Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy: The Effect on Neurodevelopment in the Child
|
|
|
- Sophia Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nutrients 2010, 2, 1-xmanuscripts; doi: /nu20x000x Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy: The Effect on Neurodevelopment in the Child Sheila A. Skeaff Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago, PO Box 56, Dunedin 9054, New Zealand; sheila.skeaff@otago.ac.nz Received: / Accepted: / Published: Abstract: Iodine is an integral part of the thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T 4 ) and triiodothyronine (T 3 ), necessary for normal growth and development. An adequate supply of maternal free T 4 (ft 4 ), generated in the brain from T 3, is needed by the fetus for thyroid hormone dependent neurodevelopment, which begins in the second half of the first trimester of pregnancy. Around the beginning of the second trimester the fetal thyroid also begins to produce hormones but the reserves of the fetal gland are low, thus maternal thyroid hormones contribute to total fetal thyroid hormone concentrations until birth. In order for pregnant women to produce enough thyroid hormones to meet both her own and her baby s requirements, iodine intake needs to increase by 50%. If this does not occurs, the mother may become iodine deficient, and subsequently the fetus. In iodine deficiency, hypothyroxinemia (i.e. low maternal ft 4 ) results in damage to the developing brain, which is further aggravated by hypothyroidism in the fetus. The most serious consequence of iodine deficiency is cretinism, characterised by profound mental retardation. There is unequivocal evidence that severe iodine deficiency in pregnancy impairs brain development in the child. However, only two intervention trials have assessed neurodevelopment in children of moderately iodine deficient mothers finding improved neurodevelopment in children of mothers supplemented earlier rather than later in pregnancy; both studies had methodological limitations. There is a need for well-designed trials to determine the effect of iodine supplementation in moderate to mildly iodine deficient pregnant women on neurodevelopment in the child. Keywords: iodine; pregnancy; child; cretinism; neurodevelopment
2 Nutrients 2010, Introduction Despite considerable progress over the last 25 years, iodine deficiency is still one of the most common micronutrient deficiencies in the world today. Iodine deficiency results in a wide spectrum of adverse consequences throughout the lifecycle. Of greatest concern is the effect of iodine deficiency on the developing brain. The most serious effect of iodine deficiency is cretinism, which occurs in women who are severely iodine deficient during pregnancy. The promotion of iodised salt by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Council for the Control of Iodine Deficiency Disorders (ICCIDD) has helped to alleviate endemic cretinism in many parts of the world. Attention is now turning to the adverse effects of moderate and mild iodine deficiency in pregnancy. Although iodine deficiency in pregnancy will affect both the mother and the child, little attention has been paid to the consequences of iodine deficiency on maternal health. This review will describe the role iodine plays, via thyroid hormones, in the development of the brain from conception to birth and present evidence of the impact of severe, moderate, and mild iodine deficiency in pregnancy on neurodevelopment in the child. 2. The Role of Thyroid Hormones in Fetal Brain Development Iodine is essential for the production of the thyroid hormones, the prohormonethyroxine (T 4 ) and the active form 3,5,3 -triiodothyronine (T 3 ), which are vital for normal growth and development particularly of the brain and central nervous system. Maternal thyroid hormones are found in the embryonic cavities ~4 weeks after conception despite the placenta acting as a barrier designed to prevent excessively high levels of ft 4 and T 3 from reaching the fetus before they are needed[1,2]. Thyroid hormones are not believed to play a role in very early fetal development as studies have shown that nuclear receptors for thyroid hormones are only present in the fetal brain from ~8-9 weeks gestation reaching adult levels by 18 weeks gestation[2]. Before midgestation, the mother is the only source of cerebral T 3, which is generated locally by type II 5 iodothyroninedeiodinase activity from maternal free T 4 (ft 4 ). The first stage of thyroid hormone dependent neurodevelopment begins in the second half of the first trimester and includes neuronal proliferation and the onset of neuronal migration in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and medial ganglionic eminence, the latter processes starting in the first trimester and continuing into the early part of the second trimester; this stage depends on an adequate supply of maternal ft 4 [2]. Towards the end of the first trimester, in response to high concentrations of placental human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg), there is a surge in maternal T 4 and a decline in thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), a mechanism thought to ensure that ft 4 is supplied to the fetus during this period[2,3]. Around the beginning of the second trimester the fetal thyroid begins to produce hormones, however, the full development of the pituitary-portal vascular system in the fetus does not occur until ~18-20 weeks gestation[1]. The second stage of thyroid hormone neurodevelopment includes such processes as neurogenesis, neuron migration, axonal growth, dendritic branching and synaptogenesis, glial cell differentiation and migration, and the onset of myelination. The third stage occurs after birth [2]. Although the concentration of T 4 in the fetus increases as gestation progresses, the reserves of the fetal gland are low and the gland itself does not fully mature until birth, thus maternal thyroid hormones continue to contribute to total fetal thyroid
3 Nutrients 2010, hormone concentrations until birth. It is no surprise, therefore, that low ft 4 occurs in premature babies as they are deprived of a maternal supply, and this may partly account for some of the developmental delay often apparent in such children[2]. In order for pregnant women to produce enough thyroid hormones to meet fetal requirements, iodine intake needs to increase by 50%. If this does not occurs, then the mother may become iodine deficient, and subsequently the fetus. The mother and the fetus, however, respond differently to this situation, with the mother remaining euthyroid and fetus becoming hypothyroid[3]. Iodine deficient pregnant women remain euthyroid for two reasons. Firstly, the increase in maternal ft 4 that occurs at the end of the first trimester in response to hcg depresses the concentration of maternal TSH. Secondly, the maternal thyroid gland responds to a state of relative iodine deficiency by invoking the same responses in the thyroid gland as would occur in the non-pregnant state, such as increased iodine trapping, preferential synthesis of T 3 over T 4, hyperplasia, and eventually goitre. Thus, the woman will appear to be euthyroid as both her TSH and T 3 concentration will fall within the normal reference range. In such situations, localisedhypothyroxinemia occurring in specific parts of the developing fetal brain is believed to be responsible for the neurodevelopmental damage seen in iodine deficiency. The autoregulatary mechanisms available to the mother do not take place in the fetus because the fetal gland has not fully matured. Consequently, in the fetus there is a decreased synthesis and secretion of T 4 and T 3, and an increase in the concentration of TSH, resulting in fetal hypothyroidism[3]. This explains why neonatal TSH is used as an index of iodine deficiency in a population. A number of studies have been undertaken in women living in areas of adequate iodine status who have low T 4 concentrations in pregnancy, usually as a result of thyroid disease. In a study of Dutch women with ft 4 <10 th percentile during pregnancy it was found that their children had poorer psychomotor development at 10 months of age [4], and again at one and two years of age [5]than children whose mothers had higher T 4 levels in pregnancy. A more recent study found that pregnant Dutch women with ft 4 <10 th percentile at 12 weeks gestation had infants with significantly lower orientation scores as assessed using the Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale than mothers with ft 4 between the 50 th and 90 th percentiles [6]. Zoeller and Rovet discuss the role of thyroid hormones on brain development using data obtained from studies of maternal hypothyroidism andmaternal hypothyroxinaemia[7]. They suggest that decreased thyroid hormones early in pregnancy may cause problems in visual attention, visual processing, and gross motor skills, while a lack of thyroid hormones later in pregnancy results in further problems with visual skills, slower processing speeds, and fine motor skills. These observational studies provide evidence that avariations in maternal hormones influence normal brain development. It is important to remember that the cause of abnormal thyroid hormone concentrations in the studies discussed in this paragraph is usually the result of thyroid dysfunction in the mother, and not from iodine deficiency per se. Nonetheless, the assumption made by scientists working in this area is that, regardless of the cause, the functional consequences of abnormal thyroid hormoneson neurodevelopment in the fetus are the same. In summary, it is clear that low concentrations of maternal T 4, in particular,can hinder the development of the fetal brain. If severe to moderate iodine deficiency is present, the damage to the developing brain in the first half of pregnancy is caused by hypothyroxinemia of a euthyroid mother, which can continue in the second half of pregnancy and is then further aggravated by hypothyroidism in the fetus. It is uncertain, however, if this occurs in situations of moderate or mild iodine deficiency.
4 Nutrients 2010, Determining the Severity of Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy One of the problems in this area of research is the difficulty in determining the severity of iodine deficiency in pregnant women. The mostly commonly used index for assessing iodine status in a population is the median urinary iodine concentration (MUIC) as determined from a casual or spot urine sample. A MUIC >100 µg/l is indicative of adequate iodine status in children, men and nonpregnant women, with a MUIC of µg/l, µg/l, and <20 µg/l indicating mild, moderate, and severe iodine deficiency, respectively[8]. In 2007, WHO recommended a MUIC >150 µg/l be used in pregnancy, however, no cut-offs for the severity of iodine deficiency in pregnancy have been proposed [8]. Furthermore, given the large variability in the iodine concentration of casual urine samples, the iodine status of an individual cannot be determined from a urine sample. In other words, a pregnant woman cannot be classified as iodine deficient based on her urinary iodine concentration [9]. Pregnant women can have their thyroid hormones measured, with TSH and ft 4 typically used to define subclinical hypothyroidism (TSH >97.5 th percentile, ft 4 in normal reference range), overt hypothyroidism (TSH >97.5 th percentile and ft 4 <2.5 th percentile), and hypothyroxinemia (TSH in normal reference range, ft 4 <2.5 th percentile) [10]. There is debate as to whether all pregnant women should be screened for abnormal thyroid hormone concentrations in the first trimester. Changes in thyroid hormones can be caused by a variety of factors such as thyroid disease, and is not specific to iodine deficiency. Indeed, WHO do not recommend the routine use of TSH, T 4 and T 3 for monitoring iodine status in the adult population as these tests are relatively insensitive in moderate to mild iodine deficiency; MUIC provides sufficient information to assess iodine status in these groups. However, because of the importance of maternal thyroid hormone concentrations for normal fetal brain development, the establishment of trimester specific international reference ranges for thyroid hormones in iodine sufficient and deficient pregnant women could be useful in identifying at-risk women. 4. The Effect of Severe Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy on Neurodevelopment in the Child Severe iodine deficiency exists when more than 30% of children have goitre, a MUIC < 20 µg/l, and the presence of cretins in a community, born to women severely iodine deficient in pregnancy. Cretinism is always associated with a significant impairment in mental function and/or defects in hearing, speech, stance, gait, hypothyroidism and growth [11]. There are two types of cretinism, although the symptoms of both types can sometimes be seen in the same individual. The more common form of cretinism is neurological cretinism,characterised by mental retardation, deaf mutism, squint, spastic diplegia, and disorders of the stance and gait. The less common form of cretinism is called myxoedematous or hypothyroid cretinism and is characterised by less severe mental retardation, dwarfism,hypothyroidism, and a variety of other physical symptoms such as coarse and dry skin, a husky voice, and delayed sexual maturation. Normal IQ in a population is 100, while the IQ of cretins has been reported to be around 30 [12]. In areas with endemic cretinism, around 5-15% of noncretinous children will have impaired mental function with an IQ of 50-69; these children are sometimes referred to as sub-cretins [11]. Although factors such as the presence of goitrogens in the diet, thyroid auto immunity, and interactions with other trace elements such as seleniumhave been
5 Nutrients 2010, postulated to have a role in the development and type of cretinism, the overarching reason for cretinism is severe iodine deficiency in the mother[13]. The importance of adequate dietary iodine in preventing cretinism was highlighted in the 1960sin a large trial of 165,000 people living in a part of Papua New Guinea with severe iodine deficiency and endemic cretinsim[14]. In this study, families were allocated to iodised oil or placebo and subsequent studies found that an injection of iodised oil before conception or in early pregnancy reduced the incidence of cretinism and improved the motor and cognitive functions of children compared with those families who received the placebo. Another study undertaken in 1990 in a remote province in China with endemic cretinism examined the effect of iodised oil given during pregnancy on neurological outcomes. Children of mothers given iodine earlier in pregnancy had improved cognitive outcomes compared to mothers given iodine later in pregnancy at both two years [15] and again when children were school-aged [16]. A meta-analysis of Chinese studies reported a decrease of 8.7 IQ points in children living in severely iodine deficient areas whose mothers were untreated in pregnancy compared to supplemented mothers also living in severely iodine deficient areas [17]. It is unequivocal that severe iodine deficiency in pregnancy results in significant impairment in cognition in the child. It has been suggested that cretinism is at the far end of a spectrum of effects that iodine deficiency can have on the central nervous system, and that varying degrees of intellectual impairment can occur across this spectrum concordant with the degree of iodine deficiency. This theory has yet to be substantiated. 5. The Effect of Moderate to Mildiodine Deficiency in Pregnancy on Neurodevelopment in the Child A number of clinical trials published between in pregnant women living in regions with moderate deficiency are summarized in Table 1 [18-25]. Daily iodine supplements ranging from 100 to 300 µg of iodine were taken by women in their first or second trimester of pregnancy. The majority of the studies showed that iodine supplements were effective in alleviating aspects of iodine deficiency in supplemented women compared to those taking the placebo. With regard to these studies, iodine expert Dr Michael Zimmermann wrote because none of the trials measured long-term clinical outcomes, such as maternal goiter or infant development, the potential adverse effects of mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency during pregnancy remain unclear [26]. In 2009, two randomised trials were published investigating the effect of iodine supplementation in moderately iodine deficient pregnant women supplemented on neurodevelopment in their children. Berbelet al recruited three groups of pregnant women living in Spain at different phases of gestation (i.e. 4-6 wks, wks, and near term), who had T 4 concentrations<10 th percentile at recruitment but normal TSH throughout pregnancy, and supplemented them with 300 µg of iodine until the end of lactation [24]. When the children were 18 months old, the development quotient of children in mothers supplemented in the first trimester (i.e. 4-6 wks) was significantly higher than that of children whose mothers received supplements from wks gestation and near term. A limitation of this study is the small numbers of children tested, with less than 20 children in each of the three groups. Furthermore, these women were specifically selected because they had low ft 4 throughout pregnancy; whether such a result would be found in iodine deficient pregnant women with ft 4 concentrations >20 th percentile is not known. A second Spanish
6 Nutrients 2010, study by Velasco et al found that children of mothers supplemented with iodine in the first trimester had higher psychomotor development scores than children from mothers who did not start supplementation until the last month of pregnancy [25]. Although some socio-demographic variables were collected in this study with no significant differences between the two groups, the children in the supplemented group had mothers and fathers who were better educated and were more likely to be an only child. These and other social characteristics, such as household income, together could influence neurodevelopment and explain the results found. Furthermore, children were tested at different ages in this study (5.5 months vs 12.4 months). Finally, both studies were not randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, and although they suggest that neurodevelopment in the child may be adversely affected by moderate iodine deficiency, they are not definitive. Table 1. Intervention studies investigating the effect of iodine supplementation in pregnancy. Author (Year) Country n Methods Baseline UIC µg/l Romano et al (1991) Italy 35 1st trimester randomised to 0 or iodine supplement ( µg I/day). Effect on child neurodevelopment 37 Not assessed. Pederson et al (1993) Denmark weeks gestatationrandomised to 0 or 200 µg I/day. 55 Not assessed. Glinoer et al (1995) Belgium 120 Euthyroid women with signs of excessive thyroid stimulation randomised to 0 or 100 µg I/day. 36 Not assessed. Liesenkötter et al (1996) Germany weeks gestation given 300 µg I/day vs untreated women. 53 Not assessed. Nohr and Laurberg (2000) Denmark 144 Retrospective allocation at term based on self-reported intake of supplements containing 150 µgi /day Not given. Not assessed. Antonangeli et al (2002) Italy 86 Healthy women weeks gestation randomised to 50 or 200 µg I/day. 74 Not assessed. Berbel et al (2009) Spain 96 Mildly hypothyroxinemic women with normal TSH until term given 200 µg I/day until end of lactation from: 4-6 (Group 1); (Group 2); or weeks gestation (Group 3). 75 Brunet-Lezine developmental quotient of children at 18 months was: in Group 1 vs 92.2 in Group 2 (p<0.05) or 87.5 in Group 3 (p<0.001).
7 Nutrients 2010, 2 7 Velasco et al (2009) Spain 191 <10 weeks gestation (Group 1)vs last month of pregnancy (Group 2) given 300 µg/i day until end of lactation. 87 Bayley Psychomotor Development Index of children was: in Group 1 vs in Group 2 (p=0.02) UIC = urinary iodine concentration TSH = Thyroid Stimulating Hormone The consequences of milder types of iodine deficiency (i.e MUIC µg/l) in pregnancy have yet to be elucidated. In countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, which have seen the reemergence of mild iodine deficiency in the last two decades, there appears to be no obvious signs of impaired neurodevelopment over this period with children meeting the usual developmental milestones at appropriate times. It is possible that in mild iodine deficiency adaptive mechanisms conserve iodine in the mother, such that the mother can supply the infant with sufficient thyroid hormones for normal brain development; the parasitic nature of the fetus in pregnancy is wellknown. To date, there are no published studies examining the effect of iodine supplementation in mildly iodine deficient pregnant women on neurodevelopment in children to date, however, by 2015 the results of several ongoing randomised, placebo-controlled, intervention trials being conducted in Thailand, India [27], Australia and New Zealand should be available. Conducting such trials will become increasingly difficult in the coming years, as more populations become iodine sufficient around the world. 6. Conclusion Severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy is a known cause of cretinism and mental retardation.at present, there are limited data on the cognitive deficits of children born to mothers who are moderately iodine deficient in pregnancy. There is a need for well designed clinical trials investigating whether routine iodine supplementation of pregnant women living in regions of mild iodine deficiency improves neurodevelopment in children. References 1. Morreale de Escobar, G.; Obregon, M.J.; Escobar del Ray, F. Maternal thyroid hormones early in pregnancy and fetal brain development. Best Prac. Res. Clin. Endocrinol.2004, 18, Williams, G.R. Neurodevelopmental and neurophysiological actions of thyroid hormones. J. Neuroendocrinol.2008, 20, Morreale de Escobar, G.; Jesus Obregon, M.; Escobar del Ray, F. Iodine deficiency and brain development in the first half of pregnancy. Public Health Nutr.2007, 10, Pop, V.J.; Kuijpens, J.L.; van Baar, A.L.; Verkerk, G.; van Son, M.M.; Vijlder, J.J.; Vulsma, T.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Drexhage, H.A.; Vader, H.L. Low maternal free thyroxine concentrations during early pregnancy are associated with impaired psychomotor development in infancy. Clin. Endocrinol.1999, 50,
8 Nutrients 2010, Pop, V.J.; Brouwers, E.P.; Vader, H.L.; Vulsma, T.; van Baar, A.L.; Vijlder, J.J. Maternal hypothyroxinaemia during early pregnancy and subsequent child development: a 3 year follow-up study. Clin. Endocrinol.2003, 59, Kooistra, L.; Crawford, S.; van Baar, A.L.; Brouwers, E.P.; Pop, V.J. Neonatal effects of maternal hypothyroxinemia during early pregnancy. Pediatrics.2006, 117, Zoeller, R.T.; Rovet, J. Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: clinical observations and experimental findings. J. Neuroendocrinol.2004, 16, WHO; UNICEF; ICCIDD. Assessment of iodine deficiency disorders and monitoring their elimination: a guide for programme managers, 3 rd Ed;. World Health Organization, \: Geneva, Switzerland, Skeaff, S.; Thomson, C.; Eastman, C. Iodine deficiency does exist but is difficult to assess in individuals (Letter). NZ Med. J.2009, 122, Costeira, M.J.; Oliveira, P.; Ares, S.; Roque, S.; Morreale de Escobar, G.; Palha, J.A. Parameters of thryoid function throughout and after pregnancy in an iodine-deficient population. Thyroid.2010, 20, Chen, Z.-P.; Hetzel, B.S. Cretinism revisited. Best Prac. Res. Clin. En.2010, 24, Rajatanavin, R.; Chailurkit, L.; Winichakoon, P.; Mahachoklertwattana, P.; Soranasataporn, S.; Wacharasin, R.; Chaisongkram, V.; Amatyakul, P.; Wanarata, L. Endemic cretinism in Thailand: a multidiciplinary study. Eur. J. Endocrinol.1997, 137, Zimmermann, M.B. Iodine deficiency. Endo. Rev.2009, 30, Pharoah, P.O.D.; Buttfield, I.H.; Hetzel, B.S. Neurological damage to the fetus resulting from severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy. Lancet.1971, 297, Cao, X.-Y.; Jiang, X.-M.; Dou, Z.-H.; Rakeman, M.A.; Zhang, M.-L.; O'Donnell, K.J.; Ma, T.; Amette, K.; DeLong, N. ; DeLong, R. Timing of vulnerability of the brain to iodine deficiency in endemic cretinism. New Eng. J. Med. 1994, 331, O'Donnell, K.J.; Rakeman, M.A.; Zhi-Hong, D.; Xue-Yi, C.; Mei, Z.Y.; DeLong, N.; Brenner, G.; Tai, M.; Dong, W. ; DeLong, G.R. Effects of iodine supplementation during pregnancy on child growth and development at school age. Dev. Med. Child Neurol.2002, 44, Qian, M.; Wang, D.; Watkins, W.E.; Gebski, V.; Yan, Y.Q.; Li, M. ; Chen, Z.P. The effects of iodine on intelligence in children: a meta-analysis of studies conducted in China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr.2005, 14, Liesenkotter, K.P.; Gopel, W.; Bogner, U.; Stach, B.; Gruters, A. Earliest prevention of endemic goiter by iodine supplementation during pregnancy. Eur. J. Endocrinol.1996, 134, Romano, R.; Jannini, E.A.; Pepe, M. The effects of iodoprophylaxis on thyroid size during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.1991, Pedersen, K.M.; Laurberg, P.; Iversen, E.; Knudsen, P.R.; Gregersen, H.E.; Rasmussen, O.S.; Larsen, K.R.; Eriksen, G.M.; Johannesen, P.L. Amelioration of some pregnancy-associated variations in thyroid function by iodine supplementation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.1993, 77, Glinoer, D.; De Nayer, P.; Delange, F.; Lemone, M.; Topper, V.; Spehl, M.; Grun, J.P.; Kinthaert, J.; Lejeune, B. A randomised trial for the treatment of mild iodine deficiency during pregnancy: maternal and neonatal effects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.1995, 80,
9 Nutrients 2010, Nohr, S.B.; Laurberg, P. Opposite variations in maternal and neonatal thyroid function inducsed by iodine supplementation during pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.2000, 85, Antonangeli, L.; Maccherini, D.; Cavaliere, R.; Di Giulio, C.; Reinhardt, B.; Pinchera, A.; Aghini- Lombardi, F. Comparison of two different doses of iodide in the prevention of gestational goiter in marginal iodine deficiency: a longitudinal study. Eur. J. Endocrinol.2002, 147, Berbel, P.; Mestre, J.L.; Santamaria, A.; Palazon, I.; Franco, A.; Graells, M.; Gonzalez-Torga, A. ; de Escobar, G.M. Delayed neurobehavioral development in children born to pregnant women with mild hypothyroxinemia during the first month of gestation: the importance of early iodine supplementation. Thyroid.2009, 19, Velasco, I.; Carreira, M.; Santiago, P.; Muela, J.A.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Sanchez-Munoz, B.; Garriga, M.J.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, M.C.; Rodriguez, A.; Caballero, F.F.; Machado, A.; Gonzalez-Romero, S.; Anarte, M.T. Soriguer, F. Effect of iodine prophylaxis during pregnancy on neurocognitive development of children during the first two years of life. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.2009, 94, Zimmermann, M.B. Iodine deficiency in pregnancy and the effects of maternal iodine supplementation in offspring: a review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr.2009, 89, 668S-672S. 27. Melse-Boonstra, A.; Jaiswal, N. Iodine deficiency in pregnancy, infancy and childhood and its consequences for brain development. Best Prac. Res. Clin. Endocrinol.2010, 24, by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (
Iodine and Thyroid Hormones
 Iodine and Thyroid Hormones Iodine and Thyroid Hormones feed-back Iodine Deficiency Characteristics Iodine Deficiency None Mild Mode Severe Median urine iodine >100 50-99 20-49
Iodine and Thyroid Hormones Iodine and Thyroid Hormones feed-back Iodine Deficiency Characteristics Iodine Deficiency None Mild Mode Severe Median urine iodine >100 50-99 20-49
Iodine deficiency (ID) is the most preventable cause of
 THYROID Volume 20, Number 11, 2010 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2010.0046 PREGNANCY AND FETAL DEVELOPMENT Patterns of Iodine Intake and Urinary Iodine Concentrations During Pregnancy and Blood
THYROID Volume 20, Number 11, 2010 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2010.0046 PREGNANCY AND FETAL DEVELOPMENT Patterns of Iodine Intake and Urinary Iodine Concentrations During Pregnancy and Blood
November 19, Dear Mr. Hernandez:
 November 19, 2017 Samuel Hernandez U.S. EPA, Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water Standards and Risk Management Division, (Mail Code 4607M), 1200 Pennsylvania Avenue NW. Washington, DC 20460; RE:
November 19, 2017 Samuel Hernandez U.S. EPA, Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water Standards and Risk Management Division, (Mail Code 4607M), 1200 Pennsylvania Avenue NW. Washington, DC 20460; RE:
Hypothyroidism in pregnancy. Nor Shaffinaz Yusoff Azmi Jabatan Perubatan Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah Kedah
 Hypothyroidism in pregnancy Nor Shaffinaz Yusoff Azmi Jabatan Perubatan Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah Kedah Agenda 1. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of maternal hypothyroidism 2. Prevention and
Hypothyroidism in pregnancy Nor Shaffinaz Yusoff Azmi Jabatan Perubatan Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah Kedah Agenda 1. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of maternal hypothyroidism 2. Prevention and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 January 26.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011 December ; 40(4): 765 777. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2011.08.001. Iodine Nutrition in Pregnancy and Lactation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011 December ; 40(4): 765 777. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2011.08.001. Iodine Nutrition in Pregnancy and Lactation
Maternal Mild Thyroid Insufficiency and Risk of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
 J O U R N A L C L U B Maternal Mild Thyroid Insufficiency and Risk of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder SOURCE CITATION: Modesto T, Tiemeier H, Peeters RP, Jaddoe VWV, Hofman A, Verhulst FC, et
J O U R N A L C L U B Maternal Mild Thyroid Insufficiency and Risk of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder SOURCE CITATION: Modesto T, Tiemeier H, Peeters RP, Jaddoe VWV, Hofman A, Verhulst FC, et
Iodine Deficiency in the UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition. Dr Alison Tedstone Department of Health
 Iodine Deficiency in the UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition Dr Alison Tedstone Department of Health Iodine deficiency disorders according to physiological group (Hetzel, 1983 1 ) Physiological
Iodine Deficiency in the UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition Dr Alison Tedstone Department of Health Iodine deficiency disorders according to physiological group (Hetzel, 1983 1 ) Physiological
How to manage hypothyroid disease in pregnancy
 For mass reproduction, content licensing and permissions contact Dowden Health Media. FIRST OF 2 PARTS How to manage hypothyroid disease in pregnancy Pregnancy complicated by hypothyroidism puts mother
For mass reproduction, content licensing and permissions contact Dowden Health Media. FIRST OF 2 PARTS How to manage hypothyroid disease in pregnancy Pregnancy complicated by hypothyroidism puts mother
Iodine deficiency disorders after a decade of universal salt iodization in a severe iodine deficiency region in China
 Indian J Med Res 130, October 2009, pp 413-417 Iodine deficiency disorders after a decade of universal salt iodization in a severe iodine deficiency region in China Yanling Wang *,**, Zhongliang Zhang,
Indian J Med Res 130, October 2009, pp 413-417 Iodine deficiency disorders after a decade of universal salt iodization in a severe iodine deficiency region in China Yanling Wang *,**, Zhongliang Zhang,
Submitted 11 May 2013: Final revision received 25 July 2014: Accepted 3 August 2014
 : page 1 of 6 doi:10.1017/s1368980014002237 Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction with adequate and excessive iodine intake in Hebei Province, People s Republic of China Long Tan 1, Zhongna Sang 1, Jun Shen
: page 1 of 6 doi:10.1017/s1368980014002237 Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction with adequate and excessive iodine intake in Hebei Province, People s Republic of China Long Tan 1, Zhongna Sang 1, Jun Shen
Iodine Deficiency and Mental Performance: A Review. Department of Community Health, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre.
 REVIEW ARTICLE Zaleha Md. Isa Department of Community Health, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre. * For reprint and all correspondence: Associate Professor Dr. Zaleha Md. Isa, Department of
REVIEW ARTICLE Zaleha Md. Isa Department of Community Health, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre. * For reprint and all correspondence: Associate Professor Dr. Zaleha Md. Isa, Department of
Review Article Iodine and Pregnancy
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Journal of Thyroid Research Volume 2011, Article ID 934104, 8 pages doi:10.4061/2011/934104 Review Article Iodine and Pregnancy Christina Yarrington 1 and Elizabeth N. Pearce
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Journal of Thyroid Research Volume 2011, Article ID 934104, 8 pages doi:10.4061/2011/934104 Review Article Iodine and Pregnancy Christina Yarrington 1 and Elizabeth N. Pearce
Should every pregnant woman be screened for thyroid disease?
 Should every pregnant woman be screened for thyroid disease? Tal Biron-Shental Rinat Gabbay-Benziv Is there a debate? Thyroid screening Guidelines Targeted case finding criteria Age > 30 years Personal
Should every pregnant woman be screened for thyroid disease? Tal Biron-Shental Rinat Gabbay-Benziv Is there a debate? Thyroid screening Guidelines Targeted case finding criteria Age > 30 years Personal
Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela
 Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela 2007-2008 Caballero Luis (*) (*) Physician responsible for the Coordination of the Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control
Urinary Iodine in School Children and Pregnant Women of Trujillo State, Venezuela 2007-2008 Caballero Luis (*) (*) Physician responsible for the Coordination of the Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control
Esther Briganti. Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy. Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher
 Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy Esther Briganti Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher Director, Melbourne Endocrine Associates Associate Professor,
Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy Esther Briganti Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher Director, Melbourne Endocrine Associates Associate Professor,
Adequate amounts of thyroid hormones are critical for nervous system function throughout life, but particularly during
 Psychomotor Development of Children from an Iodine-Deficient Region Maria Jose Costeira, MD, PhD, Pedro Oliveira, PhD, Nadine Correia Santos, PhD, Susana Ares, MD, PhD, Belen Saenz-Rico, PhD, Gabriella
Psychomotor Development of Children from an Iodine-Deficient Region Maria Jose Costeira, MD, PhD, Pedro Oliveira, PhD, Nadine Correia Santos, PhD, Susana Ares, MD, PhD, Belen Saenz-Rico, PhD, Gabriella
Systematic review of the effects of iodised salt and iodised oil on prenatal and postnatal growth
 Grant proposal to Japan Foundation for Growth Science, October 28, 2013 Systematic review of the effects of iodised salt and iodised oil on prenatal and postnatal growth Principal Investigator Prof. Michael
Grant proposal to Japan Foundation for Growth Science, October 28, 2013 Systematic review of the effects of iodised salt and iodised oil on prenatal and postnatal growth Principal Investigator Prof. Michael
Iodine supplementation of pregnant women in Europe: a review and recommendations
 (2004) 58, 979 984 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn REVIEW Iodine supplementation of pregnant women in Europe: a review and recommendations M Zimmermann
(2004) 58, 979 984 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn REVIEW Iodine supplementation of pregnant women in Europe: a review and recommendations M Zimmermann
Assessment of Knowledge of Women Regarding Iodine Nutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation at a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Research Article Assessment of Knowledge of Women Regarding Iodine Nutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation at a Tertiary Care Centre Kahkashan Jamshed Alam 1*, Manju Datta 2 1*MBBS, MS (Obstetrics
Original Research Article Assessment of Knowledge of Women Regarding Iodine Nutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation at a Tertiary Care Centre Kahkashan Jamshed Alam 1*, Manju Datta 2 1*MBBS, MS (Obstetrics
A BS TR AC T. Background Children born to women with low thyroid hormone levels have been reported to have decreased cognitive function.
 The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 february 9, 2012 vol. 366 no. 6 Antenatal Thyroid Screening and Childhood Cognitive Function John H. Lazarus, M.D., Jonathan P. Bestwick, M.Sc.,
The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 february 9, 2012 vol. 366 no. 6 Antenatal Thyroid Screening and Childhood Cognitive Function John H. Lazarus, M.D., Jonathan P. Bestwick, M.Sc.,
Iodine deficiency in Danish pregnant women
 Dan Med J 60/7 July 2013 danish medical JOURNAL 1 Iodine deficiency in Danish pregnant women Stine Linding Andersen 1, Louise Kolding Sørensen 1, Anne Krejbjerg 1, Margrethe Møller 2 & Peter Laurberg 1
Dan Med J 60/7 July 2013 danish medical JOURNAL 1 Iodine deficiency in Danish pregnant women Stine Linding Andersen 1, Louise Kolding Sørensen 1, Anne Krejbjerg 1, Margrethe Møller 2 & Peter Laurberg 1
Iodine deficiency disorders: Prof. Michael Zimmermann MD Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, Switzerland
 Iodine deficiency disorders: 2016 Prof. Michael Zimmermann MD Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, Switzerland If you had $75 billion to spend on global development where should you start? 2 In
Iodine deficiency disorders: 2016 Prof. Michael Zimmermann MD Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, Switzerland If you had $75 billion to spend on global development where should you start? 2 In
Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy
 Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy Early diagnosis and good management of maternal thyroid dysfunction are essential to ensure minimal adverse effects on
Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy Early diagnosis and good management of maternal thyroid dysfunction are essential to ensure minimal adverse effects on
British Journal of Nutrition
 (2013), 110, 31 39 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s00071145120050 Infant neurocognitive development is independent of the use of iodised salt or iodine supplements given during pregnancy Piedad Santiago
(2013), 110, 31 39 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s00071145120050 Infant neurocognitive development is independent of the use of iodised salt or iodine supplements given during pregnancy Piedad Santiago
Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy.
 Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy. Early diagnosis and good management of maternal thyroid dysfunction is essential to ensure minimal adverse effects on
Lothian Guidance for Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy. Early diagnosis and good management of maternal thyroid dysfunction is essential to ensure minimal adverse effects on
Congenital Hypothyroidism Associated with Maternal Hypothyroidism and Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy
 CASE REPORT Congenital Hypothyroidism Associated with Maternal Hypothyroidism and Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy Smita Kargutkar-Ajgaonkar Consultant Endocrinologist, Monmouth Medical Center, Long
CASE REPORT Congenital Hypothyroidism Associated with Maternal Hypothyroidism and Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy Smita Kargutkar-Ajgaonkar Consultant Endocrinologist, Monmouth Medical Center, Long
Screening and subsequent management for thyroid dysfunction pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant health(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Screening and subsequent management for thyroid dysfunction pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant health(review) SpencerL,BubnerT,BainE,MiddletonP
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Screening and subsequent management for thyroid dysfunction pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant health(review) SpencerL,BubnerT,BainE,MiddletonP
Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability
 20/3/2012 Food and Agriculture COST Action, Zürich 4-5 June Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability Dr. Maria Andersson Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland 2 3 1993
20/3/2012 Food and Agriculture COST Action, Zürich 4-5 June Iodine nutrition in Europe & iodine bioavailability Dr. Maria Andersson Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland 2 3 1993
2004 Where Do We Go from Here? Summary of Working Group Discussions on Thyroid Function and Gestational Outcomes
 THYROID Volume 15, Number 1, 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 2004 Where Do We Go from Here? Summary of Working Group Discussions on Thyroid Function and Gestational Outcomes Joseph G. Hollowell, 1 Stephen
THYROID Volume 15, Number 1, 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 2004 Where Do We Go from Here? Summary of Working Group Discussions on Thyroid Function and Gestational Outcomes Joseph G. Hollowell, 1 Stephen
Low concentrations of maternal thyroxin during early gestation: a risk factor of breech presentation?
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 925 930 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00213.x Low concentrations of maternal thyroxin during early gestation:
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 925 930 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00213.x Low concentrations of maternal thyroxin during early gestation:
Assessing infant cognitive development after prenatal iodine supplementation 1 3
 Assessing infant cognitive development after prenatal iodine supplementation 1 3 Martha Ann Bell, 4 * Alleyne P Ross, 4 and Gay Goodman 5 4 Department of Psychology, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA; and
Assessing infant cognitive development after prenatal iodine supplementation 1 3 Martha Ann Bell, 4 * Alleyne P Ross, 4 and Gay Goodman 5 4 Department of Psychology, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA; and
Maternal Thyroid Function during Early Pregnancy and Cognitive Functioning in Early Childhood: The Generation R Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Maternal Thyroid Function during Early Pregnancy and Cognitive Functioning in Early Childhood: The Generation R Study Jens Henrichs, Jacoba J. Bongers-Schokking, Jacqueline
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Maternal Thyroid Function during Early Pregnancy and Cognitive Functioning in Early Childhood: The Generation R Study Jens Henrichs, Jacoba J. Bongers-Schokking, Jacqueline
Effect of iodine supplementation in pregnant women on child neurodevelopment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
 Effect of iodine supplementation in pregnant women on child neurodevelopment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Sueppong Gowachirapant*, idhi Jaiswal*, Alida Melse-Boonstra, Valeria
Effect of iodine supplementation in pregnant women on child neurodevelopment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Sueppong Gowachirapant*, idhi Jaiswal*, Alida Melse-Boonstra, Valeria
Iodine deficiency in pregnant women and in their neonates in the central Anatolian region (Kayseri) of Turkey
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 45: 11-15 Original Iodine deficiency in pregnant women and in their neonates in the central Anatolian region (Kayseri) of Turkey Selim Kurtoðlu 1, Mustafa Akcakuþ
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 45: 11-15 Original Iodine deficiency in pregnant women and in their neonates in the central Anatolian region (Kayseri) of Turkey Selim Kurtoðlu 1, Mustafa Akcakuþ
Women Remain at Risk of Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy: The Importance of Iodine Supplementation before Conception and Throughout Gestation
 nutrients Article Women Remain at Risk of Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy: The Importance of Iodine Supplementation before Conception and Throughout Gestation Kristen L. Hynes 1, *, Judy A. Seal 2,
nutrients Article Women Remain at Risk of Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy: The Importance of Iodine Supplementation before Conception and Throughout Gestation Kristen L. Hynes 1, *, Judy A. Seal 2,
Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy
 Chapter 2 Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy Baha Zantour, Wafa Alaya, Hela Marmouch and Wafa Chebbi Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/54745 1. Introduction
Chapter 2 Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy Baha Zantour, Wafa Alaya, Hela Marmouch and Wafa Chebbi Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/54745 1. Introduction
Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management
 Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management Yuanita Asri Langi email: meralday@yahoo.co.id Endocrinology & Metabolic Division, Internal Medicine Department, Prof.dr.R.D. Kandou Hospital/ Sam Ratulangi
Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management Yuanita Asri Langi email: meralday@yahoo.co.id Endocrinology & Metabolic Division, Internal Medicine Department, Prof.dr.R.D. Kandou Hospital/ Sam Ratulangi
To evaluate the influence of ferritin on thyroid hormones in second trimester antenatal cases in Perambalur District
 Original Research Article To evaluate the influence of ferritin on thyroid hormones in second trimester antenatal cases in Perambalur District Nageshwari A 1, G. Kavitha 2* 1 Final year Postgraduate student,
Original Research Article To evaluate the influence of ferritin on thyroid hormones in second trimester antenatal cases in Perambalur District Nageshwari A 1, G. Kavitha 2* 1 Final year Postgraduate student,
La condizione di carenza iodica in Europa
 Iodine Deficiency in Europe La condizione di carenza iodica in Europa John Lazarus IGN (Iodine Global Network) Regional Coordinator W and Central Europe Lazarus@cf.ac.uk Iodine Deficiency Disorders at
Iodine Deficiency in Europe La condizione di carenza iodica in Europa John Lazarus IGN (Iodine Global Network) Regional Coordinator W and Central Europe Lazarus@cf.ac.uk Iodine Deficiency Disorders at
Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures
 Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures Susan Woskie, Pornpimol Kongtip, Noppanun Nankongnab, Wiroj Thanasanpaiboon, Napaporn Kiatdamrong, Nantha Charoonrungsirikul
Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures Susan Woskie, Pornpimol Kongtip, Noppanun Nankongnab, Wiroj Thanasanpaiboon, Napaporn Kiatdamrong, Nantha Charoonrungsirikul
Update on Gestational Thyroid Disease. Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney
 IADPSG 2016 Update on Gestational Thyroid Disease Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney IADPSG 2016 DISCLOSURES and AIM Nil to disclose Aim: to provide an overview 2017 Guidelines
IADPSG 2016 Update on Gestational Thyroid Disease Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney IADPSG 2016 DISCLOSURES and AIM Nil to disclose Aim: to provide an overview 2017 Guidelines
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico
 ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Link Article Supplementary Material Article Summary The article
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Link Article Supplementary Material Article Summary The article
Thyroid diseases in pregnancy: The importance of anamnesis
 Original Article Thyroid diseases in pregnancy: The importance of anamnesis Necati Bulmus 1, Isik Ustuner 2, Emine Seda Guvendag Guven 3, Figen Kir Sahin 4, Senol Senturk 5, Serap Baydur Sahin 6 Open Access
Original Article Thyroid diseases in pregnancy: The importance of anamnesis Necati Bulmus 1, Isik Ustuner 2, Emine Seda Guvendag Guven 3, Figen Kir Sahin 4, Senol Senturk 5, Serap Baydur Sahin 6 Open Access
Assessment of iodine status of some selected populations in Anambra state, Nigeria. Raw Materials Research and Development Council, Abuja, (NIGERIA) 2
 ISSN : 0974-7427 Volume 7 Issue 3 Assessment of iodine status of some selected populations in Anambra state, Nigeria Ifeyinwa Chidiogo Olife 1 *, Benedette Azuka Anajekwu 2, Agwu Kama Onuogbu 1 1 Raw Materials
ISSN : 0974-7427 Volume 7 Issue 3 Assessment of iodine status of some selected populations in Anambra state, Nigeria Ifeyinwa Chidiogo Olife 1 *, Benedette Azuka Anajekwu 2, Agwu Kama Onuogbu 1 1 Raw Materials
Lecture title. Name Family name Country
 Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico
 ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Summary The article by Bashash et al., 1 published in Environmental
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Summary The article by Bashash et al., 1 published in Environmental
X/00/$03.00/0 Vol. 85, No. 9 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society
 0021-972X/00/$03.00/0 Vol. 85, No. 9 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Postpartum Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnant Thyroid Peroxidase
0021-972X/00/$03.00/0 Vol. 85, No. 9 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Postpartum Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnant Thyroid Peroxidase
Intellectual Development in Children Whose Mothers Received Propylthiouracil During Pregnancy
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 51 (1978), 151156 Intellectual Development in Children Whose Mothers Received Propylthiouracil During Pregnancy GERARD N. BURROW, ETHELYN H. KLATSKIN, AND MYRON
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 51 (1978), 151156 Intellectual Development in Children Whose Mothers Received Propylthiouracil During Pregnancy GERARD N. BURROW, ETHELYN H. KLATSKIN, AND MYRON
Children Born to Women with Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy Show Abnormal Corpus Callosum Development
 Children Born to Women with Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy Show Abnormal Corpus Callosum Development Arash Samadi, Jovanka Skocic, Joanne Rovet AMERICAN THYROID ASSOCIATION ANNUAL MEETING SAN JUAN PUERTO
Children Born to Women with Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy Show Abnormal Corpus Callosum Development Arash Samadi, Jovanka Skocic, Joanne Rovet AMERICAN THYROID ASSOCIATION ANNUAL MEETING SAN JUAN PUERTO
Breast-milk iodine concentration declines over the first 6 mo postpartum in iodine-deficient women 1 3
 Breast-milk iodine concentration declines over the first 6 mo postpartum in iodine-deficient women 1 3 Hannah M Mulrine, Sheila A Skeaff, Elaine L Ferguson, Andrew R Gray, and Pierre Valeix ABSTRACT Background:
Breast-milk iodine concentration declines over the first 6 mo postpartum in iodine-deficient women 1 3 Hannah M Mulrine, Sheila A Skeaff, Elaine L Ferguson, Andrew R Gray, and Pierre Valeix ABSTRACT Background:
Monitoring Levothyroxine Dose during Pregnancy: A Prospective Study
 American Journal of Infectious Diseases 7 (3): 75-79, 2011 ISSN 1553-6203 2011 Science Publications Monitoring Levothyroxine Dose during Pregnancy: A Prospective Study 1 Juhi Agarwal, 1 Sirimavo Nair and
American Journal of Infectious Diseases 7 (3): 75-79, 2011 ISSN 1553-6203 2011 Science Publications Monitoring Levothyroxine Dose during Pregnancy: A Prospective Study 1 Juhi Agarwal, 1 Sirimavo Nair and
Maternal Iodine dietary supplements and neonatal thyroid stimulating hormone in Gippsland, Australia
 848 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2018;27(4):848-852 Original Article Maternal Iodine dietary supplements and neonatal thyroid stimulating hormone in Gippsland, Australia Eleanor Katherine Louise Mitchell PhDMed
848 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2018;27(4):848-852 Original Article Maternal Iodine dietary supplements and neonatal thyroid stimulating hormone in Gippsland, Australia Eleanor Katherine Louise Mitchell PhDMed
Iodine status remains critical in mother and infant in Central Anatolia (Kayseri) of Turkey
 Eur J Nutr (2004) 43 : 297 303 DOI 10.1007/s00394-004-0474-2 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Selim Kurtoglu Mustafa Akcakus Celebi Kocaoglu Tamer Gunes Nurten Budak Mehmet Emre Atabek Inci Karakucuk François Delange
Eur J Nutr (2004) 43 : 297 303 DOI 10.1007/s00394-004-0474-2 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Selim Kurtoglu Mustafa Akcakus Celebi Kocaoglu Tamer Gunes Nurten Budak Mehmet Emre Atabek Inci Karakucuk François Delange
Role of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies in adverse pregnancy outcomes
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Gupta A et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sept;5(9):3001-3005 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Gupta A et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sept;5(9):3001-3005 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S
 W H O L E H E A L T H A M E R I C A. C O M Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present S E P T E M B E R, 2 0 1 3 V O L U M E 1 0, I S S U E 9 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S I O D I N E
W H O L E H E A L T H A M E R I C A. C O M Dr. Paul G. Varnas & WholeHealthAmerica.com present S E P T E M B E R, 2 0 1 3 V O L U M E 1 0, I S S U E 9 T H E B E T T E R H E A L T H N E W S I O D I N E
Comparison of two different doses of iodide in the prevention of gestational goiter in marginal iodine deficiency: a longitudinal study
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 147 29 34 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Comparison of two different doses of iodide in the prevention of gestational goiter in marginal iodine deficiency: a longitudinal
European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 147 29 34 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Comparison of two different doses of iodide in the prevention of gestational goiter in marginal iodine deficiency: a longitudinal
Knowledge and practices regarding use of iodised salt and iodine deficiency disorder among the population of Rani, Kamrup(R), Assam
 Original article: Knowledge and practices regarding use of iodised salt and iodine deficiency disorder among the population of Rani, Kamrup(R), Assam Dr.Dhrubajyoti Choudhury 1, Dr. (Mrs) Rupali Baruah
Original article: Knowledge and practices regarding use of iodised salt and iodine deficiency disorder among the population of Rani, Kamrup(R), Assam Dr.Dhrubajyoti Choudhury 1, Dr. (Mrs) Rupali Baruah
Iodine Status of the U.S. Population, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, and
 THYROID Volume 21, Number 4, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2010.0077 IODINE AND ENDEMIC GOITER Iodine Status of the U.S. Population, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005
THYROID Volume 21, Number 4, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2010.0077 IODINE AND ENDEMIC GOITER Iodine Status of the U.S. Population, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005
Author(s) Noboru. Issue Date Right.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Urinary iodine concentrations of pr Sekitani, Yui; Hayashida, Naomi; Ta Alexander A.; Rudnitskiy, Stanislav Oleksandr K.; Chorniy, Sergiy A.;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Urinary iodine concentrations of pr Sekitani, Yui; Hayashida, Naomi; Ta Alexander A.; Rudnitskiy, Stanislav Oleksandr K.; Chorniy, Sergiy A.;
NEWBORN FEMALE WITH GOITER PAYAL PATEL, M.D. PEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOW FEBRUARY 12, 2015
 NEWBORN FEMALE WITH GOITER PAYAL PATEL, M.D. PEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOW FEBRUARY 12, 2015 CHIEF COMPLAINT 35 6/7 week F with goiter, born to a mother with Graves disease (GD) HPI 35 6/7 week F born
NEWBORN FEMALE WITH GOITER PAYAL PATEL, M.D. PEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOW FEBRUARY 12, 2015 CHIEF COMPLAINT 35 6/7 week F with goiter, born to a mother with Graves disease (GD) HPI 35 6/7 week F born
Clinical and Biological Consequences of Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy
 Disorders of Thyroid Function Van Vliet G, Polak M (eds): Thyroid Gland Development and Function. Endocr Dev. Basel, Karger, 2007, vol 10, pp 62 85 Clinical and Biological Consequences of Iodine Deficiency
Disorders of Thyroid Function Van Vliet G, Polak M (eds): Thyroid Gland Development and Function. Endocr Dev. Basel, Karger, 2007, vol 10, pp 62 85 Clinical and Biological Consequences of Iodine Deficiency
Prevalence of thyroid disorder in pregnancy and pregnancy outcome
 Original Research Article Prevalence of thyroid disorder in pregnancy and pregnancy outcome Praveena K.R. 1, Pramod Kumar K.R. 2*, Prasuna K.R. 3, Krishna Kumar TV 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of
Original Research Article Prevalence of thyroid disorder in pregnancy and pregnancy outcome Praveena K.R. 1, Pramod Kumar K.R. 2*, Prasuna K.R. 3, Krishna Kumar TV 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of
FACTORS INFLUENCING NEONATAL THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE LEVEL IN NAKHON PATHOM PROVINCE, THAILAND
 P-MS057 FACTORS INFLUENCING NEONATAL THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE LEVEL IN NAKHON PATHOM PROVINCE, THAILAND Samart Punpetch 1, *, Kitipong Hancharean 2, # 1 Master of Science Program in Public Health (Infectious
P-MS057 FACTORS INFLUENCING NEONATAL THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE LEVEL IN NAKHON PATHOM PROVINCE, THAILAND Samart Punpetch 1, *, Kitipong Hancharean 2, # 1 Master of Science Program in Public Health (Infectious
Universal TSH screening to detect hypothyroidism in pregnancy : a comprehensive review
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Universal TSH screening to detect hypothyroidism in pregnancy : a comprehensive review Andrea M. Fox
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Universal TSH screening to detect hypothyroidism in pregnancy : a comprehensive review Andrea M. Fox
Low Concentrations of Maternal Thyroxin During Early Gestation :A Risk Factor of Breech Presentation
 Negative feedback CONCENTRATIONS THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE OF MEDICAL MATERNAL JOURNAL THYROXIN Low Concentrations of Maternal Thyroxin During Early Gestation :A Risk Factor of Breech Presentation Nada Salih
Negative feedback CONCENTRATIONS THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE OF MEDICAL MATERNAL JOURNAL THYROXIN Low Concentrations of Maternal Thyroxin During Early Gestation :A Risk Factor of Breech Presentation Nada Salih
Arvinda Shaw. Research scholar, Dept. of Home Science, University of Calcutta, Kolkata, India. /
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 2, Issue 6, July 2014, PP 172 ISSN 2349037 (Print) & ISSN 2349036 (Online) www.arcjournals.org A Study on the Effect of Iodine Content
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 2, Issue 6, July 2014, PP 172 ISSN 2349037 (Print) & ISSN 2349036 (Online) www.arcjournals.org A Study on the Effect of Iodine Content
Research. Although thyrotropin (thyroidstimulated
 Research www.ajog.org OBSTETRICS Free T4 immunoassays are flawed during pregnancy Richard H. Lee, MD; Carole A. Spencer, PhD; Jorge H. Mestman, MD; Erin A. Miller, BS; Ivana Petrovic, MS; Lewis E. Braverman,
Research www.ajog.org OBSTETRICS Free T4 immunoassays are flawed during pregnancy Richard H. Lee, MD; Carole A. Spencer, PhD; Jorge H. Mestman, MD; Erin A. Miller, BS; Ivana Petrovic, MS; Lewis E. Braverman,
Motor nerve conduction velocity and somatosensory evoked potentials in the newborn and young child in relation to thyroid function Smit, B.J.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Motor nerve conduction velocity and somatosensory evoked potentials in the newborn and young child in relation to thyroid function Smit, B.J. Link to publication
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Motor nerve conduction velocity and somatosensory evoked potentials in the newborn and young child in relation to thyroid function Smit, B.J. Link to publication
N O T P R I N T A B L E
 . Attention to the hiding iodine deficiency in pregnant and lactating women after universal salt iodization: A multi-community study in China Y.Q. Yan 1, Z.P. Chen 1, X.M. Yang 2, H. Liu 3, J.X. Zhang
. Attention to the hiding iodine deficiency in pregnant and lactating women after universal salt iodization: A multi-community study in China Y.Q. Yan 1, Z.P. Chen 1, X.M. Yang 2, H. Liu 3, J.X. Zhang
03-Dec-17. Thyroid Disorders GOITRE. Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms
 Thyroid Disorders GOITRE Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms 1 Physiological Goiter load on thyroid supply of I - limited stress due to:
Thyroid Disorders GOITRE Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms 1 Physiological Goiter load on thyroid supply of I - limited stress due to:
Psychological consequences of congenital hypothyroidism: Cognitive, motor and psychosocial functioning van der Sluijs Veer, L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Psychological consequences of congenital hypothyroidism: Cognitive, motor and psychosocial functioning van der Sluijs Veer, L. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Psychological consequences of congenital hypothyroidism: Cognitive, motor and psychosocial functioning van der Sluijs Veer, L. Link to publication Citation for published
Network for Sustained Elimination of Iodine Deficiency A Presentation on Iodine and Pregnancy
 Network for Sustained Elimination of Iodine Deficiency A Presentation on Iodine and Pregnancy This piece on Iodine and Pregnancy can also be found on the website of the Network for Sustained Elimination
Network for Sustained Elimination of Iodine Deficiency A Presentation on Iodine and Pregnancy This piece on Iodine and Pregnancy can also be found on the website of the Network for Sustained Elimination
Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network
 Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network Jonathan Gorstein Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Global Health/ Nutrition
Effective Technical Assistance Towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency the role of the Iodine Global Network Jonathan Gorstein Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Global Health/ Nutrition
BELGIUM. Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS)
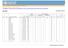 Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Iodine Deficiency The database on iodine deficiency includes data by country on goitre prevalence and/or urinary iodine concentration
Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS) WHO Global Database on Iodine Deficiency The database on iodine deficiency includes data by country on goitre prevalence and/or urinary iodine concentration
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES
 TITLE: THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY EFFECTIVE DATE: July, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnancy changes significantly the values influenced by the serum thyroid binding hormone level (i.e., total thyroxine,
TITLE: THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY EFFECTIVE DATE: July, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnancy changes significantly the values influenced by the serum thyroid binding hormone level (i.e., total thyroxine,
Thyroid function in pregnancy
 Published Online December 23, 2010 Thyroid function in pregnancy John H. Lazarus * Centre for Endocrine and Diabetes Sciences, Cardiff University School of Medicine, University Hospital of Wales, Heath
Published Online December 23, 2010 Thyroid function in pregnancy John H. Lazarus * Centre for Endocrine and Diabetes Sciences, Cardiff University School of Medicine, University Hospital of Wales, Heath
344 Thyroid Disorders
 344 Thyroid Disorders Definition/Cut-Off Value Thyroid dysfunctions that occur in pregnant and postpartum women, during fetal development, and in childhood are caused by the abnormal secretion of thyroid
344 Thyroid Disorders Definition/Cut-Off Value Thyroid dysfunctions that occur in pregnant and postpartum women, during fetal development, and in childhood are caused by the abnormal secretion of thyroid
Maternal and perinatal outcome in antenatal women with hypothyroidism
 Original Research Article Maternal and perinatal outcome in antenatal women with hypothyroidism Polumuru Usha Devi 1, Gundu Vanaja 1* 1 Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Andhra Medical
Original Research Article Maternal and perinatal outcome in antenatal women with hypothyroidism Polumuru Usha Devi 1, Gundu Vanaja 1* 1 Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Andhra Medical
DR.RUPNATHJI( DR.RUPAK NATH )
 45. Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism Burden of Suffering In the U.S., congenital hypothyroidism occurs in 1 of 3,600 4,000 infants. 1,2 Clinical diagnosis occurs in
45. Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism Burden of Suffering In the U.S., congenital hypothyroidism occurs in 1 of 3,600 4,000 infants. 1,2 Clinical diagnosis occurs in
MFMU - Background. MFMU - Background MFMU GOALS
 MFMU - Background Highlights From The MFM Units Network Ronald Wapner, MD Modern OB management (especially high risk pregnancies) has adopted principles of care, employed pharmaceuticals, applied methodologies
MFMU - Background Highlights From The MFM Units Network Ronald Wapner, MD Modern OB management (especially high risk pregnancies) has adopted principles of care, employed pharmaceuticals, applied methodologies
Clinical efficacy of therapeutic intervention for subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy
 Clinical efficacy of therapeutic intervention for subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy R. Ju 1, L. Lin 2, Y. Long 2, J. Zhang 2 and J. Huang 2 1 Gynaecology and Obstetrics Department, Beijing Chuiyangliu
Clinical efficacy of therapeutic intervention for subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy R. Ju 1, L. Lin 2, Y. Long 2, J. Zhang 2 and J. Huang 2 1 Gynaecology and Obstetrics Department, Beijing Chuiyangliu
Disclosure. Michael K. Georgieff, MD Research Support: Mead Johnson Nutrition Brain Iron Deficiency
 Disclosure In accordance with the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education Standards, parallel documents from other accrediting bodies, and Annenberg Center for Health Sciences policy, the
Disclosure In accordance with the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education Standards, parallel documents from other accrediting bodies, and Annenberg Center for Health Sciences policy, the
THE PHARMA INNOVATION - JOURNAL Assessment of Antithyroperoxidase Antibodies and Thyroid Hormones Among Sudanese Pregnant Women
 Received: 01-09-2013 Accepted: 30-09-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 9 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 01-09-2013 Accepted: 30-09-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 9 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
FOCUS. Ann Nutr Metab 2016;69(suppl 1):23 28 Docosahexaenoic Acid and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Term Infants by Suzanne Meldrum and Karen Simmer
 FOCUS The importance of DHA during CNS development has led to the hypothesis that early diet modulation of DHA may alter the normal trajectory of brain development. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Neurodevelopmental
FOCUS The importance of DHA during CNS development has led to the hypothesis that early diet modulation of DHA may alter the normal trajectory of brain development. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Neurodevelopmental
NONSYSTEMATIC OBSERVATIONS IN a moderately
 0021-972X/04/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 89(12):6054 6060 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0571 Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity
0021-972X/04/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 89(12):6054 6060 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0571 Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity
Thyroid autoimmunity in pregnancy a problem of mother and child
 Archives of Perinatal Medicine 18(2), 86-91, 2012 REVIEW PAPER Thyroid autoimmunity in pregnancy a problem of mother and child MAREK RUCHAŁA, ARIADNA ZYBEK, BARBARA BROMIŃSKA, EWELINA SZCZEPANEK-PARULSKA
Archives of Perinatal Medicine 18(2), 86-91, 2012 REVIEW PAPER Thyroid autoimmunity in pregnancy a problem of mother and child MAREK RUCHAŁA, ARIADNA ZYBEK, BARBARA BROMIŃSKA, EWELINA SZCZEPANEK-PARULSKA
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child
 Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(6):
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(6): 391-397 391 Original Article Relationship between Iodine Content in Household Iodized Salt and Thyroid Volume Distribution in Children CHAO Hong 1, ZHANG Yu Fu 2, LIU Peng
Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(6): 391-397 391 Original Article Relationship between Iodine Content in Household Iodized Salt and Thyroid Volume Distribution in Children CHAO Hong 1, ZHANG Yu Fu 2, LIU Peng
Breastmilk Iodine Concentrations Following Acute Dietary Iodine Intake
 Page 1 of 15 Breastmilk Iodine Concentrations Following Acute Dietary Iodine Intake Angela M. Leung, MD, MSc 1 Lewis E. Braverman, MD 1 Xuemei He, MD 1 Timothy Heeren, PhD 2 Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc
Page 1 of 15 Breastmilk Iodine Concentrations Following Acute Dietary Iodine Intake Angela M. Leung, MD, MSc 1 Lewis E. Braverman, MD 1 Xuemei He, MD 1 Timothy Heeren, PhD 2 Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc
ASSESSMENT OF IODINE NUTRITION STATUS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN OF NEPAL BY URINARY IODINE ASSAY
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH ASSESSMENT OF IODINE NUTRITION STATUS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN OF NEPAL BY URINARY IODINE ASSAY B Gelal 1, M Aryal 1, BK Lal Das 1, B Bhatta 2, M Lamsal 1 and
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH ASSESSMENT OF IODINE NUTRITION STATUS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN OF NEPAL BY URINARY IODINE ASSAY B Gelal 1, M Aryal 1, BK Lal Das 1, B Bhatta 2, M Lamsal 1 and
Do Thyroxine and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels Reflect Urinary Iodine Concentrations?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do Thyroxine and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels Reflect Urinary Iodine Concentrations? Offie P. Soldin,* Rochelle E. Tractenberg, and John C. Pezzullo Abstract: The toxicity of environmental
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do Thyroxine and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels Reflect Urinary Iodine Concentrations? Offie P. Soldin,* Rochelle E. Tractenberg, and John C. Pezzullo Abstract: The toxicity of environmental
Effect of Iodine Prophylaxis during Pregnancy on Neurocognitive Development of Children during the First Two Years of Life
 ORIGINAL Endocrine ARTICLE Care Effect of Iodine Prophylaxis during Pregnancy on Neurocognitive Development of Children during the First Two Years of Life Ines Velasco, Monica Carreira, Piedad Santiago,
ORIGINAL Endocrine ARTICLE Care Effect of Iodine Prophylaxis during Pregnancy on Neurocognitive Development of Children during the First Two Years of Life Ines Velasco, Monica Carreira, Piedad Santiago,
Department of Pediatrics, Tokai University School of Medicine, Isehara, Kanagawa , Japan
 Endocrine Journal 2003, 50 (4), 379 384 Persistence of Mild Hyperthyrotropinemia after Discontinuation of Three-Year Course of Low-Dose L-Thyroxine Therapy in Infants with Borderline Hypothyroidism YUICHIRO
Endocrine Journal 2003, 50 (4), 379 384 Persistence of Mild Hyperthyrotropinemia after Discontinuation of Three-Year Course of Low-Dose L-Thyroxine Therapy in Infants with Borderline Hypothyroidism YUICHIRO
Maternal fish oil supplementation in pregnancy: A 12 year follow-up of a randomised controlled test
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2015 Maternal fish oil supplementation in pregnancy: A 12 year follow-up of a randomised controlled test Suzanne Meldrum Edith Cowan University,
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2015 Maternal fish oil supplementation in pregnancy: A 12 year follow-up of a randomised controlled test Suzanne Meldrum Edith Cowan University,
The Effect of Environmental Perchlorate on Thyroid Function in Pregnant Women. from Cordoba, Argentina, and Los Angeles, California
 The Effect of Environmental Perchlorate on Thyroid Function in Pregnant Women from Cordoba, Argentina, and Los Angeles, California Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, 1 Carole A. Spencer, PhD, FACB, 2 Jorge
The Effect of Environmental Perchlorate on Thyroid Function in Pregnant Women from Cordoba, Argentina, and Los Angeles, California Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, 1 Carole A. Spencer, PhD, FACB, 2 Jorge
A randomised controlled trial of iodine supplementation in extreme preterm infants
 A randomised controlled trial of iodine supplementation in extreme preterm infants Content Introduction o What is transient hypothyroxinaemia? o Why is this important? o Causes of transient hypothyroxinaemia
A randomised controlled trial of iodine supplementation in extreme preterm infants Content Introduction o What is transient hypothyroxinaemia? o Why is this important? o Causes of transient hypothyroxinaemia
Cretinism: The Iodine-Selenium Connection Harold D. Foster, Ph.D. 1
 Cretinism: The Iodine-Selenium Connection Harold D. Foster, Ph.D. 1 Summary The major clinical and geographical differences, characteristic of the three distinct forms of endemic cretinism, are thought
Cretinism: The Iodine-Selenium Connection Harold D. Foster, Ph.D. 1 Summary The major clinical and geographical differences, characteristic of the three distinct forms of endemic cretinism, are thought
THYROID HORMONAL STATUS IN PREGNANCY AND PRE- ECLAMPSIA AND ITS CORRELATION WITH MATERNAL AGE AND PARITY
 THYROID HORMONAL STATUS IN PREGNANCY AND PRE- ECLAMPSIA AND ITS CORRELATION WITH MATERNAL AGE AND PARITY *P. Jain and R. Devi Department of Biochemistry, Gauhati Medical College and Hospital, Assam, India
THYROID HORMONAL STATUS IN PREGNANCY AND PRE- ECLAMPSIA AND ITS CORRELATION WITH MATERNAL AGE AND PARITY *P. Jain and R. Devi Department of Biochemistry, Gauhati Medical College and Hospital, Assam, India
ILSI SEA Region Seminar on Maternal, Infant and Young Child Nutrition, July 24, 2017, Bangkok, Thailand OUTCOMES
 Outline: Background on birth outcomes and maternal nutrition MATERNAL NUTRITION OUTCOMES DIETARY INTAKES AND RELATED Micronutrient deficiencies Dietary intakes and assessments Dietary diversity and pregnancy
Outline: Background on birth outcomes and maternal nutrition MATERNAL NUTRITION OUTCOMES DIETARY INTAKES AND RELATED Micronutrient deficiencies Dietary intakes and assessments Dietary diversity and pregnancy
The Thyroid and Pregnancy OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 3/19/10. Francis S. Greenspan March 19, Normal Physiology. 2.
 The Thyroid and Pregnancy Francis S. Greenspan March 19, 2010 OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 1. Normal Physiology 2. Hypothyroidism 3. Hyperthyroidism 4. Thyroid Nodules and Cancer NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Iodine Requirements:
The Thyroid and Pregnancy Francis S. Greenspan March 19, 2010 OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 1. Normal Physiology 2. Hypothyroidism 3. Hyperthyroidism 4. Thyroid Nodules and Cancer NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Iodine Requirements:
