Acute carbon monoxide poisoning in a regional hospital in Hong Kong: historical cohort study
|
|
|
- Stewart Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original ARTICLE Acute carbon monoxide poisoning in a regional hospital in Hong Kong: historical cohort study MY Chan *, Thomas TS Au, KS Leung, WW Yan This article was published on 15 Jan 2016 at A B S T R A C T Objectives: This study aimed to describe the clinical profiles of all patients with carbon monoxide poisoning admitted to a regional hospital in order to enhance the vigilance of health care professionals for delayed neurological sequelae associated with carbon monoxide poisoning and to identify the prognostic factors associated with their development. This study also aimed to assess the impact of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on the development of delayed neurological sequelae in these patients. Methods: This was a historical cohort study in which all patients with a diagnosis of carbon monoxide poisoning managed in a regional hospital in Hong Kong from 12 February 2003 to 8 November 2013 were recruited. Main outcome measures included delayed neurological sequelae. Results: Of the clinical profiles of 93 patients analysed, 24 patients received hyperbaric oxygen therapy and did not develop delayed neurological sequelae. Seven patients who did not receive hyperbaric oxygen therapy developed delayed neurological sequelae. Comparison of groups with and without delayed neurological sequelae (excluding hyperbaric oxygen therapy treated patients) revealed that loss of consciousness (P=0.038), Glasgow Coma Scale score of 3 (P=0.012), elevated troponin level (P<0.001), higher creatine kinase level (P=0.008), and intubation requirement (P=0.007) were possible prognostic factors for the development of delayed neurological sequelae. Conclusion: Although not statistically significant, this study showed a 100% protective effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy against development of severe delayed neurological sequelae in patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Further study with better study design is warranted. Loss of consciousness, low Glasgow Coma Scale score, intubation requirement, elevated troponin and higher creatine kinase levels were possible prognostic factors for development of delayed neurological sequelae in patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning. A well-defined treatment protocol, appropriate follow-up duration and neuropsychiatric tests together with a hospital-based hyperbaric chamber are recommended for management of patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Hong Kong Med J 2016;22:46 55 DOI: /hkmj MY Chan *, FHKCEM, FHKAM (Emergency Medicine) 1 TTS Au, FHKCEM, FHKAM (Emergency Medicine) 1 KS Leung, FHKCEM, FHKAM (Emergency Medicine) 2 WW Yan, FHKAM (Medicine) 1 Accident and Emergency Department 2 Department of Intensive Care Unit Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Chai Wan, Hong Kong * Corresponding author: odin@ha.org.hk New knowledge added by this study Loss of consciousness, low Glasgow Coma Scale score, intubation requirement, and elevated troponin and creatine kinase levels were possible prognostic factors for development of delayed neurological sequelae in patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Presentation of neurological sequelae can be delayed from a few months to a year. Implications for clinical practice or policy A hospital-based hyperbaric oxygen chamber is recommended to decrease the burden of off-site therapy for patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning and to facilitate timely treatment in a safe environment in Hong Kong. A well-defined treatment protocol with adequate follow-up and neuropsychiatric tests are recommended for patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Introduction Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning was not common in Hong Kong prior to The first reported case of CO poisoning from suicidal charcoal burning occurred in 1998 in Hong Kong. A middle-aged woman who was a chemical engineer invented this method of suicide that became the third most common method in Hong Kong within 2 months 46 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
2 # Acute carbon monoxide poisoning # of her death and the associated publicity. 1 To date, suicidal charcoal burning remains the top cause of suicidal death in this crowded and stressful city. Victims of CO poisoning are sent to either the mortuary or public hospitals in Hong Kong. Most patients who are admitted to hospitals eventually survive with supportive management but there is no standard treatment protocol. Treatment regimens varied in different hospitals at different times. Cases of delayed neurological sequelae (DNS) secondary to CO poisoning are well reported in the literature. 2-6 In a Cochrane review in 2011, it was stated It is possible that some patients, particularly those with more severe poisoning, may derive benefit from [hyperbaric oxygen] treatment, but this remains unproven. 7 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is now a standard treatment option in many developed countries and China for selected patients with severe CO poisoning. According to Lam et al in 2006, 8 the incidence of DNS in Hong Kong was 3.4%, which was much lower than other reported rates of 10% to 30%. 2-7 The overall incidence of DNS is likely to have been underdiagnosed and under-reported in Hong Kong because of a lack of detailed neurological examination and neuropsychiatric tests during acute management and follow-up sessions. Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital (PYNEH) has been one of the pioneer hospitals to support HBOT for CO poisoning in Hong Kong. The lack of a hospital-based hyperbaric oxygen chamber in Hospital Authority (HA) hospitals in Hong Kong has limited the number of HBOT sessions administered to patients with CO poisoning, particularly those with severe poisoning, because of the risks associated with patient management at a remote site deprived of medical support. Special arrangements would currently be required to send a patient to Ngong Shuen Chau for HBOT. To date, PYNEH has been the principal advocator of HBOT for CO poisoning patients in Hong Kong and has treated the largest number of severe cases. This 10-year retrospective study aimed to describe the clinical profile of all CO poisoning patients admitted to PYNEH with the aim of improving vigilance of health care professionals for DNS associated with CO poisoning and identifying the prognostic factors for their development. The study also aimed to assess the impact of HBOT on the development of DNS in these patients. Methods Data collection Patients with a diagnosis of CO poisoning documented in the Clinical Management System (CMS) of the HA and being managed at PYNEH between 12 February 2003 and 8 November 2013 were 急性一氧化碳中毒在香港一所分區醫院的歷史隊列研究 陳銘賢 歐德信 梁啟城 殷榮華 目的 : 描述所有入住一所分區醫院的一氧化碳中毒患者的臨床情況, 從而加強醫療界人士對一氧化碳中毒與遲發性神經系統後遺症 (DNS) 的警惕性和識別 DNS 的預後因素 本研究也旨在評估高壓氧治療對 DNS 發展的影響 方法 : 這項歷史隊列研究納入由 2003 年 2 月 12 日至 2013 年 11 月 8 日期間, 於香港一所分區醫院確診一氧化碳中毒的患者 主要結果測量包括 DNS 結果 : 分析了 93 名符合研究納入標準的患者, 其中 24 人接受高壓氧治療而沒有出現 DNS 沒有接受高壓氧治療的患者中,7 人出現 DNS 比較 DNS 和非 DNS 組別 ( 不包括高壓氧治療的患者 ) 後發現, 對發展 DNS 的可能預後因素分別為 : 昏倒 (P=0.038) 格拉斯哥昏迷指數 (GCS) 為 3(P=0.012) 心肌鈣蛋白水平上升(P<0.001) 肌酸激水平上升 (P=0.008) 以及氣管插管 (P=0.007) 結論 : 儘管統計上不顯著, 本研究顯示高壓氧治療對嚴重一氧化碳中毒患者提供了 100% 防止 DNS 的保護作用 須進一步使用更好的研究設計來探討這問題 昏倒 低 GCS 氣管插管以及提升心肌肌鈣蛋白和肌酸激水平是可能的 DNS 預後因素 在此建議要治療嚴重一氧化碳中毒的病人, 須先定立一個明確的治療方案再加上適當的精神情緒測試和覆診時間表及一所位於醫院內的高壓氧氣艙 included. This entailed recourse to the Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System (CDARS) of the HA. Relevant accident and emergency notes, radiological reports, laboratory results, and discharge summaries were retrieved. The following were recorded where available: age, sex, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, electrocardiogram (ECG), Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score at presentation, endotracheal intubation, history of or presence of loss of consciousness (LOC), blood tests for carboxyhaemoglobin (COHb) level, creatine kinase (CK) level, troponin (Tn) level, HBOT, complications from HBOT, development of DNS, co-ingestion, suicidal methods and intention. Case selection of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in our hospital The use of HBOT for severe CO poisoning was advocated in the Intensive Care Unit of PYNEH after The need for HBOT in patients who presented with CO poisoning was judged on a case-by-case basis. The indications for and contra-indications to HBOT for patients with severe CO poisoning are summarised in Table 1. The treatment protocol of HBOT for CO poisoning at Ngong Shuen Chau is shown in the Figure. Most patients were given Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
3 # Chan et al # TABLE 1. Indications and contra-indications for HBOT in patients with severe CO poisoning, with reference to the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society Indication/contra-indication Indications of HBOT for patients with severe CO poisoning features* Absolute contra-indications for HBOT Relative contra-indications for HBOT Description 1. LOC or history of LOC suspected to be caused by CO poisoning 2. Evidence of myocardial ischaemia with typical chest symptoms or electrocardiogram changes 3. COHb level >25% on admission (not absolute) 4. Pregnancy 1. Untreated pneumothorax 2. Refusal by patient or their proxies 3. High requirement of oxygen concentration (eg FiO 2 0.5, mechanical ventilation is not a contra-indication) 4. Some selected medications Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity may occur Cisplatinum wound healing may be impaired Disulfiram blocks the production of superoxide dismutase, which protects against oxygen toxicity Mafenide acetate wound healing may be impaired 1. Haemodynamically unstable (need for vasopressor/inotropes and at risk during transportation) 2. Asthma (medication required to control the condition) 3. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/bullous emphysema 4. Claustrophobia, emotionally unstable or seizures (medications, eg benzodiazepines, for controlling anxiety, insomnia, agitation, or seizures) 5. Ear or sinus surgery 6. Optic neuritis 7. Recent thoracic surgery 8. Upper respiratory infections 9. Pacemakers (their technical specifications should be reviewed prior to treatment to avoid deformation) Abbreviations: CO = carbon monoxide; COHb = carboxyhaemoglobin; FiO 2 = fraction of inspired oxygen; HBOT = hyperbaric oxygen therapy; LOC = loss of consciousness; PYNEH = Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital * Adopted in intensive care unit of PYNEH since ATA Pressure 1 ATA Patients Patients Time (mins) Patients & attendant Oxygen Air FIG. Treatment protocol of HBOT for carbon monoxide poisoning in Ngong Shuen Chau (Royal Navy table 60) Abbreviations: ATA= atmosphere absolute; HBOT = hyperbaric oxygen therapy three sessions of HBOT over 3 consecutive days. Exceptions included refusal by patients or their relatives, or operational difficulties. Statistical analyses Univariate analysis for the development of DNS was done by the Fisher s exact test for dichotomous variables and the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables, with respect to the following factors: age, sex, source of CO, cause of CO poisoning, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, GCS, GCS=3, LOC, COHb level, COHb level >25%, Tn level, Tn level >0.03 ng/ ml, CK level, CK level >200 IU/L, ECG ischaemic changes, endotracheal intubation, co-ingestion, and HBOT. The distribution of Tn and CK levels showed positive skewness, thus the parameters were expressed in terms of means and standard deviations, as well as medians and interquartile ranges. All statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (Windows version 22.0; SPSS Inc, Chicago [IL], US). The level of statistical significance was set at Results A total of 95 cases were diagnosed with CO poisoning during the study period. One case was excluded because the patient presented with cardiac arrest and succumbed shortly after admission before any blood tests were performed. Another case of DNS that resulted in convulsion, dysphasia, and double incontinence was excluded as the acute CO poisoning event occurred in Manila. The remaining 93 cases were recruited for analysis. All the demographic data and blood test results are shown in Table 2. Among the 93 patients analysed, 24 received HBOT; DNS had not developed in this group of patients. Nonetheless DNS had developed in seven patients who did not undergo HBOT. Patients with delayed neurological sequelae Among the seven cases of DNS where patients did not undergo HBOT, no formal follow-up had 48 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
4 # Acute carbon monoxide poisoning # TABLE 2. Demographic data and investigation results of all cases and comparative univariate analysis between the DNS and non- DNS groups Mean ± SD or No. (%) of patients* All cases (n=93) DNS (n=7) Non-DNS (n=86) P value Age (years) 35.6 ± ± ± Male 46.0% 57.1% 46.5% Source of CO Charcoal burning 80 (86.0%) 7 (100%) 73 (84.9%) Fire accident 6 (6.5%) 0 6 (7.0%) LPG leakage/bathing 4 (4.3%) 0 4 (4.7%) Town gas inhalation 3 (3.2%) 0 3 (3.5%) Cause Suicidal 83 (89.2%) 7 (100%) 76 (88.4%) Accidental 10 (10.8%) 0 10 (11.6%) Systolic BP (mm Hg) 126 ± ± ± Diastolic BP (mm Hg) 76 ± ± ± Heart rate (beats/min) 101 ± ± ± Temperature ( C) 36.7 ± ± ± GCS 11.5 ± ± ± GCS=3 11 (11.8%) 3 (42.9%) 8 (9.3%) LOC 51 (54.8%) 6 (85.7%) 45 (52.3%) COHb level (%) 21.8 ± ± ± COHb level >25% 38 (40.9%) 3 (42.9%) 35 (40.7%) Troponin (ng/ml) Mean ± SD 0.69 ± ± ± Median, IQR 0.02, , , 0.35 Troponin >0.03 ng/ml 22/49 (44.9%) 4/4 (100%) 18/45 (40.0%) CK (IU/L) [n=61] Mean ± SD 2368 ± ± ± Median, IQR 200, , , 669 CK >200 IU/L 30/61 (49.2%) 5/6 (83.3%) 25/55 (45.5%) ECG changes 9/90 (10.0%) 1/6 (16.7%) 8/84 (9.5%) Endotracheal intubation 25 (26.9%) 4 (57.1%) 21 (24.4%) Co-ingestion 42 (45.2%) 4 (57.1%) 38 (44.2%) HBO treatment 24 (25.8%) 0 24 (27.9%) Abbreviations: BP = blood pressure; CK = creatine kinase; CO = carbon monoxide; COHb = carboxyhaemoglobin; DNS = delayed neurological sequelae; ECG = electrocardiogram; GCS = Glasgow Coma Scale score; HBO = hyperbaric oxygen; IQR = interquartile range; LOC = loss of consciousness; LPG = liquefied petroleum gas; SD = standard deviation * Unless otherwise indicated been arranged to detect DNS associated with CO poisoning. Nonetheless, DNS was diagnosed in these cases because the neurological symptoms became evident during the same episode of hospitalisation, or the neurological symptoms were detected by their caretakers after the initial hospitalisation. The clinical profiles of these DNS patients with radiological confirmation are summarised in Table 3. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy There were 24 patients treated with HBOT. Their mean age was 36.3 (range, 19-61) years and the male-to-female ratio was 1:1. Of these 24 patients, the source of CO poisoning in 23 (96%) was charcoal burning and one (4%) patient had accidental CO poisoning due to leakage of a liquid petroleum gas combustion system while bathing. In 21 (87.5%) Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
5 # Chan et al # TABLE 3. Descriptive summary of the seven patients with DNS Patient No. Age (years)/ sex COHb (%) Day of discharge Presentation time DNS feature of DNS* Hospital Radiological findings stay for DNS 1 31/F 38.9 Day 1 1 Year Convulsion 5 Days CT brain showed hypodensities in globus pallidus 2 30/M 34.3 Day Days Dull, convulsion, bedbound with sacral sore 3 24/M 39 Day 17 1 Month Unsteady gait, parkinsonism, incontinence; MMSE=13/ /F 5.3 After O 2 given for hours 5 24/M 12.8 After O 2 given for hours 6 55/M 4.7 After O 2 given for hours 7 65/F 7.3 After O 2 given for hours Day 5 10 Months Parkinsonism, memory and functional deterioration with irritable mood; MMSE=27/30 N/A 1 Month Unsteady gait, walked with frame N/A 2 Weeks Bedbound tube feeding and noncommunicable; MMSE=8/30, convulsion Day 21 1 Month Dull and slow in response; MMSE=13/30 6 Months MRI showed globus pallidus lesions with periventricular deep white matter T2 signal 3 Months CT brain showed diffuse bilateral symmetrical hypodense areas in cerebral hemispheres. Subtle bilateral pallidal hypodensities 2 Months CT brain showed hypodense lesions in bilateral basal ganglia 1 Year MRI brain showed patchy areas of non-enhancing T1 isointense to mildly hyperintense, T2 and flair hyperintense signal changes over bilateral frontal and occipital subcortical and deep white mater, bilateral globus pallidus, and bilateral cerebral peduncles 2 Months rehabilitation hospital and 1- year old-aged home care MRI brain showed T2 hyperintensities over bilateral cerebral hemispheric white matter 4 Months MRI brain showed periventricular T2/FLAIR hyperintense foci involving bilateral white matter Outcome as of December 2014 Independent ADL Unstable gait, wheelchair for outdoor activities Independent ADL Independent ADL Live in hostel, left upper limb contracture, bilateral lower limb involuntary movement Bedbound with features of parkinsonism MMSE=26/30 Reason for no HBOT Before 2008 Before 2008 Before 2008 Before 2008 History of recurrent pneumothorax No HBOT in Ruttonjee Hospital Refused HBOT Abbreviations: ADL = activity of daily living; COHb = carboxyhaemoglobin; CT = computed tomography; DNS = delayed neurological sequelae; FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; HBOT = hyperbaric oxygen therapy; MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination score; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; N/A = not applicable; O 2 = oxygen * Refer to the time after CO poisoning patients, LOC developed prior to admission. There were four (17%) patients with GCS score of 15/15 and 20 (83%) patients with GCS score of 3-14/15. The mean COHb level was 29.2% (range, 3.3%-48.7%); Tn level was elevated in 15 (78.9%) of 19 cases; CK level was elevated in 13 (65%) of 20 cases; ECG showed acute ischaemic changes in five (21%) cases. No DNS developed in patients treated with HBOT. Complications of hyperbaric oxygen therapy Complications secondary to HBOT developed in three patients: perforated tympanic membrane in one patient, left otitis media related to grommet insertion before HBOT in one, and barotrauma with left ear pain due to blockage of the myringotomy site in another who required repeated myringotomy. Nonetheless all patients completed the whole course of HBOT without long-term sequelae. Patients with carbon monoxide poisoning and acute ischaemic electrocardiographic changes The most common ischaemic change on ECG was ST segment depression. Acute ischaemic changes were evident in nine patients. Their mean age was 42 (range, 27-61) years, and the male-to-female ratio was 5:4. Eight (89%) cases committed suicide by charcoal burning and one (11%) patient had CO poisoning due to an accidental fire. In seven (78%) patients, LOC developed prior to admission. There 50 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
6 # Acute carbon monoxide poisoning # was one (11%) patient with GCS score of 15/15, and eight (89%) patients with score of 3-14/15. The mean COHb level was 24.3% (range, 3.9%-48.7%); Tn level was elevated in seven (78%) patients and CK level was elevated in four (44%). The HBOT was offered to five (56%) patients with ischaemic ECG changes and DNS developed in one (11%) patient. Detailed descriptive analysis of the GCS of all patients showed a bimodal distribution with one mode at GCS of 3 points and the other at GCS of 15 points. Thus, GCS of 3 points was used as an indicator of severe CO poisoning. One of the clinical indications for HBOT was COHb level of >25% and served as another indicator of severe CO poisoning. Thus, GCS of 3 and COHb level of >25% were tested as possible prognostic factors for DNS. Due to variations in the clinical management, blood tests for Tn and CK were not carried out in all patients. Elevated Tn was defined as serum Tn level of >0.03 ng/ml on admission. Level of Tn was not checked throughout the clinical course in 44 patients but was elevated in 22 and normal in 27. Elevated CK was defined as serum CK level of >200 IU/L. This value was used for simplicity as the upper limit of normal is 180 IU/L in our laboratory. Level of CK was not checked throughout the clinical course in 32 patients but was raised in 30 and normal in 31. Comparative statistical analysis showed that the DNS group had significantly lower GCS score, a greater proportion of patients with GCS of 3 points, and higher levels of Tn (Table 2). However, CK levels were significantly higher in the non-dns than in the DNS group, although the proportions of elevated CK were not statistically significant. The higher CK level in the non-dns group can be explained by one single case of severe CO poisoning with prolonged LOC, pressure sores, and compartment syndrome leading to a supremely high CK level of IU/L on admission. The result is better illustrated by comparison of the median and interquartile range as shown in Table 2. The association between the possible benefit of HBOT and DNS was not TABLE 4. Comparative univariate analysis of DNS and non-dns groups, with HBOT-treated patients excluded DNS (n=7) Mean ± SD or No. (%) of patients* Non-DNS excluding HBOT (n=62) P value Age (years) 36.9 ± ± Male 57.1% 43.5% Systolic BP (mm Hg) 117 ± ± Diastolic BP (mm Hg) 70 ± ± Heart rate (beats/min) 104 ± ± Temperature ( C) 37.6 ± ± LOC 6 (85.7%) 24 (38.7%) GCS 7.6 ± ± GCS=3 3 (42.9%) 3 (4.8%) COHb level (%) 20.3 ± ± COHb level >25% 3 (42.9%) 20 (32.3%) Tn level (ng/ml) [n=29] Mean ± SD 2.56 ± ± 0.1 <0.001 Median, IQR 2.72, , <0.001 Tn >0.03 ng/ml (n=29) 4/4 (100%) 3/25 (12%) CK (IU/L) [n=41] Mean ± SD 1830 ± ± 2019 Median, IQR 1370, , 322 CK >200 IU/L (n=41) 5/6 (83.3%) 12/35 (34.3%) ECG changes 1/6 (16.7%) 3/60 (5%) 0.22 Intubation 4 (57.1%) 6 (9.7%) Co-ingestion 4 (57.1%) 31 (50.0%) Abbreviations: BP = blood pressure; CK = creatine kinase; COHb = carboxyhaemoglobin; DNS = delayed neurological sequelae; ECG = electrocardiogram; GCS = Glasgow Coma Scale score; HBOT = hyperbaric oxygen therapy; IQR = interquartile range; LOC = loss of consciousness; SD = standard deviation; Tn = troponin * Unless otherwise indicated Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
7 # Chan et al # statistically significant (P=0.184). In order to identify possible prognostic factors for DNS development and to eliminate the possible effect of HBOT, a second comparative analysis was performed between the DNS group and non-dns group after excluding those patients treated by HBOT (Table 4). This second analysis showed that when compared with the non-dns group, the DNS group had a significantly greater proportion of patients with LOC and GCS score of 3, lower GCS score, higher levels of Tn and CK, higher proportion of patients with elevated Tn, and higher tendency to have been intubated. Since the HBOT group did not develop DNS and the DNS group did not receive HBOT, another univariate analysis was performed to detect any significant difference between these two groups (Table 5). This showed that the DNS and HBOT groups were similar for all the above tested variables, except for the Tn level that was significantly higher in the DNS group. The proportion of patients with elevated Tn was similar for the two groups, however. Discussion Pathophysiology of carbon monoxide poisoning Carbon monoxide is a colourless, odourless, nonirritating but highly toxic gas produced during incomplete carbon combustion. A small amount of CO is produced after degradation of heme physiologically in human body. 9 Poisoning of CO develops only after the dose exceeds the elimination capacity. The elimination half-life of COHb in humans is approximately 208 to 358 minutes in room air, minutes in normobaric oxygen therapy, 11 and 20 minutes in 3 atmosphere absolute pressure of HBOT. 12 Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochrome oxidase with an affinity of 200 to 300 times, 30 to 60 times, and 9 times more than oxygen, respectively. The decrease in oxygen carrying and delivery capacity of blood results in tissue hypoxia. 13 Cellular hypoxia causes the release of free radicals that bind with nitric oxide (NO) from heme to produce peroxynitrite (ONOO ), further TABLE 5. Comparative univariate analysis of DNS and HBOT groups DNS (n=7) Mean ± SD or No. (%) of patients* HBOT (n=24) P value Age (years) 36.9 ± ± Male 57.1% 50% Systolic BP (mm Hg) 117 ± ± Diastolic BP (mm Hg) 70 ± ± Heart rate (beats/min) 104 ± ± Temperature ( C) 37.6 ± ± LOC 6 (85.7%) 21 (87.5%) GCS 7.6 ± ± GCS=3 3 (42.9%) 5 (20.8%) COHb level (%) 20.3 ± ± COHb level >25% 3 (42.9%) 15 (62.5%) Tn level (ng/ml) [n=23] Mean ± SD 2.56 ± ± Median, IQR 2.72, , Tn >0.03 ng/ml (n=23) 4/4 (100%) 15/19 (78.9%) CK (IU/L) [n=26] Mean ± SD 1830 ± ± Median, IQR 1370, , 2402 CK >200 IU/L (n=26) 5/6 (83.3%) 13/20 (65%) ECG changes 1/6 (16.7%) 5/24 (20.8%) Intubation 4 (57.1%) 15 (62.5%) Co-ingestion 4 (57.1%) 9 (37.5%) Abbreviations: BP = blood pressure; CK = creatine kinase; COHb = carboxyhaemoglobin; DNS = delayed neurological sequelae; ECG = electrocardiogram; GCS = Glasgow Coma Scale score; HBOT = hyperbaric oxygen therapy; IQR = interquartile range; LOC = loss of consciousness; SD = standard deviation; Tn = troponin * Unless otherwise indicated 52 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
8 # Acute carbon monoxide poisoning # inhibiting cytochrome oxidase and resulting in DNA damage and apoptosis The clinical presentation of cherry-like skin discolouration is secondary to the red colour of COHb and CO-induced vasodilation. Headache from CO poisoning is likely mediated by extracerebral and intracerebral vasodilation with displacement of NO from heme by CO. 15,17 On the other hand, DNS is likely to be caused by the combination of COHb, mitochondrial oxidative stress, NO, ONOO, oxygen free radicals, apoptosis, immune-mediated injury, inflammatory response, brain lipid peroxidation, and other unknown mechanisms Delayed neurological sequelae There is no universal agreed definition of DNS following CO poisoning. It is typically preceded by a lucid period of 2 to 40 days after the initial poisoning. 20 Clinical manifestations range from impairment of concentration, attention, learning, memory, language and motor function, as well as psychiatric functions such as depression, dementia, psychosis and mutism, to neurological dysfunction such as paralysis, convulsion, urine or faecal incontinence, gait disturbance, and Parkinson-like syndrome. According to the uniqueness of the health care system in Hong Kong, there is more than a 90% chance that patients with severe DNS will rely on the public sector for further management. In addition, all cases were analysed for detection of DNS until December 2014 in this study. All cases were followed up by CMS record for more than 1 year, thus most patients in this cohort who developed severe DNS should have been captured. Contrary to the current belief that onset of DNS development ranges typically from a few days to a few weeks, 23 this study showed that DNS might present as late as 6 months to 1 year after the index CO poisoning. Regular follow-up is required to detect the onset of DNS. Further studies are necessary to determine the optimum follow-up duration for DNS. All seven DNS cases illustrated that DNS secondary to CO poisoning can be very debilitating to both patients and their caretakers. Of 93 patients, only 55 (59.1%) were followed up in our psychiatric unit. None of the 93 patients with CO poisoning were followed up in our medical unit. No mild-tomoderate case of DNS was reported in this study, probably due to the absence of a standardised treatment protocol and formal neuropsychiatric tests for detection of DNS secondary to CO poisoning. It is therefore likely that cases of mild-to-moderate DNS are underdiagnosed and under-reported in Hong Kong. In order to diagnose DNS secondary to CO poisoning, a standardised treatment protocol with adequate follow-up and neuropsychiatric tests is recommended. We identified the following prognostic factors associated with DNS development in patients with severe CO poisoning: LOC, lower GCS score, GCS score of 3, intubation requirement, elevated Tn level, and higher levels of Tn and CK. Other investigational prognostic markers reported worldwide include S100B protein, 24 low Mini-Mental State Examination score, 25 positive computed tomography of brain, 25,26 and plasma copeptin. 27 The results of this study reveal that severe DNS did not develop in any patient with severe CO poisoning who was treated with HBOT at PYNEH between 2008 and Although the results did not reach statistical significance due to limited sample size, this 100% protective effect indicates a potential clinical benefit of HBOT to prevent severe DNS in patients with severe CO poisoning. In order to look for potential selection bias between the DNS group and HBOT group, comparative univariate analysis between the DNS and HBOT groups was performed (Table 5). The DNS groups and HBOT groups were similar in terms of the initial presentation. Although the magnitude of Tn level in the DNS group (2.56 ± 1.3 ng/ml) was statistically greater than that of HBOT group (1.10 ± 2.6 ng/ml) with a P value of 0.015, it was not clinically significant in terms of patient management. The sole different factor was the treatment of HBOT. It is strongly suggested that HBOT prevents DNS development in severe CO poisoning. The role of HBOT in the management of patients with CO poisoning remains controversial with conflicting results from large randomised controlled trials. All trials have been criticised for bias, thus there has been a pledge for a betterdesigned trial with multicentre participation. Nonetheless ethical, financial, and practical issues associated with most clinical toxicology studies make such a trial unlikely in the near future. The results of this study did show clinical significance despite a statistically insignificant result. Current literature supports the potential of HBOT to prevent or treat DNS resulting from CO poisoning. 2,4-7,22 On balance, HBOT should be considered for all patients at risk of development of neurological sequelae. 22 In Hong Kong, HBOT has been underutilised in public hospitals because of the unavailability of hospital-based hyperbaric chambers. Most patients in Hong Kong with severe CO poisoning do not receive HBOT because of the risks of transporting a critically ill patient to Ngong Shuen Chau, the inadequacy of intensive care support in the hyperbaric chamber of Ngong Shuen Chau, occupational hazards, beliefs of individual health care providers, and availability of expertise. A hospital-based hyperbaric oxygen chamber is essential to decrease the burden of HBOT and provide timely treatment in a safe environment Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
9 # Chan et al # for patients with severe CO poisoning. Records retrieved from CDARS for the period 2003 to 2013 revealed 1451 patients with CO poisoning who presented to HA hospitals. This indicates that approximately two patients with CO poisoning presented to hospitals every 5 days over the last 10 years. According to the indications for HBOT adopted in this study, the percentage of patients in whom HBOT was indicated was 67.7% (63/93). Assuming three sessions of HBOT would have been required for each patient and the percentage of patients requiring HBOT over the last 10 years was 67.7%, it can be estimated that 295 sessions of HBOT would have been required by patients treated in HA hospitals (1451 patients x 67.7% x 3 sessions / 10 years = 295). If a hyperbaric oxygen chamber is available in a public hospital, more patients with CO poisoning can be treated in a safe and controlled environment. Suppose the incidence of DNS in Hong Kong is similar to that worldwide (10%-30%), then 145 to 435 instances of DNS may have been potentially prevented in these 10 years. In addition, the length of stay in hospital may have been significantly decreased. Limitations First, selection bias existed in this study although diagnosis coding entry has been compulsory in the accident and emergency department of PYNEH since It is possible that some patients with CO poisoning were admitted with another principal diagnosis and discharged without coding of CO poisoning. If this is the case, then not all patients with CO poisoning during the study period were retrieved in this study. This was a single-centre study and results might not be applicable to all patients with CO poisoning in Hong Kong. Second, there was information bias due to its retrospective nature. Not all patients were investigated with Tn, CK, and ECG leading to potential bias. The time of investigations and oxygen treatment given to patients were not standardised giving rise to difficulty in interpretation of a relatively low COHb level at presentation. In addition, no neuropsychiatric tests were performed to detect any DNS after CO poisoning, resulting in underdiagnosis of DNS. The strength in information bias is the outcome measurement of DNS and laboratory results that provide an objective measure, unlike a questionnaire. Third, confounding bias was inevitable as 45.2% of patients had co-ingestion of medications or alcohol. This might have influenced the initial clinical presentation as well as the results. Subgroup analysis of different medications was not shown because of the diversities and complexity without significant results. Lastly, despite the length of the study period, the sample size was inadequate to provide statistically significant results. Conclusion Although not statistically significant, this study showed 100% protective effect of HBOT against development of severe DNS in patients with severe CO poisoning. Further study with better study design is warranted. This study revealed that LOC, low GCS score, intubation requirement, elevated Tn and higher CK levels were possible prognostic factors for development of DNS. As there was no standardised treatment protocol and no formal follow-up arranged for detection of DNS in patients with severe CO poisoning, mild-to-moderate DNS was probably underdiagnosed and under-reported in Hong Kong. A well-defined treatment protocol, appropriate follow-up duration, and neuropsychiatric tests together with a hospital-based hyperbaric chamber are recommended for management of patients with severe CO poisoning. Declaration No conflicts of interest were declared by the authors. References 1. Chan KP, Yip PS, Au J, Lee DT. Charcoal-burning suicide in post-transition Hong Kong. Br J Psychiatry 2005;186: Raphael JC, Elkharrat D, Jars-Guincestre MC, et al. Trial of normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen for acute carbon monoxide intoxication. Lancet 1989;2: Hu H, Pan X, Wan Y, Zhang Q, Liang W. Factors affecting the prognosis of patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Am J Emerg Med 2011;29: Scheinkestel CD, Bailey M, Myles PS, et al. Hyperbaric or normobaric oxygen for acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Med J Aust 1999;170: Thom SR, Taber RL, Mendiguren II, Clark JM, Hardy KR, Fisher AB. Delayed neuropsychologic sequelae after carbon monoxide poisoning: prevention by treatment with hyperbaric oxygen. Ann Emerg Med 1995;25: Weaver LK, Hopkins RO, Chan KJ, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen for acute carbon monoxide poisoning. N Engl J Med 2002;347: Buckley NA, Juurlink DN, Isbister G, Bennet MH, Lavonas EJ. Hyperbaric oxygen for carbon monoxide poisoning. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;(4):CD Lam KK, Fung HT, Kam CW. The severity and prognostic markers of 148 cases of carbon monoxide poisoning by burning charcoal. Hong Kong J Emerg Med 2006;13: Owens EO. Endogenous carbon monoxide production in disease. Clin Biochem 2010;43: Bruce EN, Bruce MC. A multicompartment model of carboxyhemoglobin and carboxymyoglobin responses to inhalation of carbon monoxide. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2003;95: Weaver LK, Howe S, Hopkins R, Chan KJ. Carboxyhemoglobin half-life in carbon monoxidepoisoned patients treated with 100% oxygen at atmospheric 54 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
10 # Acute carbon monoxide poisoning # pressure. Chest 2000;117: Peterson JE, Stewart RD. Absorption and elimination of carbon monoxide by inactive young men. Arch Environ Health 1970;21: Coburn RF, Mayers LB. Myoglobin oxygen tension determines from measurements of carboxyhemoglobin in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 1971;220: Zhang J, Piantadosi CA. Mitochondrial oxidative stress after carbon monoxide hypoxia in the rat brain. J Clin Invest 1992;90: Thom SR, Ohnishi TS, Ischiropoulos H. Nitric oxide release by platelets inhibits neutrophil B2 integrin function following acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1994;128: Hardy KR, Thom SR. Pathophysiology and treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 1994;32: Thom SR, Fisher D, Xu YA, Garner S, Ischiropoulos H. Role of nitric oxide-derived oxidants in vascular injury from carbon monoxide in the rat. Am J Physiol 1999;276:H Thom SR. Carbon monoxide-mediated brain lipid peroxidation in the rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990;68: Thom SR. Dehydrogenase conversion to oxidase and lipid peroxidation in brain after carbon monoxide poisoning. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992;73: Thom SR. Antagonism of carbon monoxide mediated brain lipid peroxidation by hyperbaric oxygen. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1990;105: Thom SR, Bhopale VM, Fisher D, Zhang J, Gimotty P. Delayed neuropathology after carbon monoxide poisoning is immune-mediated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101: Weaver LK. Clinical practice: carbon monoxide poisoning. N Engl J Med 2009;369: Choi IS. Delayed neurological sequelae in carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol 1983;40: Park E, Ahn J, Min YG, et al. The usefulness of the serum s100b protein for predicting delayed neurological sequelae in acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2012;50: Ku HL, Yang KC, Lee YC, Lee MB, Chou YH. Predictors of carbon monoxide poisoning induced delayed neuropsychological sequelae. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2010;32: Kudo K, Otsuka K, Yagi J, et al. Predictors for delayed encephalopathy following acute carbon monoxide poisoning. BMC Emerg Med 2014;14: Pang L, Wang HL, Wang ZH, et al. Plasma copeptin as a predictor of intoxication severity and delayed neurological sequelae in acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Peptides 2014;59: Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 1 February
Delayed presentation of symptomatic breast cancers in Hong Kong: experience in a public cancer centre
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Delayed presentation of symptomatic breast cancers in Hong Kong: experience in a public cancer centre TK Yau CW Choi Esther Ng Rebecca Yeung Inda S Soong Anne WM Lee 游子覺蔡卓偉吳如花楊美雲宋崧李詠梅
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Delayed presentation of symptomatic breast cancers in Hong Kong: experience in a public cancer centre TK Yau CW Choi Esther Ng Rebecca Yeung Inda S Soong Anne WM Lee 游子覺蔡卓偉吳如花楊美雲宋崧李詠梅
Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09
 Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09 Objectives Definitions Methodology Equation of Measurement Uncertainty Measurement Uncertainty Goal Examples Uncertainty
Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09 Objectives Definitions Methodology Equation of Measurement Uncertainty Measurement Uncertainty Goal Examples Uncertainty
A cost benefit analysis of weight management strategies
 74 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;15 (Suppl): 74-79 Original Article A cost benefit analysis of weight management strategies Jodie Yates and Chris Murphy Econtech Over the past twenty years, obesity has become
74 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;15 (Suppl): 74-79 Original Article A cost benefit analysis of weight management strategies Jodie Yates and Chris Murphy Econtech Over the past twenty years, obesity has become
Introduction CME. KY Lo *, CK Chan
 CME Original Article Characteristics and outcomes of patients with percutaneous coronary intervention for unprotected left main coronary artery disease: a Hong Kong experience KY Lo *, CK Chan This article
CME Original Article Characteristics and outcomes of patients with percutaneous coronary intervention for unprotected left main coronary artery disease: a Hong Kong experience KY Lo *, CK Chan This article
Surveillance and outcome of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer who had undergone curative-intent operation
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KC Cheng YP Yeung Patrick YY Lau William CS Meng 鄭繼志楊玉鵬劉應裕蒙家興 Surveillance and outcome of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer who had undergone curative-intent
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KC Cheng YP Yeung Patrick YY Lau William CS Meng 鄭繼志楊玉鵬劉應裕蒙家興 Surveillance and outcome of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer who had undergone curative-intent
Clinical Scenario. L1 laminectomy and decompression T11-12, L2-3 posterior instrumented fusion L1 vertebroplasty
 骨科 R1 蔡沅欣 2013.3.18 Clinical Scenario 82 y/o male Fell down about 3 months ago, no significant discomfort, except mild back pain In recent 2 months, back pain progressed, bilateral lower leg weakness and
骨科 R1 蔡沅欣 2013.3.18 Clinical Scenario 82 y/o male Fell down about 3 months ago, no significant discomfort, except mild back pain In recent 2 months, back pain progressed, bilateral lower leg weakness and
在一所巿區急症室內評估分流心電圖方案的角色
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Evaluating the role of a triage electrocardiogram protocol at an urban emergency department 在一所巿區急症室內評估分流心電圖方案的角色 BL Lim 林明良, A Vasu, GH Lim 林義賢 Objective: Our emergency
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Evaluating the role of a triage electrocardiogram protocol at an urban emergency department 在一所巿區急症室內評估分流心電圖方案的角色 BL Lim 林明良, A Vasu, GH Lim 林義賢 Objective: Our emergency
Case Conference. Basic Information. Chief Complaint PMH PDH. 2013/06/22 台南奇美醫院 Reporter: 黃鈺芬醫師. Gender: female Age: 68 y/o Attitude: philosophical
 Case Conference Basic Information 2013/06/22 台南奇美醫院 Reporter: 黃鈺芬醫師 Gender: female Age: 68 y/o Attitude: philosophical Chief Complaint Pus discharge over upper anterior area for several days PMH PDH Hypertension
Case Conference Basic Information 2013/06/22 台南奇美醫院 Reporter: 黃鈺芬醫師 Gender: female Age: 68 y/o Attitude: philosophical Chief Complaint Pus discharge over upper anterior area for several days PMH PDH Hypertension
Horng-Yih Ou, Shu-Hwa Hsiao*, Eugene Hsin Yu, and Ta-Jen Wu
 Etiologies and Clinical Manifestations of Hyperprolactinemia in A Medical Center in Southern Taiwan Horng-Yih Ou, Shu-Hwa Hsiao*, Eugene Hsin Yu, and Ta-Jen Wu Department of Internal Medicine, *Department
Etiologies and Clinical Manifestations of Hyperprolactinemia in A Medical Center in Southern Taiwan Horng-Yih Ou, Shu-Hwa Hsiao*, Eugene Hsin Yu, and Ta-Jen Wu Department of Internal Medicine, *Department
Assessment of postoperative short-term and longterm mortality risk in Chinese geriatric patients for hip fracture using the Charlson comorbidity score
 CME Original ARTICLE Assessment of postoperative short-term and longterm mortality risk in Chinese geriatric patients for hip fracture using the Charlson comorbidity score TW Lau *, Christian Fang, Frankie
CME Original ARTICLE Assessment of postoperative short-term and longterm mortality risk in Chinese geriatric patients for hip fracture using the Charlson comorbidity score TW Lau *, Christian Fang, Frankie
The epidemiology of patients with dizziness in an emergency department
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine The epidemiology of patients with dizziness in an emergency department 急症室頭暈病者的流行病學 JMY Lam 林美怡, WS Siu 蕭詠詩, TS Lam 林子森, NK Cheung 張乃光, CA Graham 簡家廉, TH Rainer
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine The epidemiology of patients with dizziness in an emergency department 急症室頭暈病者的流行病學 JMY Lam 林美怡, WS Siu 蕭詠詩, TS Lam 林子森, NK Cheung 張乃光, CA Graham 簡家廉, TH Rainer
Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes KF Lee Maria WH Mak KO Lau Harriet HY Chung
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes KF Lee Maria WH Mak KO Lau Harriet HY Chung
在急症環境下以護理點脂肪酸結合蛋白決定胸痛病人心肌梗塞之價值
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine The value of point-of-care fatty acid binding protein in patients with chest pain in determining myocardial infarction in the emergency setting 在急症環境下以護理點脂肪酸結合蛋白決定胸痛病人心肌梗塞之價值
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine The value of point-of-care fatty acid binding protein in patients with chest pain in determining myocardial infarction in the emergency setting 在急症環境下以護理點脂肪酸結合蛋白決定胸痛病人心肌梗塞之價值
兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * Cole & Rolland-Cachera, body mass index, BMI Mei et al., 2002 BMI. body mass index, BMI BMI
 78 兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * 身體組成的測量可以觀察身體的相關生長與疾病的狀態, 臨床與研究上常運用各種測量方式以定 義兒童及青少年肥胖 本文主要回顧實地測量方 式, 探討各種工具的運用與信 效度, 並以臺 灣實施現況加以討論, 以期在未來可以正確地評 估兒童及青少年肥胖 測量身體組成的方式包括 實驗室檢查法與實地測量法, 其中實地測量法包 括重高指標與脂肪分佈的測量, 而實地測量方式
78 兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * 身體組成的測量可以觀察身體的相關生長與疾病的狀態, 臨床與研究上常運用各種測量方式以定 義兒童及青少年肥胖 本文主要回顧實地測量方 式, 探討各種工具的運用與信 效度, 並以臺 灣實施現況加以討論, 以期在未來可以正確地評 估兒童及青少年肥胖 測量身體組成的方式包括 實驗室檢查法與實地測量法, 其中實地測量法包 括重高指標與脂肪分佈的測量, 而實地測量方式
SSM Wong, K Wang, EHY Yuen, JKT Wong, A King, AT Ahuja
 Hong Kong J Radiol. 2011;14:155-60 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual and Quantitative Analysis by Gallium-67 Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Management of Malignant Otitis Externa
Hong Kong J Radiol. 2011;14:155-60 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual and Quantitative Analysis by Gallium-67 Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Management of Malignant Otitis Externa
Amiodarone-induced thyroid dysfunction in the Hong Kong Chinese population
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KF Lee KM Lee TT Fung 李家輝李啟文馮騰達 Amiodarone-induced thyroid dysfunction in the Hong Kong Chinese population CME Objective To determine the frequency, risk factors, clinical
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KF Lee KM Lee TT Fung 李家輝李啟文馮騰達 Amiodarone-induced thyroid dysfunction in the Hong Kong Chinese population CME Objective To determine the frequency, risk factors, clinical
Case-control study of Sichuan and Hong Kong children with melamine-associated renal stones: renal ultrasonography and urinary IL-8 and MCP-1 levels
 Title Case-control study of and children with melamine-associated renal stones: renal ultrasonography and urinary IL-8 and MCP-1 levels Author(s) Lau, YL; Tu, W Citation Medical Journal, 213, v. 19 n.
Title Case-control study of and children with melamine-associated renal stones: renal ultrasonography and urinary IL-8 and MCP-1 levels Author(s) Lau, YL; Tu, W Citation Medical Journal, 213, v. 19 n.
A Sustainable Hospitalcommunity. Programme for Orthopaedic Patients with Chronic Pain Syndrome
 A Sustainable Hospitalcommunity Partnership Programme for Orthopaedic Patients with Chronic Pain Syndrome Cheung KK 1 Chan PH 1 Chow YY 1 Hung ATF 2 Ho JPS 2 Tse A 1 Chan I 1 Ip A 1 Wong C 1 Fung C 1 Kwok
A Sustainable Hospitalcommunity Partnership Programme for Orthopaedic Patients with Chronic Pain Syndrome Cheung KK 1 Chan PH 1 Chow YY 1 Hung ATF 2 Ho JPS 2 Tse A 1 Chan I 1 Ip A 1 Wong C 1 Fung C 1 Kwok
Acute Myocardial Injury Mimicking an ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Secondary to Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
 Case Reports Acta Cardiol Sin 2006;22:229 33 Acute Myocardial Injury Mimicking an ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Secondary to Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Yi-Chung Shih, 1,2 Chia-Ti Tsai 2 and Fu-Tien
Case Reports Acta Cardiol Sin 2006;22:229 33 Acute Myocardial Injury Mimicking an ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Secondary to Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Yi-Chung Shih, 1,2 Chia-Ti Tsai 2 and Fu-Tien
Pain management programme for Chinese patients: a 10-year outcome review
 Original ARTICLE Pain management programme for Chinese patients: a 10-year outcome review MC Chu *, Rainbow KY Law, Leo CT Cheung, Marlene L Ma, Ewert YW Tse, Tony CM Wong, PP Chen This article was published
Original ARTICLE Pain management programme for Chinese patients: a 10-year outcome review MC Chu *, Rainbow KY Law, Leo CT Cheung, Marlene L Ma, Ewert YW Tse, Tony CM Wong, PP Chen This article was published
Predictive factors for length of hospital stay following primary total knee replacement in a total joint replacement centre in Hong Kong
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predictive factors for length of hospital stay following primary total knee replacement in a total joint replacement centre in Hong Kong CK Lo *, QJ Lee, YC Wong This article was published
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predictive factors for length of hospital stay following primary total knee replacement in a total joint replacement centre in Hong Kong CK Lo *, QJ Lee, YC Wong This article was published
Total knee arthroplasty for primary knee osteoarthritis: changing pattern over the past 10 years
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E CH Yan KY Chiu FY Ng 忻振凱曲廣運吳富源 Total knee arthroplasty for primary knee osteoarthritis: changing pattern over the past 1 years CME Objective To review the epidemiology of
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E CH Yan KY Chiu FY Ng 忻振凱曲廣運吳富源 Total knee arthroplasty for primary knee osteoarthritis: changing pattern over the past 1 years CME Objective To review the epidemiology of
Children on continuous renal replacement therapy: prognostic factors
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Children on continuous renal replacement therapy: prognostic factors WF Hui Winnie KY Chan KW Lee 許桓峰陳桂如李國偉 Objectives To identify prognostic factors in children receiving
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Children on continuous renal replacement therapy: prognostic factors WF Hui Winnie KY Chan KW Lee 許桓峰陳桂如李國偉 Objectives To identify prognostic factors in children receiving
Knowledge of Radiation Dose and Awareness of Risks: a Cross-sectional Survey of Junior Clinicians
 J Hong Kong Col Radiol. 2010;13:189-94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Knowledge of Radiation Dose and Awareness of Risks: a Cross-sectional Survey of Junior Clinicians SY Luk, JLY Leung, CS Cheng Department of Radiology,
J Hong Kong Col Radiol. 2010;13:189-94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Knowledge of Radiation Dose and Awareness of Risks: a Cross-sectional Survey of Junior Clinicians SY Luk, JLY Leung, CS Cheng Department of Radiology,
Type 2 diabetes management in Hong Kong ethnic minorities: what primary care physicians need to know
 Original Article Type 2 diabetes management in Hong Kong ethnic minorities: what primary care physicians need to know Catherine XR Chen *, KH Chan This article was published on 30 January 2014 at www.hkmj.org.
Original Article Type 2 diabetes management in Hong Kong ethnic minorities: what primary care physicians need to know Catherine XR Chen *, KH Chan This article was published on 30 January 2014 at www.hkmj.org.
Use of evidence-based medicine to choose contrast enhancing agents (iso-osmolar versus low-osmolar contrast media) for CT
 . 弘光學報 64 期. Use of evidence-based medicine to choose contrast enhancing agents (iso-osmolar versus low-osmolar contrast media) for CT Ping-Liang Chen Yuan-Lin Lee Hui-Luu Zhan Hung-Chih Lai * Department
. 弘光學報 64 期. Use of evidence-based medicine to choose contrast enhancing agents (iso-osmolar versus low-osmolar contrast media) for CT Ping-Liang Chen Yuan-Lin Lee Hui-Luu Zhan Hung-Chih Lai * Department
Acute kidney injury in the paediatric intensive care unit: identification by modified RIFLE criteria
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Acute kidney injury in the paediatric intensive care unit: identification by modified RIFLE criteria WF Hui Winnie KY Chan TY Miu 許桓峰陳桂如繆定逸 Objective To evaluate the prevalence
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Acute kidney injury in the paediatric intensive care unit: identification by modified RIFLE criteria WF Hui Winnie KY Chan TY Miu 許桓峰陳桂如繆定逸 Objective To evaluate the prevalence
Concordance between side-stream end-tidal carbon dioxide and arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure in respiratory service setting
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Concordance between side-stream dioxide and arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure in respiratory service setting Grace TS Law CY Wong CW Kwan KY Wong FP Wong HN Tse 羅子珊黃澤仁關志威黃琼英黃鳳屏謝海南
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Concordance between side-stream dioxide and arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure in respiratory service setting Grace TS Law CY Wong CW Kwan KY Wong FP Wong HN Tse 羅子珊黃澤仁關志威黃琼英黃鳳屏謝海南
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Hong Kong: a territory-wide study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Hong Kong: a territory-wide study KL Fan, LP Leung *, YC Siu This article was published on 6 Jan 2017 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T Introduction: Out-of-hospital
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Hong Kong: a territory-wide study KL Fan, LP Leung *, YC Siu This article was published on 6 Jan 2017 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T Introduction: Out-of-hospital
Improving the emergency department management of post-chemotherapy sepsis in haematological malignancy patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving the emergency department management of post-chemotherapy sepsis in haematological malignancy patients HF Ko *, SS Tsui, Johnson WK Tse, WY Kwong, OY Chan, Gordon CK Wong This
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving the emergency department management of post-chemotherapy sepsis in haematological malignancy patients HF Ko *, SS Tsui, Johnson WK Tse, WY Kwong, OY Chan, Gordon CK Wong This
宫颈上皮内瘤变 ; IgG1 IgG2 亚类 ; 酶联免疫吸附试验 R A (2009)
 2009 年第 19 卷第 11 期 CHINA ONCOLOGY 2009 Vol.19 No.11 831 免疫球蛋白 G(immunoglobulin G,IgG) 是血清和细胞外液中含量最高的免疫球蛋白, 其某个亚类的升高, 可能与宫颈上皮内瘤变 (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN) 的发生 发展及转归有密切相关 然而对于 CIN 患者血清人乳头瘤病毒样颗粒
2009 年第 19 卷第 11 期 CHINA ONCOLOGY 2009 Vol.19 No.11 831 免疫球蛋白 G(immunoglobulin G,IgG) 是血清和细胞外液中含量最高的免疫球蛋白, 其某个亚类的升高, 可能与宫颈上皮内瘤变 (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN) 的发生 发展及转归有密切相关 然而对于 CIN 患者血清人乳头瘤病毒样颗粒
Is stroke thrombolysis safe and efficacious in Hong Kong?
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Edward HC Wong Alexander YL Lau Yannie OY Soo Deyond YW Siu Venus SW Hui Colin A Graham Thomas WH Leung Lawrence KS Wong 王浩中劉玉麟蘇藹欣蕭容媛許詩韻簡家簾梁慧康黃家星 Key words Brain ischemia;
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Edward HC Wong Alexander YL Lau Yannie OY Soo Deyond YW Siu Venus SW Hui Colin A Graham Thomas WH Leung Lawrence KS Wong 王浩中劉玉麟蘇藹欣蕭容媛許詩韻簡家簾梁慧康黃家星 Key words Brain ischemia;
乳癌化療指引. Breast Cancer
 乳癌化療指引 103 年 12 月第五版 99-102 年, 第一至四版 注意事項 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床詴驗, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床詴驗, 惟參與臨床詴驗之研究對象多以 70 歲以下之病人為主, 故建議 70 歲以上病人接受治療時, 應依據病人實際臨床狀況進行抗癌藥物劑量之調整! 健保藥品給付限制註記說明
乳癌化療指引 103 年 12 月第五版 99-102 年, 第一至四版 注意事項 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床詴驗, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床詴驗, 惟參與臨床詴驗之研究對象多以 70 歲以下之病人為主, 故建議 70 歲以上病人接受治療時, 應依據病人實際臨床狀況進行抗癌藥物劑量之調整! 健保藥品給付限制註記說明
Surgical Ligation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Extremely Low Birth Weight Premature Neonates
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 005;1:0 4 Congenital Heart Disease Surgical Ligation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Extremely Low Birth Weight Premature Neonates Haw-Kwei Hwang, 1 Ming-Ren Chen, 1,4
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 005;1:0 4 Congenital Heart Disease Surgical Ligation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Extremely Low Birth Weight Premature Neonates Haw-Kwei Hwang, 1 Ming-Ren Chen, 1,4
Co-morbidities of patients with knee osteoarthritis
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KW Chan HY Ngai KK Ip KH Lam WW Lai 陳國維倪浩然葉傑權林敬熹黎偉華 Co-morbidities of patients with knee osteoarthritis CME Objectives To study the co-morbidities of general practice patients
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E KW Chan HY Ngai KK Ip KH Lam WW Lai 陳國維倪浩然葉傑權林敬熹黎偉華 Co-morbidities of patients with knee osteoarthritis CME Objectives To study the co-morbidities of general practice patients
大舜政策研究中心 Dashun Policy Research Centre Ltd Annual Conference 2012
 香港樂健會社 Happy Health Society in association with 大舜政策研究中心 Dashun Policy Research Centre Ltd Annual Conference 2012 人人健康由我做起 中西結合預防癌症 Prevention of Cancer East Meets West Approaches 2012 年 12 月 22 日 ( 星期六
香港樂健會社 Happy Health Society in association with 大舜政策研究中心 Dashun Policy Research Centre Ltd Annual Conference 2012 人人健康由我做起 中西結合預防癌症 Prevention of Cancer East Meets West Approaches 2012 年 12 月 22 日 ( 星期六
如果你有過造影劑過敏 對於術前用藥, 你需要知道些什麽
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION IF YOU HAVE HAD CONTRAST ALLERGY CHINESE 如果你有過造影劑過敏 對於術前用藥, 你需要知道些什麽 本資料是爲某些病人編寫, 這些病人過去在接受造影劑時出現過中等程度或嚴重的過敏反應, 而現在已預約接受使用造影劑的造影研究 你的醫生已經決定需爲你做一項特殊的造影研究, 藉以幫助他們管理你的健康 已爲你安排好做以下其中一項掃描
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION IF YOU HAVE HAD CONTRAST ALLERGY CHINESE 如果你有過造影劑過敏 對於術前用藥, 你需要知道些什麽 本資料是爲某些病人編寫, 這些病人過去在接受造影劑時出現過中等程度或嚴重的過敏反應, 而現在已預約接受使用造影劑的造影研究 你的醫生已經決定需爲你做一項特殊的造影研究, 藉以幫助他們管理你的健康 已爲你安排好做以下其中一項掃描
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST elevation myocardial infarction: performance with focus on timeliness of treatment
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Gary SH Cheung KL Tsui CC Lau HL Chan CH Chau KL Wu CY Cheung MC Choi TS Tse KK Chan SK Li 張誠謙徐健霖劉楚釗陳曉藍周志康胡國樑張志揚蔡文俊謝德新陳國強李樹堅 Key words Angioplasty, transluminal, percutaneous
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Gary SH Cheung KL Tsui CC Lau HL Chan CH Chau KL Wu CY Cheung MC Choi TS Tse KK Chan SK Li 張誠謙徐健霖劉楚釗陳曉藍周志康胡國樑張志揚蔡文俊謝德新陳國強李樹堅 Key words Angioplasty, transluminal, percutaneous
Surgical management of primary non small-cell carcinoma of lung with synchronous solitary brain metastasis: local experience
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Surgical management of primary non small-cell carcinoma of lung with synchronous solitary brain metastasis: local experience CK Lo CH Yu CC Ma KM Ko Samuel CL Leung 勞卓堅余志雄馬燦忠高啟明梁昌倫
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Surgical management of primary non small-cell carcinoma of lung with synchronous solitary brain metastasis: local experience CK Lo CH Yu CC Ma KM Ko Samuel CL Leung 勞卓堅余志雄馬燦忠高啟明梁昌倫
Investigation of Fitness Education Model s Implementation Effects
 Journal of National Taipei Teachers College, Vol.7, No. (Mar. ) 7~8 NATIONAL TAIPEI TEACHERS COLLEGE 7 Investigation of Fitness Education Model s Implementation Effects Min-hua Chung * ABSTRACT The main
Journal of National Taipei Teachers College, Vol.7, No. (Mar. ) 7~8 NATIONAL TAIPEI TEACHERS COLLEGE 7 Investigation of Fitness Education Model s Implementation Effects Min-hua Chung * ABSTRACT The main
財團法人明日醫學基金會研究計畫申請書. Yao-Chun Hsu 高雄市燕巢區義大路 1 號 1 月 1 日起至 101 年 12 月 31 日止
 財團法人明日醫學基金會研究計畫申請書 計畫名稱 ( 中文 ) 決定慢性 B 型肝炎嚴重急性發作預後的病毒相關因子 ( 英文 ) Viral factors in determining outcomes of chronic hepatitis B patients with severe acute exacerbation 計畫類別 個別型 整合型 計畫歸屬 基礎醫學 生物醫學 臨床醫學 資訊系統
財團法人明日醫學基金會研究計畫申請書 計畫名稱 ( 中文 ) 決定慢性 B 型肝炎嚴重急性發作預後的病毒相關因子 ( 英文 ) Viral factors in determining outcomes of chronic hepatitis B patients with severe acute exacerbation 計畫類別 個別型 整合型 計畫歸屬 基礎醫學 生物醫學 臨床醫學 資訊系統
Hong Kong College of Radiologists Palliative Medicine Training Programme
 Hong Kong J Radiol. 2017;20:227-31 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1716802 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hong Kong College of Radiologists Palliative Medicine Training Programme LCY Lui 1, KH Wong 2, R Ngan 2, SWK Siu 3, E Chow
Hong Kong J Radiol. 2017;20:227-31 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1716802 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hong Kong College of Radiologists Palliative Medicine Training Programme LCY Lui 1, KH Wong 2, R Ngan 2, SWK Siu 3, E Chow
運用運動訓練維持失智老人如廁功能之探討 陳昱合張素嫺 * 方妙君 ** 蔡美利 *** 關鍵詞 : 如廁功能 失智老人 運動計畫 Chen et al., Carpenter, Hastie, Morris, Fries, & Ankri,
 265 運用運動訓練維持失智老人如廁功能之探討 陳昱合張素嫺 * 方妙君 ** 蔡美利 *** 無法自行如廁被視為失智老人日常生活活動功能邁入嚴重依賴的關鍵之一 然而目前缺乏一個以理論為基礎的照護措施來維持或促進老人如廁功能, 繼而延緩依賴程度 運動訓練介入後, 對失智老人如廁行為能力之探討 運動介入措施設計是以 Bandura 的社會認知理論為基礎, 執行為期 8 週的步行及下肢負重運動訓練 本研究採單組
265 運用運動訓練維持失智老人如廁功能之探討 陳昱合張素嫺 * 方妙君 ** 蔡美利 *** 無法自行如廁被視為失智老人日常生活活動功能邁入嚴重依賴的關鍵之一 然而目前缺乏一個以理論為基礎的照護措施來維持或促進老人如廁功能, 繼而延緩依賴程度 運動訓練介入後, 對失智老人如廁行為能力之探討 運動介入措施設計是以 Bandura 的社會認知理論為基礎, 執行為期 8 週的步行及下肢負重運動訓練 本研究採單組
Name (Block Letters) (In Chinese) (HKID No.)
 Undertaking in respect of Patient Management in Name (Block Letters) (In Chinese) (HKID No.) 1. I have read the Protocol for Patient Management in ( Protocol ) and Guidelines of management of patient with
Undertaking in respect of Patient Management in Name (Block Letters) (In Chinese) (HKID No.) 1. I have read the Protocol for Patient Management in ( Protocol ) and Guidelines of management of patient with
2013 香港中學文憑考試通識教育科試卷一練習卷 HONG KONG DIPLOMA OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 2013 LIBERAL STUDIES PAPER 1 PRACTICE PAPER
 2013 香港中學文憑考試通識教育科試卷一練習卷 HONG KONG DIPLOMA OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 2013 LIBERAL STUDIES PAPER 1 PRACTICE PAPER 卷一, 第一題 Paper 1, Question 1 樣本 1 2 評語 考生比較了眾街道在這兩天的一氧化碳的平均及最高水平 簡單點出了一些數據的變化及轉變幅度
2013 香港中學文憑考試通識教育科試卷一練習卷 HONG KONG DIPLOMA OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 2013 LIBERAL STUDIES PAPER 1 PRACTICE PAPER 卷一, 第一題 Paper 1, Question 1 樣本 1 2 評語 考生比較了眾街道在這兩天的一氧化碳的平均及最高水平 簡單點出了一些數據的變化及轉變幅度
戒菸治療新進展 郭斐然 臺大醫院家庭醫學部
 戒菸治療新進展 郭斐然 臺大醫院家庭醫學部 今天的議題 Varenicline 對精神病患之安全性 尼古丁代謝與戒菸治療之研究 Part One Varenicline 對精神病患之安全性 輝瑞公司加註的警語 曾有接受 Champix 治療的病人發生嚴重的神經精神症狀 有些停止吸菸病患因發生尼古丁戒斷症狀而使評估複雜化, 然而有些症狀仍發生在繼續吸菸的病人身上 所有正在接受 Champix 治療的病患應觀察其精神症狀,
戒菸治療新進展 郭斐然 臺大醫院家庭醫學部 今天的議題 Varenicline 對精神病患之安全性 尼古丁代謝與戒菸治療之研究 Part One Varenicline 對精神病患之安全性 輝瑞公司加註的警語 曾有接受 Champix 治療的病人發生嚴重的神經精神症狀 有些停止吸菸病患因發生尼古丁戒斷症狀而使評估複雜化, 然而有些症狀仍發生在繼續吸菸的病人身上 所有正在接受 Champix 治療的病患應觀察其精神症狀,
Lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lower extremity lymphedema: local experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lower extremity lymphedema: local experience MC Lam *, WH Luk, KH Tse This article was published on 7 Oct 2013 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lower extremity lymphedema: local experience MC Lam *, WH Luk, KH Tse This article was published on 7 Oct 2013 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T
Evolution of Shock Monitoring and ICU Scoring. NTUH Anesthesiology/SICU Yeh
 Evolution of Shock Monitoring and ICU Scoring NTUH Anesthesiology/SICU Yu-Chang Yeh Shock 組織灌流不足 (Hypoperfusion) 氧氣供應不足 / 無法利用 休克重要觀念 血壓 115/40 (65) mmhg, 有沒有休克? Usual BP 185/95 CAD ICP = 30 mmhg IAP =
Evolution of Shock Monitoring and ICU Scoring NTUH Anesthesiology/SICU Yu-Chang Yeh Shock 組織灌流不足 (Hypoperfusion) 氧氣供應不足 / 無法利用 休克重要觀念 血壓 115/40 (65) mmhg, 有沒有休克? Usual BP 185/95 CAD ICP = 30 mmhg IAP =
Surgical excision for challenging upper limb nerve sheath tumours: a single centre retrospective review of treatment results
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Surgical excision for challenging upper limb nerve sheath tumours: a single centre retrospective review of treatment results YW Hung WL Tse HS Cheng PC Ho 洪煜華謝永廉鄭喜珊何百昌 Key
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Surgical excision for challenging upper limb nerve sheath tumours: a single centre retrospective review of treatment results YW Hung WL Tse HS Cheng PC Ho 洪煜華謝永廉鄭喜珊何百昌 Key
EBM 月會. Evidence-Based Medicine. Reporter: R1 丁楷庭 DATE: 101/03/05
 EBM 月會 Evidence-Based Medicine Reporter: R1 丁楷庭 DATE: 101/03/05 Clinical scenario-1 A 61 year-old female patient Operation History: left thigh lipoma status post excision 10+ years ago at YUAN S General
EBM 月會 Evidence-Based Medicine Reporter: R1 丁楷庭 DATE: 101/03/05 Clinical scenario-1 A 61 year-old female patient Operation History: left thigh lipoma status post excision 10+ years ago at YUAN S General
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫期中進度報告
 行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫期中進度報告 CD8 T 細胞在對胞內菌保護性免疫反應的角色 (2/3) 計畫類別 : 個別型計畫計畫編號 : NSC91-2320-B-002-096- 執行期間 : 91 年 08 月 01 日至 92 年 07 月 31 日執行單位 : 國立臺灣大學醫學院免疫學研究所 計畫主持人 : 伍安怡 報告類型 : 精簡報告 處理方式 : 本計畫可公開查詢 中華民國 92
行政院國家科學委員會專題研究計畫期中進度報告 CD8 T 細胞在對胞內菌保護性免疫反應的角色 (2/3) 計畫類別 : 個別型計畫計畫編號 : NSC91-2320-B-002-096- 執行期間 : 91 年 08 月 01 日至 92 年 07 月 31 日執行單位 : 國立臺灣大學醫學院免疫學研究所 計畫主持人 : 伍安怡 報告類型 : 精簡報告 處理方式 : 本計畫可公開查詢 中華民國 92
10 Year Experience of Iatrogenic Colon Perforation: Clinical Presentation and Management
 J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) December 2010 Case Analysis 10 Year Experience of Iatrogenic Colon Perforation: Clinical Presentation and Management Yan-Jiun Huang 1 John Huang 2 Jin-Tung Liang 2 1
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) December 2010 Case Analysis 10 Year Experience of Iatrogenic Colon Perforation: Clinical Presentation and Management Yan-Jiun Huang 1 John Huang 2 Jin-Tung Liang 2 1
Size, location, and multiplicity of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the Hong Kong Chinese population with subarachnoid haemorrhage
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E HP Lai 賴曉平 KM Cheng 鄭建明 Simon CH Yu 余俊豪 KM Au Yeung 歐陽啟明 YL Cheung CM Chan WS Poon WM Lui 張毓靈陳智明潘偉生呂偉文 Key words Aneurysm, ruptured; Intracranial aneurysm; Subarachnoid hemorrhage
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E HP Lai 賴曉平 KM Cheng 鄭建明 Simon CH Yu 余俊豪 KM Au Yeung 歐陽啟明 YL Cheung CM Chan WS Poon WM Lui 張毓靈陳智明潘偉生呂偉文 Key words Aneurysm, ruptured; Intracranial aneurysm; Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Anterior cruciate ligament tear in Hong Kong Chinese patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior cruciate ligament tear in Hong Kong Chinese patients August WM Fok *, WP Yau This article was published on 19 Dec 2014 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T Objective: To investigate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior cruciate ligament tear in Hong Kong Chinese patients August WM Fok *, WP Yau This article was published on 19 Dec 2014 at www.hkmj.org. A B S T R A C T Objective: To investigate
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy increases rates of breast-conserving surgery in early operable breast cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neoadjuvant chemotherapy increases rates of breast-conserving surgery in early operable breast cancer Vivian CM Man, Polly SY Cheung * This article was published on 9 May 2017 at www.hkmj.org.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neoadjuvant chemotherapy increases rates of breast-conserving surgery in early operable breast cancer Vivian CM Man, Polly SY Cheung * This article was published on 9 May 2017 at www.hkmj.org.
Utilisation and outcome of renal replacement therapy in an Asian tertiary intensive care unit
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Utilisation and outcome of renal replacement therapy in an Asian tertiary intensive care unit Gordon YS Choi Gavin M Joynt Charles D Gomersall HY So 蔡玉生喬伊諾葛列格蘇慶餘 Key words
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Utilisation and outcome of renal replacement therapy in an Asian tertiary intensive care unit Gordon YS Choi Gavin M Joynt Charles D Gomersall HY So 蔡玉生喬伊諾葛列格蘇慶餘 Key words
Corticosteroid adulteration in proprietary Chinese medicines: a recurring problem
 Original ARTICLE Corticosteroid adulteration in proprietary Chinese medicines: a recurring problem YK Chong, CK Ching, SW Ng, Tony WL Mak * This article was published on 28 Aug 2015 at www.hkmj.org. A
Original ARTICLE Corticosteroid adulteration in proprietary Chinese medicines: a recurring problem YK Chong, CK Ching, SW Ng, Tony WL Mak * This article was published on 28 Aug 2015 at www.hkmj.org. A
Advance directives and life-sustaining treatment: attitudes of Hong Kong Chinese elders with chronic disease
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Advance directives and life-sustaining treatment: attitudes of Hong Kong Chinese elders with chronic disease Fion H Ting 丁葓 Esther Mok 莫孫淑冰 Objective To examine the attitudes
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Advance directives and life-sustaining treatment: attitudes of Hong Kong Chinese elders with chronic disease Fion H Ting 丁葓 Esther Mok 莫孫淑冰 Objective To examine the attitudes
Treatment of Anorectal Abscess with Identified Anal Fistula: One-stage or Two-stage Operation
 J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) September 200 Original Article Treatment of Anorectal Abscess with Identified Anal Fistula: One-stage or Two-stage Operation Chao-Yang Chen Shu-Wen Jao Chang-Chieh Wu
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) September 200 Original Article Treatment of Anorectal Abscess with Identified Anal Fistula: One-stage or Two-stage Operation Chao-Yang Chen Shu-Wen Jao Chang-Chieh Wu
Public lacks knowledge on chronic kidney disease: telephone survey
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Public lacks knowledge on chronic kidney disease: telephone survey KM Chow *, CC Szeto, Bonnie CH Kwan, CB Leung, Philip KT Li This article was published on 14 Mar 2014 at www.hkmj.org.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Public lacks knowledge on chronic kidney disease: telephone survey KM Chow *, CC Szeto, Bonnie CH Kwan, CB Leung, Philip KT Li This article was published on 14 Mar 2014 at www.hkmj.org.
Management of suspected deep venous thrombosis in an emergency medicine ward in Hong Kong
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Management of suspected deep venous thrombosis in an emergency medicine ward in Hong Kong 香港急症科病房對深部靜脈栓塞的治理 KKC Hung 洪磯正, CA Graham 簡家簾, WT Yim 嚴為定, ESF Yam 任淑芳,
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Management of suspected deep venous thrombosis in an emergency medicine ward in Hong Kong 香港急症科病房對深部靜脈栓塞的治理 KKC Hung 洪磯正, CA Graham 簡家簾, WT Yim 嚴為定, ESF Yam 任淑芳,
荷爾蒙補充療法及癌症 Hormone Replacement Therapy and Cancers 黃思誠 台大醫院婦產科
 荷爾蒙補充療法及癌症 Hormone Replacement Therapy and Cancers 黃思誠 台大醫院婦產科 停經後的荷爾蒙補充療法 (HRT) 可以治療停經後症候群, 如潮紅 心悸 失眠等, 也可以防止及治療骨質疏鬆 常用藥物口服動情激素 ( 如 premarin), 經皮膚吸收動情激素 (estradiol) 黃體素 ( 如 provera) 動情激素及黃體素混合經皮膚吸收劑 動情激素及
荷爾蒙補充療法及癌症 Hormone Replacement Therapy and Cancers 黃思誠 台大醫院婦產科 停經後的荷爾蒙補充療法 (HRT) 可以治療停經後症候群, 如潮紅 心悸 失眠等, 也可以防止及治療骨質疏鬆 常用藥物口服動情激素 ( 如 premarin), 經皮膚吸收動情激素 (estradiol) 黃體素 ( 如 provera) 動情激素及黃體素混合經皮膚吸收劑 動情激素及
A simplified appendicitis score in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A simplified appendicitis score in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis 診斷急性闌尾炎的一個簡化闌尾炎指數 PL Goh 吳柏良 Introduction: Scoring systems such as the Modified Alvarado Score
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A simplified appendicitis score in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis 診斷急性闌尾炎的一個簡化闌尾炎指數 PL Goh 吳柏良 Introduction: Scoring systems such as the Modified Alvarado Score
全民健康保險研究資料庫在急診醫療利用分析之應用
 全民健康保險研究資料庫開發與應用研討會 全民健康保險研究資料庫在急診醫療利用分析之應用 翁瑞宏 嘉南藥理科技大學醫管系暨碩士班助理教授 黃金安 台中榮民總醫院急診醫學科主任 2009 年 9 月 3 日 Outline Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, Wen-Chen Tsai, Wei-Hsiung Hu and Dar-Yu Yang, Analysis of Emergency
全民健康保險研究資料庫開發與應用研討會 全民健康保險研究資料庫在急診醫療利用分析之應用 翁瑞宏 嘉南藥理科技大學醫管系暨碩士班助理教授 黃金安 台中榮民總醫院急診醫學科主任 2009 年 9 月 3 日 Outline Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, Wen-Chen Tsai, Wei-Hsiung Hu and Dar-Yu Yang, Analysis of Emergency
內文 : INDICATIONS AND BENEFITS OF BISPHOSPHONATE THERAPY
 原文題目 ( 出處 ): 原文作者姓名 : 通訊作者學校 : 報告者姓名 ( 組別 ): American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws-2009 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg
原文題目 ( 出處 ): 原文作者姓名 : 通訊作者學校 : 報告者姓名 ( 組別 ): American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws-2009 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg
Occlusion therapy in amblyopia: an experience from Hong Kong
 Original ARTICLE Occlusion therapy in amblyopia: an experience from Hong Kong Emily WH Tang *, Brian CY Li, Ian YL Yeung, Kenneth KW Li This article was published on 9 January 204 at www. hkmj.org. A B
Original ARTICLE Occlusion therapy in amblyopia: an experience from Hong Kong Emily WH Tang *, Brian CY Li, Ian YL Yeung, Kenneth KW Li This article was published on 9 January 204 at www. hkmj.org. A B
乳癌化療指引. 104 年 12 月第六版 年,1 st - 5 th 版
 乳癌化療指引 104 年 12 月第六版 99-103 年,1 st - 5 th 版 注意事項 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床試驗, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床試驗, 惟參與臨床試驗之研究對象多以 70 歲以下之病人為主, 故建議 70 歲以上病人接受治療時, 應依據病人實際臨床狀況進行抗癌藥物劑量之調整! 健保藥品給付限制註記說明
乳癌化療指引 104 年 12 月第六版 99-103 年,1 st - 5 th 版 注意事項 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引 : 本院癌症團隊基於實證醫學制定此化學治療指引, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床試驗, 實證醫學之結論源自臨床試驗, 惟參與臨床試驗之研究對象多以 70 歲以下之病人為主, 故建議 70 歲以上病人接受治療時, 應依據病人實際臨床狀況進行抗癌藥物劑量之調整! 健保藥品給付限制註記說明
IMPLEMENTING THE CDC S COLORECTAL CANCER DEMONSTRATION PROGRAM:
 IMPLEMENTING THE CDC S COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING DEMONSTRATION PROGRAM: WISDOM FROM THE FIELD Rohan EA et al., Cancer 2013;119(15 suppl):2870-83 LEO CHAN 24 AUG 2013 BACKGROUND Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
IMPLEMENTING THE CDC S COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING DEMONSTRATION PROGRAM: WISDOM FROM THE FIELD Rohan EA et al., Cancer 2013;119(15 suppl):2870-83 LEO CHAN 24 AUG 2013 BACKGROUND Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
多國或衛生組織的建議 英國科學諮詢委員會 - 營養 : 美國 / 加拿大營養師協會 國際脂類研究社 : Recommendations of National or Health Organizations
 Recommendations of National or Health Organizations 多國或衛生組織的建議 Australia and New Zealand National Health and Medical Research Counci 澳大利亞和新西蘭國家衛生與醫學研究委員會 : World Health Organization 世界衛生組織 : Dutch Health
Recommendations of National or Health Organizations 多國或衛生組織的建議 Australia and New Zealand National Health and Medical Research Counci 澳大利亞和新西蘭國家衛生與醫學研究委員會 : World Health Organization 世界衛生組織 : Dutch Health
The Role of Herbal Medication in Poor TACE Response Hepatocellular Carcinoma:
 DOI 10.3966/181020932017121504006 Case Report The Role of Herbal Medication in Poor TACE Response Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report Chao-Hua Fang 1, Chin-Chuan Tsai 1,2, Chien-Lin Chen 3, Jiann-Hwa
DOI 10.3966/181020932017121504006 Case Report The Role of Herbal Medication in Poor TACE Response Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report Chao-Hua Fang 1, Chin-Chuan Tsai 1,2, Chien-Lin Chen 3, Jiann-Hwa
A Pilot High-volume Low-cost Hospital-community Partnership Programme in the Management of Orthopaedic Patients With Chronic Pain Syndrome
 A Pilot High-volume Low-cost Hospital-community Partnership Programme in the Management of Orthopaedic Patients With Chronic Pain Syndrome Cheung KK 1 Chan PH 1 Chow YY 1 Hung ATF 2 Ho JPS 2 Tse A 1 Chan
A Pilot High-volume Low-cost Hospital-community Partnership Programme in the Management of Orthopaedic Patients With Chronic Pain Syndrome Cheung KK 1 Chan PH 1 Chow YY 1 Hung ATF 2 Ho JPS 2 Tse A 1 Chan
No Definite Benefit of 5-FU/LV Chemotherapy in Patient with Stage III Colorectal Cancer but Only One Lymph Node Metastasis
 J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) March 2011 Original Article No Definite Benefit of 5-FU/LV Chemotherapy in Patient with Stage III Colorectal Cancer but Only One Lymph Node Metastasis Shang-Chiung Wang
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) March 2011 Original Article No Definite Benefit of 5-FU/LV Chemotherapy in Patient with Stage III Colorectal Cancer but Only One Lymph Node Metastasis Shang-Chiung Wang
Management of health care workers following occupational exposure to hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human immunodeficiency virus
 CME ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of health care workers following occupational exposure to hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human immunodeficiency virus Winnie WY Sin, Ada WC Lin, Kenny CW Chan *, KH Wong
CME ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of health care workers following occupational exposure to hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human immunodeficiency virus Winnie WY Sin, Ada WC Lin, Kenny CW Chan *, KH Wong
20 December 2018 Ms. M Y Kong (CICO Office)
 20 December 2018 Ms. M Y Kong (CICO Office) 1 Purpose 目的 To provide and elaborate HA TFIC s recommendations on immunization requirement for volunteers in HA hospitals. 提供及詳述醫管局感染控制專責小組對醫管局轄下義工免疫要求的建議 2
20 December 2018 Ms. M Y Kong (CICO Office) 1 Purpose 目的 To provide and elaborate HA TFIC s recommendations on immunization requirement for volunteers in HA hospitals. 提供及詳述醫管局感染控制專責小組對醫管局轄下義工免疫要求的建議 2
Appendicitis Computed Tomography Score: a Useful Tool for Predicting Perforation and Surgical Course of Acute Appendicitis
 Hong Kong J Radiol. 2015;18:267-76 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1515310 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CME Appendicitis Computed Tomography Score: a Useful Tool for Predicting Perforation and Surgical Course of Acute Appendicitis
Hong Kong J Radiol. 2015;18:267-76 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1515310 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CME Appendicitis Computed Tomography Score: a Useful Tool for Predicting Perforation and Surgical Course of Acute Appendicitis
Bayesian Trail Design 貝式試驗設計
 北院區臨床試驗中心生物統計組 Biostatistics Unit Clinical Trial Center, CGMH Bayesian Trail Design 貝式試驗設計 Lan-Yan Yang, PhD ( 楊嵐燕 ) 2018/03/05 1 Contents 1 Motivation 2 Bayesian methods 3 Examples 4 Considerations and
北院區臨床試驗中心生物統計組 Biostatistics Unit Clinical Trial Center, CGMH Bayesian Trail Design 貝式試驗設計 Lan-Yan Yang, PhD ( 楊嵐燕 ) 2018/03/05 1 Contents 1 Motivation 2 Bayesian methods 3 Examples 4 Considerations and
Predictive factors for colonoscopy complications
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predictive factors for colonoscopy complications Annie OO Chan, Louis NW Lee, Angus CW Chan, WN Ho, Queenie WL Chan *, Silvia Lau, Joseph WT Chan This article was published on 30 Jan 015
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Predictive factors for colonoscopy complications Annie OO Chan, Louis NW Lee, Angus CW Chan, WN Ho, Queenie WL Chan *, Silvia Lau, Joseph WT Chan This article was published on 30 Jan 015
Association of Osteosarcoma Necrotic Volumes with Tumour Size and Lung Metastasis: Revealed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Hong Kong J Radiol. 2011;14:73-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CME Association of Osteosarcoma Necrotic Volumes with Tumour Size and Lung Metastasis: Revealed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging M Nor Azam 1, NM Nik Munirah
Hong Kong J Radiol. 2011;14:73-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CME Association of Osteosarcoma Necrotic Volumes with Tumour Size and Lung Metastasis: Revealed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging M Nor Azam 1, NM Nik Munirah
ACUTE CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING RESULTING
 ACUTE CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING RESULTING IN ST ELEVATION MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: A RARE CASE REPORT Po-Chao Hsu, 1 Tsung-Hsien Lin, 1,2 Ho-Ming Su, 1,2 Hsiang-Chun Lee, 1 Chih-Hsin Huang, 1 Wen-Ter Lai,
ACUTE CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING RESULTING IN ST ELEVATION MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: A RARE CASE REPORT Po-Chao Hsu, 1 Tsung-Hsien Lin, 1,2 Ho-Ming Su, 1,2 Hsiang-Chun Lee, 1 Chih-Hsin Huang, 1 Wen-Ter Lai,
人格違常者的日間照護模式 - 英國治療性社區 署立嘉南療養院 社區精神科 鍾明勳醫師
 人格違常者的日間照護模式 - 英國治療性社區 署立嘉南療養院 社區精神科 鍾明勳醫師 1 英國的醫療體系 公醫福利制度 (NHS) 基本上是免費的服務只要是英國的居民 ( 簽證六個月以上 ) 都可享有 NHS 唯一的負擔大概只有處方簽費用 (7 英磅多 ) NHS 與健保最大的不同在於 NHS 是個分層分級的醫療體系不像台灣毫無分層分級 一般來說英國民眾就醫需要先經過 GP ( 家醫科醫師 ) 評估後再行轉診但是許多緊急狀況
人格違常者的日間照護模式 - 英國治療性社區 署立嘉南療養院 社區精神科 鍾明勳醫師 1 英國的醫療體系 公醫福利制度 (NHS) 基本上是免費的服務只要是英國的居民 ( 簽證六個月以上 ) 都可享有 NHS 唯一的負擔大概只有處方簽費用 (7 英磅多 ) NHS 與健保最大的不同在於 NHS 是個分層分級的醫療體系不像台灣毫無分層分級 一般來說英國民眾就醫需要先經過 GP ( 家醫科醫師 ) 評估後再行轉診但是許多緊急狀況
An original discovery: selenium deficiency and Keshan disease (an endemic heart disease)
 320 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2012;21 (3):320-326 Review An original discovery: selenium deficiency and Keshan disease (an endemic heart disease) Junshi Chen MD Institute of Nutrition and Food Safety, Chinese
320 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2012;21 (3):320-326 Review An original discovery: selenium deficiency and Keshan disease (an endemic heart disease) Junshi Chen MD Institute of Nutrition and Food Safety, Chinese
Surgical Management of Complete Rectal Prolapse. Purpose. To review our experience in the surgical management of complete
 J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) December 2007 Original Article Surgical Management of Complete Rectal Prolapse Chung-Chi Huang Hong-Hwa Chen Shung-Eing Lin Chia-Lo Chang Chien-Chang Lu Wang-Hseng Hu
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) December 2007 Original Article Surgical Management of Complete Rectal Prolapse Chung-Chi Huang Hong-Hwa Chen Shung-Eing Lin Chia-Lo Chang Chien-Chang Lu Wang-Hseng Hu
子宮頸癌. Cervical Cancer 三軍總醫院 余慕賢
 子宮頸癌 Cervical Cancer 三軍總醫院 余慕賢 96 台灣女性 10 大癌症 ( 發生率排序 ) 乳癌 7,502 66.10 結腸癌 4,471 39.39 肺癌 3,161 27.85 肝癌 2,900 25.55 子宮頸癌 1,749 15.41 甲狀腺癌 1,407 12.40 胃癌 1,301 11.46 子宮體癌 1,165 10.26 皮膚癌 1,113 9.81 卵巢癌
子宮頸癌 Cervical Cancer 三軍總醫院 余慕賢 96 台灣女性 10 大癌症 ( 發生率排序 ) 乳癌 7,502 66.10 結腸癌 4,471 39.39 肺癌 3,161 27.85 肝癌 2,900 25.55 子宮頸癌 1,749 15.41 甲狀腺癌 1,407 12.40 胃癌 1,301 11.46 子宮體癌 1,165 10.26 皮膚癌 1,113 9.81 卵巢癌
Stereotactic radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a local single-centre experience
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Stereotactic radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a local single-centre experience LC Chan Samuel KW Chiu Stephen L Chan 陳亮祖招國榮陳林 Objective To evaluate the
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Stereotactic radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a local single-centre experience LC Chan Samuel KW Chiu Stephen L Chan 陳亮祖招國榮陳林 Objective To evaluate the
一般外科 case presentation. By intern 楊容欣 指導老師 :Dr. 魏昌國
 一般外科 case presentation By intern 楊容欣 指導老師 :Dr. 魏昌國 Patient profile Name 王琴祿 Age:64 years old Gender: male ID:E101600787 Date of admission:0940517 Chief complain HCC s/p 3 PEI, AFP elevating during recent
一般外科 case presentation By intern 楊容欣 指導老師 :Dr. 魏昌國 Patient profile Name 王琴祿 Age:64 years old Gender: male ID:E101600787 Date of admission:0940517 Chief complain HCC s/p 3 PEI, AFP elevating during recent
Clinical Nursing Application of Tidal Peritoneal Dialysis
 Clinical Nursing Application of Tidal Peritoneal Dialysis 高雄長庚醫院腹膜透析室 郭麗雀 PD catheter implantation This 76 years old male has history of ESRD and initiated CAPD since 2005 PD catheter was implanted on
Clinical Nursing Application of Tidal Peritoneal Dialysis 高雄長庚醫院腹膜透析室 郭麗雀 PD catheter implantation This 76 years old male has history of ESRD and initiated CAPD since 2005 PD catheter was implanted on
Hong Kong Chinese parents attitudes towards circumcision
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Hong Kong Chinese parents attitudes towards circumcision Michael WY Leung Paula MY Tang Nicholas SY Chao Kelvin KW Liu 梁偉業鄧敏兒趙式言廖鑑榮 Objective To investigate Hong Kong Chinese
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Hong Kong Chinese parents attitudes towards circumcision Michael WY Leung Paula MY Tang Nicholas SY Chao Kelvin KW Liu 梁偉業鄧敏兒趙式言廖鑑榮 Objective To investigate Hong Kong Chinese
Brugada Syndrome in the Elderly in Taiwan Report of Two Cases
 Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:62 7 Brugada Syndrome in the Elderly in Taiwan Report of Two Cases Jyh-Ming Juang, Ling-Ping Lai, Jiunn-lee Lin and Fu-Tien Chiang Brugada syndrome is a potentially
Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:62 7 Brugada Syndrome in the Elderly in Taiwan Report of Two Cases Jyh-Ming Juang, Ling-Ping Lai, Jiunn-lee Lin and Fu-Tien Chiang Brugada syndrome is a potentially
Alleviating Cancer Pain Toward Better Quality of Life
 Alleviating Cancer Pain Toward Better Quality of Life 林至芃醫師 台大醫院麻醉部疼痛科科主任台大醫院麻醉部暨腫瘤醫學部合聘主治醫師台大醫學院醫學系臨床助理教授台灣疼痛醫學會秘書長 82 y/o male Newly diagnosed PC Initial presentation Back pain Shoulder pain Rapid progressed
Alleviating Cancer Pain Toward Better Quality of Life 林至芃醫師 台大醫院麻醉部疼痛科科主任台大醫院麻醉部暨腫瘤醫學部合聘主治醫師台大醫學院醫學系臨床助理教授台灣疼痛醫學會秘書長 82 y/o male Newly diagnosed PC Initial presentation Back pain Shoulder pain Rapid progressed
Effect of Alendronate and Teriparatide on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women
 35 Original Article Effect of Alendronate and Teriparatide on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Pei-Tsen Chen, Piya-on Numpaisal, 2 Ching-Chuan Jiang, Hongsen Chiang Departments of Physical
35 Original Article Effect of Alendronate and Teriparatide on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Pei-Tsen Chen, Piya-on Numpaisal, 2 Ching-Chuan Jiang, Hongsen Chiang Departments of Physical
Ibuprofen versus indomethacin treatment of patent ductus arteriosus: comparative effectiveness and complications
 Original Article Ibuprofen versus indomethacin treatment of patent ductus arteriosus: comparative effectiveness and complications NM Chan *, CW Law, KF Kwan This article was published on 30 January 2014
Original Article Ibuprofen versus indomethacin treatment of patent ductus arteriosus: comparative effectiveness and complications NM Chan *, CW Law, KF Kwan This article was published on 30 January 2014
Right Aortic Arch with Mirror-Image Branching in an Asymptomatic Adult: a rare case demonstrated with 64-detector computed tomography
 中華放射醫誌 Chin J Radiol 2008; 33: 87-9 87 Right Aortic Arch with Mirror-Image Branching in an Asymptomatic Adult: a rare case demonstrated with 64-detector computed tomography Shi-Zuo Liu Soa-Min Hsu Hui-Lun
中華放射醫誌 Chin J Radiol 2008; 33: 87-9 87 Right Aortic Arch with Mirror-Image Branching in an Asymptomatic Adult: a rare case demonstrated with 64-detector computed tomography Shi-Zuo Liu Soa-Min Hsu Hui-Lun
Photoselective vaporisation prostatectomy using a GreenLight High Performance System for patients with bleeding tendency
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Photoselective vaporisation prostatectomy using a GreenLight High Performance System for patients with bleeding tendency HM Tam SK Mak MC Law Ringo WH Chu Sidney KH Yip 譚皓汶麥肇敬羅敏聰朱永康葉錦洪
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Photoselective vaporisation prostatectomy using a GreenLight High Performance System for patients with bleeding tendency HM Tam SK Mak MC Law Ringo WH Chu Sidney KH Yip 譚皓汶麥肇敬羅敏聰朱永康葉錦洪
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 2012, v. 34, p
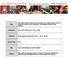 Title The Hong Kong Reference Framework for Hypertension Care for adults in primary care settings - translating evidence into practice. Author(s) Lam, CLK; Ngai, K.H.; Lee, J.P.M. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner,
Title The Hong Kong Reference Framework for Hypertension Care for adults in primary care settings - translating evidence into practice. Author(s) Lam, CLK; Ngai, K.H.; Lee, J.P.M. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner,
Module: Hope and Optimism. Hope
 Module: Hope and Optimism Hope In a nutshell: Cognitive theory of hope (C.R. Snyder, 2002) denotes that a person with high hope is able to use various pathways or waypower to achieve goals. Throughout
Module: Hope and Optimism Hope In a nutshell: Cognitive theory of hope (C.R. Snyder, 2002) denotes that a person with high hope is able to use various pathways or waypower to achieve goals. Throughout
Clinical predictors of response to cetuximabchemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical predictors of response to cetuximabchemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer Ada TW Ma Brigette BY Ma Kenny IK Lei Frankie KF Mo Anthony TC Chan 馬天慧馬碧如李英傑巫國輝陳德章
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical predictors of response to cetuximabchemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer Ada TW Ma Brigette BY Ma Kenny IK Lei Frankie KF Mo Anthony TC Chan 馬天慧馬碧如李英傑巫國輝陳德章
Relationship between population configuration and the spatial pattern of pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 in Hong Kong
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Relationship between population configuration and the spatial pattern of pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 9 in Hong Kong SS Lee NS Wong 李瑞山王艾斯 Objective To investigate the association
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Relationship between population configuration and the spatial pattern of pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 9 in Hong Kong SS Lee NS Wong 李瑞山王艾斯 Objective To investigate the association
Assessment of Doppler-derived Aortic Flow in Atrial Fibrillation Using Beats with Equal Subsequent Cycles
 Original Article Evaluation of LV Systolic Function in AF Acta Cardiol Sin 2006;22:6 23 Echocardiography Assessment of Doppler-derived Aortic Flow in Atrial Fibrillation Using Beats with Equal Subsequent
Original Article Evaluation of LV Systolic Function in AF Acta Cardiol Sin 2006;22:6 23 Echocardiography Assessment of Doppler-derived Aortic Flow in Atrial Fibrillation Using Beats with Equal Subsequent
