Quantitative measurement of ultrasound attenuation and Hepato- Renal Index in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 1, DOI: /mu hlv1qmu2 Quantitative measurement of ultrasound attenuation and Hepato- Renal Index in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Hilde Løland von Volkmann 1, Roald Flesland Havre 1,6, Else Marit Løberg 2, Terese Haaland 2, Heike Immervoll 3, John Willy Haukeland 4, Trygve Hausken 1,5, Odd Helge Gilja 1,5,6 1 Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital, 2 Department of Pathology, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway, 3 Department of Pathology, Ålesund Hospital, Norway, 4 Department of Gastroenterology, Oslo University Hospital, 5 Institute of Medicine, University of, Bergen, Norway, 6 National Centre for Ultrasound in Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital, Bergen, Norway. Abstract Objective: The aim of this study was to non-invasively explore new methods of ultrasound attenuation measurements in livers of patients with Non-Alcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease (NAFLD) and to measure the liver tissue elasticity. Material and method: Sixteen patients with NAFLD, twelve patients with liver fibrosis and fifteen healthy subjects were included. Echo Levels (ELs) in db were measured at 2 and 7cm depths in the right liver to calculate the attenuation. ELs were measured in liver and right kidney tissue to calculate the Hepato-Renal Index (HRI). This index was calculated both as a difference, HRIdiff; (EL Liver EL Kidney) and HRI-ratio; (EL Liver / EL Kidney) using built-in software of the ultrasound scanner. Liver tissue elasticity was measured using transient elastography (TE, Fibroscan ). NAFLD and liver fibrosis were confirmed by liver biopsy. Results: We found that HRI- diff was significantly higher in the NAFLD group compared with healthy subjects, 6.2 db ( ) vs.1. 9 db ( ), p= HRI- ratio was significantly lower between the same two groups, 0.9 db ( ) vs.1.01 db ( ), and p< TE, ELs and liver size showed significant differences between NAFLD patients and healthy controls. Between patients with fibrosis and NAFLD the differences were significant for TE, liver size and attenuation. Intra- and interobserver correlation and agreement of ELs were good. Conclusion: Measurements of liver tissue using HR-Indexes, ultrasound attenuation, and tissue elasticity may be useful methods to differentiate objectively between steatosis and healthy and quantify the differences. Keywords: ultrasound, NAFLD, steatosis quantification, attenuation Introduction The prevalence of fatty liver disease increases in the Western world. It is often caused by alcohol consumption (AFLD) or more frequently by Non-Alcoholic Fatty-Liver Disease (NAFLD) [1]. Steatosis is defined by accumulation of triglycerides in the liver parenchyma. In ultrasound imaging, fatty liver infiltration is characterised by hyperechogenicity of the liver parenchyma Received Accepted Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, No 1, Corresponding author: Hilde Løland von Volkmann, Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital, N5021 Bergen, Norway hilde.von.volkmann@helse-bergen.no with increased attenuation of the ultrasound waves in the deeper parts compared to healthy liver tissue. The prevalence of NAFLD is varying between 13 and 23 %, but amongst obese patients as high as 74 % [1,2]. Ultrasound (US) is a widely available and non-invasive method to examine the liver tissue. In most patients the whole organ may be evaluated in one single examination [3]. Liver biopsy is the gold standard when investigating the fat infiltration in the liver, but is an invasive method. It only evaluates approximately 1/ part of the liver parenchyma with a high risk of sampling error. A non-invasive method providing similar accuracy as provided by liver biopsy is wanted [4-6]. To establish the presence and grading of fatty infiltration based on a subjective visual examination using ultrasound substantial experience of the examiner is required.
2 A method to quantify liver steatosis by using the liver echogenicity or the increased US attenuation in fatty liver tissue would be valuable. Previous studies have compared the echogenicity of the liver with the echogenicity of the kidney calculating a Hepato- Renal Index (HRI) [7-9]. The aim of the present study was to examine non-invasive methods measuring the attenuation of ultrasound in the liver in NAFLD patients and compare with measurements in patients with established fibrosis and healthy subjects. Secondly, we compared the liver tissue elasticity in these three groups using liver elasticity measurements. Thirdly, we wanted to assess the intra- and interobserver agreement of the US measurements of liver tissue ultrasound attenuation. Materials and methods Study population This case-control study was conducted at Haukeland University Hospital. Sixteen patients, 11 females, 5 males, age 52 ± 7 years with NAFLD, twelve patients 3 females, 9 males, age 44 ± 11 years, with histologically proven liver fibrosis and fifteen healthy subjects, 9 females, 6 males, age 45 ± 9 years. The patients in the NAFLD group had all ultrasonographic homogeneous distribution of fatty infiltration in the liver. Patients with focal fatty sparing were not included. The NAFLD patients were recruited from the Department of Gastroenterology after standard work-up due to elevated liver tests. In the group where the patients had established liver fibrosis, the majority (11/12) had their fibrosis due to chronic virus (B or C) - infections. One of the patients with fibrosis had a histopathological feature of hepatitis C, but the blood test did not confirm this. For the sake of simplicity, we chose to call this group the fibrosis group. The healthy subjects were recruited from the Department of Gastroenterology and were nurses or physicians. They had no history of liver disease and had normal blood tests. The inclusion followed when the sonographic examination of the liver was normal. No liver biopsy or virus markers were taken from the healthy controls. The biopsied patients in the NAFLD and fibrosis group were recruited based on a previous liver biopsy, and not as a result of the examination All participants had normal kidney function and no history of kidney disease or malfunction. Patients or controls with pacemaker, defibrillator, pregnancy or alcohol consumption more than 20 g daily were not included. Med Ultrason 2013; 15(1): The study was conducted according to the Helsinki declaration and with the approval of the Regional Ethics Committee for medical research, Bergen, Norway. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. Ultrasonography The same gastroenterologist (HLvV) performed all examinations. The scanner used was GE Logiq 9 (Milwaukee,Wisconsin,USA) with a curvilinear transducer MHz. The liver was described as normal when the ultrasound examination showed a homogenous liver parenchyma and isoechoic eccogenecity. The affected parenchyma in the NAFLD group was described as hyperechoic compared with the right kidney. Regions of interest (ROI) were identified with a set diameter and depth avoiding visible bile ducts or vessels. The ROI was circular or oval in configuration with a diameter of 1-2 cm both in the liver and in the right kidney cortex. The measurements were performed at the same level of depth in the two organs. EchoLevel (EL) measures the mean intensity of pixels within a user defined area. The scanner utilities the intensity data from raw data per pixel and calculates the average: Average = sum (intensity per pixel) / pixels. Raw data pixel measurements imply that there is no influence of gain, dynamic range or other scanner parameters. EL is measured in db and is linear to the intensity. Zero db equals max intensity i.e. white with gray level 255. Minimum intensity equals -99 db, i.e. black with gray level zero. Y = (255/99)*EL[dB]; EL[dB] = 20*log10(E), where EL denotes Echo Level. We measured the following ultrasound parameters: EL in anterior and lateral positions,liver tissue elasticity using transient elastography, and the size of the liver in the right medio-clavicular line with measurements from the hepatic dome to the frontal inferior hepatic tip [10]. Attenuation The attenuation was estimated using EL. Steatosis was visualised by Ultrasound in all 16 NAFLD patients. EL measurements were made in regions of interest in the right liver lobe at 2 cm and 7 cm depth in the medioclavicular line (EL ant) and lateral (EL lat) in right intercostals spaces Subsequently, attenuation was calculated by subtracting the EL level at 7 cm from the EL level at 2 cm below the capsule. The frequency of the scanner was set to 4 MHz for all measurements. Hepatorenal Index Hepato-Renal Index Difference (HRI-diff: EL Liver EL Kidney) or Hepato-Renal Index Ratio (HRI-ratio: Liver EL / kidney EL) were estimated using built-in software on the scanner enabling local measurement of attenuation in db. When the right kidney cortex was 17
3 18 Hilde Løland von Volkmann et al Quantitative measurement of ultrasound attenuation and Hepato-Renal Index Fig 1. Ultrasound image showing Echo Level measurements in the right liver lobe and in the right kidney cortex. The ROI was circular or oval in configuration with a diameter of 1-2 cm both in the liver and in the right kidney cortex. It is important to measure at the same level of depth in the two organs. clearly visualized, ELs were measured in the liver and in kidney cortex at the same distance from the US probe (fig 1). Transient elastography (TE) Liver stiffness measurements (LSM) were performed by TE using Fibroscan (Echosens, Paris, France); M Probe with transducer frequency 3.5 MHz. The probe of the Fibroscanner has a small piston that creates a vibration of low amplitude and frequency. This generates a shear wave from the skin into the liver parenchyma. The US measures the traveling time of this shear-wave. This is proportional with liver tissue elasticity [11]: the higher velocity of the shear wave, the stiffer the liver. The measurements are expressed in kilo Pascal (kpa). For each examination ten consecutive TE measurements in the right liver lobe through intercostal space 9-11 are required. In previous studies with TE in patients with hepatitis, Fibroscan showed a good ability to separate between different stages of liver fibrosis, particularly between cirrhosis and non cirrhosis [6;12]. Histolopathology Liver biopsies had been obtained from the patient groups with NAFLD and fibrosis. The NAFLD and fibrosis patients were selected based on a recent liver biopsy. The histological assessment of fatty livers were graded according to criteria by Brunt and Kleiner et al in accordance with percentual fatty infiltrated hepatocytes as grade 0 (<5 %), grade1 (5-33%), grade 2 (33-66%) and grade 3 (> 66%) [13]. Fibrosis were staged as 0 (no fibrosis), 1 (perisinusoidal or periportal fibrosis), 2 (perisinusoidal and periportal fibrosis), 3 (bridging fibrosis) or 4 (cirrhosis) [14]. The histological examinations were performed by three experienced pathologists. The histological grading of the NAFLD patients were performed as a consensus between two pathologists experienced with using classification by Brunt and Kleiner. The fibrosis classification from the patients with liver fibrosis was performed by a third pathologist using Batt s and Ludwig s classification. Statistical analysis ELs are presented as median and range. Liver elasticity levels are shown as the median of 10 consecutive measurements with standard deviation for a 95% confidence interval. Shapiro Wilk s test was used to evaluate the distribution of the measurements. Not all groups had normally distributed data according to this test. We used the Mann-Whiney test to compare groups for statistical significance. P-values <0.05 was selected as the level of statistical significance. Intra-and interobserver agreements were made from 12 random subjects from the three groups. The examinations were performed blinded on images recorded on a standardized set up aiming to estimate the observer variation of this new attenuation measurement on the images per se, not the total procedure including the ultrasound acquisition. We used EL as the expression for attenuation in the anterior position and Pearson s correlation coefficient was calculated. Limits of agreement using the difference between observations vs. mean value of the two observations were calculated according to Bland and Altman [15]. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 17.0 Software. Results The histological classifications are presented in Table I. In the fibrosis group two patients had fibrosis grade 1, five had grade 2 and 3. The results of the measurements and comparison between the three groups are presented in Table II. The HRI- difference between NAFLD patients 6.2 db ( ) and the healthy controls 1.9dB ( ) was significant, p= The HRI- ratio also showed differences between the same two groups, NAFLD 0.9 ( ) vs. healthy 1.0 ( ), p< However, between the NAFLD and Fibrosis patients we did not find any differences either in the HRI-diff nor in the HRI- ratio. Between the fibrosis patients and healthy controls there were also no significant differences in the measurements of the HRI.
4 For the measurements of attenuation in the anterior and lateral positions of the liver we found significant differences between the NAFLD and healthy controls, NAFLD EL anterior 3.9 db ( ) vs. healthy, EL anterior -1.0 db ( ), p= 0.002, NAFLD EL lateral, 4.6 db ( ) vs. healthy EL lateral 0.6 ( ), p= There were no significant differences in the attenuation between fibrosis and healthy controls. Between the NAFLD and fibrosis group there were also significant differences in the anterior and lateral positions, NAFLD EL anterior 3.9 db ( ) vs. fibro- Table I. The histological classifications of NAFLD patients. NALFD patients Steatosis Inflammation Fibrosis NAFLD- Non-Alcoholic Fatty-Liver Disease Med Ultrason 2013; 15(1): sis EL anterior -0.4 db ( ), p= 0.001, NAFLD EL lateral 4.6 db ( ) vs. fibrosis group, EL lateral 2.0 db ( ) p= Tissue elasticity measurements using transient elastography showed significant difference between the three groups. The healthy group scored low, 4.35 kpa (3-6), indicating low liver stiffness, and small measurement variation. The NAFLD group, 8.5 kpa (3-21) scored less than the healthy and the fibrosis group who scored 23.6 kpa (6-66). TE measurements could be obtained from all but three NAFLD patients and one liver fibrosis patient who all had BMI greater than 30. The liver size was significantly enlarged in the NAFLD group compared to healthy controls, 15.9 cm ( ) vs.13.4 cm ( ), p< 0.001, NAFLD and fibrosis patients 16.1 cm ( ) vs.13.7 cm ( ), p= 0.003, but not between the healthy controls and the patients with fibrosis 13.4 cm vs cm ( ), p= Sub analyses were performed only in the NAFLD group. We did not find any significant differences in the measurements of the liver stiffness between the different grades of steatosis. There were also no correlations between the different indexes in this small group. Intra-and interobserver agreement The limits of agreement for intraobserver varied from to 0.25 (mean-0.08) and for interobserver from to 2.16 (mean- 0.31). The results of the intraobserver and interobserver analyses of measurements from EL at 2 cm and 7 cm beneath the liver capsule are displayed as correlation plots and as Bland-Altmann plots (fig 2-5). The correlations and agreements were very good and indicate high reproducibility of the method. 19 Table II. The results of measurements and comparisons between the three groups NAFLD median (minmax) Fibrosis median (minmax) Healthy Controls Median (min-max) NAFLD vs. Healthy controls (p) NAFLD vs. Fibrosis (p) Fibrosis vs. Healthy controls (p) HR Diff 6,2 ( ) 2,7 ( ) 1.9 ( ) HR Ratio 0.9 ( ) 0.9 ( ) 1,0 ( ) Liver size 16.1 ( ) 13.7 ( ) 13.4 ( ) Liver elasticity 8.5 (3-21) 23.6 (3-66) 4.35 (3-6) EL-lateral 4.6 ( ) 2.0 ( ) 0.6 ( ) EL anterior 3.9 ( ) ( ) 1.0 ( ) NAFLD- Non-Alcoholic Fatty-Liver Disease; HR Diff- Hepato-Renal Index Difference; HR Ratio- Hepato- Renal Index Ratio; EL- Echo- Levels
5 20 Hilde Løland von Volkmann et al Quantitative measurement of ultrasound attenuation and Hepato-Renal Index Fig 2. Intraobserver correlation for observer A, 2 measurements of ultrasound attenuation between Echo Level measurements in the right liver lobe at 2 cm and 7 cm depth. Attenuation was calculated by subtracting the EL level at 7 cm from the EL level at 2 cm below the capsule. Fig 4. Interobserver correlation between observer A and B for ultrasound attenuation measurements between 2 cm and 7 cm depth. Attenuation was calculated by subtracting the EL level at 7 cm from the EL level at 2 cm below the capsule. Fig 3. Intraobserver agreement for observer A, 2 measurements of ultrasound attenuation between Echo Level measurements in the right liver lobe at 2 cm and 7 cm depth. Attenuation was calculated by subtracting the EL level at 7 cm from the EL level at 2 cm below the capsule. Intraobserver agreement between 2 measurements made by observer A was calculated according to Bland and Altman. Fig 5. Interobserver agreement between observer A and B for ultrasound attenuation between Echo Level measurements in the right liver lobe at 2 cm and 7 cm depth. Attenuation was calculated by subtracting the EL level at 7 cm from the EL level at 2 cm below the capsule. Intraobserver agreement between observer A and B were calculated according to Bland and Altman. Discussion We found that HRI- diff was significantly higher in the NAFLD group compared with healthy subjects, and that HRI- ratio was significantly lower in the same groups. Webb et al [8] presented a high correlation between Hepato-Renal sonographic Index and steatosis, inflam- mation and fibrosis using the ratio between liver and kidney parenchyma. The Hepato-Renal index had a sensitivity and specificity of 90 % for moderate to severe steatosis to predict the degree of steatosis. Soder et al [7] compared the Hepato-Renal difference between normal-weight and obese children. Kidney measurement values were subtracted from liver values, showing significant differences.
6 The only significant difference using HRI Diff or Ratio was observed when comparing NAFLD livers with livers from healthy subjects. This suggests that comparing ELs in the liver and in the right kidney can be a method to distinguish between fatty and healthy livers and quantifying the difference objectively. Further studies regarding the impact of inflammation and/or fibrosis are warranted. The difference in EL in the lateral and anterior positions showed significantly higher US attenuation in NAFLD patients than in both healthy controls and in patients with liver fibrosis. Significant differences were demonstrated in US attenuation both between NAFLD and healthy controls and between NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adding this method to the HRI indexes may provide further diagnostic confidence in identifying fatty infiltrated livers. However, no difference in liver tissue attenuation was observed between fibrosis and healthy livers. Liver stiffness measurements using TE, demonstrated significant differences between all three groups (median values for NAFLD 8.5 kpa, healthy subjects 4.3kPa and fibrosis patients with 23.6 kpa). Interestingly, the majority of NAFLD patients had low levels of fibrosis and lowgrade inflammation in biopsy evaluation. NAFLD patients had significantly enlarged liver compared to fibrosis patients and healthy controls. However, no significant difference was observed between the fibrosis group and healthy controls. This information may be of interest when performing sonographic examination of patients with liver steatosis. The small number of patients in each group and the fact that the healthy subjects did not undergo liver biopsy constitute limitations of our study. The healthy group was not examined of chronic virus hepatitis The healthy subjects had no history of hepatitis, no sign of steatosis upon ultrasonography, no obesity and all had normal liver enzymes. A liver biopsy in healthy subjects was considered to be unethical. The fibrosis patients were a heterogeneous group with inflammation, steatosis and fibrosis. Therefore, these data need to be carefully interpreted. The fibrosis group had significantly higher liver stiffness compared to NAFLD and healthy subjects. The attenuation was also different compared to the NAFLD group. The methods tested in this small study do not allow us to draw firm conclusions regarding discrimination between fibrosis and fatty livers. EL measurement is an integrated function of the scanner which makes it easy to use and it is independent of B-mode scanner settings such as gain and focus. The patients in this study were recruited on the basis of Med Ultrason 2013; 15(1): previous liver biopsies to fit into one of three groups; healthy liver, liver fibrosis and NAFLD. The examiner was not blinded to the disease category at the time of US scanning. Using the described Echo Level, size and elasticity criteria in consecutive patient examinations in a clinical setting may yield different results and will require further study. Conclusion External ultrasound examination measuring attenuation at different depths in the liver combined with local measurement of attenuation between liver and the right kidney cortex may be a useful and easy method to discriminate NAFLD patients from healthy subjects. Ultrasound attenuation can easily be quantified by Echo Level measurements with acceptable intra- and interobserver reproducibility. Further studies are required to confirm these findings in a prospective clinical study. Conflict of interest: none Acknowledgement: The study was supported by MedViz ( an interdisciplinary research cluster from Haukeland University Hospital, University of Bergen and Christian Michelsen Research AS. References 1. Welsh JA, Karpen S, Vos MB. Increasing Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among United States Adolescents, to J Pediatr 2012 Oct 17. [Epub ahead of print]. 2. Angulo P, Lindor KD. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002; 17: S186-S Ødegaard S, Gilja OH, Gregersen H. (Eds.). Basic and New Aspects of Gastrointestinal Ultrasonography. In: Fung YC. AdvancedSeries in Biomechanics. Vol.3. World Scientific Publishing Co.Pte.Ltd. Singapore 2005: Ratziu V, Martin L, Fedchuk L, Poynard T. Can nonalcoholic steatohepatitis be diagnosed without liver biopsy? Biomark Med 2009; 3: Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, et al. Is it better to use two elastographic methods for liver fibrosis assessment? World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: Sporea I. Is there a real future for liver elastography? J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2012;21: Soder RB, Baldisserotto M, Duval da Silva V. Computer-Assisted ultrasound analysis of liver echogenicity in obese and normal-weight children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;192:W201-W
7 22 Hilde Løland von Volkmann et al Quantitative measurement of ultrasound attenuation and Hepato-Renal Index 8. Webb M, Yeshua H, Zelber-Sagi S, et al. Diagnostic value of a computerized hepatorenal index for sonographic quantification of liver steatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009; 192: Xia MF, Yan HM, He WY, et al. Standardized ultrasound hepatic/renal ratio and hepatic attenuation rate to quantify liver fat content: an improvement method. Obesity 2012; 20: Kratzer W, Fritz V, Mason RA, Haenle MM, Kaechele V; Roemerstein Study Group. Factors affecting liver size: a sonographic survey of 2080 subjects. J Ultrasound Med 2003; 22: Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Medicine Biol 2003; 29: Castera L. Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005; 41: Batts KP, Ludwig J. Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol 1995; 19: Bland JM, Altman DG. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res 1999; 8:
Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases
 4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO
 PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
 The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
JPGN Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition Publish Ahead of Print
 JPGN Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition Publish Ahead of Print DOI : 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000489 Points to be considered when Applying FibroScan S Probe for Children with Biliary Atresia
JPGN Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition Publish Ahead of Print DOI : 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000489 Points to be considered when Applying FibroScan S Probe for Children with Biliary Atresia
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning
 Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
LOGIQ S8 XDclear 2.0 Liver Procedures
 LOGIQ S8 XDclear 2.0 Liver Procedures See & quantify liver disease in a single exam Clinical Challenge Liver disease affects millions of people worldwide, and the number is growing. Clinicians need a cost-effective,
LOGIQ S8 XDclear 2.0 Liver Procedures See & quantify liver disease in a single exam Clinical Challenge Liver disease affects millions of people worldwide, and the number is growing. Clinicians need a cost-effective,
Original. Kouki MASUO 1, Hitoshi FUNAGI 2 and Kunihiko KAWAI 2
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 24 3, 209 218, September 2012 Original The Detection and Grading of the Fatty Liver Based on Histogram Analysis of Ultrasonographic Image and Considering Body Measurements and Laboratory
Showa Univ J Med Sci 24 3, 209 218, September 2012 Original The Detection and Grading of the Fatty Liver Based on Histogram Analysis of Ultrasonographic Image and Considering Body Measurements and Laboratory
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4,
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 268-272 DOI: How many measurements are needed for liver stiffness assessment by 2D-Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE) and which value should be used: the
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 268-272 DOI: How many measurements are needed for liver stiffness assessment by 2D-Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE) and which value should be used: the
Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient Elastography in Diabetics with Fatty Liver A Single Center Cross Sectional observational Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ
 iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ Clinical Case Study Lucy Wang Clinical Application Specialist ASEAN Case Study: History: 58-year-old male patient, hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier, with non clinical symptoms
iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ Clinical Case Study Lucy Wang Clinical Application Specialist ASEAN Case Study: History: 58-year-old male patient, hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier, with non clinical symptoms
ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
 ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE Prof. Ioan Sporea, MD, PhD Head of Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara, Romania WFUMB Center of Education (COE),
ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE Prof. Ioan Sporea, MD, PhD Head of Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara, Romania WFUMB Center of Education (COE),
In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
DISCLOSURES. This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea
 DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity
 Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity Dr. Katsutoshi Sugimoto Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, Japan Introduction
Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity Dr. Katsutoshi Sugimoto Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, Japan Introduction
CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US elastography
 Clinical Ultrasound in Hepatology: Training for Hepatologists UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital, London, UK June 2018 CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US
Clinical Ultrasound in Hepatology: Training for Hepatologists UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital, London, UK June 2018 CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US
Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code
 Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code In a multi-center study, Barbero-Villares et al (2012) evaluated the presence of significant liver fibrosis by transient elastography (FibroScan) in inflammatory.
Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code In a multi-center study, Barbero-Villares et al (2012) evaluated the presence of significant liver fibrosis by transient elastography (FibroScan) in inflammatory.
Research Elastography: Liver
 Research Elastography: Liver Giovanna Ferraioli EFSUMB Ultrasound Learning Center Ultrasound Unit - Infectious Diseases Dept. Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo Medical School University of Pavia,
Research Elastography: Liver Giovanna Ferraioli EFSUMB Ultrasound Learning Center Ultrasound Unit - Infectious Diseases Dept. Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo Medical School University of Pavia,
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, Ioan Sporea, Iulia Raţiu, Simona Bota, Roxana Şirli, Ana Jurchiş
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, 111-115 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.152.is1ir2 Are different cut-off values of liver stiffness assessed by Transient Elastography according to the etiology
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, 111-115 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.152.is1ir2 Are different cut-off values of liver stiffness assessed by Transient Elastography according to the etiology
Case #1. Digital Slides 11/6/ year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests. Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis
 45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii
 HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
MR Elastography of Liver
 MR Elastography of Liver Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, MD, FRCR Professor of Radiology Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Consultant, Abdominal Division Radiology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA 19 th May 2018 2018
MR Elastography of Liver Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, MD, FRCR Professor of Radiology Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Consultant, Abdominal Division Radiology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA 19 th May 2018 2018
The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
shear wave elastography
 Ultrasound ElastQ Imaging Introducing next-generation shear wave elastography Philips ElastQ Imaging Vijay Shamdasani, PhD and Hua Xie, PhD, Philips Ultrasound Tissue stiffness has long provided important
Ultrasound ElastQ Imaging Introducing next-generation shear wave elastography Philips ElastQ Imaging Vijay Shamdasani, PhD and Hua Xie, PhD, Philips Ultrasound Tissue stiffness has long provided important
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Steatohepatitis
 The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
Thyroid nodules echogenicity evaluation: a new paradigm?
 Thyroid nodules echogenicity evaluation: a new paradigm? Poster No.: C-1883 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. S. C. C. Germano, W. Schmitt, E. Rosado, R. M. R. Mateus- 1 2 1 2 2 2
Thyroid nodules echogenicity evaluation: a new paradigm? Poster No.: C-1883 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. S. C. C. Germano, W. Schmitt, E. Rosado, R. M. R. Mateus- 1 2 1 2 2 2
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI
 Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis
 Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis Hiroko Iijima Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Ultrasound Imaging Center, Hyogo College of Medicine Hiroko Iijima Department
Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis Hiroko Iijima Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Ultrasound Imaging Center, Hyogo College of Medicine Hiroko Iijima Department
Transient elastography the state of the art
 Transient elastography the state of the art Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris-7, France White Nights of Hepatology, St Petersburg, Russia, june
Transient elastography the state of the art Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris-7, France White Nights of Hepatology, St Petersburg, Russia, june
NON INVASIVE ASSESSMENT OF LIVER FIBROSIS : FIBROSCAN
 NON INVASIVE ASSESSMENT OF LIVER FIBROSIS : FIBROSCAN M. Beaugrand Service d Hépatologied Hopital J. Verdier BONDY 93143 et Université Paris XIII MAINZ 21.09.2008 ASSESSMENT OF FIBROSIS : WHY? Management
NON INVASIVE ASSESSMENT OF LIVER FIBROSIS : FIBROSCAN M. Beaugrand Service d Hépatologied Hopital J. Verdier BONDY 93143 et Université Paris XIII MAINZ 21.09.2008 ASSESSMENT OF FIBROSIS : WHY? Management
NAFLD and NASH: The Not-So-New Kids on the Block
 NAFLD and NASH: The Not-So-New Kids on the Block Mary E. Rinella, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois This program is supported by an
NAFLD and NASH: The Not-So-New Kids on the Block Mary E. Rinella, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois This program is supported by an
Elastography in the. technically difficult patient. EPIQ ultrasound system. Ultrasound
 Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Use of Ultrasound in NAFLD
 Institute for Liver and Digestive Health Use of Ultrasound in NAFLD Dr. Davide Roccarina Specialist in General Medicine Specialist Doctor in Clinical Ultrasound and non-invasive liver assessment Hepatology
Institute for Liver and Digestive Health Use of Ultrasound in NAFLD Dr. Davide Roccarina Specialist in General Medicine Specialist Doctor in Clinical Ultrasound and non-invasive liver assessment Hepatology
Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer
 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer SSID02892-01 November 2012 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using SWE on Aixplorer Introduction From a clinical standpoint, staging liver
Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer SSID02892-01 November 2012 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using SWE on Aixplorer Introduction From a clinical standpoint, staging liver
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients
 Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis
 Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis Protocol: RAD042 Effective Date: June 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis Protocol: RAD042 Effective Date: June 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies
 4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Paige et al. Use of Imaging to Predict Steatosis in Patients With NAFLD Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Jeremy S. Paige 1 Gregory S. Bernstein 1 Elhamy
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Paige et al. Use of Imaging to Predict Steatosis in Patients With NAFLD Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Jeremy S. Paige 1 Gregory S. Bernstein 1 Elhamy
Diabetes Liver Screen
 YOUR LIVER AND YOUR HEALTH Diabetes Liver Screen Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) PROF. SUZANNE NORRIS www.liverwellness.ie The spectrum of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Diabetes Liver Screen
YOUR LIVER AND YOUR HEALTH Diabetes Liver Screen Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) PROF. SUZANNE NORRIS www.liverwellness.ie The spectrum of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Diabetes Liver Screen
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
LIVER PATHOLOGY. Thursday 28 th November 2013
 LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
LIVER PATHOLOGY Thursday 28 th November 2013 Liver biopsy assessment of steatosis Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free Hospital RIBA, London Thursday 28th November 2013 NAFLD didn t exist before 2001 and liver
M30 Apoptosense ELISA. A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH
 M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
Novel multiparametric magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) protocol accurately predicts NAS score for NASH diagnosis
 Novel multiparametric magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) protocol accurately predicts NAS score for NASH diagnosis Alina M. Allen, Meng Yin, Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, Taofic Mounajjed, Todd A. Kellogg,
Novel multiparametric magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) protocol accurately predicts NAS score for NASH diagnosis Alina M. Allen, Meng Yin, Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, Taofic Mounajjed, Todd A. Kellogg,
Invasive. Sampling error. Interobserver variability. Nondynamic evaluation of
 How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients
 Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
POWERED BY. Innovation in liver disease management
 POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know
 Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know Shuchi K. Rodgers, MD Section Chief, Abdominal Imaging Director of Ultrasound Department of Radiology Einstein Medical Center rodgerss@einstein.edu
Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know Shuchi K. Rodgers, MD Section Chief, Abdominal Imaging Director of Ultrasound Department of Radiology Einstein Medical Center rodgerss@einstein.edu
Understanding your FibroScan Results
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Understanding your FibroScan Results This information will help you understand your FibroScan results. About FibroScan FibroScan is a specialized ultrasound machine for your
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Understanding your FibroScan Results This information will help you understand your FibroScan results. About FibroScan FibroScan is a specialized ultrasound machine for your
Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 309-314 DOI: Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ
Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 309-314 DOI: Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ
Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging
 Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging Olivier ucidarme Pitié Salpêtrière - UPMC Paris France Ultraschall Med. 013 Apr;34():169-84 Ultraschall Med. 013 Jun;34(3):38-53. US elastography Ultraschall
Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging Olivier ucidarme Pitié Salpêtrière - UPMC Paris France Ultraschall Med. 013 Apr;34():169-84 Ultraschall Med. 013 Jun;34(3):38-53. US elastography Ultraschall
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup
 REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar
 Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography
 Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation. VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014
 NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
Liver Disease Assessment Among PWID: The Role of Transient Elastography
 Liver Disease Assessment Among PWID: The Role of Transient Elastography Peer Brehm Christensen, Professor Department of Infectious Diseases Odense University Hospital Denmark Peer.christensen@dadlnet.dk
Liver Disease Assessment Among PWID: The Role of Transient Elastography Peer Brehm Christensen, Professor Department of Infectious Diseases Odense University Hospital Denmark Peer.christensen@dadlnet.dk
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE:
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
Repeating measurements by transient elastography in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients with high liver stiffness
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.14311 HEPATOLOGY Repeating measurements by transient elastography in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients with high liver stiffness Jeremy Chak-Lun Chow,* Grace Lai-Hung
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.14311 HEPATOLOGY Repeating measurements by transient elastography in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients with high liver stiffness Jeremy Chak-Lun Chow,* Grace Lai-Hung
Shear Wave Elastography In Characterization Of Liver Tumours
 Shear Wave Elastography In Characterization Of Liver Tumours Poster No.: C-1921 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. L. Choong 1, B. J. J. Abdullah 1, G. Kumar 2, C. H. Yeong 1, K. L.
Shear Wave Elastography In Characterization Of Liver Tumours Poster No.: C-1921 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. L. Choong 1, B. J. J. Abdullah 1, G. Kumar 2, C. H. Yeong 1, K. L.
Real-time elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors
 Realtime elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors Poster No.: C09 Congress: ECR 05 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M.
Realtime elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors Poster No.: C09 Congress: ECR 05 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M.
Diagnostic TRUS Elastography of the Prostate
 Diagnostic TRUS Elastography of the Prostate George Zacharopoulos Department of Diagnostic Ultrasound Hygeia Hospital Athens, Greece Prostate HI-RTE Why we need Elastography Better Detection of possible
Diagnostic TRUS Elastography of the Prostate George Zacharopoulos Department of Diagnostic Ultrasound Hygeia Hospital Athens, Greece Prostate HI-RTE Why we need Elastography Better Detection of possible
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH
 NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH Bachir Taouli, MD Director of Body MRI and Cancer Imaging Program Department of Radiology / Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute
NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH Bachir Taouli, MD Director of Body MRI and Cancer Imaging Program Department of Radiology / Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD. Pierre Bedossa. Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE
 PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD Pierre Bedossa Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD NAFLD: a chronic liver disease with a wide
PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD Pierre Bedossa Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD NAFLD: a chronic liver disease with a wide
Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images
 6 JEST-M, Vol 3, Issue 1, 2014 Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images Email: poojaanandram @gmail.com P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering,
6 JEST-M, Vol 3, Issue 1, 2014 Computer-Aided Quantitative Analysis of Liver using Ultrasound Images Email: poojaanandram @gmail.com P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering,
The assessment of liver fibrosis using the computerized analysis of ultrasonographic images. Is the virtual biopsy appearing as an option?
 The assessment of liver fibrosis using the computerized analysis of ultrasonographic images. Is the virtual biopsy appearing as an option? Monica Lupşor, Radu Badea, Sergiu Nedevschi, Cristian Vicaş, Simona
The assessment of liver fibrosis using the computerized analysis of ultrasonographic images. Is the virtual biopsy appearing as an option? Monica Lupşor, Radu Badea, Sergiu Nedevschi, Cristian Vicaş, Simona
Functional liver imaging Bernard Van Beers
 Functional liver imaging Bernard Van Beers Department of Radiology Beaujon University Hospital Paris Nord Laboratory of Imaging biomarkers UMR 1149 Inserm - University Paris Diderot France Functional imaging
Functional liver imaging Bernard Van Beers Department of Radiology Beaujon University Hospital Paris Nord Laboratory of Imaging biomarkers UMR 1149 Inserm - University Paris Diderot France Functional imaging
Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference method
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2017, Vol. 19, no. 2, 143-149 DOI: 10.11152/mu-910 Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference
Original papers Med Ultrason 2017, Vol. 19, no. 2, 143-149 DOI: 10.11152/mu-910 Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference
Clinical Medicine Review
 Dighe M. et al. Clinical Medicine Review, 2018 Page 1 of 15 Clinical Medicine Review Published: July 09, 2018 Citation: Dighe M. et al. (2018) Review of ultrasound elastography techniques in the liver.
Dighe M. et al. Clinical Medicine Review, 2018 Page 1 of 15 Clinical Medicine Review Published: July 09, 2018 Citation: Dighe M. et al. (2018) Review of ultrasound elastography techniques in the liver.
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis. Pierre BEDOSSA
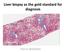 Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Bio Predictive. FibroTest Scientific Publications. Ratziu 2016 FibroMax NASH. Friedman 2016 FibroTest NASH EASL Key Publications for 2017
 EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
EFSUMB European Course Book
 Estimation of liver stiffness 27.07.2010 11:47 1 EFSUMB European Course Book Editor: Christoph F. Dietrich Estimation of liver stiffness using ultrasound waves Ioan Sporea (1), Mireen Friedrich-Rust (2),
Estimation of liver stiffness 27.07.2010 11:47 1 EFSUMB European Course Book Editor: Christoph F. Dietrich Estimation of liver stiffness using ultrasound waves Ioan Sporea (1), Mireen Friedrich-Rust (2),
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
Diagnostic Value of a Computerized Hepatorenal Index for Sonographic Quantification of Liver Steatosis
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Webb et al. Hepatorenal Index for Sonography of Liver Steatosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Diagnostic Value of a Computerized Hepatorenal Index
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Webb et al. Hepatorenal Index for Sonography of Liver Steatosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Diagnostic Value of a Computerized Hepatorenal Index
Real-time elastography as a noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C Egyptian patients: a prospective study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2016) 29, 1-5 Real-time elastography as a noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C Egyptian patients: a prospective study Lamiaa Mobarak
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2016) 29, 1-5 Real-time elastography as a noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C Egyptian patients: a prospective study Lamiaa Mobarak
Noninvasive Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Using Real-time Tissue Elastography and Transient Elastography (FibroScan)
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Noninvasive Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Using Real-time Tissue Elastography and Transient Elastography (FibroScan) Fankun Meng, MD, Ying Zheng, MD, Qi Zhang, MD, Xiaojie Mu, MD, Xiaoluan
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Noninvasive Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Using Real-time Tissue Elastography and Transient Elastography (FibroScan) Fankun Meng, MD, Ying Zheng, MD, Qi Zhang, MD, Xiaojie Mu, MD, Xiaoluan
Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016.
 Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016. Outline Definition NAFLD and NASH Magnitude of the problem
Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016. Outline Definition NAFLD and NASH Magnitude of the problem
REVIEWS. Introduction. FibroMax complete diagnosis of liver injury. Abbreviations
 REVIEWS Noninvasive Biomarkers for the Screening of Fibrosis, Steatosis and Steatohepatitis in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: FibroTest-FibroMa Eperience Mona Munteanu, Vlad Ratziu 2, Rachel Morra,
REVIEWS Noninvasive Biomarkers for the Screening of Fibrosis, Steatosis and Steatohepatitis in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: FibroTest-FibroMa Eperience Mona Munteanu, Vlad Ratziu 2, Rachel Morra,
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
 NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES
 Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis. April 2008
 Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Obesity and Liver Disease:Evaluation of Fatty Infiltration of the Liver. Using Ultrasonic Attenuation
 J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 37, S71-S77, 1991 Obesity and Liver Disease:Evaluation of Fatty Infiltration of the Liver. Using Ultrasonic Attenuation Hideyukl FUSAMOTO, Kunio SuzuM, Norlo HAYASHI, Yutaka SASAKI,
J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 37, S71-S77, 1991 Obesity and Liver Disease:Evaluation of Fatty Infiltration of the Liver. Using Ultrasonic Attenuation Hideyukl FUSAMOTO, Kunio SuzuM, Norlo HAYASHI, Yutaka SASAKI,
Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital
 Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital CEUS & US Elastography : Contents CEUS Introduction Contrast agents & imaging Clinical application US Video WS Summary US
Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital CEUS & US Elastography : Contents CEUS Introduction Contrast agents & imaging Clinical application US Video WS Summary US
Relationship between Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Hepatic Steatosis as Assessed by Ultrasound in Alcoholic or Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 2, March 2016, pp. 295-302 ORiginal Article Relationship between Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Hepatic Steatosis as Assessed by Ultrasound in Alcoholic or Nonalcoholic
Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 2, March 2016, pp. 295-302 ORiginal Article Relationship between Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Hepatic Steatosis as Assessed by Ultrasound in Alcoholic or Nonalcoholic
Original Article. Abstract. Background
 E2 Original Article THIEME Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI) for the Determination of Liver Stiffness Using Transient Elastography as a Reference in Children Authors A. Sagir
E2 Original Article THIEME Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI) for the Determination of Liver Stiffness Using Transient Elastography as a Reference in Children Authors A. Sagir
LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
We don t need a liver biopsy. We have non-invasive tests
 We don t need a liver biopsy We have non-invasive tests Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris Diderot, France PHC 2018 www.aphc.info Liver biopsy: an
We don t need a liver biopsy We have non-invasive tests Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris Diderot, France PHC 2018 www.aphc.info Liver biopsy: an
EUS guided liver biopsy
 EUS guided liver biopsy Abdul El Chafic, MD Ochsner Medical Center Department of Gastroenterology Section of Advanced endoscopy Disclosure/ Disclaimer I have a financial interest/arrangement of affiliation
EUS guided liver biopsy Abdul El Chafic, MD Ochsner Medical Center Department of Gastroenterology Section of Advanced endoscopy Disclosure/ Disclaimer I have a financial interest/arrangement of affiliation
Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease
 HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
1264 BOURSIER ET AL CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY Vol. 6, No. 11 Table 1. Study Design: Assignment of Judges According to Patient and Obser
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1263 1269 Reproducibility of Liver Stiffness Measurement by Ultrasonographic Elastometry JÉRÔME BOURSIER,*, ANSELME KONATÉ,*, GABRIELLA GOREA,* STÉPHANE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1263 1269 Reproducibility of Liver Stiffness Measurement by Ultrasonographic Elastometry JÉRÔME BOURSIER,*, ANSELME KONATÉ,*, GABRIELLA GOREA,* STÉPHANE
Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Egyptian Children with Chronic Liver Diseases.
 Curr Pediatr Res 2016; 20 (1&2): 57-63 ISSN 0971-9032 www.currentpediatrics.com Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Egyptian Children with Chronic Liver Diseases. Tawhida Abdel Ghaffar 1, Azza
Curr Pediatr Res 2016; 20 (1&2): 57-63 ISSN 0971-9032 www.currentpediatrics.com Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Egyptian Children with Chronic Liver Diseases. Tawhida Abdel Ghaffar 1, Azza
FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD
 FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD Division of Gastroenterology & Inborn Errors Products (DGIEP) Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Office of New Drugs Office of Drug Evaluation III
FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD Division of Gastroenterology & Inborn Errors Products (DGIEP) Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Office of New Drugs Office of Drug Evaluation III
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Radiology Update 2017
 Radiology Update 2017 John K. Phillips, MD Affiliated Assistant Professor of Radiology University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center Chief, Radiology and Nuclear Medicine VA Memphis Disclosures Financial:
Radiology Update 2017 John K. Phillips, MD Affiliated Assistant Professor of Radiology University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center Chief, Radiology and Nuclear Medicine VA Memphis Disclosures Financial:
Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine
 Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
