Severe thyroid-associated orbitopathy in Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Report of 2 cases
|
|
|
- Jasmine Miranda Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endocrine Journal 2011, 58 Or i g i n a l Advance Publication doi: /endocrj. K11E-019 Severe thyroid-associated orbitopathy in Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Report of 2 cases Ai Yoshihara 1), Jaeduk Yoshimura Noh 1), Ayako Nakachi 1), Hidemi Ohye 1), Shiori Sato 1), Kenichi Sekiya 1), Yuka Kosuga 1), Miho Suzuki 1), Masako Matsumoto 1), Yo Kunii 1), Natsuko Watanabe 1), Koji Mukasa 1), Yoichi Inoue 2), Kunihiko Ito 1) and Koichi Ito 1) 1) Ito Hospital, Tokyo , Japan 2) Olympia Eye Hospital, Tokyo , Japan Abstract. Thyroid-associated orbitopathy (TAO) is characterized by immune-mediated inflammation of the extraocular muscles surrounding orbital connective tissue and adipose tissue. Severe orbitopathy related to autoimmune thyroid disease often occurs in patients with Grave s disease, but it is rare in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis. The pathogenesis of TAO is unclear. Several studies have noted a strong correlation between the levels of antibodies to thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) and TAO in Graves disease. Mild upper eyelid retraction has been reported to be common in Hashimoto s thyroiditis patients, however severe orbitopathy is rare. We report two cases of severe TAO in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis who required systemic glucocorticoid therapy and orbital irradiation to treat the TAO. The activity of the TAO was high in both patients, because their clinical activity scores (CAS) for the orbitopathy were high, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed enlargement of the extraocular muscles and an increase in T2 signal intensity and prolonged T2 relaxation time which indicate an active stage of inflammation. We tested the presence of TRAb by three different assays and were negative in both patients. Since the eye muscle damage cannot be due to TSH receptor antibodies, other pathogenetic mechanisms may be responsible for the orbitopathy in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Key words: Hashimoto s thyroiditis, Thyroid-associated orbitopathy, Thyrotropin receptor antibody Thyroid-associated orbitopathy (TAO) is characterized by immune-mediated inflammation of the extraocular muscles surrounding orbital connective tissue and adipose tissue. TAO generally occurs in patients with hyperthyroidism due to Graves disease, and it sometimes occurs in euthyroid and hypothyroid patients. Most euthyroid and hypothyroid patients with TAO are thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) -positive, and they are diagnosed as having euthyroid Graves disease or hypothyroid Graves disease. Although it is widely accepted that TAO is an autoimmune disorder, its pathogenesis is unclear. Several studies have noted a strong correlation between antibodies to thyrotropin receptor and TAO in Graves disease [1-6], and serum TRAb levels have been found to correlate Received Jan. 12, 2011; Accepted Feb. 17, 2011 as K11E-019 Released online in J-STAGE as advance publication Mar. 17, 2011 Correspondence to: Ai Yoshihara, M.D., Ito Hospital, Jingumae, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo , Japan a-yoshihara@ex.ito-hospital.jp positively with clinical features of orbitopathy [7]. The TRAb hypothesis cannot be used to explain TAO in Hashimoto s thyroiditis, because Hashimoto s thyroiditis patients usually test negative for TRAb. Mild upper eyelid retraction has been reported to be common in Hashimoto s thyroiditis patients [8]. Severe orbitopathy is rare in Hashimoto s thyroiditis, and only a few cases have ever been reported [9-11]. We report two cases of severe TAO in Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Laboratory Methods TSH and free thyroxine (ft 4 ) levels were measured by electrochemiluminescence immunoassays (ECLusys TSH and ECLusys FT4, respectively; Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). The manufacturer s reference limits were mu/l and pmol/l, respectively. TSH receptor antibody (TRAb: thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulin) levels were determined with a commercial The Japan Endocrine Society
2 2 Yoshihara et al. radioimmunoassay kit (RSR, Cardiff, UK; TRAb-CT) and expressed as percentage (%) inhibition of binding according to the manufacturer s instructions (normal range <10%). We also determined TRAb by a twostep radioreceptor assay (DYNO test TRAb Human Kit YAMASA ; Yamasa Corp., Tokyo, Japan: normal range <1.0 IU/L; TRAb-Dyno). Thyroid-stimulating antibody (TSAb) was measured with a commercial bioassay radioimmunoassay kit (Yamasa Corp., Tokyo, Japan) and expressed as a percentage of camp production generated in porcine thyroid cells that contained test pooled immunoglobulin (normal range, <180%). TSH-stimulation blocking antibody (TSBAb) activity was assayed by measuring inhibition of TSH-induced camp production, with values above 45% indicating the presence of TSBAb activity. Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) and thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb) were determined by solid-phase RIAs (Cosmic Corp., Tokyo, Japan), and the normal range of both is below 0.3 U/mL. Case Reports Case 1 A 64-year-old woman consulted an ophthalmologist with a chief complaint of diplopia, and an ophthalmological examination showed a mild supraduction deficiency. Laboratory examination results indicated hypothyroidism; the TSH level was 37.8 mu/l. The TPOAb level was >60 U/mL, and TRAb-CT was <0.1%. The patient had never smoked. She was diagnosed with Hashimoto s thyroiditis and treated with levothyroxine 50 µg daily for the hypothyroidism and with oral prednisone, 30 mg daily tapered by 10 mg per month, for the orbitopathy. Despite this treatment, the diplopia became exacerbated 7 months later, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed enlargement of the left medial rectus muscle and left inferior rectus muscle. The active form of orbitopathy was diagnosed, and methylprednisolone pulse therapy was administered, but when her diplopia failed to improve, she was referred to our hospital for further examination and treatment. When first examined at our hospital the patient was being treated with levothyroxine 50 µg daily, and her TSH level was 3.81 mu/l. Her thyroid hormone levels were within the reference values. TRAb testing was negative; the results were 7.5% by TRAb-CT and below 1.0 IU/L by TRAb-Dyno. A TSAb test was also negative (126%). The TgAb level was 7.2 U/mL, and the TPOAb level was 50 U/mL. Ultrasonography showed a thyroid gland with heterogeneously decreased echogenicity and no nodules. The laboratory data are shown in Table 1. The degree of exophthalmoses measured with the Hertel exophtalmometer was 15 mm in both eyes. The clinical activity score (CAS) for the orbitopathy in this patient was Table 1 Clinical course and laboratory data in Case 1. ft Case 1 4 TSH TRAb-CT TRAb-Dyno (pmol/l) (mu/l) (%) (IU/L) TSAb (%) TSBAb (%) TgAb TPOAb Treatment 1 year before 37.8 <0.1 >60 LT4 50 μg following methylprednisolone pulse therapy First visit < >50 LT4 50 μg + orbital irradiation 5 months LT4 100 μg 7 months LT4 100 μg 11 months LT4 100 μg 17 months LT4 75 μg 23 months LT4 75 μg + orbital decompression surgery 6 years LT4 75 μg Levothyroxine was administered to treat the patient s hypothyroidism, and methylprednisolone pulse therapy, orbital irradiation, and orbital decompression surgery were performed to treat the orbitopathy. TRAb and TSAb tests have remained negative during the 6-year follow-up period. ft 4 : free thyroxine (normal range: pmol/l), TSH: thyrotropin (normal range: mu/l), TRAb- CT: TSH receptor antibody (normal range: <10%), TRAb-dyno: TSH receptor antibody (normal range: <1.0 IU/L), TSAb: Thyroidstimulating antibody (normal range: <180%), TSBAb: TSH stimulation blocking antibody (normal range: <45%), TgAb thyroglobulin antibody (normal range: <0.3 U/mL), TPOAb: Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody (normal range: <0.3 U/mL) LT4: levothyroxine, PSL: prednisolone
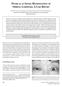
3 Orbitopathy in Hashimoto s thyroiditis 3 Case 1 Fig. 1 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the eyes in Case 1 showed enlargement of the left medial rectus muscle and left inferior rectus muscle (yellow arrows). Case 2 Fig. 2 MRI of the eyes in Case 2 revealed bilateral enlargement of the medial rectus muscle and inferior rectus muscle (yellow arrows). 3: one point each for diffuse redness of the conjunctiva, a swollen caruncle, and increased proptosis. MRI showed enlargement of the left inferior rectus muscle and an increase in T2 signal intensity and prolonged T2 relaxation time (Fig. 1). Treatment consisted of orbital irradiation (15 Gy), and there was slight improvement in the diplopia. Orbital decompression surgery was then performed, and the diplopia finally resolved. Her thyroid function has remained stable during 6 years of treatment with levothyroxine 75 µg daily. Case 2 A 44-year-old woman suffered from bilateral blepharedema and diplopia for several months. Subsequently she consulted a neurologist and an ophthalmologist. MRI of the eyes revealed bilateral enlargement of the medial rectus muscle and inferior rectus muscle and an increase in T2 signal intensity and prolonged T2 relaxation time (Fig. 2). Exophthalmos measured by Hertel exophthalmometry was 17 mm in the right eye and 16 mm in the left eye. The laboratory data indicated subclinical hypothyroidism; the TSH level was 8.16 mu/l, and the free thyroxine (ft 4 ) level 15.2 pmol/l. The TPOAb level was >50 U/mL, TgAb 1160 U/mL, TRAb below 0.1%, TSAb was 113%. The patient had never smoked. She was treated with levothy-
4 4 Yoshihara et al. Table 2 Clinical course and laboratory data in Case 2. ft Case 2 4 TSH TRAb-CT TRAb-Dyno (pmol/l) (mu/l) (%) (IU/L) TSAb (%) TgAb TPOAb 5 months before months before < LT4 75 μg First visit <1.0 Treatment LT4 75 μg + orbital irradiation +PSL 15 mg tapered gradually 1 month LT4 75 μg + PSL 5 mg 2 months LT4 75 μg + PSL 5 mg 5 months >50 LT4 75 μg + PSL 5 mg 8 months LT4 75 μg 6 years LT4 75 μg Levothyroxine was administered to treat subclinical hypothyroidism, and orbital irradiation and oral prednisone were used to treat the orbitopathy. TRAb and TSAb tests have remained negative throughout the 6-year follow-up period, and the patient s symptoms and thyroid function have been stable during the follow-up period. roxine 75 µg daily for subclinical hypothyroidism, and referred to our hospital. Examination yielded a CAS of 4: one point each for a painful oppressive feeling behind the globe, redness of the eyelids, swelling of the eyelids, and increased proptosis. She was treated with orbital irradiation (15 Gy), and the diploplia improved slightly. The patient was also treated with oral prednisone 15 mg daily, and the dose was tapered in 5 mg decrements depending on the symptoms. The diplopia gradually improved after the start of treatment. TRAb and TSAb test results have remained negative during the 6-year follow-up period (Table 2). The symptoms and thyroid function have remained stable during the 6 years of treatment with levothyroxine 75 µg daily. Discussion TAO usually occurs in Graves s disease with hyperthyroidism, and sometimes in euthyroid and hypothyroid patients. Since most euthyroid and hypothyroid patients with orbitopathy are TRAb-positive, they are diagnosed as having euthyroid Graves disease or hypothyroid Graves disease. When euthyroid and hypothyroid patients with orbitopathy are TRAbnegative, other diseases need to be considered in the differential diagnosis, including cavernous carotid fistula, sphenoid meningioma, other orbital tumors, such as lymphoma, idiopathic orbital myositis [12], and IgG 4- related disease [13-15]. MRI of the brain showed no signs of a tumor occupying the orbital cavity or of a cavernous carotid fistula in either Case 1 or Case 2. Neither patient had any clinical manifestations of lymphoma [16]. The main clinical features of idiopathic orbital myositis are orbital pain exacerbated by eye movement and a rapid response to systemic corticosteroid therapy, but neither of our patients complained of orbital pain, thereby ruling out idiopathic orbital myositis. IgG 4 -related disease is a recently proposed clinical entity that is characterized by several unique clinical findings. Ocular adnexal IgG 4 -related disease is often manifested by enlargement of lacrimal and salivary glands, but the extraocular muscles are usually not involved [17, 18]. The main clinical signs of TAO include exophthalmos, eyelid retraction and lag, diplopia and optic neuropathy. In the early stages of TAO the inflamed and enlarged eye muscle does not stretch normally, leading to double vision as a consequence [19]. In the previous study which evaluated the extraocular muscle enlargement in TAO in Graves disease, the most frequently affected muscle was the inferior rectus muscle, followed by the medial rectus muscle [7, 20]. In our cases, left medial rectus muscle and left inferior rectus muscle were enlarged in case 1, bilateral medial rectus muscle and inferior rectus muscle were enlarged in case 2. The typical MRI findings, clinical course, and the presence of antibodies to thyroid antigens in our two patients led to the diagnosis of TAO. The activity of the TAO was high in both patients, because a CAS of 3 or more indicates active orbitopathy [21], and increased T2 signal intensity and a prolonged T2 relaxation time indicate an active stage of inflammation [22]. Severe orbitopathy is rare in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis, and only few such cases have been reported [9-11]. In one of the cases the patient was reported to be TRAb-positive, and hypothyroid
5 Orbitopathy in Hashimoto s thyroiditis 5 Graves disease was suspected [9]. Since the other two case reports did not mention the presence of TRAb [10, 11], hypothyroid or euthyroid Graves disease could not be excluded. The pathogenesis of TAO and the mechanism of the link to thyroid autoimmunity are poorly understood. Several antigens have been identified as possible autoantibody targets, including TRAb [23, 24], the skeletal muscle calcium binding protein calsequestrin, and the fibroblast cell membrane protein collagen XIII [25-28]. There is accumulating evidence that the TSH receptor is present in the orbit and expressed on orbital fibroblasts. These findings support the hypothesis that TRAb is not only the cause of Graves disease, but is also responsible for TAO. Hashimoto s thyroiditis is not usually associated with overt orbitopathy, however, Tjiang et al. reported that mild eye signs were present in 34% of their patients [8], and they predominantly consisted of upper eyelid retraction. Since patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis test negative for TRAb, the TRAb hypothesis cannot be used to explain the etiology of eye signs in Hashimoto s thyroiditis. An alternative explanation for the ophthalmopathy in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis is specific production of antibody against an eye muscle antigen, such as calsequestrin, flavoprotein, or G2s [29]. We did not test either of our two patients for such antibodies, and further investigation is needed. We have reported two cases of severe TAO in which testing for the presence of TRAb by three different assays was negative. Since the eye muscle damage cannot be due to TSH receptor antibodies, other pathogenetic mechanisms may be responsible for the orbitopathy in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis. References 1. Gerding MN, van der Meer JW, Broenink M, Bakker O, Wiersinga WM, Prummel MF (2000) Association of thyrotrophin receptor antibodies with the clinical features of Graves ophthalmopathy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 52: Bartalena L (2005) Graves ophthalmopathy: search for shared autoantigen(s) continues. J Endocrinol Invest 28: Bahn RS (2004) TSH receptor expression in orbital tissue and its role in the pathogenesis of Graves ophthalmopathy. J Endocrinol Invest 27: Agretti P, De Marco G, De Servi M, Marcocci C, Vitti P, Pinchera A, Tonacchera M (2005) Evidence for protein and mrna TSHr expression in fibroblasts from patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) after adipocytic differentiation. Eur J Endocrinol 152: Eckstein AK, Losch C, Glowacka D, Schott M, Mann K, Esser J, Morgenthaler NG (2009) Euthyroid and primarily hypothyroid patients develop milder and significantly more asymmetrical Graves ophthalmopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 93: Noh JY, Hamada N, Inoue Y, Abe Y, Ito K (2000) Thyroid-stimulating antibody is related to Graves ophthalmopathy, but thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin is related to hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves disease. Thyroid 10: Bahn RS (2010) Graves ophthalmopathy. N Engl J Med 362: Tjiang H, Lahooti H, McCorquodale T, Parmar KR, Wall JR (2010) Eye and eyelid abnormalities are common in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Thyroid 20: Grzesiuk W, Szydlarska D, Pragacz A, Bar-Andziak E (2008) Thyroid-associated orbitopathy in patients with Hashimoto s thyroiditis: a case report. Pol Arch Med Wewn 118: Tomer Y (2000) Unilateral ophthalmopathy in a patient with Hashimoto s thyroiditis. Thyroid 10: Miyagi K, Koh CS, Inoue A, Tsukada N, Yanagisawa N (1988) [A case of dysthyroid ophthalmopathy with chronic thyroiditis and anti-extraocular muscle antibody]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 28: Scott IU, Siatkowski RM (1997) Idiopathic orbital myositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 9: Cheuk W, Chan JK (2010) IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease: A Critical Appraisal of an Evolving Clinicopathologic Entity. Adv Anat Pathol 17: Hamed G, Tsushima K, Yasuo M, Kubo K, Yamazaki S, Kawa S, Hamano H, Yamamoto H (2007) Inflammatory lesions of the lung, submandibular gland, bile duct and prostate in a patient with IgG4-associated multifocal systemic fibrosclerosis. Respirology 12: Mehta M, Jakobiec F, Fay A (2009) Idiopathic fibroinflammatory disease of the face, eyelids, and periorbital membrane with immunoglobulin G4-positive plasma cells. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133: Leo M, Pinchera A, Marcocci C (2009) Orbital lymphoma masquerading as thyroid-associated orbitopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94: Sato Y, Ohshima K, Ichimura K, Sato M, Yamadori I, Tanaka T, Takata K, Morito T, Kondo E, Yoshino T (2008) Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uni-
6 6 Yoshihara et al. form clinicopathology. Pathol Int 58: Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Shinomura Y, Imai K (2006) A new conceptualization for Mikulicz s disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol 16: Yamada M, Li AW, Wall JR (2000) Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: clinical features, pathogenesis, and management. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 37: Murakami Y, Kanamoto T, Tuboi T, Maeda T, Inoue Y (2001) Evaluation of extraocular muscle enlargement in dysthyroid ophthalmopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 45: Mourits MP, Prummel MF, Wiersinga WM, Koornneef L (1997) Clinical activity score as a guide in the management of patients with Graves ophthalmopathy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 47: Yokoyama N, Nagataki S, Uetani M, Ashizawa K, Eguchi K (2002) Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of disease activity in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Thyroid 12: Bahn RS (2003) Clinical review 157: Pathophysiology of Graves ophthalmopathy: the cycle of disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: Starkey KJ, Janezic A, Jones G, Jordan N, Baker G, Ludgate M (2003) Adipose thyrotrophin receptor expression is elevated in Graves and thyroid eye diseases ex vivo and indicates adipogenesis in progress in vivo. J Mol Endocrinol 30: Gopinath B, Ma G, Wall JR (2007) Eye signs and serum eye muscle and collagen XIII antibodies in patients with transient and progressive thyroiditis. Thyroid 17: Gopinath B, Musselman R, Adams CL, Tani J, Beard N, Wall JR (2006) Study of serum antibodies against three eye muscle antigens and the connective tissue antigen collagen XIII in patients with Graves disease with and without ophthalmopathy: correlation with clinical features. Thyroid 16: Lahooti H, Parmar KR, Wall JR (2010) Pathogenesis of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: does autoimmunity against calsequestrin and collagen XIII play a role? Clin Ophthalmol 4: Wall JR, Lahooti H (2010) Pathogenesis of thyroid eye disease--does autoimmunity against the TSH receptor explain all cases? Endokrynol Pol 61: Miller A, Arthurs B, Boucher A, Liberman A, Bernard N, Rodien P, Salvi M, Wall JR (1992) Significance of antibodies reactive with a 64 kda eye muscle membrane antigen in patients with thyroid autoimmunity. Thyroid 2:
Original 2016, 63 (2), Ito Hospital, Tokyo, Japan 2) Olympia Eye Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
 2016, 63 (2), 151-157 Original TSH receptor antibody titers measured with a third-generation assay did not reflect the activity of Graves ophthalmopathy in untreated Japanese Graves disease patients Koji
2016, 63 (2), 151-157 Original TSH receptor antibody titers measured with a third-generation assay did not reflect the activity of Graves ophthalmopathy in untreated Japanese Graves disease patients Koji
CLINICAL ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH GRAVES ORBITOPATHY
 44 MEDICINSKI GLASNIK / str. 44-48 Biljana Nedeljković-Beleslin 1 CLINICAL ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH GRAVES ORBITOPATHY Abstract: Clinical examination is the basis of a good assessment of a patient with
44 MEDICINSKI GLASNIK / str. 44-48 Biljana Nedeljković-Beleslin 1 CLINICAL ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH GRAVES ORBITOPATHY Abstract: Clinical examination is the basis of a good assessment of a patient with
Euthyroid and primarily hypothyroid patients develop milder and significantly more asymmetrical Graves ophthalmopathy
 1 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Essen, Essen, Germany; 2 Institute for Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology University of Essen, Essen, Germany; 3 Department of Medicine, Division
1 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Essen, Essen, Germany; 2 Institute for Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology University of Essen, Essen, Germany; 3 Department of Medicine, Division
Thyroid-Stimulating Antibody in a Patient with Euthyroid Graves' Disease
 Endocrine Journal 2000, 47 (2), 197-201 NOTE Thyroid-Stimulating Antibody in a Patient with Euthyroid Graves' Disease TosHIHIDE KUBO, JURI TOKI, Yuji KADO, MAKOTO KURIHARA, TADASHI MORIWAKE*, SUSUMU KANZAKI*
Endocrine Journal 2000, 47 (2), 197-201 NOTE Thyroid-Stimulating Antibody in a Patient with Euthyroid Graves' Disease TosHIHIDE KUBO, JURI TOKI, Yuji KADO, MAKOTO KURIHARA, TADASHI MORIWAKE*, SUSUMU KANZAKI*
Six Things That Changed How I Manage Graves Disease
 Six Things That Changed How I Manage Graves Disease Anthony DeWilde, OD FAAO Kansas City VAMC 6 Things 1. Thyroid status 2. Pathogenesis 3. Ocular signs/symptoms 4. Labs 5. Smoking 6. Mental Health Graves
Six Things That Changed How I Manage Graves Disease Anthony DeWilde, OD FAAO Kansas City VAMC 6 Things 1. Thyroid status 2. Pathogenesis 3. Ocular signs/symptoms 4. Labs 5. Smoking 6. Mental Health Graves
Clinical Study The Influence of Prior Hyperthyroidism on Euthyroid Graves Ophthalmopathy
 Ophthalmology, Article ID 426898, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/426898 Clinical Study The Influence of Prior Hyperthyroidism on Euthyroid Graves Ophthalmopathy Karolien Termote, 1 Brigitte Decallonne,
Ophthalmology, Article ID 426898, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/426898 Clinical Study The Influence of Prior Hyperthyroidism on Euthyroid Graves Ophthalmopathy Karolien Termote, 1 Brigitte Decallonne,
Research Article Determinants of Extraocular Muscle Volume in Patients with Graves Disease
 Thyroid Research Volume 2012, Article ID 368536, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368536 Research Article Determinants of Extraocular Muscle Volume in Patients with Graves Disease Samer El-Kaissi 1 and Jack R.
Thyroid Research Volume 2012, Article ID 368536, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368536 Research Article Determinants of Extraocular Muscle Volume in Patients with Graves Disease Samer El-Kaissi 1 and Jack R.
Evaluation of Extraocular Muscle Enlargement in Dysthyroid Ophthalmopathy
 Evaluation of Extraocular Muscle Enlargement in Dysthyroid Ophthalmopathy Yoko Murakami*,, Takashi Kanamoto*,, Toshikazu Tuboi*,, Toshine Maeda* and Yoichi Inoue* *Olympia Eye Hospital, Tokyo, Japan; Department
Evaluation of Extraocular Muscle Enlargement in Dysthyroid Ophthalmopathy Yoko Murakami*,, Takashi Kanamoto*,, Toshikazu Tuboi*,, Toshine Maeda* and Yoichi Inoue* *Olympia Eye Hospital, Tokyo, Japan; Department
Serum Interleukin Profile in Patients with Graves Orbithopathy
 Acta Medica Marisiensis 2013;59(1):31-35 DOI: 10.2478/amma-2013-0007 RESEARCH ARTICLE Serum Interleukin Profile in Patients with Graves Orbithopathy Réti Zsuzsánna, Kun IZ, Radu Pop Corina Cristina University
Acta Medica Marisiensis 2013;59(1):31-35 DOI: 10.2478/amma-2013-0007 RESEARCH ARTICLE Serum Interleukin Profile in Patients with Graves Orbithopathy Réti Zsuzsánna, Kun IZ, Radu Pop Corina Cristina University
! Women greater than men (4:1)» Typical of other autoimmune diseases
 1 2 3 4 : Overview and Diagnosis Suzanne K. Freitag, M.D. Director, Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School! I have no financial disclosures. Learning Objectives!
1 2 3 4 : Overview and Diagnosis Suzanne K. Freitag, M.D. Director, Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School! I have no financial disclosures. Learning Objectives!
Magnetic resonance imaging determination of extraocular eye muscle volume in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy and proptosis
 ACTA OPHTHALMOLOGICA SCANDINAVICA 26 Magnetic resonance imaging determination of extraocular eye muscle volume in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy and proptosis Jan Kvetny, 1 Katriina Bøcker
ACTA OPHTHALMOLOGICA SCANDINAVICA 26 Magnetic resonance imaging determination of extraocular eye muscle volume in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy and proptosis Jan Kvetny, 1 Katriina Bøcker
This slide kit covers more complex thyroid eye disease.
 An imbalance in the normal level of thyroid hormone in the body can cause thyroid eye disease. If you wish to explore information on the basics of thyroid eye diseases, please first see: https://www.excemed.org/manage-thyroid-online/resources/thyroid-eyedisease
An imbalance in the normal level of thyroid hormone in the body can cause thyroid eye disease. If you wish to explore information on the basics of thyroid eye diseases, please first see: https://www.excemed.org/manage-thyroid-online/resources/thyroid-eyedisease
idiopathic orbital inflammation.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of compressive optic neuropa idiopathic orbital inflammation. Haraguchi, Ai; Ando, Takao; Ueki, I Usa, Toshiro; Yamasaki, Satoshi; Or Acta
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of compressive optic neuropa idiopathic orbital inflammation. Haraguchi, Ai; Ando, Takao; Ueki, I Usa, Toshiro; Yamasaki, Satoshi; Or Acta
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Risk Factors Associated with the Severity of Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy in Korean Patients
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2010;24(5):267-273 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.5.267 Risk Factors Associated with the Severity of Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy in Korean Patients Original
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2010;24(5):267-273 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.5.267 Risk Factors Associated with the Severity of Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy in Korean Patients Original
Eye findings and immunological markers in probands and their euthyroid relatives from a single family with multiple cases of thyroid autoimmunity
 Ardley et al. Thyroid Research 2012, 5:4 RESEARCH Eye findings and immunological markers in probands and their euthyroid relatives from a single family with multiple cases of thyroid autoimmunity Melissa
Ardley et al. Thyroid Research 2012, 5:4 RESEARCH Eye findings and immunological markers in probands and their euthyroid relatives from a single family with multiple cases of thyroid autoimmunity Melissa
and primarily hypothyroid patients develop milder and significantly more asymmetric Graves ophthalmopathy.
 Euthyroid and primarily hypothyroid patients develop milder and significantly more asymmetric Graves ophthalmopathy Anja Eckstein, Christian Loesch, Diana Glowacka, Matthias Schott, Klaus Mann, Joachim
Euthyroid and primarily hypothyroid patients develop milder and significantly more asymmetric Graves ophthalmopathy Anja Eckstein, Christian Loesch, Diana Glowacka, Matthias Schott, Klaus Mann, Joachim
What was going on. Thyroid Related Orbitopathy. Pathophysiology. Definition GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY 3/16/2017
 GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY What was going on A. She found out the increase to her Premium and Deductible for employee health care next year B. She is getting an over agressive Physical Exam by
GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY What was going on A. She found out the increase to her Premium and Deductible for employee health care next year B. She is getting an over agressive Physical Exam by
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
 C A S E REPORT pissn: 2384-3799 eissn: 2466-1899 Int J Thyroidol 2017 November 10(2): 102-106 https://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2017.10.2.102 Development of Graves Ophthalmopathy after Radioactive Iodine Ablation
C A S E REPORT pissn: 2384-3799 eissn: 2466-1899 Int J Thyroidol 2017 November 10(2): 102-106 https://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2017.10.2.102 Development of Graves Ophthalmopathy after Radioactive Iodine Ablation
James A. Garrity MD Department of Ophthalmology. Marius N. Stan MD Division of Endocrinology. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 James A. Garrity MD Department of Ophthalmology Marius N. Stan MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Epidemiologic and diagnostic considerations for Graves orbitopathy (GO) 1. How common?
James A. Garrity MD Department of Ophthalmology Marius N. Stan MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Epidemiologic and diagnostic considerations for Graves orbitopathy (GO) 1. How common?
Orbital and Ocular Adnexal Disorders with Red Eyes
 Orbital and Ocular Adnexal Disorders with Red Eyes Jason Lee Associate Consultant Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Practical Ophthalmology for the Family Physician 21 Jan 2017 No financial
Orbital and Ocular Adnexal Disorders with Red Eyes Jason Lee Associate Consultant Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Practical Ophthalmology for the Family Physician 21 Jan 2017 No financial
Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THYROID-STIMULATING IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS AND OCULAR FINDINGS IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH GRAVES DISEASE
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THYROID-STIMULATING IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS AND OCULAR FINDINGS IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH GRAVES DISEASE BY Olga M. Acuna MD, Ioanna Athannassaki MD, AND Evelyn A. Paysse MD * ABSTRACT
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THYROID-STIMULATING IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS AND OCULAR FINDINGS IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH GRAVES DISEASE BY Olga M. Acuna MD, Ioanna Athannassaki MD, AND Evelyn A. Paysse MD * ABSTRACT
Grave s orbitopathy an approach to clinical evaluation and management
 Grave s orbitopathy an approach to clinical evaluation and management T W N Karunasena 1, M W S Niranjala 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism 2012; 2: 106-110 Abstract Grave s
Grave s orbitopathy an approach to clinical evaluation and management T W N Karunasena 1, M W S Niranjala 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism 2012; 2: 106-110 Abstract Grave s
Graves Ophthalmopathy: The Role of Thyroid Cross Reacting Autoantigens and The Effect of Thyroid Ablation
 Int J Endocrinol Metab 2006; 4: 47-51 Graves Ophthalmopathy: The Role of Thyroid Cross Reacting Autoantigens and The Effect of Thyroid Ablation Latrofa F, Marino M, Marcocci C, Pinchera A. Department of
Int J Endocrinol Metab 2006; 4: 47-51 Graves Ophthalmopathy: The Role of Thyroid Cross Reacting Autoantigens and The Effect of Thyroid Ablation Latrofa F, Marino M, Marcocci C, Pinchera A. Department of
Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview. Graves Disease Hyperthyroidism TSIgs (anti-tsh-receptor-abs) Graves Disease 10/22/2010
 Graves Disease Robert Graves Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview Robert C. Kersten Dept. of Ophthalmology UCSF Triad Hyperthyroidism Eye findings Pretibial Myxedema (phalangeal acropachy-1%) Most common auto-immune
Graves Disease Robert Graves Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview Robert C. Kersten Dept. of Ophthalmology UCSF Triad Hyperthyroidism Eye findings Pretibial Myxedema (phalangeal acropachy-1%) Most common auto-immune
T he pathogenic mechanism of thyroid associated orbitopathy
 724 EXTENDED REPORT Quantification of cells expressing the thyrotropin receptor in extraocular muscles in thyroid associated orbitopathy A Boschi, Ch Daumerie, M Spiritus, C Beguin, M Senou, D Yuksel,
724 EXTENDED REPORT Quantification of cells expressing the thyrotropin receptor in extraocular muscles in thyroid associated orbitopathy A Boschi, Ch Daumerie, M Spiritus, C Beguin, M Senou, D Yuksel,
Exophthalmos in a young woman with no Graves disease a case report of IgG4- related orbitopathy
 Erdei et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:5 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0672-y CASE REPORT Open Access Exophthalmos in a young woman with no Graves disease a case report of IgG4- related orbitopathy Annamaria
Erdei et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:5 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0672-y CASE REPORT Open Access Exophthalmos in a young woman with no Graves disease a case report of IgG4- related orbitopathy Annamaria
IgG4-related Ocular Adnexal Disease Mimicking Thyroid-associated Orbitopathy
 CASE REPORT IgG4-related Ocular Adnexal Disease Mimicking Thyroid-associated Orbitopathy Hidefumi Inaba 1, Takahiro Hayakawa 1, Waka Miyamoto 1,KenTakeshima 1, Hiroyuki Yamaoka 1, Yasushi Furukawa 1, Hiromichi
CASE REPORT IgG4-related Ocular Adnexal Disease Mimicking Thyroid-associated Orbitopathy Hidefumi Inaba 1, Takahiro Hayakawa 1, Waka Miyamoto 1,KenTakeshima 1, Hiroyuki Yamaoka 1, Yasushi Furukawa 1, Hiromichi
of Graves' Disease Associated with Painful itis
 Endocrine Journal 1997, 44 (4), 611-616 NOTE A Case Thyroid of Graves' Disease Associated with Painful itis SHIGENORI NAKAMURA, YUKIE SAIO, AND MASATOSHI ISHIMORI Department of Internal Medicine, Gifu
Endocrine Journal 1997, 44 (4), 611-616 NOTE A Case Thyroid of Graves' Disease Associated with Painful itis SHIGENORI NAKAMURA, YUKIE SAIO, AND MASATOSHI ISHIMORI Department of Internal Medicine, Gifu
Prevalence of Graves ophthalmopathy in patients with Graves disease presenting to a referral centre in north India
 Indian J Med Res 139, January 2014, pp 99-104 Prevalence of Graves ophthalmopathy in patients with Graves disease presenting to a referral centre in north India Sagili Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy, Anu Jain *,
Indian J Med Res 139, January 2014, pp 99-104 Prevalence of Graves ophthalmopathy in patients with Graves disease presenting to a referral centre in north India Sagili Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy, Anu Jain *,
Extraocular muscle repositioning as the last therapeutic option for a patient with a severe course of Graves Ophthalmopathy: a case report
 Rau et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0718-1 CASE REPORT Open Access Extraocular muscle repositioning as the last therapeutic option for a patient with a severe course
Rau et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0718-1 CASE REPORT Open Access Extraocular muscle repositioning as the last therapeutic option for a patient with a severe course
Grave s disease (1 0 )
 THYROID DYSFUNCTION Grave s disease (1 0 ) Autoimmune - activating AB s to TSH receptor High concentrations of circulating thyroid hormones Weight loss, tachycardia, tiredness Diffuse goitre - TSH stimulating
THYROID DYSFUNCTION Grave s disease (1 0 ) Autoimmune - activating AB s to TSH receptor High concentrations of circulating thyroid hormones Weight loss, tachycardia, tiredness Diffuse goitre - TSH stimulating
Orbital facia. Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia
 Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
SUMMARY OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS COMPARING DIFFERENT ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY REGIMENTS AND ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY TO PLACEBO OR CORTICOSTEROIDS
 TABLE e4. SUMMARY OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS COMPARING DIFFERENT ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY REGIMENTS AND ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY TO PLACEBO OR CORTICOSTEROIDS Study Treatment Groups Primary Outcome Measure
TABLE e4. SUMMARY OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS COMPARING DIFFERENT ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY REGIMENTS AND ORBITAL RADIOTHERAPY TO PLACEBO OR CORTICOSTEROIDS Study Treatment Groups Primary Outcome Measure
Graves orbitopathy (GO), the main extrathyroidal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Prevalence and Natural History of Graves Orbitopathy in a Large Series of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Graves Hyperthyroidism Seen at a Single Center M. L. Tanda, E. Piantanida,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Prevalence and Natural History of Graves Orbitopathy in a Large Series of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Graves Hyperthyroidism Seen at a Single Center M. L. Tanda, E. Piantanida,
NOTE. Endocrinol. Japon. 1982, 29 (4), Abstract
 Endocrinol. Japon. 1982, 29 (4), 495-501 NOTE Treatment of Graves' Ophthalmopathy by Steroid Therapy, Orbital Radiation Therapy, Plasmapheresis and Thyroxine Replacement KUNIHIRO YAMAMOTO, KOSHI SAITO,
Endocrinol. Japon. 1982, 29 (4), 495-501 NOTE Treatment of Graves' Ophthalmopathy by Steroid Therapy, Orbital Radiation Therapy, Plasmapheresis and Thyroxine Replacement KUNIHIRO YAMAMOTO, KOSHI SAITO,
Validation of VISA classification for Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy
 25 Original Article Validation of VISA classification for Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy Dr M. Subrahmanyam 1, Dr P. Modini 2, Dr K.J. Sivacharan 3, Dr B. Kavya 4 Abstract Aim : To Validate the VISA classification
25 Original Article Validation of VISA classification for Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy Dr M. Subrahmanyam 1, Dr P. Modini 2, Dr K.J. Sivacharan 3, Dr B. Kavya 4 Abstract Aim : To Validate the VISA classification
Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy (TAO): Effects of Medical And Surgical Treatments
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2017), PP 33-38 www.iosrjournals.org Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy (TAO):
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2017), PP 33-38 www.iosrjournals.org Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy (TAO):
Graves Ophthalmopathy Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment CONSTANCE L. FRY, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF OPHTHALMOLOGY UT HEALTH SAN ANTONIO
 Graves Ophthalmopathy Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment CONSTANCE L. FRY, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF OPHTHALMOLOGY UT HEALTH SAN ANTONIO Ophthalmic Manifestations GO is the #1 cause of unilateral and
Graves Ophthalmopathy Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment CONSTANCE L. FRY, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF OPHTHALMOLOGY UT HEALTH SAN ANTONIO Ophthalmic Manifestations GO is the #1 cause of unilateral and
Results of Transmedial-Canthal Ethmoidal Decompression for Severe Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy
 Results of Transmedial-Canthal Ethmoidal Decompression for Severe Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy Kenji Ohtsuka and Yasushi Nakamura Department of Ophthalmology, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine,
Results of Transmedial-Canthal Ethmoidal Decompression for Severe Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy Kenji Ohtsuka and Yasushi Nakamura Department of Ophthalmology, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine,
Research Article The Influence of Juvenile Graves Ophthalmopathy on Graves Disease Course
 Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 4853905, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4853905 Research Article The Influence of Juvenile Graves Ophthalmopathy on Graves Disease Course Jurate Jankauskiene
Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 4853905, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4853905 Research Article The Influence of Juvenile Graves Ophthalmopathy on Graves Disease Course Jurate Jankauskiene
Prevalence and Severity of Ophthalmic Manifestations of Graves Disease in Mashhad. University Endocrine Clinics
 Prevalence and Severity of Ophthalmic Manifestations of Graves Disease in Mashhad University Endocrine Clinics Mohammad Etezad-Razavi, MD, 1 Robabeh-Beygom Aboutorabi, MD 2 Siamak Zarei-Ghanavati, MD,
Prevalence and Severity of Ophthalmic Manifestations of Graves Disease in Mashhad University Endocrine Clinics Mohammad Etezad-Razavi, MD, 1 Robabeh-Beygom Aboutorabi, MD 2 Siamak Zarei-Ghanavati, MD,
MASATERU HORIMOTO, MITSUSHIGE NISHIKAWA, CHISATO UNO, NoRIO YOSHIKAWA, NORIMICHI TANIGUCHI AND MITSUO INADA
 Relationship among Thyrotropin (TSH), Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulins, and Results of Triiodothyronine (T3) Suppression Test in Patients with Graves' Disease MASATERU HORIMOTO, MITSUSHIGE NISHIKAWA,
Relationship among Thyrotropin (TSH), Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulins, and Results of Triiodothyronine (T3) Suppression Test in Patients with Graves' Disease MASATERU HORIMOTO, MITSUSHIGE NISHIKAWA,
Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
Graves' disease (GD) is the most common cause
 Thyroid peroxidase antibody positivity and triiodothyronine levels are associated with pediatric Graves' ophthalmopathy Jung Hyun Lee, So Hyun Park, Dae Gyun Koh, Byung Kyu Suh Gyeonggi-do, Korea Background:
Thyroid peroxidase antibody positivity and triiodothyronine levels are associated with pediatric Graves' ophthalmopathy Jung Hyun Lee, So Hyun Park, Dae Gyun Koh, Byung Kyu Suh Gyeonggi-do, Korea Background:
Association of the Ultrasonographic Findings of Subacute Thyroiditis with Thyroid Pain and Laboratory Findings
 Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (3), 583 588 Association of the Ultrasonographic Findings of Subacute Thyroiditis with Thyroid Pain and Laboratory Findings NARIKO OMORI, KAZUE OMORI AND KAZUE TAKANO Department
Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (3), 583 588 Association of the Ultrasonographic Findings of Subacute Thyroiditis with Thyroid Pain and Laboratory Findings NARIKO OMORI, KAZUE OMORI AND KAZUE TAKANO Department
The treatment of thyroid-associated. High dose intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy versus oral prednisone for thyroidassociated
 High dose intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy versus oral prednisone for thyroidassociated ophthalmopathy Ritva Kauppinen-Mäkelin 1, Anni Karma 2, Eeva Leinonen 1, Eliisa Löyttyniemi 3, Oili Salonen
High dose intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy versus oral prednisone for thyroidassociated ophthalmopathy Ritva Kauppinen-Mäkelin 1, Anni Karma 2, Eeva Leinonen 1, Eliisa Löyttyniemi 3, Oili Salonen
Clinical Study Assessment of Visual Acuity, Refraction Changes, and Proptosis in Different Ages of Patients with Thyroid Diseases
 International Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 643275, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/643275 Clinical Study Assessment of Visual Acuity, Refraction Changes, and Proptosis in Different Ages of Patients with
International Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 643275, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/643275 Clinical Study Assessment of Visual Acuity, Refraction Changes, and Proptosis in Different Ages of Patients with
Efficacy and safety of combined parenteral and oral steroid therapy in Graves orbitopathy
 HORMONES 2014, 13(2):222-228 Research paper Efficacy and safety of combined parenteral and oral steroid therapy in Graves orbitopathy Biljana Nedeljkovic Beleslin, 1,2 Jasmina Ciric, 1,2 Milos Zarkovic,
HORMONES 2014, 13(2):222-228 Research paper Efficacy and safety of combined parenteral and oral steroid therapy in Graves orbitopathy Biljana Nedeljkovic Beleslin, 1,2 Jasmina Ciric, 1,2 Milos Zarkovic,
Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular Glands and Extraocular Muscles
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Features of Patients with Basedow s Disease and High Serum IgG4 Levels Keiichi Torimoto, Yosuke Okada, Akira Kurozumi, Manabu Narisawa, Tadashi Arao and Yoshiya Tanaka Abstract
Slide notes: This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications,
 1 This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications, including ophthalmic complications, treatments (both permanent solutions
1 This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications, including ophthalmic complications, treatments (both permanent solutions
Original. Advance Publication doi: /endocrj. EJ Endocrine Journal 2015
 Endocrine Journal 2015 Original Advance Publication doi: 10.1507/endocrj. EJ15-0157 Distribution of serum immunoglobulin G4 levels in Hashimoto s thyroiditis and clinical features of Hashimoto s thyroiditis
Endocrine Journal 2015 Original Advance Publication doi: 10.1507/endocrj. EJ15-0157 Distribution of serum immunoglobulin G4 levels in Hashimoto s thyroiditis and clinical features of Hashimoto s thyroiditis
Thyroid Function. Thyroid Antibodies. Analyte Information
 Thyroid Function Thyroid Antibodies Analyte Information - 1-2013-04-30 Thyroid Antibodies Determination of thyroid autoantibodies are, besides TSH and FT4, one of the most important diagnostic parameters.
Thyroid Function Thyroid Antibodies Analyte Information - 1-2013-04-30 Thyroid Antibodies Determination of thyroid autoantibodies are, besides TSH and FT4, one of the most important diagnostic parameters.
Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients C.A. Tiegs-Heiden, L.J. Eckel, C.H. Hunt, F.E. Diehn, K.M. Schwartz, D.F. Kallmes, D.R. Salomão,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients C.A. Tiegs-Heiden, L.J. Eckel, C.H. Hunt, F.E. Diehn, K.M. Schwartz, D.F. Kallmes, D.R. Salomão,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Volumetric measurements in Graves orbitopathy Regensburg, N.I. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Volumetric measurements in Graves orbitopathy Regensburg, N.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Regensburg, N. I. (2010). Volumetric measurements
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Volumetric measurements in Graves orbitopathy Regensburg, N.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Regensburg, N. I. (2010). Volumetric measurements
Thyrotropin-producing pituitary adenoma simultaneously existing with Graves disease: a case report
 Arai et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:9 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-1172-4 CASE REPORT Thyrotropin-producing pituitary adenoma simultaneously existing with Graves disease: a case report Nobuhiko
Arai et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:9 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-1172-4 CASE REPORT Thyrotropin-producing pituitary adenoma simultaneously existing with Graves disease: a case report Nobuhiko
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Clinical activity score as a guide in the management of patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy Mourits, M.P.; Prummel, M.F.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Koornneef, L. Published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Clinical activity score as a guide in the management of patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy Mourits, M.P.; Prummel, M.F.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Koornneef, L. Published
Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
THE STIR SEQUENCE MRI IN THE ASSESSMENT OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES IN THYROID EYE DISEASE
 THE STR SEQUENCE MR N THE ASSESSMENT OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES N THYROD EYE DSEASE H. B. HOH! R. D. LATT 2 C. WAKELEy2 J. KABALA2 P. GODDARD 2 M. J. POTTS! and R. A. HARRAD! Bristol SUMMARY Nineteen patients
THE STR SEQUENCE MR N THE ASSESSMENT OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES N THYROD EYE DSEASE H. B. HOH! R. D. LATT 2 C. WAKELEy2 J. KABALA2 P. GODDARD 2 M. J. POTTS! and R. A. HARRAD! Bristol SUMMARY Nineteen patients
Chapter I.A.1: Thyroid Evaluation Laboratory Testing
 Chapter I.A.1: Thyroid Evaluation Laboratory Testing Jennifer L. Poehls, MD and Rebecca S. Sippel, MD, FACS THYROID FUNCTION TESTS Overview Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is produced by the anterior
Chapter I.A.1: Thyroid Evaluation Laboratory Testing Jennifer L. Poehls, MD and Rebecca S. Sippel, MD, FACS THYROID FUNCTION TESTS Overview Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is produced by the anterior
Graves ophthalmopathy: a preventable disease?
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 146 457 461 ISSN 0804-4643 MINI REVIEW Graves ophthalmopathy: a preventable disease? Luigi Bartalena, Claudio Marcocci 1 and Aldo Pinchera 1 Cattedra di Endocrinologia,
European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 146 457 461 ISSN 0804-4643 MINI REVIEW Graves ophthalmopathy: a preventable disease? Luigi Bartalena, Claudio Marcocci 1 and Aldo Pinchera 1 Cattedra di Endocrinologia,
Setting: The study was conducted at the University Hospital Thyroid-Eye Clinic.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Double Vision Is a Major Manifestation in Moderate to Severe Graves Orbitopathy, but It Correlates Negatively With Inflammatory Signs and Proptosis Peter Laurberg, Dalia C. Berman, Inge
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Double Vision Is a Major Manifestation in Moderate to Severe Graves Orbitopathy, but It Correlates Negatively With Inflammatory Signs and Proptosis Peter Laurberg, Dalia C. Berman, Inge
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci
 CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
Thyroid Stimulating Antibodies Are Highly Prevalent in Hashimoto s Thyroiditis and Associated Orbitopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid Stimulating Antibodies Are Highly Prevalent in Hashimoto s Thyroiditis and Associated Orbitopathy George J. Kahaly,* Tanja Diana,* Jennifer Glang, Michael Kanitz, Susanne Pitz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid Stimulating Antibodies Are Highly Prevalent in Hashimoto s Thyroiditis and Associated Orbitopathy George J. Kahaly,* Tanja Diana,* Jennifer Glang, Michael Kanitz, Susanne Pitz,
A utoimmune thyroid diseases are the most common
 378 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analytical and diagnostic accuracy of second generation assays for thyrotrophin receptor antibodies with radioactive and chemiluminescent tracers D Villalta, E Orunesu, R Tozzoli,
378 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analytical and diagnostic accuracy of second generation assays for thyrotrophin receptor antibodies with radioactive and chemiluminescent tracers D Villalta, E Orunesu, R Tozzoli,
Analysis of Lag Behind Thyrotropin State After Radioiodine Therapy in Hyperthyroid Patients
 Analysis of Lag Behind Thyrotropin State After Radioiodine Therapy in Hyperthyroid Patients ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mohshi Um Mokaddema, Fatima Begum, Simoon Salekin, Tanzina Naushin, Sharmin Quddus, Nabeel Fahmi
Analysis of Lag Behind Thyrotropin State After Radioiodine Therapy in Hyperthyroid Patients ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mohshi Um Mokaddema, Fatima Begum, Simoon Salekin, Tanzina Naushin, Sharmin Quddus, Nabeel Fahmi
What s New in Thyroid Eye Disease? James A. Garrity MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 What s New in Thyroid Eye Disease? James A. Garrity MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN What s New in Thyroid Eye Disease? Diagnosis - TRAb/TSI: diagnosis/prognosis - IgG4: diagnostic confusion Therapy - Surgery:
What s New in Thyroid Eye Disease? James A. Garrity MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN What s New in Thyroid Eye Disease? Diagnosis - TRAb/TSI: diagnosis/prognosis - IgG4: diagnostic confusion Therapy - Surgery:
CALCULATION OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLE VOLUME IN PATIENTS WITH GRAVES OPHTHALMOPATHY AND THE CORRELATION WITH DISEASE SEVERITY AND CLINICAL
 CALCULATION OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLE VOLUME IN PATIENTS WITH GRAVES OPHTHALMOPATHY AND THE CORRELATION WITH DISEASE SEVERITY AND CLINICAL ACTIVITY OF THE GRAVES DISEASE REBECCA RUTH STACK A THESIS SUBMITTED
CALCULATION OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLE VOLUME IN PATIENTS WITH GRAVES OPHTHALMOPATHY AND THE CORRELATION WITH DISEASE SEVERITY AND CLINICAL ACTIVITY OF THE GRAVES DISEASE REBECCA RUTH STACK A THESIS SUBMITTED
Disclosures. Learning objectives. Case 1A. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues. I have nothing to disclose.
 Disclosures Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues I have nothing to disclose. Chrysoula Dosiou, MD, MS Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Endocrinology Stanford University School
Disclosures Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues I have nothing to disclose. Chrysoula Dosiou, MD, MS Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Endocrinology Stanford University School
Changes in pediatric thyroid sonograms in or nearby the Kanto region before and after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant
 Endocrine Journal 2014, 61 (9), 875-881 Original Changes in pediatric thyroid sonograms in or nearby the Kanto region before and after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant Kenji Iwaku,
Endocrine Journal 2014, 61 (9), 875-881 Original Changes in pediatric thyroid sonograms in or nearby the Kanto region before and after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant Kenji Iwaku,
Clinical Study Methotrexate for the Treatment of Thyroid Eye Disease
 Ophthalmology, Article ID 128903, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/128903 Clinical Study Methotrexate for the Treatment of Thyroid Eye Disease Diego Strianese, 1 Adriana Iuliano, 1 Mariantonia Ferrara,
Ophthalmology, Article ID 128903, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/128903 Clinical Study Methotrexate for the Treatment of Thyroid Eye Disease Diego Strianese, 1 Adriana Iuliano, 1 Mariantonia Ferrara,
Non-specific Activities against Ruthenium Crosslinker as a New Cause of Assay Interference in an Electrochemilluminescent
 CASE REPORT Non-specific Activities against Ruthenium Crosslinker as a New Cause of Assay Interference in an Electrochemilluminescent Immunoassay Takao Ando 1, Jun-ichi Yasui 1, Naoko Inokuchi 2, Toshiro
CASE REPORT Non-specific Activities against Ruthenium Crosslinker as a New Cause of Assay Interference in an Electrochemilluminescent Immunoassay Takao Ando 1, Jun-ichi Yasui 1, Naoko Inokuchi 2, Toshiro
Azienda Ospedaliera-Universitaria Mater Domini, Catanzaro, Italy
 Article 1 Subclinical Visual Field Alterations are Commonly Present in Patients with Graves Orbitopathy and are Mainly Related to the Clinical Activity of the Disease Authors A. F. L a bo nia 1, G. C.
Article 1 Subclinical Visual Field Alterations are Commonly Present in Patients with Graves Orbitopathy and are Mainly Related to the Clinical Activity of the Disease Authors A. F. L a bo nia 1, G. C.
10 Congresso Nazionale Associazione Italiana della Tiroide Cagliari, dicembre 2016 Orbitopa)a basedowiana acuta
 10 Congresso Nazionale Associazione Italiana della Tiroide Cagliari, 15-17 dicembre 2016 Orbitopa)a basedowiana acuta Luigi Bartalena Università dell Insubria a Varese Prevalence of Graves orbitopathy
10 Congresso Nazionale Associazione Italiana della Tiroide Cagliari, 15-17 dicembre 2016 Orbitopa)a basedowiana acuta Luigi Bartalena Università dell Insubria a Varese Prevalence of Graves orbitopathy
Thyroid Disease and Thyroid Eye Disease
 Disclosures Disclosure Statement (next slide) Thyroid Dysfunction and the Eye Greg Caldwell OD, FAAO The Denver Metro Optometric Society Russell Pavilion at St. Joseph Hospital Denver, CO January 25, 2014
Disclosures Disclosure Statement (next slide) Thyroid Dysfunction and the Eye Greg Caldwell OD, FAAO The Denver Metro Optometric Society Russell Pavilion at St. Joseph Hospital Denver, CO January 25, 2014
CLINICAL REVIEW. Thyroid eye disease. Petros Perros, 1 Christopher Neoh, 2 Jane Dickinson 2. For the full versions of these articles see bmj.
 For the full versions of these articles see bmj.com CLINICAL REVIEW Thyroid eye disease Petros Perros, 1 Christopher Neoh, 2 Jane Dickinson 2 1 Department of Endocrinology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle
For the full versions of these articles see bmj.com CLINICAL REVIEW Thyroid eye disease Petros Perros, 1 Christopher Neoh, 2 Jane Dickinson 2 1 Department of Endocrinology, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle
Diagnostic Imaging in Patients with Orbital Cellulitis and Inflammatory Pseudotumor. Fumiyuki Uehara, M.D. Norio Ohba, M.D.
 Diagnostic Imaging in Patients with Orbital Cellulitis and Inflammatory Pseudotumor Fumiyuki Uehara, M.D. Norio Ohba, M.D. We have had the opportunity, at an eye clinic, to examine and treat a patient
Diagnostic Imaging in Patients with Orbital Cellulitis and Inflammatory Pseudotumor Fumiyuki Uehara, M.D. Norio Ohba, M.D. We have had the opportunity, at an eye clinic, to examine and treat a patient
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment. April Janet A. Schlechte, M.D.
 Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment Family Practice Refresher Course April 2015 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships with any
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment Family Practice Refresher Course April 2015 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships with any
Graves Disease. What is Graves disease?
 Graves Disease What is Graves disease? The thyroid gland s production of thyroid hormones (T 3 and T 4 ) is triggered by thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), which is made by the pituitary gland. Graves disease,
Graves Disease What is Graves disease? The thyroid gland s production of thyroid hormones (T 3 and T 4 ) is triggered by thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), which is made by the pituitary gland. Graves disease,
A Clinical Study on Patients Presenting with Thyroid Swelling and Its Correlation with TFT, USG, FNAC and Anti TPO Antibodies
 A Clinical Study on Patients Presenting with Thyroid Swelling and Its Correlation with TFT, USG, FNAC and Anti TPO Antibodies 1* Hanushraj. R, 2 Sudharsan.S, 3 Balasubramaniyan. S, 4 Pradeep Kumar. M 1,4,
A Clinical Study on Patients Presenting with Thyroid Swelling and Its Correlation with TFT, USG, FNAC and Anti TPO Antibodies 1* Hanushraj. R, 2 Sudharsan.S, 3 Balasubramaniyan. S, 4 Pradeep Kumar. M 1,4,
Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Elevated serum concentrations of metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and their inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in patients with Graves orbitopathy
 Original papers Elevated serum concentratio of metalloproteinases (MMP-2, ) and their inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in patients with Graves orbitopathy Katarzyna Kapelko-Słowik 1, A F, Mirosław Słowik 2,
Original papers Elevated serum concentratio of metalloproteinases (MMP-2, ) and their inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in patients with Graves orbitopathy Katarzyna Kapelko-Słowik 1, A F, Mirosław Słowik 2,
The Change of Lacrimal Gland Volume in Korean Patients with Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2016;30(5):319-325 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.319 Original Article The Change of Lacrimal Gland Volume in Korean Patients with Thyroid-associated
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2016;30(5):319-325 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.319 Original Article The Change of Lacrimal Gland Volume in Korean Patients with Thyroid-associated
Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders
 Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders free T4 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders The total T4 may be elevated in pregnancy and with OCP use Graves I 123
Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders free T4 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders The total T4 may be elevated in pregnancy and with OCP use Graves I 123
PTOSIS AS AN INITIAL MANIFESTATION OF ORBITAL LYMPHOMA: A CASE REPORT
 M.W. Hsu, C.H. Chung, C.H. Chang, et al PTOSIS AS AN INITIAL MANIFESTATION OF ORBITAL LYMPHOMA: A CASE REPORT Min-Wen Hsu, Chia-Hung Chung, Cheng-Hsien Chang, Pei-Shin Hu, and Shiuh-Liang Hsu Department
M.W. Hsu, C.H. Chung, C.H. Chang, et al PTOSIS AS AN INITIAL MANIFESTATION OF ORBITAL LYMPHOMA: A CASE REPORT Min-Wen Hsu, Chia-Hung Chung, Cheng-Hsien Chang, Pei-Shin Hu, and Shiuh-Liang Hsu Department
Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease
 International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
Lecture title. Name Family name Country
 Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
The gold standard in Graves disease diagnosis. Thermo Scientific B R A H M S TRAK human Immunodiagnostic Assays
 Thermo Scientific B R A H M S TRAK human Immunodiagnostic Assays The gold standard in Graves disease diagnosis Is it really Graves disease? Will my patient relapse? Which course of Graves ophthalmopathy
Thermo Scientific B R A H M S TRAK human Immunodiagnostic Assays The gold standard in Graves disease diagnosis Is it really Graves disease? Will my patient relapse? Which course of Graves ophthalmopathy
Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study Grigoris Effraimidis,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study Grigoris Effraimidis,
Protocol. This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work.
 Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Marcocci C, Kahaly GJ, Krassas GE, et al. Selenium and the course of
Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Marcocci C, Kahaly GJ, Krassas GE, et al. Selenium and the course of
Wiersinga WM, Kahaly GJ (eds): Graves Orbitopathy: A Multidisciplinary Approach Questions and Answers. Basel, Karger, 2010, pp 33 39
 Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Wiersinga WM, Kahaly GJ (eds): Graves Orbitopathy: A Multidisciplinary Approach Questions and Answers. Basel, Karger, 2010, pp 33 39 Epidemiology C. Daumerie Department of Endocrinology,
Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Wiersinga WM, Kahaly GJ (eds): Graves Orbitopathy: A Multidisciplinary Approach Questions and Answers. Basel, Karger, 2010, pp 33 39 Epidemiology C. Daumerie Department of Endocrinology,
Case S.L. PMHx. Warning: Side-Effects May Include Upset-Stomach and Psychosis 7/12/12. ! CC: Upper and lower eyelids swollen
 Warning: Side-Effects May Include Upset-Stomach and Psychosis Daniel R. Lefebvre, M.D. Case Presentation Case S.L.! CC: Upper and lower eyelids swollen! HPI: 51 y/o female! eye swelling left > right X
Warning: Side-Effects May Include Upset-Stomach and Psychosis Daniel R. Lefebvre, M.D. Case Presentation Case S.L.! CC: Upper and lower eyelids swollen! HPI: 51 y/o female! eye swelling left > right X
7/12/12. Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome. What s in a title? Why orbital pseudotumor is no longer a useful concept. orbital pseudotumor
 Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome Daniel R. Lefebvre, MD Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery What s in a title? orbital pseudotumor Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease Non-
Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome Daniel R. Lefebvre, MD Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery What s in a title? orbital pseudotumor Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease Non-
Thyroid orbitopathy. Thyroid orbitopathy (TO) is an organ. CLINICAL PRACTICE: Therapeutic review
 CLINICAL PRACTICE: Therapeutic review Thyroid orbitopathy Shirley Fung, MBBS, is a research resident, Oculoplastic and Orbital Unit, Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Adelaide Hospital, University of
CLINICAL PRACTICE: Therapeutic review Thyroid orbitopathy Shirley Fung, MBBS, is a research resident, Oculoplastic and Orbital Unit, Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Adelaide Hospital, University of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. CM Ng HKL Yuen KL Choi MK Chan KT Yuen YW Ng SC Tiu
 Key words: Eye diseases; Graves disease; Orbit/radiation effects; Steroids; Treatment outcome "#$% =L=" CM Ng HKL Yuen KL Choi MK Chan KT Yuen YW Ng SC Tiu Hong Kong Med J 2005;11:322-30 Queen Elizabeth
Key words: Eye diseases; Graves disease; Orbit/radiation effects; Steroids; Treatment outcome "#$% =L=" CM Ng HKL Yuen KL Choi MK Chan KT Yuen YW Ng SC Tiu Hong Kong Med J 2005;11:322-30 Queen Elizabeth
THYROID EYE DISEASE. A General Overview
 JAMES R. PATRINELY, MD, FACS CHARLES N.S. SOPARKAR, MD, PHD, FACS 3730 KIRBY DRIVE, SUITE 900, HOUSTON, TX 77098 TELEPHONE (713) 795-0705 FAX (713) 807-0630 THYROID EYE DISEASE A General Overview INTRODUCTION,
JAMES R. PATRINELY, MD, FACS CHARLES N.S. SOPARKAR, MD, PHD, FACS 3730 KIRBY DRIVE, SUITE 900, HOUSTON, TX 77098 TELEPHONE (713) 795-0705 FAX (713) 807-0630 THYROID EYE DISEASE A General Overview INTRODUCTION,
LABORATORY TESTS FOR EVALUATION OF THYROID DISORDERS
 LABORATORY TESTS FOR EVALUATION OF THYROID DISORDERS Maryam Tohidi Anatomical & clinical pathologist Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences THYROID GLAND (15-25 gr), (12-20 gr), 2 lobes connected by
LABORATORY TESTS FOR EVALUATION OF THYROID DISORDERS Maryam Tohidi Anatomical & clinical pathologist Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences THYROID GLAND (15-25 gr), (12-20 gr), 2 lobes connected by
