A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
|
|
|
- Georgia Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34: A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT Original Article Kyungseop So, Eunju Sung 1, * Total Healthcare Center, 1 Department of Family Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Background: The prevalence of alcohol use disorder (AUD) is very high in Korea. To identify AUD in the busy practice setting, brevity of screening tools is very important. We derived the brief Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) and evaluated its performance as a brief screening test. Methods: One hundred male drinkers from Kangbuk Samsung Hospital primary care outpatient clinic and psychiatric ward for alcoholism treatment completed questionnaires including the AUDIT, cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye-opener (CAGE), and National Alcoholism Screening Test (NAST) from April to July, AUD (alcohol abuse and dependence), defined by a physician in accordance with Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV, was used as a diagnostic criteria. To derive the brief AUDIT, factor analysis was performed using the principal component extraction method with a varimax rotated solution. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to investigate the discrimination ability of the brief AUDIT. Areas under the ROC curve were compared performance of screening questionnaires with 95% confidence intervals. Results: The derived brief AUDIT consists of 4 items: frequency of heavy drinking (item 3), impaired control over drinking (item 4), increased salience of drinking (item 5), and alcohol-related injury (item 9). Brief AUDIT exhibited an AUD screening accuracy better than CAGE, and equally to that of NAST. Areas under the ROC curves were 0.87 ( ), 0.76 ( ), and 0.81 ( ) for the brief AUDIT, CAGE, and NAST for AUD, and 0.97 ( ), 0.93 ( ) and 0.93 ( ) for alcohol dependence. Conclusion: The new brief AUDIT seems to be effective in detecting male AUD in the primary care setting in Korea. Further evaluation for women and different age groups is needed. Keywords: Alcohol; Mass Screening; Primary Health Care INTRODUCTION Received: October 30, 2012, Accepted: December 28, 2012 *Corresponding Author: Eunju Sung Tel: , Fax: eunjusung68@gmail.com Korean Journal of Family Medicine Copyright 2013 The Korean Academy of Family Medicine This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The proportion of Korean adults who drink alcohol is among the world s highest and is increasing from 45.8% in 1989 to 59.2% in ,2) According to the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey, the overall age-adjusted prevalence of alcohol use disorder (AUD: alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence) in 2009 was 38.8%. Men were about 7 times as likely as women to meet the criteria for AUD. 3) A large portion of Korean men drink alcohol excessively. In addition, the prevalence Korean J Fam Med Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan
2 of AUD is much higher in Korea compared to other countries. 4-6) Alcohol is implicated in a wide variety of diseases, disorders, and injuries, as well as many social and legal problems. The majority of excessive drinkers are undiagnosed. Often they present with symptoms or problems that would not normally be linked to their drinking. Brief intervention is a low-cost, effective preventive measure for heavy drinkers in outpatient settings. Therefore, screening heavy drinkers who need brief intervention is very important, especially in primary care. 7) Cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye-opener (CAGE), the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST), National Alcoholism Screening Test (NAST), and Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) are well known tools to screen for AUD. CAGE is the briefest effective screening test for lifetime alcohol abuse and/or dependence but it is insensitive for detecting heavy drinking and does not distinguish between active and past AUD. 8) MAST was devised as a structured interview instrument, and consists of 25 questions. 9) NAST (Alcoholism Screening Test of Seoul National Mental Hospital) was devised to screen Korean alcoholism. It was originally designed with 12 items to screen AUD in those who need psychiatric intervention in psychiatric inpatients. 10) The AUDIT is the first screening test designed specifically for use in primary care settings, and validated in Korea. 11) The AUDIT was developed to screen for excessive drinking and in particular to help practitioners identify people who would benefit from reducing or ceasing drinking. 12,13) Although its sensitivity, specificity, and other psychometric properties compare at least equally or exceed those of other screening instruments, the length of the AUDIT may preclude its use in settings where brevity is critical, such as in a primary care setting or emergency room. For such purposes, abbreviated versions of the AUDIT exist such as AUDIT-consumption (C), AUDIT-Primary Care, AUDIT-3, Rapid Alcohol Problems Screen (RAPS), RAPS4-quantityfrequency, and Alcohol Screening Test (FAST) ) Among them, AUDIT-C, which consists of the first 3 items of the AUDIT (the consumption factor items), has generated wide research interest. 19) Recently, AUDIT-C appeared to perform better than AUDIT-3 in the Korean primary care setting, but validated only against the full AUDIT rather than against an independent, formal alcohol diagnosis or hazardous drinking criterion. 20) As alcohol drinking behavior depends heavily on culture and ethnicity, we tried to derive a Korean short version of the AUDIT (brief AUDIT). We evaluated the brief AUDIT as a quick screening test for AUD, and compared the performance of the brief AUDIT with that of other validated alcohol screening questionnaires. METHODS 1. Study Population This study was conducted at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital primary care outpatient clinic and psychiatric ward for alcoholism treatment. The study population was 85 male drinkers from the primary care setting, and 15 male alcohol dependency patients from a psychiatric hospital from April to July, 2007, who consented with the study. The questionnaire was filled out by patients, and then their physician (1 psychiatrist and 4 family physicians) defined AUD in accordance with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV without knowing the results of the questionnaire. 2. Measures The questionnaire consisted of demographic factors, AUDIT, CAGE, and NAST. The AUDIT core questionnaire consists of 10 items: three questions on quantity and frequency of drinking, three items on alcohol dependence and four questions on problems caused by drinking. Weighted scoring with respect to the frequency or the time of occurrence results in total scores ranging from 0 to ) The CAGE is an acronym based on its four items: cut down on drinking, annoyed by criticism, guilty feelings, and eye opener. NAST consists of 12 items: easily feels self-pity, prefers drinking alone, drinks in the morning, feels a compelling desire to drink continuously, has difficulty resisting the impulse to drink, has recent amnesia about events during drunkenness, feels drinking is harmful to social life, has had damage to occupation, has a spouse about to leave, suffers from alcohol withdrawal symptom, suffers from serious alcohol withdrawal symptom, has had treatment for alcohol related problems. 10) 3. Statistical Analysis To derive brief AUDIT, factor analysis was performed using the principal component extraction method with a varimax 12 Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan 2013 Korean J Fam Med
3 rotated solution. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare brief AUDIT between groups (normal, alcohol abuse, and alcohol dependence). Pearson correlation analysis was used to assess the relationship between tests. Screening performance was evaluated by means of sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio and areas under receiver operating characteristics (ROCs). ROC curves plotted sensitivity versus 1-specificity, and areas under the curves and their 95% confidence intervals were determined. The area under an ROC curve (AUROC) is a measure of a screening test s overall screening performance taking into account all possible screening thresholds. Areas under ROC curves closer to 1.0 indicate a better performance and an area under a curve of 0.5 yields no useful information. Cronbach s alpha was calculated to assess internal consistency of brief AUDIT. All statistics were performed using the SPSS ver (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Table 1. Demographic characteristics of study subjects Characteristics Number Age (y) < RESULTS 1. Characteristics of Study Population Among subjects in the study population, 49 (49%) were defined as the normal group, 27 (27%) as abusive of alcohol, and 24 (24%) as alcohol-dependent. Mean age was 45.4 ± 11.0 (standard deviation) years. Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the study population. 2. Development of Brief Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Factor analysis was conducted to select questions from 10 items. Principal component extraction method identified 2 factors, and they accounted for 65% of total variance. The two factors and their components are presented in Table 2. One was alcohol-dependency and related problems (impaired control over drinking, increased salience of drinking, morning drinking, guilt after drinking, blackouts, alcohol-related injuries, and others concerned about drinking), and the other was consumption (frequency, typical quantity, and frequency of heavy drinking). To derive items for brief AUDIT, two criteria were adjusted. First, items with a factor loading value over 0.8 were selected. Items number 2, 3, 4, 5, and 9 were selected. Items 4, 5, and 9 belonged to factor one, and 2 and 3 to factor two (Table 2). Second, items which do not attribute Cronbach s alpha value were excluded. The AUDIT showed Cronbach s alpha of After exclusion Education Elementary school 6 Middle school 11 High school 25 University 58 Occupation White collar 44 Blue collar 22 Others 34 Marital status Married 69 Unmarried 19 Divorced 11 Separation by death 1 Total 100 Table 2. Result of factor analysis for Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test* Item Factor 1 Factor 2 Content Increased salience of drinking Alcohol-related injuries Impaired control over drinking Guilt after drinking Morning drinking Blackouts Others concerned about drinking Typical quantity Frequency of heavy drinking Frequency of drinking *Values are factor loading. Korean J Fam Med Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan
4 of item 2, alpha was (Table 3). Item 2 was near the typical quantity. Among consumption items, it seemed frequency of heavy drinking (item 3) perform better than the typical quantity (item 2). Item 3 is the one of AUDIT-3. So, item 3 was left for the brief AUDIT. The final items for the brief AUDIT were frequency of heavy drinking (item 3), impaired control over drinking (item 4), increased salience of drinking (item 5), and alcohol-related injury (item 9). The score system was applied the same as in AUDIT, total scores ranging from 0 to 16. Cronbach s alpha was calculated to assess internal consistency of the brief AUDIT. The brief AUDIT showed an alpha value of The Cronbach s alpha of NAST, CAGE, and original AUDIT were 0.86, 0.69, and 0.87 each. The internal consistency analysis yielded high Cronbach s alpha values for the full and brief AUDIT and NAST. CAGE was not sufficiently consistent compared to that of other questionnaires. 3. Performance of Brief Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test The brief AUDIT showed a high correlation with the 10-item original AUDIT, with a coefficient of 0.93, good correlation with NAST of 0.80, and CAGE of 0.76 (P < 0.05). The brief AUDIT discriminated AUD diagnosis as presented in Table 4. The mean of each group was 3.8, that of alcohol abuse 6.0, and alcohol dependence The difference was statistically significant (F = , df = 2, P < 0.001) (Table 4). ROC curves are depicted in the Figure 1, and the AUC for each ROC curve was calculated. Sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio by cut-off points are presented in Table 5. Optimum cut-off value was identified with the ROC curve. The brief AUDIT threshold that simultaneously maximized sensitivity and specificity for detecting AUD was 6 (sensitivity 83.3%, specificity 96.1%), and for alcohol dependence was 10 (sensitivity 83.3%, specificity 96.1%) (Table 5). As we included hospitalized AUD patients in the study, it is possible that our values are higher than in the primary care setting. The purpose of the brief AUDIT is to detect AUD in a short time. As maximizing sensitivity is the best policy for screening disease like AUDs, we chose a cutoff point of 5 (sensitivity 80.4%, positive likelihood ratio [+LR] 2.62) for AUDs, and 9 (sensitivity 87.5%, +LR Table 3. Item analysis of Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Item Scale variance if item deleted Corrected item-total correlation Squared multiple correlation Cronbach s alpha if item deleted Table 4. Comparison of brief AUDIT scores between normal, alcohol abuse, and AD Normal (n = 49) Alcohol abuse (n = 27) AD (n = 24) F df P-value* Mean ± SD 3.8 ± ± ± AUDIT: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test, AD: alcohol dependence. *Analysis of variance and post-hoc. 14 Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan 2013 Korean J Fam Med
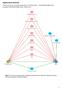
5 9.51) for alcohol dependence (Table 5). The brief AUDIT s AUROC curve for AUD was 0.87 ± 0.04 (standard error [SE]). The brief AUDIT had a greater AUROC curve than either CAGE 0.76 ± 0.05 (SE), or NAST 0.82 ± 0.04 (SE) for alcohol abuse. The brief AUDIT s AUROC curve for alcohol dependence was 0.97 ± 0.01 (SE). It was greater than that of NAST 0.93 ± 0.02 (SE) or CAGE 0.93 ± 0.03 (SE) (Table 6). DISCUSSION To our knowledge, this is the first study to derive a short form of the AUDIT (brief AUDIT) and compare the performance of Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic curves of the brief Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), National Alcoholism Screening Test (NAST), and cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye-opener (CAGE) for alcohol use disorder (A) and alcohol dependence (B). Table 5. Performance of brief AUDIT questionnaire for detecting any AUDs or AD Cut-off score (AUDs) Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) +LR -LR AUDs AD AUDIT: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test, AUD: alcohol use disorders, AD: alcohol dependence, +LR: positive likelihood ratio, -LR: negative likelihood ratio. Table 6. AUCs comparison of brief AUDIT with CAGE and NAST Group Brief AUDIT CAGE NAST AUC 95% CI AUC 95% CI AUC 95% CI Any AUDs AD AUC: area under the curve, AUDIT: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test, CAGE: cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye-opener, NAST: National Alcoholism Screening Test, CI: confidence interval, AUD: alcohol use disorders, AD: alcohol dependence. Korean J Fam Med Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan
6 it with that of well known AUD screening questionnaires, CAGE, and NAST, in the primary care setting in Korea. The new brief AUDIT consists of 4 items: frequency of heavy drinking (item 3), impaired control over drinking (item 4), increased salience of drinking (item 5), and alcohol-related injury (item 9), with a scoring range from 0 to 16. The brief AUDIT discriminated AUD very well. The cut-off point was 5 to detect any AUD (sensitivity 80.4%, specificity 69.4%), and 9 for alcohol dependence (sensitivity 87.5%, specificity 90.8%). The brief AUDIT s AUROC curve for alcohol-use disorder was 0.87 ± 0.04 (SE), and for alcohol dependence was 0.97 ± 0.01 (SE). The brief AUDIT had a greater AUROC curve than either CAGE 0.76 ± 0.05 (SE), or NAST 0.82 ± 0.04 (SE) for Any AUD, and greater than either NAST 0.93 ± 0.02 (SE) or CAGE 0.93 ± 0.03 (SE) for alcohol dependence. As we targeted primary outpatient setting, we put weight for higher sensitivity to detect any AUD and higher specificity for alcohol dependence. AUDIT was originally designed for practitioners to screen problem drinkers, i.e., drinking problems less severe than diagnosable disorders of AUD as well as AUD. The full 10- item AUDIT with its multidimensional scoring for each item has been called cumbersome for use in some settings where rapidity of scoring, as well as accuracy, is important. 21) Many abbreviated versions of AUDIT were generated and tested to meet this practical need. AUDIT-C, the most commonly tested derived AUDIT, consists of the first 3 items of the AUDIT (the consumption factor items). AUDIT-C was reported useful to screen problem drinkers, and AUD in western countries. FAST is a 4-item scale consisting of item 3 (modified for men by increasing the number of drinks from 1 occasion to 8) as well as items 5, 8, and 10 from the original AUDIT. Unfortunately, these researchers validated the abbreviated scale only against the full AUDIT rather than also against an independent, formal alcohol diagnosis or hazardous drinking criterion. 22) Drinking behavior of the western population may be quite different from that of Korea. Heavy drinking is very popular because alcohol is accepted generously and quite often, and is socially forced in work-related gatherings, especially for men. This consumption factor might not be enough to discriminate AUD, however it is the main reason we decided to derive a short version for Koreans rather than using the existing one. We compared the performance of the brief AUDIT with the AUDIT-C and FAST. The AUROC against AUD was for the brief AUDIT, for the AUDIT-C, and for FAST. The AUROC for alcohol dependence was for the brief AUDIT, for the AUDIT-C, and for FAST (data not presented). The performance of the brief AUDIT was about equal to FAST, and better than the AUDIT-C. The performance of the AUDIT-C to detect AUD against formal alcohol diagnosis need to be further evaluated for Koreans. The AUDIT questionnaire is measured consistently over time and is particularly useful in detecting recent problem drinking. Investigators in a six-country World Health Organization project developed the AUDIT to screen patients in primary health care settings for hazardous or harmful drinking and serve as a basis for discussion with patents in brief therapy. 12) Hazardous drinkers are individuals at high risk for alcohol-related damage to physical or psychological health; harmful drinkers already experience such problems. 23) The original cut-off point to detect hazardous drinker is 8, yielding a sensitivity of 0.90 s, and specificity of 0.80 s. To find the hazardous drinking cut-off point, the gold standard criteria need to be multidimensional: heavy consumption (i.e., 14 or more drinks per week), laboratory results or clinical diagnosis like alcoholic hepatitis, as well as diagnosis of AUD. The performance of AUDIT against those criteria needs to be evaluated further to make the AUDIT more practical, and at the same time, accurate for Koreans. Also, further study to evaluate the performance of the abbreviated version of the AUDIT against other criteria than AUD might be useful to detect problem drinkers. Limitations of this study were as follows. Firstly, the study subjects were not representative of the entire population. Women were excluded, and the age range of study subjects was 32 to 63. Cut-off points could be different for different populations, as alcohol affects women differently. Women were excluded because alcohol screening questionnaires function differently in men and women 19) and we could not recruit an adequate number of women through which to base any conclusions regarding questionnaire performance. Also we collected 15% of study subjects from the psychiatric ward and not only from primary outpatient clinics for the same reason. Secondly, performance of the brief AUDIT on criteria of problem drinking was not measured as mentioned above. Thirdly, test-retest was not evaluated. Lastly, we used the same population to derive and validate the brief AUDIT. 16 Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan 2013 Korean J Fam Med
7 The brief AUDIT was short and performed well to screen alcohol-use disorders in middle-aged men. It will facilitate screening for alcohol problems where significant constraints on time exist. Further research to evaluate performance of the brief AUDIT against criteria of problem drinking in large populations including other age groups and women are needed to verify its effectiveness. CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. REFERENCES 1. Koh KH. Estimates of alcohol consumption based on pure alcohol content and their comparison with data of other countries. Health Welf Policy Forum 2000;6: Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III). Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare; Park SH, Kim CH, Kim DJ, Suk KT, Park HY, Lee JG, et al. Secular trends in prevalence of alcohol use disorder and its correlates in Korean adults: results from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005 and Subst Abus 2012;33: Lee CK, Kwak YS, Yamamoto J, Rhee H, Kim YS, Han JH, et al. Psychiatric epidemiology in Korea. Part I: Gender and age differences in Seoul. J Nerv Ment Dis 1990;178: Lee CK, Kwak YS, Yamamoto J, Rhee H, Kim YS, Han JH, et al. Psychiatric epidemiology in Korea. Part II: Urban and rural differences. J Nerv Ment Dis 1990;178: Min S, Noh S, Shin J, Ahn JS, Kim TH. Alcohol dependence, mortality, and chronic health conditions in a rural population in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2008;23: Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG; World Health Organization. AUDIT: the alcohol use disorders identification test: guidelines for use in primary health care. 2nd ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; Mayfield D, McLeod G, Hall P. The CAGE questionnaire: validation of a new alcoholism screening instrument. Am J Psychiatry 1974;131: Selzer ML. The Michigan alcoholism screening test: the quest for a new diagnostic instrument. Am J Psychiatry 1971;127: Kim KB, Hahn KS, Lee JK, Rhee MK, Kim YK, Kim CK. The preliminary study of the Korean alcoholism screening test (III). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 1991;30: Kim JS, Oh MK, Park BK, Lee MK, Kim GJ. Screening criteria of alcoholism by alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) in Korea. J Korean Acad Fam Med 1999;20: Allen JP, Litten RZ, Fertig JB, Babor T. A review of research on the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1997;21: Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, de la Fuente JR, Grant M. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption-- II. Addiction 1993;88: Cherpitel CJ, Bazargan S. Screening for alcohol problems: comparison of the audit, RAPS4 and RAPS4-QF among African American and Hispanic patients in an inner city emergency department. Drug Alcohol Depend 2003;71: Cherpitel CJ, Ye Y, Moskalewicz J, Swiatkiewicz G. Screening for alcohol problems in two emergency service samples in Poland: comparison of the RAPS4, CAGE and AUDIT. Drug Alcohol Depend 2005;80: Gomez A, Conde A, Santana JM, Jorrin A. Diagnostic usefulness of brief versions of Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) for detecting hazardous drinkers in primary care settings. J Stud Alcohol 2005;66: Gordon AJ, Maisto SA, McNeil M, Kraemer KL, Conigliaro RL, Kelley ME, et al. Three questions can detect hazardous drinkers. J Fam Pract 2001;50: Piccinelli M, Tessari E, Bortolomasi M, Piasere O, Semenzin M, Garzotto N, et al. Efficacy of the alcohol use disorders identification test as a screening tool for hazardous alcohol Korean J Fam Med Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan
8 intake and related disorders in primary care: a validity study. BMJ 1997;314: Reinert DF, Allen JP. The alcohol use disorders identification test: an update of research findings. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007;31: Seong JH, Lee CH, Do HJ, Oh SW, Lym YL, Choi JK, et al. Performance of the AUDIT Alcohol Consumption Questions (AUDIT-C) and AUDIT-K question 3 alone in screening for problem drinking. Korean J Fam Med 2009;30: Hearne R, Connolly A, Sheehan J. Alcohol abuse: prevalence and detection in a general hospital. J R Soc Med 2002;95: Hodgson R, Alwyn T, John B, Thom B, Smith A. The fast alcohol screening test. Alcohol Alcohol 2002;37: Allen JP, Reinert DF, Volk RJ. The alcohol use disorders identification test: an aid to recognition of alcohol problems in primary care patients. Prev Med 2001;33: Vol. 34, No. 1 Jan 2013 Korean J Fam Med
Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and Alcohol Use Disorders
 Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Association between Alcoholism Family History and Alcohol Screening Scores among Alcohol-dependent Patients
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/0.9758/cpn.203..2.89 pissn 738-088 / eissn 2093-4327 Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 203;(2):89-95 Copyrightc 203, Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/0.9758/cpn.203..2.89 pissn 738-088 / eissn 2093-4327 Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 203;(2):89-95 Copyrightc 203, Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology
Department of Emergency Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 2018;5(2):113-119 https://doi.org/10.15441/ceem.17.228 Validation and proposal for cut-off values of an abbreviated version of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test using the
Clin Exp Emerg Med 2018;5(2):113-119 https://doi.org/10.15441/ceem.17.228 Validation and proposal for cut-off values of an abbreviated version of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test using the
VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND
 VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Somsong Nanakorn 1, Katsuhiro Fukuda 2, Itsuro Ogimoto 2, Tawee Tangseree 3 and Suchart Treethiptikhun 4
VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Somsong Nanakorn 1, Katsuhiro Fukuda 2, Itsuro Ogimoto 2, Tawee Tangseree 3 and Suchart Treethiptikhun 4
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey
 Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test
 JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care attenders?
 Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
New Approach to the Validity of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Stratum-Specific Likelihood Ratios Analysis
 0145-6008/05/2904-0602$03.00/0 ALCOHOLISM: CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Vol. 29, No. 4 April 2005 New Approach to the Validity of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Stratum-Specific Likelihood
0145-6008/05/2904-0602$03.00/0 ALCOHOLISM: CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Vol. 29, No. 4 April 2005 New Approach to the Validity of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Stratum-Specific Likelihood
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
The Role of Alcoholics Insight in Abstinence from Alcohol in Male Korean Alcohol Dependents
 J Korean Med Sci 2007; 22: 132-7 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Role of Alcoholics Insight in Abstinence from Alcohol in Male Korean Alcohol Dependents This study was
J Korean Med Sci 2007; 22: 132-7 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Role of Alcoholics Insight in Abstinence from Alcohol in Male Korean Alcohol Dependents This study was
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students
 Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
The Effects of National Health Insurance Denture Coverage Policies for the Elderly on the Unmet Dental Needs of the Edentulous Elderly
 J Dent Hyg Sci Vol. 18, No. 3, 2018, pp.182-187 https://doi.org/10.17135/jdhs.2018.18.3.182 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Effects of National Health Insurance Denture Coverage Policies for the Elderly on the Unmet
J Dent Hyg Sci Vol. 18, No. 3, 2018, pp.182-187 https://doi.org/10.17135/jdhs.2018.18.3.182 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Effects of National Health Insurance Denture Coverage Policies for the Elderly on the Unmet
Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires
 Q J Med 2002; 95:591 595 Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires M.T. MCCUSKER 1, J. BASQUILLE 1,M.KHWAJA 1, I.M. MURRAY-LYON 2 and J. CATALAN 3 From
Q J Med 2002; 95:591 595 Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires M.T. MCCUSKER 1, J. BASQUILLE 1,M.KHWAJA 1, I.M. MURRAY-LYON 2 and J. CATALAN 3 From
ALCOHOL DRUG EVALUATION PREPARATION
 Alcohol/Drug Evaluation The alcohol drug evaluation is critical to the success of your case. We want you to get the best evaluation possible with the least amount of treatment, or classes, necessary. In
Alcohol/Drug Evaluation The alcohol drug evaluation is critical to the success of your case. We want you to get the best evaluation possible with the least amount of treatment, or classes, necessary. In
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care
 Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
A study of South Korean casino employees and gambling problems
 Occupational Medicine 2008;58:191 197 Published online 15 March 2008 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqn025 A study of South Korean casino employees and gambling problems Tae Kyung Lee 1, Richard A. LaBrie 2, Hak Seung
Occupational Medicine 2008;58:191 197 Published online 15 March 2008 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqn025 A study of South Korean casino employees and gambling problems Tae Kyung Lee 1, Richard A. LaBrie 2, Hak Seung
A study on the effects of exercise motivation of the elderly people on euphoria
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2017;13(4):387-392 A study on the effects of exercise motivation of the elderly people on euphoria Ah-Ra Oh 1, Eun-Surk Yi 2, * 1 Department of Physical
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2017;13(4):387-392 A study on the effects of exercise motivation of the elderly people on euphoria Ah-Ra Oh 1, Eun-Surk Yi 2, * 1 Department of Physical
BRIEF REPORT FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH UNTREATED REMISSIONS FROM ALCOHOL ABUSE OR DEPENDENCE
 Pergamon Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 317 321, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0306-4603/00/$ see front matter PII S0306-4603(98)00130-0 BRIEF
Pergamon Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 317 321, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0306-4603/00/$ see front matter PII S0306-4603(98)00130-0 BRIEF
1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18
 1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18 Dr. Laura Carone, FY1 Dr Venkataramana Thiagarajan, GPVTS2 Dr. Mariam Benaris, Consultant Psychiatrist & audit team lead Dr James
1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18 Dr. Laura Carone, FY1 Dr Venkataramana Thiagarajan, GPVTS2 Dr. Mariam Benaris, Consultant Psychiatrist & audit team lead Dr James
EDRS. trends. bulletin. Alcohol use disorders amongst a group of regular ecstasy users. Key findings. july Introduction.
 ecstasy and related drug trends july 2011 bulletin Authors: Sheena Arora and Lucy Burns, National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales Suggested citation: Arora, S. & Burns,
ecstasy and related drug trends july 2011 bulletin Authors: Sheena Arora and Lucy Burns, National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales Suggested citation: Arora, S. & Burns,
Psychology Research Institute, University of Ulster, Northland Road, Londonderry, BT48 7JL, UK
 Patterns of Alcohol Consumption and Related Behaviour in Great Britain: A Latent Class Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) Gillian W. Smith * and Mark Shevlin Psychology Research
Patterns of Alcohol Consumption and Related Behaviour in Great Britain: A Latent Class Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) Gillian W. Smith * and Mark Shevlin Psychology Research
A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean university hospital pediatric dental clinic
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification. Clinical background
 Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification POMH-UK Quality Improvement Programme. Topic 14a: baseline Clinical background 1 2014 The Royal College of Psychiatrists. For further information
Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification POMH-UK Quality Improvement Programme. Topic 14a: baseline Clinical background 1 2014 The Royal College of Psychiatrists. For further information
Effect of oral health education on the planned behavior theory variables among hospitalized alcoholic patients using structural equation model.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (19): 8316-8320 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of oral health education on the planned behavior theory variables among hospitalized alcoholic patients using structural
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (19): 8316-8320 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of oral health education on the planned behavior theory variables among hospitalized alcoholic patients using structural
The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse. ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage:
 The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse Encompassing All Addictive Disorders ISSN: 0095-2990 (Print) 1097-9891 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iada20 A review of the Alcohol
The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse Encompassing All Addictive Disorders ISSN: 0095-2990 (Print) 1097-9891 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iada20 A review of the Alcohol
Validating the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test With Persons Who Have a Serious Mental Illness
 O Hare et al. / ALCOHOL USE IDENTIFICATION TEST 10.1177/1049731503257667 ARTICLE RESEARCH ON SOCIAL WORK PRACTICE Validating the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test With Persons Who Have a Serious
O Hare et al. / ALCOHOL USE IDENTIFICATION TEST 10.1177/1049731503257667 ARTICLE RESEARCH ON SOCIAL WORK PRACTICE Validating the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test With Persons Who Have a Serious
The Clinical Effects of Carthami-Flos Pharmacopuncture on Posterior Neck pain of Menopausal Women
 ISSN 2093-6966 Journal of Pharmacopuncture 71 http://dx.doi.org/10.3831/kpi.2011.14.4.071 Received : Nov 10, 2011 Revised : Nov 25, 2011 Accepted : Nov 30, 2011 KEY WORDS: Carthami-Flos; Neck pain, Pharmacopuncture;
ISSN 2093-6966 Journal of Pharmacopuncture 71 http://dx.doi.org/10.3831/kpi.2011.14.4.071 Received : Nov 10, 2011 Revised : Nov 25, 2011 Accepted : Nov 30, 2011 KEY WORDS: Carthami-Flos; Neck pain, Pharmacopuncture;
Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis
 pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
Socioeconomic status risk factors for cardiovascular diseases by sex in Korean adults
 , pp.44-49 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013 Socioeconomic status risk factors for cardiovascular diseases by sex in Korean adults Eun Sun So a, Myung Hee Lee 1 * a Assistant professor, College of Nursing,
, pp.44-49 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013 Socioeconomic status risk factors for cardiovascular diseases by sex in Korean adults Eun Sun So a, Myung Hee Lee 1 * a Assistant professor, College of Nursing,
Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores
 Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 31 (2006) 17 24 Regular article Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores Samuel H. Rikoon, (B.A.) a, John S. Cacciola,
Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 31 (2006) 17 24 Regular article Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores Samuel H. Rikoon, (B.A.) a, John S. Cacciola,
Bianca Calabria 1*, Anton Clifford 2, Anthony P Shakeshaft 1, Katherine M Conigrave 1,3,4, Lynette Simpson 5, Donna Bliss 6 and Julaine Allan 7
 Calabria et al. Addiction Science & Clinical Practice 2014, 9:17 RESEARCH Open Access Identifying Aboriginal-specific AUDIT-C and AUDIT-3 cutoff scores for at-risk, high-risk, and likely dependent s using
Calabria et al. Addiction Science & Clinical Practice 2014, 9:17 RESEARCH Open Access Identifying Aboriginal-specific AUDIT-C and AUDIT-3 cutoff scores for at-risk, high-risk, and likely dependent s using
MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE
 Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(2)131-137 MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE SURENDRA K.MATTOO, D.BASU, A.MALHOTRA & R.MALHOTRA ABSTRACT Motivation for
Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(2)131-137 MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE SURENDRA K.MATTOO, D.BASU, A.MALHOTRA & R.MALHOTRA ABSTRACT Motivation for
Chapter 3. Psychometric Properties
 Chapter 3 Psychometric Properties Reliability The reliability of an assessment tool like the DECA-C is defined as, the consistency of scores obtained by the same person when reexamined with the same test
Chapter 3 Psychometric Properties Reliability The reliability of an assessment tool like the DECA-C is defined as, the consistency of scores obtained by the same person when reexamined with the same test
A Study of a Diet Improvement Method for Controlling High Sodium Intake Based on Protective Motivation Theory
 pissn 1229-1153 / eissn 2465-9223 J. Food Hyg. Saf. Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 89~93 (2018) https://doi.org/10.13103/jfhs.2018.33.2.89 Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety Available online at http://www.foodhygiene.or.kr
pissn 1229-1153 / eissn 2465-9223 J. Food Hyg. Saf. Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 89~93 (2018) https://doi.org/10.13103/jfhs.2018.33.2.89 Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety Available online at http://www.foodhygiene.or.kr
Protective Factors against Prenatal Depression in Pregnant Women
 , pp.78-82 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.122.15 Protective Factors against Prenatal Depression in Pregnant Women Sung Hee Lee 1 and Seung A Lee 2 1 College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University,
, pp.78-82 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.122.15 Protective Factors against Prenatal Depression in Pregnant Women Sung Hee Lee 1 and Seung A Lee 2 1 College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University,
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice. Citation for published version: Holloway, A 2015, 'Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice.' Practice Nursing, vol. 26, no. 1. DOI: 10.12968/pnur.2015.26.1.10
Edinburgh Research Explorer Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice. Citation for published version: Holloway, A 2015, 'Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice.' Practice Nursing, vol. 26, no. 1. DOI: 10.12968/pnur.2015.26.1.10
A Study on Knowledge and Attitudes Regarding Sexuality of Elderly People in Korea
 Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (2007) Vol. 37, No. 2, 179 184 A Study on Knowledge and Attitudes Regarding Sexuality of Elderly People in Korea Kyung-Ja Lee 1, Myoung-Sook Kwon 2, Mi Ja Kim 2, Seong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (2007) Vol. 37, No. 2, 179 184 A Study on Knowledge and Attitudes Regarding Sexuality of Elderly People in Korea Kyung-Ja Lee 1, Myoung-Sook Kwon 2, Mi Ja Kim 2, Seong
Screening for Normal Cognition, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia with the Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2017.08.24 Print ISSN 1738-3684 / On-line ISSN 1976-36 OPEN ACCESS Screening for Normal Cognition, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia with the Korean Dementia
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2017.08.24 Print ISSN 1738-3684 / On-line ISSN 1976-36 OPEN ACCESS Screening for Normal Cognition, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia with the Korean Dementia
Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013
 Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013 The Company You Keep 1 Antitrust 2 New York Life adheres to the letter and spirit of the antitrust laws.
Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013 The Company You Keep 1 Antitrust 2 New York Life adheres to the letter and spirit of the antitrust laws.
The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners
 Practice The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners N Bowes A Sutton S Jenkins FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES, NOMS CYMRU, HMP CARDIFF J McMurran INSTITUTE OF MENTAL HEALTH, UNIVERSITY
Practice The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners N Bowes A Sutton S Jenkins FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES, NOMS CYMRU, HMP CARDIFF J McMurran INSTITUTE OF MENTAL HEALTH, UNIVERSITY
Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR
 Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR ALCOHOL IS A DRUG Drinking alcohol is the most common type of drug use in Australia Despite, Ice epidemic,
Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR ALCOHOL IS A DRUG Drinking alcohol is the most common type of drug use in Australia Despite, Ice epidemic,
The Effects of Posture on Neck Flexion Angle While Using a Smartphone according to Duration
 J Korean Soc Phys Med, 2016; 11(3): 35-39 http://dx.doi.org/10.13066/kspm.2016.11.3.35 Online ISSN: 2287-7215 Print ISSN: 1975-311X Research Article Open Access The Effects of Posture on Neck Flexion Angle
J Korean Soc Phys Med, 2016; 11(3): 35-39 http://dx.doi.org/10.13066/kspm.2016.11.3.35 Online ISSN: 2287-7215 Print ISSN: 1975-311X Research Article Open Access The Effects of Posture on Neck Flexion Angle
A Comparative Study of Alcoholism & Its Risk Factors in Male and Female Drinkers
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 5, Issue 1, DIP: 18.01.118/20170501 DOI: 10.25215/0501.118 http://www.ijip.in October-December, 2017 Original
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 5, Issue 1, DIP: 18.01.118/20170501 DOI: 10.25215/0501.118 http://www.ijip.in October-December, 2017 Original
Propriety of Internet Use Time for Internet Addiction among Korean Adolescents
 Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 26), pp.23-27 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.26. Propriety of Internet Use Time for Internet Addiction among Korean Adolescents Eun Sun So 1, Young-Ran Chin 2 1 Chonbuk
Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 26), pp.23-27 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.26. Propriety of Internet Use Time for Internet Addiction among Korean Adolescents Eun Sun So 1, Young-Ran Chin 2 1 Chonbuk
Economic Hardship and Elderly Suicidal Ideation: with a Focus on the Double Mediating Effects of Depression and Family Relationship
 , pp.64-68 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.101.15 Economic Hardship and Elderly Suicidal Ideation: with a Focus on the Double Mediating Effects of Depression and Family Relationship Jung-Bin, Yang
, pp.64-68 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.101.15 Economic Hardship and Elderly Suicidal Ideation: with a Focus on the Double Mediating Effects of Depression and Family Relationship Jung-Bin, Yang
Predictors of Antenatal Depression in Unmarried Pregnant Women
 , pp.72-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.104.16 Predictors of Antenatal Depression in Unmarried Pregnant Women Sung Hee Lee 1* 1 College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
, pp.72-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.104.16 Predictors of Antenatal Depression in Unmarried Pregnant Women Sung Hee Lee 1* 1 College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their drinking or advice to cut down on the AUDIT scale?
 Cunningham et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology (2017) 17:158 DOI 10.1186/s12874-017-0435-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their
Cunningham et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology (2017) 17:158 DOI 10.1186/s12874-017-0435-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their
ALCOHOL USE DISORDERS AND ASSOCIATED FACTORS AMONG PATIENTS ADMITTED TO MEDICAL UNITS, AT TEACHING HOSPITAL KANDY
 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/sljm.v27i1.75 Sri Lanka Journal of Medicine Vol. 27 No.1, 2018 RESEARCH PAPER. ALCOHOL USE DISORDERS AND ASSOCIATED FACTORS AMONG PATIENTS ADMITTED TO MEDICAL UNITS, AT TEACHING
DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/sljm.v27i1.75 Sri Lanka Journal of Medicine Vol. 27 No.1, 2018 RESEARCH PAPER. ALCOHOL USE DISORDERS AND ASSOCIATED FACTORS AMONG PATIENTS ADMITTED TO MEDICAL UNITS, AT TEACHING
Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE AND RISK OF ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL IN MEDICAL INPATIENTS
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 515 519, 2005 Advance Access publication 15 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh189 COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 515 519, 2005 Advance Access publication 15 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh189 COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE
The Reliability and Validity of the Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-IADL)
 The Reliability and Validity of the Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-IADL Sue J. Kang, M.S., Seong Hye Choi, M.D.*, Byung H. Lee, M.A., Jay C. Kwon, M.D., Duk L. Na, M.D., Seol-Heui Han
The Reliability and Validity of the Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-IADL Sue J. Kang, M.S., Seong Hye Choi, M.D.*, Byung H. Lee, M.A., Jay C. Kwon, M.D., Duk L. Na, M.D., Seol-Heui Han
Smoking and hazardous alcohol
 Screening for Substance Abuse and Psychiatric Disorders Among Women Patients in a VA Health Care System Tania M. Davis, Ph.D. Kristen R. Bush, M.P.H. Daniel R. Kivlahan, Ph.D. Dorcas J. Dobie, M.D. Katharine
Screening for Substance Abuse and Psychiatric Disorders Among Women Patients in a VA Health Care System Tania M. Davis, Ph.D. Kristen R. Bush, M.P.H. Daniel R. Kivlahan, Ph.D. Dorcas J. Dobie, M.D. Katharine
Musculoskeletal Problems Affect the Quality of Life of Patients with Parkinson s Disease
 https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.18022 / J Mov Disord 2018;11(3):133-138 pissn 2005-940X / eissn 2093-4939 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Problems Affect the Quality of Life of Patients with Parkinson s
https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.18022 / J Mov Disord 2018;11(3):133-138 pissn 2005-940X / eissn 2093-4939 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Problems Affect the Quality of Life of Patients with Parkinson s
Internet Dependency among University Entrants: A Pilot Study
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 2, No.4, DIP: 18.01.068/20160302 ISBN: 978-1-329-85570-0 http://www.ijip.in January - March, 2016 Internet
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 2, No.4, DIP: 18.01.068/20160302 ISBN: 978-1-329-85570-0 http://www.ijip.in January - March, 2016 Internet
Alcohol Problems in Intimate Relationships
 Alcohol Problems in Intimate Relationships Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Alcohol Problems and Your Practice An Alcohol Problems Framework
Alcohol Problems in Intimate Relationships Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Alcohol Problems and Your Practice An Alcohol Problems Framework
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Data Harmonization Measure
 Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Measure Drug and Alcohol Use Drug and Alcohol Measure References: 1) Adapted from: Babor, T.F., Higgins-Biddle, J.C., Saunders, J.B. & Monteiro,
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Measure Drug and Alcohol Use Drug and Alcohol Measure References: 1) Adapted from: Babor, T.F., Higgins-Biddle, J.C., Saunders, J.B. & Monteiro,
Investigation of HAZARDOUS DRINKING. 2 November 2010 best tests
 Investigation of HAZARDOUS DRINKING 2 November 2010 best tests Key concepts: Approximately 20 25% of New Zealanders consume alcohol at a harmful or hazardous level In approximately three-quarters of patients
Investigation of HAZARDOUS DRINKING 2 November 2010 best tests Key concepts: Approximately 20 25% of New Zealanders consume alcohol at a harmful or hazardous level In approximately three-quarters of patients
Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2
 Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2 Pocket Card SBIRT Health Effects of Substance Abuse Alcohol Use Disorders Identification test (AUDIT) NAME: Date: The following questions concern information about your alcohol
Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2 Pocket Card SBIRT Health Effects of Substance Abuse Alcohol Use Disorders Identification test (AUDIT) NAME: Date: The following questions concern information about your alcohol
ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE DISORDERS IN THE GENERAL POPULATION
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol 40, No 5, pp 441 446, 2005 Advance Access publication 11 July 2005 doi:101093/alcalc/agh183 ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol 40, No 5, pp 441 446, 2005 Advance Access publication 11 July 2005 doi:101093/alcalc/agh183 ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE
Validity of the Sinhala Version of the General Health Questionnaires Item 12 and 30: Using Different Sampling Strategies and Scoring Methods
 Original Research Article Validity of the Sinhala Version of the General Health Questionnaires Item 12 and 30: Using Different Sampling Strategies and Scoring Methods H T C S Abeysena 1, P L Jayawardana
Original Research Article Validity of the Sinhala Version of the General Health Questionnaires Item 12 and 30: Using Different Sampling Strategies and Scoring Methods H T C S Abeysena 1, P L Jayawardana
Past Year Alcohol Consumption Patterns, Alcohol Problems and Alcohol-Related Diagnoses in the New Zealand Mental Health Survey
 Past Year Alcohol Consumption Patterns, Alcohol Problems and Alcohol-Related Diagnoses in the New Zealand Mental Health Survey Jessie Elisabeth Wells * and Magnus Andrew McGee Department of Population
Past Year Alcohol Consumption Patterns, Alcohol Problems and Alcohol-Related Diagnoses in the New Zealand Mental Health Survey Jessie Elisabeth Wells * and Magnus Andrew McGee Department of Population
Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA Scale)
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Associations between the Risk of Internet Addiction and Problem Behaviors among Korean Adolescents
 Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:115-122 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.2.115 Associations between the Risk of Internet Addiction and Problem Behaviors among Korean Adolescents Original Article Jisun
Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:115-122 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.2.115 Associations between the Risk of Internet Addiction and Problem Behaviors among Korean Adolescents Original Article Jisun
Beacon Health Strategies Comorbid Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Screening Program Description
 Purpose The purpose of Beacon s Comorbid Mental Health Substance Use Disorder Screening Program is to establish a formal process of assessing and ensuring early detection and treatment cooccurring mental
Purpose The purpose of Beacon s Comorbid Mental Health Substance Use Disorder Screening Program is to establish a formal process of assessing and ensuring early detection and treatment cooccurring mental
Adult Substance Use and Driving Survey-Revised (ASUDS-R) Psychometric Properties and Construct Validity
 T2007 Seattle, Washington Adult Substance Use and Driving Survey-Revised (ASUDS-R) Psychometric Properties and Construct Validity Kenneth W. Wanberg¹ and David S. Timken² ¹Center for Addictions Research
T2007 Seattle, Washington Adult Substance Use and Driving Survey-Revised (ASUDS-R) Psychometric Properties and Construct Validity Kenneth W. Wanberg¹ and David S. Timken² ¹Center for Addictions Research
Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys
 J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
Comparison of Multiple DUI Offenders Selecting Either Antabuse or 12-Step Treatment Programs
 Comparison of Multiple DUI Offenders Selecting Either Antabuse or 12-Step Treatment Programs Mary-EIlen Fortini Occupational Health Services 125 East Sir Francis Drake Blvd. Larkspur, CA USA 94939-1860
Comparison of Multiple DUI Offenders Selecting Either Antabuse or 12-Step Treatment Programs Mary-EIlen Fortini Occupational Health Services 125 East Sir Francis Drake Blvd. Larkspur, CA USA 94939-1860
Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric Properties of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette College of Education Faculty Research and Publications Education, College of 5-1-2004 Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric
Marquette University e-publications@marquette College of Education Faculty Research and Publications Education, College of 5-1-2004 Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric
Dynamic Deconstructive Psychotherapy
 This program description was created for SAMHSA s National Registry for Evidence-based Programs and Practices (NREPP). Please note that SAMHSA has discontinued the NREPP program and these program descriptions
This program description was created for SAMHSA s National Registry for Evidence-based Programs and Practices (NREPP). Please note that SAMHSA has discontinued the NREPP program and these program descriptions
The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion
 Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.169-173 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion Jin Hee Shin 1, Mee Lan Park²,
Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.169-173 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion Jin Hee Shin 1, Mee Lan Park²,
Survey on KnowledgeLevel, Perception, and Attitudes of Dental Hygiene Students Toward Mental Disordersin Korea
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(43), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i43/105016, November 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Survey on KnowledgeLevel, Perception, and Attitudes
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(43), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i43/105016, November 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Survey on KnowledgeLevel, Perception, and Attitudes
Title: Associations of sitting time and occupation with metabolic syndrome in South Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
 Author s response to reviews Title: Associations of sitting time and occupation with metabolic syndrome in South Korean adults: a cross-sectional study Authors: Jin Young Nam (jynam@yuhs.ac) Juyoung Kim
Author s response to reviews Title: Associations of sitting time and occupation with metabolic syndrome in South Korean adults: a cross-sectional study Authors: Jin Young Nam (jynam@yuhs.ac) Juyoung Kim
SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders
 SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-21-02 ABSTRACT The SAQ-Short Form (SAQ-SF) is an adult offender assessment test that accurately
SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-21-02 ABSTRACT The SAQ-Short Form (SAQ-SF) is an adult offender assessment test that accurately
A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2015;11(4):215-219 A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women Bog Ja Jeoung 1, *, Yang Chool Lee 2 1 Department
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2015;11(4):215-219 A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women Bog Ja Jeoung 1, *, Yang Chool Lee 2 1 Department
Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection and treatment of hazardous and harmful
 REVIEW ARTICLE Hazardous and Harmful Alcohol Consumption in Primary Care M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; David A. Fiellin, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection
REVIEW ARTICLE Hazardous and Harmful Alcohol Consumption in Primary Care M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; David A. Fiellin, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection
KAP Keys. For Clinicians. Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care Clinicians. CSAT s Knowledge Application Program
 KAP KEYS Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care CSAT s Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care U.S.
KAP KEYS Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care CSAT s Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care U.S.
The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea
 Review http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.303 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea Dae Jung Kim Department of Endocrinology
Review http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.303 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea Dae Jung Kim Department of Endocrinology
Screening for Substance Use in Clinical Settings
 Screening for Substance Use in Clinical Settings Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) Core Curriculum The University of Iowa Goals for Today Understand universal screening Identify
Screening for Substance Use in Clinical Settings Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) Core Curriculum The University of Iowa Goals for Today Understand universal screening Identify
Supplementary Materials:
 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States.
 Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States. Mariana Cremonte UMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Rubén Ledesma UNMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Cheryl Cherpitel
Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States. Mariana Cremonte UMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Rubén Ledesma UNMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Cheryl Cherpitel
Causes of Different Estimates of the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korea
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2011;26:440-448 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Causes of Different Estimates of the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korea Hyeon Chang Kim 1 and Dae Jung Kim 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2011;26:440-448 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Causes of Different Estimates of the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korea Hyeon Chang Kim 1 and Dae Jung Kim 2
Depression and Depressive Symptoms in Korean Women
 Depression and Depressive Symptoms in Korean Women Nam-Soon Kim Research Fellow, KIHASA Introduction Depression refers to a psychiatric condition exemplified by diminution of interest, changes in appetite
Depression and Depressive Symptoms in Korean Women Nam-Soon Kim Research Fellow, KIHASA Introduction Depression refers to a psychiatric condition exemplified by diminution of interest, changes in appetite
Dietary behaviors and body image recognition of college students according to the self-rated health condition
 Nutrition Research and Practice (2008), 2(2), 107-113 c2007 The Korean Nutrition Society and the Korean Society of Community Nutrition Dietary behaviors and body image recognition of college students according
Nutrition Research and Practice (2008), 2(2), 107-113 c2007 The Korean Nutrition Society and the Korean Society of Community Nutrition Dietary behaviors and body image recognition of college students according
A Study on the Oral Health State in Children at Age 5 and the Oral Health Behavior in Mothers for Some Parts of Gyeonggi Region
 Journal of Dental Hygiene Science Vol. 9, No. 1 pp. 11~120 (2009) 일부경기지역 세아동의구강건강실태와어머니의구강건강행위에관한연구 w x Á Á 1 y w e, w e w A Study on the Oral Health State in Children at Age and the Oral Health Behavior
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science Vol. 9, No. 1 pp. 11~120 (2009) 일부경기지역 세아동의구강건강실태와어머니의구강건강행위에관한연구 w x Á Á 1 y w e, w e w A Study on the Oral Health State in Children at Age and the Oral Health Behavior
Population based latent class analysis of drinking behaviour and related psychological problems and cognitive impairment.
 Population based latent class analysis of drinking behaviour and related psychological problems and cognitive impairment. Mark Shevlin & Gillian W. Smith Psychology Research Institute, University of Ulster
Population based latent class analysis of drinking behaviour and related psychological problems and cognitive impairment. Mark Shevlin & Gillian W. Smith Psychology Research Institute, University of Ulster
Initial Assessment in Counseling. Chapter 6
 Initial Assessment in Counseling Chapter 6 Information Gathered in the Initial Interview Demographic information Client background information Health and medical history Client s Presenting concerns Other
Initial Assessment in Counseling Chapter 6 Information Gathered in the Initial Interview Demographic information Client background information Health and medical history Client s Presenting concerns Other
Substance Abuse Questionnaire Standardization Study
 Substance Abuse Questionnaire Standardization Study Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-7-02 Abstract The Substance Abuse Questionnaire (SAQ) was standardized on a sample of 3,184 adult counseling clients. The
Substance Abuse Questionnaire Standardization Study Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-7-02 Abstract The Substance Abuse Questionnaire (SAQ) was standardized on a sample of 3,184 adult counseling clients. The
The Symptom Trajectory of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Korean School-Age Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2017.11.01.1 Print ISSN 1738-3684 / On-line ISSN 1976-3026 OPEN ACCESS The Symptom Trajectory of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Korean School-Age
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2017.11.01.1 Print ISSN 1738-3684 / On-line ISSN 1976-3026 OPEN ACCESS The Symptom Trajectory of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Korean School-Age
Predicting Factors of Antenatal Depression among Women of Advanced Maternal Age
 Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.167-171 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Predicting Factors of Antenatal Depression among Women of Advanced Maternal Age Sung Hee Lee 1, Eun Ja Jung 2* 1
Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.167-171 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Predicting Factors of Antenatal Depression among Women of Advanced Maternal Age Sung Hee Lee 1, Eun Ja Jung 2* 1
Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication
 Serveur Académique Lausannois SERVAL serval.unil.ch Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication This paper has been peer-reviewed but dos not include the final publisher proof-corrections
Serveur Académique Lausannois SERVAL serval.unil.ch Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication This paper has been peer-reviewed but dos not include the final publisher proof-corrections
Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010
 Original Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:530-535 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.4.530 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010 Yun Mi
Original Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:530-535 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.4.530 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010 Yun Mi
Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 2001 and 2013: experience at a single center in Korea
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 214;2:162-167 Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 21 and 213: experience at a single center
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 214;2:162-167 Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 21 and 213: experience at a single center
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS
 BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS FOR THE CO-LOCATION OF BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A PRIMARY CARESETTING Date: August 29, 2017 Introduction Today s Presenter Jacqueline Delmont, MD, MBA Delmont Healthcare
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS FOR THE CO-LOCATION OF BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A PRIMARY CARESETTING Date: August 29, 2017 Introduction Today s Presenter Jacqueline Delmont, MD, MBA Delmont Healthcare
A Study on Students Satisfaction with On-Site Dental Technological Clinical Practice: Focusing on 4-Year Undergraduate Students
 Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2018;14(1):73-80 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2018.14.1.73 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Study on Students Satisfaction with On-Site Dental
Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2018;14(1):73-80 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2018.14.1.73 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Study on Students Satisfaction with On-Site Dental
Setting Non-profit psychiatric hospital. The economic analysis was carried out in the USA.
 Inpatient alcohol treatment in a private healthcare setting: which patients benefit and at what cost? Pettinati H M, Meyers K, Evans B D, Ruetsch C R, Kaplan F N, Jensen J M, Hadley T R Record Status This
Inpatient alcohol treatment in a private healthcare setting: which patients benefit and at what cost? Pettinati H M, Meyers K, Evans B D, Ruetsch C R, Kaplan F N, Jensen J M, Hadley T R Record Status This
Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar
 Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar Saw Morgan Soe Win 1, Chitlada Areesantichai 2. 1 College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University,
Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar Saw Morgan Soe Win 1, Chitlada Areesantichai 2. 1 College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University,
