Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes. Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD
|
|
|
- Alberta Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD
2 THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes Non-parenchymal Cells -Endothelial Cells -Kupffer Cells -Hepatic Stellate Cells -Myofibroblasts -Natural Killer Cells - B Lymphocytes Extra Cellular Matrix -Collagen -Laminin -Proteoglycans -Fibronectin INTRODUCTION
3 Portal Flow Distribution THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Central Vein Portal Triad Sinusoids the zone 3 receives less oxygen and nutrients than zone 1, where the blood flow of the hepatic artery branch and portal vein is poured to conform the sinusoids. INTRODUCTION
4 LIVER INJURY AND REGENERATION PERSISTENT INFLAMMATORY CONDITIONS Infections-Rejection- biliary / vascular complications- steatohepatitis TRANSPLANTED LIVER ACTIVATE IMMUNE RESPONSE Hepatic Stellate Cells ACTIVATION ALLOGRAFT FIBOSIS FIBROSIS & CIRRHOSIS & CIRRHOSIS Activated HSCs Myofibroblast phenotype PERPETUATION OF PRO- FIBROGENIC STATUS Stromal Stiffness FIBROGENESIS Production & Degradation of Extra Cellular Matrix EXTRA CELLULAR MATRIX ACCUMULATION INTRODUCTION
5 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION PATHOGENESIS & EVOLUTION LIVER ALLOGRAFT FIBROSIS ASSESSMENT & MONITORING Liver Biopsy Non-invasive Methods PREVENTION & REVERSION INTRODUCTION
6 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION High proportion of fibrosis described in the long-term, mainly associated to inflammation, chronic hepatitis & chronic rejection -Evolutive process? Patient predisposing condition? Could be related to posttransplant persistent injuries? INTRODUCTION
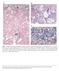
7 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION ASSESSMENT & MONITORING QUANTITATIVE MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS Quantify the fibrosis area found in the liver biopsy specimen stained by PicroSirius-Red. Invasive Approach-Liver Biopsy- GOLD STANDARD PicroSirious-Red Collagen I-II-III Counterstained SEMIQUANTITATIVE HISTOLOGIC SCORING SYSTEMS Pathologists review the liver biopsy classifying fibrosis in mild moderate or severe according the scores Masson s Trichrome Collagen Nuclei Cytoplasm INTRODUCTION
8 Fibrosis Semiquantitative Assessment Histological Scoring Systems DESIGNED TO STAGE CHRONIC HEPATITIS NO FOR TRANSPLANTED LIVERS SCHEUER system (1991) Combines Necroinflammation and Fibrosis grade 0-4 Portal inflammation & necrosis Lobular inflammation & necrosis Portal Fibrosis METAVIR system (1994) Combines piecemeal and lobular necrosis with inflammation and fibrosis Activity & Necroinflammation A 0-3 Portal Fibrosis 0-4 ISHAK system (1995) Periportal or periseptal interface hepatitis 0-4 Confluent necrosis 0-6 Focal (spotty) lytic necrosis, apoptosis and focal inflammation 0-4 Portal and Bridging Fibrosis 0-6 Portal inflammation 0-4 INTRODUCTION
9 LIVER BIOPSY Fibrosis at the Three Main Areas of the Liver Parenchyma Portal Fibrosis Sinusoidal fibrosis Centrilobullar fibrosis Conventional systems used to stage fibrosis in the native liver fail to recognize these patterns of graft fibrosis. INTRODUCTION
10 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION ASSESSMENT & MONITORING Non-Invasive Approach Hepatic Imaging Multiparametric MRI No Ped TX Transient Elastography (AUROC ) Acoustic radiation force impulse (AFRI) (AUROC 0.8) Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) (AUROC 0.92) No Ped TX Evaluation area= 1-3 cm 3 Transient Elastography Equipment expensive, range of probes are needed, influenced by obesity & inflammation. Reproducible measurements are not possible in 20% of patients. More difficult in split or reduced grafts. Less accurate in middle fibrosis. INTRODUCTION
11 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION ASSESSMENT & MONITORING Non-Invasive Approach Serum markers of fibrosis Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Animo-terminal propeptide of type III collagen (PIIINP) Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1) APRI: AST/ platelet ratio index Type 4 collagen S, Fibronectin & Laminin HA: appeared to be a fair predictor of liver allograft fibrosis (Hartley JL, et al. JPGN 2006; ) ELF panel* ELF panel*: accurate in pediatric NAFLD (AUROC 0.92); no correlation with the degree of pediatric allograft fibrosis. (Goldschmidt I, et al Ped Transpl. 2013; 17:525-34) MicroRNAs: Intrahepatic micrornas are predictive of inflammation, rejection & proliferation.(need LB) Markers of cell Death: CK18, sensitive marker of fibrosis in ped NAFLD. INTRODUCTION
12 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION ASSESSMENT & MONITORING Non-Invasive Approach Immunological investigation Autoantibody positivity (SMA- ANA), reflect cause of graft injury; related to chronic hepatitis & fibrosis Class II donor-specific human leukocyte antigen antibodies (DSAs), mostly DQ, has been associated with graft inflammation, fibrosis, De novo AIH Donor-specific T cells have been shown to predict the risk of acute rejection following pediatric TX INTRODUCTION
13 FIBROSIS IN PEDIATRIC LIVER TRANSPLANTATION PATHOGENESIS & EVOLUTION -How is the evolution of activated HSCs in pediatric liver allograft along the time? The Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells which express myofibroblastic phenotype, are the main source of collagen in the injured liver ASSESSMENT & MONITORING Activated HSCs are identified by ASMAimmunoreactivity in the liver biopsy ASMA immunoreactivity PREVENTION & REVERSION -Could the activated HSCs predict high fibrosis development in the long term? INTRODUCTION
14 Major Aims To Analyze The History Of Pediatric Liver Allograft Fibrosis Over Time To Evaluate The Influence Of Clinical Variables & Immunosuppression In Fibrosis Development DESIGN & VALIDATION OF A NEW ALLOGRAFT FIBROSIS SCORING SYSTEM CORRELATION OF NON-INVASIVE METHODS WITH LIVER BIOPSY TO STUDY THE DYNAMICS OF PEDIATRIC LIVER ALLOGRAFT FIBROSIS EVOLUTION OF ACTIVATED HEPATIC STELLATE CELLS IN THE LIVER ALLOGRAFTS
15 Patients & Methods Retrospective analysis of 170 Pediatric LT recipients Exclusion Criteria: Re-transplantation; inadequate LB; incomplete follow-up(< 3 LB) = 31 Clinical -Biochemical & Serologic Assessment Pre-LT factors: Donor Age Donor type Ischemia Time Recipient age-gender-weight height- blood pressure Liver Transplant indication CMV - EBV status Post-LT factors: Vascular and biliary complications Infections (0-6 months) Autoantibodies & gammaglobulins % History of Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease Available data of Doppler ultrasound- TE Adequate and available protocol liver biopsy LT 6 months years
16 Patients & Methods- Histologic Assessment 170 Pediatric LT recipients - 31 Excluded 139 patients years 6 months Liver Biopsies = Available & adequate protocol liver biopsy Normal Histology : absent or minimal non-specific portal infiltrate. Acute & Chronic rejection* Portal inflammation Centrilobular dropout Steatosis Ductal proliferation Cholestasis De Novo autoimmune hepatitis** Necroinflammatory activity Fibrosis staging *AR Episodes: increased liver enzymes ([AST] [ALT] [GGT]:NR 5 50 IU/L, histological features (Banff )and treatment with i.v Steroid. **De novo AIH: progressive graft dysfunction, increased autoantibodies and serum gamma-globulin levels, with histologic features of chronic active hepatitis (portal inflammation with limiting plate disruption, and lobular hepatitis with or without plasma cell infiltration)
17 Design of a new histological fibrosis scoring Liver Allograft Fibrosis Score (LAFSc)
18 Histologic Features and Staging definitions of the Liver Allograft Fibrosis Score= 0-9 (LAFSc) Structure 0 I II III Portal Tract No Fibrosis 0-3 Non-expanding fibrosis in less than 50% of portal tracts. Fibrosis in more than 50% of portal tracts and/or expansion into short fibrous septa into the periportal parenchyma. Marked expansion of most or all portal tracts with bridging fibrosis expanding to other portal tracts or central areas with or without occasional nodules. Sinusoids (zones 1, 2) No Fibrosis 0-3 Little fibrosis with thin focal collagen deposits involving less than 50% of sinusoids. Little fibrosis with thin diffuse collagen deposits involving more than 50% of sinusoids, or thicker but focal fibrosis in less than 50% of sinusoids. Thick, marked, diffuse sinusoidal fibrosis. Centrolobular Vein (zone 3) No Fibrosis 0-3 Circular perivenular fibrosis involving less than 50% of central veins without invasion into the perivenular parenchyma. Circular perivenular fibrosis in more than 50% of central areas and/or expansion into short fibrous septa into the perivenular parenchyma. Marked centrolobular fibrosis with bridging to other central areas and/or portal tracts. Design of a new histologic fibrosis scoring
19 Patients & Methods Clinical, biochemical and serological data POPULATION INCLUDED Available & Adequate LB at 6 months and 7 years Data of Non-invasive methods (TE & APRI index) at 7 years 38 patients/ 76 LB LT Protocol liver biopsies 38 LB at 6 months Liver Transplant indication Donor Type Immunosupression received at LT 38 LB at 7 years Demographic Data Median LT- age (yrs) 1.6 (r: ) Biliary Atresia 21 (55%) Metabolic Diseases 8 (21%) Cholestasis 8 (21%) Tumors 1 (3%) Living Related Donor (n) 23 (60%) Deceased Donor (n) TAC + Steroides TAC + Basiliximab TAC monotherapy years 15 (40%) 18 (47%) 14 (37%) 6 (16%) Validation of the new semi-quantitative scoring system Design of a new histologic fibrosis scoring
20 Patients & Methods- Histologic Assessment LT Protocol liver biopsies LB at 6 months 38 LB at 7 years years 1 76 New tissue sections cut & stained for Hematoxilin & Eosin (inflammationactivity) Masson s Trichrome (fibrosis scored by the New Score, METAVIR- Ishak) 2 COMPUTER-ASSISTED MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS used as reference PATTERN for the new score validation (PicroSirius-Red stain), that measure the proportion of collagen found at the digitalized image of each liver biopsy. 3 Morphometric analysis results were correlated with the New Score, METAVIR, Ishak & TE APRI index 4 Correlation between Pathologists (intra/inter observers agreement) H&E and Masson s trichrome-stained samples evaluated by external pathologist Design of a new histologic fibrosis scoring
21 Results I Fibrosis staged by LAFSc- METAVIR & Ishak systems 6 MONTHS 7 YEARS Correlation among morphometric analysis with LAFSc- METAVIR & Ishak LAFSc was the most accurate semi-quantitative score for evaluating fibrosis Design of a new histologic fibrosis scoring
22 Results I Correlation between collagen deposits (morphometric analysis) & LAFSc Equation R2 F gl1 gl2 p= Linear Regression Quadratic Regression Reproducibility of Liver allograft fibrosis score analysed by observers High intra-observer agreement 0.97, p < Inter-observer agreement: and 0.79, p < Intraclass correlation coefficient Design of a new histologic fibrosis scoring
23 Results I Correlation among morphometric analysis and semi-quantitative scoring with non-invasive methods for fibrosis assessment (n=38) No correlation was found among TE or APRI index with morphometric analysis, METAVIR, Ishak & LAFSc Design of a new histological fibrosis scoring
24 Dynamics Of Allograft Fibrosis In Pediatric Liver Transplantation
25 Patients & Methods 139 Pediatric LT receptors POPULATION INCLUDED 54 -Clinical, biochemical, serological data, -Immunosuppression -Doppler Ultrasound -Available & adequate LB at 6 months, 3 and 7 yrs. Protocol liver biopsies- long-term follow-up years Liver Transplant Indication 54 LB 6 months 54 LB 3 years Demographic Data 54 LB 7 years Median age at LT (years, range) 1.28 ( ) Median Weight at LT (kg, range) 7.66 ( ) Biliary Atresia P.I.F. Cholestasis Metabolic diseases Tumors Alagille Syndrome 30 (55%) 9 (16%) 8 (15%) 5 (9%) 2 (4%) Donor Type Living Related Donor/ Deceased Donor (n,%) 29 (53%) - 25 (47%) Median donor age (years, range) 30.1 ( ) Median Ischemia time (minutes, range) (68-892) Immunosuppression received at LT TAC+ Steroids TAC+ Basiliximab TAC monotherapy 24 (44%) 23 (43%) 7 (13%) Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
26 Patients & Methods 54 Pediatric LT receptors 54 LB 6 months Protocol liver biopsies LB 3 years 54 LB 7 years 10 years Clinical Considerations Histologic Assessment 162 LB -Normal vs increased liver enzymes along the time (NV= 5-50 AST, ALT, GGT) -Patients who did not received Steroids anytime. -Tacrolimus monotherapy < 4ng/ml with normal liver enzymes ( prope-t) -Two or more immunosuppressors or Tacrolimus monotherapy > 4 ng/ml. -New tissue sections stained for H&E, Masson s Trichrome, PicroSirious-Red & Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells (ASMA immunostaining) -Pathologist Review & Fibrosis scoring: METAVIR (F0- F4) & Liver Allograft Fibrosis Score (LAFSc 0-9) - Fibrosis & ASMA-positive area quantified by morphometric analysis 1-Correlation among fibrosis with clinical variables, IS and histologic features associated 2-Correlation among ASMA-positive area with fibrosis (LAFSc & PSR%) at same period /long-term Statistical Methods: SPSS 18.0 Chicago. IL. Results expressed as percentage, median, mean and SD; statistical significance for p-values < Relation among variables evaluated by Pearson correlation. Linear and quadratic regressions were fitted to analyze relationship among variables. Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
27 Results II- Histologic Assessment of Allograft Fibrosis LAFSc Proportion of Fibrosis staged by LAFSc F0 F1 20 F2 F3 15 F4 F5 10 F6 5 F7 F8 LAFSc 6 months 3 years 7 years X±SD 2.9 (0.5) 3.3( 1.8) 4.3 (1.8) IC 95% m% 3y% 7y% F9 Fibrosis progressed along the time in 40 (74%) patients. Stable or reduced fibrosis was found in 14 (26%) patients. Patients with increased liver enzymes show similar amount of fibrosis than those with normal liver function Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
28 Results II- Fibrosis evolution at parenchymal areas 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% Portal Fibrosis Centrilobular Fibrosis Sinusoidal Fibrosis 6m 3y 7y F0 F1 F2 F3 6m 3y 7y 6m 3y 7y 100% 100% 80% % % % % 37 40% % % % 0% 0 0 F0 F1 F2 F3 F0 F1 F2 F3 Linear progression p<0.01 Linear progression p<0.01 No linear p=0.2 6 m 3 y 7 y 6 m 3 y 7 y 6 m 3 y 7 y Mean CI 95% Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
29 Results III- Evolution of Fibrosis & Activated-HSCs (ASMA) Fibrosis progressed along the time p<0.001 Activated HSCs decreased along the time p< 0.01 FIBRO SIS EVO LUTIO N MO NT H S 3 Y E AR S 7 Y E AR S no fibrosis % mild % moderate % severe % Lineal (moderate %) LAFSc : mild = 1-3; moderate= 4-6; severe = 7-9 Increment by areas in the long-term Sinusoidal 33% Centrilobular 45% Portal 57% 6 months 3 years 7 years Median ASMA 6.9 ( ) 5.7 (0.4-38) 4.1 (0.7-18) IC 95% Activated-HSCs showed inverse evolution respect to Fibrosis in the long-term Liver Transplantation 2016 Jun;22(6):822-9 Relevance of Hepatic Stellate Cells
30 PSR% Results III- Evolution of Fibrosis according to Activated -HSCs at 6m Activated-HSCs at 6 months = > 8% = 20 patients = < 8% = 34 patients FIBROSIS E VOLUTION Activated-HSCs 8 at 6 months a risk factor for fibrosis development at 7 years MONTHS 3 YEARS 7 YEARS TIME PSR% r p<0.01 LAFSc r p=0.03 Statitistical method: Mixed regression Fibrosis 6m Fibrosis 3 y Fibrosis 7 y p-value ASMA ± ± ± 8 <0.001 ASMA ± ± ± 7 = 0.04 p-value =0.03 =0.8 < 0.01 Note: p-values represent the significance between means Liver Transplantation 2016 Jun;22(6):822-9 Relevance of Hepatic Stellate Cells
31 Results IV Demographic data of the 139 LT recipients Number of patients / Liver biopsies (n) 139 (69 boys) /595 Median age at LT (years, range, range) 1.4 ( ) Median Weight at LT (kg, range) 8.4 ( ) LT Indication: (n, %) Biliary Atresia Metabolic diseases Progressive Intrahepatic Familial Cholestasis Tumors Alagille Syndrome Others 75 (54%) 21 (15%) 17 (12%) 11 (8%) 11 (8%) 4 (4%) Living Related Donor/ Deceased Donor (n, %) Split Liver/ Reduced Deceased Donor Median donor age (years, range) 29 ( ) Median Ischemia time (minutes, range) (66-892) Immunosuppression at LT (n, %):TAC+ Basiliximab 42 (30%) TAC+ Steroids 33 (24%) TAC monotherapy 28 (20%) TAC+MMf+Steroids 13 (9%) TAC+MMF+Daclizumab 8 (6%) TAC+Basiliximab+MMf 6 (4%) TAC+MMf 6 (4%) TAC+Steroids+Daclizumab 3 (2%) 66 (47 %) / 66 (47%) 4 (3%) / 3 ( 2.5%) Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
32 Results IV Evolution of clinical variables studied Time of follow-up Clinical Variables 0-6m. 1 yrs 2 yrs 3 yrs 5 yrs 7 yrs 10 yrs LB:595/ Patients Vascular complications 12 (10%) 1 (1%) 2 (2%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) 1 (2%) Biliary complications 19 (16%) 2 (2%) 3 (3%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) (4%) Post-LT AA 26 (23%) 30 (27%) 29 (26%) 15 (15%) 8 (10%) 6 (10%) 3 (12%) AR Steroids treated 64 (56%) 8 (7%) 8 (7%) 5 (5%) 4 (5%) 5 (9%) PTLD (EBER +) n=28 8 (7%) 9 (8%) 7 (6%) 2 (2%) 1 (1%) (4%) Gammaglobulins> 15% 40 (35%) 38 (34%) 48 (44%) 32 (33%) 59(73%) 43 (75%) 16 (67%) Gammaglobulins (X) Abbreviations: LB, liver biopsy; LT, liver transplantation; AA, autoantibodies; AR, acute rejection; PTLD, post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease; EBER, Epstein Barr virus RNA +.
33 N=139pts. 595LB Results IV Fibrosis evolution over time 6 months 1 year 2 years 3 years 5 years 7 years 10 years Sinusoidal Centrilobular Portal LAFSc Lineal (LAFSc) Portal Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
34 Results IV Fibrosis evolution over time 60 increment % reduction % unchanged % Lineal (reduction %) N=139pts. 595LB mo-2y. 3-5 y y. increment % reduction % unchanged % LIVER ALLOGRAFT FIBROSIS IS A DYNAMIC PROCESS Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
35 Results IV Association between fibrosis & clinical variables Clinical Variables Fibrosis Fibrosis Fibrosis Location N=54 N=139 Deceased donor grafts p<0.001 p<0.02 Portal p= p= p=0.01 (46.3%) (47.5%) Lymphoproliferative disease p=0.001 p=0.01 Portal p=0.01(7y) (18.5%) (20%) Ischemia time > 400 min p<0.01 p<0.03 Portal p=0.06 (6m), p<0.01(3y) Vascular complications (0-6m) p=0.04 p=0.04 Centrilobular p=0.04 (7y) (11%) (10%) Gammaglobulins > 15% p=0.02 p=0.03 Centrilobular p=0.02 (7y) Positives AutoAntibodies (>1/40) p=0.01 p=0.01 Centrilobular p=0.01 (3y) Biliary complications 0-6 m p=0.01 (24%) p=0.03 (16%) Sinusoidal p=0.05 (6m) p=0.01 (3y) Male gender p=0.01 (50%) p=0.002 (50%) Sinusoidal p=0.001 Centrilobular p=0.04 (7y) Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
36 Results IV Main histological features found at 595 LB Periodos of evaluation Total 6m 1yr. 2yrs. 3yrs. 5yrs. 7yrs. 10yrs. LB No fibrosis 2% 6 (5%) 3 (3%) 3 (3%) (1%) Isolated Fibrosis 14% 9 (8%) 16 (14%) 16 (14%) 15 (16%) 13 (16%) 11 (19%) 2 (8%) Fibrosis + mild portal Infiltrate 22% 24 (21%) 29 (26%) 25 (23%) 14 (15%) 18 (22%) 14 (24%) 8 (33%) Ductal proliferation Steatosis Inflammatory Infiltrate Cholestasis Interface hepatitis Normal liver histology 5%, 3% & 1 % of LB at 6 mo. 3 & 5 years. Isolated Fibrosis 8-19% over time. Fibrosis + mild unspecific portal inflammatory infiltrate 15-33% over time (70% NLE) 44% 57 (49%) 51 (45%) 47 (43%) 44 (46%) 36 (44%) 20 (35%) 9 (37%) 21% 29 (25%) 29 (26%) 21 (19%) 17 (18%) 12 (15%) 11 (19%) 5 (21%) 81% 94 (82%) 100 (89%) 85 (77%) 80 (83%) 61 (75%) 44 (77%) 22 (91%) 12% 25 (22%) 15 (13%) 15 (14%) 10 (10%) 6 (7%) 1 (2%) 1 (4%) 17% 18 (16%) 18 (16%) 19 (17%) 21 (22%) 11 (14%) 11 (19%) 2 (8%) Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
37 Results IV- Histological Features associated to fibrosis PORTAL FIBROSIS Unspecific inflammation: 1y p=0.001; 3y p=0.002; 5y p<0.001 Ductal proliferation: 6mo p<0.001; 1y p=0.002; 5y p=0.003; 7y p=0.02 Cholestasis: 6mo p=0.007 CENTRILOBULAR FIBROSIS Steatosis 5 & 10 y p= 0.04 SINUSOIDAL FIBROSIS Steatosis 6 mo;1y & 2 y p<0.001 Ductal proliferation: 1y p=0.006; 2y p= 0.005; 5y p=0.03 Patients with steatosis did not show waning of it Cellular drop out & interface hepatitis did not show correlation with fibrosis location Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
38 0 LAFSc 10 (PSR%) 0 25 Results IV Immunosuppression-Fibrosis evolution over time Steroids vs Steroids-free patients N=54 24 yes 21(87%) kept on ST 1 year x dose: 0.25 ± 0.1 mg/kg 13(54%) kept on ST 2 years x dose: 0.11 ± 0.1 mg/kg 37 vs 17 [p=0.8] Steroids at LT 30 no 13 (43%)Further ST for AR x dose: 0.3 ± 0.1 mg/kg 6 m 3 y 7y Steroids CI 95% Steroids-free CI 95% N=139 STEROIDS 97 (70%) STEROIDS-free 42 (30%) [p=0.2] 6m Steroid therapy was not associated with reduced fibrosis in this population Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
39 Patients at 7 years Prope-T (n=18) Non Prope-T (n=36) N= 54 Mean PSR% = 19.0 ± ± 9.4 Mean LAFSc = 3.9 ± ± 1.7 Fibrosis evolution in Prope-Tolerance vs Non Prope-Tolerance LB (n=595) LAFSc Results IV Immunosuppression-Fibrosis according to Prope- Tolerance status [p=0.5] [p=0.8] 0 10 [p=0.6] 6m Total LB 595 PROPE T 175 NO PROPE T 420 Period 6 mo. 1 y 2 y 3 y 5 y 7 y 10 y Total PROPE T (11%) 26 (24%) 44 (46%) 36 (44%) 39 (68%) 17 (71%) NO PROPE T 122 (100%) 98 (89%) 84(76%) 52(54%) 45(56%) 18 (32%) 7 (29%) Prope-tolerance did not contribute to increase fibrosis Dynamics of liver allograft fibrosis
40 Discussion & Future Perspectives
41 Pediatric liver allograft fibrosis could be seen as a dynamic process with gradual progression over time. Fibrosis progression does not mean abnormal liver function, irreversible cirrhosis or re-transplant indication LAFSc identified fibrosis at portal, centrilobular and sinusoidal areas, being the most accurate score for evaluating allograft fibrosis Fibrosis placed at specific areas of the liver parenchyma could be related to clinical complications or transplant events DISCUSSION
42 To date, the non-invasive methods for fibrosis assessment have been unable to replace LB. The steroids could not prevent fibrosis development No evidence of higher fibrosis was found in patients with low immunosuppression A high proportion of activated-hscs found at early stages of LT seems to be a risk factor for early and long-term fibrosis development. DISCUSSION
43 Future Perspectives Pediatric liver allograft fibrosis need to be categorized by an accurate method specifically designed to stage allograft fibrosis Centralized studies are needed to confirm pediatric allograft fibrosis evolution Studies evaluating the antifibrogenic properties of IS are mandatory, to adequate the treatment to fibrosis stage. To develop accurate non-invasive tools for fibrosis assessment to avoid the liver biopsy DISCUSSION
44 Thanks for your attention
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
11 th Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology - An Update
 11 th Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology - An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Enghien les
11 th Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology - An Update Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Enghien les
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel. Basel,
 Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
Viral Hepatitis (I) Luigi Terracciano Department of Pathology University Hospital Basel Basel, 19. 04. 2016 Definition Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver characterized by a variable combination
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
Figure 1. Actuarial survival of patients with ABO I, ABO compatible, and ABO identical grafts.
 New Insights into Antibody Mediated Graft Injury after Pediatric Liver Transplantation S.V. McDiarmid MD Professor of Pediatrics and Surgery David Geffen School of Medicine University of California, Los
New Insights into Antibody Mediated Graft Injury after Pediatric Liver Transplantation S.V. McDiarmid MD Professor of Pediatrics and Surgery David Geffen School of Medicine University of California, Los
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) Case n 2 ( B 00 / 8249 ) Case n 3 ( B 98 / 8352 )
 Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Slide Seminar Case n 1 ( B 92 / 4208 ) 16 month-old girl. HBV serology +. Clinic in favour of chronic hepatitis. 4 portal triads! classification limited Viral B chronic hepatitis Mild activity (Fig. 1
Liver Transplant Pathology a general view
 Liver Transplant Pathology a general view Dr S E Davies Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust ACP/BSG Meeting Leeds 2012 Liver transplantation When and where? Who and why? How?
Liver Transplant Pathology a general view Dr S E Davies Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust ACP/BSG Meeting Leeds 2012 Liver transplantation When and where? Who and why? How?
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Journal of Asian Scientific Research
 Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 COULD SERUM LAMININ REPLACE LIVER BIOPSY AS GOLD STANDARD FOR PREDICTING SIGNIFICANT FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS
Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 COULD SERUM LAMININ REPLACE LIVER BIOPSY AS GOLD STANDARD FOR PREDICTING SIGNIFICANT FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Laura Smart 9/22/2011
 Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Overall Goals and Objectives for Transplant Hepatology EPAs:
 Overall Goals and Objectives for Transplant Hepatology EPAs: 1. DIAGNOSTIC LIST During the one-year Advanced Pediatric Transplant Hepatology Program, fellows are expected to develop comprehensive skills
Overall Goals and Objectives for Transplant Hepatology EPAs: 1. DIAGNOSTIC LIST During the one-year Advanced Pediatric Transplant Hepatology Program, fellows are expected to develop comprehensive skills
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease. Naveen Gara, MD
 Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES
 Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
Autoimmune hepatitis
 Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant
 SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER
 HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
Histopathology of De Novo Autoimmune Hepatitis
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 18:811-818, 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of De Novo Autoimmune Hepatitis Ananya Pongpaibul, 1 Robert S. Venick, 2 Sue V. McDiarmid, 3 and Charles R. Lassman 4 1 Department
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 18:811-818, 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of De Novo Autoimmune Hepatitis Ananya Pongpaibul, 1 Robert S. Venick, 2 Sue V. McDiarmid, 3 and Charles R. Lassman 4 1 Department
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
No evidence of C4d association with AMR However, C3d and AMR correlated well
 C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
Liver 102: Injury and Healing
 Liver 102: Injury and Healing Dawn Pease, MSN, RN, ANP-BC Brackenridge Specialty Clinics University Medical Center Brackenridge Austin, TX Seton Healthcare Family Liver 102 Outline Biochemical patterns
Liver 102: Injury and Healing Dawn Pease, MSN, RN, ANP-BC Brackenridge Specialty Clinics University Medical Center Brackenridge Austin, TX Seton Healthcare Family Liver 102 Outline Biochemical patterns
Case #1. Digital Slides 11/6/ year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests. Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis
 45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D
 BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
BSG/ACP annual course Royal College of Pathologists Infections and Inflammations of the Hepato-Biliary System Hepatitis B and D Amar Paul Dhillon Royal Free & University College Medical School Thurs 10
New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV
 New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV Jidong Jia, MD, PhD Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University 2016-3-14 Disclosure Consultation for Abbvie
New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV Jidong Jia, MD, PhD Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University 2016-3-14 Disclosure Consultation for Abbvie
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Induction Immunosuppression With Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin in Pediatric Liver Transplantation
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 12:1210-1214, 2006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction Immunosuppression With Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin in Pediatric Liver Transplantation Ashesh Shah, 1 Avinash Agarwal, 1 Richard Mangus,
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 12:1210-1214, 2006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction Immunosuppression With Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin in Pediatric Liver Transplantation Ashesh Shah, 1 Avinash Agarwal, 1 Richard Mangus,
Management of Rejection
 Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Chronic liver allograft dysfunction. An unsolved problem
 Chronic liver allograft dysfunction An unsolved problem % patient survival % patient survival 100 Kaplan-Meier estimates by sex and age group 100 90 90 80 80 70 70 60 60 50 50 40 40 30 20 10 Males Females
Chronic liver allograft dysfunction An unsolved problem % patient survival % patient survival 100 Kaplan-Meier estimates by sex and age group 100 90 90 80 80 70 70 60 60 50 50 40 40 30 20 10 Males Females
Serologic Markers CONVENTIONAL ANTIBODIES ANTIBODIES UNCONVENTIONAL. AIH Type I
 Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology
 Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis
 Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
 The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies
 4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Supplemental Tables. Parasitic Schistosomiasis increase < 1. Genetic Hemochromatosis increase < 1. autoimmune Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) increase < 1
 Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1 Various etiologies of liver cirrhosis and their association with liver stiffness and AST/ALT ratio Disease category Cause Example LS AST/ALT Inflammatory liver
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France 41 year-old woman, coming to emergency department for fatigue
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France 41 year-old woman, coming to emergency department for fatigue
Case Report of Successful Treatment of Fibrosing Cholestatic Hepatitis C with Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin after Liver Transplantation
 108 Diagnostic Problems in Hepatology Case Report of Successful Treatment of Fibrosing Cholestatic Hepatitis C with Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin after Liver Transplantation Brian Kim, MD 1 Anshu Trivedi, MD
108 Diagnostic Problems in Hepatology Case Report of Successful Treatment of Fibrosing Cholestatic Hepatitis C with Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin after Liver Transplantation Brian Kim, MD 1 Anshu Trivedi, MD
Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft. Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
 Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 Gerald J Berry, MD Professor of Pathology Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 Gerald J Berry, MD Professor of Pathology Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist Andrew Aronsohn, MD Associate Professor of Medicine University of Chicago Chicago, Illinois Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist Andrew Aronsohn, MD Associate Professor of Medicine University of Chicago Chicago, Illinois Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
(C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes
 (A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
(A) (B) (C) Fig 5.1 Classical non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation (the trio of changes representing the minimal histological criteria of steatohepatitis)
Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver
 Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver Kirk D. Jones, MD and Linda D. Ferrell, MD W i several thousand liver transplants being performed each year and many patients being managed in
Interpretation of Biopsy Findings in the Transplant Liver Kirk D. Jones, MD and Linda D. Ferrell, MD W i several thousand liver transplants being performed each year and many patients being managed in
Long term liver transplant management
 Long term liver transplant management Dr Bill Griffiths Cambridge Liver Unit Royal College of Physicians 5.7.17 Success of Liver Transplantation Current survival, 1 st elective transplant: 1 yr survival
Long term liver transplant management Dr Bill Griffiths Cambridge Liver Unit Royal College of Physicians 5.7.17 Success of Liver Transplantation Current survival, 1 st elective transplant: 1 yr survival
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
Withdrawal of Immunosuppression in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients in Korea
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.784 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(6): 784-788, 2009 Withdrawal of Immunosuppression in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients in Korea Jee
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.784 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(6): 784-788, 2009 Withdrawal of Immunosuppression in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients in Korea Jee
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI
 Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis
 What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis A combination of improved surgical techniques, donor organ preservation, selection
What s new in liver transplantation? Romil Saxena, MD, FRCPath (UK) Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis A combination of improved surgical techniques, donor organ preservation, selection
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Anatomic Pathology / MINOCYCLINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Minocycline as a Cause of Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Report of Four Cases and Comparison With Autoimmune Hepatitis Neal S. Goldstein,
Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases
 4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation. Dr.E Nemati. Professor of Nephrology
 Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings
 6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant
 ArtIcle Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant Kemal Murat Haberal, 1 Hale Turnaoğlu, 1 Adnan
ArtIcle Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant Kemal Murat Haberal, 1 Hale Turnaoğlu, 1 Adnan
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials
 The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
MP Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation. VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014
 NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease
 Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern. November 14th, 2018
 Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies
 Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Renal Pathology- Transplantation. Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic
 Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Defining the need for Liver Transplantation
 Autoimmune Hepatitis: Defining the need for Liver Transplantation Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London Outline Autoimmune Hepatitis Background
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Defining the need for Liver Transplantation Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London Outline Autoimmune Hepatitis Background
Xiao-Ling Chi, Mei-Jie Shi, Huan-Ming Xiao, Yu-Bao Xie, and Gao-Shu Cai. Correspondence should be addressed to Xiao-Ling Chi;
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice
 Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice Donald G. Ormonde,* W. Bastiaan de Boer, Anthony Kierath, Roger Bell, Keith B. Shilkin, Anthony K. House, Gary P. Jeffrey,*,
Banff Schema for Grading Liver Allograft Rejection: Utility in Clinical Practice Donald G. Ormonde,* W. Bastiaan de Boer, Anthony Kierath, Roger Bell, Keith B. Shilkin, Anthony K. House, Gary P. Jeffrey,*,
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Objective At the end of this lecture, the learner will be able to: Outline the appropriate evaluation of a person infected with HCV in order to assess the benefits and risks of
Pretreatment Evaluation Objective At the end of this lecture, the learner will be able to: Outline the appropriate evaluation of a person infected with HCV in order to assess the benefits and risks of
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO
 PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning
 Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Effect of the number of portal area on modified histological activity index of viral hepatitis and histological findings
 Original Article Effect of the number of portal area on modified histological activity index of viral hepatitis and histological findings M Gurbuzel, G Saygı, F Ozyigit 1, AF Oguzoncül 2, HG Gulsen 3,
Original Article Effect of the number of portal area on modified histological activity index of viral hepatitis and histological findings M Gurbuzel, G Saygı, F Ozyigit 1, AF Oguzoncül 2, HG Gulsen 3,
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management
 HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy. Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH
 Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient Elastography in Diabetics with Fatty Liver A Single Center Cross Sectional observational Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes
 A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes DR A. WITHERS, DR A. GRIEVE DEPARTMENT OF PAEDIATRIC SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
A review of histological parameters and CMV serology in Biliary atresia, and its relationship to long-term outcomes DR A. WITHERS, DR A. GRIEVE DEPARTMENT OF PAEDIATRIC SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network
 Evidence Note Number 82 July 2018 In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic
Evidence Note Number 82 July 2018 In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic
