observational studies Descriptive studies
|
|
|
- Susan Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 form one stage within this broader sequence, which begins with laboratory studies using animal models, thence to human testing: Phase I: The new drug or treatment is tested in a small group of people for the first time to determine safe dosage and to identify possible side effects. Phase II: The drug or treatment is given to a larger group at the recommended dosage to determine its efficacy under controlled circumstances and to evaluate safety. This is generally not a randomized study. Phase III: The drug or treatment is tested on large groups to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, compare it to commonly used treatments, and to collect information for the safe use of the drug. Phase III testing normally involves a series of randomized trials. At the end of this phase, the drug may be approved for public use. The approval may limit how the drug can be used, for instance in specific diseases or in certain age groups. Phase IV: After the treatment enters the marketplace, information continues to be collected to describe effectiveness on different populations and to detect possible side effects. This does not involve an RCT and is called post-marketing surveillance; it is based on reports of side effects from physicians (and patients) so it requires the active participation of treating physicians and is necessary to detect rare or slowly developing side effects. see Links: The clinical trials registry 5.7 Observational Studies In observational studies, the researcher observes what happens to people under exposure conditions that have been self-selected or have been determined by influences outside the control of the researcher. The researcher can choose what exposures to study, but does not influence them. As this is a non-randomized design, the major problem in inferring causation is that the exposed and unexposed groups may differ on other key factors that may themselves be true causes of the outcome, rather than the characteristics under study. Such factors are known as confounders. Descriptive studies Descriptive studies describe how things are; they do not set out to test hypotheses. For instance the Canadian Community Health Survey describes health and health habits in the Canadian population, or a family physician might describe the demography of patients attending her practice. They are usually cross-sectional in design. Surveys are often used in a descriptive manner, for example to establish disease prevalence, or to record who uses health services and what patients think of them. This kind of information can be useful for clinicians deciding what kinds of information to offer their patients, or what services they ought to provide. They are particularly useful for public health and health care planning. Descriptive information is often collected by surveys or by surveillance programmes, covering person, place, and time of disease occurrences. 129
2 Analytical studies The critical distinction between a descriptive and an analytical study is that the latter is designed to test a hypothesis. When an outcome variable, such as heart disease, is studied in relation to an exposure variable such as body weight, the study does more than count: it tests a hypothesis predicting an association between the two. Analytical observational studies can be of three types, depending on the time sequence and sampling procedures used to collect data. Cross-sectional studies Here, subjects are selected irrespective of the presence or absence of the characteristics of interest for hypothesis testing. One of the most common cross-sectional analytical studies is the survey, in which a random sample is drawn to give an accurate representation of the population. It is similar to a descriptive survey except that the purpose of the analysis is to record associations between variables, rather than merely to report frequencies of their occurrence. As an example of a cross-sectional study, a researcher might draw a random sample of people to test hypotheses concerning the association between feelings of stress and the use of medical services. The researcher might ask whether people had visited a doctor in the last 2 weeks, and if they were under stress in the last year. Suppose the sample included over 18,000 people about stress and doctor visits, producing the following result: Table 5.5: Stress and physician visits: calculating the association between two variables Doctor visit in the last 2 weeks? yes no Total Stress in the last year? yes 1,442 3,209 4,651 no 2,633 11,223 13,856 Total 4,075 14,432 18,507 Note that this result can be reported in either of two ways: 1. Of those who suffered stress in the last year, 31% (1442/4651) visited their doctor in the last 2 weeks compared with only 19% (2633/13856) of those who did not suffer stress. 2. Of those who visited their doctor in the last 2 weeks, 35% (1442/4075) suffered stress in the previous year, compared with 22% (3209/14432) of those who did not visit their doctor. Either approach is correct. The researcher is free to decide which way to report the results; the study design allows both types of analysis. All that can be concluded is that there is an association between the two variables. It might be supposed that stress predisposes people to visit their doctor, or could it be that the prospect of a visit to the doctor causes stress, or perhaps something else (fear of an underlying illness?) causes both? This study cannot provide support for an inference of causation because in this cross-sectional study it is impossible to know if stress pre-dated the doctor visit. 130
3 Cohort studies see Nerd s Corner: Ecological studies A cohort is a group of people who can be sampled and enumerated, who share a defining characteristic and who can be followed over time: members of a birth cohort share the same year of birth, for example. Cohort studies of health commonly study causal factors; the characteristic of interest is usually some sort of exposure that is thought to increase the likelihood of a health outcome. A cohort study typically begins with a sample of people who do not have the disease of interest; it collects information on exposure to the factor being studied, and follows exposed and unexposed people over time (Figure 5.2). The numbers of newly occurring (incident) cases of disease are recorded and compared between the exposure groups. Cohort studies are also known as longitudinal or follow-up studies. Figure 5.2: Schema of a cohort study see Nerd s Corner: Cohort In simple cohort studies the results can be fitted into a 2 by 2 table (2 rows by 2 columns: don t count the Total column). Table 5.6: Generic format for a 2 x 2 table linking an exposure to an outcome. 131
4 Outcome (e.g., disease) present Outcome (e.g., disease) absent Total Exposure (or risk factor) present a b a + b Exposure (or risk factor) absent c d c + d The incidence, or risk of disease in the exposed group, is calculated as a / (a + b). Correspondingly, the risk in the non-exposed people is c / (c + d). These risks can be compared to get a risk ratio (often called a relative risk, or RR) that gives an estimate of the strength of the association between the exposure and the outcome: [a/(a + b)] / [c/(c + d)]. A relative risk of 1.0 indicates that exposed people are neither more nor less likely to get the disease than unexposed people: there is no association between exposure and disease. A relative risk greater than 1.0 implies that, compared to a person not exposed to the factor, a person who has been exposed has a greater chance of becoming diseased, while a relative risk of less than 1.0 implies a protective effect, that is exposed people have a lower chance of becoming diseased compared to unexposed people. The fact that exposure was recorded before the outcomes is the main advantage of cohort studies; they can clearly establish the causal criterion of a temporal sequence between exposure and outcome as long as study participants truly did not have the disease at the outset. Furthermore, because recording of exposures and outcomes is planned from the beginning of the study period, data recording can be standardized. Definition of exposure groups Imagine a cohort study designed to test the hypothesis that exposure to welding fumes causes diseases of the respiratory tract. The sample could be drawn on the basis of a crude indicator of exposure, such as using occupation as a proxy (welders are assumed to be exposed; a non-welding occupations would be presumed to be unexposed). This approach is frequently used in occupational and military epidemiology. A more detailed alternative would be to quantify levels of exposure (e.g., from the person s welding history); this requires considerably more information but would permit dose-response to be estimated - one of the criteria for inferring causation (see Table 5.4). In an extension of this quantified approach, a cohort study might not select an unexposed group to follow, but rather select a sample of individuals with sufficient variability in their exposure to permit comparisons across all levels of exposure, or to permit mathematical modelling of exposure. Cohort studies of diet, exercise, or smoking often use this approach, deriving information from a baseline questionnaire. This approach has been used in community cohort studies such as the Framingham Heart Study. see Illustrative Material: The Framingham Study see Here be Dragons: A cohort study proves? 132
5 Case-control studies Case-control studies (see Case-control study in Glossary) compare a group of patients with a particular outcome (e.g., cases of pathologist-confirmed pancreatic cancer) to an otherwise similar group of people without the disease (the controls). As shown in Figure 5.3, reports or records of exposure (e.g., alcohol consumption) before the onset of the disease are then compared between the groups. The name of the design reminds you that groups to be compared are defined in terms of the outcome of interest: present (cases) or absent (controls). Figure 5.3: Schema of a case-control design Notice that a case-control study does not allow the calculation of the incidence or risk of the disease, because it begins with people who already have it and a predetermined number who do not. Therefore, a risk ratio cannot be calculated. Instead, the study identifies the exposure status of a sample of cases and another of controls. This information allows the calculation of the odds of a case having been exposed the ratio of a:c in the 2 x 2 table (Table 5.7). This can be compared to the odds of a control having been exposed, the ratio of b:d. The result of the case-control study is then expressed as the ratio of these 2 odds, giving the Odds Ratio (OR): (a/c) / (b/d). To make the calculation easier, this is usually simplified algebraically to ad/bc. Table 5.7: Generic 2 x 2 table for calculating an odds ratio Outcome (or disease) present Outcome (or disease) absent Outcome (or disease) present a b Exposure (or risk factor) absent c d 133
6 The OR calculated from a case-control study can approximate a relative risk, but only when the disease is rare (say, up to around 5% in the sample, as is the case for many chronic conditions). The interpretation of the value of an OR is the same as a RR. Like a relative risk, an OR of 1.0 implies no association between exposure and disease. A value over 1.0 implies a greater chance of diseased people having been exposed compared to controls. A value below 1.0 implies that the factor is protective. This might occur, for example, if a case-control study showed that eating a low fat diet protected against heart disease. Key contrast between cohort and case-control studies In cohort studies, the participants groups are classified according to their exposure status (whether or not they have the risk factor). In case-control studies, the different groups are identified according to their health outcomes (whether or not they have the disease). see Here be Dragons: Prospective or retrospective? 5.8 Measures of Risk: Attributable Risk and Number Needed to Treat The RR and OR indicate how much an individual s risk of disease is increased by having been exposed to a causal factor, in relative terms. Both statistics answer the question Compared to someone without the risk factor, how many times as likely am I to get the disease?, giving the answer as a ratio: You are twice as likely, or 10% more likely. A patient s question, however, often concerns absolute risk, which relates to disease incidence and answers the question What is my chance of getting the disease (in the next year, ten years, my lifetime)? The answer is given as a proportion, such as 1 in 10, or 1 in 100. An important point to bear in mind when communicating with a patient is that if the disease is rare, the RR of having a risk factor can appear quite frightening 100% greater risk of death in the next year even though the absolute risk is small. A relative increase of 100% on an absolute risk of 1 in a million is still only 2 in a million. Judging the magnitude of a risk introduces the concept of attributable risk, which indicates the number of cases of a disease among exposed individuals that can be attributed to that exposure: Attributable risk = Incidence in the exposed group incidence in the unexposed. This tells us how much extra disease has been caused by this exposure, in absolute terms: 1 case per million persons in the example above. In the case of a factor that protects against disease, such as a vaccination, it tells us how many cases can be avoided. Sometimes this value is expressed as a proportion of the incidence in exposed persons, yielding the exposed attributable fraction, EAF: EAF = [Incidence (exposed) - Incidence (unexposed) ] / Incidence (exposed) 134
Dose and Response for Chemicals
 Dose and Response for Chemicals 5 5 DOSE AND RESPONSE FOR CHEMICALS All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison. The right dose differentiates a poison and a remedy. Paracelsus, 16th
Dose and Response for Chemicals 5 5 DOSE AND RESPONSE FOR CHEMICALS All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison. The right dose differentiates a poison and a remedy. Paracelsus, 16th
UNIT 5 - Association Causation, Effect Modification and Validity
 5 UNIT 5 - Association Causation, Effect Modification and Validity Introduction In Unit 1 we introduced the concept of causality in epidemiology and presented different ways in which causes can be understood
5 UNIT 5 - Association Causation, Effect Modification and Validity Introduction In Unit 1 we introduced the concept of causality in epidemiology and presented different ways in which causes can be understood
Causal Association : Cause To Effect. Dr. Akhilesh Bhargava MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur
 Causal Association : Cause To Effect Dr. MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur Measure of Association- Concepts If more disease occurs in a group that smokes compared to the
Causal Association : Cause To Effect Dr. MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur Measure of Association- Concepts If more disease occurs in a group that smokes compared to the
CPH601 Chapter 3 Risk Assessment
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of David M. Mannino 2013 CPH601 Chapter 3 Risk Assessment David M. Mannino Available at: https://works.bepress.com/david_mannino/64/ + Risk Assessment David
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of David M. Mannino 2013 CPH601 Chapter 3 Risk Assessment David M. Mannino Available at: https://works.bepress.com/david_mannino/64/ + Risk Assessment David
Case-control studies. Hans Wolff. Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire. WHO- Postgraduate course 2007 CC studies
 Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
Study Design STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY DESIGN
 STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL Daniel E. Ford, MD, MPH Vice Dean for Clinical Investigation Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Introduction to Clinical Research July 15, 2014 STUDY DESIGN Provides
STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL Daniel E. Ford, MD, MPH Vice Dean for Clinical Investigation Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Introduction to Clinical Research July 15, 2014 STUDY DESIGN Provides
3. Factors such as race, age, sex, and a person s physiological state are all considered determinants of disease. a. True
 / False 1. Epidemiology is the basic science of public health. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: CNIA.BOYL.17.2.1 - Define epidemiology. 2. Within the field of epidemiology, the term distribution refers to the relationship
/ False 1. Epidemiology is the basic science of public health. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: CNIA.BOYL.17.2.1 - Define epidemiology. 2. Within the field of epidemiology, the term distribution refers to the relationship
Incorporating Clinical Information into the Label
 ECC Population Health Group LLC expertise-driven consulting in global maternal-child health & pharmacoepidemiology Incorporating Clinical Information into the Label Labels without Categories: A Workshop
ECC Population Health Group LLC expertise-driven consulting in global maternal-child health & pharmacoepidemiology Incorporating Clinical Information into the Label Labels without Categories: A Workshop
Data that can be classified as belonging to a distinct number of categories >>result in categorical responses. And this includes:
 This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
Stratified Tables. Example: Effect of seat belt use on accident fatality
 Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio
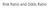 Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio Risk and Odds Risk is a probability as calculated from one outcome probability = ALL possible outcomes Odds is opposed to probability, and is calculated from one outcome Odds
Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio Risk and Odds Risk is a probability as calculated from one outcome probability = ALL possible outcomes Odds is opposed to probability, and is calculated from one outcome Odds
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club. A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology. August, 2013
 Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Is There An Association?
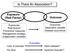 Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance
 Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance Ebbing Lautenbach, MD, MPH, MSCE University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Nothing to disclose PENN Outline Definitions / Historical
Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance Ebbing Lautenbach, MD, MPH, MSCE University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Nothing to disclose PENN Outline Definitions / Historical
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies
 Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM
 ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research
 Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research Howard Cabral, Ph.D., M.P.H. Boston University CTSI Boston University School of Public Health Department of Biostatistics May 15, 2013 1 Overview of Basic
Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research Howard Cabral, Ph.D., M.P.H. Boston University CTSI Boston University School of Public Health Department of Biostatistics May 15, 2013 1 Overview of Basic
Risk Study. Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Definition
 Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN
 CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN Detty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetrics & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta, Indonesia Conceptualizing a Research Design The Research Design The
CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN Detty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetrics & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta, Indonesia Conceptualizing a Research Design The Research Design The
Study Designs in Epidemiology
 Study Designs in Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH First semester 2017/ 2018 Department of Family and Community Medicine School of Medicine/ The University of Jordan Epidemiologic Study
Study Designs in Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH First semester 2017/ 2018 Department of Family and Community Medicine School of Medicine/ The University of Jordan Epidemiologic Study
In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis.
 Control Case In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis. This depicts a patient who finds himself lying with a corpse (definitely a case ).
Control Case In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis. This depicts a patient who finds himself lying with a corpse (definitely a case ).
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD.
 INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
ASSOCIATION & CAUSATION IN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES. Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Medicine, 2016/ 2017 The University of Jordan
 ASSOCIATION & CAUSATION IN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Medicine, 2016/ 2017 The University of Jordan Association and Causation Which of these foods will stop cancer? (Not so fast)
ASSOCIATION & CAUSATION IN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Medicine, 2016/ 2017 The University of Jordan Association and Causation Which of these foods will stop cancer? (Not so fast)
GLOSSARY OF GENERAL TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF GENERAL TERMS Absolute risk reduction Absolute risk reduction (ARR) is the difference between the event rate in the control group (CER) and the event rate in the treated group (EER). ARR =
GLOSSARY OF GENERAL TERMS Absolute risk reduction Absolute risk reduction (ARR) is the difference between the event rate in the control group (CER) and the event rate in the treated group (EER). ARR =
17/10/2012. Could a persistent cough be whooping cough? Epidemiology and Statistics Module Lecture 3. Sandra Eldridge
 Could a persistent be whooping? Epidemiology and Statistics Module Lecture 3 Sandra Eldridge Aims of lecture To explain how to interpret a confidence interval To explain the different ways of comparing
Could a persistent be whooping? Epidemiology and Statistics Module Lecture 3 Sandra Eldridge Aims of lecture To explain how to interpret a confidence interval To explain the different ways of comparing
You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study.
 You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Light, Singer and Willett Or, not as catchy but perhaps more accurate: Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study. Producing Data The Role of
You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Light, Singer and Willett Or, not as catchy but perhaps more accurate: Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study. Producing Data The Role of
Quantitative and qualitative research
 Quantitative and qualitative research Quantitative and qualitative research 1 Qualitative vs quantitative 2 Overview of qualitative research 3 Qualitative research techniques 3 Overview of quantitative
Quantitative and qualitative research Quantitative and qualitative research 1 Qualitative vs quantitative 2 Overview of qualitative research 3 Qualitative research techniques 3 Overview of quantitative
Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association
 Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association Patrick Breheny October 27 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 40 Introduction Study designs leading to contingency
Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association Patrick Breheny October 27 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 40 Introduction Study designs leading to contingency
MAT Mathematics in Today's World
 MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time 1. What does a sample tell us about the population? 2. Practical problems in sample surveys. Last Time Parameter: Number that describes a population Statistic:
MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time 1. What does a sample tell us about the population? 2. Practical problems in sample surveys. Last Time Parameter: Number that describes a population Statistic:
Research Methodology Workshop. Study Type
 Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
Epidemiologic Study Designs. (RCTs)
 Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Making comparisons. Previous sessions looked at how to describe a single group of subjects However, we are often interested in comparing two groups
 Making comparisons Previous sessions looked at how to describe a single group of subjects However, we are often interested in comparing two groups Data can be interpreted using the following fundamental
Making comparisons Previous sessions looked at how to describe a single group of subjects However, we are often interested in comparing two groups Data can be interpreted using the following fundamental
Underlying Theory & Basic Issues
 Underlying Theory & Basic Issues Dewayne E Perry ENS 623 Perry@ece.utexas.edu 1 All Too True 2 Validity In software engineering, we worry about various issues: E-Type systems: Usefulness is it doing what
Underlying Theory & Basic Issues Dewayne E Perry ENS 623 Perry@ece.utexas.edu 1 All Too True 2 Validity In software engineering, we worry about various issues: E-Type systems: Usefulness is it doing what
Observational Medical Studies. HRP 261 1/13/ am
 Observational Medical Studies HRP 261 1/13/03 10-11 11 am To Drink or Not to Drink? Volume 348:163-164 January 9, 2003 Ira J. Goldberg, M.D. A number of epidemiologic studies have found an association
Observational Medical Studies HRP 261 1/13/03 10-11 11 am To Drink or Not to Drink? Volume 348:163-164 January 9, 2003 Ira J. Goldberg, M.D. A number of epidemiologic studies have found an association
Objective: To describe a new approach to neighborhood effects studies based on residential mobility and demonstrate this approach in the context of
 Objective: To describe a new approach to neighborhood effects studies based on residential mobility and demonstrate this approach in the context of neighborhood deprivation and preterm birth. Key Points:
Objective: To describe a new approach to neighborhood effects studies based on residential mobility and demonstrate this approach in the context of neighborhood deprivation and preterm birth. Key Points:
Computer Science 101 Project 2: Predator Prey Model
 Computer Science 101 Project 2: Predator Prey Model Real-life situations usually are complicated and difficult to model exactly because of the large number of variables present in real systems. Computer
Computer Science 101 Project 2: Predator Prey Model Real-life situations usually are complicated and difficult to model exactly because of the large number of variables present in real systems. Computer
University of Wollongong. Research Online. Australian Health Services Research Institute
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2011 Measurement of error Janet E. Sansoni University of Wollongong, jans@uow.edu.au Publication
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2011 Measurement of error Janet E. Sansoni University of Wollongong, jans@uow.edu.au Publication
Trial Designs. Professor Peter Cameron
 Trial Designs Professor Peter Cameron OVERVIEW Review of Observational methods Principles of experimental design applied to observational studies Population Selection Looking for bias Inference Analysis
Trial Designs Professor Peter Cameron OVERVIEW Review of Observational methods Principles of experimental design applied to observational studies Population Selection Looking for bias Inference Analysis
Measuring association in contingency tables
 Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Introduction to Biostatistics (BIOS 4120) 1 / 28 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher
Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Introduction to Biostatistics (BIOS 4120) 1 / 28 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher
Graphic Organizers. Compare/Contrast. 1. Different. 2. Different. Alike
 1 Compare/Contrast When you compare and contrast people, places, objects, or ideas, you are looking for how they are alike and how they are different. One way to organize your information is to use a Venn
1 Compare/Contrast When you compare and contrast people, places, objects, or ideas, you are looking for how they are alike and how they are different. One way to organize your information is to use a Venn
Bias. Sam Bracebridge
 Bias Sam Bracebridge Bias Errors in epidemiological measurements Based on the slides of Sam Bracebridge By the end of the lecture fellows will be able to Define bias Identify different types of bias Explain
Bias Sam Bracebridge Bias Errors in epidemiological measurements Based on the slides of Sam Bracebridge By the end of the lecture fellows will be able to Define bias Identify different types of bias Explain
Introduction to Research Methods
 Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Unit 4 Probabilities in Epidemiology
 BIOSTATS 540 Fall 2018 4. Probabilities in Epidemiology Page 1 of 23 Unit 4 Probabilities in Epidemiology All knowledge degenerates into probability - David Hume With just a little bit of thinking, we
BIOSTATS 540 Fall 2018 4. Probabilities in Epidemiology Page 1 of 23 Unit 4 Probabilities in Epidemiology All knowledge degenerates into probability - David Hume With just a little bit of thinking, we
ANATOMY OF A RESEARCH ARTICLE
 ANATOMY OF A RESEARCH ARTICLE by Joseph E. Muscolino D.C. Introduction As massage therapy enters its place among the professions of complimentary alternative medicine (CAM), the need for research becomes
ANATOMY OF A RESEARCH ARTICLE by Joseph E. Muscolino D.C. Introduction As massage therapy enters its place among the professions of complimentary alternative medicine (CAM), the need for research becomes
Chapter 02. Basic Research Methodology
 Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Study design. Chapter 64. Research Methodology S.B. MARTINS, A. ZIN, W. ZIN
 Chapter 64 Study design S.B. MARTINS, A. ZIN, W. ZIN Research Methodology Scientific methodology comprises a set of rules and procedures to investigate the phenomena of interest. These rules and procedures
Chapter 64 Study design S.B. MARTINS, A. ZIN, W. ZIN Research Methodology Scientific methodology comprises a set of rules and procedures to investigate the phenomena of interest. These rules and procedures
t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved
 t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You may print this text out and use
t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You may print this text out and use
Epidemiologic Methods I & II Epidem 201AB Winter & Spring 2002
 DETAILED COURSE OUTLINE Epidemiologic Methods I & II Epidem 201AB Winter & Spring 2002 Hal Morgenstern, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology UCLA School of Public Health Page 1 I. THE NATURE OF EPIDEMIOLOGIC
DETAILED COURSE OUTLINE Epidemiologic Methods I & II Epidem 201AB Winter & Spring 2002 Hal Morgenstern, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology UCLA School of Public Health Page 1 I. THE NATURE OF EPIDEMIOLOGIC
Overview of Study Designs
 Overview of Study Designs Kyoungmi Kim, Ph.D. July 13 & 20, 2016 This seminar is jointly supported by the following NIH-funded centers: We are video recording this seminar so please hold questions until
Overview of Study Designs Kyoungmi Kim, Ph.D. July 13 & 20, 2016 This seminar is jointly supported by the following NIH-funded centers: We are video recording this seminar so please hold questions until
Chapter 13. Experiments and Observational Studies
 Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies 1 /36 Homework Read Chpt 13 Do p312 1, 7, 9, 11, 17, 20, 25, 27, 29, 33, 40, 41 2 /36 Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers do not
Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies 1 /36 Homework Read Chpt 13 Do p312 1, 7, 9, 11, 17, 20, 25, 27, 29, 33, 40, 41 2 /36 Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers do not
Faculty of Medicine. Introduction to Community Medicine Course ( ) Unit 4 Epidemiology. Introduction to Epidemiology.
 Faculty of Medicine Introduction to Community Medicine Course (31505201) Unit 4 Epidemiology Introduction to Epidemiology Disease Causation By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 25-10-2016 1 Presentation outline
Faculty of Medicine Introduction to Community Medicine Course (31505201) Unit 4 Epidemiology Introduction to Epidemiology Disease Causation By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 25-10-2016 1 Presentation outline
sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify
![sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify](/thumbs/80/80506400.jpg) BE.104 Spring Epidemiology: Test Development and Relative Risk J. L. Sherley Agent X? Cause Health First, Some definitions Morbidity = Mortality = sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify death Easy
BE.104 Spring Epidemiology: Test Development and Relative Risk J. L. Sherley Agent X? Cause Health First, Some definitions Morbidity = Mortality = sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify death Easy
CHAPTER 19: CONTROLS. One reprieve from the correlation-does-notimply-causation
 INTERPRETATION AND CONCLUSIONS CHAPTER 19: CONTROLS One reprieve from the correlation-does-notimply-causation difficulty is to seek out data that avoid certain problems with interpretation. Controls are
INTERPRETATION AND CONCLUSIONS CHAPTER 19: CONTROLS One reprieve from the correlation-does-notimply-causation difficulty is to seek out data that avoid certain problems with interpretation. Controls are
ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL
 ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH 510 - APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL 4 2013 Question 1: What makes the first study a case-control study? The first case study is a case-control study because
ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH 510 - APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL 4 2013 Question 1: What makes the first study a case-control study? The first case study is a case-control study because
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency
 Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency (The correct answer is underlined in bold text) 1. This statistic is used to estimate the risk of acquiring a disease. It may be measured as
Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency (The correct answer is underlined in bold text) 1. This statistic is used to estimate the risk of acquiring a disease. It may be measured as
Introduction to Epidemiology. Introduction to Epidemiology. Introduction to Epidemiology. Introduction to Epidemiology. Introduction to Epidemiology
 Executive Veterinary Program University of Illinois December 11 12, 2014 and Causal Inference Dr. Randall Singer Professor of Epidemiology Epidemiology study of the distribution and determinants of health-related
Executive Veterinary Program University of Illinois December 11 12, 2014 and Causal Inference Dr. Randall Singer Professor of Epidemiology Epidemiology study of the distribution and determinants of health-related
Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination
 DEPARTMENT OF EPIDEMIOLOGY, BIOSTATISTICS, AND OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination Epidemiology Stream Thursday, 6 December 2007 1:00 4:00 PM 1. This is a closed book exam. Bilingual dictionaries
DEPARTMENT OF EPIDEMIOLOGY, BIOSTATISTICS, AND OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination Epidemiology Stream Thursday, 6 December 2007 1:00 4:00 PM 1. This is a closed book exam. Bilingual dictionaries
Icebreaker Outbreak investigation with the disease detectives
 The card game Disease detectives can be used as an icebreaker exercise to get to know the epidemiological methods of relative risk, epidemic curve and food item-specific risk of illness in a playful way.
The card game Disease detectives can be used as an icebreaker exercise to get to know the epidemiological methods of relative risk, epidemic curve and food item-specific risk of illness in a playful way.
Quantitative Methods. Lonnie Berger. Research Training Policy Practice
 Quantitative Methods Lonnie Berger Research Training Policy Practice Defining Quantitative and Qualitative Research Quantitative methods: systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via
Quantitative Methods Lonnie Berger Research Training Policy Practice Defining Quantitative and Qualitative Research Quantitative methods: systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via
What Are Your Odds? : An Interactive Web Application to Visualize Health Outcomes
 What Are Your Odds? : An Interactive Web Application to Visualize Health Outcomes Abstract Spreading health knowledge and promoting healthy behavior can impact the lives of many people. Our project aims
What Are Your Odds? : An Interactive Web Application to Visualize Health Outcomes Abstract Spreading health knowledge and promoting healthy behavior can impact the lives of many people. Our project aims
Measures of Association
 Measures of Association Lakkana Thaikruea M.D., M.S., Ph.D. Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand Introduction One of epidemiological studies goal is to determine
Measures of Association Lakkana Thaikruea M.D., M.S., Ph.D. Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand Introduction One of epidemiological studies goal is to determine
In this chapter we discuss validity issues for quantitative research and for qualitative research.
 Chapter 8 Validity of Research Results (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) In this chapter we discuss validity issues for
Chapter 8 Validity of Research Results (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) In this chapter we discuss validity issues for
W e have previously described the disease impact
 606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
11 questions to help you make sense of a case control study
 Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) making sense of evidence 11 questions to help you make sense of a case control study How to use this appraisal tool Three broad issues need to be considered when
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) making sense of evidence 11 questions to help you make sense of a case control study How to use this appraisal tool Three broad issues need to be considered when
Fundamentals of Psychophysics
 Fundamentals of Psychophysics John Greenwood Department of Experimental Psychology!! NEUR3045! Contact: john.greenwood@ucl.ac.uk 1 Visual neuroscience physiology stimulus How do we see the world? neuroimaging
Fundamentals of Psychophysics John Greenwood Department of Experimental Psychology!! NEUR3045! Contact: john.greenwood@ucl.ac.uk 1 Visual neuroscience physiology stimulus How do we see the world? neuroimaging
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research Steps in Nonexperimental Research
 Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
Purpose. Study Designs. Objectives. Observational Studies. Analytic Studies
 Purpose Study Designs H.S. Teitelbaum, DO, PhD, MPH, FAOCOPM AOCOPM Annual Meeting Introduce notions of study design Clarify common terminology used with description and interpretation of information collected
Purpose Study Designs H.S. Teitelbaum, DO, PhD, MPH, FAOCOPM AOCOPM Annual Meeting Introduce notions of study design Clarify common terminology used with description and interpretation of information collected
You re listening to an audio module from BMJ Learning. Hallo. I'm Anna Sayburn, Senior Editor with the BMJ Group s Consumer Health Team.
 Transcript of learning module Shared decision making (Dur: 26' 13") Contributors: Anna Sayburn and Alf Collins Available online at: http://learning.bmj.com/ V/O: You re listening to an audio module from
Transcript of learning module Shared decision making (Dur: 26' 13") Contributors: Anna Sayburn and Alf Collins Available online at: http://learning.bmj.com/ V/O: You re listening to an audio module from
Part 1: Epidemiological terminology. Part 2: Epidemiological concepts. Participant s Names:
 Part 1: Epidemiological terminology Participant s Names: _ a. Define the following terms: (award 2 points for each word that is defined correctly) 1. Fomite: a physical object that serves to transmit an
Part 1: Epidemiological terminology Participant s Names: _ a. Define the following terms: (award 2 points for each word that is defined correctly) 1. Fomite: a physical object that serves to transmit an
Quantitative Research Methods and Tools
 Quantitative Research Methods and Tools Fraser Health Authority, 2011 The Fraser Health Authority ( FH ) authorizes the use, reproduction and/or modification of this publication for purposes other than
Quantitative Research Methods and Tools Fraser Health Authority, 2011 The Fraser Health Authority ( FH ) authorizes the use, reproduction and/or modification of this publication for purposes other than
These methods have been explained in partial or complex ways in the original Mind Reading book and our rare Risk Assessment book.
 These methods have been explained in partial or complex ways in the original Mind Reading book and our rare Risk Assessment book. In this lesson we will teach you a few of these principles and applications,
These methods have been explained in partial or complex ways in the original Mind Reading book and our rare Risk Assessment book. In this lesson we will teach you a few of these principles and applications,
Evidence Informed Practice Online Learning Module Glossary
 Term Abstract Associations Attrition Bias Background and Significance Baseline Basic Science Bias Blinding Definition An abstract is a summary of a research article. It usually includes the purpose, methods,
Term Abstract Associations Attrition Bias Background and Significance Baseline Basic Science Bias Blinding Definition An abstract is a summary of a research article. It usually includes the purpose, methods,
INTERNAL VALIDITY, BIAS AND CONFOUNDING
 OCW Epidemiology and Biostatistics, 2010 J. Forrester, PhD Tufts University School of Medicine October 6, 2010 INTERNAL VALIDITY, BIAS AND CONFOUNDING Learning objectives for this session: 1) Understand
OCW Epidemiology and Biostatistics, 2010 J. Forrester, PhD Tufts University School of Medicine October 6, 2010 INTERNAL VALIDITY, BIAS AND CONFOUNDING Learning objectives for this session: 1) Understand
Measurement. Reliability vs. Validity. Reliability vs. Validity
 MEASUREMENT Outline 1. Measurement - Reliability vs. Validity - Validity - Threats to Internal Validity - Construct Validity (measurement validity) - Face validity - Content validity - Predictive validity
MEASUREMENT Outline 1. Measurement - Reliability vs. Validity - Validity - Threats to Internal Validity - Construct Validity (measurement validity) - Face validity - Content validity - Predictive validity
Chapter 13: Experiments
 Chapter 13: Experiments The objective of sampling is to describe a population. In the process of collecting the sample, sample units are not to be modified or affected by the researcher. In contrast, experimental
Chapter 13: Experiments The objective of sampling is to describe a population. In the process of collecting the sample, sample units are not to be modified or affected by the researcher. In contrast, experimental
The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature
 Excerpted from 5 Steps to Reducing Stress: Recognizing What Works Recognizing Stress The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature as well as your preferred way of initiating a relaxation
Excerpted from 5 Steps to Reducing Stress: Recognizing What Works Recognizing Stress The first step to managing stress is to understand its nature as well as your preferred way of initiating a relaxation
20. Experiments. November 7,
 20. Experiments November 7, 2015 1 Experiments are motivated by our desire to know causation combined with the fact that we typically only have correlations. The cause of a correlation may be the two variables
20. Experiments November 7, 2015 1 Experiments are motivated by our desire to know causation combined with the fact that we typically only have correlations. The cause of a correlation may be the two variables
Lesson Marginal, Joint, and Conditional Probabilities from Two-Way Tables
 STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The United States Census Bureau collects large amounts of data on the American public. The two-way table below gives the current marital status by
STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The United States Census Bureau collects large amounts of data on the American public. The two-way table below gives the current marital status by
Journal Club Critical Appraisal Worksheets. Dr David Walbridge
 Journal Club Critical Appraisal Worksheets Dr David Walbridge The Four Part Question The purpose of a structured EBM question is: To be directly relevant to the clinical situation or problem To express
Journal Club Critical Appraisal Worksheets Dr David Walbridge The Four Part Question The purpose of a structured EBM question is: To be directly relevant to the clinical situation or problem To express
Human Experimentation
 Human Experimentation 1. Introduction: Medical science involves a lot of trial and error. To determine whether or not a new treatment works, or what its side-effects are, and so on, we have to TEST it.
Human Experimentation 1. Introduction: Medical science involves a lot of trial and error. To determine whether or not a new treatment works, or what its side-effects are, and so on, we have to TEST it.
Design strategies in quantitative research an introduction
 Design strategies in quantitative research an introduction Key messages Research design can be broadly divided in to descriptive and analytical. Descriptive studies look at the individual, location and
Design strategies in quantitative research an introduction Key messages Research design can be broadly divided in to descriptive and analytical. Descriptive studies look at the individual, location and
Evaluation Models STUDIES OF DIAGNOSTIC EFFICIENCY
 2. Evaluation Model 2 Evaluation Models To understand the strengths and weaknesses of evaluation, one must keep in mind its fundamental purpose: to inform those who make decisions. The inferences drawn
2. Evaluation Model 2 Evaluation Models To understand the strengths and weaknesses of evaluation, one must keep in mind its fundamental purpose: to inform those who make decisions. The inferences drawn
Clinical Research Scientific Writing. K. A. Koram NMIMR
 Clinical Research Scientific Writing K. A. Koram NMIMR Clinical Research Branch of medical science that determines the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment
Clinical Research Scientific Writing K. A. Koram NMIMR Clinical Research Branch of medical science that determines the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment
CRITICAL APPRAISAL SKILLS PROGRAMME Making sense of evidence about clinical effectiveness. 11 questions to help you make sense of case control study
 CRITICAL APPRAISAL SKILLS PROGRAMME Making sense of evidence about clinical effectiveness 11 questions to help you make sense of case control study General comments Three broad issues need to be considered
CRITICAL APPRAISAL SKILLS PROGRAMME Making sense of evidence about clinical effectiveness 11 questions to help you make sense of case control study General comments Three broad issues need to be considered
Measurement of Association and Impact. Attributable Risk Attributable Risk in Exposed Population Attributable risk
 Measurement of Association and Impact Attributable Risk Attributable Risk in Exposed Population Attributable risk Attributable Risk (AR) - Measures of association based on the absolute difference between
Measurement of Association and Impact Attributable Risk Attributable Risk in Exposed Population Attributable risk Attributable Risk (AR) - Measures of association based on the absolute difference between
CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA
 Data Analysis: Describing Data CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA In the analysis process, the researcher tries to evaluate the data collected both from written documents and from other sources such
Data Analysis: Describing Data CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA In the analysis process, the researcher tries to evaluate the data collected both from written documents and from other sources such
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Eleventh Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series 1.1-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Eleventh Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola 1.1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics 1-1 Review and Preview 1-2 Statistical Thinking 1-3
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Eleventh Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola 1.1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics 1-1 Review and Preview 1-2 Statistical Thinking 1-3
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology
 AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations)
 Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations) This is an experiment in the economics of strategic decision making. Various agencies have provided funds for this research.
Appendix: Instructions for Treatment Index B (Human Opponents, With Recommendations) This is an experiment in the economics of strategic decision making. Various agencies have provided funds for this research.
Chapter 8 Estimating with Confidence
 Chapter 8 Estimating with Confidence Introduction Our goal in many statistical settings is to use a sample statistic to estimate a population parameter. In Chapter 4, we learned if we randomly select the
Chapter 8 Estimating with Confidence Introduction Our goal in many statistical settings is to use a sample statistic to estimate a population parameter. In Chapter 4, we learned if we randomly select the
Observational Study Designs. Review. Today. Measures of disease occurrence. Cohort Studies
 Observational Study Designs Denise Boudreau, PhD Center for Health Studies Group Health Cooperative Today Review cohort studies Case-control studies Design Identifying cases and controls Measuring exposure
Observational Study Designs Denise Boudreau, PhD Center for Health Studies Group Health Cooperative Today Review cohort studies Case-control studies Design Identifying cases and controls Measuring exposure
This is an edited transcript of a telephone interview recorded in February 2010.
 Sound Advice This is an edited transcript of a telephone interview recorded in February 2010. Dr. Max Wiznitzer is a pediatric neurologist at Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital in Cleveland, Ohio, and
Sound Advice This is an edited transcript of a telephone interview recorded in February 2010. Dr. Max Wiznitzer is a pediatric neurologist at Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital in Cleveland, Ohio, and
Interpretation of Epidemiologic Studies
 Interpretation of Epidemiologic Studies Paolo Boffetta Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, USA International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France Outline Introduction to epidemiology Issues
Interpretation of Epidemiologic Studies Paolo Boffetta Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, USA International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France Outline Introduction to epidemiology Issues
Epidemiology 101. Nutritional Epidemiology Methods and Interpretation Criteria
 Slide 1 Epidemiology 101 Nutritional Epidemiology Methods and Interpretation Criteria Andrew Milkowski PhD Adjunct Professor University of Wisconsin Muscle Biology Laboratory amilkowski@ansci.wisc.edu
Slide 1 Epidemiology 101 Nutritional Epidemiology Methods and Interpretation Criteria Andrew Milkowski PhD Adjunct Professor University of Wisconsin Muscle Biology Laboratory amilkowski@ansci.wisc.edu
UNIT. Experiments and the Common Cold. Biology. Unit Description. Unit Requirements
 UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
Bias and confounding. Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, Section of Social Medicine
 Bias and confounding Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, maka@sund.ku.dk PhD-course in Epidemiology l 7 February 2017 l Slide number 1 The world according to an epidemiologist Exposure Outcome
Bias and confounding Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, maka@sund.ku.dk PhD-course in Epidemiology l 7 February 2017 l Slide number 1 The world according to an epidemiologist Exposure Outcome
Framework for Causation Analysis of Toxic Exposure Claims. CLCW SME Training August, 2017
 Framework for Causation Analysis of Toxic Exposure Claims CLCW SME Training August, 2017 Purpose Examiners are frequently asked: is the condition attributable to a specific event? It is incumbent on SME
Framework for Causation Analysis of Toxic Exposure Claims CLCW SME Training August, 2017 Purpose Examiners are frequently asked: is the condition attributable to a specific event? It is incumbent on SME
General Biostatistics Concepts
 General Biostatistics Concepts Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. What is Biostatistics? 2. Types of Measurements
General Biostatistics Concepts Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. What is Biostatistics? 2. Types of Measurements
WORKSHEET: Etiology/Harm
 Updated 9/10/2013 Name: WORKSHEET: Etiology/Harm Citation: McGregor SE, Courneya KS, Kopciuk KA, Tosevski C, Friedenreich CM. Case control study of lifetime alcohol intake and prostate cancer risk. Cancer
Updated 9/10/2013 Name: WORKSHEET: Etiology/Harm Citation: McGregor SE, Courneya KS, Kopciuk KA, Tosevski C, Friedenreich CM. Case control study of lifetime alcohol intake and prostate cancer risk. Cancer
