Portogram shows opacification of gastroesophageal varices.
|
|
|
- Edwina Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Portogram shows opacification of gastroesophageal varices. courtesyhttp://emedicine.medscape.com/article/ overview
2 DR.Thulfiqar Baiae General surgeon 27thDec.2016 Courtesy
3 Objectives: # The causes of portal hypertension. #The management of : Portal hypertension. Acute bleeding varices.(behavior) #The prevention of the hepatic encephalopathy.(skill)
4 Liver blood supply The blood supply to the liver is unique, 80 per cent being derived from the portal vein and 20 per cent from the hepatic artery.
5 Liver blood supply The portal vein arises from the confluence of the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas. It has some important tributaries, including the left gastric vein which joins just above the pancreas.
6
7 Liver blood supply The portal vein often gives off two large branches to the right lobe, which are usually outside the liver for a short length, before giving a left portal vein branch that runs behind the left hepatic duct.
8 Liver blood supply The portal vein forms from the superior mesenteric and splenic veins, and divides into right and left branches in the hilum of the liver.
9
10
11
12
13
14 A patient with endstage liver cirrhosis disease, demonstrating muscle wasting and gross abdominal distension due to ascites.
15
16 Features of chronic liver disease.
17 Black_ John_ Burnand_ Kevin_ Thomas_ William-Browse_s Introduction to the Investigation and Management of Surgical Disease-Hodder Education (2010)
18 Classifying the severity of chronic liver disease Two prognostic models used to assess the severity of chronic liver disease and perioperative risk.
19 Classifying the severity of chronic liver disease The Child Turcotte Pugh (CTP) Classification The Model for EndStage Liver Disease (MELD) score.
20 Classifying the severity of chronic liver disease The Child Turcotte Pugh (CTP) classification has been modified from the original Child classification which was developed to predict mortality following shunt surgery in cirrhotic patients.
21
22
23 Classifying the severity of chronic liver disease The Model for EndStage Liver Disease (MELD) score was originally developed to predict short-term prognosis in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt insertion, but has now been adopted to prioritise patients awaiting liver transplantation. The survival probability of patients with end-stage liver disease is computed based on the patient s international normalised ratio (INR), serum bilirubin and serum creatinine.
24
25 IMAGING THE LIVER Doppler ultrasound allows flow in the hepatic artery, portal vein and hepatic veins to be assessed. The venous phase of the intravenous contrast (CT)maps the branches of the portal vein within the liver and the drainage via the hepatic veins. A liver biopsy to confirm or exclude chronic liver disease can also be performed during laparoscopy.
26
27 Sagittal ultrasound image of the liver in a patient with cirrhosis demonstrates nodularity of the liver surface and extensive ascites.
28
29 Doppler ultrasound illustrates portal vein flow with a normal direction.
30 IMAGING THE LIVER Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) provides high-quality images of the hepatic artery and portal vein, without the need for arterial cannulation. It is used as an alternative to selective hepatic angiography for diagnosis. It is particularly useful in patients with chronic liver disease and coagulopathy in whom the patency of the portal vein and its branches is in question.
31
32 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan showing massive hepatosplenomegaly. Note the prominent portal system and the left kidney, which is superimposed over the grossly enlarged spleen.
33
34 An elevation in portal pressure. It is most commonly found in the presence of liver cirrhosis. It may be present in patients with Extrahepatic portal vein occlusion, Intrahepatic veno-occlusive disease Occlusion of the main hepatic veins (Budd Chiari syndrome (BCS)).
35 Another classification of causes: Outside the portal vein. Inside the portal vein. In the wall of portal vein.
36 Black_ John_ Burnand_ Kevin_ Thomas_ William-Browse_s Introduction to the Investigation and Management of Surgical Disease-Hodder Education (2010)
37 ? أ.م.د جمال الخضيريcourtesy
38 Portal hypertension produces no symptoms, it is usually diagnosed following presentation with decompensated chronic liver disease and encephalopathy, ascites or variceal bleeding.
39 Varices usually present with the acute onset of a large-volume haematemesis. The lower oesophagus is the most common site for variceal bleeding.
40 The diagnosis may be suspected if the patient is known to have liver cirrhosis, but it needs to be confirmed following initial resuscitation (upper gastrointestinal endoscopy)of the patient.
41 Variceal haemorrhage is an emergency. Patients with massive haemorrhage should be admitted to the intensive treatment unit (ITU). Venous access should be obtained through two large bore peripheral cannulae. Colloids should be administered while adequate blood is obtained (initially ten units). Blood volume should be replaced with colloids, plasma expanders and blood transfusions.
42 Liver function tests will reveal underlying liver disease, and a coagulation profile will reveal any underlying coagulopathy. Hypervolaemia should be avoided since this may increase portal pressure and exacerbate the bleeding. Vitamin K is administered (10 mg intravenously ), but correction of a coagulopathy will require the administration of fresh-frozen plasma (FFP). An associated thrombocytopenia is usually secondary to hypersplenism due to cirrhosis and is treated if the platelet count falls below /L.
43 Treatment with a splanchnic vasoconstrictor should be started. Administration of a prophylactic antibiotic is recommended to prevent or treat associated bacterial infection. As soon as the patient is haemodynamically stabilised an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy should be performed to establish the diagnosis because 50 % of patients with portal hypertension will have a nonvariceal source of bleeding.
44 Variceal bleeding is often associated with hepatic encephalopathy and, in these circumstances and when bleeding is severe, endotracheal intubation will be required for endoscopy. Bronchial aspiration is a frequent complication of variceal bleeding
45 If the rate of blood loss prohibits endoscopic evaluation, a Sengstaken Blakemore tube may be inserted to provide temporary haemostasis. Balloon tamponade is very effective in stopping bleeding and once the patient is stabilised, a more definitive treatment can be carried out.
46
47 Oesophageal balloon tamponade.
48 A Bailey & Love MCQs and EMQs in Surgery REVISION GUIDE SECOND EDITIO
49 A Bailey & Love MCQs and EMQs in Surgery REVISION GUIDE SECOND EDITIO Sengstaken-Blakemore tube
50
51 Once inserted, the gastric balloon is inflated with 300 ml of air and retracted to the gastric fundus, where the varices at the oesophagogastric junction are tamponaded by the subsequent inflation of the oesophageal balloon to a pressure of 40 mmhg. The two remaining channels allow gastric and oesophageal aspiration.
52 An x-ray is used to confirm the position of the tube. The balloons should be temporarily deflated after 12 hours to prevent pressure necrosis of the oesophagus. Aspiration pneumonia and oesophageal ulceration are other complications.
53 Drug treatment Splanchnic vasoconstrictors reduce portal flow and pressure and should be started early in the treatment of variceal haemorrhage. Vasopressin is a potent vasocontrictor and has been the most extensively used drug for the initial control of variceal haemorrhage, but it can cause myocardial ischaemia, arrhythmias, mesenteric and limb ischaemia. Terlipressin, somatostatin and octreotide are safer than vasopressin and equally effective.
54 Endoscopic treatment Treatment with a vasoconstrictor combined with endoscopic therapy is the standard medical treatment for acute variceal bleeding. The majority of variceal bleeds will respond to a single course.
55
56 Grade 2 oesophageal varices
57 A Bailey & Love MCQs and EMQs in Surgery REVISION GUIDE SECOND EDITIO
58 Endoscopy demonstrating Oesophageal varices A Bailey & Love MCQs and EMQs in Surgery REVISION GUIDE SECOND EDITIO
59 Endoscopic treatment The two most commonly used endoscopic techniques are Endoscopic band ligation which involves placing a constricting rubber band at the base of the varix, Banding is significantly better in preventing rebleeding and is the preferred option. Endoscopic sclerotherapy which involves injection of a sclerosant, such as polidocanol (1 3 %) or ethanolamine (5%), into or around the varix. Both are effective in controlling the bleed.
60
61 The application of bands to ligate the vessel and reduce blood flow
62 Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts (TIPSS) The emergency management of variceal haemorrhage has been revolutionised by the introduction of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts (TIPSS) in 1988.
63
64 The angiogram following insertion of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (open arrow). Injection of contrast into the portal vein flows through the metallic stent and outlines the right hepatic vein. Pressure measurements are taken from within the portal vein before and after insertion.
65 It (TIPSS) has become the main treatment of variceal haemorrhage that has not responded to drug treatment and endoscopic therapy. The shunts are inserted under local anaesthetic, analgesia and sedation using fluoroscopic guidance and ultrasonography. Via the internal jugular vein and SVC, a guidewire is inserted into a hepatic vein and through the hepatic parenchyma into a branch of the portal vein.
66 (TIPSS) The track through the parenchyma is then dilated with a balloon catheter to allow insertion of a metallic stent, which is expanded once a satisfactory position is achieved to form a channel between systemic and portal venous systems. A satisfactory drop in portal venous pressure is usually associated with good control of the variceal haemorrhage.
67 (TIPSS) The main early complication of this technique is perforation of the liver capsule, which can be associated with fatal intraperitoneal haemorrhage. Occlusion may result in further variceal haemorrhage and occurs more commonly in patients with wellcompensated liver disease and good synthetic function. Post-shunt encephalopathy is the confusional state caused by the portal blood bypassing the detoxification of the liver. It occurs in about 40 per cent of patients, a similar incidence to that found after surgical shunts. If severe, the lumen of the TIPSS can be reduced by insertion of a smaller stent.
68 The main long-term complication of (TIPSS) is stenosis of the shunt, which is common (approximately 50 per cent at one year) and may present as further variceal haemorrhage. The main contraindication to (TIPSS) is portal vein occlusion.
69 The Surgical shunts for variceal haemorrhage The increasing availability of liver transplantation and TIPSS has greatly reduced the indications for surgical shunts.
70 The Surgical shunts for variceal haemorrhage It is rarely considered for the acute management of variceal haemorrhage, as the morbidity and mortality in these circumstances are high. The main current indication for a surgical shunt is a patient with Child s grade A cirrhosis, in whom the initial bleed has been controlled by sclerotherapy. Longterm β-blocker therapy and chronic sclerotherapy or banding are the main alternatives.
71 The Surgical shunts for variceal haemorrhage Surgical shunts are an effective method of preventing rebleeding from oesophageal or gastric varices, as they reduce the pressure in the portal circulation by diverting the blood into the low-pressure systemic circulation.
72 The Surgical shunts for variceal haemorrhage Shunts may be divided into Selective (e.g. splenorenal) and Non-selective (e.g. portocaval
73 Shunts may be divided into Selective (e.g. splenorenal) is attempting to preserve blood flow to the liver while decompressing the left side of the portal circulation responsible for giving rise to the oesophageal and gastric varices. Selective shunts may be associated with a lower incidence of portal systemic encephalopathy (PSE), a confusional state commonly found in patients with chronic liver disease who have undergone radiological or surgical portosystemic shunts.
74 Surgical shunts. There is no evidence that prophylactic shunting is beneficial in patients with varices that have not bled.
75 Surgical shunts. Surgical shunts for portal hypertension involve shunting portal blood into the systemic veins. This commonly involves : Side-to-side portocaval anastomosis. End-to-side portocaval anastomosis. Mesocaval anastomosis. Splenorenal anastomosis.
76 Surgical shunts. Side-to-side portocaval anastomosis
77 Surgical shunts. End-to-side portocaval anastomosis
78 Surgical shunts. Mesocaval anastomosis
79 Surgical shunts. Splenorenal anastomosis
80 Oesophageal stapled transection This technique for the management of bleeding oesophageal varices uses the circular stapling device for stapling and resecting a doughnut ring of the lower oesophagus. As with surgical shunts in the acute situation, it was associated with a high perioperative mortality and has been largely abandoned in centres where TIPSS is available.
81 Management of recurrent variceal bleeds secondary to splenic or portal vein thrombosis Treatment is by splenectomy and gastro-oesophageal devascularisation, in which the blood supply to the greater and lesser curve of the stomach and lower oesophagus is divided.
82 Management of recurrent variceal bleeds secondary to splenic or portal vein thrombosis Splenic vein thrombosis may be seen secondary to chronic pancreatitis, and portal vein thrombosis is a common late complication of liver cirrhosis.
83 Variceal bleeding and orthotopic liver transplantation Liver transplantation is the only therapy which will treat portal hypertension and the underlying liver disease.
84 Variceal bleeding and orthotopic liver transplantation The management of variceal bleeding should always take into account the possibility of liver transplantation when this is available.
85 Variceal bleeding and orthotopic liver transplantation TIPSS would be the preferred management for bleeds resistant to sclerotherapy, as long as placement is optimal. Previous surgical shunts greatly increase the morbidity associated with orthotopic liver transplantation.
86
87 أ.م.د جمال الخضيريcourtesy
88 أ.م.د جمال الخضيريcourtesy
PORTAL HYPERTENSION. Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN
 PORTAL HYPERTENSION Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN DEFINITION Portal hypertension is present if portal venous pressure exceeds 10mmHg (1.3kPa). Normal portal venous pressure is 5 10mmHg (0.7 1.3kPa),
PORTAL HYPERTENSION Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN DEFINITION Portal hypertension is present if portal venous pressure exceeds 10mmHg (1.3kPa). Normal portal venous pressure is 5 10mmHg (0.7 1.3kPa),
VARICEAL BLEEDING. Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta.
 VARICEAL BLEEDING Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta Disclosures: None OUTLINE Pathophysiology of portal hypertension Splanchnic
VARICEAL BLEEDING Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta Disclosures: None OUTLINE Pathophysiology of portal hypertension Splanchnic
Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices
 Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices Rino Alvani Gani Hepatobiliary Division Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia Cipto Mangunkusumo National
Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices Rino Alvani Gani Hepatobiliary Division Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia Cipto Mangunkusumo National
GI bleeding in chronic liver disease
 GI bleeding in chronic liver disease Stuart McPherson Consultant Hepatologist Liver Unit, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne and Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University. Case 54 year old
GI bleeding in chronic liver disease Stuart McPherson Consultant Hepatologist Liver Unit, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne and Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University. Case 54 year old
Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center
 Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center Differentiate the types of varices Identify glue preparations utilized when treating gastric varices Review the process of glue administration
Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center Differentiate the types of varices Identify glue preparations utilized when treating gastric varices Review the process of glue administration
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 - 100 - SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The problem of portal hypertension and its alarming complications is still attracting the attentions of surgeons and physicians all over the world. Portal hypertension usually
- 100 - SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The problem of portal hypertension and its alarming complications is still attracting the attentions of surgeons and physicians all over the world. Portal hypertension usually
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
 Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association
 CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
Portal hypertension and ascites
 Portal hypertension and ascites Muhammad S Mirza Guruprasad P Aithal Abstract Portal pressure is the product of portal blood flow and resistance; an increase in either leads to increased portal pressure.
Portal hypertension and ascites Muhammad S Mirza Guruprasad P Aithal Abstract Portal pressure is the product of portal blood flow and resistance; an increase in either leads to increased portal pressure.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
Patrick S. Kamath, MD, and David M. Nagorney, MD
 gastrointestinal tract and abdomen PORTAL HYPERTENSION Patrick S. Kamath, MD, and David M. Nagorney, MD Portal hypertension is diagnosed when the hepatic veinpressure gradient (HVPG), which reflects hepatic
gastrointestinal tract and abdomen PORTAL HYPERTENSION Patrick S. Kamath, MD, and David M. Nagorney, MD Portal hypertension is diagnosed when the hepatic veinpressure gradient (HVPG), which reflects hepatic
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما
 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACLF. See Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) Acute kidney injury (AKI) in ACLF patients, 967 Acute liver failure (ALF), 957 964 causes
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACLF. See Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) Acute kidney injury (AKI) in ACLF patients, 967 Acute liver failure (ALF), 957 964 causes
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS)
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Your liver doctor has recommended that you have a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Your liver doctor has recommended that you have a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic
Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension. Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology
 Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Objectives Review indications and contraindications for TIPS Define a treatment algorithm
Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Objectives Review indications and contraindications for TIPS Define a treatment algorithm
NYU School of Medicine Department of Radiology Rotation-Specific House Staff Evaluation
 Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Etiology of liver cirrhosis
 Liver cirrhosis 1 Liver cirrhosis Liver cirrhosis is the progressive replacement of normal hepatic cells by fibrous scar tissue, This scarring is accompanied by the loss of viable hepatocytes, which are
Liver cirrhosis 1 Liver cirrhosis Liver cirrhosis is the progressive replacement of normal hepatic cells by fibrous scar tissue, This scarring is accompanied by the loss of viable hepatocytes, which are
Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation. Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph
 Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation? Risk of esophageal variceal
Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation? Risk of esophageal variceal
Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute Esophageal Variceal Bleeding
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 910986, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/910986 Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 910986, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/910986 Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute
Liver failure &portal hypertension
 Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute
 Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure called a transjugular intrahepatic
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure called a transjugular intrahepatic
Decompensated chronic liver disease
 Decompensated chronic liver disease Definition of decompensated chronic liver disease Patients with chronic liver disease can present with acute decompensation due to various causes. The decompensation
Decompensated chronic liver disease Definition of decompensated chronic liver disease Patients with chronic liver disease can present with acute decompensation due to various causes. The decompensation
Transjugular Intrahepatic
 Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): A Clinical and Procedural Review Mark R. Werley, M.D. and John Briguglio, M.D. Lancaster Radiology Associates, Ltd. INTRODUCTION This article reviews
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): A Clinical and Procedural Review Mark R. Werley, M.D. and John Briguglio, M.D. Lancaster Radiology Associates, Ltd. INTRODUCTION This article reviews
Clinical guideline Published: 13 June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg141
 Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding in over 16s: management Clinical guideline Published: June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg141 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding in over 16s: management Clinical guideline Published: June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg141 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Gastrointestinal bleeding: the management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding 1.1 Short title Acute upper GI bleeding
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Gastrointestinal bleeding: the management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding 1.1 Short title Acute upper GI bleeding
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding. Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami
 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis
 ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, M.D., 1 Arun J. Sanyal, M.D., 2 Norman D. Grace,
ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, M.D., 1 Arun J. Sanyal, M.D., 2 Norman D. Grace,
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings
 Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Reduction for Management of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy
 CLINICAL IMAGES Ochsner Journal 17:311 316, 2017 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Reduction for Management of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy
CLINICAL IMAGES Ochsner Journal 17:311 316, 2017 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Reduction for Management of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy
Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients
 Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients Safi Dokmak HBP department and liver transplantation Beaujon Hospital, Clichy, France Cairo, 5 April 2016 Cirrhosis Prevalence in France (1%)* Patients
Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients Safi Dokmak HBP department and liver transplantation Beaujon Hospital, Clichy, France Cairo, 5 April 2016 Cirrhosis Prevalence in France (1%)* Patients
LIVER CIRRHOSIS. The liver extracts nutrients from the blood and processes them for later use.
 LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
TIPS. D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK
 TIPS D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK TIPS Technique Ascites Budd Chiari Variceal Bleeding Historical Experimental Development 1967 Piccone Shunt between recanalized umbilical vein and saphenous
TIPS D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK TIPS Technique Ascites Budd Chiari Variceal Bleeding Historical Experimental Development 1967 Piccone Shunt between recanalized umbilical vein and saphenous
Management of Chronic Liver Failure/Cirrhosis Complications in Hospitals. By: Dr. Kevin Dolehide
 Management of Chronic Liver Failure/Cirrhosis Complications in Hospitals By: Dr. Kevin Dolehide Overview DX Cirrhosis and Prognosis Compensated Decompensated Complications Of Cirrhosis Management Of Complications
Management of Chronic Liver Failure/Cirrhosis Complications in Hospitals By: Dr. Kevin Dolehide Overview DX Cirrhosis and Prognosis Compensated Decompensated Complications Of Cirrhosis Management Of Complications
Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap. Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds
 Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds Scale UK 100,000 /year Commonest Vascular IR on-call 75% UGIB 65% NVUGIB
Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds Scale UK 100,000 /year Commonest Vascular IR on-call 75% UGIB 65% NVUGIB
Obliterative hepatocavopathy ultrasound and cavography findings
 doi:10.2478/v10019-008-0020-6 case report Obliterative hepatocavopathy ultrasound and cavography findings Ramazan Kutlu Department of Radiology, Inonu University School of Medicine, Malatya, Turkey ackgound.
doi:10.2478/v10019-008-0020-6 case report Obliterative hepatocavopathy ultrasound and cavography findings Ramazan Kutlu Department of Radiology, Inonu University School of Medicine, Malatya, Turkey ackgound.
British Society of Gastroenterology. St. Elsewhere's Hospital. National Comparative Audit of Blood Transfusion
 British Society of Gastroenterology UK Com parat ive Audit of Upper Gast roint est inal Bleeding and t he Use of Blood Transfusion Extract December 2007 St. Elsewhere's Hospital National Comparative Audit
British Society of Gastroenterology UK Com parat ive Audit of Upper Gast roint est inal Bleeding and t he Use of Blood Transfusion Extract December 2007 St. Elsewhere's Hospital National Comparative Audit
Emergency - Upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage
 Emergency - Upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage Definitions in upper gastrointestinal (UGI) haemorrhage UGI haemorrhage: bleeding that arises proximal to the ligament of Treitz i.e. from the oesophagus,
Emergency - Upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage Definitions in upper gastrointestinal (UGI) haemorrhage UGI haemorrhage: bleeding that arises proximal to the ligament of Treitz i.e. from the oesophagus,
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12:
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12: 805-809. CLINICAL PEARL Indications for Use of TIPS in Treating Portal Hypertension Elizabeth C. Verna,
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12: 805-809. CLINICAL PEARL Indications for Use of TIPS in Treating Portal Hypertension Elizabeth C. Verna,
Clinical Study A Single-Institution Review of Portosystemic Shunts in Children: An Ongoing Discussion
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation HPB Surgery Volume 2010, Article ID 964597, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2010/964597 Clinical Study A Single-Institution Review of Portosystemic Shunts in Children: An Ongoing Discussion
Hindawi Publishing Corporation HPB Surgery Volume 2010, Article ID 964597, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2010/964597 Clinical Study A Single-Institution Review of Portosystemic Shunts in Children: An Ongoing Discussion
Blood and guts.. Haemodynamics / resuscitation. Haemodynamics / resuscitation. Blood and guts. Dr Jonathan Hoare
 Blood and guts. Dr Jonathan Hoare Consultant St Mary s Hospital Dr Jonathan Hoare Consultant St Mary s Hospital, Paddington Blood and guts.. Presentation Initial assessment and management risk stratification
Blood and guts. Dr Jonathan Hoare Consultant St Mary s Hospital Dr Jonathan Hoare Consultant St Mary s Hospital, Paddington Blood and guts.. Presentation Initial assessment and management risk stratification
Emergency Surgery Course Graz, March UPPER GI BLEEDING. Carlos Mesquita Coimbra
 UPPER GI BLEEDING Carlos Mesquita Coimbra Aim Causes Management Problem Above angle of Treitz Common emergency 1-2/1000 pts 10% rebleeed 1% angioembolization 20% over 60
UPPER GI BLEEDING Carlos Mesquita Coimbra Aim Causes Management Problem Above angle of Treitz Common emergency 1-2/1000 pts 10% rebleeed 1% angioembolization 20% over 60
DRAFT. Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect. What is a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect This handout explains a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and what to expect when
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect This handout explains a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and what to expect when
Central role: - Regulating the immune system - Influencing metabolic and endocrine functions
 Spleen Central role: - Regulating the immune system - Influencing metabolic and endocrine functions Anatomy: An encapsulated mass of vascular and lymphatic tissue The largest RES organ 9-11 th ribs 4 impressions
Spleen Central role: - Regulating the immune system - Influencing metabolic and endocrine functions Anatomy: An encapsulated mass of vascular and lymphatic tissue The largest RES organ 9-11 th ribs 4 impressions
ACUTE VARICEAL BLEEDING MULTIMODAL APPROACH
 FALK symposium. Liver Cirrhosis: from pathophysiology to disease management Dresden, October 13-14 14 2007 ACUTE VARICEAL BLEEDING MULTIMODAL APPROACH Professor Andrew K Burroughs Hepato-biliary biliary-pancreatic
FALK symposium. Liver Cirrhosis: from pathophysiology to disease management Dresden, October 13-14 14 2007 ACUTE VARICEAL BLEEDING MULTIMODAL APPROACH Professor Andrew K Burroughs Hepato-biliary biliary-pancreatic
Thrombocytopenia and Chronic Liver Disease
 Thrombocytopenia and Chronic Liver Disease Severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count
Thrombocytopenia and Chronic Liver Disease Severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
Review Article Role of Self-Expandable Metal Stents in Acute Variceal Bleeding
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Hepatology Volume 2012, Article ID 418369, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/418369 Review Article Role of Self-Expandable Metal Stents in Acute Variceal
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Hepatology Volume 2012, Article ID 418369, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/418369 Review Article Role of Self-Expandable Metal Stents in Acute Variceal
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management Nizar A. Mukhtar, MD Co-director, SMC Liver Tumor Board April 30, 2016 1 Objectives Review screening/surveillance guidelines Discuss diagnostic algorithm
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management Nizar A. Mukhtar, MD Co-director, SMC Liver Tumor Board April 30, 2016 1 Objectives Review screening/surveillance guidelines Discuss diagnostic algorithm
Contraindications. Indications. Complications. Currently TIPS is considered second or third line therapy for:
 Contraindications Absolute Relative Primary prevention variceal bleeding HCC if centrally located Active congestive heart failure Obstruction all hepatic veins Thomas D. Boyer, M.D. University of Arizona
Contraindications Absolute Relative Primary prevention variceal bleeding HCC if centrally located Active congestive heart failure Obstruction all hepatic veins Thomas D. Boyer, M.D. University of Arizona
The Yellow Patient. Dr Chiradeep Raychaudhuri, Consultant Hepatologist, Hull University Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
 The Yellow Patient Dr Chiradeep Raychaudhuri, Consultant Hepatologist, Hull University Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust there s a yellow patient in bed 40. It s one of yours. Liver Cirrhosis Why.When.What.etc.
The Yellow Patient Dr Chiradeep Raychaudhuri, Consultant Hepatologist, Hull University Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust there s a yellow patient in bed 40. It s one of yours. Liver Cirrhosis Why.When.What.etc.
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE. The Role of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in the Management of Portal Hypertension. Preamble.
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Role of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in the Management of Portal Hypertension Thomas D. Boyer 1 and Ziv J. Haskal 2 Preamble The recommendations in this article
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Role of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in the Management of Portal Hypertension Thomas D. Boyer 1 and Ziv J. Haskal 2 Preamble The recommendations in this article
NS 17. McArdle J (1999) Understanding oesophageal varices. Nursing Standard. 14, 9, Date of acceptance: June
 Understanding Joseph McArdle BSc, DipHE, RGN, is Training and Nurse Development Co-ordinator, Royal Liverpool University Hospitals Trust. By reading this article and writing a Practice Profile, you can
Understanding Joseph McArdle BSc, DipHE, RGN, is Training and Nurse Development Co-ordinator, Royal Liverpool University Hospitals Trust. By reading this article and writing a Practice Profile, you can
ICU Volume 14 - Issue 2 - Summer Matrix
 ICU Volume 14 - Issue 2 - Summer 2014 - Matrix Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Authors David Osman, MD Medical Intensive Care Unit Paris-South University Hospitals Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris
ICU Volume 14 - Issue 2 - Summer 2014 - Matrix Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Authors David Osman, MD Medical Intensive Care Unit Paris-South University Hospitals Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris
EDUCATION PRACTICE. Management of Refractory Ascites. Clinical Scenario. The Problem
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1187 1191 EDUCATION PRACTICE Management of Refractory Ascites ANDRÉS CÁRDENAS and PERE GINÈS Liver Unit, Institute of Digestive Diseases, Hospital Clínic,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1187 1191 EDUCATION PRACTICE Management of Refractory Ascites ANDRÉS CÁRDENAS and PERE GINÈS Liver Unit, Institute of Digestive Diseases, Hospital Clínic,
Direct Intrahepatic Porta-Caval Shunt Technique & Tips-Tricks. Pierre GOFFETTE, MD, St-Luc University Hospital University of Leuven Brussels
 Direct Intrahepatic Porta-Caval Shunt Technique & Tips-Tricks Pierre GOFFETTE, MD, St-Luc University Hospital University of Leuven Brussels Pierre Goffette, M.D. Consultant/Advisory Board: Covidien (Neuro)
Direct Intrahepatic Porta-Caval Shunt Technique & Tips-Tricks Pierre GOFFETTE, MD, St-Luc University Hospital University of Leuven Brussels Pierre Goffette, M.D. Consultant/Advisory Board: Covidien (Neuro)
Upper GI Bleeds. AMU Nurse Teaching Dr Clare Pollard ST6 AIM & GIM
 Upper GI Bleeds AMU Nurse Teaching Dr Clare Pollard ST6 AIM & GIM Peptic ulcer disease - GU - DU Talk Plan Important considerations in this group of patients- what you need to know Mallory Weis Tear Other
Upper GI Bleeds AMU Nurse Teaching Dr Clare Pollard ST6 AIM & GIM Peptic ulcer disease - GU - DU Talk Plan Important considerations in this group of patients- what you need to know Mallory Weis Tear Other
PORTAL HYPERTENSION An Introduction to the Culprit of Many Liver Failure Complications
 PORTAL HYPERTENSION An Introduction to the Culprit of Many Liver Failure Complications Edy G. Trujillo, RN, MSN, ACNP-BC Liver Transplant RRUCLA Medical Center July 31, 2018 What Do We All Look Forward
PORTAL HYPERTENSION An Introduction to the Culprit of Many Liver Failure Complications Edy G. Trujillo, RN, MSN, ACNP-BC Liver Transplant RRUCLA Medical Center July 31, 2018 What Do We All Look Forward
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS: PRACTICE ESSENTIALS AND PATIENT SELF-MANAGEMENT
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS: PRACTICE ESSENTIALS AND PATIENT SELF-MANAGEMENT Sherona Bau, ACNP The Pfleger Liver Institute 200 UCLA Medical Plaza, Suite 214 Los Angeles, CA 90095 September 30, 2017 I
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS: PRACTICE ESSENTIALS AND PATIENT SELF-MANAGEMENT Sherona Bau, ACNP The Pfleger Liver Institute 200 UCLA Medical Plaza, Suite 214 Los Angeles, CA 90095 September 30, 2017 I
Left-sided portal hypertension with a patent splenic vein: An impossible or a not-so-uncommon scenario?
 Khan et al. 108 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Left-sided portal hypertension with a patent splenic vein: An impossible or a not-so-uncommon scenario? Iftikhar Khan, Ghassan Ramahi, Saif Zaabi,
Khan et al. 108 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Left-sided portal hypertension with a patent splenic vein: An impossible or a not-so-uncommon scenario? Iftikhar Khan, Ghassan Ramahi, Saif Zaabi,
Preliminary study of the permeability and safety of covered stents-grafts in pediatric TIPS
 Preliminary study of the permeability and safety of covered stents-grafts in pediatric TIPS Poster No.: C-0354 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Bueno Palomino, L. Zurera Tendero,
Preliminary study of the permeability and safety of covered stents-grafts in pediatric TIPS Poster No.: C-0354 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Bueno Palomino, L. Zurera Tendero,
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure
 Patient Education Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure This handout explains what a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is and what to expect when you have
Patient Education Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure This handout explains what a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is and what to expect when you have
Management of Cirrhosis Related Complications
 Management of Cirrhosis Related Complications Ke-Qin Hu, MD, FAASLD Professor of Clinical Medicine Director of Hepatology University of California, Irvine Disclosure I have no disclosure related to this
Management of Cirrhosis Related Complications Ke-Qin Hu, MD, FAASLD Professor of Clinical Medicine Director of Hepatology University of California, Irvine Disclosure I have no disclosure related to this
Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) Standard Operating Procedure
 Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Title Oesophagogastric Tamponade Tube Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Upper GI Haemorrhage Author G Cowan, C
Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Title Oesophagogastric Tamponade Tube Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Upper GI Haemorrhage Author G Cowan, C
Historical perspective
 Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Barbara Rus Gadžijev Peter Popovič Klinični inštitut za radiologijo UKC Ljubljana
 STROKOVNI SESTANEK ZDRUŽENJA HEMATOLOGOV SLOVENIJE IN ZDRUŽENJA ZA TRANSFUZIJSKO MEDICINO, Terme Zreče, 17.-18.4.2015 Barbara Rus Gadžijev Peter Popovič Klinični inštitut za radiologijo UKC Ljubljana goals,
STROKOVNI SESTANEK ZDRUŽENJA HEMATOLOGOV SLOVENIJE IN ZDRUŽENJA ZA TRANSFUZIJSKO MEDICINO, Terme Zreče, 17.-18.4.2015 Barbara Rus Gadžijev Peter Popovič Klinični inštitut za radiologijo UKC Ljubljana goals,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Complications of Cirrhosis
 Complications of Cirrhosis Causes of Cirrhosis Alcohol Chronic Viral Hepatitis (B/C) Haemochromatosis Autoimmune Hepatitis NAFLD/NASH Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis 1-AT deficiency
Complications of Cirrhosis Causes of Cirrhosis Alcohol Chronic Viral Hepatitis (B/C) Haemochromatosis Autoimmune Hepatitis NAFLD/NASH Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis 1-AT deficiency
ischaemia during infusions lasting for up to six hours. Subsequently these workers and others in America used this technique in man for the rapid
 Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices by infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery Gut, 1973, 14, 59-63 IAIN M. MURRAY-LYON, R. N. H. PUGH, H. B. NUNNERLEY, J. W. LAWS, J. L. DAWSON,
Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices by infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery Gut, 1973, 14, 59-63 IAIN M. MURRAY-LYON, R. N. H. PUGH, H. B. NUNNERLEY, J. W. LAWS, J. L. DAWSON,
Denver Shunts vs TIPS for Ascites
 Denver Shunts vs TIPS for Ascites Hooman Yarmohammadi MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Interventional Radiology & Image Guided Therapies Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, USA Hooman
Denver Shunts vs TIPS for Ascites Hooman Yarmohammadi MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Interventional Radiology & Image Guided Therapies Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, USA Hooman
Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites. Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University
 Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Topic Definition, pathogenesis Current therapeutic options Experimental treatments
Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Topic Definition, pathogenesis Current therapeutic options Experimental treatments
Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart. O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R Joswiak, D Thakar, C Wood, G Walsh
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R
Before Endoscopy? Indications Thermal Coagulation Injection Therapy Combination Therapy Fibrin Sealant Endoclips Argon Plasma Coagulation Lysine -
 Dr Simon Smale Before Endoscopy? Indications Thermal Coagulation Injection Therapy Combination Therapy Fibrin Sealant Endoclips Argon Plasma Coagulation Lysine - Haemmostop Variceal Banding Histoacryl
Dr Simon Smale Before Endoscopy? Indications Thermal Coagulation Injection Therapy Combination Therapy Fibrin Sealant Endoclips Argon Plasma Coagulation Lysine - Haemmostop Variceal Banding Histoacryl
V ariceal haemorrhage is a major cause of mortality and
 270 LIVER DISEASE The role of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPSS) in the management of bleeding gastric : clinical and haemodynamic correlations D Tripathi, G Therapondos, E
270 LIVER DISEASE The role of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPSS) in the management of bleeding gastric : clinical and haemodynamic correlations D Tripathi, G Therapondos, E
DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL
 DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL 1. This Protocol sets out the medical evidence that must be delivered to the Administrator for proof of Disease Level. It is subject to such further and other Protocols
DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL 1. This Protocol sets out the medical evidence that must be delivered to the Administrator for proof of Disease Level. It is subject to such further and other Protocols
Surgical Rescue of Surgical Failures
 HPB Surgery, 1999, Vol. 11, pp. 151-155 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
HPB Surgery, 1999, Vol. 11, pp. 151-155 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
Warren shunt - significance in present time, an experience at tertiary care hospital in India
 International Surgery Journal Khan MS et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Aug;3(3):1345-1350 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20162708
International Surgery Journal Khan MS et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Aug;3(3):1345-1350 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20162708
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in children. Nguyễn Diệu Vinh, MD Department of Gastroenterology
 Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in children Nguyễn Diệu Vinh, MD Department of Gastroenterology INTRODUCTION Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding : arising proximal to the ligament of Treitz in the distal
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in children Nguyễn Diệu Vinh, MD Department of Gastroenterology INTRODUCTION Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding : arising proximal to the ligament of Treitz in the distal
V ariceal bleeding is a serious complication of portal
 431 LIVER Randomised controlled trial of long term portographic follow up versus variceal band ligation following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt for preventing oesophageal variceal
431 LIVER Randomised controlled trial of long term portographic follow up versus variceal band ligation following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt for preventing oesophageal variceal
Diagnostic Procedures. Measurement of Hepatic venous pressure in management of cirrhosis. Clinician s opinion
 5 th AISF Post-Meeting Course Diagnostic and Therapeutic Invasive Procedures in Hepatology Rome, February 25 th Diagnostic Procedures Measurement of Hepatic venous pressure in management of cirrhosis Clinician
5 th AISF Post-Meeting Course Diagnostic and Therapeutic Invasive Procedures in Hepatology Rome, February 25 th Diagnostic Procedures Measurement of Hepatic venous pressure in management of cirrhosis Clinician
GASTROINESTINAL BLEEDING. Dr.Ammar I. Abdul-Latif
 GASTROINESTINAL BLEEDING Dr.Ammar I. Abdul-Latif CLASSIFICATION OF G.I.BLEEDING GIB Appearance Acuity Site Apparent Acute Upper Obscure Chronic Lower UPPER&LOWER G.I.BLEEDING CAUSES OF UPPER G.I. BLEEDING
GASTROINESTINAL BLEEDING Dr.Ammar I. Abdul-Latif CLASSIFICATION OF G.I.BLEEDING GIB Appearance Acuity Site Apparent Acute Upper Obscure Chronic Lower UPPER&LOWER G.I.BLEEDING CAUSES OF UPPER G.I. BLEEDING
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Liver Failure. The most severe clinical consequence of liver disease is liver failure:
 Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Portal hypertension is the main complication of cirrhosis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:726 748 Current Management of the Complications of Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Variceal Hemorrhage, Ascites, and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis GUADALUPE GARCIA TSAO
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:726 748 Current Management of the Complications of Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Variceal Hemorrhage, Ascites, and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis GUADALUPE GARCIA TSAO
Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer. Nakarin Inmutto MD
 Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer Nakarin Inmutto MD Liver cancer Primary liver cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis Interventional Radiologist Diagnosis Imaging US / CT
Interventional Radiology in Liver Cancer Nakarin Inmutto MD Liver cancer Primary liver cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis Interventional Radiologist Diagnosis Imaging US / CT
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
following the last documented transfusion; thereafter, evaluate the residual impairment(s).
 Adult Listings 5.01 Category of Impairments, Digestive System 5.02 Gastrointestinal hemorrhaging from any cause, requiring blood transfusion (with or without hospitalization) of at least 2 units of blood
Adult Listings 5.01 Category of Impairments, Digestive System 5.02 Gastrointestinal hemorrhaging from any cause, requiring blood transfusion (with or without hospitalization) of at least 2 units of blood
Assessment of Liver Function: Implications for HCC Treatment
 Assessment of Liver Function: Implications for HCC Treatment A/P Dan Yock Young MBBS, PhD, MRCP, MMed. FAMS Chair, University Medicine Cluster. NUHS Head, Department of Medicine, National University of
Assessment of Liver Function: Implications for HCC Treatment A/P Dan Yock Young MBBS, PhD, MRCP, MMed. FAMS Chair, University Medicine Cluster. NUHS Head, Department of Medicine, National University of
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
INFORMED CONSENT FOR LAPAROSCOPIC ADJUSTABLE GASTRIC BAND. Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand.
 Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to undergo laparoscopic placement of a laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band for the purposes of weight loss. I met
Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to undergo laparoscopic placement of a laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band for the purposes of weight loss. I met
ABDOMINAL PAIN (SEE ALSO ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM)
 ABDOMINAL PAIN (SEE ALSO ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM) Evaluating abdominal pain is difficult misdiagnosis of this symptom generates more formal complaints than any other clinical mistake made in our department.
ABDOMINAL PAIN (SEE ALSO ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM) Evaluating abdominal pain is difficult misdiagnosis of this symptom generates more formal complaints than any other clinical mistake made in our department.
Surgical conditions of liver Somkit Mingphruedhi, M.D.
 Surgical conditions of liver Somkit Mingphruedhi, M.D. Division of HPB Surgery, Department of Surgery Ramathibodi Hospital Anatomy IVC Portal Vein Hepatic Artery Splenic Vein Gallbladder CBD SMV Anatomy
Surgical conditions of liver Somkit Mingphruedhi, M.D. Division of HPB Surgery, Department of Surgery Ramathibodi Hospital Anatomy IVC Portal Vein Hepatic Artery Splenic Vein Gallbladder CBD SMV Anatomy
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165)
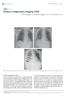 Singapore Med J 2016; 57(2): 92-96 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016033 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165) Wan Ying Chan 1, MBBS, Hsueh Wen Cheong 1, MBBS, FRCR, Tien Jin Tan 1, MBBS, FRCR 1a 1b 1c
Singapore Med J 2016; 57(2): 92-96 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016033 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165) Wan Ying Chan 1, MBBS, Hsueh Wen Cheong 1, MBBS, FRCR, Tien Jin Tan 1, MBBS, FRCR 1a 1b 1c
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
[7] Greene, B. S., Loubeau, J. M., Peoples, J. B. and Elliott, D. W. (1991). Are pancreatoenteric anastomoses improved
![[7] Greene, B. S., Loubeau, J. M., Peoples, J. B. and Elliott, D. W. (1991). Are pancreatoenteric anastomoses improved [7] Greene, B. S., Loubeau, J. M., Peoples, J. B. and Elliott, D. W. (1991). Are pancreatoenteric anastomoses improved](/thumbs/82/86447000.jpg) 136 HPB INTERNATIONAL mosis. In our experience, roughly 10% of patients will have low volume amylase-rich fluid draining via the drains. Over 85% of these low volume pancreatic fistulas will heal with
136 HPB INTERNATIONAL mosis. In our experience, roughly 10% of patients will have low volume amylase-rich fluid draining via the drains. Over 85% of these low volume pancreatic fistulas will heal with
S planchnic vein thrombosis is not an uncommon
 691 LIVER Splanchnic vein thrombosis in candidates for liver transplantation: usefulness of screening and anticoagulation C Francoz, J Belghiti, V Vilgrain, D Sommacale, V Paradis, B Condat, M H Denninger,
691 LIVER Splanchnic vein thrombosis in candidates for liver transplantation: usefulness of screening and anticoagulation C Francoz, J Belghiti, V Vilgrain, D Sommacale, V Paradis, B Condat, M H Denninger,
urhealth March 2018 Nu Mu Lambda...
 March 2018 1 Health & Wellness Committee Bro. Trenton Taylor Committee Chair Bro. William J. Bennett, M.D., Ph.D. Medical Editor Contents Portal Hypertension 3 12 Renal Artery Stenosis 13-16 Holiday Depression
March 2018 1 Health & Wellness Committee Bro. Trenton Taylor Committee Chair Bro. William J. Bennett, M.D., Ph.D. Medical Editor Contents Portal Hypertension 3 12 Renal Artery Stenosis 13-16 Holiday Depression
LIVER. Question 1 ~ Anatomy. Answer 1 ~ Anatomy 1/5/2018. SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017
 SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
SEMCME Board Review January 11-12, 2017 Surgical Treatment of Hepatobiliary and Splenic Disorders Michael J. Jacobs, MD, FACS, FICS Clinical Professor of Surgery- MSU CHM Associate Chair of Surgery Director
