Efficacy of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
- Norah Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficacy of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma Eun Hye Kim Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University
2 Efficacy of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma Directed by Professor Sang Hoon Ahn The Master's Thesis submitted to the Department of Medicine the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Medical Science Eun Hye Kim June 2012
3 This certifies that the Master's Thesis of Eun Hye Kim is approved Thesis Supervisor : Sang Hoon Ahn Thesis Committee Member#1 : Ja Kyung Kim Thesis Committee Member#2 : Jeon Han Park The Graduate School Yonsei University June 2012
4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First of all, I would like to express my deep and sincere gratitude to Professor Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. for his supervision and encouraging suggestions throughout my academic life. I am deeply indebted to Professor Ja Kyung Kim, M.D., Ph.D., who have led academic discussions and encouraged me to broaden my horizons. I am grateful to Professor Jeon Han Park, M.D., Ph.D. for his precious and constructive advices. Their guidance not only improved my dissertation but also will benefit my future work. I also sincerely thank to Professor Jun Yong Park, M.D. for his helpful advices and encouragement. Finally I wish to thank my family who has been with me and always given me lots of support and love.
5 <TABLE OF CONTENTS> ABSTRACT 1 I. INTRODUCTION 3 II. MATERIALS AND METHODS 5 1. Patients 5 2. Study design 5 3. Diagnosis of HCC and staging system 7 4. Laboratory assay 7 5. Statistical analysis 8 III. RESULTS 8 1. Patient characteristics 8 2. Effect of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status 9 3. Effect of telbivudine on liver function 11 IV. DISCUSSION 12 V. CONCLUSION 14 REFERENCES 15 ABSTRACT(IN KOREAN) 18
6 LIST OF FIGURE Figure 1. Effects of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status in the HCC group and non-hcc groups 11 LIST OF TABLES Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients 9 Table 2. Baseline tumor characteristics and clinical courses in the HCC group 10 Table 3. Virological response on telbivudine therapy 12 Table 4. Changes in liver function during telbivudine therapy in all patients 13
7 ABSTRACT Efficacy of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma Eun Hye Kim Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University (Directed by Professor Sang Hoon Ahn) Background: Antiviral therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues has been shown to be effective in improving liver function in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). However, antiviral efficacy and safety of telbivudine therapy, one of the nucleoside analogues for CHB has not been evaluated in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Methods: A total of 223 CHB patients consecutively treated with 600 mg/day telbivudine for at least 6 months, 80 had HCC (HCC group; A) whilst 143 did not have HCC (non-hcc group; B). During telbivudine treatment, biochemical, virological and serological parameters were regularly monitored. Results: There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between two groups. The median duration of telbivudine treatment was 16.1 months. At Month 21, a median change in serum HBV DNA from baseline was similar between the groups (A vs B: -3.5 vs -4.0 log 10 IU/ml, P = 0.671). The 1
8 cumulative complete virologic response (serum HBV DNA < 12 IU/ml) was also comparable (A vs B: 57.5% vs 65.7%, P = 0.318). ALT normalization was 63% in the HCC group and 81% in the non-hcc group. HBeAg seroconversion was 5.7% in the HCC group and 4.4% in the non-hcc group. The cumulative rate of viral breakthrough was higher in the non-hcc group, but it could not reach to significant difference (17.5% vs 29.3%, P = 0.055). There was no hepatitis flare in both group, representing telbivudine was effective to prevent HBV reactivation during anti-hcc treatment. Telbivudine treatment improved liver function showing an increase in serum albumin level (P <0.001) and decrease in Child-Pugh scores (P <0.001). No serious side effects were found in all patients. Conclusion: Telbivudine had comparable antiviral efficacy and safety both in patients with HCC and non-hcc. During telbivudine treatment, there appears to be no hepatitis flare due to HBV reactivation from anti-hcc treatment and liver function of patients has been improved Key Words : chronic hepatitis B, hepatocellular carcinoma, telbivudine 2
9 Efficacy of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma Eun Hye Kim Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University (Directed by Professor Sang Hoon Ahn) I. INTRODUCTION Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer in the world 1 and is characterized by grave prognosis with poor survival 2. HCC is commonly detected at an advanced stage, and only 10-30% of HCC cases are eligible for curative surgical resection at the time of tumor diagnosis 3, 4. Although diverse therapeutic approaches, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CCRT), and sorafenib have been attempted in advanced HCC patients, overall response rates have been unsatisfactory and the median survival time is less than 1 year from the time of initial diagnosis 5. In particular, 70-80% of HCC patients in Asia have hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, and a large number of patients with HCC are simultaneously diagnosed with HBV infection 2, 6. Previous studies have demonstrated that 3
10 prolonged HBV suppression using antiviral therapy in patients with HBV-related HCC is equally important as treating the tumor, because the maintenance of underlying liver function can assist in deciding HCC treatment strategies and improve overall survival 1, 7, 8. Several nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) have been developed over the past decade, and used to treat chronic hepatitis B (CHB) 9, 10. In addition to lamivudine, there are currently four oral NAs available for treatment of CHB, including adefovir dipivoxil, entecavir, telbivudine, clevudine and tenofovir, which have all shown greater antiviral activity compared with placebo or lamivudine in patients with CHB Based on the results of the GLOBE trial, telbivudine (ß-L-2 -deoxythymidine), as a synthetic nucleoside analogue and bioavailable L-nucleoside with specific anti-hbv activity in vitro, has become a new option for clinicians to treat the patients with CHB 9, 16. The GLOBE trial showed that telbivudine has more potent anti-viral activity and less viral resistance compared with lamivudine 12. However, the efficacy of antiviral therapy on HBV status and underlying liver function in patients with HBV-related HCC is still unclear. Thus, it has been investigated whether telbivudine treatment for patients with HBV-related HCC could also induce biochemical, serological and virological improvements as much as in CHB patients without HCC. 4
11 II. MATERIALS AND METHODS 1. Patients All consecutive patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) in Severance Hospital (Seoul, South Korea) who started on telbivudine 600 mg once daily between March 2010 and September 2011 were enrolled in this study. Inclusion criteria were serum HBsAg present 6 months, age 16 years, previously treatment-naïve, with subsequent treatment period of at least 6 months of telbivudine. Telbivudine was commenced when serum HBV DNA was over 10,000 copies/ml for hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive patients, over 1,000 copies/ml for hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-negative patients and when either ALT level was >2 x upper limit of normal or liver biopsy showed significant fibrosis/cirrhosis. The exclusion criteria were 1) younger than 16 years, 2) previous antiviral treatment for CHB, 3) survival time of less than 6 months after enrollment, 4) insufficient data, 5) poor compliance with the antiviral drug regime, 6) coexistence of other malignancies or serious medical illness, 7) co-infection with hepatitis C or D virus or human immunodeficiency virus, 8) transfer to other hospital or loss of follow-up. A total of 223 patients were fulfilled with the above criteria and followed up for analysis. 2. Study design From March 2010 to September 2011, all consecutive patients with CHB who 5
12 have taken oral telbivudine 600 mg once daily were analyzed. All patients underwent baseline examinations, including serum HBV DNA, detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) and anti-hbe, liver function tests (ALT, AST, total bilirubin, albumin and total protein), creatinine levels, prothrombin time and complete blood counts (white cell counts, hemoglobin and platelet counts). Liver function tests, HBeAg, anti-hbe and HBV DNA were monitored every 3-6 months thereafter. Virological response was defined as undetectable serum HBV DNA (<12 IU/ml) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) at any time point during telbivudine therapy. Virologic breakthrough (VB) was defined as an increase in serum HBV DNA of >1 log 10 IU/ml from the nadir during telbivudine therapy. Biochemical response (BR) was defined as normalization of serum ALT level from abnormal baseline levels; a threshold of 40 IU/l was used as the upper limit of normal (ULN) range. Biochemical breakthrough (BB) was defined as an increase in serum ALT level above the ULN after achieving ALT normalization. Serological response was defined as HBeAg loss or HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg positive patients. HBeAg seroconversion was defined as the loss of HBeAg with the development of anti-hbe on at least two consecutive follow-ups. Genotypic resistance was defined as the appearance of viral populations bearing amino acid substitutions in the reverse transcriptase region of the HBV genome that conferred resistance to antiviral drugs in patients with VB. Liver cirrhosis was defined as follows: (1) liver cirrhosis confirmed by biopsy, (2) either 6
13 current or past evidence of cirrhosis-related complications (for example, ascites, varices or hepatic encephalopathy) or (3) a platelet count <100,000/mm 3 with ultrasonographic findings suggestive of cirrhosis, including a blunted or nodular liver edge accompanied by splenomegaly (>12 cm). 3. Diagnosis of HCC and staging system Diagnosis of HCC was based on pathologic confirmation or typical appearance of HCC on either two dynamic imaging examinations (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) or one dynamic imaging technique with elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP; >400 ng/ml). HCC was staged using the TNM system, based on modified Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) classifications, which was adopted from the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. 4. Laboratory assay Serum HBV DNA levels were quantified with a real-time PCR assay on a COBAS TaqMan 48 analyzer (Roche Molecular Systems, Branchburg, NJ, USA; the lower detection limit was 12 IU/ml). HBV serological tests for HBsAg, HBeAg, and anti-hbe were conducted with enzyme-linked immunoassays (Dade Behring, Marburg, Germany). Biochemical data including levels of ALT, AST, total bilirubin, albumin, creatinine, platelet and prothrombin time were measured using a sequential multiple auto-analyzer 7
14 (Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Genotypic resistance to telbivudine was analyzed using restriction fragment mass polymorphism (RFMP), as previously described Analytical sensitivity in detecting telbivudine-resistant strains was estimated to be 300 copies/ml. 5. Statistical analysis Continuous variables were expressed as means ± standard deviations (SDs). Serum HBV DNA concentration was expressed on a logarithmic scale. Baseline characteristics of the HCC and non-hcc groups were compared by Student s t-test for continuous variables and a chi-square test (or Fisher s exact test) for categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the cumulative incidences of ALT normalization, HBeAg seroconversion, viral breakthrough and HBV DNA non-detectable rates by PCR. Results were considered to be statistically significant when P < All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). III. RESULTS 1. Patient characteristics A total of 223 CHB patients who have been treated with telbivudine were enrolled, of these, 80 patients had concurrent HCC (HCC group) and 143 did not have HCC (non-hcc group). The baseline characteristics of the two groups are summarized in Table 1. The mean duration of telbivudine therapy was
15 months in the HCC group and 16.4 months in the non-hcc group (P = 0.144). Compared with the HCC group, the non-hcc group had significantly higher AST and ALT levels (P < in both). Serum albumin level was also higher in the non-hcc group (P < 0.001). The other parameters such as age, sex, liver cirrhosis rate, platelet, bilirubin, prothrombin time, HBeAg positivity rate, serum HBV DNA and splenomegaly rate were not significantly different between two groups. Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients Characteristic Total HCC group Non-HCC group (n=223) (n=80) (n=143) P value Age (year) 53.3± ± ± Sex (male/female) 136/87 55/25 81/ Liver cirrhosis (%) 123(55.2) 51(63.8) 72(50.3) AST (IU/L) 67.8± ± ±68.8 <0.001 ALT (IU/L) 69.9± ± ±86.8 <0.001 Platelet (x10 3 /mm 3 ) 147.0± ± ± Total bilirubin (mg/dl) 1.0± ± ± Albumin (g/dl) 3.9± ± ±0.5 <0.001 Prothrombin time (INR) 1.0± ± ± HBeAg positivity (%) 102(45.7) 35(43.8) 67(46.9) HBV DNA (log 10 IU/ml) 6.0± ± ± Splenomegaly (%) 101(45.3) 43(53.8) 58(40.6) Duration of telbivudine (months) 16.1± ± ± The baseline tumor characteristics, initial anti-hcc treatment modality and survival of the HCC group are listed in Table 2. Among HCC patients, 9 patients were dead during telbivudine therapy. The causes of deaths were disease progression for 5 patients, septic shock due to pneumonia for 2 patients and esophageal variceal bleeding for 2 patients. There was no anti-hcc 9
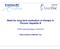
16 treatment-related death. Table 2. Baseline tumor and clinical characteristics in patients with HCC Tumor characteristics Value (number) Tumor size (<2/2-5/5-10/ 10cm) 18/40/18/4 Tumor number (1/2/3-4/ 5) 37/17/15/11 Tumor type (well-defined/ill-defined) 53/27 Portal vein invasion (yes/no) 19/61 Modified UICC stage (I/II/III/IVa/IVb) 25/31/14/9/1 Initial treatment (surgery/rfa/tace/chemotherapy/ 24/3/44/8/1 supportive care) Number of survivors (yes/no) 71/9 Mean follow-up duration from diagnosis (months) 15.7±4.2 Child-Pugh score (A/B/C) 40/10/1 2. Effect of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status When compared clinical outcomes between the two groups during 21 months of telbivudine therapy, it was found that the cumulative rates of ALT normalization in the HCC and non-hcc group were 93.5% (29/31) and 92.4% (86/93), respectively (Fig. 1A); the cumulative rates of HBeAg seroconversion were 5.7% (2/35) and 4.4% (3/67), respectively (Fig. 1B); the cumulative rates of viral breakthrough were higher in the non-hcc group (29.4% vs 17.5%) but it could not reach to statistical significance (P = 0.055) (Fig. 1C, Table 3); the cumulative rates of virological response were 57.5% (46/80) and 65.7% (94/143), respectively (Fig. 1D). 10
17 A. P = B. P =
18 C. P = D. P =
19 Fig. 1. Effects of telbivudine on hepatitis B viral status in the HCC group and non-hcc groups. (A) Cumulative rates of ALT normalization during 21 months of telbivudine therapy. The cumulative rates were 93.5% (29/31) in the HCC group and 92.4% (86/93) in the non-hcc group. (B) Cumulative rates of HBeAg seroconversion during 21 months of telbivudine therapy. The cumulative rates were 5.7% (2/35) in the HCC group and 4.4% (3/67) in the non-hcc group. (C) Cumulative rates of viral breakthrough during 21 months of telbivudine therapy. The cumulative rates were 17.5% (14/80) in the HCC group and 29.4% (42/143) in the non-hcc group. (D) Cumulative rates of virological response were 57.5% (46/80) in the HCC group and 65.7% (94/143) in the non-hcc group. The mean decline of serum HBV DNA from baseline was significant in the both groups. At Month 21, a mean change of serum HBV DNA was -3.5 log 10 IU/ml in the HCC group and -4.0 log 10 IU/ml in the non-hcc group (P = 0.671) (Table 3). The viral breakthrough rates were 17.5% in the HCC group and 29.4% in the non-hcc group without significant difference. The rate of viral breakthrough in combination with genotypic resistance was similar between the groups (12.5% in HCC vs 14.7% in non-hcc, p = 0.651). There was no hepatitis flare up during anti-hcc treatment in HCC group during the follow-up (Table 3). 13
20 Table 3. Virological response on telbivudine therapy Variables HCC group Non-HCC group (n=80) (n=143) P value Median log 10 HBV DNA at baseline 5.7± ± Median change in HBV DNA, log 10 IU/ml From baseline to month 3-3.3± ± From baseline to month 6-3.7± ± From baseline to month 9-3.9± ± From baseline to month ± ± From baseline to month ± ± From baseline to month ± ± From baseline to month ± ± HBV DNA < 12 IU/ml Month 3, n/n (%) 19/80 (23.8%) 28/143 (19.6%) Month 6, n/n (%) 29/80 (36.3%) 56/143 (39.2%) Month 9, n/n (%) 31/74 (41.9%) 56/129 (43.4%) Month 12, n/n (%) 31/67 (46.3%) 57/117 (48.7%) Month 15, n/n (%) 29/56 (51.8%) 47/103 (45.6%) Month 18, n/n (%) 12/25 (48.0%) 26/61 (42.6%) Month 21, n/n (%) 4/10 (40.0%) 12/37 (32.4%) Antiviral resistance at Month 21 VB 14/80 (17.5%) 42/143 (29.4%) VB + GR 10/80 (12.5%) 21/143 (14.7%) Hepatitis flare Variables are expressed as mean ± SD or n (%) GR, genotypic resistance; VB, virologic breakthrough Hepatitis flare was defined as the elevation of ALT level to more than 10 times of the upper normal limit. 3. Effect of telbivudine on underlying liver function The effect of telbivudine therapy on underlying liver function was evaluated in the HCC and non-hcc groups by measuring Child-Pugh scores and several laboratory parameters before and after telbivudine treatment (Table 4). The ALT level showed significant change from 69.9±74.6 IU/L at baseline to 35.4±40.7 after 12 months of telbivudine therapy (P < 0.05). AST level (67.8±60.3 vs. 45.7±56.5), albumin levels (3.9±0.5 vs. 4.1±0.5) and Child-Pugh scores 14
21 (5.6±1.2 vs. 5.3±0.9) also showed significant change (P < 0.05). Table 4. Changes in liver function during telbivudine therapy in all patients (n=223) Variables Baseline 12 months P value AST (IU/L) 67.8± ± ALT (IU/L) 69.9± ±40.7 <0.001 Albumin (g/dl) 3.9± ±0.5 <0.001 Child-Pugh score 5.6± ±0.9 <0.001 IV. DISCUSSION There have been increasing evidence that telbivudine treatment can induce biochemical, virological and serological improvements in CHB patients without HCC 9, 20, 21. However, the antiviral efficacy of telbivudine therapy on viral suppression and change of underlying liver function in patients with HBV-related HCC has not been reported. This study demonstrated the benefits of telbivudine therapy for patients with HBV-related HCC. During 24 months of telbivudine therapy in GLOBE study, the rates of ALT normalization were 69.5% in patients with HBeAg-positive CHB and 77.8% in patients with HBeAg-negative CHB 12. Similar rates of ALT normalization, 63% and 81% in the HCC group and non-hcc group, respectively were shown in this study. No significant difference in HBeAg positivity was also shown between the two groups (HCC vs. non-hcc group, 43.8% vs. 46.9%). Telbivudine treatment resulted in significant improvements in underlying liver function in this study, as shown by an increase in serum albumin level and 15
22 decreased AST, ALT and Child-Pugh scores. These results suggested that telbivudine has a benefit on improving liver function. In this study, the rate of liver cirrhosis was slightly higher in HCC group (63.8%) than that (50.3%) of non-hcc group without statistical difference. However, the increase of the cumulative rates of ALT normalization and serum HBV DNA reduction were similarly found in each group. This result suggests compatible efficacy of telbivudine between non-cirrhotic and cirrhotic patients. The prognosis of decompensated cirrhosis is dismal, and 3-5% of patients with compensated HBV cirrhosis has been reported to develop hepatic decompensation 3, 5, 7. Similar to non-cirrhotic patients with CHB, HBV-host interaction may continue in cirrhotic patients, and the annual incidence of hepatitis flares in HBV cirrhosis has been estimated at 10-20% 3, Although the majority of hepatitis flares was self-limited, approximately 10-20% were complicated by hepatic decompensation 25. Moreover, treatment strategies for HBV-related HCC, including surgical resection, radiation therapy and systemic chemotherapy have resulted in HBV reactivation and exacerbation of hepatitis 4, 22, 23, 25. Therefore, antiviral treatment to control viral replication and thus to improve underlying liver function in managing patients with HBV-related HCC, may be as important as treating the tumor themselves. In this study, telbivudine treatment led to improvement of liver function and absence of hepatitis flare through successful viral suppression. Therefore, this study might advocate the necessity of antiviral therapy in HBV-related HCC patients. 16
23 Many studies have proven that antiviral treatment in patients with HCC resulted in successful treatment of the tumors 3. Likewise, telbivudine can restore HBV-associated viral and biochemical deterioration in patients with HBV-related HCC by improving underlying liver function and making the more aggressive treatment of HCC possible. V. CONCLUSION In conclusion, this study demonstrated that virological, serological and biochemical responses of telbivudine therapy were similar between CHB patients with and without HCC. Telbivudine treatment improved underlying liver function and prevented hepatitis flare due to HBV reactivation. These findings suggest that telbivudine treatment in patients with HBV-related HCC may be beneficial for active treatment of HCC. 17
24 REFERENCES 1. Ahn SH, Chan HL, Chen PJ, Cheng J, Goenka MK, Hou J, et al. Chronic hepatitis B: whom to treat and for how long? Propositions, challenges, and future directions. Hepatology international 2010;4: Ahn SH, Yuen L, Han KH, Littlejohn M, Chang HY, Damerow H, et al. Molecular and clinical characteristics of hepatitis B virus in Korea. Journal of medical virology 2010;82: Tziomalos K. Effect of antiviral treatment on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World journal of hepatology 2010;2: Kim JH, Park JW, Koh DW, Lee WJ, Kim CM. Efficacy of lamivudine on hepatitis B viral status and liver function in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2009;29: Song HU, Hwang SG. [Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma]. The Korean journal of gastroenterology = Taehan Sohwagi Hakhoe chi 2007;49: Ahn SH, Park YN, Park JY, Chang HY, Lee JM, Shin JE, et al. Long-term clinical and histological outcomes in patients with spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. Journal of hepatology 2005;42: Cheng SQ, Wu MC, Chen H, Shen F, Yang JH, Cong WM, et al. [Anti-viral therapy using lamivudine and thymosin is helpful to prevent recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma with coexisting active hepatitis B]. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chinese journal of oncology] 2005;27: Hann HW. Active antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva gastroenterologica e dietologica 2008;54: Buti MA. [Telbivudine in the treatment of the chronic B hepatitis]. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;31: Fontana RJ. Side effects of long-term oral antiviral therapy for hepatitis B. Hepatology 2009;49:S Hann HW. Telbivudine: an effective anti-hbv drug for chronic hepatitis B patients with early on-treatment responses. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy 2010;11: Liaw YF, Gane E, Leung N, Zeuzem S, Wang Y, Lai CL, et al. 2-Year GLOBE trial results: telbivudine Is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2009;136: Matthews SJ. Telbivudine for the management of chronic hepatitis 18
25 B virus infection. Clin Ther 2007;29: McKeage K, Keam SJ. Telbivudine: a review of its use in compensated chronic hepatitis B. Drugs 2010;70: Yurdaydin C, Akarca US. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B with telbivudine: wise hepatologists needed in hepatitis B endemic countries where treatment options are limited. Liver Int 2011;31: Gane EJ, Wang Y, Liaw YF, Hou J, Thongsawat S, Wan M, et al. Efficacy and safety of prolonged 3-year telbivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int 2011;31: Kim HS, Han KH, Ahn SH, Kim EO, Chang HY, Moon MS, et al. Evaluation of methods for monitoring drug resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients during lamivudine therapy based on mass spectrometry and reverse hybridization. Antiviral therapy 2005;10: Lee JM, Ahn SH, Kim HS, Park H, Chang HY, Kim do Y, et al. Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers in prediction of treatment response to entecavir. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2011;53: Han KH, Hong SP, Choi SH, Shin SK, Cho SW, Ahn SH, et al. Comparison of multiplex restriction fragment mass polymorphism and sequencing analyses for detecting entecavir resistance in chronic hepatitis B. Antiviral therapy 2011;16: Telbivudine: rhabdomyolysis and neuropathy. Prescrire Int 2010;19: Ahn SH, Kweon YO, Paik SW, Sohn JH, Lee KS, Kim DJ, et al. Telbivudine in combination with adefovir versus adefovir monotherapy in HBeAg-positive, lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology international Yeo W, Johnson PJ. Diagnosis, prevention and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation during anticancer therapy. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2006;43: Kim JH, Park JW, Kim TH, Koh DW, Lee WJ, Kim CM. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 2007;69: Shen YC, Hsu C, Chen LT, Cheng CC, Hu FC, Cheng AL. Adjuvant interferon therapy after curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a meta-regression approach. J Hepatol 2010;52: Mahmood S, Niiyama G, Kamei A, Izumi A, Nakata K, Ikeda H, et al. 19
26 Influence of viral load and genotype in the progression of Hepatitis B-associated liver cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2005;25: Romano PR, McCallus DE, Pachuk CJ. RNA interference-mediated prevention and therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2006;25:
27 ABSTRACT (IN KOREAN) B형간염바이러스에의한간암환자에서바이러스억제및간기능향상에대한텔비부딘의효능평가 < 지도교수안상훈 > 연세대학교대학원의학과 김은혜 배경 : 뉴클레오사이드 / 뉴클레오티드유사체와같은항바이러스제치료는만성 B형간염환자의간기능에개선에도움이되는것으로알려져있다. 그러나현재까지 B형간염바이러스에의한간암환자에서텔비부딘의항바이러스효과와안전성은밝혀져있지않다. 방법 : 적어도 6개월이상하루 600 mg 텔비부딘을복용한총 223명의만성간염환자들을대상으로하였다. 만성 B형간염바이러스에의한간암환자는 80명 ( 간암환자군, A), 만성 B형간염만있는환자는 143명 ( 비간암환자군, B) 이연구에참여하였다. 이들을대상으로텔비부딘치료기간동안의생화학적, 바이러스학적, 혈청학적지표들을정기적으로관찰하였다. 결과 : 처음두그룹간의생화학적, 바이러스학적, 혈청학적지표들은차이가없었다. 텔비부딘을복용한중간값은 16.1 개월이었다. 21개월동안추적관찰한결과양군의혈청 HBV DNA 감소량은 A군과 B군각각에서중간값 -3.5 log 10 IU/ml 와 21
28 -4.0 log 10 IU/ml (P = 0.671) 이었다. 완전바이러스반응인혈청 HBV DNA 가 12 IU/ml 이하로감소된누적율은양군에서각각 57.5% 와 65.7% 로두군간의유의한차이는없었다. (P = 0.318) 혈청 HBV DNA 감소율도양군에서각각 57.5%, 65.7% 였고통계적으로유의한차이는없었다. ALT 정상화비율은간암환자와비간암환자군에서각각 63%, 81% 였다. HBeAg 혈청전환률은간암환자와비간암환자군에서각각 5.7%, 4.4% 였다. 단, 텔비부딘항생제내성을갖는비율은간암환자와비간암환자군에서각각 17.5%, 29.3% 로비간암환자군에서높게나타났으나, 통계적으로유의한차이는없었다. (P = 0.055). 치료기간중양군에서돌발성간염은없었으며이는텔비부딘이간암을치료할때 B형간염의재활성을막는데효과가있다는것을나타낸다고할수있다. 또한텔비부딘치료후알부민값의상승 (P <0.001) 과 Child-Pugh score의감소 (P <0.001) 를확인할수있었고이로미루어텔비부딘치료는간기능의향상을가져옴을알수있었다. 모든환자에서텔비부딘의심각한부작용은관찰되지않았다. 결론 : 본연구를통해간암환자와비간암환자에서텔비부딘의효능에차이가없음을알수있었다. 텔비부딘치료를하는동안간암치료를받는환자에서 B형간염의재활성을통한돌발성간염은나타나지않았고간기능의향상되는것을알수있었다 핵심되는말 : B형간염바이러스, B형간염, 간암, 텔비부딘 22
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future
 Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
 The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B
 Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Partial virological response
Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Partial virological response
Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B
 Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:469 477 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1772) Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon 1, Seung Up Kim
Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:469 477 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1772) Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon 1, Seung Up Kim
Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B
 Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B Dr James YY Fung, FRACP, MD Department of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Liver Transplant Center Queen Mary Hospital State Key Laboratory for Liver
Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B Dr James YY Fung, FRACP, MD Department of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Liver Transplant Center Queen Mary Hospital State Key Laboratory for Liver
Who to Treat? Consider biopsy Treat. > 2 ULN Treat Treat Treat Treat CIRRHOTIC PATIENTS Compensated Treat HBV DNA detectable treat
 Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development
 Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute of Digestive Disease Director, Center for Liver Health Assistant Dean,
Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute of Digestive Disease Director, Center for Liver Health Assistant Dean,
Management of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance
 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term 2015
 THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: nucleot(s)ide analogues vs. pegylated interferon
 Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
Antiviral Therapy 14:
 Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 2013
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy. Thomas Berg
 Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major public health
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Compensated Cirrhosis Patients With Low Viral Load Dong Hyun Sinn, 1 Junggyu Lee, 1 Juna Goo, 2 Kyunga Kim, 2 Geum-Youn Gwak, 1 Yong-Han
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Compensated Cirrhosis Patients With Low Viral Load Dong Hyun Sinn, 1 Junggyu Lee, 1 Juna Goo, 2 Kyunga Kim, 2 Geum-Youn Gwak, 1 Yong-Han
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting
 29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status Asokananda Konar
 Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Pro-Con: To stop or not to stop hepatitis B treatment? To Stop HBV Treatment Resat Ozaras, MD, Professor Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa Medical School, Infection Dept. HBV Therapy Nucleos(t)ide analogues
Pro-Con: To stop or not to stop hepatitis B treatment? To Stop HBV Treatment Resat Ozaras, MD, Professor Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa Medical School, Infection Dept. HBV Therapy Nucleos(t)ide analogues
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia
 Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17: (doi: /IMP1945)
 Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
CURRENT TREATMENT. Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance
 Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Help Predict Disease Progression in Patients With Low Hepatitis B Virus Loads. Hepatology Feb 2013
 Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Help Predict Disease Progression in Patients With Low Hepatitis B Virus Loads Hepatology Feb 2013 Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg is the glycosylated envelope
Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Help Predict Disease Progression in Patients With Low Hepatitis B Virus Loads Hepatology Feb 2013 Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg is the glycosylated envelope
Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation
 BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
C hronic hepatitis B (CHB) virus infection affects more
 161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy. Watcharasak Chotiyaputta
 Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy Watcharasak Chotiyaputta Progression of Liver Disease Goal of HBV Treatment: prevention the development of cirrhosis
Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy Watcharasak Chotiyaputta Progression of Liver Disease Goal of HBV Treatment: prevention the development of cirrhosis
Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease
 Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis
 HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd
 entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 December 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 December 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona
 Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update.
 Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea -
 Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
The presence of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) is
 Assessment of Current Criteria for Primary Nonresponse in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Entecavir Therapy Young-Joo Yang, 1 Ju Hyun Shim, 2 Kang Mo Kim, 2 Young-Suk Lim, 2 and Han Chu Lee 2 A
Assessment of Current Criteria for Primary Nonresponse in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Entecavir Therapy Young-Joo Yang, 1 Ju Hyun Shim, 2 Kang Mo Kim, 2 Young-Suk Lim, 2 and Han Chu Lee 2 A
Slides are the property of the author and AASLD. Permission is required from both AASLD and the author for reuse.
 Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
B C Outlines. Child-Pugh scores
 B C 2016-12-09 Outlines Child-Pugh scores CT MRI Fibroscan / ARFI Histologic Scoring Systems for Fibrosis Fibrosis METAVIR Ishak None 0 0 Portal fibrosis (some) 1 1 Portal fibrosis (most) 1 2 Bridging
B C 2016-12-09 Outlines Child-Pugh scores CT MRI Fibroscan / ARFI Histologic Scoring Systems for Fibrosis Fibrosis METAVIR Ishak None 0 0 Portal fibrosis (some) 1 1 Portal fibrosis (most) 1 2 Bridging
J.C. WANG, L.L. HE, Q. CHEN 1. Introduction. Abstract. BACKGROUND: Either combination. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B. Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona.
 NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of, and/or, received speaker fee from
NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of, and/or, received speaker fee from
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 2015
 How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
Jong Young Choi, M.D.
 The Liver Week 2014 Jong Young Choi, M.D. Dept. of Internal Medicine The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine The clinical study for natural history of LC is not many. Most of them was done
The Liver Week 2014 Jong Young Choi, M.D. Dept. of Internal Medicine The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine The clinical study for natural history of LC is not many. Most of them was done
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a major
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:541 545 Hepatitis B Virus DNA Level Predicts Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B WEN JUEI JENG, I SHYAN SHEEN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:541 545 Hepatitis B Virus DNA Level Predicts Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B WEN JUEI JENG, I SHYAN SHEEN,
Final Clinical Study Report. to the Dossier SYNOPSIS. Final Clinical Study Report for Study AI463110
 BMS-475 AI463 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier For National Authority Use Only) Name of Finished Product: Baraclude Name of Active Ingredient:
BMS-475 AI463 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier For National Authority Use Only) Name of Finished Product: Baraclude Name of Active Ingredient:
Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis B by nucleosides and nucleotides. K. Zhdanov
 EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated Cirrhosis
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 6, November 2017, pp. 828-834 ORiginal Article Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 6, November 2017, pp. 828-834 ORiginal Article Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B
 Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Anna SF Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Anna SF Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Chronic HBV Management in 2013
 Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition
 Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition Anna S. Lok, MD, DSc Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research
Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition Anna S. Lok, MD, DSc Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research
Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:32-41 Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients Hyo Jin Kim,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:32-41 Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients Hyo Jin Kim,
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Chronic Hepatitis B Drug: Baraclude (entecavir), Epivir (lamivudine), Hepsera (adefovir), Intron A (interferon alfa- 2b), Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a), Tyzeka (telbivudine),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Chronic Hepatitis B Drug: Baraclude (entecavir), Epivir (lamivudine), Hepsera (adefovir), Intron A (interferon alfa- 2b), Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a), Tyzeka (telbivudine),
Landmarks for Prevention and Treatment
 HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my patient with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? Dr. Nancy Leung BSc(Lon) MSc(Lon) MBBS(Lon) MD(Lon), FRCP(Lon) FRCP(Edin) FHKCP FHKAM Consultant Physician, Alice
HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my patient with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? Dr. Nancy Leung BSc(Lon) MSc(Lon) MBBS(Lon) MD(Lon), FRCP(Lon) FRCP(Edin) FHKCP FHKAM Consultant Physician, Alice
Prognostic factors in patients with hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing nucleoside analog antiviral therapy
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 6: 1213-1218, 2013 Prognostic factors in patients with hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing nucleoside analog antiviral therapy HIROKI NISHIKAWA 1, NORIHIRO NISHIJIMA
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 6: 1213-1218, 2013 Prognostic factors in patients with hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing nucleoside analog antiviral therapy HIROKI NISHIKAWA 1, NORIHIRO NISHIJIMA
Disclaimer. Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only
 Disclaimer Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only Any unsolicited request from HCP must be forwarded to Medical Information Housekeeping
Disclaimer Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only Any unsolicited request from HCP must be forwarded to Medical Information Housekeeping
Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection with Recovery
 Hepatitis B: Clear as Mud Melissa Osborn, MD, MSCR Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA 1 Objectives 1. Distinguish the various stages in the natural history of chronic hepatitis
Hepatitis B: Clear as Mud Melissa Osborn, MD, MSCR Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA 1 Objectives 1. Distinguish the various stages in the natural history of chronic hepatitis
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection
 Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
 Hepatitis Research and Treatment, Article ID 615621, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/615621 Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Hamid Ullah
Hepatitis Research and Treatment, Article ID 615621, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/615621 Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Hamid Ullah
Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Seroclearance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:889 893 Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Seroclearance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen MYRON JOHN TONG,*, MICHAEL ONG NGUYEN, LORI TERESE TONG,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:889 893 Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Seroclearance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen MYRON JOHN TONG,*, MICHAEL ONG NGUYEN, LORI TERESE TONG,
HBV Diagnosis and Treatment
 HBV Diagnosis and Treatment Anna S. F. Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA
HBV Diagnosis and Treatment Anna S. F. Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
 EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection European Association for the Study of the Liver Introduction Our understanding of the natural history of hepatitis B
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection European Association for the Study of the Liver Introduction Our understanding of the natural history of hepatitis B
High Rates of Viral Suppression After Long-term Entecavir Treatment of Asian Patients With Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1047 1050 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS High Rates of Viral Suppression After Long-term Entecavir Treatment of Asian Patients With Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1047 1050 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS High Rates of Viral Suppression After Long-term Entecavir Treatment of Asian Patients With Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive
Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy
 Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature,
Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature,
Hepatitis B Update. Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL. Gastroenterology
 Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Hepatitis B Virus. Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019
 Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment. New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p
 Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:505 512 Predictive Factors for Early HBeAg Seroconversion in Acute Exacerbation of Patients With HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B HYOUNG SU KIM,* HA JUNG KIM, WOON GEON SHIN,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:505 512 Predictive Factors for Early HBeAg Seroconversion in Acute Exacerbation of Patients With HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B HYOUNG SU KIM,* HA JUNG KIM, WOON GEON SHIN,*
casebasedhepatitis bmanagement Management of Hepatitis B: A Case-based Approach
 casebasedhepatitis bmanagement Management of Hepatitis B: A Case-based Approach In order to receive credit for this activity, please complete the post-test by recording the best answer to each question
casebasedhepatitis bmanagement Management of Hepatitis B: A Case-based Approach In order to receive credit for this activity, please complete the post-test by recording the best answer to each question
Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:261-267 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.4.261 Original Article Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:261-267 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.4.261 Original Article Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant
tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245mg, film-coated tablet (Viread ) SMC No. (720/11) Gilead Sciences Ltd
 tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245mg, film-coated tablet (Viread ) SMC No. (720/11) Gilead Sciences Ltd 05 August 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above
tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245mg, film-coated tablet (Viread ) SMC No. (720/11) Gilead Sciences Ltd 05 August 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above
HBV NATURAL HISTORY. Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus- Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.18.8665 Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus Related HCC Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy of
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.18.8665 Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus Related HCC Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy of
Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes!
 18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections
 Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Is there a need for combination therapy? No. Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain
 Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Our better understanding of the natural
 TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir
 Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics. Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology
 Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But
 HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Insttuto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of,
HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Insttuto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of,
The natural course of chronic HBV infection can be divided into four, which are not always continuous.
 HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is a major global health problem. The WHO reports that there are 350 million carriers worldwide. This disease is the leading cause of liver cancer in the world and frequently leads
HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is a major global health problem. The WHO reports that there are 350 million carriers worldwide. This disease is the leading cause of liver cancer in the world and frequently leads
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B
 Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
Hepatitis B. What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013
 Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs!
 Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs! Robert G Gish MD Professor Consultant Stanford University Medical Director, Hepatitis B Foundation Singapore Viral Hepatitis Meeting 2014 1 Disclosures Dr
Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs! Robert G Gish MD Professor Consultant Stanford University Medical Director, Hepatitis B Foundation Singapore Viral Hepatitis Meeting 2014 1 Disclosures Dr
MedInform. HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Original Article
 DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
What have we learned from HBV clinical cohorts?
 PHC 2015: Hepatitis B What have we learned from HBV clinical cohorts? Jia-Horng Kao MD, Ph D Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, Hepatitis Research Center, Department of Internal Medicine, National
PHC 2015: Hepatitis B What have we learned from HBV clinical cohorts? Jia-Horng Kao MD, Ph D Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, Hepatitis Research Center, Department of Internal Medicine, National
Treatment of chronic hepatitis delta Case report
 Treatment of chronic hepatitis delta Case report George Papatheodoridis Professor in Medicine & Gastroenterology Medical School of National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Director of Academic Department
Treatment of chronic hepatitis delta Case report George Papatheodoridis Professor in Medicine & Gastroenterology Medical School of National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Director of Academic Department
Natural History of HBV Infection
 Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
An Update HBV Treatment
 An Update HBV Treatment Epidemiology Natural history Treatment Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Translational Liver Research Division of Gastroenterology BIDMC, Harvard
An Update HBV Treatment Epidemiology Natural history Treatment Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Translational Liver Research Division of Gastroenterology BIDMC, Harvard
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls. Agenda
 Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy in patients with nucleoside-refractory hepatitis B
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:75-83 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.75 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:75-83 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.75 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy
ARTICLE IN PRESS. A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:xxx REVIEW A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update EMMET B. KEEFFE,* DOUGLAS T. DIETERICH,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:xxx REVIEW A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update EMMET B. KEEFFE,* DOUGLAS T. DIETERICH,
COMPARISON OF HBV RIBONUCLEASE H DOMAIN IN NAÏVE AND DRUG RESISTANT PATIENTS
 HBV RIBONUCLEASE H DOMAIN IN PATIENTS WITH DRUG RESISTANT COMPARISON OF HBV RIBONUCLEASE H DOMAIN IN NAÏVE AND DRUG RESISTANT PATIENTS Surachai Amornsawadwattana, Pattaratida Sa-Nguanmoo, Preeyaporn Vichaiwattana,
HBV RIBONUCLEASE H DOMAIN IN PATIENTS WITH DRUG RESISTANT COMPARISON OF HBV RIBONUCLEASE H DOMAIN IN NAÏVE AND DRUG RESISTANT PATIENTS Surachai Amornsawadwattana, Pattaratida Sa-Nguanmoo, Preeyaporn Vichaiwattana,
Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy
 Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy Wonseok Kang Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy Wonseok Kang Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
February 8, World Journal of Gastroenterology. Re: ESPS Manuscript No Dear Dr. Qi:
 February 8, 2017 World Journal of Gastroenterology Re: ESPS Manuscript No. 32025 Dear Dr. Qi: My co-authors and I respectfully submit the accompanying revised manuscript, Early hepatitis B viral DNA clearance
February 8, 2017 World Journal of Gastroenterology Re: ESPS Manuscript No. 32025 Dear Dr. Qi: My co-authors and I respectfully submit the accompanying revised manuscript, Early hepatitis B viral DNA clearance
March 29, :15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D
 March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine and entecavir
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2017;23:230-238 Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2017;23:230-238 Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine
A Message to Presenters
 A Message to Presenters As a healthcare professional speaking on behalf of Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), any presentation you make on our behalf must be consistent with the current FDA-approved product labeling
A Message to Presenters As a healthcare professional speaking on behalf of Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), any presentation you make on our behalf must be consistent with the current FDA-approved product labeling
Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
Hepatitis B Reactivation
 Hepatitis B Reactivation IOM, December 1 st, 2015 Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Adjunct Professor, Division of Epidemiology University of California at
Hepatitis B Reactivation IOM, December 1 st, 2015 Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Adjunct Professor, Division of Epidemiology University of California at
Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245 mg film-coated tablet (Viread ) No. (479/08) Gilead Sciences 06 June 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment
Scottish Medicines Consortium tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245 mg film-coated tablet (Viread ) No. (479/08) Gilead Sciences 06 June 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease is
 Antiviral Activity and Safety of LB80380 in Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Lamivudine-Resistant Disease Man-Fung Yuen, 1 * Kwang-Hyub Han, 2 * Soon-Ho Um, 3 Seung Kew
Antiviral Activity and Safety of LB80380 in Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Lamivudine-Resistant Disease Man-Fung Yuen, 1 * Kwang-Hyub Han, 2 * Soon-Ho Um, 3 Seung Kew
