Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol University Hospital and The American Center
|
|
|
- Rodney Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEPATOBILIARY IMAGING CPT CODE: UPDATED: JULY 2017 Indications: Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis (both calculus and acalculous disease) Determination of patency of common bile duct when ultrasound examination not diagnostic (e.g., very early obstruction) Evaluation of biliary dyskinesia (gallbladder ejection fraction [GBEF] test) for chronic cholecystitis Identification of biliary leaks Differentiation of biliary atresia from neonatal hepatitis Evaluation of presence, or absence of, spleen (with T-99m SC Liver Scan). Suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction or partial biliary obstruction due to stones or stricture. Patient Preps: Acute Cholecystitis See Acute Cholecystitis algorithm below, Appendix 2 No Pre-Treatment: Fasting for a minimum of 2 hours, but preferably 4 hours before this test. Parental alimentation (ex. TPN) is allowable and considered to be a fasting state. Pre-Treatment: Record any recent hydromorphone (Dilaudid), fentanyl, or morphine used in last 12 hours; refer to morphine use section below and opioid table in Appendix 1. In patients who have fasted for greater than 24 hours, on parenteral nutrition, or with a history of alcoholic liver disease, Sincalide (Kinevac) should be administered prior to tracer injection. Sincalide administration of 0.02 microgram/kg is to be over 30 min. Mebrofenin injection can be started min after Sincalide infusion is completed. On-call cases of fasting state for pretreatment sincalide administration should be determined by the technologist with the patient s nurse (**If there is any question or lack of information of fasting state, sincalide pre-treatment should be administered prior to imaging to clear the gallbladder.**) In case of sincalide shortage, consider ensure PO pre-treatment prior to fasting as tolerated and allowed by the referring clinician Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD): Fasting for minimum of 2 hours. Patients should not have had any opiate drug (hydromorphone, fentanyl or morphine) within 6 hours; refer to opioid table in Appendix 1 for adjustments to the 6 hours. Patients then should be pretreated with Sincalide (Kinevac) at a rate of 0.02 microgram/kg over 30 minutes. Mebrofenin injection can be started min post Sincalide infusion. Gall Bladder Ejection Fraction Fasting for a minimum of 2 hours, but preferably 4 hours before this test. Patients should not have had any opiate drug (hydromorphone, fentanyl or morphine) within 6 hours; refer to opioid table in Appendix 1 for adjustments to the 6 hours. Page 1 of 11
2 Infant: neonatal hepatitis vs biliary atresia To differentiate between neonatal hepatitis and biliary atresia pre-treatment with Phenobarbital, 5 mg/kg/day given orally in two (2) divided doses for 3-5 days, or ursodeoxycholic salt, 20 mg/kg/day 2-3 days, if needed to increase hepatocyte function, at ordering providers discretion. If patient is already on either of these medications and dosage, no pre-treatment is needed. Protocol/Prep Modifications: If Total bilirubin >10 (within the last week) Consult with the Nuclear Medicine Physician, a 1.5 to 2-fold increase in dosage may be prescribed and a longer imaging time requested. Critically ill patients with sepsis Require a IV Sincalide administration of 0.02 microgram/kg is to be over 30 min prior to scan and possibly larger doses of morphine (0.08 mg/kg) (especially when acute acalculous cholecystitis) (requires faculty approval) with more delayed images (30-40 min post morphine). If the patient is on gastric tube feedings, Sincalide is unnecessary. If tube feeding is into the proximal small bowel then Sincalide pre-treatment is required. Scheduling: Acute Cholecystitis, Leak or Biliary Atresia: Allow 90 min of camera time. Delayed images are at 2 hours and 3-4 hours post-injection. Imaging 24 hours post-injection is possible. GBEF: Injection: allow 15 min. Scan: Image 45 min post injection, allow 90 min camera time. Modified Protocols: If pre-treatment is required account for the additional 30 minute infusion time. Then schedule as above for acute cholecystitis. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD): Pre-Treatment: Infusion of Sincalide over 30 minutes. Injection: minutes after completion of Sincalide begin imaging for 60 min. Allow 90 minutes of camera time. Delayed images are not typically needed. Radiopharmaceutical & Dose: 99mTc-Mebrofenin 5 mci +/- 20% (4-6 mci) IV, adjusted for weight per nomogram. If patient is jaundiced (bilirubin > 10): NM physician should be consulted prior to dosing 99mTc-Mebrofenin to determine possible increase in dose (1.5-2 times) and/or adjustment of imaging times. Sincalide 0.02 microgram/kg IV diluted with NaCl to 50 ml and infused over 30 minutes as a pre-treatment and over 60 minutes when for GBEF. Sincalide (Kinevac) Preparation (Gallbladder EF): Reconstitution: Add 5 ml of sterile water to Kinevac vial containing 5 microgram to create a solution of 1 microgram/ml. Dose Preparation: Obtain patient s weight in kg and calculate dose at 0.02 microgram/kg. Withdraw dosage from vial and add to a 60 ml syringe loaded with 0.9% NaCl. Total volume with Kinevac and NaCl to be 50 ml. Dose is stable for 1 hour post-dilution of saline. Infusion Pump: Attach extension tubing to 60 ml syringe of Kinevac and place in infusion pump. Set up pump as single dose, B-D syringe, 50 ml dose for 60 min. Page 2 of 11
3 Morphine Use in Hepatobiliary Scans: Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol Morphine 0.04 milligram/kg IV when indicated per protocol. Confirm patient is not allergic to morphine. Record any hydromorphone (Demerol), fentanyl, or morphine used in last 12 hours. If the patient is on opioids (within 5 half-lives refer to OPIOD REFERENCE TABLE below (Appendix 1), get approval from referring clinician regarding approval to administer morphine for hepatobiliary scan. If the patient is an outpatient confirm they have a designated driver. The use of intravenous Morphine (0.04mg/kg to a max of 4 mg) is used as part of the functional assessment of the gallbladder in the hepatobiliary scan protocol. The hepatobiliary scan protocol includes the use of IV Morphine to elevate the pressure in the extrahepatic bile duct system and so fill the gallbladder. This has been established to improve the sensitivity and specificity of diagnosing acute cholecystitis. The section of nuclear medicine has used this Morphine-augmented protocol for 15 years without a single incident, and never had to inject a reversal agent. This sectional protocol establishes that the Hospital-wide conscious sedation does not apply to this diagnostic test (just as it does not apply to pain relief use of narcotics). The protocol does require a physician be available to supervise the administration of the Morphine, but this physician does not need to be credentialed for conscious sedation. PROCEDURE WHEN USING MORPHINE FOR PATIENT EXAMS: Fill out the sign-out form that is kept in the safe with the morphine. Do NOT fill out the pharmacy charge form. Morphine is supplied 4 mg/ml at 1.0 ml. Morphine that is NOT used for the exam must be disposed of and accounted for. This must be witnessed by another person, disposed of, and initialed by both parties. Update balance sheet with patient name and data. Return paperwork to safe, and lock. NOTE: If the dose of Morphine is more than 4.0 milligram, CONSULT WITH STAFF BEFORE INFUSION. Imaging Device: GE Infinia, Optima, Millennium VG or Millennium MPS gamma camera with LEHR collimator. Imaging Procedure: Acute Cholecystitis See Acute Cholecystitis algorithm below, Appendix 2 1) Technologist will verify the patient prep of NPO status and when/what they last ate. Also verify what opiates they are on and when the last dose was given. The Faculty or Resident will as well verify NPO and opiate status including can morphine if needed be administered on top of current opioids. a) NM Faculty or Resident will determine if pre-treatment with Sincalide is needed and place the IP order. b) If pre-treatment is given imaging cannot start earlier than minutes post the completion of the 30 minute Sincalide infusion. 2) Position patient supine under the camera. 3) Image immediately post injection Page 3 of 11
4 4) Dynamic Acquisition in the anterior projection unless otherwise indicated: a) 1 st Set: 1 min/frame x 30 min, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. Start acquisition at injection. Label the image set: Anterior 0-30 minutes. b) 2 nd Set: 1 min/frame x 90 min, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. Start at the end of 1 st set. This set can be stopped minutes post morphine or when gall bladder is visualized. Label the image set: Anterior minutes. Adjust 90 as needed afterwards based on actual study timing. 5) Evaluate with NM faculty/resident at 30 minutes: a) Is there sufficient hepatocyte function? (Blood pool clearance from the heart). If no, consider 24 hour delayed imaging. b) Is there common bile duct and duodenum visualize, but the gallbladder does not, consider morphine or delayed imaging. i) If morphine is indicated: (1) Obtain patient weight in kg and calculate dose at 0.04 milligram/kg. Use larger doses of morphine in acute acalculous cholecystitis (requires faculty approval). (2) The NM Faculty or Resident or Nuclear Medicine technologist is to slowly administer the morphine over a 2-minute period at 40 minutes post radiopharmaceutical injection. If this administration is later than 40 minutes consider an additional half dose 99mTc- Mebrofennin, based on the original dose, before the morphine administration. (a) The duodenum should demonstrate decreased and changing activity to confirm the sphincter of Oddi has contracted. (b) Gastric reflux often occurs in about 60%of patients with morphine. (c) The sedation policy does not apply to this diagnostic use of IV morphine. See disclaimer above. (3) Continue imaging to minutes post morphine or until the gallbladder is visualized. ii) If delayed imaging is indicated: Image at 2 hours and 3 to 4 hours post injection. 6) Once the gallbladder is believed to be visualized confirm with a Right lateral (or steep RAO if the lateral is not obtainable) and LAO views with 5 minute statics in a 128x128 matrix. Image labels include the time post 99mTc-Mebrofenin injection. i.e. Rt Lat 30 min. The technologist can take these views as a part of the evaluation in point 5 above if they feel the gallbladder is filling. a) If these views confirm gallbladder, imaging is complete. b) If these views do not confirm the gallbladder i) Set up and start another 1 min/frame x 90 min, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. Label the image set: Anterior xx-yy minutes. Adjust xx and yy as needed afterwards based on actual study timing. ii) Return to point 5 above if morphine or delayed imaging has not been done. If both have been done, at the discretion of the NM Faculty/Resident the exam is likely complete with an Acute Cholecystis result. Page 4 of 11
5 GBEF (Gallbladder Ejection Fraction) with Sincalide 1) Place an IV (per hospital policy). 2) Check availability of camera with imaging technologist. 3) Inject the patient with 99mTc Mebrofenin via IV push. 4) Sincalide Infusion Imaging Parameters a) Imaging should be started 45 minutes post injection. b) Dynamic acquisition 1 min/frame x 65 frames, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc, c) CHECK POSTIONING WITH NUC MED PHYSICIAN DURING THE FIRST 5-MIN OF THE DYNAMIC ACQUISITION BEFORE ADMINISTERING SINCALIDE. ADMINISTER SINCALIDE IF: Most of the activity is in the gallbladder and bowel with relatively little in the liver. Ensure the gallbladder is separated from the duodenum by utilizing the LAO view, if necessary. NM Faculty or Resident could ask for a delay in starting the Sincalide infusion. Another preinfusion imaging set will be required. Exam could also be canceled if the gallbladder does not fill sufficiently. d) Sincalide administration is typically minutes post 99mTc Mebrofenin injection. e) Sincalide is infused over 60 minutes. Imaging is complete when the Sincalide infusion is complete. GBEF (Gallbladder Ejection Fraction) with 8 fl. oz. (240 ml) of Ensure Plus 1) Place an IV (per hospital policy). 2) Check availability of camera with imaging technologist. 3) Inject the patient with 99mTc Mebrofenin via IV push. 4) Pre-Ensure Plus Imaging Parameters. a) Imaging should be performed 45 minutes post injection. b) Dynamic acquisition 1 min/frame x 5 frames, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. c) Check images to ensure GB is not over the duodenum, and if so, use LAO view to separate GB from duodenum. d) CHECK WITH NUC MED PHYSICIAN AT COMPLETION OF 5-MIN DYNAMIC BEFORE PROCEEDING FURTHER. ALLOW DRINKING OF 8 fl. oz of Ensure Plus IF: Most of the activity is in the gallbladder and bowel with relatively little in the liver. Verify the gallbladder is separated from the duodenum by utilizing the LAO view, if necessary. 5) Post-Ensure Plus Imaging Parameters. a) Have patient drink one entire bottle of 8 fl oz of Ensure Plus within 2-3 minutes. b) Immediately post-ensure, start a new dynamic acquisition 1 min/frame x 60 frames, 128x128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. Leak 1. Position patient supine under camera. 2. Image immediately after injection. 3. Dynamic acquisition 1 min/frame x 60 frames, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. a. If the patient has a drainage bag i. Do your best to get it into the field of view free of body structures. ii. If unable to image the drainage bag free of body structures then image bag after the 60 minute dynamic by placing lead under the drainage bag and acquire two static images 256x256, for 5 minutes, 1.0 zoom. Image one is the bag itself. Image 2 using a point source mark the top, bottom and sides of the drainage bag. iii. At interpreter request a Right Lateral Decubitus and Right lateral. 256x256, for 5 minutes, 1.0 zoom. 4. Delayed images at 2-4 hours will usually be necessary and 24 hour delayed images may be needed. Page 5 of 11
6 Hepatobiliary for Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction with Sincalide 1. Place an IV (per hospital policy). 2. Infuse the patient with Sincalide over 30 minutes as described above. 3. Anterior projection imaging should be started minutes post Sincalide infusion. Dynamic acquisition 1 min/frame x 60 frames, 128 x 128, 1.0 zoom, 20% window peaked for 99mTc. 4. Process the ROI and generate time-activity curves post imaging. See data analysis below. 5. Check images and data generation with the reading room prior to releasing the patient. Comments: A Nuclear Medicine staff or resident physician should be consulted to determine if additional views are indicated. Data Analysis: Acute Cholecystosis Combine all sequentially acquired dynamic images into one dynamic. Reframed combined dynamic and any other later dynamic into 5 minute/frame image sets. Screen cap reframed 5 minute/frame image sets Annotate view/projection, orientation, 2 nd 99mTc-Mebrofenin dose if given, morphine injection time and time delay between images sets. Screen Cap label add to the front of the screen cap label: Anterior 0-xx minutes. Screen cap static images Annotate view/projection, orientation, time reference post initial 99mTc-Mebrofenin injection. GBEF (Gallbladder Ejection Fraction) Prior to analysis of GBEF perform motion correction. Analyze with the GE Protocol UWH Gallbladder EF. On the GB composite image the GB ROI is drawn around the gallbladder and the BKGD ROI is drawn to include a segment of the liver and body background. When drawing the ROI s other liver abdominal anatomy is not to be in the region (e.g. bowel or bile ducts). The application uses these ROI s to create a Bkgd corrected GB emptying curve. The application then selects the frame with the highest counts and uses that to calculate the EF. Verify and adjust the cursor placement as follows; peak activity (green cursor) and nadir/least activity (yellow cursor) are correctly placed on the GB emptying curve then create Dynamic Screen Capture this GBEF result page. Note: This screen cap includes the 1 minute dynamic image set with the ROI that can be cined in PACS. CHECK for any bowel and outside activity interference. Do a cine review of the dynamic images with the ROI and check for bowel of other activity entering the ROI that is not gallbladder. If there is extra activity, redraw the ROI to eliminate this extra activity. Extra activity causes an error in the GBEF calculation. 1) Reframed dynamic image set into 5 minute/frame image set. 2) Screen cap reframed 5 minute/frame image sets a) Annotate view/projection, orientation b) Screen Cap label add to the front of the screen cap label: Anterior 0-xx minutes. 3) Screen cap static images a) Annotate view/projection, orientation, time reference post initial 99mTc-Mebrofenin injection. Page 6 of 11
7 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD) Prior to analysis check raw images to determine if the Motion Correction program needs to be performed. 1) Use the predefined ROI Comparative Analysis protocol 2) Combine 1 min/frame into one 60 min image. 3) Draw a region of interest around the right lobe of the liver and one around the common bile duct. Make sure these ROIs do not overlap the small bowel or liver. (Check with physician if hard to define proper ROI) 4) Draw a background ROI 5) Take the right lobe ROI and subtract the background ROI, create a time activity curve. 6) Take the common bile duct ROI and subtract the background ROI, create a time activity curve. 7) Properly annotate each ROI and SCREENCAP 8) Reframe the dynamic image set into 5 minute/frame image sets and screen cap as a 12 on one display. a) Annotate view/projection, orientation b) Screen Cap label add to the front of the screen cap label: ANT 0-60 minutes. LEAK 1) Reframed dynamic image set into 5 minute/frame image set. 2) Screen cap reframed 5 minute/frame image sets a) Annotate view/projection, orientation b) Screen Cap label add to the front of the screen cap label: Anterior 0-xx minutes. 3) Screen cap static images a) Annotate view/projection, orientation, time reference post initial 99mTc-Mebrofenin injection. PACS: Acute Cholecystitis or Leak Send all 1-minute dynamic datasets Send all reframed dynamic datasets Send all static images Send all Screen Caps Using paper scanner scan in the worksheet. GBEF (Gallbladder Ejection Fraction) or Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD) Send all 1-minute dynamic datasets Send all reframed 5-minute dynamic datasets Send all Screen Caps Send the data generated images (automatic GBEF result page, SOD time-activity curves). Using paper scanner scan in the worksheet. Interpretation: Non-visualization of the gallbladder suggests obstruction of the cystic duct and this is the nuclear medicine physiological requirement of acute calculous or acalculous cholecystitis. In acalculous cholecystitis the cystic duct can be patent resulting in a false negative test. The gallbladder is normally visualized by minutes, somewhat slower in the post-prandial state. Reflux of tracer into the stomach frequently indicates gastric disorder but is common in normal patients. If there is poor visualization of the intrahepatic biliary ducts or delayed blood clearance, then hepatocyte dysfunction is likely, and the bilirubin should be reviewed. When there is hepatocyte dysfunction, delayed imaging is often needed. When using morphine, watch for emptying of the duodenum as evidence of spasm of sphincter of Oddi. This is required to raise intra-cbd pressure and therefore fill the gallbladder in chronic cholecystitis and possibly acalculous cholecystitis. Page 7 of 11
8 The hepatobiliary scan can actually diagnose obstruction of the CBD prior to US (but this will only occur in first 4 or 5 days). Image for 60 min and then obtain delayed view (4-5 hours). With obstruction, the development of raised intra-cbd pressure occurs, and as this increases and becomes persistent, CBD dilatation occurs. US detection is then very sensitive. With this passage of time there becomes backpressure on the hepatocyte so that the biliary tract is no longer visualized on our scan, but then hepatocyte dysfunction is documented by delayed plasma clearance of tracer. In biliary dyskinesia, ensure that patient movement and non-gallbladder tracer do not move out of the ROI used to calculate EF. Tight regions should be created about the gallbladder at the start of the CCK-8 infusion (or Ensure). Without attention to this detail, many false negative and positive scans will occur. The GBEF should be measured with background subtraction and the background should represent contaminating activities (e.g., liver and bowel). The true highest and lowest counts are used if they differ from the automatic calculations. Normal GBEF for our institution is >38% In biliary atresia, there is minor urinary excretion (more with Disofenin than Mebrofenin), but no gastrointestinal tract excretion. Severe neonatal hepatitis can emulate biliary atresia but preadministration of Phenobarbital results in increased hepatobiliary excretion and so separates these two conditions. In patients with a possible Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD), a numerical score should be reported in the interpretation (SOD score > 5 is abnormal). Table: Sostre Criteria for Scoring Scintigrams All patients with normal sphincter had scores of 0-4. Patients with SOD had values of 5-12 Criteria Score Peak time a. < 10 min 0 b. 10 min 1 2. Time of biliary visualization a. < 15 min 0 b. 15 min 1 3. Prominence of biliary tree a. Not prominent 0 b. Prominent major hepatic ducts 1 c. Prominent small hepatic ducts 2 4. Bowel visualization a. < 15 min 0 b min 1 c. > 30 min 2 5. CBD emptying a. > 50% 0 b. < 50% 1 c. No change 2 d. Shows increasing activity 3 6. CBD-to-liver ratio a. CBD (60min) Liver (60min) 0 b. Liver (60min) < CBD (60min) < 1 Liver (15min) c. Liver (60min) < CBD (60min) = 2 Liver (15min) d. Liver (60min) < Liver (15min) < 3 CBD (60min) Page 8 of 11
9 Appendices: Appendix 1: OPIOD REFERENCE TABLE FOR HEPATOBILIARY SCANNING Drug Morphine (Kadian, MS Contin-ER preps) IV, PO Hydromorphone (Dilaudid-IR prep, Exalgo-ER prep) IV, PO Codeine PO Oxycodone IR prep, oxycontin-er prep PO Hydrocodone norco) PO Meperidine (Demerol) IV, PO Fentanyl (Duragesic) IV, topical, lozenge T ½ (hrs) Immediate Release T ½ (hrs) Extended Release 5 t ½ s (hrs) Immediate Release 5 t ½ s (hrs) Extended Release in liver dz (patch) 2-4 (IV) in liver dz (patch) (IV) Page 9 of 11
10 Appendix 2 Page 10 of 11
11 References: 1. Hepatobiliary Imaging Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction, THE JOHNS HOPKINS HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY AND RADIOLOGICAL SCIENCE POLICY/PROCEDURE MANUAL NUCLEAR MEDICINE, SNM Practice Guideline for Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy 4.0*, JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY Vol. 38 No. 4 December 2010 Reviewed By: Group review by the Nuclear Medicine Faculty, Residents and Technologists Scott B. Perlman, MD, MS Derek Fuerbringer, CNMT Kandace Nowakowski Chief, Nuclear Medicine Manager, Nuclear Medicine Manager, Nuclear Medicine University Hospital The American Center Scott Knishka, RPh, BCNP Radiopharmacist John Vetter, PhD, DABR Medical Physicist Page 11 of 11
TRA Medical Imaging BILIARY SCAN Protocols
 TRA Medical Imaging BILIARY SCAN Protocols Reviewed by: Last reviewed: Contact: (866) 761-4200 and choose option 1. Purpose: Pt Prep: Radiopharm and Dose: Equipment Set-Up: Time Required: Other Materials
TRA Medical Imaging BILIARY SCAN Protocols Reviewed by: Last reviewed: Contact: (866) 761-4200 and choose option 1. Purpose: Pt Prep: Radiopharm and Dose: Equipment Set-Up: Time Required: Other Materials
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Hepatocellular Dysfunction
 www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol University Hospital and The American Center
 KIDNEY FLOW / FUNCTION WITH DIURETIC CPT CODE: 78708 UPDATED: FEBRUARY 2017 Indications: The scan is designed to differentiate dilated renal collecting systems (calyces, pelves, or ureters) from obstructed
KIDNEY FLOW / FUNCTION WITH DIURETIC CPT CODE: 78708 UPDATED: FEBRUARY 2017 Indications: The scan is designed to differentiate dilated renal collecting systems (calyces, pelves, or ureters) from obstructed
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol University Hospital and The American Center
 University Hospital and The American Center Bone Scan Limited & Multiple (Specific Regions) CPT CODE: Limited 78300 UPDATED: March 2017 Multiple 78305 Definitions: Indications: Limited is limited to one
University Hospital and The American Center Bone Scan Limited & Multiple (Specific Regions) CPT CODE: Limited 78300 UPDATED: March 2017 Multiple 78305 Definitions: Indications: Limited is limited to one
Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Measurement
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Primary Indications: In patients with chronic abdominal pain, hepatobiliary imaging with gallbladder ejection fraction
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Primary Indications: In patients with chronic abdominal pain, hepatobiliary imaging with gallbladder ejection fraction
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol
 Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol MYOCARDIAL PLANAR STRESS &/OR REST CPT CODE: 78460-61, 78464-65, 78478, 78480 FOR USE WITH THALLIUM 201 AGENTS ONLY UPDATED: MARCH 2012 Indications: Diagnosis
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol MYOCARDIAL PLANAR STRESS &/OR REST CPT CODE: 78460-61, 78464-65, 78478, 78480 FOR USE WITH THALLIUM 201 AGENTS ONLY UPDATED: MARCH 2012 Indications: Diagnosis
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol
 Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol MYOCARDIAL SPECT PERFUSION REST and REDISTRIBUTION CPT CODE: 78460, 78464 FOR USE WITH THALLIUM 201 ONLY UPDATED: MARCH 2012 Indications: Patient Prep:
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol MYOCARDIAL SPECT PERFUSION REST and REDISTRIBUTION CPT CODE: 78460, 78464 FOR USE WITH THALLIUM 201 ONLY UPDATED: MARCH 2012 Indications: Patient Prep:
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. for. BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation
 February 9, 2010 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS for BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT BRIDATEC 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION N-(3-bromo-2,4,6-trimethylphenylcarbamoyl
February 9, 2010 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS for BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT BRIDATEC 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION N-(3-bromo-2,4,6-trimethylphenylcarbamoyl
Sphincter of Oddi spasm (SOS) is a rare disorder whose diagnosis is a great clinical challenge.
 IJNM, 19(3): 75-80, 2004 Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Spasm with Quantitative Cholescintigraphy Gerbail T. Krishnamurthy and Shakuntala Krishnamurthy Department of Nuclear Medicine Tuality Community
IJNM, 19(3): 75-80, 2004 Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Spasm with Quantitative Cholescintigraphy Gerbail T. Krishnamurthy and Shakuntala Krishnamurthy Department of Nuclear Medicine Tuality Community
Medford Radiology Group. Guideline: NM.HEPATOBILIARY Effective Date: 09/16/2016 Last Revision Date: 09/16/2016 HEPATOBILIARY SCAN.
 HEPATOBILIARY STUDY Medford Radiology Group Guideline: NM.HEPATOBILIARY Effective Date: 09/16/2016 Last Revision Date: 09/16/2016 SUBJECT: HEPATOBILIARY SCAN Overview Biliary tract scintigraphy can be
HEPATOBILIARY STUDY Medford Radiology Group Guideline: NM.HEPATOBILIARY Effective Date: 09/16/2016 Last Revision Date: 09/16/2016 SUBJECT: HEPATOBILIARY SCAN Overview Biliary tract scintigraphy can be
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID)
 GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
Scintigraphy (Nuclear Medicine Imaging) in Patients with Perplexing Abdominal Complaints
 Scintigraphy (Nuclear Medicine Imaging) in Patients with Perplexing Abdominal Complaints Mark Tulchinsky, MD, FACNM, CCD Professor of Radiology and Medicine Penn State University College of Medicine Hershey,
Scintigraphy (Nuclear Medicine Imaging) in Patients with Perplexing Abdominal Complaints Mark Tulchinsky, MD, FACNM, CCD Professor of Radiology and Medicine Penn State University College of Medicine Hershey,
Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy:
 Cholecystokinin-Augmented Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy: Dissecting the Art from Science Mark Tulchinsky, MD, FACNP Professor of Radiology and Medicine Penn State University College of Medicine Hershey, Pennsylvania
Cholecystokinin-Augmented Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy: Dissecting the Art from Science Mark Tulchinsky, MD, FACNP Professor of Radiology and Medicine Penn State University College of Medicine Hershey, Pennsylvania
Nuclear Medicine - Hepatobiliary
 Scan for mobile link. Nuclear Medicine - Hepatobiliary Hepatobiliary nuclear medicine imaging helps evaluate the parts of the biliary system, including the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, using small
Scan for mobile link. Nuclear Medicine - Hepatobiliary Hepatobiliary nuclear medicine imaging helps evaluate the parts of the biliary system, including the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, using small
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Mft ] ~;;I~ [I) I~ t?l3 ilr!f S; [,j ~ M
![Mft ] ~;;I~ [I) I~ t?l3 ilr!f S; [,j ~ M Mft ] ~;;I~ [I) I~ t?l3 ilr!f S; [,j ~ M](/thumbs/72/67248163.jpg) Mft ] ~;;I~ [I) I~ t?l3 ilr!f S; [,j ~ M Hepatobiliary Imaging Update Maggie Chester and Jerry Glowniak Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon This is the
Mft ] ~;;I~ [I) I~ t?l3 ilr!f S; [,j ~ M Hepatobiliary Imaging Update Maggie Chester and Jerry Glowniak Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon This is the
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (Tc-99m-Sulfur Colloid in Egg)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (Tc-99m-Sulfur Colloid in Egg) Overview Indications The Gastric Emptying Study demonstrates the movement of an ingested
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (Tc-99m-Sulfur Colloid in Egg) Overview Indications The Gastric Emptying Study demonstrates the movement of an ingested
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
 BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
Nonparenteral medications
 Nonparenteral medications Capsules and unscored tablets are rounded to the nearest whole tablet. Scored tablets are rounded to the nearest 1/2 tablet. Liquid medications are rounded to one decimal place
Nonparenteral medications Capsules and unscored tablets are rounded to the nearest whole tablet. Scored tablets are rounded to the nearest 1/2 tablet. Liquid medications are rounded to one decimal place
Nuclear medicine in renal scarring
 Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Biliary
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Biliary Page 1 of 6 12/18 Biliary Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for basic ultrasound
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Biliary Page 1 of 6 12/18 Biliary Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for basic ultrasound
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
GUNDERSEN HEATLH SYSTEM NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPARTMENT PROTOCOL MANUAL
 GUNDERSEN HEATLH SYSTEM NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPARTMENT PROTOCOL MANUAL PROCEDURE: POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET) SECTION: PET 12.1 ORIGINAL DATE: 2 13 02 DATE REVISED: 6 14-17 REVIEWED: ANNUAL 1 Indications
GUNDERSEN HEATLH SYSTEM NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPARTMENT PROTOCOL MANUAL PROCEDURE: POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET) SECTION: PET 12.1 ORIGINAL DATE: 2 13 02 DATE REVISED: 6 14-17 REVIEWED: ANNUAL 1 Indications
** Medication exercises ** NICU Phase II
 ** Medication exercises ** NICU Phase II A) Baby A has had a bowel resection six hours ago. She weighs 3 kg. Post-op, she is quite agitated and she is on a fentanyl drip at 2 micrograms/kg/hr (#1). She
** Medication exercises ** NICU Phase II A) Baby A has had a bowel resection six hours ago. She weighs 3 kg. Post-op, she is quite agitated and she is on a fentanyl drip at 2 micrograms/kg/hr (#1). She
Morphine-Modified Hepatobiliary Scanning Protocol for the Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis
 Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Solomon et al. Imaging Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Robert W. Solomon 1,2 Abraham Albert
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Solomon et al. Imaging Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Original Research Robert W. Solomon 1,2 Abraham Albert
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Nuclear medicine in gastrointestinal system. Assoc. prof. V. Marković, MD, PhD Assoc. prof. A. Punda, MD, PhD A. Barić, MD, nucl. med. spec.
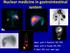 Nuclear medicine in gastrointestinal system Assoc. prof. V. Marković, MD, PhD Assoc. prof. A. Punda, MD, PhD A. Barić, MD, nucl. med. spec. Hepatobiliary imaging Hepatobiliary imaging is nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine in gastrointestinal system Assoc. prof. V. Marković, MD, PhD Assoc. prof. A. Punda, MD, PhD A. Barić, MD, nucl. med. spec. Hepatobiliary imaging Hepatobiliary imaging is nuclear medicine
PAIN MANAGEMENT PGY-1. Aaron D. Storms, MD Carin van Zyl, MD Adult and Pediatric Palliative Care, LAC+USC Keck School of Medicine of USC
 PAIN MANAGEMENT PGY-1 Aaron D. Storms, MD Carin van Zyl, MD Adult and Pediatric Palliative Care, LAC+USC Keck School of Medicine of USC Perception Matters A builder aged 29 came to the accident and emergency
PAIN MANAGEMENT PGY-1 Aaron D. Storms, MD Carin van Zyl, MD Adult and Pediatric Palliative Care, LAC+USC Keck School of Medicine of USC Perception Matters A builder aged 29 came to the accident and emergency
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Paediatrics. John Buscombe
 Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception
 Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy in Patients with Bile Leaks
 Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy in Patients with Bile Leaks Sandra L. Carichner and Conrad E. Nagle William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, Michigan Hepatobilillry scintigraphy has been recognized as u useful tool
Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy in Patients with Bile Leaks Sandra L. Carichner and Conrad E. Nagle William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, Michigan Hepatobilillry scintigraphy has been recognized as u useful tool
Po dilaudid versus iv dilaudid
 Po dilaudid versus iv dilaudid Search IM/IV/SC 120 mg ratios of morphine to methadone in patients with neuropathic pain versus non-neuropathic an equianalgesic ratio for PO. Dilaudid official prescribing
Po dilaudid versus iv dilaudid Search IM/IV/SC 120 mg ratios of morphine to methadone in patients with neuropathic pain versus non-neuropathic an equianalgesic ratio for PO. Dilaudid official prescribing
Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile)
 Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Long Term Care Formulary HCD - 08
 1 of 5 PREAMBLE Opioids are an important component of the pharmaceutical armamentarium for management of chronic pain. The superiority of analgesic effect of one narcotic over another is not generally
1 of 5 PREAMBLE Opioids are an important component of the pharmaceutical armamentarium for management of chronic pain. The superiority of analgesic effect of one narcotic over another is not generally
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno. Objectives. Why?
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses)
 weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
Gastrointestinal tract
 Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Dual-Tracer Gated Myocardial Scintigraphy
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 7 Dual-Tracer Gated Myocardial Scintigraphy Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected coronary
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 7 Dual-Tracer Gated Myocardial Scintigraphy Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected coronary
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Anatomy of the liver Liver scintigraphy The labelled colloid (200 MBq 99mTc-Fyton) is phagocyted by the Kuppfer-cells
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Anatomy of the liver Liver scintigraphy The labelled colloid (200 MBq 99mTc-Fyton) is phagocyted by the Kuppfer-cells
Sacred Heart Hospital on the Emerald Coast
 - Nuclear Medicine - Regular Hours: 7:30 am 4:30 pm Monday Friday See *1 Scheduling/Orders: Ph. (850) 278-3800 Fax (850) 278-3787 Results: Health Information Mgmt (Med Records) Ph. (850) 278-3020 Contact
- Nuclear Medicine - Regular Hours: 7:30 am 4:30 pm Monday Friday See *1 Scheduling/Orders: Ph. (850) 278-3800 Fax (850) 278-3787 Results: Health Information Mgmt (Med Records) Ph. (850) 278-3020 Contact
Utilization of Cholecystokinin Cholescintigraphy in Clinical Practice
 COLLECTIVE REVIEWS Utilization of Cholecystokinin Cholescintigraphy in Clinical Practice Bryan K Richmond, MD, MBA, FACS, John DiBaise, MD, Harvey Ziessman, MD Cholecystokinin-cholescintigraphy (CCK-HIDA)
COLLECTIVE REVIEWS Utilization of Cholecystokinin Cholescintigraphy in Clinical Practice Bryan K Richmond, MD, MBA, FACS, John DiBaise, MD, Harvey Ziessman, MD Cholecystokinin-cholescintigraphy (CCK-HIDA)
10 mg hydrocodone equals how much oxycodone
 Cari untuk: Cari Cari 10 mg hydrocodone equals how much oxycodone Posts about dilaudid 8 vs oxycodone 30 written by buyprescriptionmedication. Can you help me with the conversion of Oxycodone IR (5mg tab)
Cari untuk: Cari Cari 10 mg hydrocodone equals how much oxycodone Posts about dilaudid 8 vs oxycodone 30 written by buyprescriptionmedication. Can you help me with the conversion of Oxycodone IR (5mg tab)
New Hampshire Healthy Families CLINICAL POLICY
 New Hampshire Healthy Families CLINICAL POLICY DEPARTMENT: Pharmacy DOCUMENT NAME: Opioid Analgesics PAGE: 1 o f 6 REFERENCE NUMBER: NH.PPA.13 EFFECTIVE DATE: 6/1/2016 REPLACES DOCUMENT: N/A RETIRED: REVIEWED:
New Hampshire Healthy Families CLINICAL POLICY DEPARTMENT: Pharmacy DOCUMENT NAME: Opioid Analgesics PAGE: 1 o f 6 REFERENCE NUMBER: NH.PPA.13 EFFECTIVE DATE: 6/1/2016 REPLACES DOCUMENT: N/A RETIRED: REVIEWED:
Brain Perfusion SPECT
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Brain Perfusion SPECT Primary Indications: Brain perfusion SPECT is most commonly performed (1) to aid in identification of the epileptogenic focus in patients
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Brain Perfusion SPECT Primary Indications: Brain perfusion SPECT is most commonly performed (1) to aid in identification of the epileptogenic focus in patients
Cox College Springfield, MO. Dosage Calculation Competency Level II Practice Sheet STUDENT NAME: DATE: STUDENT I.D. #: ADVISOR:
 Cox College Springfield, MO Dosage Calculation Competency Level II Practice Sheet Updated 4/2015 STUDENT NAME: DATE: / / STUDENT I.D. #: ADVISOR: A 95% must be achieved on the competency exam to progress
Cox College Springfield, MO Dosage Calculation Competency Level II Practice Sheet Updated 4/2015 STUDENT NAME: DATE: / / STUDENT I.D. #: ADVISOR: A 95% must be achieved on the competency exam to progress
Biliary Atresia. Who is at risk for biliary atresia?
 Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Continuous Bladder Irrigation
 Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
 35 BILIARY DISEASE Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction A G Craig, D Peter, GTPSaccone, P Ziesing, A Wycherley, J Toouli... See end of article
35 BILIARY DISEASE Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction A G Craig, D Peter, GTPSaccone, P Ziesing, A Wycherley, J Toouli... See end of article
TABLE 1 Principal Radiation Emission Data Radiation Mean % per Disintegration Mean Energy (kev) Gamma
 KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
Shining a Light on MEDs Understanding morphine equivalent dose
 Shining a Light on MEDs Understanding morphine equivalent dose In the workers compensation industry, 60.2 percent of claimants utilize opioid analgesics for the treatment of pain caused by a workplace
Shining a Light on MEDs Understanding morphine equivalent dose In the workers compensation industry, 60.2 percent of claimants utilize opioid analgesics for the treatment of pain caused by a workplace
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care
 Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography)
 Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION
 DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
Appendix B: Constant Rate Infusions Example Calculations
 Appendix B: Constant Rate Infusions Example Calculations For Syringe Pump 1. A 20 lb patient needs a 5 µg/kg fentanyl loading dose before being placed on a fentanyl constant rate infusion (CRI) at 3 µg/kg/h
Appendix B: Constant Rate Infusions Example Calculations For Syringe Pump 1. A 20 lb patient needs a 5 µg/kg fentanyl loading dose before being placed on a fentanyl constant rate infusion (CRI) at 3 µg/kg/h
Nuclear Medicine Imaging of Liver, Spleen and Gallbladder
 Nuclear Medicine Imaging of Liver, Spleen and Gallbladder An Introductory Guide For Patients And Their Families You may be wondering why your doctor ordered a nuclear medicine scan of your liver and spleen
Nuclear Medicine Imaging of Liver, Spleen and Gallbladder An Introductory Guide For Patients And Their Families You may be wondering why your doctor ordered a nuclear medicine scan of your liver and spleen
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT
 ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
Nephrostomy. Radiology Department. Patient information leaflet
 Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Within the proportion the two outside numbers are referred to as the extremes. The two inside numbers are referred to as the means.
 Basic Formulas Speaker: Jana Ogden This lecture will demonstrate the expectations for performing a variety of the more complex calculations. You are expected to refer to your text and complete the designated
Basic Formulas Speaker: Jana Ogden This lecture will demonstrate the expectations for performing a variety of the more complex calculations. You are expected to refer to your text and complete the designated
Small bowel atresia. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Narcotic Equivalence Converter Narcotic Route Dose Duration; Select a drug: mg Convert to: mg Adapted from Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia.
 Narcotic Equivalence Converter Narcotic Route Dose Duration; Select a drug: mg Convert to: mg Adapted from Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia. Created: Monday, March 12. Online calculator to convert equianalgesic
Narcotic Equivalence Converter Narcotic Route Dose Duration; Select a drug: mg Convert to: mg Adapted from Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia. Created: Monday, March 12. Online calculator to convert equianalgesic
PAIN. TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics. NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose
 NON-OPIOID SHORT-ACTING LONG-ACTING **** O PAIN TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose Tramadol 50 mg Ultram Every 4 hours 1-2 tabs,
NON-OPIOID SHORT-ACTING LONG-ACTING **** O PAIN TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose Tramadol 50 mg Ultram Every 4 hours 1-2 tabs,
Current Management of Biliary Atresia. Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007
 Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
15mg oxycodone is equivalent to how much morphine
 15mg oxycodone is equivalent to how much morphine The Borg System is 100 % 15mg oxycodone is equivalent to how much morphine nursing home activity director cover letter 15 mg oxycodone equal to how much
15mg oxycodone is equivalent to how much morphine The Borg System is 100 % 15mg oxycodone is equivalent to how much morphine nursing home activity director cover letter 15 mg oxycodone equal to how much
Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications
 Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications Injectable Medications Injection or intravenous (IV) infusion More invasive than administration by mouth, rectum, or through the skin Common methods
Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications Injectable Medications Injection or intravenous (IV) infusion More invasive than administration by mouth, rectum, or through the skin Common methods
Revised 16 February, of 7
 341 State Street Suite G Madison, WI 53703 ph: (608) 251 4454 f: (608) 251 3853 6333 University Avenue, Middleton WI 53562 ph: (608) 310 5389 f: (608) 285 9603 INTRANASAL OR INTRAMUSCULAR NALOXONE PROTOCOL:
341 State Street Suite G Madison, WI 53703 ph: (608) 251 4454 f: (608) 251 3853 6333 University Avenue, Middleton WI 53562 ph: (608) 310 5389 f: (608) 285 9603 INTRANASAL OR INTRAMUSCULAR NALOXONE PROTOCOL:
MUGA Scan. A Patient s Guide. Copyrighted Material. HeartWise Patient Education
 MUGA Scan Copyrighted Material HeartWise Patient Education 800-747-1606 A Patient s Guide What Is a MUGA Scan? A multiple gated acquisition (or MUGA) scan is a test that uses a radioactive substance, called
MUGA Scan Copyrighted Material HeartWise Patient Education 800-747-1606 A Patient s Guide What Is a MUGA Scan? A multiple gated acquisition (or MUGA) scan is a test that uses a radioactive substance, called
Dose equivalent of fentanyl patch to oxycontin
 Dose equivalent of fentanyl patch to oxycontin 10-3-2018 Detailed dosage guidelines and administration information for OxyContin (oxycodone hydrochloride). Includes dose adjustments, warnings and precautions.
Dose equivalent of fentanyl patch to oxycontin 10-3-2018 Detailed dosage guidelines and administration information for OxyContin (oxycodone hydrochloride). Includes dose adjustments, warnings and precautions.
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations
 Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Dr. R. Pradheep. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern. Railway. Hospital.
 Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
Morphine Sulfate Hydromorphone Oxymorphone
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.02.33 Subject: Morphine Drug Class Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: June 19, 2015 Morphine Sulfate Hydromorphone
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.02.33 Subject: Morphine Drug Class Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: June 19, 2015 Morphine Sulfate Hydromorphone
PET/CT & Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Practice. Tuesday, February 21, The 8 th Snowmass 2017: Westin Snowmass Resort Snowmass Village, Colorado
 The 8 th Snowmass 2017: PET/CT & Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Practice Tuesday, February 21, 2017 Westin Snowmass Resort Snowmass Village, Colorado Educational Symposia TABLE OF CONTENTS TUESDAY, FEBRUARY
The 8 th Snowmass 2017: PET/CT & Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Practice Tuesday, February 21, 2017 Westin Snowmass Resort Snowmass Village, Colorado Educational Symposia TABLE OF CONTENTS TUESDAY, FEBRUARY
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS
 PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
Delaware Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines
 Delaware Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines This guideline is intended for physicians working in hospital-based Emergency Departments (EDs) and free-standing emergency centers in the state
Delaware Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines This guideline is intended for physicians working in hospital-based Emergency Departments (EDs) and free-standing emergency centers in the state
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
Background. RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation. Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial
 RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa
 MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: 4:52 Subject: Purpose: Policy: Dobutamine Cardiac Perfusion Scan To administer medication to
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: 4:52 Subject: Purpose: Policy: Dobutamine Cardiac Perfusion Scan To administer medication to
