Comparison of the Efficacy and Side Effects of Intravenous and Intramuscular Injection of Ketamine for Children Requiring Sedation: A
|
|
|
- Ezra Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: ) Comparison of the Efficacy and Side Effects of Intravenous and Intramuscular Injection of Ketamine for Children Requiring Sedation: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Study Arash Forouzan 1, *Meisam Moezzi 1, Vahid Aghdam 1, 2, Ali Delirrooyfard 1, Kambiz Masoumi 11 1 Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. 2 Student Research Committee, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. Abstract Background Ketamine is an antagonist receptor of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), and phencyclidine derivate sedative agent. Thus the aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM) injection of Ketamine for sedation procedure of children. Materials and Methods In this randomized clinical trial the patients, 1-6 year-old children referred to Emergency Department of Ahvaz Golestan and Imam Khomeini Hospitals, Ahvaz city, Iran, were divided randomly into two groups (IV and IM groups). Patients in the IV group received ketamine with dose of 1.5 mg/kg intravenously and the patients in the IM group received ketamine with dose of 4 mg/kg intramuscularly. Then efficacy and side effects in both groups were performed every 5 minutes for the first for the first 15 minutes. Results 222 patients with indication for sedation were enrolled. Results showed that in 1 st min, most of the patients that received IM ketamine were in level 1 of sedation (67.6 %, n= 73); while the majority of patients that received IV ketamine were in level 1 to 3 of sedation (28.9%, 24.6% and 26.3%, respectively) (P<0.001). Moreover, in 5 th min, most of the patients that received IV ketamine were in level 6 of sedation (62.3%), while those who received IM ketamine were in level 5 of sedation (52.8%) (P<0.001), which was better in IV group. While in 15 th min, we did not find significant differences between the groups (P=0.057). Conclusion The results of this study showed the beneficial effects of IV ketamine in making better sedation levels in pediatric patients for different purpose (medical and para-clinical procedures). Key Words: Children, Efficacy, Emergency Department, Sedation, Ketamine. *Please cite this article as: Forouzan A, Moezzi M, Aghdam V, Delirrooyfard A, Masoumi K. Comparison of the Efficacy and Side Effects of Intravenous and Intramuscular Injection of Ketamine for Children Requiring Sedation: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Study. Int J Pediatr 2019; 7(5): DOI: /ijp *Corresponding Author: Meisam Moezzi (M.D), Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. meisam.moezzi@yahoo.com Received date: Dec.18, 2018; Accepted date: Jan.22, 2019 Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
2 Efficacy and side effects of Ketamine 1- INTRODUCTION Up to 80% of children have anxiety and stress before surgical and medical interventions (1, 2), which can decrease the quality of medical procedures. On the other hand, the best way to decrease children's anxiety is sedation, which helps children to bear painful and unpleasant procedures, but sedation has several sideeffects such as an imbalance in hemodynamic status especially in children in emergency departments (ED) (2, 3). Ketamine is an antagonist receptor of N- methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), and phencyclidine derivate sedative agent (4-6), which is an appropriate choice for short and painful procedures in children due to some specific properties such as rapid onset, relatively short-term effects, and excellent sedative and analgesic effects with low risk of emergence phenomena and complications (7-13). There are two different methods for ketamine administration including intravenous (IV), and intramuscular (IM) that have been performed in several studies in order to diagnose the best way to do this procedure with lower incidence rate of side effects (9, 14-16). Despite the different studies on this issue, the superiority of either IV or IM application of the drug is still under debate. Based on these studies, choosing the route of administration depends on different factors including ED facilities, patient characteristics and comfort, and physician s experience and preference, drug s complications and side effects, and onset and duration of drug action (15-17). To the best of our knowledge, there is not enough prospective study about this issue; however, the obtained results were antitheses, therefore, this study was designed to evaluate and compare clinical efficacy and side effects of IV and IM injection of Ketamine for sedation procedure of children. 2- MATERIALS AND METHODS 2-1. Study design and population This is a prospective double-blind clinical trial. Children requiring sedation presented to ED at Ahvaz Golestan and Imam Khomeini Hospitals with two separate research teams, in Ahvaz, in the southwest of Iran, from November 2016 to May This study is registered in the Iranian registry of clinical trials (IRCT N1, Methods The participants were randomly allocated in two groups using a block randomization procedure with matched subjects in each block based on sex and age. The patient and the nurse did not know the type of prescription. After obtaining informed consent, eligible patients were enrolled (Figure.1). The baseline characteristics and complete history of drug allergy were recorded in a form for both groups before intervention Measuring tools The blood pressure and sedation levels were recorded with an emergency physician who was not aware of the doses and the route of ketamine administration. The sedation levels were recorded with Ramsay Sedation Scale (18) in 1, 5 and 15 minutes after drug administration in both groups. Based on this scale, the sedation levels were divided to 6 different levels from anxious, agitated, restless (as level 1) to no response to light glabellar tap or loud auditory stimulus (as level 6). Moreover, the side effects of ketamine such as nausea and vomiting were measured visually, restlessness based on the child's crying that despite the efforts of parents, continued for more than 2 minutes, apnea on the basis of pulse oximetry and respiratory status and whether changes in the pattern of breathing, laryngospasm basis of pulse oximetry and the clinical Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
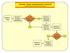
3 Forouzan et al. signs, seizure based on clinical manifestations, laryngotracheal secretions according to clinical symptoms, troubled dreams and the number of waking up with crying based on parents reports 24 hours after injection were recorded. The hemodynamic parameters, side effects and the efficacy findings of patients receiving IV ketamine were compared to patients receiving IM ketamine Intervention Patients in the IV group received ketamine with dose of 1.5 mg/kg intravenously and patients in the IM group received ketamine with dose of 4 mg/kg intramuscularly Ethical consideration The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University (IR.AJUMS.REC ). Fig1: Consort diagram Inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Consisted of 1-6 year-old patients referred to Emergency Department of Ahvaz Golestan and Imam Khomeini Hospitals needing sedation for medical procedures (sutures, joint relocations, dental procedures), or for any para-clinical procedures (ultrasound, CT- scan, and Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
4 Efficacy and side effects of Ketamine MRI), and whose parent or guardian signed a consent form to participate in the study Exclusion criteria Did not sign the consent form, having sensitivity to ketamine, evidence of abnormal brain findings such as hydrocephalus, microcephaly, mass and increased intracranial pressure, seizures, having the history of apnea, difficulty in breathing, airway problems, cardiovascular disorders, a history of severe brain trauma, lack of sedation with the administered dose and needing higher dose of ketamine, age below 1 year or more than 6 years, and dissatisfaction to continue participation in study. We also excluded patients with incomplete data Data Analyses Data were analyzed and reported only for patients who completed the trial. Statistical analysis of data was performed using SPSS software version To compare qualitative variables between groups Chisquare test was performed. The normal distribution of all studied parameters was checked with Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Student t-test and paired t-test, Mann- Whitney and Wilcoxon were used for variables. The two tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. 3- RESULTS Two hundred twenty-two patients completed the study; 114 from IV group and 108 from IM group. The study flowchart is shown in Figure.1. The baseline characteristics of patients are listed in Table.1. Eight patients dropped out and finally, because of unavailability for assessment visit, and 222 patients completed the study. Results showed that the mean of systolic blood pressure (SBP) at different times was variable between two groups, in 1 st min it was significantly higher in IV group (P<0.001) (Table.2); while it was higher in IM group in 15 th min (P=0.004). Moreover, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) had the same condition, while in 1 st min it was just significantly different between the groups but was higher in IV group as compared to IM group (P<0.001) (Table.2). We found that administration ketamine in IV route made better sedation levels in pediatric patients. In other words, we found that in 1 st min, most of the patients that received IM ketamine were in level 1 of sedation (67.6 %, n= 73), while most of the patients that received IV ketamine were in level 1 to 3 of sedation (28.9 %, 24.6 % and 26.3 %, respectively) (P<0.001) (Table.2). Moreover, in 5 th min, most of the patients that received IV ketamine were in level 6 of sedation (62.3 %, n= 71), while the majority of patients who received IM ketamine were in level 5 of sedation (52.8 %, n= 57) (P<0.001), which was better in IV group. While in 15 th min, we did not find significant differences between the groups (P=0.057) (Table.2). Furthermore, in terms of complications (vomiting, dysphoria and laryngotracheal secretions), we did not find significant differences (P>0.05) (Table.2). Table-1: The characteristics of children require sedation in Emergency Department Variables Group IV IM P-value Age (year) 2.44 ± ± Gender (male) 73 (64 %) 69 (63.9 %) Doses (mg) 21.7 ± ± 14.7 <0.001 IV: Intravenous, IM: Intramuscular. Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
5 Forouzan et al. Table-2: Studied variables during different periods of time in both IV and IM groups Variables Group IV IM P-value Before intervention ± ± SBP 1 th min ± ± <0.001 (mmhg) 5 th min ± ± th min ± ± Before intervention ± ± DBP 1 th min ± ± <0.001 (mmhg) 5 th min ± ± th min ± ± Time of sedation (s) ± ± 46.6 <0.001 Level 1 33 (28.9 %) 73 (67.6 %) Sedation Level 2 28 (24.6 %) 32 (29.6 %) levels in Level 3 30 (26.3 %) 2 (1.9 %) < th min Level 4 19 (16.7 %) 0 Level 5 4 (3.5 %) 1 (0.9 %) Sedation levels in 5 th min Sedation levels in 15 th min Level (0.9 %) Level (1.9 %) Level 4 5 (4.4 %) 27 (25 %) Level 5 38 (33.3 %) 57 (52.8%) Level 6 71 (62.3 %) 21 (19.4 %) Level (1.9 %) Level 2 1 (0.9 %) 1 (0.9 %) Level 3 2 (1.8 %) 2 (1.9 %) Level 4 6 (5.3 %) 11 (10.2%) Level 5 77 (68.1 %) 52 (48.1 %) Level 6 27 (23.9 %) 40 (37 %) <0.001 Vomiting 5 (4.4 %) 3 (2.8 %) 0.52 Dysphoria 10 (8.8 %) 6 (5.6 %) Laryngotracheal secretions 8 (7 %) 7 (6.5 %) IV: Intravenous; IM: Intramuscular; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; Sedation levels: level 1: Anxious, agitated, restless, Level 2: Cooperative, oriented, tranquil, Level 3: Responsive to commands only, Level 4: Brisk response to light glabella tap or loud auditory stimulus, Level 5: Sluggish response to light glabella tap or loud auditory stimulus, Level 6: No response to light glabella tap or loud auditory stimulus DISCUSSION This study evaluated and compared clinical efficacy and side effects of IV and IM injection of Ketamine for sedation procedure of children. We found that administration of ketamine in IV route made better sedation levels in pediatric patients in short periods of time, without causing serious complications. In the study performed by Rezazadeh et al. it was shown that efficacy and safety of IV and IM methods of ketamine usage in the pediatric procedural sedation were widely similar, but the intravenously administration of the ketamine can be proposed as the preferable mode (19). Ramaswamy et al. showed that time from drug injection to discharge was shorter in the IV compared to IM ketamine group, both overall and for the short-suture group. However, time from triage to discharge was similar (16). In another study performed by Gharavifard et al. it was shown that although the sedative and analgesic effects of IM and IV ketamine are not significantly different, duration of effect and onset of action are more desirable in the IV group for suturing, fracture reduction, and foreign body removal. Meanwhile, the IM method can lead to lesser need of rescue doses (20). The results of these studies were similar to Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
6 Efficacy and side effects of Ketamine ours. While a study performed by Roback et al. showed that ketamine 4 mg/kg IM was more effective than 1 mg/kg IV in pediatric sedation for orthopedic procedures but demonstrated significantly longer recovery times and more vomiting (14). These differences in both efficacy and rate of complications in was in contrast to our study, which may be due to studied population with different demographic features (such as age and gender) with different indication for sedation, different dosage in IV group and different race. According to the metaanalysis study done by Green et al., administrating high IV doses of the ketamine (initial dose 2.5mg/kg and a total dose 5mg/ kg), the IM method of ketamine injection and the increasing age can be proposed as the predictors of the emesis. The peak age is 12 years old. It was also concluded in their study that a low level of IM ketamine and high doses of the IV ketamine might result in patients recovery agitation (21, 22). Different adverse effects can occur by combining ketamine with other drugs, for example, the occurrence of oxygen desaturation is more frequent when midazolam was added to IV ketamine than applying ketamine alone (23, 24). Ketamine stimulates oral secretions, and there is no consensus on whether coadministration of an anticholinergic is essential, with evidence from observational studies and RCTs to support both sides of the argument (12, 17, 25) Limitations of the study The study had several limitations such as short follow- up duration, and small sample size. 5- CONCLUSION The results of this study showed the beneficial effects of IV ketamine in making better sedation levels in pediatric patients for different purpose (medical and para-clinical procedures), and significantly leads to make better sedation levels without serious complications in the short term. 6- CONFLICT OF INTEREST: None. 7- REFERENCES 1. Cravero JP, Havidich JE. Pediatric sedation - Evolution and revolution. Paediatr Anaesth 2011;21: Krauss B, Green SM. Procedural sedation and analgesia in children. Lancet 2006; 367: Meyer S, Grundmann U, Gottschling S, Kleinschmidt S, Gortner L. Sedation and analgesia for brief diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children. Eur J Pediatr 2007; 166: Majidinejad S, Esmailian M, Emadi M. Comparison of Intravenous Ketamine with Morphine in Pain Relief of Long Bones Fractures: a Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Emergency. 2014; 2(2): Hosseini M, Karami Z, Janzadenh A, Jameie SB, Mashhadi ZH, Yousefifard M, et al. The Effect of Intrathecal Administration of Muscimol on Modulation of Neuropathic Pain Symptoms Resulting from Spinal Cord Injury; an Experimental Study.Emergency. 2014; 2(4): Azizkhani R, Kanani S, Sharifi A, Golshahi K, Masoumi B, Ahmadi O. Oral Chloral Hydrate Compare with Rectal Thiopental in Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia; a Randomized Clinical Trial.Emergency. 2014; 2(2): Graudins A, Meek R, Egerton- Warburton D, Oakley E, Seith R. The PICHFORK (Pain in Children Fentanyl or Ketamine) trial: a randomized controlled trial comparing intranasal ketamine and fentanyl for the relief of moderate to severe pain in children with limb injuries. Ann Emerg Med. 2015; 65(3): Forrester KR, Thomas SM, Gupta NK, Karumuri M, Gerard JM. Repeat Intravenous Ketamine Dosing in Children Undergoing Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
7 Forouzan et al. Emergency Department Procedural Sedation. J Emerg Med. 2019; 56(1): Green SM, Rothrock SG, Harris T, Hopkins GA, Garrett W, Sherwin T. Intravenous ketamine for pediatric sedation in the emergency department: safety profile with 156 cases. Acad Emerg Med.1998; 5(10): Höfler J, Trinka E. Intravenous ketamine in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2018; 59: McGlone R, Howes M, Joshi M. The Lancaster experience of 2.0 to 2.5 mg/kg intramuscular ketamine for paediatric sedation: 501 cases and analysis. Emerg Med J. 2004; 21(3): Brown L, Green SM, Sherwin TS, Besh B, Denmark TK, Moynihan JA, et al. Ketamine with and without atropine: what's the risk of excessive salivation? Acad Emerg Med. 2003; 10(5): Hornik CP, Gonzalez D, van den Anker J, Atz AM, Yogev R, Poindexter BB, et al. Population Pharmacokinetics of Intramuscular and Intravenous Ketamine in Children. J Clin Pharmacol Roback MG, Wathen JE, MacKenzie T, Bajaj L. A randomized, controlled trial of IV versus IM ketamine for sedation of pediatric patients receiving emergency department orthopedic procedures. Ann Emerg Med.2006; 48(5): Green SM, Krauss B. Should I give ketamine IV or IM? Ann Emerg Med. 2006; 48(5): Ramaswamy P, Babl FE, Deasy C, Sharwood LN. Pediatric procedural sedation with ketamine: time to discharge after intramuscular versus intravenous administration. Acad Emerg Med. 2009; 16(2): Green SM, Krauss B. Clinical practice guideline for emergency department ketamine dissociative sedation in children. Ann Emerg Med. 2004; 44(5): Namigar T, Serap K, Esra AT, Özgül O, Can ÖA, Aysel A, et al. The correlation among the Ramsay sedation scale, Richmond agitation sedation scale and Riker sedation agitation scale during midazolam-remifentanil sedation. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2017; 67(4): Rezazadeh BB, Gharavifard M, Moghadam H, Rezvani B. Comparison between intravenous and intramuscular administration of ketamine in children sedation referred to emergency department. Rev Clin Med 2015; 2(1): Gharavifard M, Boroumand Reza Zadeh B, Zamani Moghadam H. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Intravenous and Intramuscular Ketamine for PediatricProcedural Sedation and Analgesia. Emerg (Tehran). 2015; 3(2): Green SM, Roback MG, Krauss B, Brown L, McGlone RG, Agrawal D, et al. Predictors of emesis and recovery agitation with emergency department ketamine sedation: an individual-patient data meta-analysis of 8,282 children. Ann Emerg Med. 2009; 54: Motamed H, Maleki Verki M, Mozafari J, Forouzan A. Ketamine Associated Vomiting in Children Requiring Sedation: A Prospective Randomized Open Trial Study. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2018; 6(12): Wathen JE, Roback MG, Mackenzie T, Bothner JP. Does midazolam alter the clinical effects of intravenous ketamine sedation in children? A double-blind, randomized, controlled, emergency department trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2000; 36: Elkoundi A, Bentalha A, El Koraichi A, El Kettani SE. Nebulized ketamine to avoid mechanical ventilation in a pediatric patient with severe asthma exacerbation. Am J Emerg Med. 2018; 36(4):734-e Xu J, Herndon C, Anderson S, Getson P, Foorsov V, Harbut RE, et al. Intravenous ketamine infusion for complex regional pain syndrome: survey, consensus, and a reference protocol. Pain Med doi: /pm/pny024. Int J Pediatr, Vol.7, N.5, Serial No.65, May
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation. Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital
 Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
A Randomized, Controlled Trial of IV Versus IM Ketamine for Sedation of Pediatric Patients Receiving Emergency Department Orthopedic Procedures
 PAIN MANAGEMENT/ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Randomized, Controlled Trial of IV Versus IM Ketamine for Sedation of Pediatric Patients Receiving Emergency Department Orthopedic Procedures Mark G. Roback, MD Joe
PAIN MANAGEMENT/ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Randomized, Controlled Trial of IV Versus IM Ketamine for Sedation of Pediatric Patients Receiving Emergency Department Orthopedic Procedures Mark G. Roback, MD Joe
Effect of Ondansetron on the Incidence of Vomiting Associated With Ketamine Sedation in Children: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
 PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of Ondansetron on the Incidence of Vomiting Associated With Ketamine Sedation in Children: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial William T. Langston,
PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of Ondansetron on the Incidence of Vomiting Associated With Ketamine Sedation in Children: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial William T. Langston,
GUIDELINE FOR KETAMINE SEDATION OF CHILDREN IN EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS
 QULAITY IN EMERGENCY CARE COMMITTEE GUIDELINE FOR KETAMINE SEDATION OF CHILDREN IN EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS Published: Apr 2009 (reviewed Oct 2016) Summary of recommendations 1. Before ketamine is used all
QULAITY IN EMERGENCY CARE COMMITTEE GUIDELINE FOR KETAMINE SEDATION OF CHILDREN IN EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS Published: Apr 2009 (reviewed Oct 2016) Summary of recommendations 1. Before ketamine is used all
Ali Mohammadshahi 1, Ali Omraninava 1 *, Amir Masoud Hashemian 2 and Mohammad Mehdi Forouzanfar 3
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, August 2014. Vol. 11(2), 993-997 Comparission Between Midazolam and Midazolam Plus Diphenhydramine Efficacy of Sedation in Children Undergoing CT-scan admitted
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, August 2014. Vol. 11(2), 993-997 Comparission Between Midazolam and Midazolam Plus Diphenhydramine Efficacy of Sedation in Children Undergoing CT-scan admitted
Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related?
 PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related? Mark G. Roback, MD Lalit Bajaj, MD, MPH
PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related? Mark G. Roback, MD Lalit Bajaj, MD, MPH
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY Shah R.B 1, Patel R.D 1, Patel J.J 2, Mishra A.A 3, Thosani R.M 1. U N Mehta Institute
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY Shah R.B 1, Patel R.D 1, Patel J.J 2, Mishra A.A 3, Thosani R.M 1. U N Mehta Institute
Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia
 Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia NOTE: CONTENT CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS TAKEN FROM ROSEN S EMERGENCY MEDICINE 9th Ed. Italicized text is quoted directly from Rosen s. Key Concepts: 1.
Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia NOTE: CONTENT CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS TAKEN FROM ROSEN S EMERGENCY MEDICINE 9th Ed. Italicized text is quoted directly from Rosen s. Key Concepts: 1.
Comparison of sedative effectiveness of thiopental versus midazolam in reduction of shoulder dislocation
 Original Article Comparison of sedative effectiveness of thiopental versus midazolam in reduction of shoulder dislocation 125 Elnaz Vahidi, Rezvan Hemati, Mehdi Momeni, Amirhossein Jahanshir, Morteza Saeedi
Original Article Comparison of sedative effectiveness of thiopental versus midazolam in reduction of shoulder dislocation 125 Elnaz Vahidi, Rezvan Hemati, Mehdi Momeni, Amirhossein Jahanshir, Morteza Saeedi
USAGE OF VARIOUS CONCENTRATIONS OF KETAFOL FOR DILATATION AND CURETTAGE
 USAGE OF VARIOUS CONCENTRATIONS OF KETAFOL FOR DILATATION AND CURETTAGE Sadeq Mohammad Da meh, MD*; Mohammad Abdellatif Adaileh; MD - Ali Dakhilallah Almajali, MD; Khaled Suleiman El-Share; MD- Khaled
USAGE OF VARIOUS CONCENTRATIONS OF KETAFOL FOR DILATATION AND CURETTAGE Sadeq Mohammad Da meh, MD*; Mohammad Abdellatif Adaileh; MD - Ali Dakhilallah Almajali, MD; Khaled Suleiman El-Share; MD- Khaled
Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER
 Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER Hal Irvine MD FCFP Rural FP Anesthetist Sundre, Alberta June 17, 2011 Disclosure I do not have any affiliations (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization
Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER Hal Irvine MD FCFP Rural FP Anesthetist Sundre, Alberta June 17, 2011 Disclosure I do not have any affiliations (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization
PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN
 RESEARCH ARTICLE PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN Mukesh Somvanshi 1, *, Archana Tripathi 2, Anil Rajoriya 3 1 Associate Professor,
RESEARCH ARTICLE PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN Mukesh Somvanshi 1, *, Archana Tripathi 2, Anil Rajoriya 3 1 Associate Professor,
Comparing the analgesic effect of intranasal fentanyl and ketamine in children
 Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 775-782 (2017) Comparing the analgesic effect of intranasal fentanyl and ketamine in children Golikhatir Iraj 1, Montazer Seyed Hossein 1 *, Aghilli
Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 775-782 (2017) Comparing the analgesic effect of intranasal fentanyl and ketamine in children Golikhatir Iraj 1, Montazer Seyed Hossein 1 *, Aghilli
Sublingual Buprenorphine Efficacy in Renal Colic Pain Relief: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
 Pain Ther (2017) 6:227 234 DOI 10.1007/s40122-017-0082-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sublingual Buprenorphine Efficacy in Renal Colic Pain Relief: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Javad Mozafari. Kambiz
Pain Ther (2017) 6:227 234 DOI 10.1007/s40122-017-0082-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sublingual Buprenorphine Efficacy in Renal Colic Pain Relief: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Javad Mozafari. Kambiz
What the s wrong with this person?
 Ketamine for Prehospital Management of Excited Delirium Syndrome: Is it all just a bunch of hype?!? Financial Disclosure Asa M. Margolis, DO, MPH, MS, FACEP Assistant Professor Division of Special Operation
Ketamine for Prehospital Management of Excited Delirium Syndrome: Is it all just a bunch of hype?!? Financial Disclosure Asa M. Margolis, DO, MPH, MS, FACEP Assistant Professor Division of Special Operation
Remifentanil versus Fentanyl/Midazolam in Painless Reduction of Anterior Shoulder Dislocation; a Randomized Clinical Trial
 Emergency 2016; 4 (2): 92-96 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remifentanil versus Fentanyl/Midazolam in Painless Reduction of Anterior Shoulder Dislocation; a Randomized Clinical Trial Mohammad Gharavifard 1, Azadeh
Emergency 2016; 4 (2): 92-96 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remifentanil versus Fentanyl/Midazolam in Painless Reduction of Anterior Shoulder Dislocation; a Randomized Clinical Trial Mohammad Gharavifard 1, Azadeh
Sedation in Children
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
Pain & Sedation Management in PICU. Marut Chantra, M.D.
 Pain & Sedation Management in PICU Marut Chantra, M.D. Pain Diseases Trauma Procedures Rogers Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care, 5 th ed, 2015 Emotional Distress Separation from parents Unfamiliar
Pain & Sedation Management in PICU Marut Chantra, M.D. Pain Diseases Trauma Procedures Rogers Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care, 5 th ed, 2015 Emotional Distress Separation from parents Unfamiliar
Analgesic-Sedatives Drug Dose Onset
 Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee. Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014
 RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014 The modern day practice of emergency medicine requires a practitioner to be skilled in procedural sedation
RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014 The modern day practice of emergency medicine requires a practitioner to be skilled in procedural sedation
Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a)
 Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a) Introduction The majority of acute painful crises in patients with sickle cell disease will be managed independently
Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a) Introduction The majority of acute painful crises in patients with sickle cell disease will be managed independently
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine, fentanyl, tympanoplasty, monitored anaesthesia care. INTRODUCTION:
 13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Analgo sedation in Pediatric Emergency Medicine. Juliusz Jakubaszko
 Analgo sedation in Pediatric Emergency Medicine Juliusz Jakubaszko COI Disclosure I have no relevant relationship or financial/ material support to disclose. PRESENTER: JULIUSZ JAKUBASZKO Wroclaw University
Analgo sedation in Pediatric Emergency Medicine Juliusz Jakubaszko COI Disclosure I have no relevant relationship or financial/ material support to disclose. PRESENTER: JULIUSZ JAKUBASZKO Wroclaw University
DEEP SEDATION TEST QUESTIONS
 Mailing Address: Phone: Fax: The Study Guide is provided for those physicians eligible to apply for Deep Sedation privileges. The Study Guide is approximately 41 pages, so you may consider printing only
Mailing Address: Phone: Fax: The Study Guide is provided for those physicians eligible to apply for Deep Sedation privileges. The Study Guide is approximately 41 pages, so you may consider printing only
Comparison of oral and intra venous midazolam for sedation in children undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
 Comparison of oral and intra venous midazolam for sedation in children undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy Downloaded from caspianjp.ir at 15:03 +0330 on Saturday November 24th 2018 Mohammadreza
Comparison of oral and intra venous midazolam for sedation in children undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy Downloaded from caspianjp.ir at 15:03 +0330 on Saturday November 24th 2018 Mohammadreza
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT
 SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
The Game Plan. Should I Be Doing This? The Perfect Drug. Procedural Sedation
 Procedural Sedation Sanjay Arora MD Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine at USC Los Angeles County + USC Medical Center May 23, 2012 The Game Plan Who shouldn t get sedation
Procedural Sedation Sanjay Arora MD Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine at USC Los Angeles County + USC Medical Center May 23, 2012 The Game Plan Who shouldn t get sedation
Procedural Sedation. Conscious Sedation AAP Sedation Guidelines: Disclosures. What does it mean for my practice? We have no disclosures
 2016 AAP Sedation Guidelines: What does it mean for my practice? Amber P. Rogers MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Section of Hospital Medicine and Anesthesiology Corrie E. Chumpitazi MD FAAP FACEP Assistant
2016 AAP Sedation Guidelines: What does it mean for my practice? Amber P. Rogers MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Section of Hospital Medicine and Anesthesiology Corrie E. Chumpitazi MD FAAP FACEP Assistant
Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the ED
 Overview Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the ED Susan Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Division of Emergency Medicine Terminology Goals Indications Presedation Assessment Consent Issues
Overview Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the ED Susan Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Division of Emergency Medicine Terminology Goals Indications Presedation Assessment Consent Issues
DROPERIDOL, FENTANYL AND MORPHINE FOR I.V. SURGICAL PREMEDICATION
 Br.J. Anaesth. (97),, 463 DROPERIDOL, FENTANYL AND MORPHINE FOR I.V. SURGICAL PREMEDICATION J. T. CONNER, G. HERR, R. L. KATZ, F. DOREY, R. R. PAGANO AND D. SCHEHL SUMMARY. mg and morphine mg alone and
Br.J. Anaesth. (97),, 463 DROPERIDOL, FENTANYL AND MORPHINE FOR I.V. SURGICAL PREMEDICATION J. T. CONNER, G. HERR, R. L. KATZ, F. DOREY, R. R. PAGANO AND D. SCHEHL SUMMARY. mg and morphine mg alone and
What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews
 PROGRESSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews Lisa Hartling, PhD, Andrea Milne, MLIS, Michelle Foisy, MA, Eddy S. Lang, MD,
PROGRESSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews Lisa Hartling, PhD, Andrea Milne, MLIS, Michelle Foisy, MA, Eddy S. Lang, MD,
MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT
 MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT MAC PS 2013-002 Appropriate treatment of acute pain in the prehospital arena offers an opportunity to positively impact many patients.
MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT MAC PS 2013-002 Appropriate treatment of acute pain in the prehospital arena offers an opportunity to positively impact many patients.
Sedation and Analgesia in the Critically Ill
 12th Congress of the World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine August 29 (Sat.) September 1 (Tue.), 2015 COEX, Seoul, Korea ONE STEP FURTHER: THE PURSUIT OF EXCELLENCE IN CRITICAL
12th Congress of the World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine August 29 (Sat.) September 1 (Tue.), 2015 COEX, Seoul, Korea ONE STEP FURTHER: THE PURSUIT OF EXCELLENCE IN CRITICAL
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)
 Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Clinical Policy: Evidence-Based Approach to Pharmacologic Agents Used in Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department
 PAIN MANAGEMENT/CLINICAL POLICY Clinical Policy: Evidence-Based Approach to Pharmacologic Agents Used in Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department From the EMSC Grant Panel (Writing
PAIN MANAGEMENT/CLINICAL POLICY Clinical Policy: Evidence-Based Approach to Pharmacologic Agents Used in Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department From the EMSC Grant Panel (Writing
Pediatric Procedural Sedation
 Pediatric Procedural Sedation Case 1: 2 year old complex facial laceration Judith R. Klein, MD, FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH Department of Emergency Medicine Objectives: The
Pediatric Procedural Sedation Case 1: 2 year old complex facial laceration Judith R. Klein, MD, FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH Department of Emergency Medicine Objectives: The
Pediatric Dental Sedation
 Pediatric Dental Sedation L. Stephen Long, MD Pediatric Anesthesiologist Children s Dental Anesthesia Group UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Oakland Part 1: Pediatric Airways and Lungs 1 Three questions:
Pediatric Dental Sedation L. Stephen Long, MD Pediatric Anesthesiologist Children s Dental Anesthesia Group UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Oakland Part 1: Pediatric Airways and Lungs 1 Three questions:
PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older)
 Name Score PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older) 1. Pre-procedure evaluation for moderate sedation should involve all of the following EXCEPT: a) Airway Exam b) Anesthetic history
Name Score PHYSICIAN COMPETENCY FOR ADULT DEEP SEDATION (Ages 14 and older) 1. Pre-procedure evaluation for moderate sedation should involve all of the following EXCEPT: a) Airway Exam b) Anesthetic history
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management
 Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Preoperative Anxiety
 Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
POLICY FOR PROCEDURAL SEDATION: CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE
 POLICY FOR PROCEDURAL SEDATION: CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Page 1 of 24 NOVEMBER 2018 Title: Policy for Procedural Sedation: Children and Young People Author(s) Children s Peri-Operative Group (Dr Patrick
POLICY FOR PROCEDURAL SEDATION: CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Page 1 of 24 NOVEMBER 2018 Title: Policy for Procedural Sedation: Children and Young People Author(s) Children s Peri-Operative Group (Dr Patrick
POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION. August 2012 J Pelletier
 POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION August 2012 J Pelletier Intubated patients experience pain and anxiety Mechanical ventilation, endotracheal tube Blood draws, positioning, suctioning Surgical procedures,
POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION August 2012 J Pelletier Intubated patients experience pain and anxiety Mechanical ventilation, endotracheal tube Blood draws, positioning, suctioning Surgical procedures,
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of
 Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico
 Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico Balance is not that easy! Weaning Weaning is the liberation of a patient from
Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico Balance is not that easy! Weaning Weaning is the liberation of a patient from
Conscious sedation in children
 Michael Sury FRCA PhD Matrix reference 2D06, 3A07, 3D00 Key points Effective sedation techniques are specific to the procedure. Conscious sedation in children can be time-consuming but may save anaesthesia
Michael Sury FRCA PhD Matrix reference 2D06, 3A07, 3D00 Key points Effective sedation techniques are specific to the procedure. Conscious sedation in children can be time-consuming but may save anaesthesia
REVIEW ARTICLE. Sedation and Analgesia for Pediatric Fracture Reduction in the Emergency Department. one of the most common injuries
 REVIEW ARTICLE Sedation and Analgesia for Pediatric Fracture Reduction in the Emergency Department A Systematic Review Russell T. Migita, MD; Eileen J. Klein, MD, MPH; Michelle M. Garrison, MPH Objective:
REVIEW ARTICLE Sedation and Analgesia for Pediatric Fracture Reduction in the Emergency Department A Systematic Review Russell T. Migita, MD; Eileen J. Klein, MD, MPH; Michelle M. Garrison, MPH Objective:
Oral Chloral Hydrate Compare with Rectal Thiopental in Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia; a Randomized Clinical Trial
 85 Emergency (2014); 2 (2): 85-89 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Chloral Hydrate Compare with Rectal Thiopental in Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia; a Randomized Clinical Trial Reza Azizkhani 1, Soheila
85 Emergency (2014); 2 (2): 85-89 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Chloral Hydrate Compare with Rectal Thiopental in Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia; a Randomized Clinical Trial Reza Azizkhani 1, Soheila
The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting. by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S.
 The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S. I. Introduction: One of the most common challenges that the dentist who treats children faces is the
The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S. I. Introduction: One of the most common challenges that the dentist who treats children faces is the
Is lorazepam effective at preventing nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy? A randomized controlled trial
 (Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2017, 68, 131-135) Is lorazepam effective at preventing nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy? A randomized controlled trial F. Javaherforoosh Zadeh (*), A. Ghomeishi
(Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2017, 68, 131-135) Is lorazepam effective at preventing nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy? A randomized controlled trial F. Javaherforoosh Zadeh (*), A. Ghomeishi
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Sevoflurane. Anaesthesia. Difficult to intubate (DTI) Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A prospective, open-label, multicenter, post marketing, observational study to investigate the effectiveness of Sevoflurane anaesthesia in difficult-to-intubate Egyptian patients. Keywords
1.0 Abstract Title A prospective, open-label, multicenter, post marketing, observational study to investigate the effectiveness of Sevoflurane anaesthesia in difficult-to-intubate Egyptian patients. Keywords
Goals for sedation during mechanical ventilation
 New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
Sedation Hold/Interruption and Weaning Protocol ( Wake-up and Breathe )
 PROTOCOL Sedation Hold/Interruption and Weaning Protocol ( Wake-up and Breathe ) Page 1 of 6 Scope: Population: Outcome: Critical care clinicians and providers. All ICU patients intubated or mechanically
PROTOCOL Sedation Hold/Interruption and Weaning Protocol ( Wake-up and Breathe ) Page 1 of 6 Scope: Population: Outcome: Critical care clinicians and providers. All ICU patients intubated or mechanically
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
Kayalvizhi 1, J. Radhika 1* Original Research Article. Abstract
 Original Research Article Comparative evaluation of safety and efficacy of epidural bupivacaine with morphine and ketamine vs epidural bupivacaine with morphine alone for postoperative analgesia Kayalvizhi
Original Research Article Comparative evaluation of safety and efficacy of epidural bupivacaine with morphine and ketamine vs epidural bupivacaine with morphine alone for postoperative analgesia Kayalvizhi
Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV
 Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV Abstract Ketofol, a sedative/analgesic combination of ketamine and propofol, which can be administered as a mixture in the same syringe or independently,
Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV Abstract Ketofol, a sedative/analgesic combination of ketamine and propofol, which can be administered as a mixture in the same syringe or independently,
Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; 10/09; 10/10 Manual of Administrative Policy Source Sedation Committee
 Code No. 711 Section Subject Moderate Sedation (formerly termed Conscious Sedation ) Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; Manual of Administrative Policy Source
Code No. 711 Section Subject Moderate Sedation (formerly termed Conscious Sedation ) Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; Manual of Administrative Policy Source
Effects of intravenous analgesia with combined dezocine and butorphanol on postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients
 Effects of intravenous analgesia with combined dezocine and butorphanol on postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients B.X. Ren, J. Zong, J.C. Tang, D.P. Sun, X. Hui, R.Q. Li, J.L. Zhang and Y.
Effects of intravenous analgesia with combined dezocine and butorphanol on postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients B.X. Ren, J. Zong, J.C. Tang, D.P. Sun, X. Hui, R.Q. Li, J.L. Zhang and Y.
PHYSICIAN'S ORDERS Mark in for desired orders. If is blank, order is inactive. VENTILATOR SEDATION / ANALGESIC / DELIRIUM ORDER
 Nursing Daily awakenings PHYSICIAN'S ORDERS Mark in for desired orders. If is blank, order is inactive. VENTILATOR SEDATION / ANALGESIC / DELIRIUM ORDER Do not perform daily awakenings: Rationale: Daily
Nursing Daily awakenings PHYSICIAN'S ORDERS Mark in for desired orders. If is blank, order is inactive. VENTILATOR SEDATION / ANALGESIC / DELIRIUM ORDER Do not perform daily awakenings: Rationale: Daily
Original Research Article
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN ORAL MIDAZOLAM AND NITROUS OXIDE-OXYGEN FOR DENTAL EXTRACTIONS IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS Archana S. Mhatre 1, Sunanda Panigrahi 2, Sujata B. Pawar 3 1Associate Professor, Department
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN ORAL MIDAZOLAM AND NITROUS OXIDE-OXYGEN FOR DENTAL EXTRACTIONS IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS Archana S. Mhatre 1, Sunanda Panigrahi 2, Sujata B. Pawar 3 1Associate Professor, Department
ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL. Subject: Moderate Sedation/Analgesia- Procedural ( Conscious Sedation ) Policy
 BRYN MAWR HOSPITAL LANKENAU HOSPITAL PAOLI HOSPITAL Working Together to Serve the Community ADMINISTRATE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Subject: Moderate Sedation/Analgesia- Procedural ( Conscious Sedation
BRYN MAWR HOSPITAL LANKENAU HOSPITAL PAOLI HOSPITAL Working Together to Serve the Community ADMINISTRATE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Subject: Moderate Sedation/Analgesia- Procedural ( Conscious Sedation
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (8), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (8), Page 2981-2985 A Study to Evaluate KM/Propofol versus KM Alone for Procedural Sedation in Children Abdulrahman Fayez Kinsara 1, Ahmad
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (8), Page 2981-2985 A Study to Evaluate KM/Propofol versus KM Alone for Procedural Sedation in Children Abdulrahman Fayez Kinsara 1, Ahmad
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES
 SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
MORPHINE ADMINISTRATION
 Introduction Individualised Administration Drug of Choice Route of Administration & Doses Monitoring of Neonates & high risk patients Team Management Responsibility Morphine Protocol Flow Chart Introduction
Introduction Individualised Administration Drug of Choice Route of Administration & Doses Monitoring of Neonates & high risk patients Team Management Responsibility Morphine Protocol Flow Chart Introduction
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients:
 Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Original Contributions
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.08.076 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 23 28, 2008 Copyright 2008 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/08 $ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.08.076 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 23 28, 2008 Copyright 2008 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/08 $ see front matter
General Anesthesia. Mohamed A. Yaseen
 General Anesthesia Mohamed A. Yaseen M.S,c Surgery Before Anesthesia General Anesthesia ( GA ) Drug induced absence of perception of all sensation allowing surgery or other painful procedure to be carried
General Anesthesia Mohamed A. Yaseen M.S,c Surgery Before Anesthesia General Anesthesia ( GA ) Drug induced absence of perception of all sensation allowing surgery or other painful procedure to be carried
Colonoscopy is one of the most commonly performed outpatient method for the
 Original Article Sedation with etomidate-fentanyl versus propofol-fentanyl in colonoscopies: A prospective randomized study Nadia Banihashem (MD) 1 Ebrahim Alijanpour (MD) 1 Majid Basirat (MD) 1 Javad
Original Article Sedation with etomidate-fentanyl versus propofol-fentanyl in colonoscopies: A prospective randomized study Nadia Banihashem (MD) 1 Ebrahim Alijanpour (MD) 1 Majid Basirat (MD) 1 Javad
2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION. Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY
 2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW All ALS EMS System Two EMT-Ps on each
2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW All ALS EMS System Two EMT-Ps on each
CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH
 CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH Background Adequate analgesia is a vital aspect of early management of
CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH Background Adequate analgesia is a vital aspect of early management of
SEDATION / ANALGESIA for Brain Failure Patient INASNACC
 SEDATION / ANALGESIA for Brain Failure Patient INASNACC Neuroendocrinological metabolic responses to surgical or traumatic injury Endocrine : increase in ACTH, cortisol, ADH, GH, glucagon, renin, aldosteron,
SEDATION / ANALGESIA for Brain Failure Patient INASNACC Neuroendocrinological metabolic responses to surgical or traumatic injury Endocrine : increase in ACTH, cortisol, ADH, GH, glucagon, renin, aldosteron,
Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist
 Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist Tonsillectomy is a common surgery in children Post tonsillectomy pain is an important concern. Duration &severity of pain depend on:
Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist Tonsillectomy is a common surgery in children Post tonsillectomy pain is an important concern. Duration &severity of pain depend on:
A SERIES OF PAEDIATRIC TOPICS DR DANIEL WATSON
 A SERIES OF PAEDIATRIC TOPICS DR DANIEL WATSON March 2014 Who am I? MBChB Otago 1996 FACEM 2004 Staff specialist Wellington ED 2004- ~ 55k presentations PA ~ 20% paediatric APLS instructor Locum work NT
A SERIES OF PAEDIATRIC TOPICS DR DANIEL WATSON March 2014 Who am I? MBChB Otago 1996 FACEM 2004 Staff specialist Wellington ED 2004- ~ 55k presentations PA ~ 20% paediatric APLS instructor Locum work NT
Neostigmine as an adjunct to Bupivacaine, for caudal block in burned children, undergoing skin grafting of the lower extremities
 Neostigmine as an adjunct to Bupivacaine, for caudal block in burned children, undergoing skin grafting of the lower extremities Dr. Pramod Gupta, Dr Amy Grace MD Department of Anaesthesiology and Critical
Neostigmine as an adjunct to Bupivacaine, for caudal block in burned children, undergoing skin grafting of the lower extremities Dr. Pramod Gupta, Dr Amy Grace MD Department of Anaesthesiology and Critical
Guideline for Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department
 Guideline for Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department Introduction: Pain is often an inherent part of a child s presenting complaint, and is frequently exacerbated by many
Guideline for Pediatric Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in the Emergency Department Introduction: Pain is often an inherent part of a child s presenting complaint, and is frequently exacerbated by many
PEDIATRIC SEDATION PEDIATRIC PAIN CONTROL
 PEDIATRIC SEDATION PEDIATRIC PAIN CONTROL Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD, FAAEM, FACEP, FAAP Underused Concern about respiratory depression Easy to overlook expression of pain in infants and small children Length
PEDIATRIC SEDATION PEDIATRIC PAIN CONTROL Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD, FAAEM, FACEP, FAAP Underused Concern about respiratory depression Easy to overlook expression of pain in infants and small children Length
Care in the Last Days of Life
 Care in the Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision making and good practice in person-centred care for patients who are deteriorating and at risk of dying. The patient
Care in the Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision making and good practice in person-centred care for patients who are deteriorating and at risk of dying. The patient
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures
 Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine
 Research Article ISSN: 2474-9206 Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine Evaluating the Effect of Various Doses of Magnesium Sulfate on Quality of Cataract Intra Operative Sedation and Recovery Mojtaba Rahimi
Research Article ISSN: 2474-9206 Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine Evaluating the Effect of Various Doses of Magnesium Sulfate on Quality of Cataract Intra Operative Sedation and Recovery Mojtaba Rahimi
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia
 The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
1
 Disclosures I do not have a vested interest in or affiliation with any corporate organization offering financial support or grant monies for this continuing education activity, or any affiliation with
Disclosures I do not have a vested interest in or affiliation with any corporate organization offering financial support or grant monies for this continuing education activity, or any affiliation with
Respiratory Depression
 Respiratory Depression H. William Gottschalk, D.D.S. Fellow, Academy of General Dentistry Fellow, American Dental Society of Anesthesiology Diplomate, American Board of Dental Anesthesiology Diplomate,
Respiratory Depression H. William Gottschalk, D.D.S. Fellow, Academy of General Dentistry Fellow, American Dental Society of Anesthesiology Diplomate, American Board of Dental Anesthesiology Diplomate,
A Comparison of Buccal Midazolam and Intravenous Diazepam for the Acute Treatment of Seizures in Children
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2012; Vol 22 (No 3), Pp: 303-308 A Comparison of Buccal Midazolam and Intravenous Diazepam for the Acute Treatment of Seizures in Children Seyed-Hassan Tonekaboni 1,2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2012; Vol 22 (No 3), Pp: 303-308 A Comparison of Buccal Midazolam and Intravenous Diazepam for the Acute Treatment of Seizures in Children Seyed-Hassan Tonekaboni 1,2,
Medication Do s and Don ts
 Medication Do s and Don ts Hadar Tucker, MCEP 2018 Pretest 1-what is the maximum effective dose of Ibuprofen for pain? A) 400 mg B) 600 mg C) 800 mg D) 1000mg 1 Pretest 2 How long does it take for the
Medication Do s and Don ts Hadar Tucker, MCEP 2018 Pretest 1-what is the maximum effective dose of Ibuprofen for pain? A) 400 mg B) 600 mg C) 800 mg D) 1000mg 1 Pretest 2 How long does it take for the
The following criteria must be met in order to obtain pediatric clinical privileges for pediatric sedation.
 Pediatric Sedation Sedation of children is different from sedation of adults. Sedatives are generally administered to gain the cooperation of the child. The ability of the child to cooperate depends on
Pediatric Sedation Sedation of children is different from sedation of adults. Sedatives are generally administered to gain the cooperation of the child. The ability of the child to cooperate depends on
Efficacy of Chloral Hydrate and Promethazine for Sedation during Electroencephalography in Children; a Randomised Clinical Trial
 Original Article ل Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 27-31 Efficacy of Chloral Hydrate and Promethazine for Sedation during Electroencephalography in Children; a Randomised Clinical Trial Fallah,
Original Article ل Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 27-31 Efficacy of Chloral Hydrate and Promethazine for Sedation during Electroencephalography in Children; a Randomised Clinical Trial Fallah,
ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM. Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 7: Referrals
 ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 3: Diagnostic Evaluation Decision 4: High Risk / High User Decision
ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 3: Diagnostic Evaluation Decision 4: High Risk / High User Decision
Moderate and Deep Sedation Pathway
 A Quick Reference to the Advocate System Sedation Policy *This information is meant as a guideline only and not a substitute for physician order or clinical judgment Introduction: This Pediatric Emergency
A Quick Reference to the Advocate System Sedation Policy *This information is meant as a guideline only and not a substitute for physician order or clinical judgment Introduction: This Pediatric Emergency
Guidelines for sedation and/or analgesia by non-anaesthesiology doctors
 European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2007; 24: 563 567 r 2007 Copyright European Society of Anaesthesiology doi: 10.1017/S0265021507000452 Guidelines Guidelines for sedation and/or analgesia by non-anaesthesiology
European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2007; 24: 563 567 r 2007 Copyright European Society of Anaesthesiology doi: 10.1017/S0265021507000452 Guidelines Guidelines for sedation and/or analgesia by non-anaesthesiology
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Sedation is a dynamic process.
 19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
Procedural Sedation A/Prof Vasilios Nimorakiotakis (Bill Nimo) Deputy Director Clinical Associate Professor
 Procedural Sedation A/Prof Vasilios Nimorakiotakis (Bill Nimo) MBBS, FACEM, FACRRM, Dip Mgt Deputy Director Emergency Department Epworth Richmond Clinical Associate Professor The University of Melbourne
Procedural Sedation A/Prof Vasilios Nimorakiotakis (Bill Nimo) MBBS, FACEM, FACRRM, Dip Mgt Deputy Director Emergency Department Epworth Richmond Clinical Associate Professor The University of Melbourne
Pre-medication with controlled-release oxycodone in the management of postoperative pain after ambulatory laparoscopic gynaecological surgery
 Page 1 of 5 Anaesthetics & Critical Care Pre-medication with controlled-release oxycodone in the management of postoperative pain after ambulatory laparoscopic gynaecological surgery B Lim 1, SY Thong
Page 1 of 5 Anaesthetics & Critical Care Pre-medication with controlled-release oxycodone in the management of postoperative pain after ambulatory laparoscopic gynaecological surgery B Lim 1, SY Thong
The Benefits of Ketamine in the Prehospital Environment by Appropriately Trained Professionals July 2016 Sean Eaton, FP-C
 The Benefits of Ketamine in the Prehospital Environment by Appropriately Trained Professionals July 2016 Sean Eaton, FP-C Introduction First introduced in the 1960 s as an alternative to PCP for anesthesia
The Benefits of Ketamine in the Prehospital Environment by Appropriately Trained Professionals July 2016 Sean Eaton, FP-C Introduction First introduced in the 1960 s as an alternative to PCP for anesthesia
Emergency nurses are frequently asked to assist in
 PEDIATRIC INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, PART 3: RIP VAN WINKLE S APPROACH TO PEDIATRIC PROCEDURAL SEDATION Authors: Patricia A. Normandin, DNP, RN, CEN, CPN, CPEN,
PEDIATRIC INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, PART 3: RIP VAN WINKLE S APPROACH TO PEDIATRIC PROCEDURAL SEDATION Authors: Patricia A. Normandin, DNP, RN, CEN, CPN, CPEN,
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia. Disclosure
 Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia Michael Young IWK Health Centre 1 Disclosure No financial or other conflict of interest Lots of borrowed slides and content: Erin Killorn Chris McCrossin Michelle McTimoney
Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia Michael Young IWK Health Centre 1 Disclosure No financial or other conflict of interest Lots of borrowed slides and content: Erin Killorn Chris McCrossin Michelle McTimoney
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 74/Dec 29, 2014 Page 15535
 RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
