correct compression rate 13 Correct compression depth 14 Hands off time minimised during resuscitation * Candidate is advised that patient has returned to spontaneous pulse 15 Check breathing Candidate is advised that patient is in respiratory arrest 16 Consider OPA (max) ventilations per minute (Adult) End of adult CPR skill assessment Candidate is read an appropriate Infant or Child assessment 18 Assemble equipment (Connect O 2 and reservoir to BVM) 19 Assess responsiveness 20 Open airway 21 Assess breathing and pulse no longer than 10 seconds Candidate is advised no breathing & pulse < 60 with signs of poor perfusion 22 Ventilate five times 23 Request ALS and additional personnel 24 Ensure chest rise 26 Commence chest compressions (30:2) 27 Correct hand/finger position 28 Provide CPR for 2 minutes/ until defibrillator arrives 29 Minimise hands off time * 30 Correct compression rate 31 Correct compression depth 32 Verbalise need to transport to ED if no change after 10 minutes Rule: Sum line 14 and 29 = 2 7 P a g e
8 Assessment Name: CPR-Adult and Neonate Resuscitation Unique Identifier: PARA_BLSN_P001 1 Assemble equipment (Connect O 2 and ensure reservoir on BVM) 2 Check responsiveness 3 Open airway 4 Check breathing & pulse no longer than 10 seconds Candidate is advised there is no pulse 6 Commence chest compressions 7 Request ALS and additional personnel 8 Provide two ventilations 9 Ensure chest rise 10 Provide CPR for 2 minutes 11 Correct hand placement 12 Correct compression rate 13 Correct compression depth 14 Hands off time minimised during resuscitation * Candidate is advised that patient has a spontaneous return of circulation 15 Check breathing Candidate is advised that patient is in respiratory arrest 16 Consider OPA ventilations (max) per minute Neonate resuscitation assessment (the patient has just been born) 18 Check for presence of clear amniotic fluid/breathing/crying/muscle tone 19 Provide warmth 20 Clear airway (if necessary) 21 Dry 22 Stimulate 23 Re-position baby 24 Assess colour and tone 25 Request ALS 26 Apply ECG monitor to assess heart rate (Verbalise) 27 Assess breathing, heart rate and colour (Examiner to provide appropriate information) Candidate advised neonate is apnoeic & Heart rate < Provide 5 positive pressure ventilations (room air) 29 Monitor heart rate Examiner states Heart rate is < Compressions (100/120 per min) and ventilations (3:1) for 30 seconds * 31 Hands off chest time minimised during the scenario Rule: Sum line 14 and 30 = 2 8 P a g e
9 Assessment Name: Initial Patient Assessment Trauma Unresponsive Adult Unique Identifier: PARA_PSTA_P001 Level / Section: Paramedic / Trauma 1 Assess and manage catastrophic haemorrhage 2 Apply manual in-line immobilisation 3 Assess responsiveness 4 Open airway (trauma jaw thrust) 5 Does not compromise c-spine * 6 Request ALS as appropriate Candidate is advised Assisting Practitioner now assumes C-spine control 7 Apply Suction (Simulate) 8 Insert airway adjunct (Simulate) 9 Assess breathing Candidate is advised of patient s breathing rate 10 Inspect chest 11 Palpate chest 12 Auscultate chest 13 Appropriate O 2 therapy 14 Assess circulation (Rate /strength) 15 Assess for obvious life threatening injury 16 Apply cervical collar 17 Assess AVPU 18 Assess PERRL Candidate is advised of injuries present 19 Treat life threatening injuries only 20 Identify correct clinical status decision (Verbalise) 21 Complete baseline vital signs (Verbalise) 22 Verbalise treatment plan 23 Complete PCR (Verbalise) Rule: Sum line 5 = 1 9 P a g e
10 Assessment Name: Altered Level of Consciousness Unique Identifier: PARA_ALOCA_P001 1 Assess responsiveness 2 Establish and maintain patent airway (consider recovery position) 3 Assess breathing 4 Administer oxygen therapy (As appropriate) 5 Assess circulation Candidate is advised You have now completed your initial primary survey 6 Assess skin (colour/rash) 7 Assess AVPU 8 Assess PERRL 9 Assess temperature 10 Verbalise clinical status 11 Consider ALS activation (Verbalise) 12 Acquire SpO 2 13 Apply ECG Monitor 14 Calculates GCS score 15 Gather SAMPLE Hx 16 Check for medications/ medi-alert jewellery 17 Assess base line vital signs (Verbalise) 18 Blood sugar measurement (request) * Candidate is advised of blood sugar measurement 19 Identify appropriate clinical pathway /Differential diagnosis 20 Re-evaluate clinical status (Verbalise) 21 Re-check vital signs (Verbalise) 22 Correct working diagnosis identified 23 Good communication with patient Rule: Line 18 = 1 10 P a g e
11 Assessment Name: Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis - Adult Unique Identifier: PARA_ARAA_P001 1 Assess responsiveness 2 Establish and maintain patent airway 3 Assess breathing 4 Administer oxygen therapy (As appropriate) 5 Assess circulation 6 Assess skin 7 Assess AVPU 8 Verbalise clinical status 9 Consider ALS activation (Verbalise) 10 State correct transport decision Candidate is advised You have now completed your initial primary survey 11 Acquire SpO 2 12 Apply ECG Monitor 13 Identify how exposure occurred 14 Identify effects of the exposure on patient 15 Identify condition progression 16 Assess base line vital signs (Verbalise) 17 Assess PERRL Interventions 18 Identify pharmacological treatment plan (Right patient) * 19 Right medication(s) identified 20 Right route(s) identified 21 Right dose(s) identified 22 Right time (intervals) 23 Right documentation 24 Re-check clinical status Post intervention 25 Verbalise appropriate further interventions 26 Good communication with patient 27 Seeks consent as appropriate during scenario Rule: Sum line 18 = 1 11 P a g e
12 Assessment Name: Initial Patient Assessment Adult Acute Coronary Syndrome Unique Identifier: PARA_PSACS_P001 1 Assess responsiveness 2 Establish and maintain patent airway 3 Assess breathing 4 Request ALS (Verbalise) 5 Apply 3 lead ECG and SpO 2 6 Oxygen therapy (As appropriate) 7 Assess circulation 8 Assess skin (colour/temperature/condition) 9 Assess AVPU 10 Assess clinical status Candidate is advised You have now completed your initial primary survey 11 Consider Aspirin 12 State contraindications 13 State dose and route 14 Baseline vital signs 15 Apply 12 lead ECG 16 Print strip 17 Identifies rhythm (Examiner to supply 12 lead ECG) * 18 Gather SAMPLE Hx 19 Gather OPQRST information 20 Consider GTN 21 State contraindications 22 State dose and route 23 STEMI Yes/No 24 Time to PPCI 25 Contacts PPCI to discuss Ticagrelor 26 State contraindications 27 State dose and route 28 Minimises on-scene time 29 Re-check clinical status Post intervention 30 Reassess vital signs 31 Good communication with the patient throughout the assessment Rule: Sum line 17 = 1 12 P a g e
13 Assessment Name: Initial Patient Assessment Paediatric Trauma Not alert Unique Identifier: PARA_PSTP_P001 Level / Section: Paramedic / Paediatric Emergencies 1 Perform PAT assessment (Paediatric Assessment Triangle) * 2 Identify and control catastrophic haemorrhage 3 Request ALS (If appropriate) 4 Maintain in line immobilisation 5 Assess airway 6 Suction if required 7 Selects appropriate airway adjunct /manoeuvre 8 C-spine not compromised * Candidate is advised Assisting Practitioner now controls the head, airway is secure 9 Assess breathing 10 Appropriate O 2 therapy 11 Inspect chest for injuries and appropriate management 12 Auscultate for breath sounds 13 Assess circulation (rate and strength) 14 C-Collar measure and apply 15 Assess AVPU appropriately 16 Assess PERRL 17 Expose and assess for life threatening injury 18 Good communication with patient Paediatric weight calculation 19 State weight of the child in the given scenario 20 State clinical status Rule: Sum line 1 and 8 = 2 13 P a g e
14 Assessment Name: Management of Haemorrhage Unique Identifier: PARA_EHA_P001 Level / Section: Paramedic / Trauma 1 Assess if Haemorrhage is catastrophic 2 Position patient sitting/lying 3 Elevate extremity 4 Examine wound 5 Apply direct pressure to the wound (pad and bandage) * 6 Consider Haemostatic agent 7 Consider wound closure clips or tourniquet (for limb injury) 8 Explain procedure to patient 9 Administer O 2 Candidate is advised wound is still bleeding 10 Apply additional dressing/bandages Candidate is advised wound is still bleeding and is life threatening 11 Depress proximal pressure point Candidate is advised wound is still bleeding and is life threatening 12 Select and apply appropriate size tourniquet (if not already applied) 13 Tourniquet applied correctly (not applied over joint) 14 Document time and site of application 15 Ensure tourniquet remains visible at all times Candidate is advised the patient is in compensatory shock 16 Properly position patient (supine with legs elevated) 17 Prevent heat loss, cover patient appropriately 18 Consider ALS Candidate is advised patient is in uncompensated shock 19 Advise immediate transport * 20 Good communication with patient 21 Seeks consent as appropriate during scenario 22 Checks CSM as appropriate during scenario Rule: Sum line 5 and 19 = 2 14 P a g e
15 Assessment Name: Vital Signs Unique Identifier: PARA_PSMA_P001 Level / Section: Paramedic / Patient Assessment Carotid or Radial pulse (Examiner note: ask candidate to take a pulse) 1 Locate the required artery with at least two fingers 2 Count pulsations for at least 15 seconds 3 Calculate and report rate (Within 4 beats/min) * 4 Report quality (Strength) and rhythm (Regular/irregular) CSM (Examiner note: ask candidate to check CSMs) 5 Palpate a peripheral pulse and count aloud 6 Assess sensory function on a limb 7 Assess motor function on a limb Blood Pressure (auscultation) (Examiner note: ask candidate to take BP) 8 Place cuff on arm 9 Palpate pulse in ante-cubital area 10 Place diaphragm in appropriate location 11 Inflate the cuff 12 Slowly release air from cuff 13 Report systolic blood pressure 14 Report diastolic blood pressure Respiratory assessment (Examiner note: ask candidate to assess breathing) 15 Place hand lightly over patient s diaphragm, observe chest rise, or uses another technique to identify a respiratory cycle 16 Count respiratory cycle for at least 30 seconds 17 Calculate and report the minute rate (Within +/-2) 18 Report rate (Number), quality (Normal, shallow, laboured, noisy), and rhythm (Regular, irregular) 19 Auscultate, 4 point to posterior chest wall 20 Auscultate, 4 point to anterior chest wall 21 Assess for equal air entry Communications 22 Good communication with patient during assessments 23 Seeks consent as appropriate during assessments Rule: Sum line 3 15 P a g e
Emergency First Response (EFR) Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017
 Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
Emergency First Response (EFR) Assessment Sheets September 2011
 Emergency First Response () Assessment Sheets September 2011 Airway Management & Ventilation Current Version: Version 2 (Sep 2011) Airway Management & Ventilation TRAUMA JAW THRUST 1 Hand position 2 Perform
Emergency First Response () Assessment Sheets September 2011 Airway Management & Ventilation Current Version: Version 2 (Sep 2011) Airway Management & Ventilation TRAUMA JAW THRUST 1 Hand position 2 Perform
CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS
 CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS PRACTICAL STATIONS CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS 1. CARDIAC ARREST MANAGEMENT 2. AIRWAY & RESPIRATORY MANAGEMENT 3. SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS PRACTICAL STATIONS CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS 1. CARDIAC ARREST MANAGEMENT 2. AIRWAY & RESPIRATORY MANAGEMENT 3. SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
Medical First Responder Program Protocols
 Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
SEMINOLE COUNTY EMS PROVISIONAL EMT SKILLS VERIFICATION
 The following individual has completed the Seminole County EMS Provisional EMT Skills Verification check in the following areas: Oxygen, Airway and Ventilation Skills ALS Assistance Trauma Management Medical
The following individual has completed the Seminole County EMS Provisional EMT Skills Verification check in the following areas: Oxygen, Airway and Ventilation Skills ALS Assistance Trauma Management Medical
MASSACHUSETTS DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Basic EMT Practical Examination Cardiac Arrest Management
 Basic EMT Practical Examination 6.0 - Cardiac Arrest Management Station 1 RESUSCITATION & DEFIBRILLATION No Point WHILE FUNCTIONING AS FIRST RESCUER: Point 1. Verbalizes or takes body substance isolation
Basic EMT Practical Examination 6.0 - Cardiac Arrest Management Station 1 RESUSCITATION & DEFIBRILLATION No Point WHILE FUNCTIONING AS FIRST RESCUER: Point 1. Verbalizes or takes body substance isolation
BLS Practical Skills Examination
 New York State Department of Health BLS Practical Skills Examination ertified First Responder and Emergency Medical Technician 2017 REQUIRED TESTING S EMT - The following skills are identified as being
New York State Department of Health BLS Practical Skills Examination ertified First Responder and Emergency Medical Technician 2017 REQUIRED TESTING S EMT - The following skills are identified as being
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Emergency Care Progress Log
 Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station
 Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station 1. Preparation a. Assemble equipment beforehand. b. Make sure that you have what you need and that it is functioning properly. 2.
Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station 1. Preparation a. Assemble equipment beforehand. b. Make sure that you have what you need and that it is functioning properly. 2.
Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient
 Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient This appendix and the one following provide guidance on the initial approach and management of common medical emergencies which may arise in general
Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient This appendix and the one following provide guidance on the initial approach and management of common medical emergencies which may arise in general
San Benito County EMS Agency Section 700: Patient Care Procedures
 Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
EMT OSCE Equipment List
 EMT OSCE Equipment List Document Management Data (To be removed prior to publication) Title: LIS009 EMT OSCE Equipment List V 6 Owner LD Approved by: Examination Quality Committee Approval Date: Mar 2017
EMT OSCE Equipment List Document Management Data (To be removed prior to publication) Title: LIS009 EMT OSCE Equipment List V 6 Owner LD Approved by: Examination Quality Committee Approval Date: Mar 2017
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (BLS)
 ADULT Suspected Foreign Body Airway Obstruction (FBAO) 1 If conscious, ask, "Are you choking?" 2 If patient is unable to speak and/or shakes head yes, give abdominal thrusts, (chest thrusts if pregnant
ADULT Suspected Foreign Body Airway Obstruction (FBAO) 1 If conscious, ask, "Are you choking?" 2 If patient is unable to speak and/or shakes head yes, give abdominal thrusts, (chest thrusts if pregnant
1. The 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR recommended BLS sequence of steps are:
 BLS Basic Life Support Practice Test Questions 1. The 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR recommended BLS sequence of steps are: a. Airway, Breathing, Check Pulse b. Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing c. Airway,
BLS Basic Life Support Practice Test Questions 1. The 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR recommended BLS sequence of steps are: a. Airway, Breathing, Check Pulse b. Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing c. Airway,
PLEASE PRINT CLEARLY!
 Indiana Emergency Medical Services Commission EMT-B Practical Examination Report Form PLEASE PRINT CLEARLY! Course Number: Course Completion Date: Name Last Name First Name Middle Initial SSN Address Street
Indiana Emergency Medical Services Commission EMT-B Practical Examination Report Form PLEASE PRINT CLEARLY! Course Number: Course Completion Date: Name Last Name First Name Middle Initial SSN Address Street
EMT. Chapter 8 Review
 EMT Chapter 8 Review 1. During the scene size-up, you should routinely determine all of the following, EXCEPT: A. the mechanism of injury or nature of illness. B. the ratio of pediatric patients to adult
EMT Chapter 8 Review 1. During the scene size-up, you should routinely determine all of the following, EXCEPT: A. the mechanism of injury or nature of illness. B. the ratio of pediatric patients to adult
HeartCode PALS. PALS Actions Overview > Legend. Contents
 HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
2017 Northern Mine Rescue Contest Written Exam (First Aid Competition)
 2017 Northern Mine Rescue Contest Written Exam (First Aid Competition) 2017 2010 June 5, 2017 Findley Lake, New York 2017 Northern Mine Rescue Contest Written Exam First Aid Competition Directions: Fill
2017 Northern Mine Rescue Contest Written Exam (First Aid Competition) 2017 2010 June 5, 2017 Findley Lake, New York 2017 Northern Mine Rescue Contest Written Exam First Aid Competition Directions: Fill
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
FIRST AID WRITTEN EXAM. Team Name: 1. Participation in a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD) is mandatory. a. TRUE b. FALSE
 2015 NEW IBERIA MINE RESCUE CONTEST FIRST AID WRITTEN EXAM Name: Date: 1. Participation in a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD) is mandatory. 2. The use of accessory muscles in the chest, abdomen
2015 NEW IBERIA MINE RESCUE CONTEST FIRST AID WRITTEN EXAM Name: Date: 1. Participation in a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD) is mandatory. 2. The use of accessory muscles in the chest, abdomen
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Airway, Oxygen and Ventilation Skills/Upper Airway Adjuncts and Suction Bag-Valve-Mask/Apneic Patient Bleeding Control/Shock Management Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Immobilization Skills/Joint Injury
Airway, Oxygen and Ventilation Skills/Upper Airway Adjuncts and Suction Bag-Valve-Mask/Apneic Patient Bleeding Control/Shock Management Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Immobilization Skills/Joint Injury
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS)
 TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to
 1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only. In
1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only. In
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only.
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only.
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline. Advanced Paediatric Life Support. Sequence of actions. 1. Establish basic life support
 Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Frontline First Aid First Responder Session Quizzes
 Session 1 1. One of the 4 parts of the Patient Assessment Model is: a. Injury Survey b. Patient Survey c. Critical Survey d. Ongoing Survey 2. One of the Secondary responsibilities of the First Responder
Session 1 1. One of the 4 parts of the Patient Assessment Model is: a. Injury Survey b. Patient Survey c. Critical Survey d. Ongoing Survey 2. One of the Secondary responsibilities of the First Responder
CPR Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
 CPR Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR = sequence of immediate actions to sustain flow of oxygenated blood unconsciousness and not breathing normally > start CPR! vital functions: Consciousness Breathing
CPR Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR = sequence of immediate actions to sustain flow of oxygenated blood unconsciousness and not breathing normally > start CPR! vital functions: Consciousness Breathing
Basic Airway Management
 Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
In-hospital Resuscitation
 In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
Paediatric Resuscitation. EMS Rounds Gurinder Sangha MD Paediatric Emergency Fellow June 18, 2009
 Paediatric Resuscitation EMS Rounds Gurinder Sangha MD Paediatric Emergency Fellow June 18, 2009 Essentials of Resuscitation Airway Breathing Circulation AIRWAY Differences in Paediatric Airway Shorter
Paediatric Resuscitation EMS Rounds Gurinder Sangha MD Paediatric Emergency Fellow June 18, 2009 Essentials of Resuscitation Airway Breathing Circulation AIRWAY Differences in Paediatric Airway Shorter
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005
 THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Airway Adjuncts and Suction
 Airway Adjuncts and Suction Oropharyngeal Airway Selects appropriately sized airway. Measures airway. Inserts airway without pushing the tongue posteriorly. Examiner States: patient is gagging and becoming
Airway Adjuncts and Suction Oropharyngeal Airway Selects appropriately sized airway. Measures airway. Inserts airway without pushing the tongue posteriorly. Examiner States: patient is gagging and becoming
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs
 Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Airway and Ventilation. Emergency Medical Response
 Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
Waitin In The Wings. Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider
 Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT
 Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons who need airway management. Airway management is
Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons who need airway management. Airway management is
Airway Management. DFMRT Casualty Care Examination Course. Revision notes for. January Les Gordon
 Airway Management Revision notes for DFMRT Casualty Care Examination Course January 2013 Les Gordon Indicating special information in Revision Notes presentations New information since Casualty Care in
Airway Management Revision notes for DFMRT Casualty Care Examination Course January 2013 Les Gordon Indicating special information in Revision Notes presentations New information since Casualty Care in
2007 Recertification Session. Airway review
 2007 Recertification Session Airway review Level of awareness: This is similar to the AVPU, the GCS is performed later Verbal, loud verbal, or pain stimulus. If pain stimulus, consider a trapezeus squeeze
2007 Recertification Session Airway review Level of awareness: This is similar to the AVPU, the GCS is performed later Verbal, loud verbal, or pain stimulus. If pain stimulus, consider a trapezeus squeeze
It s as easy as ABC. Dr Andrew Smith
 It s as easy as ABC Dr Andrew Smith ABCDE A simple method to apply to your assessment of patients. It is a good failsafe in all situations i.e. At an end of an OSCE when you re put under pressure! Correct
It s as easy as ABC Dr Andrew Smith ABCDE A simple method to apply to your assessment of patients. It is a good failsafe in all situations i.e. At an end of an OSCE when you re put under pressure! Correct
Advanced Airway Management. University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track
 Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History. Chapter 5
 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Skill Evaluation Sheets
 Skill Evaluation Sheets Skill Drill 2-: How to Remove Gloves Skill Drill 4-: Primary Check: RAP-CAB Skill Drill 4-2: Perform a Secondary Check Skill Drill 5-: Adult CPR Skill Drill 5-2: Child CPR Skill
Skill Evaluation Sheets Skill Drill 2-: How to Remove Gloves Skill Drill 4-: Primary Check: RAP-CAB Skill Drill 4-2: Perform a Secondary Check Skill Drill 5-: Adult CPR Skill Drill 5-2: Child CPR Skill
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management
 yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
yregion I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Airway Management Overview: Managing a patient s airway may be necessitated due to upper or lower airway obstruction, inadequate
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
Basic Assessment and Treatment of Trauma
 Basic Assessment and Treatment of Trauma Final Exam Version 1 1. In which of the following scenarios would the potential for serious injury or death be the GREATEST? A. 77-kg (170-lb) man who falls 1.2
Basic Assessment and Treatment of Trauma Final Exam Version 1 1. In which of the following scenarios would the potential for serious injury or death be the GREATEST? A. 77-kg (170-lb) man who falls 1.2
IRECA BLS Challenge 2015 Scenario 1
 Scenario 1 Team Name Team Number Captain Name Judge 1 # Judge 2 # JUDGE S SHEET Overview: This scenario challenges the competitors to use basic triage techniques and then to do the most good for the most
Scenario 1 Team Name Team Number Captain Name Judge 1 # Judge 2 # JUDGE S SHEET Overview: This scenario challenges the competitors to use basic triage techniques and then to do the most good for the most
Core Subject Part 4. Identify the principles of approaching the sick patient.
 The Role of The Dental Care Professional During a Medical Emergency: General Dental Council Standards and The Management of The Collapsed Patient Using the ABCDE Approach Aims: Core Subject Part 4 To provide
The Role of The Dental Care Professional During a Medical Emergency: General Dental Council Standards and The Management of The Collapsed Patient Using the ABCDE Approach Aims: Core Subject Part 4 To provide
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
BLS ROUTINE MEDICAL CARE
 BLS ROUTINE MEDICAL CARE Scene safety # Assure scene safety prior to patient contact C-spine # Perform manual cervical spine stabilization if indicated (Follow the cervical spine protocol.) ABCs # Assess
BLS ROUTINE MEDICAL CARE Scene safety # Assure scene safety prior to patient contact C-spine # Perform manual cervical spine stabilization if indicated (Follow the cervical spine protocol.) ABCs # Assess
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Chapter 10. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Airway Management, Artificial Ventilation, and Oxygenation
 Chapter 10 Airway Management, Artificial Ventilation, and Oxygenation Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
Chapter 10 Airway Management, Artificial Ventilation, and Oxygenation Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, Page 1
 Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
Old protocol is top bullet and italicized. Revised protocol is subsequent bullets and color coded:
 Old protocol is top bullet and italicized Revised protocol is subsequent bullets and color coded: RED is a State Change Blue is unique to Suffolk County VI. If patient has not taken aspirin and has no
Old protocol is top bullet and italicized Revised protocol is subsequent bullets and color coded: RED is a State Change Blue is unique to Suffolk County VI. If patient has not taken aspirin and has no
Pediatric Advanced Life Support
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
ADVANCED AIRWAY MANAGEMENT
 The Advanced Airway Management protocol should be used on all patients requiring advanced airway management procedures. This protocol is divided into three sections the Crash Airway Algorithm, the Rapid
The Advanced Airway Management protocol should be used on all patients requiring advanced airway management procedures. This protocol is divided into three sections the Crash Airway Algorithm, the Rapid
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
Summary Report for Individual Task Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved
 Report Date: 12 Jul 2011 Summary Report for Individual Task 081-833-3005 Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
Report Date: 12 Jul 2011 Summary Report for Individual Task 081-833-3005 Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
Code Blue III PLUS. Emergency Care Simulators
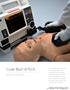 Code Blue III PLUS Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback, not only
Code Blue III PLUS Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback, not only
WHY IS FIRST AID IMPORTANT?
 Chapter 1 -BACKGROUND INFORMATION WHY IS FIRST AID IMPORTANT? 1. 2. SOME THINGS I SHOULD HAVE IN MY FIRST AID KIT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. VOCABULARY Place the key points of the first aid term in the box provided
Chapter 1 -BACKGROUND INFORMATION WHY IS FIRST AID IMPORTANT? 1. 2. SOME THINGS I SHOULD HAVE IN MY FIRST AID KIT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. VOCABULARY Place the key points of the first aid term in the box provided
Chapter 11. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking
 Chapter 11 Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
Chapter 11 Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT
 Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons who need airway management. Airway management is
Australian Resuscitation Advisory Network BLS Guideline 1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Scope Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to all persons who need airway management. Airway management is
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
It s as easy as ABC. Dr Andrew Smith
 It s as easy as ABC Dr Andrew Smith ABCDE A useful framework to apply to your assessment and management of (unwell) patients. Correct problems before moving on and reassess Call for help early it shows
It s as easy as ABC Dr Andrew Smith ABCDE A useful framework to apply to your assessment and management of (unwell) patients. Correct problems before moving on and reassess Call for help early it shows
The student guide to simulation
 CETL 2008 1 The following guide will introduce you to what the simulators can do But firstly a few words on communication Please verbally and non-verbally communicate with the simulator as if it were a
CETL 2008 1 The following guide will introduce you to what the simulators can do But firstly a few words on communication Please verbally and non-verbally communicate with the simulator as if it were a
REGION 1 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic, EMT Intermediate, EMT Paramedic. SMO: Pediatric Assessment Guidelines
 REGION 1 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic, EMT Intermediate, EMT Paramedic SMO: Pediatric Assessment Guidelines Overview: Pediatric patients account for about 10% or less of
REGION 1 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic, EMT Intermediate, EMT Paramedic SMO: Pediatric Assessment Guidelines Overview: Pediatric patients account for about 10% or less of
Airway management. Dr. Dóra Ujvárosy Medical Unversity of Debrecen Emergency Department
 Airway management Dr. Dóra Ujvárosy Medical Unversity of Debrecen Emergency Department Airway management Airway management is the medical process of ensuring there is an open pathway between a patient
Airway management Dr. Dóra Ujvárosy Medical Unversity of Debrecen Emergency Department Airway management Airway management is the medical process of ensuring there is an open pathway between a patient
Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket
 BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
Advanced Life Support
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Version Effective date Changes Prepared By CPR + AED
 Version Effective date Changes Prepared By Ver 1.0 23 rd June 2017 First Issue Muhammad Fauzy, Principal Trainer CPR + AED 218E Changi Road, PKMS Building #03-05A Singapore 419737 Tel: 87508086 Fax: 6440
Version Effective date Changes Prepared By Ver 1.0 23 rd June 2017 First Issue Muhammad Fauzy, Principal Trainer CPR + AED 218E Changi Road, PKMS Building #03-05A Singapore 419737 Tel: 87508086 Fax: 6440
Cardiovascular Emergencies. Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular Emergencies Chapter 12 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed 931,108 lives in the US during 2001. 2,551 per day Almost two people per minute! CVD accounts for 38.5%
Cardiovascular Emergencies Chapter 12 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed 931,108 lives in the US during 2001. 2,551 per day Almost two people per minute! CVD accounts for 38.5%
General Medical Procedure. Emergency Airway Techniques (General Airway Protocol)
 General Medical Procedure Appropriate airway management is often the most important intervention a prehospital care provider makes, as ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is crucial to the survival
General Medical Procedure Appropriate airway management is often the most important intervention a prehospital care provider makes, as ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is crucial to the survival
EMERGENCY CARE. Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT
 EMERGENCY CARE Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT 800.882.6655 Our Code Blue III ALS training simulators allow you to teach high-performance, quality CPR by providing you with real-time
EMERGENCY CARE Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT 800.882.6655 Our Code Blue III ALS training simulators allow you to teach high-performance, quality CPR by providing you with real-time
Examples EMERGENCY SITUATIONS IN SPORTS
 Examples EMERGENCY SITUATIONS IN SPORTS Dr Kaspar Rõivassepp Orthopedic surgeon (North Estonian Medical Centre, Estonian Football Association) 23.08.2015 IX Baltic Sports Medicine Conference The most serious
Examples EMERGENCY SITUATIONS IN SPORTS Dr Kaspar Rõivassepp Orthopedic surgeon (North Estonian Medical Centre, Estonian Football Association) 23.08.2015 IX Baltic Sports Medicine Conference The most serious
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Adult Intubation Skill Sheet
 Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Chapter 32. Injuries to the Spine by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
 Chapter Injuries to the Spine Topics Anatomy and physiology of the spine Spinal injuries Guidelines for immobilization Special considerations Enrichment Introduction Injuries to the spine are among the
Chapter Injuries to the Spine Topics Anatomy and physiology of the spine Spinal injuries Guidelines for immobilization Special considerations Enrichment Introduction Injuries to the spine are among the
Maternal Collapse Guideline
 Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Anatomy and Physiology. The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway.
 Airway management Anatomy and Physiology The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway. Non-instrumental airway management Head Tilt and Chin Lift Jaw Thrust Advanced
Airway management Anatomy and Physiology The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway. Non-instrumental airway management Head Tilt and Chin Lift Jaw Thrust Advanced
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest
 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL Medical. Feb 2011 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL
The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL Medical. Feb 2011 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL
EMT-1 Skills. Practical Examination Workbook
 EMT- Skills Practical Examination Workbook Merced County EMS Agency Fall 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS FORWARD... 3 SKILLS DESCRIPTIONS AND OBJECTIVES... 4 PATIENT ASSESSMENT - TRAUMA... 8 PATIENT ASSESSMENT
EMT- Skills Practical Examination Workbook Merced County EMS Agency Fall 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS FORWARD... 3 SKILLS DESCRIPTIONS AND OBJECTIVES... 4 PATIENT ASSESSMENT - TRAUMA... 8 PATIENT ASSESSMENT
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session
 Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
VAO BASIC SUPPORT CLINICAL APPROACH TO THE PATIENT HANDOUT
 CLINICAL APPROACH TO THE PATIENT HANDOUT 1 I am the most important part of patient care. How can you expect to treat a patient appropriately if you don t follow through on basic primary care? Remember:
CLINICAL APPROACH TO THE PATIENT HANDOUT 1 I am the most important part of patient care. How can you expect to treat a patient appropriately if you don t follow through on basic primary care? Remember:
Airway Management Adult
 Airway Management Adult Goals: Provide effective oxygenation and ventilation; recognize and alleviate respiratory distress or failure; provide necessary interventions quickly and safely to patients who
Airway Management Adult Goals: Provide effective oxygenation and ventilation; recognize and alleviate respiratory distress or failure; provide necessary interventions quickly and safely to patients who
EMT. Chapter 14 Review
 EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
12-Lead ECG. Cardioversion. Evaluator: Evaluator: Identifies indications and contraindication for 12-Lead. Identifies indications for cardioversion
 12-Lead ECG Cardioversion Identifies indications and contraindication for 12-Lead Identifies indications for cardioversion Assembles equipment Turns monitor on, applies pads and cables appropriately Prepares
12-Lead ECG Cardioversion Identifies indications and contraindication for 12-Lead Identifies indications for cardioversion Assembles equipment Turns monitor on, applies pads and cables appropriately Prepares
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
