21 Endocrine organs and cells
|
|
|
- Frederick Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should be able to: Explain the difference between exocrine and endocrine organs and cells. Explain the organisation of the endocrine system, organs, and diffuse endocrine cells. Explain the characteristics of the endocrine organs and diffuse endocrine cells. Explain the blood supply to each gland. Recognise endocrine organs, and regions and cells within each endocrine organ. Slides Slide name Slide number Stain Main Pituitary gland 52 H/E Thyroid gland 55 H/E Parathyroid gland 54 H/E Adrenal gland 56 H/E Pancreas 50 H/E Other Kidney 76 Ovary 89 and 106 H/E Corpus luteum 91 H/E Testis 84 H/E Pineal gland 34 H/E Thymus 62 H/E Digestive glands & cells Various Heart 77,20,86 & 47 H/E & Y/H Adipose tissue Various
2 Tasks 1. Complete a topic sheet for all the slides listed above; the five primary endocrine organs as well as secondary organs and cells. You can use the prepared topic sheets, or create your own using the provided templates. The headings in the two alternatives are described below. Select one of the two alternatives. Topic sheets can be done in conjunction with specific slide related tasks as presented in the Objectives and Tasks document. There is no need to duplicate anything. The focus of this topic sheet is the Endocrine system and answers should reflect this. A) Topic sheet format 1 Topic, keyword or organ: All content on the topic sheet refers to this central topic, keyword or organ. Name the topic, give its functions and make an annotated drawing to illustrate the topic. List and Functions: List all cells, tissues and structures related to the topic or keyword and provide their functions. Describe: Write short descriptions of the cells, tissues and structures related to the topic or keyword. Draw: Make a diagram or drawing of each of the cells, tissues and structures listed. Related: What other knowledge areas relate to the central topic item and should be reviewed for elaborative information? Questions: Make at least 3 questions relating to the central topic item. Unsure about? What are you still unsure about and need to clarify for better understanding? B) Topic sheet format 2 Keyword: The primary keyword for this page. All information on this page must relate to the keyword. Definition: Write a concise definition of the keyword. Used in a sentence: Use the keyword in a meaningful sentence related to Histology. Annotated picture: Make an annotated drawing to illustrate key concepts of the keyword. Questions with the keyword as answer: Construct several questions related to the keyword. Other words linked to the keyword: Elaborate and interconnect with other material related to the keyword. This can be anatomy, physiology, pharmacology or clinical. Make one or more sentences linking the keyword and linked words: Short notes connecting the words used. What needs revision? What needs to be revised or clarified for better understanding of the keyword? 2. Complete the detailed tasks for each of the five primary endocrine organs as described below. Follow the instructions carefully and do not jump any steps or questions. 3. Complete the supplementary integrative set of questions for the complete topic. 4. If you are unsure about a task, answers to a question or find a possible error, contact the relevant facilitator and clarify. Do not wait until the last moment the different sections build on each other and uncertainty about concepts will cause you to have trouble with the whole section.
3 Slide 52: Pituitary gland 1. Make an annotated line drawing showing the different component parts of the pituitary gland at very low magnification. Indicate the embryological origin of each part. Indicate blood flow into and out of the pituitary gland. 1. What is colloid? 2. Name three types of capillaries and give an example where each occur. 3. What is a portal system? 4. What cells make up the pars distalis of the pituitary gland? 5. What cells occur in the pars nervosa of the pituitary gland? 6. What are pituicytes? 7. What are Herring bodies? 8. What is the function of Herring bodies? 9. Describe an axon on cross, oblique and longitudinal section. Make a line drawing to assist. 10. Provide the function for each of the cells, tissues, structures and organs above. 2. View the pituitary gland at very low magnification. At this magnification, you should be able to see the whole gland. 3. Identify the following: 1. Pars distalis, pars intermedia and pars nervosa. 4. Cells in the pituitary gland are arranged in. of cells are separated by and capillaries. On a slide at high and very high magnification, find of cells, and. 5. The pars distalis of the pituitary gland contains five cell types. Complete the following table with regards to the five cell types: Cell Type % of cells Size of cells Shape Staining Nucleus Somatotrope 50% Medium Oval Acidophil Round & central Lactotrope 15-20% Large Polygonal Acidophil/Chromophil Oval and central Corticotrope 15-20% Medium Polygonal Basophil Round & eccentric Gonadotrope 10% Small Oval Basophil Round & eccentric Thyrotrope 5% Large Polygonal Basophil Round & eccentric 6. Find colloid on a slide. 7. Find an example of each of the cells making up the posterior part of the pituitary gland. 8. What constitutes the bulk of the pars nervosa? Find the pars nervosa at low magnification and the corresponding high magnification view.
4 1. Where does the structures constituting the bulk of the pars nervosa originate? 2. What are unique about the structures in the pars nervosa? 3. Why are they different from similar structures elsewhere in the body? 9. Find an example of Herring bodies on a slide. 1. In which part of the pituitary gland does Herring bodies occur? Slide 55: Thyroid gland 1. Make a list of the component parts of the thyroid gland. Include cells, tissues and structures. Give the function of each of the component parts. 1. What are the two divisions of epithelial tissues? 2. How are epithelium classified? 3. What are the two divisions of secretory epithelium? 4. What is colloid? 5. What is the functional unit of the thyroid gland called? 6. What type of capillary is present in the thyroid? 7. How are cells in the thyroid arranged? 8. Follicular epithelium is simple cuboidal. 9. Name the two types of cells contained in follicular epithelium. 2. View a low magnification of the thyroid gland. On this view, you should be able to see the structures composing the thyroid gland. Cellular detail must be reviewed at higher magnification, keeping the macroscopic positions in mind. 3. View the thyroid at high magnification. Cells and tissues should be visible. Identify the following: 1. Follicles 2. Clear cells 3. Connective tissue 4. Make an annotated drawing of the thyroid gland, indicating the structures identified above. Give the function of each. Clearly indicate the capsule, lobes and lobules. 1. What 2. What are parafollicular cells? 3. What are clear cells? 4. Where are clear cells found? 5. How is the connective tissue organised? 6. What other structures inside the pancreas could be mistaken for endocrine tissue?
5 Slide 54: Parathyroid glands 1. View the parathyroid gland on low magnification. On this view, the gland, its capsule and surrounding adipose tissue should be visible. 1. Comparing low magnification views, what is the main difference in connective tissue arrangement between the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands? 2. What are the main secretory cells of the parathyroid gland? 3. What other type of cells are present? 4. What type of cell is prominently visible, even at low magnification? 5. What types of connective tissue is present in the parathyroid gland? 6. Describe the size, nucleus and cytoplasm of principal (chief) cells and oxyphil cells. 2. View the parathyroid gland on high magnification. Cellular detail, including red blood cells (where present), should be visible. Find examples of chief cells, oxyphil cells and connective tissue. 3. Make annotated drawings of the parathyroid gland. Indicate the cells of the parathyroid gland and the three types of connective tissue prominently seen in the parathyroid gland. 1. How can we differentiate between chief cells and oxyphil cells on the slide? 2. How is the connective tissue arranged? Slide 56: Adrenal glands 1. View the slide on low magnification. The gland and it capsule should be visible. 1. Epithelium are divided into two main groups. What are the two main groups? 2. Glandular epithelia are often described based on the cellular organisation in the gland. What are the organisation seen in exocrine glands? What are the organisation seen in endocrine glands? 3. How are the cells in the adrenal gland arranged? 4. Compare the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands and adrenal glands with regard to capsule and connective tissue arrangement. 2. At low magnification, identify the following: 1. Capsule 2. Cortex and medulla 1. What is typical of the capsule of the adrenal glands?
6 2. What zones can be identified in the cortex? 3. At high magnification, find the capsule of the gland. Are there components of the outer capsule penetrating the gland? What structures are present in the capsule? 4. At high magnification, identify the zones of the cortex. 1. How is the cortex supplied with blood? 2. Describe the dual blood supply system of the medulla. 3. What are the main products of each of the three zones of the cortex? 4. Describe the cells typical of each of the three zones of the cortex. 5. Chromaffin cells in the medulla are considered the equivalent of postganglionic neurons. Why? 6. In addition to chromaffin cells, what other cells with connections to the abdominal organs are present in the adrenal medulla? 5. At high magnification, find the medulla of the adrenal gland. Identify as many of the components of the medulla listed above. 1. What are the distinguishing features of the medulla? 6. Make an annotated drawing of the adrenal gland. Show detail of the different components. Slide 50: Pancreas 1. View the slide at low magnification. You should see lobes, ducts and blood vessels. 1. What are the main components of the pancreas? 2. Classify the pancreas, using the classification of epithelium. 3. What cells, tissues and structures do you expect to find in the pancreas? List the functions of each of these as it pertains to the pancreas. 4. How is the tissue of the endocrine pancreas arranged? 5. Name the three types of connective tissue fibers. Give an example of the distribution of each. Give the function of each type of connective tissue fiber. 2. Identify the lobes, ducts and blood vessels of the pancreas. Identify the exocrine and endocrine tissue of the pancreas. 1. What is typical of the epithelium of ducts? 2. What types of cells form an island? 3. What structures are found between the endocrine cells?
7 3. View the pancreas at high magnification. Identify the islands of Langerhans, cords of island cells, capillaries and exocrine tissue. 4. Make an annotated drawing of a section of exocrine acini and the endocrine areas. Make a line diagram to illustrate the hierarchy of ducts and blood vessels supplying and draining the pancreas. Clearly indicate endocrine and exocrine structures. Questions 1. How does the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus communicate? 2. What four elements make up the thyroid gland? 3. Name the divisions and zones of the adrenal glands and the hormones secreted by each. 4. Name the five distinct types of endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary. 5. What changes take place in the thyroid follicular cells during an active secretory phase? 6. Name the three main cell types seen in the parathyroid. 7. What do the cells of the adrenal medulla contain? 8. Name the four main cell types of the endocrine pancreas. 9. Make a table listing nine endocrine glands/organs and the hormonal secretions of each. 10. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. 11. List the hormones released by the heart, kidneys, and other organs with secondary endocrine functions. 12. Describe the types of intercellular communication, their importance, mechanisms, and effects. 13. What role does thyroid hormones play in the regulation of basal metabolism? 14. Name the five distinct types of endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary. 15. What changes take place in the thyroid follicular cells during an active secretory phase? 16. Name the three main cell types seen in the parathyroid. 17. What do the cells of the adrenal medulla contain? 18. Name the four main cell types of the endocrine pancreas. 19. What are the general characteristics of the endocrine system? 20. Oxyphil cells are located in which organ? 21. What is unique about the structure of the thyroid gland. 22. Compare the structure of the thyroid with that of the parathyroid. 23. What is the cell source of calcitonin, melatonin, cortisol and epinephrine?
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB
 Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
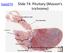 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Endocrine Glands and Hormones "What are endocrine glands and what do they make?
 Endocrine Glands and Hormones "What are endocrine glands and what do they make? Model 1:Development of glands. Exocrine Gland Endocrine Gland Critical thinking questions 1. Based on the model, which of
Endocrine Glands and Hormones "What are endocrine glands and what do they make? Model 1:Development of glands. Exocrine Gland Endocrine Gland Critical thinking questions 1. Based on the model, which of
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Lab Exercise Endocrine System
 Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide
 Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed to help you recognize
Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed to help you recognize
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Classic Endocrine Glands
 1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Fig The Endocrine System The connective tissue will be very well vascularized. Due to their need to distribute their products by the blood, the
 Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: A. Kent Christensen, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: A. Kent Christensen, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Histology. Dr.shatarat
 Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
Gastrointestinal Tract
 CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination
 I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Gross anatomy. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran
 Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
The Endocrine System. Qian XiaoJing. Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE QIAN
 The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
DR. DARWISH H. BADRAN. Parathyroid glands
 Parathyroid glands History 1849 - Sir Richard owen provided 1st accurate description of normal parathyroid glands after examining Indian Rhinoceros 1879 - Anton Wölfer described tetany in a patient
Parathyroid glands History 1849 - Sir Richard owen provided 1st accurate description of normal parathyroid glands after examining Indian Rhinoceros 1879 - Anton Wölfer described tetany in a patient
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland 1. Endocrine Glands 2. Exocrine Glands Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
 Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9)
 NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Anatomy & Physiology Revealed Instructions. 1. From the Module dropdown menu, chose the 12. Digestive system.
 #10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
#10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45. Intercellular communication. Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Signaling by local regulators 11/26/2017
 Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
The Endocrine System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris
 18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
ENDOCRINE GLANDS. Pituitary Gland
 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as:
 3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
