Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires
|
|
|
- Ashlie Garrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q J Med 2002; 95: Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires M.T. MCCUSKER 1, J. BASQUILLE 1,M.KHWAJA 1, I.M. MURRAY-LYON 2 and J. CATALAN 3 From the 1 Brent, Kensington, Chelsea and Westminster Mental Health Trust Substance Misuse Service, London, 2 Department of Gastroenterology, Chelsea & Westminster Hospital, London, and 3 Department of Psychological Medicine, Imperial College, London, UK Received 29 August 2001 and in revised form 16 May 2002 Summary Background: Hazardous and harmful use of alcohol remains a public health concern, and many general hospital admissions are alcohol-related. Aim: To compare the CAGE and Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) questionnaires in screening general medical admissions for harmful or hazardous drinking. Design: Prospective questionnaire-based study. Methods: Both questionnaires were administered, and demographic data collected. Results: One hundred and three patients were included. Of these, 36% were identified by the AUDIT to be drinking hazardously or harmfully, and 22% were identified as CAGE cases. All CAGE cases were also AUDIT cases. Discussion: As the CAGE and the AUDIT are designed to identify different populations, it is not surprising that significantly fewer cases were identified using the CAGE. The AUDIT identifies not just the harmful drinkers detected by the CAGE, but also hazardous drinkers, who have not yet reached that level of harm. As drinkers at an earlier stage may respond better to interventions aimed at reducing their consumption, the AUDIT is preferable in clinical practice. Introduction Alcohol is consumed by over 90% of the adult population in the UK, and for the foreseeable future is likely to remain our favourite drug. The consumption of small to moderate amounts of alcohol is not thought to be harmful, and may protect against coronary heart disease and stroke. 1 However, hazardous and/or harmful use of alcohol remains a major public health concern, especially as household surveys suggest that as many as 27% of individuals drink more than the weekly limits recommended by the Royal Colleges of Psychiatrists, General Practitioners and Physicians, of 14 units for women and 21 units for men. 2 Up to 30% of male admissions to general hospital, and up to 15% of female admissions, are alcohol related. 3 5 Similar rates are reported in psychiatric settings. 6 Unfortunately, problem drinking in patients is often unrecognized by doctors. 6 8 Consequently, several authors have suggested the routine use of validated screening instruments such as the CAGE questionnaire, 9 Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST), 10 or Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) to assist identification of excessive drinking. 11,12 The CAGE was developed in the 1970s as a short interviewer-administered test to screen for alcoholism or covert problem drinking. CAGE is an acronym referring to four questions pertaining to lifetime drinking experience. Two or more positive answers are believed to indicate covert problem drinking. Although CAGE and MAST are able to detect severe forms of alcohol disorders, i.e. ICD-10 Address correspondence to Ms M.T. McCusker, Department of Addictive Behaviour & Psychological Medicine, St. George s Hospital Medical School, London SW17 0RE. m.mccusker@sghms.ac.uk ß Association of Physicians 2002
2 592 M.T. McCusker et al. diagnoses of harmful (consumption which has caused damage to health) or dependent drinking, 13 these screening tools do not identify those with hazardous use of alcohol. Hazardous drinking is alcohol consumption which confers risk of physical or psychological harm. 14 Individuals in this category will be drinking over medically recommended limits for low-risk drinking (14 units/week for women and 21 for men), but will have so far either avoided or failed to recognize significant alcohol-related problems. This is of clinical relevance, as evidence suggests that brief counselling interventions made at an earlier stage are more likely to be effective, 15,16 but the majority of patients do not seek help until there are established, and often serious complications resulting from their drinking. 17 The AUDIT questionnaire is sensitive enough to detect hazardous as well as harmful drinking, both when used in primary care settings and, more recently, in hospitals. 12,18 It is a validated questionnaire consisting of 10 questions, giving a maximum score of 40, and includes items assessing alcohol consumption, problems and dependency. 12 A cut-off score of 08 is recommended for routine screening of hazardous or harmful use. 15 Comparative studies of the two screening tools indicate that the CAGE is better at identifying lifetime alcohol abuse and dependence (alcohol use disorders, AUDs) in different populations, but the AUDIT is preferred for the detection of hazardous and harmful drinking. 18,22 Two studies dispute the superiority of the CAGE in detecting AUDs, recommending the AUDIT in preference. 23,24 However, one of these limited their study sample to elderly medical patients, and the other was a review of alcohol screening questionnaires for women. We used the AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires to screen for problem drinking in patients admitted as a medical emergency to a busy teaching hospital. A copy of the AUDIT can be found in the Appendix. Methods Participants Subjects were recruited from the Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, a district general and teaching hospital serving inner West London. Over a 9-month period (June 1997 to February 1998) 156 (77 male, 79 female) new medical admissions, aged 017 years, were approached by one of the two Specialist Registrars (JB and MK), and were invited to participate in the study. The two investigators attended the hospital on different days of the week and identified new medical admissions (defined as those admitted in the previous 24 h period). All patients admitted to the medical wards on the day chosen were approached. Using this approach, all days of the week were covered although some days were more represented than others, as it depended on the Specialist Registrars availability. The investigators also examined the notes of new admissions in order to determine the primary reason for admission. Instruments to detect problem drinking Patients who agreed to participate were screened using the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) and the CAGE questionnaires. Other data Demographic data and reason for admission were also collected for each patient. Participants identified by the AUDIT as having a drinking problem were asked if they would be interested in receiving treatment, and if they agreed, were contacted by the Trust alcohol service. Results There were 156 eligible patients (77 males, 44%), of whom 56 (26 males, 34%) were excluded. Reasons for exclusion included: too ill (n = 28); refusal (n = 11); transferred from the ward before they could be assessed (n = 7); did not comprehend English (n = 3), and blindness (thus unable to complete the questionnaires) (n = 2). Those excluded from the study were slightly older than those who participated (excluded median 71"21.7 years vs. included 56"23.9 years; p-0.05) and were less likely to have been admitted with diseases of the genitourinary tract (2% vs. 11%; p-0.05) or with respiratory tract problems (8% vs. 20%; p-0.05). Demographic characteristics and reason for admission Of the 103 patients who participated in the study, there was an equal proportion of male (n = 52) and female (n = 51) subjects. The median age of patients interviewed was 56 (SD 23.9) years. The sample was predominantly White (90%; 93/103); 76% (77/103) described themselves as White/UK, 4% (4/103) as White/Irish; 12% (12/103) as White/ Other. Of the remaining ten, four (4%) described
3 Screening for drinking problems 593 themselves as Afro-Caribbean, one (1%) as Black/ UK, one (1%) as Chinese, one (1%) as Indian, one (1%) as Bangladeshi/UK and one (1%) as Pakistani. AUDIT questionnaire results AUDIT cases (hazardous or harmful drinking) represented 36% (37/103) of participants. Almost half of the males (48%) were cases, compared with just under a quarter of females (24%) and a male:female ratio of 2:1 (68%:32%; x 2 = 6.74; p = 0.013). The mean age of AUDIT cases was 57 (SD 22.7) years. Cases were not younger than noncases (mean age 56, SD 24.8). AUDIT cases were more likely to be White than other ethnic groups (n = 35 vs. n = 1; x 2 = 4.33, p = 0.052). CAGE questionnaire results Only 22% of participants were CAGE cases, compared to the 36% of AUDIT cases. CAGE cases were younger than non-cases (mean"sd age 48"20.0 vs. 58"24.7 years; t = 1.74; p = 0.046). Comparison of CAGE and AUDIT performance Significantly fewer cases were identified using the CAGE than the AUDIT (22% and 36% respectively; x 2 = 51.4; p ). As expected, all CAGE cases were also AUDIT cases. Twenty-two (61%) of the AUDIT cases were also CAGE cases. Discussion The prevalence of excessive drinking amongst medical admissions to the general hospital is substantial and the proportions identified will not only vary with the population being surveyed, but also with the instrument used to detect excessive drinking. The AUDIT identified 36% of this general hospital population as being hazardous or harmful drinkers, while the CAGE detected only 22% as cases. The differences in performance of the two instruments is likely to be due to the fact that the CAGE identifies mostly the more severe end of the problem drinking spectrum, while the AUDIT detects anyone with hazardous drinking or worse. These findings add to those already published on the greater sensitivity of AUDIT to CAGE. Previous studies have shown this to be true in different US populations, such as trauma patients, 19 Latinos, 20 and elderly veterans. 23 A greater proportion of AUDIT (and CAGE) cases were male. Although this has been supported by others, 18,25 our study detected more women problem drinkers than were found in these two UK studies, at 20% compared to 5%. Although the CAGE cases tended to be younger than the noncases, supporting the findings of others, 6 this difference was not apparent for hazardous/harmful drinkers. As the sample size was small, based on acute medical admissions to one particular hospital, the findings may not be generally applicable. The time available to undertake the study (9 months) and the rate of medical admissions to the hospital also limited the sample. We did not include a gold standard measure of alcohol misuse, in the form of a detailed interview. However, both the CAGE and the AUDIT have been well-validated, 9,12 and the latter has been specifically validated for use in the general medical setting. 25 We were not aiming to repeat such work, rather to compare the two screening instruments. The prevalence of hazardous/harmful drinking, as indicated by the AUDIT, was higher in our study than that reported by other UK investigators. Sharkey et al. reported 16% of medical in-patients in Northern Ireland were drinking at hazardous or harmful levels. 26 However, they found a higher rate (39%) in those patients attending the accident and emergency department. A recent US study found 28% of current drinking medical in-patients scored positively on the AUDIT. 27 Australian investigators reported a similar rate of hazardous or harmful drinking to that found in our study (41%); however, the study was conducted using a structured interview schedule to detect hazardous and harmful drinking, rather than a screening tool. 28 The rate of problem drinking detected by the CAGE in this study was in accordance with several previous studies Several authors have commented on the limitations of the CAGE. Although developed to identify the more severe drinker, it fails to do so adequately by including previous problem drinkers and missing those without insight. 31 Knowledge and concern about safe levels of drinking vary with social climate, and influence responses to the questions about guilt and the need to cut down consumption. 32 In summary, our study indicates the advantage of the AUDIT over the CAGE as a screening tool for use in the general medical setting. The advantage of the AUDIT is that it identifies not just all those harmful drinkers likely to be picked up by the CAGE, but also hazardous drinkers who have not yet reached that level of harm. In recent years there has been a move to encourage brief alcohol interventions as a public health measure. Such
4 594 M.T. McCusker et al. interventions have been shown to be effective in reducing alcohol consumption by over 20% in hazardous drinkers. 33 Based on the assumption that heavy drinkers at an earlier stage (hazardous drinkers) in their drinking career will be more responsive to brief interventions, we recommend the routine use of the AUDIT for screening in routine clinical practice. References 1. Sacco RL, Elkind M, Boden-Albala B, Feng Lin I, et al. The protective effect of moderate alcohol consumption on ischaemic stroke. JAMA 1999; 281: Farrell M, Howes S, Taylor C, Glynn L, et al. Substance misuse and psychiatric co-morbidity: an overview of the OPCS national psychiatric morbidity survey. Addiction 1998; 23: Lockhart SP, Carter YH, Straffen AM, Pang KK, et al. Detecting alcohol consumption as a cause of emergency medical admissions. J Roy Soc Med 1986; 79: Jariwalla AG, Adams PH, Hore BD. Alcohol and acute general medical admissions to hospital. Health Trends 1979; 11: Jarman CMB, Kellett JM. Alcoholism in the general hospital. Br Med J 1979; 2: Moore RD, Bone LR, Geller G, Mamon JA, et al. Prevalence, detection and treatment of alcoholism in hospitalised patients. JAMA 1989; 261: Feldman E, Mayou R, Hawton K, Ardern M, Smith EBO. Psychiatric disorders in medical inpatients. Q J Med 1987; 63: Barrison IG, Viola L, Murray-Lyon IM. Do housemen take an adequate drinking history? Br Med J 1980; 281: Mayfield D, McLeod G, Hall P. The CAGE questionnaire: validation of a new alcoholism screening instrument. Am J Psych 1974; 131: Seltzer ML. The Michigan alcoholism screening test: the quest for a new diagnostic instrument. Am J Psych 1971; 12: Babor TF, De la Fuente JR, Saunders J, Grant M. AUDIT: the alcohol use disorders identification test guidelines for use in primary health care. Geneva, World Health Organization, Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, De la Fuente JR, Grant M. Development of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-11. Addiction 1993; 88: World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, Chapter 5. Mental and Behavioural Disorders due to Psychoactive Substance Use. Geneva, World Health Organization, Edwards G, Arif A, Hodgson R. Nomenclature and classification of drug and alcohol related problems: a WHO Memorandum. Bull WHO 1982; 59: Chick J, Lloyd G, Crombie E. Counselling problem drinkers in medical wards: a controlled study. Br Med J 1985; 290: Saunders JB, Foulds K. Brief and early intervention: experience from studies of harmful drinking. Aust NZ J Med 1992; 22: Bucholz KK, Homan SM, Helzer JE. When do alcoholics first discuss drinking problems? J Stud Alcohol 1992; 53: Mackenzie DM, Langa A, Brown TM. Identifying hazardous or harmful alcohol use in medical admissions: a comparison of AUDIT, CAGE, and Brief MAST. Alcohol Alcoholism 1996; 31: Soderstom CA, Smith GS, Kufera JA, Dischinger PC, Hebel JR, McDuff DR, Gorelick DA, Kerns TJ, Reid KM. The accuracy of the CAGE, the Brief Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test, and the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test in screening trauma center patients for alcoholism. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 1997; 43: Saitz R, Lepore MF, Sullivan LM, Amaro H, Samet JH. Alcohol abuse and dependence in Latinos living in the United States: validation of the CAGE (4M) questions. Arch Int Med 1999; 159: Morton JL, Jones TV, Manganaro MA. Performance of alcoholism screening questionnaires in elderly veterans. Am J Med 1996; 101: Reid MC, Fiellen DA, O Connor PG. Hazardous and harmful alcohol consumption in primary care. Arch Int Med 1999; 159: Clay SW. Comparison of AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires in screening for alcohol use disorders in elderly primary care outpatients. J Am Osteopath Assoc 1997; 97: Bradley KA, Boyd-Wickizier J, Powell SH, Burman ML. Alcohol screening questionnaires in women: a critical review. JAMA 1998; 280: Sharkey J, Brennan D, Curran P. The pattern of alcohol consumption of a general hospital population in North Belfast. Alcohol Alcoholism 1996; 31: Bohn MJ, Babor TF, Kranzler HR. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. J Stud Alcohol 1995; 56: Conigliaro J, Lofgren RP, Hanusa BH. Screening for problem drinking: impact on physician behaviour and patient drinking habits. J Gen Intern Med 1998; 13: Conigrave KM, Burns FH, Reznik RB, Saunders JB. Problem drinking in emergency department patients: the scope for early intervention. Med J Aust 1991; 154: Barrison IG, Viola L, Mumford J, Murray RM, Gordon M, et al. Detecting excessive drinking among medical admissions to a general hospital. Health Trends 1982; 14: Bush B, Shaw S, Cleary P, Delbanco TL, Aronson MD. Screening for alcohol abuse using the CAGE questionnaire. Am J Med 1987; 82: Waterson EJ, Murray-Lyon IM. Are the CAGE questions outdated? Br J Addict 1988; 83: Bisson J, Nadeau L, Demers A. The validity of the CAGE to screen for heavy drinking and drinking problems in a general population survey. Addiction 1999; 94: Effective Health Care Team. Brief interventions and alcohol use. Effective Health Care Bulletin No. 7. University of Leeds.
5 Appendix: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) Please circle the answer that is correct for you. Screening for drinking problems 595 How often do you have a drink containing alcohol? Never Monthly or less 2 4 times per month 2 3 times per week 4 or more times per week How many drinks containing alcohol do you have on a typical day when you are drinking? 1 or 2 3 or 4 5 or 6 7, 8 or 9 10 or more How often do you have six or more drinks on one occasion? How often during the last year have you found that you were not able to stop drinking once you had started? How often during the last year have you failed to do what was normally expected from you because of drinking? How often during the last year have you been unable to remember what happened the night before because you had been drinking? How often during the last year have you had a feeling of guilt or remorse after drinking? How often during the last year have you been unable to remember what happened the night before because you had been drinking? Have you or someone else been injured as a result of your drinking? No Yes, but not inthe last year Yes, during the last year Has a relative or friend, or a doctor or other health worker been concerned about your drinking or suggested you cut down? No Yes, but not in the last year Yes, during the last year
Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care attenders?
 Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test
 JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification. Clinical background
 Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification POMH-UK Quality Improvement Programme. Topic 14a: baseline Clinical background 1 2014 The Royal College of Psychiatrists. For further information
Prescribing for substance misuse: alcohol detoxification POMH-UK Quality Improvement Programme. Topic 14a: baseline Clinical background 1 2014 The Royal College of Psychiatrists. For further information
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners
 Practice The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners N Bowes A Sutton S Jenkins FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES, NOMS CYMRU, HMP CARDIFF J McMurran INSTITUTE OF MENTAL HEALTH, UNIVERSITY
Practice The alcohol treatment needs of violent and non-violent prisoners N Bowes A Sutton S Jenkins FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES, NOMS CYMRU, HMP CARDIFF J McMurran INSTITUTE OF MENTAL HEALTH, UNIVERSITY
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
 Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:11-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.1.11 A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:11-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.1.11 A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015
 LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015 LBPN Care Path Aim: To develop and implement standard protocols, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical
LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015 LBPN Care Path Aim: To develop and implement standard protocols, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical
SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires
 SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires 1. Brief Screens: NIAAA quantity and frequency Single alcohol screening question) Single drug screening question Conjoint screening questions 2. Full
SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires 1. Brief Screens: NIAAA quantity and frequency Single alcohol screening question) Single drug screening question Conjoint screening questions 2. Full
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey
 Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE AND RISK OF ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL IN MEDICAL INPATIENTS
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 515 519, 2005 Advance Access publication 15 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh189 COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 515 519, 2005 Advance Access publication 15 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh189 COMBINING THE AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS TO ASSESS ALCOHOL USE
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Data Harmonization Measure
 Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Measure Drug and Alcohol Use Drug and Alcohol Measure References: 1) Adapted from: Babor, T.F., Higgins-Biddle, J.C., Saunders, J.B. & Monteiro,
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Criminal Justice Populations: Measure Drug and Alcohol Use Drug and Alcohol Measure References: 1) Adapted from: Babor, T.F., Higgins-Biddle, J.C., Saunders, J.B. & Monteiro,
PATTERNS AND TRENDS: SURVEY OF ALCOHOL USE and CONSEQUENCES in MELBOURNE S VIETNAMESE COMMUNITY. June, 2009
 PATTERNS AND TRENDS: SURVEY OF ALCOHOL USE and CONSEQUENCES in MELBOURNE S VIETNAMESE COMMUNITY June, 2009 Institute of Studies, Odyssey House Victoria Centre for Psychiatric Nursing Research and Practice,
PATTERNS AND TRENDS: SURVEY OF ALCOHOL USE and CONSEQUENCES in MELBOURNE S VIETNAMESE COMMUNITY June, 2009 Institute of Studies, Odyssey House Victoria Centre for Psychiatric Nursing Research and Practice,
EDRS. trends. bulletin. Alcohol use disorders amongst a group of regular ecstasy users. Key findings. july Introduction.
 ecstasy and related drug trends july 2011 bulletin Authors: Sheena Arora and Lucy Burns, National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales Suggested citation: Arora, S. & Burns,
ecstasy and related drug trends july 2011 bulletin Authors: Sheena Arora and Lucy Burns, National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales Suggested citation: Arora, S. & Burns,
Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and Alcohol Use Disorders
 Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Alcohol misuse and cognitive impairment in older people: An exploratory study
 Alcohol misuse and cognitive impairment in older people: An exploratory study January 2014 Key findings There may be a significant amount of undiagnosed cognitive impairment in older people (aged 55 and
Alcohol misuse and cognitive impairment in older people: An exploratory study January 2014 Key findings There may be a significant amount of undiagnosed cognitive impairment in older people (aged 55 and
Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2
 Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2 Pocket Card SBIRT Health Effects of Substance Abuse Alcohol Use Disorders Identification test (AUDIT) NAME: Date: The following questions concern information about your alcohol
Pocket Card SBIRT Side 1 and 2 Pocket Card SBIRT Health Effects of Substance Abuse Alcohol Use Disorders Identification test (AUDIT) NAME: Date: The following questions concern information about your alcohol
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care
 Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
Smoking and hazardous alcohol
 Screening for Substance Abuse and Psychiatric Disorders Among Women Patients in a VA Health Care System Tania M. Davis, Ph.D. Kristen R. Bush, M.P.H. Daniel R. Kivlahan, Ph.D. Dorcas J. Dobie, M.D. Katharine
Screening for Substance Abuse and Psychiatric Disorders Among Women Patients in a VA Health Care System Tania M. Davis, Ph.D. Kristen R. Bush, M.P.H. Daniel R. Kivlahan, Ph.D. Dorcas J. Dobie, M.D. Katharine
How to cite this report: Peel Public Health. A Look at Peel Youth in Grades 7-12: Alcohol. Results from the 2013 Ontario Student Drug Use and Health
 How to cite this report: A Look at Peel Youth in Grades 7-12: Alcohol. Results from the 2013 Ontario Student Drug Use and Health Survey, A Peel Health Technical Report. 2015. TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
How to cite this report: A Look at Peel Youth in Grades 7-12: Alcohol. Results from the 2013 Ontario Student Drug Use and Health Survey, A Peel Health Technical Report. 2015. TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
DrinkCheck. Is your drinking okay?
 DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? WHAT SORT OF DRINKER ARE YOU? Test your drinking... DrinkCheck can help you find out more about your drinking. Just complete the questionnaire and add up your score. Then
DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? WHAT SORT OF DRINKER ARE YOU? Test your drinking... DrinkCheck can help you find out more about your drinking. Just complete the questionnaire and add up your score. Then
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students
 Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
DMRI Drug Misuse Research Initiative
 DMRI Drug Misuse Research Initiative Executive Summary Comorbidity in the national psychiatric morbidity surveys Research Report submitted to the Department of Health in February 2004 Report prepared by:
DMRI Drug Misuse Research Initiative Executive Summary Comorbidity in the national psychiatric morbidity surveys Research Report submitted to the Department of Health in February 2004 Report prepared by:
Alcohol advice and local support
 Alcohol advice and local support This information leaflet has been given to you by your doctor or nurse to provide further information and advice about alcohol and where you can get local support. How
Alcohol advice and local support This information leaflet has been given to you by your doctor or nurse to provide further information and advice about alcohol and where you can get local support. How
Alcohol use in advanced age: Findings from LiLACS NZ
 Alcohol use in advanced age: Findings from LiLACS NZ Te Puāwaitanga O Ngā Tapuwae Kia Ora Tonu This report presents key findings about alcohol use in advanced age including patterns of use and the relationship
Alcohol use in advanced age: Findings from LiLACS NZ Te Puāwaitanga O Ngā Tapuwae Kia Ora Tonu This report presents key findings about alcohol use in advanced age including patterns of use and the relationship
Alcohol Indicators Report Executive Summary
 Alcohol Indicators Report Executive Summary A framework of alcohol indicators describing the consumption of use, patterns of use, and alcohol-related harms in Nova Scotia NOVEMBER 2005 Foreword Alcohol
Alcohol Indicators Report Executive Summary A framework of alcohol indicators describing the consumption of use, patterns of use, and alcohol-related harms in Nova Scotia NOVEMBER 2005 Foreword Alcohol
Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders
 Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders Abstract Melissa A. Miller, M.S. and Mark T. Fillmore, Ph.D. Department of Psychology, University of Kentucky
Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders Abstract Melissa A. Miller, M.S. and Mark T. Fillmore, Ph.D. Department of Psychology, University of Kentucky
Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR
 Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR ALCOHOL IS A DRUG Drinking alcohol is the most common type of drug use in Australia Despite, Ice epidemic,
Alcohol health promotion utilising a harm minimisation approach PREVENTIVE HEALTH MATTERS WEBINAR ALCOHOL IS A DRUG Drinking alcohol is the most common type of drug use in Australia Despite, Ice epidemic,
SECOND AUSTRALIAN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT SURVEY OF MENTAL HEALTH AND WELLBEING HIGHLIGHTS
 The Mental Health of Children and Adolescents 3 SECOND AUSTRALIAN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT SURVEY OF MENTAL HEALTH AND WELLBEING HIGHLIGHTS A second national survey of the mental health and wellbeing of Australian
The Mental Health of Children and Adolescents 3 SECOND AUSTRALIAN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT SURVEY OF MENTAL HEALTH AND WELLBEING HIGHLIGHTS A second national survey of the mental health and wellbeing of Australian
EVALUATION OF AN INTERRELATED TIERED INTERVENTION TO REDUCE HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING
 EVALUATION OF AN INTERRELATED TIERED INTERVENTION TO REDUCE HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING Ciara Close, Research Fellow, Centre for Public Health, QUB ALCOHOL MISUSE Alcohol misuse means drinking excessively
EVALUATION OF AN INTERRELATED TIERED INTERVENTION TO REDUCE HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING Ciara Close, Research Fellow, Centre for Public Health, QUB ALCOHOL MISUSE Alcohol misuse means drinking excessively
1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18
 1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18 Dr. Laura Carone, FY1 Dr Venkataramana Thiagarajan, GPVTS2 Dr. Mariam Benaris, Consultant Psychiatrist & audit team lead Dr James
1522 Alcohol Consumption Documentation on Bradgate MHU Re-audit 2017/18 Dr. Laura Carone, FY1 Dr Venkataramana Thiagarajan, GPVTS2 Dr. Mariam Benaris, Consultant Psychiatrist & audit team lead Dr James
DrinkCheck. Is your drinking okay?
 DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? WHAT SO OF DRIN ARE YOU DrinkCheck can help you about your drinking. Just questionnaire and add u Then find out what it me *DrinkCheck is for people 8 years or older.
DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? WHAT SO OF DRIN ARE YOU DrinkCheck can help you about your drinking. Just questionnaire and add u Then find out what it me *DrinkCheck is for people 8 years or older.
words excluding references
 Psychological problems in New Zealand primary health care: A report on the pilot phase of the Mental Health and General Practice Investigation (MaGPIe) NZ Med J 2001; 114, 11-13 The MaGPIe Research Group
Psychological problems in New Zealand primary health care: A report on the pilot phase of the Mental Health and General Practice Investigation (MaGPIe) NZ Med J 2001; 114, 11-13 The MaGPIe Research Group
What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their drinking or advice to cut down on the AUDIT scale?
 Cunningham et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology (2017) 17:158 DOI 10.1186/s12874-017-0435-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their
Cunningham et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology (2017) 17:158 DOI 10.1186/s12874-017-0435-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE What does it mean when people say that they have received expressions of concern about their
Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection and treatment of hazardous and harmful
 REVIEW ARTICLE Hazardous and Harmful Alcohol Consumption in Primary Care M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; David A. Fiellin, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection
REVIEW ARTICLE Hazardous and Harmful Alcohol Consumption in Primary Care M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; David A. Fiellin, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Increasing emphasis has been placed on the detection
Hazardous drinking in 2011/12: Findings from the New Zealand Health Survey
 Hazardous drinking in 11/12: Findings from the New Zealand Health Survey This report presents key findings about alcohol use and hazardous drinking among adults aged 15 years and over, which come from
Hazardous drinking in 11/12: Findings from the New Zealand Health Survey This report presents key findings about alcohol use and hazardous drinking among adults aged 15 years and over, which come from
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi: /bmj ee (published 16 January 2004)
 Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.37956.562130.ee (published 16 January 2004) Effectiveness of opportunistic brief interventions for problem drinking in a general hospital setting: systematic
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.37956.562130.ee (published 16 January 2004) Effectiveness of opportunistic brief interventions for problem drinking in a general hospital setting: systematic
DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay?
 DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? What so of drin are you DrinkCheck can help you about your drinking. Just questionnaire and add u Then find out what it mea *DrinkCheck is for people 18 years or older.
DrinkCheck Is your drinking okay? What so of drin are you DrinkCheck can help you about your drinking. Just questionnaire and add u Then find out what it mea *DrinkCheck is for people 18 years or older.
Can Amazon s Mechanical Turk be used to recruit participants for Internet intervention trials?
 Can Amazon s Mechanical Turk be used to recruit participants for Internet intervention trials? A pilot study involving an RCT of a brief online intervention for hazardous alcohol use John Cunningham Centre
Can Amazon s Mechanical Turk be used to recruit participants for Internet intervention trials? A pilot study involving an RCT of a brief online intervention for hazardous alcohol use John Cunningham Centre
Running head: RANK-FRAMING IN SOCIAL NORMS INTERVENTIONS 1
 Running head: RANK-FRAMING IN SOCIAL NORMS INTERVENTIONS 1 Title: Brief report: Improving social norms interventions: Rank-framing increases excessive alcohol drinkers' information-seeking The work was
Running head: RANK-FRAMING IN SOCIAL NORMS INTERVENTIONS 1 Title: Brief report: Improving social norms interventions: Rank-framing increases excessive alcohol drinkers' information-seeking The work was
Suicide Risk Assessment
 Psychiatry for General Practitioners Study Days 2017 December 13th 2017 Suicide Risk Assessment Keith Hawton Psychiatry for General Practitioners Study Days 2017 December 13th 2017 Suicide Risk Assessment:
Psychiatry for General Practitioners Study Days 2017 December 13th 2017 Suicide Risk Assessment Keith Hawton Psychiatry for General Practitioners Study Days 2017 December 13th 2017 Suicide Risk Assessment:
Chapter 11: SF-36 Health Status Questionnaire: Health Risk Behaviours, Specific Conditions and Health Service Utilisation
 Chapter 11: SF-36 Status Questionnaire: Risk Behaviours, Specific Conditions and Service Utilisation Key points Smoking status had some impact on self-reported health, particularly amongst non- Mäori,
Chapter 11: SF-36 Status Questionnaire: Risk Behaviours, Specific Conditions and Service Utilisation Key points Smoking status had some impact on self-reported health, particularly amongst non- Mäori,
health impacts factsheet
 Health services are central to tackling harm at the individual level among those with alcoholuse disorders and other conditions caused by harmful use of alcohol. The World Health Organisation (WHO) states
Health services are central to tackling harm at the individual level among those with alcoholuse disorders and other conditions caused by harmful use of alcohol. The World Health Organisation (WHO) states
Alcohol dependence what actually works
 what actually works Alcohol dependence is the most common addiction that a generalist will encounter. D Wilson, FCPsych (SA) Psychiatrist and Head of Addictions Division, University of Cape Town/Groote
what actually works Alcohol dependence is the most common addiction that a generalist will encounter. D Wilson, FCPsych (SA) Psychiatrist and Head of Addictions Division, University of Cape Town/Groote
Alcohol Interventions: NICE guidelines and beyond. Professor Colin Drummond
 Alcohol Interventions: NICE guidelines and beyond Professor Colin Drummond What this presentation covers Background Scope Methodology What is new? Implications for practice Implementation International
Alcohol Interventions: NICE guidelines and beyond Professor Colin Drummond What this presentation covers Background Scope Methodology What is new? Implications for practice Implementation International
Dr. Úna M MB, BCh, LRCP&SI, MRCPsych, DipHS
 Dr. Úna M MB, BCh, LRCP&SI, MRCPsych, DipHS GMC Registration No. 2563088 DBS No. 001551517153 PROFESSIONAL QUALIFICATIONS & EXPERTISE Professional Qualification Consultant Psychiatrist Areas of Expertise
Dr. Úna M MB, BCh, LRCP&SI, MRCPsych, DipHS GMC Registration No. 2563088 DBS No. 001551517153 PROFESSIONAL QUALIFICATIONS & EXPERTISE Professional Qualification Consultant Psychiatrist Areas of Expertise
Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening
 Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening patients for substance use in a clinical setting. 1
Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening patients for substance use in a clinical setting. 1
What is a Trauma Center? What is a Trauma Center? Minnesota Trauma Centers. Alcohol Screening and Brief Intervention in the Trauma Center Setting
 What is a Trauma Center? Alcohol Screening and Brief Intervention in the Trauma Center Setting Alison Pence, MPH North Memorial Medical Center Robbinsdale,, MN Trauma Center is a designation given by the
What is a Trauma Center? Alcohol Screening and Brief Intervention in the Trauma Center Setting Alison Pence, MPH North Memorial Medical Center Robbinsdale,, MN Trauma Center is a designation given by the
Yellow PracticeNewPatient Information Card
 Yellow PracticeNewPatient Infmation Card Date / / Surname MR/MRS/MISS/MS First Name(s) Date of Birth / / Home Tel: Wk Tel: Mobile Tel: Email Address: Address Post Code Height Weight Occupation Are you
Yellow PracticeNewPatient Infmation Card Date / / Surname MR/MRS/MISS/MS First Name(s) Date of Birth / / Home Tel: Wk Tel: Mobile Tel: Email Address: Address Post Code Height Weight Occupation Are you
Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust. Board of Directors Meeting
 Agenda item Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust Board of Directors Meeting Meeting Date: 29th November 2017 Title and Author of Paper: National CQC Community Mental Health Survey & National
Agenda item Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust Board of Directors Meeting Meeting Date: 29th November 2017 Title and Author of Paper: National CQC Community Mental Health Survey & National
Assessment of Fitness to Drive to be completed by medical practitioner
 COMMERCIAL VEHICLE DRIVER MEDICAL ASSESSMENT This Medical Assessment meets the requirements of the following Western Australian Government Authorities; Department of Commerce, WorkSafe - Occupational Safety
COMMERCIAL VEHICLE DRIVER MEDICAL ASSESSMENT This Medical Assessment meets the requirements of the following Western Australian Government Authorities; Department of Commerce, WorkSafe - Occupational Safety
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice. Citation for published version: Holloway, A 2015, 'Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice.' Practice Nursing, vol. 26, no. 1. DOI: 10.12968/pnur.2015.26.1.10
Edinburgh Research Explorer Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice. Citation for published version: Holloway, A 2015, 'Alcohol-Related Harm in the Practice.' Practice Nursing, vol. 26, no. 1. DOI: 10.12968/pnur.2015.26.1.10
Substance Misuse Nurse service Belfast Trust
 Substance Misuse Nurse service Belfast Trust Alcohol is the most widely available socially acceptable drug in Northern Ireland It can be an addictive substance It is a depressant- slows down the central
Substance Misuse Nurse service Belfast Trust Alcohol is the most widely available socially acceptable drug in Northern Ireland It can be an addictive substance It is a depressant- slows down the central
Substance use among year olds in the UK: Key findings from the 2011 European Survey Project on Alcohol and Drugs (ESPAD)
 Substance use among 15-16 year olds in the UK: Key findings from the 2011 European Survey Project on Alcohol and Drugs (ESPAD) Amanda M. Atkinson, Harry R. Sumnall & Mark A. Bellis 1. Introduction The
Substance use among 15-16 year olds in the UK: Key findings from the 2011 European Survey Project on Alcohol and Drugs (ESPAD) Amanda M. Atkinson, Harry R. Sumnall & Mark A. Bellis 1. Introduction The
I t is established that regular light to moderate drinking is
 32 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Taking up regular drinking in middle age: effect on major coronary heart disease events and mortality S G Wannamethee, A G Shaper... See end of article for authors affiliations...
32 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Taking up regular drinking in middle age: effect on major coronary heart disease events and mortality S G Wannamethee, A G Shaper... See end of article for authors affiliations...
The Cost of Alcohol Frequent Attenders: Staging an Intervention
 The Cost of Alcohol Frequent Attenders: Staging an Intervention K. Adams, E. Clarke, R. McCorry The Liver Unit Royal Victoria Hospital Belfast Health and Social Care Trust Background Alcohol related harm
The Cost of Alcohol Frequent Attenders: Staging an Intervention K. Adams, E. Clarke, R. McCorry The Liver Unit Royal Victoria Hospital Belfast Health and Social Care Trust Background Alcohol related harm
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS
 BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS FOR THE CO-LOCATION OF BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A PRIMARY CARESETTING Date: August 29, 2017 Introduction Today s Presenter Jacqueline Delmont, MD, MBA Delmont Healthcare
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SCREENING TOOLS FOR THE CO-LOCATION OF BEHAVIORAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A PRIMARY CARESETTING Date: August 29, 2017 Introduction Today s Presenter Jacqueline Delmont, MD, MBA Delmont Healthcare
The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, Alcohol dependence technical overview
 The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2016 Alcohol dependence technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2016 Alcohol dependence technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
Implementing the alcohol specialist nurse service within Salford Royal EAU/AAA. Ruth Brown & Hailey Pennington
 Implementing the alcohol specialist nurse service within Salford Royal EAU/AAA Ruth Brown & Hailey Pennington Aim of ASN role Integration of ASN Alcohol screening Pathways, policy, protocol and leaflet
Implementing the alcohol specialist nurse service within Salford Royal EAU/AAA Ruth Brown & Hailey Pennington Aim of ASN role Integration of ASN Alcohol screening Pathways, policy, protocol and leaflet
Screening and Addressing Alcohol Use In Primary Care
 Screening and Addressing Alcohol Use In Primary Care Mark R. Loush, LMSW, CAADC August 15, 20167 Objectives Identify the primary reasons why screening for alcohol in primary care is important Understand
Screening and Addressing Alcohol Use In Primary Care Mark R. Loush, LMSW, CAADC August 15, 20167 Objectives Identify the primary reasons why screening for alcohol in primary care is important Understand
The audit is managed by the Royal College of Psychiatrists in partnership with:
 Background The National Audit of Dementia (NAD) care in general hospitals is commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership on behalf of NHS England and the Welsh Government, as part of
Background The National Audit of Dementia (NAD) care in general hospitals is commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership on behalf of NHS England and the Welsh Government, as part of
PUBLIC HEALTH INTERVENTION GUIDANCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE PUBLIC HEALTH INTERVENTION GUIDANCE 1 Guidance title SCOPE Interventions delivered in primary and secondary schools to prevent and/or reduce alcohol
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE PUBLIC HEALTH INTERVENTION GUIDANCE 1 Guidance title SCOPE Interventions delivered in primary and secondary schools to prevent and/or reduce alcohol
URL: <http://dx.doi.org/ /j.drugalcdep >
 Citation: Heather, Nick, Smailes, David and Cassidy, Paul (2008) Development of a readiness ruler for use with alcohol brief interventions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 98 (3). pp. 235-240. ISSN 0376-8716
Citation: Heather, Nick, Smailes, David and Cassidy, Paul (2008) Development of a readiness ruler for use with alcohol brief interventions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 98 (3). pp. 235-240. ISSN 0376-8716
Brief interventions for alcohol misuse Training and material for non-specialists
 Brief interventions for alcohol misuse Training and material for non-specialists Executive summary This report summarises Swanswell s development of a six-session brief intervention and training programme
Brief interventions for alcohol misuse Training and material for non-specialists Executive summary This report summarises Swanswell s development of a six-session brief intervention and training programme
Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA
 Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA 2 Evidence-Based Screening and Brief Interventions for Alcohol and Psychoactive Medication Misuse in Older Adults 3 Speakers Frederic C. Blow, Ph.D. Professor
Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA 2 Evidence-Based Screening and Brief Interventions for Alcohol and Psychoactive Medication Misuse in Older Adults 3 Speakers Frederic C. Blow, Ph.D. Professor
Substance Misuse in Older People
 Substance Misuse in Older People Dr Tony Rao Consultant Old Age Psychiatrist, SLAM NHS Foundation Trust Visiting Researcher, Institute of Psychiatry, Neurology and Neuroscience Chair of Substance Misuse
Substance Misuse in Older People Dr Tony Rao Consultant Old Age Psychiatrist, SLAM NHS Foundation Trust Visiting Researcher, Institute of Psychiatry, Neurology and Neuroscience Chair of Substance Misuse
Taking an alcohol history
 Taking an alcohol history Dr Tony Rao Consultant Old Age Psychiatrist, SLAM NHS Foundation Trust Visiting Researcher, Institute of Psychiatry, Neurology and Neuroscience Alcohol related brain damage Alcohol
Taking an alcohol history Dr Tony Rao Consultant Old Age Psychiatrist, SLAM NHS Foundation Trust Visiting Researcher, Institute of Psychiatry, Neurology and Neuroscience Alcohol related brain damage Alcohol
VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND
 VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Somsong Nanakorn 1, Katsuhiro Fukuda 2, Itsuro Ogimoto 2, Tawee Tangseree 3 and Suchart Treethiptikhun 4
VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Somsong Nanakorn 1, Katsuhiro Fukuda 2, Itsuro Ogimoto 2, Tawee Tangseree 3 and Suchart Treethiptikhun 4
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems Per E. Danielsson, MD; Frederick P. Rivara, MD, MPH; Larry M. Gentilello, MD; Ronald V. Maier, MD Background: Alcohol screening
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems Per E. Danielsson, MD; Frederick P. Rivara, MD, MPH; Larry M. Gentilello, MD; Ronald V. Maier, MD Background: Alcohol screening
21 units per week. 14 units per week
 Patient Support Worksheet: Supporting Your Commitment To Reduce Your Drinking About this worksheet In talking to your healthcare professional you have already taken the first step towards overcoming your
Patient Support Worksheet: Supporting Your Commitment To Reduce Your Drinking About this worksheet In talking to your healthcare professional you have already taken the first step towards overcoming your
Blood alcohol levels in suicide cases
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1992; 46: 256-260 Health Department of Western Australia, PO Box 8172, Stirling Street, Perth, Western Australia 6000: Epidemiology Branch L Hayward Neurosciences
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1992; 46: 256-260 Health Department of Western Australia, PO Box 8172, Stirling Street, Perth, Western Australia 6000: Epidemiology Branch L Hayward Neurosciences
Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
Psychology Research Institute, University of Ulster, Northland Road, Londonderry, BT48 7JL, UK
 Patterns of Alcohol Consumption and Related Behaviour in Great Britain: A Latent Class Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) Gillian W. Smith * and Mark Shevlin Psychology Research
Patterns of Alcohol Consumption and Related Behaviour in Great Britain: A Latent Class Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) Gillian W. Smith * and Mark Shevlin Psychology Research
Conway PMS. NHS Health Check Questionnaire
 Conway PMS NHS Health Check Questionnaire We would be grateful if you could kindly complete this survey. Please be as honest as possible to help us to help you. Name: Male Female D of B: dd / mm / yyyy
Conway PMS NHS Health Check Questionnaire We would be grateful if you could kindly complete this survey. Please be as honest as possible to help us to help you. Name: Male Female D of B: dd / mm / yyyy
Template Control Page. Substance Misuse Newham Template Guide. Substance Misuse Newham. Date September 2015 DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT REVISION HISTORY
 Template Control Page Substance Misuse Newham Template Guide Title Substance Misuse Newham Author CEG Status Active Date September 2015 DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT REVISION HISTORY Version Date Summary of Changes
Template Control Page Substance Misuse Newham Template Guide Title Substance Misuse Newham Author CEG Status Active Date September 2015 DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT REVISION HISTORY Version Date Summary of Changes
Northwick Park Mental Health Centre Smoking Cessation Report October Plan. Act. Study. Introduction
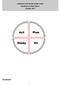 Northwick Park Mental Health Centre Smoking Cessation Report October 2017 Act Plan Study Do Introduction 1 In 2013 the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommended that health organisations
Northwick Park Mental Health Centre Smoking Cessation Report October 2017 Act Plan Study Do Introduction 1 In 2013 the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommended that health organisations
THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Screening and Brief Intervention for Risky Substance Use
 Screening and Brief Intervention for Risky Substance Use Trauma and Analgesia: Balancing Patient Comfort and Opioid-Related Risks Joe Glass, PhD MSW Assistant Scientific Investigator Group Health Research
Screening and Brief Intervention for Risky Substance Use Trauma and Analgesia: Balancing Patient Comfort and Opioid-Related Risks Joe Glass, PhD MSW Assistant Scientific Investigator Group Health Research
A Guide to Behavioral Health Screenings: Utilizing Screening tools to Improve Identification of Depression and Alcohol Misuse in Primary Care
 A Guide to Behavioral Health Screenings: Utilizing Screening tools to Improve Identification of Depression and Alcohol Misuse in Primary Care HealthInsight New Mexico Team John Siebel, MD Medical Director
A Guide to Behavioral Health Screenings: Utilizing Screening tools to Improve Identification of Depression and Alcohol Misuse in Primary Care HealthInsight New Mexico Team John Siebel, MD Medical Director
The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse. ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage:
 The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse Encompassing All Addictive Disorders ISSN: 0095-2990 (Print) 1097-9891 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iada20 A review of the Alcohol
The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse Encompassing All Addictive Disorders ISSN: 0095-2990 (Print) 1097-9891 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iada20 A review of the Alcohol
Admissions of patients with alcohol intoxication in the Emergency Department: a growing phenomenon
 Published 7 August 2014, doi:10.4414/smw.2014.13982 Cite this as: Admissions of patients with alcohol intoxication in the Emergency Department: a growing phenomenon Nicolas Bertholet a, Angéline Adam a,b,
Published 7 August 2014, doi:10.4414/smw.2014.13982 Cite this as: Admissions of patients with alcohol intoxication in the Emergency Department: a growing phenomenon Nicolas Bertholet a, Angéline Adam a,b,
AMPHORA meeting in Stockholm October 2012 Brief Interventions Workshop
 AMPHORA meeting in Stockholm October 2012 Brief Interventions Workshop Amy Wolstenholme Colin Drummond Paolo Deluca Institute of Psychiatry, King s College London Alcohol Policy Conference Stockholm, 18/10/12
AMPHORA meeting in Stockholm October 2012 Brief Interventions Workshop Amy Wolstenholme Colin Drummond Paolo Deluca Institute of Psychiatry, King s College London Alcohol Policy Conference Stockholm, 18/10/12
Unrecorded Alcohol in Vietnam
 Unrecorded Alcohol in Vietnam Results of a Population Survey February 2018 Over the past decade, there has been a growing effort to measure and describe alcohol consumption and prevailing drinking patterns
Unrecorded Alcohol in Vietnam Results of a Population Survey February 2018 Over the past decade, there has been a growing effort to measure and describe alcohol consumption and prevailing drinking patterns
Specialty substance use disorder services following brief alcohol intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
 Specialty substance use disorder services following brief alcohol intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials May 27, 2016 Joseph E. Glass, PhD, MSW Assistant Professor School of Social
Specialty substance use disorder services following brief alcohol intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials May 27, 2016 Joseph E. Glass, PhD, MSW Assistant Professor School of Social
An Internist s Guide to Unhealthy Alcohol Use. Ryan Graddy, MD JHU SOM
 An Internist s Guide to Unhealthy Alcohol Use Ryan Graddy, MD JHU SOM Disclosures None Learning Objectives Understand the terminology used to describe unhealthy alcohol use Identify means of screening
An Internist s Guide to Unhealthy Alcohol Use Ryan Graddy, MD JHU SOM Disclosures None Learning Objectives Understand the terminology used to describe unhealthy alcohol use Identify means of screening
A SOCIAL MARKETING CAMPAIGN AGAINST HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING IN ENGLAND
 A SOCIAL MARKETING CAMPAIGN AGAINST HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING IN ENGLAND Nick Heather PhD, Division of Psychology, Northumbria University, UK Presentation at 5 th INEBRIA Conference, Ribeirao Preto,
A SOCIAL MARKETING CAMPAIGN AGAINST HAZARDOUS AND HARMFUL DRINKING IN ENGLAND Nick Heather PhD, Division of Psychology, Northumbria University, UK Presentation at 5 th INEBRIA Conference, Ribeirao Preto,
Implementation of Screening and Interventions for Unhealthy Alcohol Use. Dan Jonas, MD, MPH
 Implementation of Screening and Interventions for Unhealthy Alcohol Use Dan Jonas, MD, MPH Our team Shana Ratner, MD Colleen Barclay, MPH Julia Tompkins, MSW,LCSW-A Bailey Minish Tamrah Watson, MSN, RN,
Implementation of Screening and Interventions for Unhealthy Alcohol Use Dan Jonas, MD, MPH Our team Shana Ratner, MD Colleen Barclay, MPH Julia Tompkins, MSW,LCSW-A Bailey Minish Tamrah Watson, MSN, RN,
Mortality in relation to alcohol consumption: a prospective study among male British doctors
 IJE vol.34 no.1 International Epidemiological Association 2005; all rights reserved. International Journal of Epidemiology 2005;34:199 204 Advance Access publication 12 January 2005 doi:10.1093/ije/dyh369
IJE vol.34 no.1 International Epidemiological Association 2005; all rights reserved. International Journal of Epidemiology 2005;34:199 204 Advance Access publication 12 January 2005 doi:10.1093/ije/dyh369
Effective Interventions Unit
 Effective Interventions Unit Measuring staff attitudes to people with drug problems: The development of a tool Hazel Watson William Maclaren Fraser Shaw* Andrew Nolan Glasgow Caledonian University *Greater
Effective Interventions Unit Measuring staff attitudes to people with drug problems: The development of a tool Hazel Watson William Maclaren Fraser Shaw* Andrew Nolan Glasgow Caledonian University *Greater
Ecstasy and Related Drugs Reporting System drug trends bulletin April 2014
 Ecstasy and Related Drugs Reporting System April 2014 The Ecstasy and Related Drugs Reporting System: A comparison of GLB and heterosexual participants. Authors: Rachel Sutherland and Lucy Burns National
Ecstasy and Related Drugs Reporting System April 2014 The Ecstasy and Related Drugs Reporting System: A comparison of GLB and heterosexual participants. Authors: Rachel Sutherland and Lucy Burns National
The Impact of Substance Use Disorders on Hospital Use
 www.ccsa.ca www.cclt.ca Report in Short The Impact of Substance Use Disorders on Hospital Use What Is this Report About? This report: Describes trends in individuals hospitalized because of a primary diagnosis
www.ccsa.ca www.cclt.ca Report in Short The Impact of Substance Use Disorders on Hospital Use What Is this Report About? This report: Describes trends in individuals hospitalized because of a primary diagnosis
Responding Effectively to BPD Challenges for the Service System. Katerina Volny Peter McKenzie
 Responding Effectively to BPD Challenges for the Service System Katerina Volny Peter McKenzie Borderline Personality Disorder A common mental illness characterised by poor control of emotions and impulses,
Responding Effectively to BPD Challenges for the Service System Katerina Volny Peter McKenzie Borderline Personality Disorder A common mental illness characterised by poor control of emotions and impulses,
Dual Diagnosis. Themed Review Report 2006/07 SHA Regional Reports East Midlands
 Dual Diagnosis Themed Review Report 2006/07 SHA Regional Reports East Midlands Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 2 Recommendations 2 Themed Review 06/07 data 3 Additional information 13 Weighted population
Dual Diagnosis Themed Review Report 2006/07 SHA Regional Reports East Midlands Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 2 Recommendations 2 Themed Review 06/07 data 3 Additional information 13 Weighted population
Hull Citysafe. Survey analysis. Title: Mine s a Lambrini? A report examining alcohol consumption among young people in Hull.
 Hull Citysafe Survey analysis Title: Mine s a Lambrini? A report examining alcohol consumption among young people in Hull April 2008 Prepared By: Lindsey Baxter Crime & Disorder analyst Katy Stevenson
Hull Citysafe Survey analysis Title: Mine s a Lambrini? A report examining alcohol consumption among young people in Hull April 2008 Prepared By: Lindsey Baxter Crime & Disorder analyst Katy Stevenson
Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
 Postgrad Med J (1993) 69, 696-700 A) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 199: Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
Postgrad Med J (1993) 69, 696-700 A) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 199: Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
Characteristics of People who Report Both Driving after Drinking and Driving after Cannabis Use
 Characteristics of People who Report Both Driving after Drinking and Driving after Cannabis Use Branka Agic 1,2, Gina Stoduto 1, Gillian Sayer 1,2, Anca Ialomiteanu 1, Christine M. Wickens 1, Robert E.
Characteristics of People who Report Both Driving after Drinking and Driving after Cannabis Use Branka Agic 1,2, Gina Stoduto 1, Gillian Sayer 1,2, Anca Ialomiteanu 1, Christine M. Wickens 1, Robert E.
Evaluating the interactive effects of responsible drinking messages and attentional bias on actual drinking behaviours
 Evaluating the interactive effects of responsible drinking messages and attentional bias on actual drinking behaviours February 2017 Key findings Responsible drinking posters do not attract significant
Evaluating the interactive effects of responsible drinking messages and attentional bias on actual drinking behaviours February 2017 Key findings Responsible drinking posters do not attract significant
St George Hospital Renal Supportive Care Psychosocial Day, 10 th August Michael Noel, Supportive and Palliative Care Physician, Nepean Hospital
 St George Hospital Renal Supportive Care Psychosocial Day, 10 th August 2017 Michael Noel, Supportive and Palliative Care Physician, Nepean Hospital Michael.Noel@health.nsw.gov.au Hannah Burgess, Renal
St George Hospital Renal Supportive Care Psychosocial Day, 10 th August 2017 Michael Noel, Supportive and Palliative Care Physician, Nepean Hospital Michael.Noel@health.nsw.gov.au Hannah Burgess, Renal
