substance year week species NOEL LOEL target organs symptoms at LOEL appl. Fungicides
|
|
|
- Myrtle Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 F dog liver AST, a.ph. F rat adrenal, kidney weight; BUN F rat liver fatty infiltration, weight F mouse body weight F dog 8 80 liver, kidney mortality; liver + kidney w.; anemia, ALAT, a.ph.,album., salivation F rat urinary bladder urothelial hyperplasia; cholest. F mouse 4 12 liver vacuolation, rel. weight F dog urinary bladder, mucosal hyperplasia ALAT albumin F rat liver hypertrophy, weight F dog liver, thyroid hyperplasia in liver + thyroid F mouse urinary bladder mucosal hyperplasia F dog thyroid hyperplasia F rat < thyroid hyperplasia F dog vomiting; food intake F rat < blood, kidney, adrenal MCV, MCH, cholest., kidney + adrenal w., tubular dilatation + necrosis in kidney; body w. + food F mouse adrenal abs. + rel. weight; body w.+ food intake F dog vomiting, water consumpt. F rat liver, kidney hypertrophy; colored urine F mouse liver glycogen depletion F dog blood, gastrointestine WBC, clotting time, diarrhoea body w. + food + water intake F mouse urinary bladder mortality; urinary tract lesions, urogenital tract lesions; food F rat liver, thyroid hypertrophy, eosinoph. foci, weight; GGT, a.ph., hypertrophy and hyperplasia of thyroidal epithelia; follicular cell tumors; b.w. + food intake F dog 3 15 liver hepatitis-like lesions, weight F mouse prostate, adrenal, weights; GGT, BUN kidney F rat liver, blood weight; leucocyt. F dog 5 20 testes atrophy of semineferous tubules LDH F rat 5 50 blood, heart LDH, eosinoph.; weight F rat forestomach, blood hyperkeratosis and proliferation of endothelium; leucocytes, prot. F dog 4 24 ALAT, globul. album. F rat 7 35 thyroid, gastrointestine TG, T4, hyperkeratosis of oesophagus, Ca2+, body w. F dog liver, kidney, blood, eye, skin ALAT, GLDH, a.ph., 0-demeth. PNOD, P450, liver weight, portal inflammat. ph and urinary vol, excret. of protein platel.+neutroph., alopecia, dermatitis, cataract, degenerat. of lens F mouse gastrointestine hyperkerat. of mucosa food int. crouching posture F dog skin, liver dermatitsis, bilateral cataracts, alopecia; ALAT, GLDH F rat body weight F rat thyroid hyperplasia; body w. + food F mouse liver weight; body w. F dog < water consumpt. appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation,
2 F dog blood anemia, reticulocytosis; b.w. F mouse body w. + food intake F rat muscle skeletar muscular atrophy F rat kidney, prostate urinary incontinence; enlargement and edema of prostate F dog body weight F mouse 75 no effect F dog body weight F rat kidney urinary incontinence F rat < blood, liver T.G., glucose, prot., Hb; rel. weight F dog 5 10 ALAT, a.ph.; body w. F rat liver, ChE weight plasma-che F dog 5 10 ALAT, a.ph. F dog a.ph., ALAT F rat ChE, liver brain-che; liver w.; b.w. F mouse 3 15 ChE RBC-ChE F rat body weight gain F mouse liver centrilob. enlargement F dog liver, kidney, blood rel. liver rel. kidney w.; albumin protein, MCV, platelets F dog liver weight F mouse liver granulomatous inflamm. in liver weight; body weight F rat body weight + food intake F rat liver weight, prot.,album., Ca2+ K+ F dog a.ph. body w. gain + food F mouse liver, adrenal hypertrophy, weight; adrenal w.; globulins album./glob. F rat liver AST, a.ph. body w.+ food int. F dog liver, kidney AST, a.ph.; urine vol. + ph gravity, IgG, body w. + food F mouse liver, skin mortality; hyperplasia, adenoma + carcinoma, weight; acanthosis, hyperkeratosis b.w. F rat pituitary, liver mortality; pituitary adenoma; bile duct prolif.+ portal sclerosis F dog 0.6 no effect F rat 7 10 liver pnod, weight F dog 20 no effect F mouse liver, blood weight bilirubin F dog blood activated partial thromblast.time F rat glucose F mouse body weight F rat blood, gastrointestine (forestomach), kidney anemia; ulceration, mucosal hyperplasia, inflammat., erosion BUN bilirub., album.; body w.+food F dog blood anemia, prot., album., body w. F dog liver, weight; cholest., protein F mouse eye, urinary bladder retinal atrophy; protein-like bodies in urinary bladder; b.w. + food F rat blood, lpancreas, kidney anemia; hematopoiesis in liver; acinar atrophy in pancreas, steatosis/fatty infiltration of pancreas; kidney w.; b.w. F mouse lung weight, protein F dog liver, thyroid cyt.p-450, liver + thyroid w. food intake appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation, 2
3 F rat a.ph. F rat ChE RBC + plasma-che, ALAT F dog ChE RBC + plasma-che F mouse ChE RBC + plasma-che F /81 52 dog ChE, kidney RBC + plasma-che, spec. gravity F rat ChE, kidney RBC + plasma-che, LDH, gravity F dog < gastrointestine infiltration with round cells, emesis, diarrhoea F rat < gastrointestine, skin lesions, hyperkerat. of tail skin body weight gain + food intake F dog emesis F mouse liver weight F rat 100 no effect F rat liver GGT in liver + blood, weight F dog < liver, adrenal rel.liver + adrenal w. F mouse 2 5 cholest., TG F rat 8 21 liver GGT, cholest., hypertrophy, weight, fat deposition F dog 2 7 kidney hypertrophy of prox. tubular cells F dog blood anemia, platelets F mouse liver hypertrophy, weight F rat 2 8 blood platelets F dog a.ph. adrenal swelling and discolorat. of glandul. F rat 15 (7.5) 50 (25) F dog liver, blood, bladder, adrenal F (< 1992) F /92 (< 1992) 99 mouse 23 (180) 104 rat 7.5 (50) cells and fat droplets; body w. swollen livers,hepatic cord atrophy macrophages; a.ph., anemia; small granulomata in mucosa of urinary bladder; adrenal w. 115 liver, testes, hypertrophy; vacuolat. + hypertrophy gastrointestine of testicular interst. cells; hyperkeratosis of non-gland liver, testes,blood weight; interstitial testicul. cell hyperplasia, spermatozoa in epididymides; hemosiderin in spleen; vacuol. in adrenals F rat body weight gain F dog liver a.ph., AST; weight 3 F rat liver weight F dog gastrointestine vomiting, diarrhoea, body w. F mouse liver weight F dog blood platelets body w. + food F mouse body w. + food intake F rat GGT ALAT body w. F dog CNS, thymus prostate a.ph., tremor, thymus + prostate weight F rat liver, heart, blood liver + heart w., anemia F mouse liver, weight; a.ph., ALAT F dog liver, prostate a.ph.; liver weight, lipidosis; prostate weight F rat food intake F /93 13 rat eye statiations of the lens (1993) (13) (15) (22) F dog blood thromocytes, Jolly bodies appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation,
4 F mouse liver, testes, adrenal liver weight; focal hyperplasia in Leydig cells; lipogenic pigments in adrenal gland; TG, cholest., album. F (1982) 52 (26) dog 2.5 (7) 5 adrenal, testes, prostate, blood hemosiderin; adrenal + testes w. prostate atrophy F rat < 2.3 (28) 2.3 liver, adrenal, prostate, ovary, eye foci; lipidosis of adrenal cortex; interstit. fibrosis of prostate; lipidosis of ovarial interstit. cells; lenticular degeneration F dog liver, bile duct proliferat.; ALAT, a.ph gastrointestine salivation,vomiting, diarrhoea body w. F mouse 9 36 liver, heart, testes weights F rat liver, thyroid hypertrophy, weight; follicular neoplasia; body w. F rat blood, liver, spleen, kidney RBC, reticul. liver, spleen + kidney w. F dog blood, gall bladder erythropoiesis in spleen,hematopoi. in bone marrow, hemosid. in Kupffer cells;thickening of mucosa F dog blood RBC, Heinz bodies; hemosiderosis in cortical renal tubules; erythropoiesis in bone marrow F mouse spleen, kidney weight; creatinine; b.w. F rat kidney, blood hemosiderosis in spleen, spleen + kidney w.; Heinz bodies,bilirub. F dog liver pnod, cyt.p450, cholest. body weight + food F rat 8 40 liver enlargement, weight F rat 7 28 liver, kidney AST, ALAT, GLDH, BUN, creatinine F mouse body weight F dog 15 (> 2.5) 60 liver pnod; a.ph. F rat 5 25 ALAT F dog 3 5 blood, kidney RBC-parameters, ketonuria F mouse liver rel.weight, body weight 4 F rat 5 10 liver AST, a.ph.; body w. F dog 1 5 skin, thymus, prostate ALAT, a.ph.; inflamm. and conjunctivities prost. and thym.w. F / dog adrenal ALAT, a.ph.; adrenal effects F rat 5 25 body weight F mouse liver eosinophil. foci, weight body w. F rat kidney vacuolar swelling of tubular epithelial cells F dog cholest. F dog blood MCV; body weight F / rat thyroid weight (1969) (< 5) (5) F mouse liver hypertrophy F /85 78 rat 5 15 liver, kidney weights; body w. F mouse 40 no effect F / dog liver ground glass of cytoplasm; b.w. F dog blood anemia, iron; bilirubin F rat 4 20 kidney granular pigments in renal cortex appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation,
5 F rat liver, testes,kidney cholest.,hypertrophy liver + testes w., urobilinogen body w F dog liver a.ph., weight, albumin, emesis body weight gain F dog liver, blood weight, brown pigment; a.ph. anemia; body w. + food F rat liver, thyroid weight, cholest.; thyroid neoplasia; acanthosis, b.w. F dog liver, blood cholest., ALAT, a.ph., weight; leucocyt., neutroph., platelets F rat liver, blood fatty vacuol., a.ph., weight Hb, body weight gain F dog kidney, adrenal, liver, blood cytoplasm. pigments in cortical tubul. epithel.; cortical fatty vacuol. in adrenals; liver w. a.ph., globuline, Hb, album. F mouse body w. + food intake F rat liver periacinar fatty vacuol. F dog < thyroid protein-bound iodine F rat kidney weight,glomerulonephr. ALAT F / dog liver, kidney, bile duct prolif., pigmentation, gastrointestine pericholangitis, portal fibrosis; glomerulcytosis, degenerative changein epithel. cells of prox. tubulus; chronic gastritis F mouse forestomach squamous hyperplasia/hyperkerat. F rat stomach, fore-stomach, kidney, adrenal squamous hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, erosion, ulcer; papilloma in forestomach; nephrosis, renal epithelial hyperplasia in prox. tubules kidney + adrenal w. F /71 (1972) 13 (26) rat 24 (6) 120 (30) blood anemia; hemosiderin deposition in liver, spleen, lung, kidney, heart F dog blood hemosiderin deposition in liver, spleen and bone marrow F dog blood hemosiderin in Kupffer cells and in bone marrow F (1972) 104 (26) rat 9.6 (6) 96 (30) blood hemosiderin in spleen and Kupffer cells, Hb; body w. F mouse mortality; body w. F rat blood, liver, kidney thyroid anemia; hepatocell. lipofuscin chol., album., weight; glomerulonephritis, weight; follicular thyroid hyperplasia, weight F (1991) 13 (13) dog < 50 (< 1.25) 50 (1.25) liver, thyroid ALAT, vacuolat. of cytoplasm; follic. cell hypertrophy in thyroid F dog 8 40 liver, thyroid weight; hyperplasia of follicul. epithelium, weight; cholest., T4, BUN F mouse liver hypertrophy, adenomas F rat liver, thyroid, kidney, adrenal mortality; hypertrophy + lipofuscin; thyorid follicular cell hyperplasia, weight; nephro-pathy, weight, urinary protein; lipidosis of adrenal cortex; cholest., BUN, creatinine, TSH, T3, T4 F dog liver ALAT, a.ph., bile duct proliferat. F mouse liver hypertrophy, weight F dog 620 no effect appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation, 5
6 F rat liver,kidney weight; creatinine F rat thyroid, uterus thyroid + uterus w., leukopenia body weight gain + food intake F dog body weight + food intake F rat thyroid, kidney T3, kidney w. F dog 3 15 kidney, thymus weight; a.ph.; thymus w. F dog 1 5 kidney, liver blood urine, pigments, kidney + liver w., hepatocell. hypertrophy F mouse 3 15 kidney chronic nephrosis of cortical tubules, weight F rat 1 6 kidney neoplasia, proteinuria, urinary blood; GGT F dog liver ALAT, AST; bad condition (1.25) F rat liver, heart liver and heart weight F rat liver, kidney liver + kidney w.; body w. F dog adrenal, testes vacuol. + degenerative changes in cells of zona fascicul.; failure in spermatogenesis, Œweight Œbody w. + food intake F dog < liver weight F rat testes spermatogenesis F /78 13 rat liver hepatomegaly F dog liver weight F dog cholest. F mouse liver foci, neoplastic nodules, hepatoblastoma, weight F rat blood Hb, HT; body w. F dog body weight F rat liver ALAT, AST F mouse 5 12 liver weight; body w. F dog 1 50 liver APND, weight F rat 1 10 liver APND, fatty changes, prolif. of SER, weight F dog 1 5 adrenal cortical vacuolation of zona fasciculata; a.ph. F rat 1 10 liver, kidney fatty changes, clear cell foci, weight; urine ph F mouse 1 5 liver, blood fatty changes; WBC F dog a.ph.; body weight F mouse liver hypertrophy, fatty changes, necrosis + bile stasis; ALAT, SDH; body w. F rat 1 24 liver, blood hypertrophy; platelets, leucocyt body w. + food F rat body weight F dog 26 no effect F dog liver, kidney hypertrophy; a.ph., ALAT, TG BUN F mouse 5 20 body weight F rat a.ph. F /83 13 rat 3 6 liver, blood, weight, bilirubin, Hb gastrointestine leuco salivation, diarrhoea F dog liver, blood, prostate ALAT, a.ph., weight; RBC,Hb prostate weight F mouse 6 25 liver weight F48 78 mouse liver adenomas, fatty vacuol., weight F / rat liver swollen livers; food intake F dog liver swollen livers, hypertrophy, a.ph appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation, 6
7 F dog liver pnod F rat 100 no effect (4) (3) (10) F mouse < liver hypertrophy F /76 (1976) 104 rat 15 (2.5) 25 (25) blood RBC, Hb; body w. F dog liver aminopyrine-n-dem., cyt.p-450 weight; a.ph. F rat adrenal, liver vacuolated adrenal cells in zona fascicul.; cyt. P450; body w. F dog liver pnod, a.ph.; body w. F dog adrenal hypertrophy of zona fascicul. cells F mouse liver periportal vacuolation F rat liver, blood pnod, pigments in Kupffer cells; hemosiderin in spleen; body w., food intake F rat liver hypertrophy, vacuolation F dog liver a.ph., weight, hypertrophy F mouse liver cell necrosis, hypertrophy AST F dog body weight F mouse liver hypertrophy + vacuol., weight F rat 3 30 liver, thyroid hypertrophy and vacuolation, weight; cholest.; focal cystic hyperplasia in thyroid + follicular cell neoplasia, adenoma + carcinoma, weight; body w. F dog liver, blood karyomegaly, pigmentation, hematopoietic nodules F (1971) 104 rat 2 (0.6) 7.5 adrenal, kidney weight; renal tubular cell hyperplasia; BUN, glucose cholest., TG; body w. F rat liver weight (230) F dog ALAT, a.ph.; album./glob. F dog liver, testes cirrhosis; cholest., a.ph., ALAT testicul. degeneration; anorexia body w. +food intake F mouse < liver, thymus, brain carcinoma + adenoma, weight thymus + brain w. F rat 125 no effect F rat liver weight, food intake F dog liver, eye bile duct hyperplasia, weight; retinal changes F rat liver, pancreas altered hepatocytes, weight; exocrine degranulat; cholest. F dog 1 10 nose, bone marrow, liver, blood nasal dryness; myeloid/erythroid ratio in bone marrow; liver w. cholest., leucocyt. F mouse 1 10 liver granulomatous hepatitis, weight F rat liver, kidney, cholest., hypertrophy, weight BUN, colored urine, regenerative tubular epithel. and granular casts F dog gastrointestine dark and soft stool F dog gastrointestine dark and soft stool F rat kidney, liver blue urine; liver weight F mouse kidney, liver, urinary bladder blue urine; centrilob. hypertrophy; epithelial hyperplasia F / rat liver, adrenal, blood weight; fatty degeneration of zona fasc. leucocyt.,. body weight gain appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation, 7
8 F dog liver, gastrointestine weight; salivat., vomiting, fluid feces, body w. F /84 52 dog 3 15 liver weight, cholest. + triglyc. F mouse adrenal, liver adrenal +liver w., degenerat. and hypertrophy of hepatocytes F rat a.ph., ALAT F rat < thyroi cholest., phospholip.; hypertr. of thyroid follicle epithelia F dog body weight + food intake F mouse liver cell necrosis, depletion of glycogen F mouse liver, thyroid MFO; follicul. cell hyperplasia F rat thyroid T4, TSH F dog 3 26 thyroid,blood, enlarged/dark thyroids; anemia; thymus cholest.,bilirub.; lymphoid deplet hematopoiesis in bone marrow F dog 5 20 blood, testes, liver Hb, RBC, PCV, testes w. liver w. body w. + food F mouse body w. F / rat thyroid increased height of follic. epithel. T4; body w. F rat blood, kidney anemia; weight; hematopoiesis F dog K+ in serum F rat urinary bladder, urinary tract F dog testes degeneration calculi and mineralisation, epithelial hyperplasia and neo-plasia; hyperplasia and inflammat. in urinary tract F rat liver rel. liver w. body w. F dog blood Hb, PCV, WBC F dog blood RBC, PCV F rat blood, kidney anemia, BUN F rat liver hypertrophy F dog 5 50 gastrointestine diarrhoea F mouse liver rel. weight, blue stain of pelvis 8 F dog Œbody w. F mouse liver, thymus, spleen, lymph node weight; enlarged thymus, spleen + lymph nodes; food + water int. F rat liver, kidney, blood gastrointestine hepatocell. tumors, necrosis, atrophy, degeneration; nephro-pathy, cysts, urobilinogen; anemia; diarrhoea, body w. F62 13 rat liver, thyroid hypertrophy; thyroid follicular cell (10) (40) hypertrophy; body weight + food F62 13 dog gastrointestine emesis, saliv.; body w. + food F rat blood, thyroid Hb, HT; thyroid w.; b.w. F dog liver, kidney, adrenal liver, kidney, adrenal w. F mouse heart, liver, kidney mortality; atrial thrombosis of myocard; liver + kidney w. body w. + food intake F rat body weight + food intake F dog 80 no effect observed F /76 (1976) 13 (13) rat 20 (7.5) 25 (25) thymus, adrenal thymus w. adrenal w. F (1986) 13 (52) dog 25 (12.5) 75 (62.5) appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation, liver a.ph., PAS-react.; apathy, b.w. F dog kidney, liver alterations of cortical tubuli; a.ph., ALAT, GLDH, BUN, creatinine, glucose in urine; b.w.
9 F rat bone alterations F rat body weight gain F dog food intake F mouse 2 50 liver hypertrophy, weight, cholest. 2 < F dog 6.25 no effect F mouse liver hypertrophy, weight F rat adrenal weight; glucose; body w. F rat 1 4 piloerection body weight gain F dog liver, kidney a.ph., GGT, TG, album., hepatomegaly, weight; creatin. F mouse liver cell necrosis, eosinophilia, vacuol. F dog liver a.ph., cholest., bilirubin, albumin; hepatocytic pigment, intrahepatocytic bodies F mouse liver nodules + tumors, inflammation, single cell necrosis, hypertrophy body weight F rat liver GGT, cholest., protein, globul. TG; liver w. F rat liver hepatic MFO F dog liver hypertrophy F dog liver hypertrophy, weight; a.ph. F rat testes atrophy, weight F mouse liver MFO-activity F rat blood anemia, Na+, Cl- F dog blood, liver, anemia, emesis, diarrhoea gastrointestinal a.ph., TG, weight F dog a.ph. F rat liver hepatocell. hypertrophy F /79 52 rat liver, kidney vacuolation, weight, nitrosoanisole metabolism; creatinine F dog < liver, gastrointestine cholestasis; diarrhoea F mouse liver, blood hyperplasia,vacuol. ALAT,BUN 9 F dog spleen weight F rat sorbitol-dh (1980) 9 (0.75) (3) F dog liver a.ph., cholest., ALAT, GLDH, SDH; food intake F rat liver ALAT, AST F mouse 120 appl., application design, with asterisks () application via capsule or stomach intubation,
Table 3 Insecticides 1
 Table 3 1 I07 13 rat 2.5 10 blood, liver, spleen anemia; hepatic inflamm.,siderosis of Kupffer cells, liver +spleen w. I07 13 dog 2.6 13.5 blood erythropoiesis; hematopoiesis in spleen I01 1972 52 dog
Table 3 1 I07 13 rat 2.5 10 blood, liver, spleen anemia; hepatic inflamm.,siderosis of Kupffer cells, liver +spleen w. I07 13 dog 2.6 13.5 blood erythropoiesis; hematopoiesis in spleen I01 1972 52 dog
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
The Blood Chemistry Panel Explained
 The Blood Chemistry Panel Explained The Senior Profile (for senior and geriatric patients) As our dogs and cats enter their senior years, we recognize that they are more likely to have health problems
The Blood Chemistry Panel Explained The Senior Profile (for senior and geriatric patients) As our dogs and cats enter their senior years, we recognize that they are more likely to have health problems
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION
 DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
INFLUENCES OF EXCESSIVE EXERCISE ON THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF RAT ORGANS
 INFLUENCES OF EXCESSIVE EXERCISE ON THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF RAT ORGANS KAZUO ASAHINA, FUJIKO KITAHARA, MIYOKO YAMANAKA AND TOSHIKO AKIBA* Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Toho University,
INFLUENCES OF EXCESSIVE EXERCISE ON THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF RAT ORGANS KAZUO ASAHINA, FUJIKO KITAHARA, MIYOKO YAMANAKA AND TOSHIKO AKIBA* Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Toho University,
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Control Data of Rat
 BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Control Data of BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Rat Taconic Biosciences -1- BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Environmental Conditions and Investigation Items Environmental Conditions (Isolated Barrier
BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Control Data of BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Rat Taconic Biosciences -1- BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Environmental Conditions and Investigation Items Environmental Conditions (Isolated Barrier
Hemosiderin. Livia Vida 2018
 Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Interpretation of the liver hypertrophy in the toxicological evaluation of veterinary medicinal products
 Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
Pathological Pigmentation
 Pathological Pigmentation By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology, Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Pathological Pigmentation: Pigments: Pigments are colored substances accumulate abnormally within the tissue and
Pathological Pigmentation By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology, Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Pathological Pigmentation: Pigments: Pigments are colored substances accumulate abnormally within the tissue and
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Theses for the Final Exam of Pathology
 Theses for the Final Exam of Pathology (Asterisks indicate the pool of theoretical questions for the semi-final practical exam) GENERAL PATHOLOGY I. POSTMORTEM SIGNS NECROSIS 1. Postmortem changes, causes
Theses for the Final Exam of Pathology (Asterisks indicate the pool of theoretical questions for the semi-final practical exam) GENERAL PATHOLOGY I. POSTMORTEM SIGNS NECROSIS 1. Postmortem changes, causes
Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment
 Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment Akira Inomata, D.V.M., Ph.D., D.J.S.T.P. Tsukuba Drug Safety, Global Drug Safety, Biopharmaceutical Assessments Core Function
Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment Akira Inomata, D.V.M., Ph.D., D.J.S.T.P. Tsukuba Drug Safety, Global Drug Safety, Biopharmaceutical Assessments Core Function
Effect of Vidahi-Tikshna-Ushna-Snigdh Ahara on Raktavaha Srotas An Experimental Study
 Effect of Vidahi-Tikshna-Ushna-Snigdh Ahara on Raktavaha Srotas An Experimental Study Vd. Hitesh Vyas Dr. Anil D. Avhad Department of Basic Principles Institute for Post Graduate Teaching and Research
Effect of Vidahi-Tikshna-Ushna-Snigdh Ahara on Raktavaha Srotas An Experimental Study Vd. Hitesh Vyas Dr. Anil D. Avhad Department of Basic Principles Institute for Post Graduate Teaching and Research
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder
 Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER
 CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
What s your diagnosis?
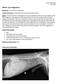 What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg
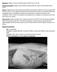 Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
M. G. Robertson Biology Professor Delta College BLOOD - THE ELIXIR OF LIFE ROBERTSON DOPPELGANGERS. Phil Collins. Flea. Robin Williams.
 M. G. Robertson Biology Professor Delta College BLOOD - THE ELIXIR OF LIFE ROBERTSON DOPPELGANGERS Phil Collins Flea Steve Jobs Sting Robin Williams BLOOD COMPONENTS 8% by weight; 4-6 liters by volume
M. G. Robertson Biology Professor Delta College BLOOD - THE ELIXIR OF LIFE ROBERTSON DOPPELGANGERS Phil Collins Flea Steve Jobs Sting Robin Williams BLOOD COMPONENTS 8% by weight; 4-6 liters by volume
TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS
 TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director () Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (UP) AFLATOXICOSIS Aflatoxicosis is a toxic condition of poultry widely prevalent
TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director () Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (UP) AFLATOXICOSIS Aflatoxicosis is a toxic condition of poultry widely prevalent
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
& CBC Analysis. Getting the Most from the. Session 3. Foundations of Functional Blood Chemistry Analysis Session 3 Dr.
 Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 3 Li L:iver and Gallbladder Markers SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT & GGTP Getting the Most from the Liver Panel http://www.fmtown.com 1 Liver Panel Reference Ranges
Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 3 Li L:iver and Gallbladder Markers SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT & GGTP Getting the Most from the Liver Panel http://www.fmtown.com 1 Liver Panel Reference Ranges
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY
 CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT. Lecture 5. Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Morphological changes (accumulations) occur inside and outside cells
 MIXED ACCUMULATIONS (DEGENERATIONS) Morphological changes (accumulations) occur inside and outside cells The group includes: - chromoproteins metabolism disturbances; - lipoproteins metabolism disturbances;
MIXED ACCUMULATIONS (DEGENERATIONS) Morphological changes (accumulations) occur inside and outside cells The group includes: - chromoproteins metabolism disturbances; - lipoproteins metabolism disturbances;
Gastrointestinal Markers
 Gastrointestinal Markers Session 2 Gastrointestinal System Reference Ranges Optimal Range Ttl Total Protein ti 69 6.9 74 7.4 Globulin 2.4 2.8 BUN 10 16 Creatinine 0.8 1.1 Phosphorous 3.0 4.0 Eosinophils
Gastrointestinal Markers Session 2 Gastrointestinal System Reference Ranges Optimal Range Ttl Total Protein ti 69 6.9 74 7.4 Globulin 2.4 2.8 BUN 10 16 Creatinine 0.8 1.1 Phosphorous 3.0 4.0 Eosinophils
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC. Opinion. on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320)
 Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
no concerns hepatic shunt, high protein diet, kidney failure, metabolic acidosis
 TAKING THE WORK OUT OF INTERPRETING LAB WORK CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Brandy Helewa, CVT, RVT, VTS (ECC) Penn Foster College - Scranton, PA Knowing what the results on your
TAKING THE WORK OUT OF INTERPRETING LAB WORK CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Brandy Helewa, CVT, RVT, VTS (ECC) Penn Foster College - Scranton, PA Knowing what the results on your
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Multiphasic Blood Analysis
 Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Blood Test Results Report
 Blood Test Results Report The Blood Test Results Report lists the results of the patient s Chemistry Screen and CBC and shows you whether or not an individual element is outside of the optimal range and/or
Blood Test Results Report The Blood Test Results Report lists the results of the patient s Chemistry Screen and CBC and shows you whether or not an individual element is outside of the optimal range and/or
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
155.2 Malignant neoplasm of liver not specified as primary or secondary. C22.9 Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary
 ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY
 AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
LIVER & SPLEEN. Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust,
 This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
WELLNESS LABS EXPLANATION OF RESULTS BASIC METABOLIC PANEL
 WELLNESS LABS EXPLANATION OF RESULTS BASIC METABOLIC PANEL BUN Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a waste product of protein breakdown and is produced when excess protein in your body is broken down and used
WELLNESS LABS EXPLANATION OF RESULTS BASIC METABOLIC PANEL BUN Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a waste product of protein breakdown and is produced when excess protein in your body is broken down and used
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
ASPEN MOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER. Lab Health Fair
 ASPEN MOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER Lab Health Fair GENERAL HEALTH PANEL: CMP CMP The Comprehensive Metabolic Panel is used as a broad screening tool to evaluate organ function and check for conditions such
ASPEN MOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER Lab Health Fair GENERAL HEALTH PANEL: CMP CMP The Comprehensive Metabolic Panel is used as a broad screening tool to evaluate organ function and check for conditions such
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results
 SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
Atrophy. Dystrophy. II. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry. Lucie Tučková
 Atrophy. Dystrophy. II. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Lucie Tučková Atrophy Decrease in size of the cell or organ Reduction in cell size and/or cell number, or both Atrophic cells may have diminished
Atrophy. Dystrophy. II. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Lucie Tučková Atrophy Decrease in size of the cell or organ Reduction in cell size and/or cell number, or both Atrophic cells may have diminished
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
-Liver function tests -
 -Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
-Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
2015 Lab Animal 8/22/ Mouse. 2. Rat. 3. Mouse. Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse
 1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
Topics of this lecture : RBC. Structural characteristics Hemoglobin Erythropoiesis Erythrocytes destruction
 Topics of this lecture : RBC Structural characteristics Hemoglobin Erythropoiesis Erythrocytes destruction Structural characteristics Its small size and biconcave shape provides more surface area than
Topics of this lecture : RBC Structural characteristics Hemoglobin Erythropoiesis Erythrocytes destruction Structural characteristics Its small size and biconcave shape provides more surface area than
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610
 Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer, and email.
Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer, and email.
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Chapter 14 The Urinary System. Anatomy
 Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders
 Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
-1- Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks).
 -1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
-1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
Chronic inflammation. 07-Dec-15. Macrophage Tissue destruction
 Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder
 Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination
 I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models: pelvis
 159 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1: Urinary System Anatomy,
159 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1: Urinary System Anatomy,
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Reproductive Tract Pathology in Hyperkeratosis
 Reproductive Tract Pathology in Hyperkeratosis of Cattle and Sheep Kenneth McEntee, D.V.M., and Peter Olafson, D.V.M. HYPERKERATOSIS (X disease) of cattle was first observed in May, 1941, in New York State.
Reproductive Tract Pathology in Hyperkeratosis of Cattle and Sheep Kenneth McEntee, D.V.M., and Peter Olafson, D.V.M. HYPERKERATOSIS (X disease) of cattle was first observed in May, 1941, in New York State.
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1)
 2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems.
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems. GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM We will examine
GASTROINTESTINAL AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems. GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM We will examine
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
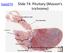 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM
 6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM Cloudy Swelling Hydropic Degeneration Mucinous Degeneration Mucoid Degeneration Psuedomucin Amyloid Infilteration Hyaline Degeneration Fatty Changes Glycogen Infilteration
6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM Cloudy Swelling Hydropic Degeneration Mucinous Degeneration Mucoid Degeneration Psuedomucin Amyloid Infilteration Hyaline Degeneration Fatty Changes Glycogen Infilteration
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary, digestive, urinary, respiratory and reproductive systems
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2008 UNIT 2 Key Concepts: REVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS A. OVERVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS 1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2008 UNIT 2 Key Concepts: REVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS A. OVERVIEW OF BODY SYSTEMS 1. Five body systems are in contact with the external environment, the integumentary,
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
