Shawn A. McClure D.M.D., M.D. Miami Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Professor, Director of Research Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
|
|
|
- Pearl Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shawn A. McClure D.M.D., M.D. Miami Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Professor, Director of Research Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery NOVA/NSU COLLEGE OF DENTAL MEDICINE 1
2 Diseases of Head and Neck: What Should a Primary Care Physician Be Looking For? June 22 nd, 2012
3 If the patient complains of a painless mass or lump in the neck, what initial examination should the physician proceed to do immediately? Look in the oral cavity 3
4 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Proper positioning of the fingers Have the patient open and close slowly. 4
5 EXTRAORAL EXAM 5
6 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Preauricular nodes. Palpation of the anterior cervical nodes. 6
7 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Bilateral palpation of the occipital nodes. Be sure to also observe the skin in this area. Postauricular nodes. 7
8 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Palpation of the posterior cervical nodes. Bilateral palpation of the supraclavicular lymph nodes. 8
9 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Palpate the submandibular lymph nodes using a cupped hand as shown. Digital palpation of the submental lymph nodes. 9
10 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Palpation of the parotid gland. Palpation of the submandibular glands. 10
11 EXTRAORAL EXAMINATION Bimanual palpation of the thyroid gland. Hold the fingers lightly over the gland while the patient swallows. 11
12 Differential of Neck Masses CONGENITAL NECK MASS Branchial cleft cyst Thyroglossal duct cyst Vascular anomalies Laryngocele Ranula Teratoma Dermoid cyst Thymic cyst INFLAMMATORY NECK MASS Infectious inflammatory disorders - Reactive viral lymphadenopathy - Bacterial lymphadenopathy Noninfectious inflammatory disorders NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Metastatic head and neck carcinoma Thyroid masses Salivary gland neoplasm Paragangliomas Schwannoma Lymphoma Lipoma and benign skin cysts 12
13 Dermoid Cyst 13
14 Dermoid Cyst 14
15 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION 15
16 Proper Head & Neck Examination 16
17 17
18 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Palpating the hard palate. Use firm pressure. Normal structures of the anterior palate hard palate. 18
19 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Normal structures of the posterior hard palate. Observe the dimensions (height and width) of the vault. 19
20 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Visual examination of the upper labial mucosa. Visual examination of the lower labial mucosa. 20
21 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Use digital palpation pressing the tissues against the body of the mandible for both the lingual and the facial aspects. The mirror is used to visualize the anterior lingual portion of the mandible. 21
22 INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Examination of the lateral borders of the tongue. Visual examination of the floor of the mouth. Note the normal structures of the area. 22
23 23
24 First level bullet Second level bullet Third level bullet Fourth level bullet Fifth level bullet 24
25 25
26 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders
27 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections
28 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections Herpes Simplex
29 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Infections: Herpes Simplex Majority of infections with HSV are subclinical Either HSV type 1 or 2 may be involved
30 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Infections: Herpes Simplex Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis Infants, young children, immunosuppressed individuals
31 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Infections: Herpes Simplex Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis Multiple, painful, discrete vesicles that rupture to form ulcers Cervical lymphadenopathy, malaise, and fever
32 Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
33 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections: Herpes Simplex Recurrent herpetic infections Viral latency after clinical or subclinical infection Reactivated by febrile illness, trauma, or other forms of stress
34 Recurrent Herpes
35 Recurrent Herpes
36 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections: Candida (Monilia) Albicans Stomatitis in young children and in adults with debilitating diseases prolonged broad spectrum antibiotics, or immunosuppressive therapy
37 Thrush
38 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections: Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis Severe necrotizing gingivitis occurring in patients with poor oral hygiene and decreased resistance to bacterial infection
39 Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
40 Relation of Periodontal Disease and Systemic Diseases Periodontal disease, a chronic inflammatory disease, is linked to other health risks. Heart Disease and Stroke Pregnancy Problems Diabetes Respiratory Diseases 40
41 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Infections: Viral Papillary Lesions Associated with Human Papilloma Virus Exophytic and appear as cauliflower-like lesions High rate of recurrence 41
42 Condyloma 42
43
44 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Recurrent Aphthous Ulcers Idiopathic disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of painful, round or oval yellow-white ulcers surrounded by an erythematous halo
45 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Recurrent aphthous stomatitis Three forms Minor type Major type Herpetiform type
46 Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis
47 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Pyogenic Granuloma Asymptomatic tumescence composed of granulation tissue
48 Pyogenic granuloma
49 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Lichen planus
50 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Lichen Planus (autoimmune) Common chronic inflammatory mucocutaneous disease Oral lesions may be the only manifestation* Disease of middle age that affects the sexes nearly equally
51 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Lichen planus Several forms
52 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory disorders Lichen planus Several forms Reticular form
53 Lichen planus
54 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Inflammatory Disorders Lichen planus Several forms Reticular form Erosive form
55 Erosive Lichen Planus
56 PRECANCEROUS LESIONS?
57 Clinical appearance Minimal pain during early growth phase. Exophytic Endophytic Leukoplakia Erythroplakic Erythroleukoplakic
58 Leukoplakia: Premalignant Lesions A white patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically A descriptive term, not a histological diagnosis. Generally asymptomatic Presents as a white lesion that may be flat, slightly elevated with rugated or smooth texture The buccal mucosa, lower lip vermilion and gingiva account for most oral cavity leukoplakia More than 70% of patients with leukoplakia are smokers The malignant transformation of these lesions has been studied extensively with no definitive conclusions
59 Leukoplakia
60 Premalignant Lesions Erythroplakia A red patch that cannot be characterized clinically More likely to present with dysplasia or carcinoma in situ Common sites are floor of the mouth and retromolar fossa. Appearance can be bright red, homogenous, and may or may not have a sharply demarcated border Often associated with areas of leukoplakia (Erythroleukoplakia)
61 Erythroplakia
62 HOW DOES ORAL CANCER PRESENT IN THE MOUTH?
63 63
64 Oral Cancer Oral cancer accounts for around 3% of all newly diagnosed cancers Eighth most common cancer affecting males in the United States Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): 85-95% of all oral cancer Other malignant lesions can be found in the oral cavity such as: Salivary Gland Tumors Melanoma Sarcoma Lymphoma Metastatic disease Even with recent advances in locoregional control and adjunctive therapy, 5 year survival rates have not improved significantly
65 Risk Factors No single causative agent can be attributed to the development of all oral cancers Tobacco and alcohol appear to have a great impact on malignancy development Smokers are 2 to 12 times more likely to develop malignancies in the oral cavity than non smokers 90% of individuals with oral cancer report a smoking history.
66 Exophytic lesion Typically irregular or papillary surface forming the mass Superficial color can be from NORMAL, to red, to white depending on keratinization or ulcerated Tumor feels indurated
67 Endophytic lesion Typically have depressed irregularly shaped ulcerated central area with surrounding rolled border of normal or white mucosa Rolled border from invasion of tumor downward and laterally
68 Risk Factors The United States has an aggressive anti-smoking campaign, resulting in the decrease of smokers and oropharyngeal malignancies but increase in the incidence of HNC in young men, non-smokers, and non-drinkers
69 HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS
70 Human Papillomavirus 85% of humans will have and HPV infection during their lifetime, enter via a break in the stratified squamous epithelium of the oral mucosa 90-95% are associated with HPV 16 Mork et al demonstrated 14 times greater risk in people testing positive for HPV 16
71 Human Papillomavirus Enter the cell via endocytosis Enter the nucleus and the viral genome is incorporated into the cell line Main culprit,, has a higher affinity to bind to tumor suppression genes
72 Prognosis HPV-positive patients have better overall survival outcomes than HPV-negative HPV-positive tumors are much more radiosensitive Tachezy et al, showed HPV-positive tumors have an absence of p53 mutations
73 Tongue 22 to 49% of all oral cancer Anterior 2/3: 75% of cases Posterior one-third: 25% of cases Metastasis to level II, followed by levels III and I. Possibility of skip metastasis to level IV About 40% will have cervical node metastasis at time of presentation
74 Floor of Mouth Second most common location for oral cavity SSC Resection is treatment of choice for most surgeons Anterior lesions may require sialodochoplasty
75 Retromolar Trigone Can resemble oropharyngeal primary cancer in behavior Larger lesions may invade the pterygomandibular space and extend towards the skull base Surgical Management: -Wide local excision -Marginal mandibulectomy -Segmental Resection Elective neck radiation or selective neck dissection should be considered in T2 or greater lesions
76 Lip Cancer Approximately 2 to 42% of oral cavity cancers. Often seen in white males with increased sun exposure Metastasis from the lower lip: submental, submandibular, and perifacial nodes Metastasis from upper lip and commisure: Preauricular, periparotid, and submandibular nodes
77 Lip Cancer Surgical Treatment: -CO2 laser ablation -Vermilionectomy - Wedge resection Infrequent nodal metastasis- Neck dissection usually not indicated Five-year survival of 90% for stage I and Stage II
78 Buccal Mucosa Represents 2 to 10% of all SCC of the oral cavity Cervical lymph node metastases seen in 10 to 25% of patients First-echelon lymphatic drainage is level I followed by level II
79 Buccal Mucosa Excision often results in complex defects of the cheek that can be difficult to reconstruct 2-Year Survival Rate Early Stage: % Stage III: 41% Stage IV: 15%
80 Alveolar Ridge 2 to 18% of oral cancers Mandible more common than maxilla About 30% of these tumors will exhibit some bony involvement at time of presentation Metastasis more common in mandibular ridge tumors than in maxillary tumors. Nodal drainage most frequently to levels I and II (25 to 30% at diagnosis)
81 Alveolar Ridge Surgical Management May Include: -Partial or total maxillectomy -Marginal Mandibulectomy -Segmental Mandibulectomy Overall 5-year survival rate is 50 to 65% Poor outcome is associated with: -advanced stage -perineural spread -positive margins
82 Hard Palate About 3 to 6% of all oral cavity SCC Metastasis in 10-25% of patients at time of presentation Metastasis usually to levels I and II Metastaor nodes that are not palpable on a clinical examination sis can be to retropharyngeal nodes Elective treatment of the neck mostly for T3 or T4 lesions
83 Staging
84 Pigmented Lesions BLUE/PURPLE VASCULAR LESIONS: Hemangioma Varix Angiosarcoma Kaposi s Sarcoma Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia 84
85 Hemangioma Kaposi s Sarcoma 85
86 Pigmented Lesions BROWN MELANOTIC LESIONS Ephelis and Oral Melanotic Macule Nevocellular Nevus and Blue Nevus Malignant Melanoma Drug-Induced Melanosis Physiologic Pigmentation Café au Lait Pigmentation Smoker s Melanosis Pigmented Lichen Planus Endocrinopathic Pigmentation HIV Oral Melanosis Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome 86
87 Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome Physiologic Pigmentation Café au Lait 87
88 Pigmented Lesions BROWN HEME-ASSOCIATED LESIONS Ecchymosis Petechia Hemochromatosis 88
89 Ecchymosis 89
90 Pigmented Lesion GRAY/BLACK PIGMENTATIONS Amalgam Tattoo Graphite Tattoo Hairy Tongue Pigmentation Related to Heavy-Metal Ingestion 90
91 Amalgam Tattoo Hairy Tongue 91
92 92
93 Oral Mucosal Melanoma Mucosal melanoma of the head and neck is a relatively rare condition, representing 8-15% of all malignant melanomas of the head and neck region and accounting for less than 1% of all melanomas. The prognosis is grim, with most published reports documenting a dismal 5-year survival rate of 10-15%. 93
94 94
95 95
96 96
97 97
98 98
99 99
100 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Tumor like conditions Fibroma
101 Selected diseases of the oral mucosa Tumor like conditions Fibroma Hyperplastic fibrous lesion resulting from trauma or chronic irritation
102 Fibroma
103 Selected diseases of the tongue Geographic tongue
104 Geographic tongue
105 Selected Diseases of the Tongue Geographic Tongue Median Rhomboid Glossitis
106 Median Rhomboid Glossitis
107 Selected diseases of the tongue Geographic tongue Median rhomboid glossitis Hairy tongue
108 Black Hairy Tongue
109 Selected diseases of the tongue Geographic tongue Median rhomboid glossitis Hairy tongue Fissured ( scrotal ) tongue
110 Fissured Tongue
111 Paget s disease
112 Paget s Disease
113 Pathology of the Jaws
114 Pathology of the Jaws Miscellaneous Jaw Lesions Overgrowth of Mature Bone Tori ( torus ) Midline of palate
115 Maxillary Tori
116 Pathology of the Jaws Miscellaneous Jaw Lesions Overgrowth of mature bone Tori ( torus ) Midline of palate Lingual surface of mandible
117 Mandibular Tori
118 Pathology of the Jaws Miscellaneous Jaw Lesions Overgrowth of mature bone Tori (Torus) Midline of palate Lingual surface of mandible Exostosis ( exostoses ) Buccal surfaces of maxilla and mandible
119 Exostosis
120 Salivary Glands
121 3 paired glands Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual 121
122 MINOR SALIVARY GLANDS Minor salivary glands are located beneath the mucosa Tongue Buccal mucosa Floor of the mouth Oropharynx Upper and lower lip
123 MINOR SALIVARY GLANDS Extraoral sites Paranasal sinuses Hypopharynx Nasopharynx Larynx Neck
124 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Inflammatory diseases Acute bacterial infection Signs and symptoms: Pain, tenderness, and swelling Red, swollen duct orifice Pus may be expressed by massage of the gland or duct
125 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Obstructive disorders Sialolithiasis: Ductal inflammation or stasis can lead to the formation of salivary stones (sialoliths) that obstruct the flow of saliva Most common in the submandibular gland
126 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Obstructive Disorders: Sialolithiasis Mucocele: Involves minor salivary glands Results from obstruction or damage to the duct releasing mucus to form a cyst like pool of mucus Most common location is lower lip
127 Mucocele
128 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Obstructive disorders Sialolithiasis Mucocele Ranula: Involves, most frequently, the sublingual gland and, less frequently, the submandibular gland
129 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Obstructive disorders Sialolithiasis Mucocele Ranula: Relatively large blue to transparent mass in the floor of the mouth that displaces the tongue Obstruction due to a sialolith or mucus plug that results in mucus extravasation that pools superior to the mylohyoid muscle
130 Ranula
131 Epidemiological Data Salivary gland tumors comprise: 3-6% of all tumors of the head and neck (Shah) Less than 1% of all malignancies of the head and neck
132 Epidemiological Data 65% Parotid glands 22% minor salivary glands 8% submandibular glands
133 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary Gland Tumors: Benign Vs. Malignant Parotid: 80/20 Submandibular 50/50 Sublingual 20/80 Minor depends on location
134 First level bullet Second level bullet Third level bullet Fourth level bullet Fifth level bullet 134
135 Aetiological and Risk Factors of Salivary Gland Tumors 1. In contrast to majority of head and neck tumors: not related to tobacco and alcohol 2. Chronic inflammation is not clearly defined as a risk factor Licitra, Oncology 2003
136 Pathology of the salivary glands Salivary gland tumors Benign: Pleomorphic adenoma Most common salivary gland tumor* Variable mix of epithelial and mesenchymal elements Slow growing, but can reach considerable size
137 Pleomorphic Adenoma
138 Pathology of the salivary glands Salivary gland tumors Benign Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum ( Warthin s tumor )
139 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Benign Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum ( Warthin s tumor ) Occurs most frequently in the tail of the parotid gland of white, middle aged men
140 Warthin s Tumor
141 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant (20%)
142 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Most common malignant salivary gland tumor* Parotid glands ( 60% to 70% ) Minor glands ( 15% to 20% ) Submandibular glands ( 10% )
143 Pathology of the salivary glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Most common salivary malignancy in children*
144 Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
145 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Consists of mucus secreting cells and epidermoid cells Range from low grade, well differentiated tumors to high grade aggressive cancers
146 Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
147 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Malignant mixed tumors
148 148
149 Pathology of the salivary glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Malignant mixed tumors Represents the malignant form of pleomorphic adenoma Involves the parotid glands, less often the submandibular glands, and rarely the minor salivary glands
150 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Adenoid cystic carcinomas
151 Pathology of the Salivary Glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Adenoid cystic carcinomas Most frequent neoplasms of minor salivary glands* 16% to 25% of all tumors 50% of all malignant tumors
152 Pathology of the salivary glands Salivary gland tumors Malignant Adenoid cystic carcinomas Slow growing, but have a relentless course Affinity for perineural invasion Recurrence is common and ultimate prognosis is poor
153 153
154 154
155 Maxillofacial Metastasis Metastasis to the maxillofacial region is a rare occurrence, with most of the literature considering 1% of all new head and neck cancers to be metastasis from distant sites. Hirshberg,A. Oral Oncology, Eur J Cancer 1995
156 Primary Tumor According to the literature in larger series the most common sources of primary tumors are: 1. Breast 2. Lung 3. Kidney 4. Bone 5. Colon Hirshberg, A. Oral Oncol, Eur J Cancer 1995
157 Maxillofacial Metastasis Overall there were twenty six patients. 16 Males 10 Females Average age of 63.8 yrs (45-87) Average age of Males 64 yrs Average age of Females 64 yrs MF mets (n=26) Males (16) Females (10) Ave age 64 Ave age 64
158 Clinical Presentation Facial Swelling % Gingival Swelling % Pain % Paresthesia % Pathologic Fracture % TMD % Non-Healing Extraction 2 7.6% Facial Nerve Palsy 1 3.8% Loose Teeth 1 3.8%
159 Primary Tumor According to the literature in larger series the most common sources of primary tumors are: 1. Breast 2. Lung 3. Kidney 4. Bone 5. Colon Hirshberg, A. Oral Oncol, Eur J Cancer 1995
160 At the time of presentation: 16 (62%) had unknown primaries and the metastasis led to the diagnosis of the primary tumor 10 patients had known primaries - average time of diagnosis of a metastatic lesion 31.5 months - range of months
161
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES. Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Cancers of the Oral Cavity.
 Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity
 Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
The Oral Cavity. Image source:
 The Oral Cavity Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The major structures of the oral cavity are the lips, the teeth, the alveolar ridges (bony areas that
The Oral Cavity Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The major structures of the oral cavity are the lips, the teeth, the alveolar ridges (bony areas that
Index. Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 273 278 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acanthosis nigricans, familial, 251 Amalgam tattoo, 197 198 Amphotericin B, 62 Ankyloglossia, 11 Anti-inflammatory
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 273 278 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acanthosis nigricans, familial, 251 Amalgam tattoo, 197 198 Amphotericin B, 62 Ankyloglossia, 11 Anti-inflammatory
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM
 WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM COMPLETING THE FORM GENERAL INFORMATION Affix the Participant ID label in the space indicated. Record the visit number. Be
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM COMPLETING THE FORM GENERAL INFORMATION Affix the Participant ID label in the space indicated. Record the visit number. Be
4Ps LUMPS AND BUMPS B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS. Most Common BUMP in the oral cavity Fibroma INTERDENTAL PAPILLAE LESIONS
 B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
That. Name QUIZ. 60 SEPTEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com
 QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
Contents. 1 Normal Anatomy Introduction... 17
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Oral Health & HIV. Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape
 Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Head and Neck Cancer How to recognize it in your office
 Head and Neck Cancer How to recognize it in your office Peter M Hunt, MD, FACS Associates in ENT/Head & Neck Surgery Director CHI Memorial Head & Neck and Melanoma Centers of Excellence September 8, 2018
Head and Neck Cancer How to recognize it in your office Peter M Hunt, MD, FACS Associates in ENT/Head & Neck Surgery Director CHI Memorial Head & Neck and Melanoma Centers of Excellence September 8, 2018
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Salivary Gland Imaging. Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016
 Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Oral Lesions & Oral Cancer Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Overview
Oral Lesions & Oral Cancer Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Overview
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School
 Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS
 OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS INTRODUCTION 2 % 4 % of all malignant Tumors in west Asia India 40% Men ^ Age :Over 60 yrs 90% of all oral cancers results from Tobacco and Alcohol Pan (Betel Leaf,Nut, Lime), Reverse
OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS INTRODUCTION 2 % 4 % of all malignant Tumors in west Asia India 40% Men ^ Age :Over 60 yrs 90% of all oral cancers results from Tobacco and Alcohol Pan (Betel Leaf,Nut, Lime), Reverse
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms
 My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
INFECTION. HIV Infection DWI
 HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck. Raymond P. Wood II:
 Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Palatal Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients. Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology
 Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Oral Cancer Risk and Detection
 Oral Cancer Risk and Detection Evan M. Graboyes, MD Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery Cancer Control Program, Hollings Cancer Center Medical University of South Carolina
Oral Cancer Risk and Detection Evan M. Graboyes, MD Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery Cancer Control Program, Hollings Cancer Center Medical University of South Carolina
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem.
 Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Pathology of Selected Head and Neck Lesions. Adel Assaad MD Department of Pathology
 Pathology of Selected Head and Neck Lesions Adel Assaad MD Department of Pathology 1 NOSE Infections 2 Zygomycosis (Mucormycosis) Opportunistic infection caused by "bread mold fungi," including Rhizopus,
Pathology of Selected Head and Neck Lesions Adel Assaad MD Department of Pathology 1 NOSE Infections 2 Zygomycosis (Mucormycosis) Opportunistic infection caused by "bread mold fungi," including Rhizopus,
Diagnostic sieve. Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border. Time bombs for medical GPs! Normal oral mucosa
 Sat 12 June 2010 Millennium WS 28 + 38 2.00-2.55; 3.05-4.00 PM Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border Laurence J. Walsh BDSc, PhD, DDSc, FFOP(RCPA), GCEd, FICD, FPFA, FADI, FIADFE The University of Queensland
Sat 12 June 2010 Millennium WS 28 + 38 2.00-2.55; 3.05-4.00 PM Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border Laurence J. Walsh BDSc, PhD, DDSc, FFOP(RCPA), GCEd, FICD, FPFA, FADI, FIADFE The University of Queensland
Head and Neck Case Studies
 Head and Neck Case Studies John Chaplin & Nick McIvor www.headneck.co.nz Head and Neck lumps every lump must have a diagnosis Working diagnosis» +/- investigations Review» +/- investigations auckland head
Head and Neck Case Studies John Chaplin & Nick McIvor www.headneck.co.nz Head and Neck lumps every lump must have a diagnosis Working diagnosis» +/- investigations Review» +/- investigations auckland head
INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION
 INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION www.dentalelle.com Dentalelle Tutoring Intraoral/Extraoral Examination 1. If you notice a typical finding after reviewing the head and neck on a new patient, what does this
INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION www.dentalelle.com Dentalelle Tutoring Intraoral/Extraoral Examination 1. If you notice a typical finding after reviewing the head and neck on a new patient, what does this
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
PEDIATRICS WK 3 HEAD AND NECK ALISON WALLACE MD, PHD
 PEDIATRICS WK 3 HEAD AND NECK ALISON WALLACE MD, PHD Topics 1. Cervical lymphadenopathy 2. Lymphatic malformation 3. Thyroglossal duct cysts 4. Branchial cleft cysts 5. Thyroid masses CASE 1 Case 1 A 2
PEDIATRICS WK 3 HEAD AND NECK ALISON WALLACE MD, PHD Topics 1. Cervical lymphadenopathy 2. Lymphatic malformation 3. Thyroglossal duct cysts 4. Branchial cleft cysts 5. Thyroid masses CASE 1 Case 1 A 2
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY
 Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY Patient History May 7, 2007 Otolaryngology Head & Neck Subjective: Patient was recently seen by a dentist, who noted a roughness in his lower alveolus, and wanted to
Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY Patient History May 7, 2007 Otolaryngology Head & Neck Subjective: Patient was recently seen by a dentist, who noted a roughness in his lower alveolus, and wanted to
Dr Nick McIvor. Dr John Chaplin. Head & Neck Surgeon Auckland City Hospital Auckland. Auckland Head & Neck Surgeon Gillies Hospital Auckland
 Dr Nick McIvor Head & Neck Surgeon Auckland City Hospital Auckland Dr John Chaplin Auckland Head & Neck Surgeon Gillies Hospital Auckland 14:00-14:55 WS #148: Case Studies of Lumps in the Neck 15:05-16:00
Dr Nick McIvor Head & Neck Surgeon Auckland City Hospital Auckland Dr John Chaplin Auckland Head & Neck Surgeon Gillies Hospital Auckland 14:00-14:55 WS #148: Case Studies of Lumps in the Neck 15:05-16:00
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT
 BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection
 Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
Histopathological study of neoplastic lesions of oral cavity and oropharynx
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
Salivary Glands. The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major
 Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Case Scenario. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults
 Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Annual Refresher Course for
Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Annual Refresher Course for
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology
 Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Polymorphous Low-Grade. December 5 th, 2008
 Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma December 5 th, 2008 Epidemiology Represents 2 nd or 3 rd most common minor salivary gland malignancy (17-26%) 1 st mucoepidermoid carcinoma Rare in reported Asian
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma December 5 th, 2008 Epidemiology Represents 2 nd or 3 rd most common minor salivary gland malignancy (17-26%) 1 st mucoepidermoid carcinoma Rare in reported Asian
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Oral Tumors in Dogs Gingival Enlargement
 Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles. Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer
 Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
Benign Oral cavity lesions. Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery
 Benign Oral cavity lesions Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Anatomy Histology Physiology Pathology Clinical cases Introduction The oral cavity
Benign Oral cavity lesions Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Anatomy Histology Physiology Pathology Clinical cases Introduction The oral cavity
Oral Cancer FAQs. What is oral cancer? How many people are diagnosed with oral cancer each year?
 Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies. Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
Case Scenario 1. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD
 2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9120: Spit Happens (and Sometimes it Doesn t): The Diagnosis and Treatment of Salivary Gland Disease Thursday, April 5 9 am - 12
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9120: Spit Happens (and Sometimes it Doesn t): The Diagnosis and Treatment of Salivary Gland Disease Thursday, April 5 9 am - 12
TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES
 TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES One will be able to recognize pathological entities One will be able to establish a reasonable differential diagnosis One will be able to identify various types of lesions
TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES One will be able to recognize pathological entities One will be able to establish a reasonable differential diagnosis One will be able to identify various types of lesions
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 Collecting Cancer Data: Lip and Oral 2013 2014 NAACCR Webinar Series October 3, 2013 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
Collecting Cancer Data: Lip and Oral 2013 2014 NAACCR Webinar Series October 3, 2013 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
Hemangioma. Hemangioma is an abnormal build up of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs.
 LESSON 5 Oncology. Tumours of maxillofacial area and neck. Hemangioma Hemangioma is an abnormal build up of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs. Causes The classically recognized hemangioma is
LESSON 5 Oncology. Tumours of maxillofacial area and neck. Hemangioma Hemangioma is an abnormal build up of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs. Causes The classically recognized hemangioma is
A Guide to Clinical Differential Diagnosis of Oral Mucosal Lesions
 Continuing Education Brought to you by A Guide to Clinical Differential Diagnosis of Oral Mucosal Lesions Course Author(s): Michael W. Finkelstein, DDS, MS; Emily Lanzel, DDS, MS; John W. Hellstein, DDS,
Continuing Education Brought to you by A Guide to Clinical Differential Diagnosis of Oral Mucosal Lesions Course Author(s): Michael W. Finkelstein, DDS, MS; Emily Lanzel, DDS, MS; John W. Hellstein, DDS,
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation
 Journal of Government Dental College and Hospital, October 2017, Vol.-04, Issue- 01, P. 20-25 Original article: Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation 1 Dr. Jigna S Shah (MDS) 1, 2 Dr.
Journal of Government Dental College and Hospital, October 2017, Vol.-04, Issue- 01, P. 20-25 Original article: Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation 1 Dr. Jigna S Shah (MDS) 1, 2 Dr.
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition. Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
See the latest estimates for new cases of salivary gland cancers in the US and what research is currently being done.
 About Salivary Gland Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with salivary gland cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to
About Salivary Gland Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with salivary gland cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to
Objectives. Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System. Role of Salivary Gland FNA 04/26/2018
 Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes
 1 Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas HNSCC 5 th -6 th most common cancer 400,000/year 50% mortality Considerable
1 Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas HNSCC 5 th -6 th most common cancer 400,000/year 50% mortality Considerable
Finding Dangerous Mucosa
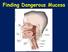 Finding Dangerous Mucosa 2 Oral Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma Salivary Gland Adenocarcinoma Malignant Lymphoma Metastatic Carcinoma Sarcoma 4 Incidence of Cancer in the United States For Oral and Oropharyngeal
Finding Dangerous Mucosa 2 Oral Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma Salivary Gland Adenocarcinoma Malignant Lymphoma Metastatic Carcinoma Sarcoma 4 Incidence of Cancer in the United States For Oral and Oropharyngeal
(loco-regional disease)
 (loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
(loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
Cystic Head and Neck Lesions
 Cystic Head and Neck Lesions Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 19 March 2018 Key points Huge variety of cystic lesions in H&N May be cystic, necrotic, or solid but cystic-appearing Patient age, clinical
Cystic Head and Neck Lesions Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 19 March 2018 Key points Huge variety of cystic lesions in H&N May be cystic, necrotic, or solid but cystic-appearing Patient age, clinical
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 :
 Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours)
 PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
ENT in Primary Care. Learning Objectives. Eustachian Tube (ET) Dysfunction. Eustachian Tube (ET) Dysfunction. Middle Ear Effusion
 Learning Objectives ENT in Primary Care Paul A. Kedeshian, MD Associate Clinical Professor David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Department of Head and Neck Surgery Identifying common ENT problems and
Learning Objectives ENT in Primary Care Paul A. Kedeshian, MD Associate Clinical Professor David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Department of Head and Neck Surgery Identifying common ENT problems and
Head and Neck Pathology Macroscopy and Dissection Dr Tim Bracey
 Head and Neck Pathology Macroscopy and Dissection Dr Tim Bracey Outline Introduction - importance of macro Lip, tongue and oropharynx Larynx Bony resections Salivary glands* will not be covered specifically
Head and Neck Pathology Macroscopy and Dissection Dr Tim Bracey Outline Introduction - importance of macro Lip, tongue and oropharynx Larynx Bony resections Salivary glands* will not be covered specifically
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Neck lumps in children
 Neck lumps in children Midline Lateral Midline neck lumps Thyroglossal cyst - 80% Dermoid cyst Submental lymph node Ectopic thyroid Some rare lesions Thyroglossal cyst Diagnosis: midline, usually overlying
Neck lumps in children Midline Lateral Midline neck lumps Thyroglossal cyst - 80% Dermoid cyst Submental lymph node Ectopic thyroid Some rare lesions Thyroglossal cyst Diagnosis: midline, usually overlying
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION OF ENLARGED LYMPH NODE: Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
 Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
THE TONGUE. In Clinical Diagnosis
 THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013
 EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Ulcerations
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Ulcerations Dr. Nagamani Narayana Department of Oral Biology University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Dentistry Objectives Differential diagnosis of oral ulcerations
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Ulcerations Dr. Nagamani Narayana Department of Oral Biology University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Dentistry Objectives Differential diagnosis of oral ulcerations
Neck mass Evaluation & Management OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY
 Neck mass Evaluation & Management MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CONSULTANT OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY KSU, MEDICAL CITY & KKUH Objectives Obtain map overview in neck
Neck mass Evaluation & Management MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CONSULTANT OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY KSU, MEDICAL CITY & KKUH Objectives Obtain map overview in neck
PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER
 PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER Oral cancer is increasing in incidence worldwide. Throughout the world, malignant neoplasms of the mouth and pharynx rate as the fifth most common cancer in men and the seventh
PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER Oral cancer is increasing in incidence worldwide. Throughout the world, malignant neoplasms of the mouth and pharynx rate as the fifth most common cancer in men and the seventh
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
