Thyroid disease for R2
|
|
|
- Sandra Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thyroid disease for R2 Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD. 5 February 2013
2 Thyroid Thyrotoxicosis/Thyroiditis Amiodarone and thyroid dysfunction Thyroid storm Hypothyroidism Thyroid nodule
3 Thyrotoxicosis Refers to the classic physiologic manifestations of excessive quantities of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism Reserved for disorders that result from sustained overproduction of hormone by thyroid itself.
4 Causes of Thyrotoxicosis Primary hyperthyroidism Graves disease Toxic multinodular goiter Toxic adenoma Thyrotoxicosis without hyperthyroidism Subacute thyroiditis Silent thyroiditis Amiodarone Thyrotoxicosis factitia Secondary hyperthyroidism TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma Chorionic gonadotropin-induced Gestational hyperthyroidism
5 Graves disease Autoimmune thyroid disease Autoantibodies specific to Graves disease are directed against the TSHR (TSHRAbs) and behave as thyroid stimulating antibodies
6 Clinical manifestations Fatigue Heat intolerance Weight loss to an effective diet Dyspnea Palpitation
7 Eyes Lid retraction.. Stare Lid lag Increased adrenergic tone Graves Orbitopathy Soft tissue involvement Proptosis Extraocular muscle involvement Corneal involment
8 Thyroid gland Diffuse goiter Soft to firm and rubbery Bruits : upper and lower pole
9 Cardiovascular System Tachycardia Widening of the pulse pressure Atrial fibrillation Heart failure Anxiety / Psychosis Tremor Myopathy Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
10 Skin and Hair Warm and moist skin Palmar erythema Hair : fine and friable Plummer s nails: Onycholysis typical involving the 4 th and 5 th fingers Vitiligo Graves disease Thyroid acropachy Pretibial myxedema
11 Onycholysis Thyroid acropachy Pretibial myxedema
12 Laboratory TSH, T 3 & T 4 Positive TSHRAbs Increased radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU)
13 Treatments Antithyroid Drugs : PTU, MMI B-Adrenergic antagonist drugs Glucocorticoids Inorganic Iodide Iodine-Containing Compounds Potassium Perchlorate Lithium Carbonate Rituximab Radioactive iodine Surgery
14 Antithyroid Drugs : Thionamides Propylthiouracil (PTU), Methimazole (MMI) Inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis Immunosuppressive actions PTU : blocking of the conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) Dose adjustment is not necessary in persons who have impaired liver or kidney function. Try medication yrs.
15 Characteristic MMI PTU Relative potency Administration oral oral Serum half-life (hours) Duration of action (hours) > Metabolism during liver disease Metabolism during kidney disease Transplacental passage and level in breast milk Inhibition of T4/T3 conversion Decreased Normal Low Normal Normal Even lower Dosing 1-2 times daily 2-3 times daily No Yes Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
16 Major toxic reactions with ATDs Side effect Frequency Comments Polyarthritis 1-2% - ANCA+ vasculitis Rare Mostly PTU Agranulocytosis % May be more common with PTU Hepatitis % PTU Cholestasis Rare MMI
17 Mild side effects Skin reactions : rash, pruritus Arthralgias Gastrointestinal symptom Abnormal sense of taste Occasional sialadenitis
18 Agranulocytosis Defined as an absolute granulocyte count < 500/mL Often occurs within the first 3 months of therapy Most experts do not recommend routine monitoring of granulocyte count during treatment. Patients should be instructed to stop medication and to seek medical attention if they develop a fever or a sore throat. If the granulocyte count <1000/mL, the drug should be stopped. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
19 Long-Term Follow-up Recurrence rate is 50-60% Most cases of relapse occur within 3-6 months of stopping the drug. Most women in remission who become pregnant have a postpartum relapse of GD or develop postpartum thyroiditis Life-long follow-up is recommended. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
20 RADIOACTIVE IODINE RAI is considered effective, safe, and relatively inexpensive. Isotope of choice is 131 I. Increased risk of ophthalmopathy Following 131 I therapy, 50-70% of patients become euthyroid within 6-8 weeks Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
21 SURGERY Indications Patient preference Children, adolescents, pregnant women Large goiters (whether causing pressure symptoms or for cosmetic reasons) Suspicion of thyroid malignancy +/-Pre-existing Graves ophthalmopathy Total or nearly total thyroidectomy Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
22 Complications Permanent damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve Hypoparathyroidism Transient hypocalcemia Postoperative bleeding Wound infections The formation of keloids Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 38 (2009)
23 Thionamides Advantages -No radiation hazard -No surgical and anesthesiologic risks -No permanent hypothyroidism -OPD Disadvantages -Recurrent rate high (>50%) -Frequent testing required -Common mild side effect -Rare but potentially lethal side effects Radioactive iodine -Definitive treatment -No surgical and anesthesiologic risks -OPD, rapidly performed -Rapid control of hyperthyroidism in most -Low cost -Side effects mild, rare, transient -Normalizes thyroid size within 1 yr -Potential radiation hazard -Worsening of thyroid eye disease -Decreasing efficacy with increasing goiter size -May need to be repeated -Hypothyroidism eventually develops in most cases Thyroidectomy -Definitive treatment -No radiation hazard -Rapid normalization -Definitive histological -Most effective in cases with pressure symptoms -Cost, IPD -Anesthesiologic risks -Hypoparathyroidism 1-2% -Damage recurrent laryngeal nerve, bleeding, infection -Hypothyroidism
24 Toxic multinodular goiter Hyperthyroidism arises in MNG Autonomous function Usually occurs after the age of 50 in patients who have had nontoxic MNG Treatment: Radioactive iodine or surgery
25 Toxic adenoma Hyperfunctioning nodule Nodule diameter > 3 cm Typically in patients in their years old Treatment: Radioactive iodine or surgery
26 Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis Subacute nonsuppurative thyroiditis, de Quervain's thyroiditis, viral thyroiditis, or subacute thyroiditis History of an upper respiratory infection, typically 2-8 weeks beforehand Mumps, coxsackie, influenza, adenoviruses and echoviruses Predominates in female, years old
27 Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis Malaise, upper respiratory tract infection Gradual or sudden pain in thyroid gland, radiates to the ear, jaw by turning head or swallowing Neck pain, tender diffuse goiter Transient, usually subsiding in 2-8 weeks
28 Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis Thyrotoxic phase Day Hypothyroidism phase Day Euthyroidism
29 Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis Laboratory Elevated T4 and/or T3, RAIU that is low, High ESR/CRP FNA Widespread infiltration with neutrophils, lymphocytes, histiocytes and giant cells
30 Radioiodine uptake และ thyroid scan พบว าม low uptake
31 Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis High dose aspirin 600 mg oral q 4-6 hours NSAIDs COX2 Severe pain : glucocorticoids (prednisolone mg/day) Thyrotoxic phase : β-adrenagic blockers Hypothyroidism : Levothyroxine µg/day
32 Painless thyroiditis Silent thyroiditis, subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis, and lymphocytic thyroiditis Variant form of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, Amiodarone, Lithium Any woman (who is not postpartum) or man with symptoms < 2 months Small diffuse goiter or no thyroid enlargement Key : mild hyperthyroidism of short duration, little or no thyroid enlargement, and no signs of Graves'
33 Postpartum thyroiditis Variant form of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) ~50% of patients have elevated antitpo Hyperthyroidism : mild, anxiety, weakness, irritability, palpitations, tachycardia and tremor Hypothyroidism : mild, lack of energy, sluggishness, dry skin and postpartum depression
34 Postpartum thyroiditis Hyper thyroidism Hypo thyroidism Delivery Euthyroidism 1-4 months 2-8 weeks 2 weeks to several months
35 Amiodarone and thyroid dysfunction Risk ~ 2-30% Depending upon underlying thyroid status, dietary iodine intake, and subclinical thyroid disorders Intrinsic drug effects Extrinsic drug effects
36 Intrinsic drug effect
37 Extrinsic drug effect Wolff-Chaikoff effect Iodine transport and thyroid hormone synthesis are transiently inhibited Fail to escape" from the Wolff-Chaikoff effect Autoimmune thyroid disease Jod-Basedow Autonomous function
38 Normal, euthyroid individuals Acute phase After 3-6 months T % T3 30% rt3 20% TSH upper norm T4 T3 rt3 TSH upper norm lower norm upper norm normal
39 Amiodarone-induced hypothyroidism Hashimoto's thyroiditis or positive antithyroid antibodies more likely to develop persistent hypothyroidism Amiodarone is usually not discontinued unless it fails to control the underlying arrhythmia. Replacement with T4 while amiodarone is continued. Hypothyroidism may persist after withdrawal of amiodarone in patients who have underlying chronic autoimmune thyroiditis
40 Amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis (AIT) Prednisolone 40 to 60 mg/day JCEM 2001 Vol. 86 No. 1
41 Endocrine Reviews 22(2):
42 Thyroid storm Thyroid storm is an extreme accentuation of the thyrotoxicosis. Uncommon but serious complication. Incidence of thyroid storm less than 10% of patients hospitalized for thyrotoxicosis Mortality rate due to thyroid storm 20-30% 1,2 [1] Jameson L, Weetman A. Disorders of the thyroid gland. In: Braunwald E, Fauci A, Kasper D, et al, editors. Harrison s principles of internal medicine. 15th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill; p [2] Tietgens ST, Leinung MC. Thyroid storm. Med Clin North Am 1995;79:
43 Thyroid storm Underlying cause of thyrotoxicosis Graves disease Solitary toxic adenoma Toxic multinodular goiter Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
44 Clinical features Abrupt onset Preexisting thyrotoxicosis has been treated incompletely or has not been treated at all Precipitation Infection Trauma Surgical emergencies or operations Less common : radiation thyroiditis, DKA, toxemia of pregnancy. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology 11 th edition
45 Clinical features Fever Marked tachycardia of sinus or ectopic origin and arrhythmias Pulmonary edema or congestive heart failure Tremulousness and restlessness Delirium Nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain Stupor and coma Williams Textbook of Endocrinology 11 th edition
46
47 Diagnosis Elevated free T4 and free T3 Depressed TSH (<0.05 µu/ml) Hyperglycemia, hypercalcemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, leukocytosis and elevated liver enzymes. Chest radiograph : helpful to seek a possible infectious source as a precipitant. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
48 ECG manifestations of thyrotoxicosis Sinus tachycardia ~ 40% of cases Atrial fibrillation ~ 10% of cases Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
49 Treatments Aims Correct the severe thyrotoxicosis Correct the precipitating illness General support The patient thought to have thyroid storm should monitored in a medical intensive care unit during the initial phases of therapy.
50 Thyroid storm PTU mg / day Iodine: start after PTU at least 1-2 hr SSKI 5 drops q 6 hr Lugol s 10 drops oral q 6 hr or Propanolol : 160 mg/day Dexamethasone : 8 mg/d = 2 mg iv q 6 hr for 3-4 days Precipitating cause
51 PTU via rectal route PTU can be effectively absorbed via the rectal route. The enema form appeared to provide better bioavailability than the suppository form. Water-suspension enema was prepared by grinding 50-mg tablets of PTU into small pieces with a mortar and pestle and suspend it in 90 ml of sterile water. The suspension was administered by a disposable urinary catheter via rectum. THYROID Volume 12, Number 7, 2002
52 -Significant decrease in serum FT3 levels was demonstrated at 30 minutes after PTU administration and throughout the study in both groups. -No change of FT4 levels of both groups was demonstrated. *p < 0.05 when changes of serum FT3 levels were compared to baseline of each group. THYROID Volume 12, Number 7, 2002
53 Beta-adrenergic blockade May result in hypotension in some patients who have heart failure and are being treated for thyrotoxicosis Beneficial in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis, careful consideration is required If the cause of the heart failure were likely to be underlying tachycardia, beta-blockade would be particularly useful Relative contraindications History of moderate to severe heart failure Presence of reactive airway disease Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
54 Anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation in the setting of thyrotoxicosis Thyrotoxic patients who have atrial fibrillation, antithrombotic therapies should be selected based on the presence of stroke risk factors. Thyrotoxic patients may require a lower maintenance dose of warfarin than euthyroid patients because of increased clearance of vitamin K dependent clotting factors. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
55 Definitive therapy Radioactive iodine ablation May not be able to be used for several weeks or months following treatment with iodine for thyroid storm. Following the resolution of thyroid storm, the patient continues to require close follow-up with plans for definitive therapy to prevent a future recurrence of life-threatening thyrotoxicosis Surgery Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 35 (2006)
56 Hypothyroidism Puffy appearance Enlargement of tongue Loss of temporal aspect of eyebrows Queen Ann s sign Dryness and coarseness of the skin
57 Cardiovascular System Bradycardia Narrowing of pulse pressure Pericardial effusion Respiratory System Pleural effusion (rare) Obstructive sleep apnea Depression of the both hypoxic and hypercapnic ventilatory drives alveolar hypoventilation, CO 2 retention
58 Alimentary Weight gain, loss appetite Constipation Ascites : associated with pleural & pericardial effusion CNS and PNS Loss of intellectual function Depression/ dementia Delayed muscle contraction and relaxation Myoclonus Carpal tunnel syndrome
59 Hashimoto s Thyroiditis Autoimmune thyroid disease Chronic thyroiditis : intrathyroidal lymphocytic infiltration Autoantibodies to thyroid peroxidase (TPOAb) and thyroglobulin (TgAb) Goiter, Firm in consistency Thyroid lymphoma : should be suspected if there is rapid, usually painful, enlargement of the thyroid gland
60 Levothyroxine (LT 4 ) Half-life : 7 days About 80% of the hormone is absorbed relative slowly. Typical dose : µg/kg IBW per day Complete equilibration of free T 4 ~ 6 weeks Adverse effects: Bone loss, AF Monitoring Primary hypothyroidism : TSH Secondary hypothyroidism : free T 4
61 Benign Nodules (95%) Carcinomas (5%) Hyperplastic nodules (85%) Papillary (81%) Adenomas (15%) Follicular and Hurthle cell (14%) Cysts (<1%) Medullary (3%) Anaplastic (2%)
62 Clinical findings in favor of malignant thyroid nodules Historical features Young (<20 years) or Old (>60 years) Male Neck irradiation during childhood or adolescent Rapid growth Recent changes in speaking, breathing or swallowing Family history of thyroid malignancy or MEN2
63 Clinical findings in favor of malignant thyroid nodules Physical examination Firm and irregular consistency Fixation to overlying tissues Vocal cord paralysis Regional lymph adenopathy
64 Evaluation of Newly Discovered Thyroid Nodules Nodules >1 cm should be evaluated There may be nodules <1 cm that require evaluation because of Suspicious US findings Associated lymphadenopathy History of head and neck irradiation History of thyroid cancer in one or more first-degree relatives Rapid growth and hoarseness Pertinent physical findings suggesting possible malignancy Thyroid Volume 19 Number 11, 2009
65
66 Low TSH History, physical, TSH Normal or high TSH 123 I or 99 Tc scan Not functioning Diagnostic US Hyperfunctioning Nodule on US Do FNA No nodule on US Evaluate and Tx for hyperthyroidism Result of FNA Elevated TSH Evaluate and tx for hypothyroidism Normal TSH FNA not indicated Thyroid Volume 19 Number 11, 2009
67 Result of FNA Nondiagnostic Repeat US guided FNA Nondiagnostic Close F/U or surgery Malignant PTC Pre-op US Surgery Not hyperfunctioning Suspicious for PTC Interminate Hürthle cell neoplasm Follicular neoplasm Consider 123 I scan if TSH low normal Benign Follow Hyperfunctioning Thyroid Volume 19 Number 11, 2009
68 Management of Benign nodule Ultrasound monitoring, initially at 6 to 12 months, then at increasing intervals over time Cystic degeneration and hemorrhage are the most common causes of sudden enlargement Small changes in nodule size on serial ultrasonography do not require a repeat aspiration. **Repeat aspiration when there is substantial growth >50 % change in volume >20 % increase in nodule diameter with a minimum increase in two or more dimensions of at least 2 mm Change in the texture of a nodule, or New symptoms are attributed to a nodule
69 Nontoxic multinodular goiter (MNG) Prevalence 12%, Female predominate Mostly asymptomic Large goiters, which may compress the trachea, esophagus and neck vessels Inspiratory stridor, dysphagia, choking sensation
70
71 Pemberton s sign
72 Management of MNG FNA Small and asymptomatic goiter can be monitored by clinical examination and evaluated periodically with U/S No significant benefit of thyroxine therapy Surgery : obstructive symptoms, large goiters, substernal goiter
CHAPTER-II Thyroid Diseases. by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of Pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university
 CHAPTER-II Thyroid Diseases by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of Pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university Aspects That Will Be Addressed Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Hyperthyroidism
CHAPTER-II Thyroid Diseases by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of Pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university Aspects That Will Be Addressed Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Hyperthyroidism
Effect of thyroid hormones of metabolism Thyroid Diseases
 Effect of thyroid hormones of metabolism Thyroid Diseases Medical Perspective Aspects That Will Be Addressed Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion Basic physiology Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis
Effect of thyroid hormones of metabolism Thyroid Diseases Medical Perspective Aspects That Will Be Addressed Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion Basic physiology Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis
OUTLINE. Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Production Common Tests to Evaluate the Thyroid Hyperthyroidism - Graves disease, toxic nodules, thyroiditis
 THYROID DISEASE OUTLINE Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Production Common Tests to Evaluate the Thyroid Hyperthyroidism - Graves disease, toxic nodules, thyroiditis OUTLINE Hypothyroidism - Hashimoto s thyroiditis,
THYROID DISEASE OUTLINE Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Production Common Tests to Evaluate the Thyroid Hyperthyroidism - Graves disease, toxic nodules, thyroiditis OUTLINE Hypothyroidism - Hashimoto s thyroiditis,
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment. April Janet A. Schlechte, M.D.
 Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment Family Practice Refresher Course April 2015 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships with any
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment Family Practice Refresher Course April 2015 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships with any
Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2)
 Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2) Thyroid diseases Thyrotoxicosis Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Graves disease Goiters Neoplasms Chronic Lymphocytic (Hashimoto) Thyroiditis Subacute Granulomatous
Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2) Thyroid diseases Thyrotoxicosis Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Graves disease Goiters Neoplasms Chronic Lymphocytic (Hashimoto) Thyroiditis Subacute Granulomatous
Disorders of the Thyroid Gland
 Disorders of the Thyroid Gland István Takács MD., PhD, 1st Department of Medicine, Semmelweis University Connection to the dentistry: close to each other higher operation risk radiating pain macroglossia
Disorders of the Thyroid Gland István Takács MD., PhD, 1st Department of Medicine, Semmelweis University Connection to the dentistry: close to each other higher operation risk radiating pain macroglossia
Thyroid disorders. Dr Enas Abusalim
 Thyroid disorders Dr Enas Abusalim Thyroid physiology The hypothalamic pituitary thyroid axis And peripheral conversion of T4 to T3, WHERE, AND BY WHAT ENZYME?? Only relatively small concentrations of
Thyroid disorders Dr Enas Abusalim Thyroid physiology The hypothalamic pituitary thyroid axis And peripheral conversion of T4 to T3, WHERE, AND BY WHAT ENZYME?? Only relatively small concentrations of
Pathophysiology of Thyroid Disorders. PHCL 415 Hadeel Alkofide April 2010
 Pathophysiology of Thyroid Disorders PHCL 415 Hadeel Alkofide April 2010 1 Learning Objectives Understand the pathophysiology of hyperthyroidism & hypothyroidism Describe the signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism
Pathophysiology of Thyroid Disorders PHCL 415 Hadeel Alkofide April 2010 1 Learning Objectives Understand the pathophysiology of hyperthyroidism & hypothyroidism Describe the signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism
Toxic MNG Thyroiditis 5-15
 Hyperthyroidism Facts Prevalence 0.5-1.0%, more common in women Thyrotoxicosis is excess thyroid hormones from endogenous or exogenous sources Hyperthyroidism is excess thyroid hormones from thyroid gland
Hyperthyroidism Facts Prevalence 0.5-1.0%, more common in women Thyrotoxicosis is excess thyroid hormones from endogenous or exogenous sources Hyperthyroidism is excess thyroid hormones from thyroid gland
Hyperthyroidism. Objectives. Clinical Manifestations. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Implications for Primary Care. hyperthyroidism
 1 Hyperthyroidism Implications for Primary Care Laura A. Ruby, DNP, CRNP Wellspan Endocrinology 2 Objectives! Discuss the clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism! Review the use of the diagnostic studies!
1 Hyperthyroidism Implications for Primary Care Laura A. Ruby, DNP, CRNP Wellspan Endocrinology 2 Objectives! Discuss the clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism! Review the use of the diagnostic studies!
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES
 TITLE: THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY EFFECTIVE DATE: July, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnancy changes significantly the values influenced by the serum thyroid binding hormone level (i.e., total thyroxine,
TITLE: THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY EFFECTIVE DATE: July, 2013 POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnancy changes significantly the values influenced by the serum thyroid binding hormone level (i.e., total thyroxine,
THYROTOXICOSIS DR.J.BALA KUMAR 2 ND YR SURGERY PG
 THYROTOXICOSIS DR.J.BALA KUMAR 2 ND YR SURGERY PG What is the difference between thyrotoxicosis and hyperthyroidism Thyrotoxicosis Thyrotoxicosis is defined as the state of thyroid hormone excess and is
THYROTOXICOSIS DR.J.BALA KUMAR 2 ND YR SURGERY PG What is the difference between thyrotoxicosis and hyperthyroidism Thyrotoxicosis Thyrotoxicosis is defined as the state of thyroid hormone excess and is
Laura Trask, MD FACP Central Maine Endocrinology Lewiston, ME
 Laura Trask, MD FACP Central Maine Endocrinology Lewiston, ME 795-7520 traskla@cmhc.org No disclosures Objectives To have an understanding of hyperthyroidism To have an understanding of the management
Laura Trask, MD FACP Central Maine Endocrinology Lewiston, ME 795-7520 traskla@cmhc.org No disclosures Objectives To have an understanding of hyperthyroidism To have an understanding of the management
The Thyroid: No mystery. Just need all the pieces to the puzzle.
 The Thyroid: No mystery. Just need all the pieces to the puzzle. Todd Chennell, MS, RN ANP-C Endocrine surgery University of Rochester 2018 1 According to the American Thyroid Association, 12 percent of
The Thyroid: No mystery. Just need all the pieces to the puzzle. Todd Chennell, MS, RN ANP-C Endocrine surgery University of Rochester 2018 1 According to the American Thyroid Association, 12 percent of
DISORDERS OF THE THYROID GLAND SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, & TREATMENT ENDOCRINE SYSTEM AT A GLANCE OBJECTIVES ANATOMY OF THE THYROID
 OBJECTIVES DISORDERS OF THE THYROID GLAND SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, & TREATMENT Stephanie Blackburn, MHS, MLS(ASCP) CM LSU Health Shreveport Clinical Laboratory Science Program Discuss the synthesis and action
OBJECTIVES DISORDERS OF THE THYROID GLAND SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, & TREATMENT Stephanie Blackburn, MHS, MLS(ASCP) CM LSU Health Shreveport Clinical Laboratory Science Program Discuss the synthesis and action
Slide notes: This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications,
 1 This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications, including ophthalmic complications, treatments (both permanent solutions
1 This presentation provides information on Graves disease, a systemic autoimmune disease. Epidemiology, pathology, complications, including ophthalmic complications, treatments (both permanent solutions
Lecture title. Name Family name Country
 Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
Lecture title Name Family name Country Nguyen Thy Khue, MD, PhD Department of Endocrinology HCMC University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MEDIC Clinic Hochiminh City, Viet Nam Provided no information regarding
Disclosures. Learning objectives. Case 1A. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues. I have nothing to disclose.
 Disclosures Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues I have nothing to disclose. Chrysoula Dosiou, MD, MS Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Endocrinology Stanford University School
Disclosures Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Medical and Surgical Issues I have nothing to disclose. Chrysoula Dosiou, MD, MS Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Endocrinology Stanford University School
Dharma Lindarto Div. Endokrin-Metabolisme dan Diabetes. Dep Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK USU / RSUP HAM Medan
 HYPERTHYROIDISM Dharma Lindarto Div. Endokrin-Metabolisme dan Diabetes. Dep Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK USU / RSUP HAM Medan Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Tiroid Disease Multi N Aspect fungtion morphology eutiroid,
HYPERTHYROIDISM Dharma Lindarto Div. Endokrin-Metabolisme dan Diabetes. Dep Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK USU / RSUP HAM Medan Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Tiroid Disease Multi N Aspect fungtion morphology eutiroid,
The Number Games and Thyroid Function Arshia Panahloo Consultant Endocrinologist St George s Hospital
 The Number Games and Thyroid Function Arshia Panahloo Consultant Endocrinologist St George s Hospital Presentation Today: Common thyroid problems and treatments Pregnancy related thyroid problems The suppressed
The Number Games and Thyroid Function Arshia Panahloo Consultant Endocrinologist St George s Hospital Presentation Today: Common thyroid problems and treatments Pregnancy related thyroid problems The suppressed
Update In Hyperthyroidism
 Update In Hyperthyroidism CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Copyright
Update In Hyperthyroidism CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Copyright
TANJA KEMP INTERNAL MEDICINE: ENDOCRINOLOGY
 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS IN THE ELDERLY (part 2) TANJA KEMP INTERNAL MEDICINE: ENDOCRINOLOGY Pituitary axis Target organs of the pituitary gland Negative feedback Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid axis Thyroid
ENDOCRINE DISORDERS IN THE ELDERLY (part 2) TANJA KEMP INTERNAL MEDICINE: ENDOCRINOLOGY Pituitary axis Target organs of the pituitary gland Negative feedback Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid axis Thyroid
Evaluation and Management of Thyroid Nodules. Nick Vernetti, MD, FACE Palm Medical Group Las Vegas, Nevada
 Evaluation and Management of Thyroid Nodules Nick Vernetti, MD, FACE Palm Medical Group Las Vegas, Nevada Disclosure Consulting Amgen Speaking Amgen Objectives Understand the significance of incidental
Evaluation and Management of Thyroid Nodules Nick Vernetti, MD, FACE Palm Medical Group Las Vegas, Nevada Disclosure Consulting Amgen Speaking Amgen Objectives Understand the significance of incidental
Thyroid Hormones (T 4 & T 3 )
 1 Thyroid Hormones (T 4 & T 3 ) Normalize growth and development, body temperature, and energy levels. Used as thyroid replacement therapy in hypothyroidism. Thyroxine (T 4 ) is peripherally metabolized
1 Thyroid Hormones (T 4 & T 3 ) Normalize growth and development, body temperature, and energy levels. Used as thyroid replacement therapy in hypothyroidism. Thyroxine (T 4 ) is peripherally metabolized
4) Thyroid Gland Defects - Dr. Tara
 4) Thyroid Gland Defects - Dr. Tara Thyroid Pituitary Axis TRH secreted in the hypothalamus stimulates production and Secretion of TSH TSH stimulates secretion of T3, T4 T4 has negative feedback on secretion
4) Thyroid Gland Defects - Dr. Tara Thyroid Pituitary Axis TRH secreted in the hypothalamus stimulates production and Secretion of TSH TSH stimulates secretion of T3, T4 T4 has negative feedback on secretion
Systemic Management of Graves Disease. Robert James Graves, M.D., FRCS ( ) Graves Disease: Endocrinopathy or Ophthalmopathy?
 Systemic Management of Graves Disease Rona Z. Silkiss, M.D., FACS Associate Clinical Professor, UCSF Chief, Division of Ophthalmic Plastic and Orbital Surgery California Pacific Medical Center No financial
Systemic Management of Graves Disease Rona Z. Silkiss, M.D., FACS Associate Clinical Professor, UCSF Chief, Division of Ophthalmic Plastic and Orbital Surgery California Pacific Medical Center No financial
John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD. Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989
 John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989 No Disclosures Disease Of the Thyroid Iodide Metabolism/Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone Trap Oxidation Organification(catalyzed
John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989 No Disclosures Disease Of the Thyroid Iodide Metabolism/Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone Trap Oxidation Organification(catalyzed
Thyroid gland defects. Dr. Tara Husain
 Thyroid gland defects Dr. Tara Husain Thyroid Pituitary Axis TRH secreted in the hypothalamus stimulates production and Secretion of TSH TSH stimulates secretion of T3,T4 T4 has negative feed back on secretion
Thyroid gland defects Dr. Tara Husain Thyroid Pituitary Axis TRH secreted in the hypothalamus stimulates production and Secretion of TSH TSH stimulates secretion of T3,T4 T4 has negative feed back on secretion
Thyroid Gland. Patient Information
 Thyroid Gland Patient Information Contact details for Endocrine and Thyroid Clinics Hawke s Bay Fallen Soldiers Memorial Hospital Villa 16 Phone: 06 8788109 ext 5891 Text: 0274 102 559 Email: endoclinic@hbdhb.govt.nz
Thyroid Gland Patient Information Contact details for Endocrine and Thyroid Clinics Hawke s Bay Fallen Soldiers Memorial Hospital Villa 16 Phone: 06 8788109 ext 5891 Text: 0274 102 559 Email: endoclinic@hbdhb.govt.nz
Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging. Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist
 Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: Imaging modalities Outline ACR-SNM-SPR guidelines
Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: Imaging modalities Outline ACR-SNM-SPR guidelines
Women s Health in General Practice Symposium 2015 Thyroid & Parathyroid Cases
 Women s Health in General Practice Symposium 2015 Thyroid & Parathyroid Cases Bill Fleming Epworth Freemasons Hospital 1 Common Endocrine Presentations anatomical problems thyroid nodule / goitre embryological
Women s Health in General Practice Symposium 2015 Thyroid & Parathyroid Cases Bill Fleming Epworth Freemasons Hospital 1 Common Endocrine Presentations anatomical problems thyroid nodule / goitre embryological
THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN
 THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN Michelle Schweiger, D.O. Center for Pediatric and Adolescent Endocrinology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Neither I nor any immediate family members have any financial interests
THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN Michelle Schweiger, D.O. Center for Pediatric and Adolescent Endocrinology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Neither I nor any immediate family members have any financial interests
Thyroid Disease. I have no disclosures. Overview TSH. Matthew Kim, M.D. July, 2012
 Thyroid Disease I have no disclosures Matthew Kim, M.D. July, 2012 Overview Thyroid Function Tests Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Subclinical Thyroid Disease Thyroid Nodules Questions TSH Best single screening
Thyroid Disease I have no disclosures Matthew Kim, M.D. July, 2012 Overview Thyroid Function Tests Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Subclinical Thyroid Disease Thyroid Nodules Questions TSH Best single screening
Disorders of Thyroid Function
 Disorders of Thyroid Function Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Thyroid Hormone Axis Hypothalamus TRH
Disorders of Thyroid Function Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Thyroid Hormone Axis Hypothalamus TRH
Alvin C. Powers, M.D. 1/27/06
 Thyroid Histology Follicular Cells ECF side Apical lumen Thyroid Follicles -200-400 um Parafollicular or C-cells Colloid Photos from University of Manchester and tutorial created by Dr. James Crimando,
Thyroid Histology Follicular Cells ECF side Apical lumen Thyroid Follicles -200-400 um Parafollicular or C-cells Colloid Photos from University of Manchester and tutorial created by Dr. James Crimando,
Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management
 Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management Yuanita Asri Langi email: meralday@yahoo.co.id Endocrinology & Metabolic Division, Internal Medicine Department, Prof.dr.R.D. Kandou Hospital/ Sam Ratulangi
Thyrotoxicosis in Pregnancy: Diagnose and Management Yuanita Asri Langi email: meralday@yahoo.co.id Endocrinology & Metabolic Division, Internal Medicine Department, Prof.dr.R.D. Kandou Hospital/ Sam Ratulangi
Thyroid nodules. Most thyroid nodules are benign
 Thyroid nodules Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica E. Gosnell MD Assistant Professor March 22, 2011 Most thyroid nodules are benign thyroid nodules occur in 77% of the world s population palpable
Thyroid nodules Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica E. Gosnell MD Assistant Professor March 22, 2011 Most thyroid nodules are benign thyroid nodules occur in 77% of the world s population palpable
HYPERTHYROIDISM. Hypothalamus. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Anterior pituitary gland. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Thyroid gland T4, T3
 HYPERTHYROIDISM Hypothalamus Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Anterior pituitary gland Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Thyroid gland T4, T3 In hyperthyroidism, there is an increased production of
HYPERTHYROIDISM Hypothalamus Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Anterior pituitary gland Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Thyroid gland T4, T3 In hyperthyroidism, there is an increased production of
Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders
 Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders free T4 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders The total T4 may be elevated in pregnancy and with OCP use Graves I 123
Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders free T4 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Disorders The total T4 may be elevated in pregnancy and with OCP use Graves I 123
Endocrine system pathology
 Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Thyroiditis Diagnosis and Management issues. Prof. Md. Enamul Karim Professor of Medicine Dhaka Medical College
 Thyroiditis Diagnosis and Management issues Prof. Md. Enamul Karim Professor of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Definition Thyroiditis is a general term that refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Thyroiditis Diagnosis and Management issues Prof. Md. Enamul Karim Professor of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Definition Thyroiditis is a general term that refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Pathology. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid), Graves Disease (Basedow Disease) and more. Definitions. See online here
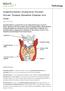 Pathology Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid), Graves Disease (Basedow Disease) and more See online here Hyperthyroidism is caused by the excess of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Graves disease is the most
Pathology Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid), Graves Disease (Basedow Disease) and more See online here Hyperthyroidism is caused by the excess of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Graves disease is the most
03-Dec-17. Thyroid Disorders GOITRE. Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms
 Thyroid Disorders GOITRE Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms 1 Physiological Goiter load on thyroid supply of I - limited stress due to:
Thyroid Disorders GOITRE Grossly enlarged thyroid - in hypothyroidism in hyperthyroidism - production of anatomical symptoms 1 Physiological Goiter load on thyroid supply of I - limited stress due to:
THYROID FUNCTION TEST and RADIONUCLIDE THERAPY
 THYROID FUNCTION TEST and RADIONUCLIDE THERAPY Ajalaya Teyateeti, M.D. Division of Nuclear Medicine Department of Radiology I. Thyroid function test OUTLINE Application and interpretation of in vitro TFT
THYROID FUNCTION TEST and RADIONUCLIDE THERAPY Ajalaya Teyateeti, M.D. Division of Nuclear Medicine Department of Radiology I. Thyroid function test OUTLINE Application and interpretation of in vitro TFT
Lectures presented. 3 rd year
 Lectures presented 3 rd year-2016-2017 The metabolic response to trauma Basic concepts: Homeostasis is a mechanism by which the internal environment of the human being is driven constant. It involves a
Lectures presented 3 rd year-2016-2017 The metabolic response to trauma Basic concepts: Homeostasis is a mechanism by which the internal environment of the human being is driven constant. It involves a
Canadian Endocrine Review Course 2014
 Canadian Endocrine Review Course 2014 Amiodarone & Thyrotoxicosis Iodine, A Catch 22 Ally P.H. Prebtani Associate Professor of Medicine Internal Medicine, Endocrinology & Metabolism McMaster University
Canadian Endocrine Review Course 2014 Amiodarone & Thyrotoxicosis Iodine, A Catch 22 Ally P.H. Prebtani Associate Professor of Medicine Internal Medicine, Endocrinology & Metabolism McMaster University
Thyroid nodules 3/22/2011. Most thyroid nodules are benign. Thyroid nodules: differential diagnosis
 Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules Postgraduate Course in General Surgery thyroid nodules occur in 77% of the world s population palpable thyroid nodules occur in about 5% of women and 1%
Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules Postgraduate Course in General Surgery thyroid nodules occur in 77% of the world s population palpable thyroid nodules occur in about 5% of women and 1%
Thyroid Plus. Central Thyroid Regulation & Activity. Peripheral Thyroid Function. Thyroid Auto Immunity. Key Guide. Patient: DOB: Sex: F MRN:
 Thyroid Plus Patient: DOB: Sex: F MRN: Order Number: Completed: Received: Collected: Sample Type - Serum Result Reference Range Units Central Thyroid Regulation & Activity Total Thyroxine (T4) 127 127
Thyroid Plus Patient: DOB: Sex: F MRN: Order Number: Completed: Received: Collected: Sample Type - Serum Result Reference Range Units Central Thyroid Regulation & Activity Total Thyroxine (T4) 127 127
Approach to Thyroid Dysfunction in the Elderly
 Approach to Thyroid Dysfunction in the Elderly Fernando Melaragno Endocrinology Objective The objective of this lecture is to review the epidemiology, clinical presentation, risks and complications, and
Approach to Thyroid Dysfunction in the Elderly Fernando Melaragno Endocrinology Objective The objective of this lecture is to review the epidemiology, clinical presentation, risks and complications, and
5/18/2013. Most thyroid nodules are benign. Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation
 Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation Incidence Etiology Risk factors Diagnosis Gene classification system Treatment Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica
Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation Incidence Etiology Risk factors Diagnosis Gene classification system Treatment Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica
Sample Type - Serum Result Reference Range Units. Central Thyroid Regulation Surrey & Activity KT3 4Q. Peripheral Thyroid D Function mark
 Thyroid Plus Sample Type - Serum Result Reference Range Units Central Thyroid Regulation Surrey & Activity KT3 4Q Total Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroid Plus Sample Type - Serum Result Reference Range Units Central Thyroid Regulation Surrey & Activity KT3 4Q Total Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroid Nodule. Disclosure. Learning Objectives P A P A P A 3/18/2014. Nothing to disclose.
 Thyroid Nodule Evaluating the patient with a thyroid nodule and some management options. Miguel V. Valdez PA C Disclosure Nothing to disclose. Learning Objectives Examination of thyroid gland Options for
Thyroid Nodule Evaluating the patient with a thyroid nodule and some management options. Miguel V. Valdez PA C Disclosure Nothing to disclose. Learning Objectives Examination of thyroid gland Options for
SUBACUTE THYROIDITIS. Ibrahim Elebrashy
 SUBACUTE THYROIDITIS Ibrahim Elebrashy Prof. Internal Medicine Head of the Internal Medicine Department Head of the Diabetes & Endocrinology Center Faculty Of Medicine-Cairo University DeQuervain s thyroiditis,
SUBACUTE THYROIDITIS Ibrahim Elebrashy Prof. Internal Medicine Head of the Internal Medicine Department Head of the Diabetes & Endocrinology Center Faculty Of Medicine-Cairo University DeQuervain s thyroiditis,
Hyperthyroidism. Causes. Diagnosis. Christopher Theberge
 Hyperthyroidism Pronunciations: (Hyperthyroidism) Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) is a condition where the thyroid gland synthesizes and secretes the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine
Hyperthyroidism Pronunciations: (Hyperthyroidism) Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) is a condition where the thyroid gland synthesizes and secretes the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine
Approach to thyroid dysfunction
 Approach to thyroid dysfunction Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC Twitter: @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or
Approach to thyroid dysfunction Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC Twitter: @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or
Anaesthesia In Thyroid Disorder. Dr. Umme Salma Ayesha Hoque MBBS, DA Medical Officer Department of Anaesthesiology and SICU BIRDEM General Hospital
 Anaesthesia In Thyroid Disorder Dr. Umme Salma Ayesha Hoque MBBS, DA Medical Officer Department of Anaesthesiology and SICU BIRDEM General Hospital Anatomy Endocrine gland : Consist of two lobe Located
Anaesthesia In Thyroid Disorder Dr. Umme Salma Ayesha Hoque MBBS, DA Medical Officer Department of Anaesthesiology and SICU BIRDEM General Hospital Anatomy Endocrine gland : Consist of two lobe Located
Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine April 2014
 Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine April 2014 Anatomy and histology of the thyroid gland Located in neck adjacent to the 5 th cervical vertebra (C5). Composed
Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine April 2014 Anatomy and histology of the thyroid gland Located in neck adjacent to the 5 th cervical vertebra (C5). Composed
Quality Control and Interpretation of Laboratory. Nursing and Midwifery. Dr. M. Navidhamidi
 Quality Control and Interpretation of Laboratory Tests of Thyroid Hormones for Nursing and Midwifery Dr. M. Navidhamidi Tehran University of Medical Sciences ١ Physiopathology of Thyroid Gland ٢ Thyroid
Quality Control and Interpretation of Laboratory Tests of Thyroid Hormones for Nursing and Midwifery Dr. M. Navidhamidi Tehran University of Medical Sciences ١ Physiopathology of Thyroid Gland ٢ Thyroid
The Thyroid and Pregnancy OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 3/19/10. Francis S. Greenspan March 19, Normal Physiology. 2.
 The Thyroid and Pregnancy Francis S. Greenspan March 19, 2010 OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 1. Normal Physiology 2. Hypothyroidism 3. Hyperthyroidism 4. Thyroid Nodules and Cancer NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Iodine Requirements:
The Thyroid and Pregnancy Francis S. Greenspan March 19, 2010 OUTLINE OF DISCUSSION 1. Normal Physiology 2. Hypothyroidism 3. Hyperthyroidism 4. Thyroid Nodules and Cancer NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Iodine Requirements:
Updates in Thyroid Disease. Thyroid Outline. Thyroid 10/5/2015. Leila Wing, MD. Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
 Updates in Thyroid Disease Leila Wing, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Background Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid nodules Thyroid Cancer Conclusions Resources/References Thyroid Outline
Updates in Thyroid Disease Leila Wing, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Background Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid nodules Thyroid Cancer Conclusions Resources/References Thyroid Outline
Thyroid Disease Part 2
 Thyroid Disease Part 2 by H. David Bergman, Ph.D. Dean, College of Pharmacy, Southwestern Oklahoma State University Goals and Objectives Goals: To provide the pharmacist with information regarding the
Thyroid Disease Part 2 by H. David Bergman, Ph.D. Dean, College of Pharmacy, Southwestern Oklahoma State University Goals and Objectives Goals: To provide the pharmacist with information regarding the
19th Century Thyroidology
 1 19th Century Thyroidology Dr. Kinnicutt s patient (1893) A cold, tired, constipated middle aged woman Slow pulse rate Low body temperature From physiology it was likely patient needed thyroid replacement
1 19th Century Thyroidology Dr. Kinnicutt s patient (1893) A cold, tired, constipated middle aged woman Slow pulse rate Low body temperature From physiology it was likely patient needed thyroid replacement
Evaluation and Management of Thyroid Nodules. Overview of Thyroid Nodules and Their Management. Thyroid Nodule detection: U/S versus Exam
 Overview of Thyroid Nodules and Their Management Matthew D. Ringel, M.D. Professor of Medicine Divisions of Endocrinology and Oncology, The Ohio State University Co-Director, Thyroid Cancer Unit Arthur
Overview of Thyroid Nodules and Their Management Matthew D. Ringel, M.D. Professor of Medicine Divisions of Endocrinology and Oncology, The Ohio State University Co-Director, Thyroid Cancer Unit Arthur
Iodine 131 thyroid Therapy. Sara G. Johnson, MBA, CNMT, NCT President SNMMI-TS VA Healthcare System San Diego
 Iodine 131 thyroid Therapy Sara G. Johnson, MBA, CNMT, NCT President SNMMI-TS VA Healthcare System San Diego OBJECTIVES Describe the basics of thyroid gland anatomy and physiology Outline the disease process
Iodine 131 thyroid Therapy Sara G. Johnson, MBA, CNMT, NCT President SNMMI-TS VA Healthcare System San Diego OBJECTIVES Describe the basics of thyroid gland anatomy and physiology Outline the disease process
An Approach to: Thyroid Function Tests. Rinkoo Dalan Consultant Department of Endocrinology Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 An Approach to: Thyroid Function Tests Rinkoo Dalan Consultant Department of Endocrinology Tan Tock Seng Hospital Regulation of Thyroid axis Hypothalamus TRH T3,T4 ---- TRH Median Eminence (base of brain)
An Approach to: Thyroid Function Tests Rinkoo Dalan Consultant Department of Endocrinology Tan Tock Seng Hospital Regulation of Thyroid axis Hypothalamus TRH T3,T4 ---- TRH Median Eminence (base of brain)
Approach to Thyroid Nodules
 Approach to Thyroid Nodules Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC Twitter: @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Approach to Thyroid Nodules Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC Twitter: @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Non Thyroid Surgery. In patients with Thyroid disorders
 Non Thyroid Surgery In patients with Thyroid disorders The Thyroid disease problem. Is Thyroid disease a problem with anaesthetic? Why worry? The Physiology The evidence. A pragmatic approach From: The
Non Thyroid Surgery In patients with Thyroid disorders The Thyroid disease problem. Is Thyroid disease a problem with anaesthetic? Why worry? The Physiology The evidence. A pragmatic approach From: The
THYROID CANCER IN CHILDREN. Humberto Lugo-Vicente MD FACS FAAP Professor Pediatric Surgery UPR School of Medicine
 THYROID CANCER IN CHILDREN Humberto Lugo-Vicente MD FACS FAAP Professor Pediatric Surgery UPR School of Medicine Thyroid nodules Rare Female predominance 4-fold as likely to be malignant Hx Radiation exposure?
THYROID CANCER IN CHILDREN Humberto Lugo-Vicente MD FACS FAAP Professor Pediatric Surgery UPR School of Medicine Thyroid nodules Rare Female predominance 4-fold as likely to be malignant Hx Radiation exposure?
None. Thyroid Potpourri for the Primary Care Physician. Evaluating Thyroid Function. Disclosures. Learning Objectives
 Thyroid Potpourri for the Primary Care Physician Ramya Vedula DO, MPH, ECNU Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Princeton Medical Group Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson
Thyroid Potpourri for the Primary Care Physician Ramya Vedula DO, MPH, ECNU Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Princeton Medical Group Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson
Amiodarone Induced Thyrotoxicosis Treatment? (AIT)
 Amiodarone Induced Thyrotoxicosis Treatment? (AIT) Presentation of a Case Report Annelies Tonnelier Brigitte Velkeniers 14-12-2013 1 1. Background 1. Case report 2. Investigations 3. Diagnosis 4. Treatment
Amiodarone Induced Thyrotoxicosis Treatment? (AIT) Presentation of a Case Report Annelies Tonnelier Brigitte Velkeniers 14-12-2013 1 1. Background 1. Case report 2. Investigations 3. Diagnosis 4. Treatment
Mastering Thyroid Disorders. Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine
 Mastering Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine Cases 68 yr old female with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04, normal free T4 79
Mastering Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine Cases 68 yr old female with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04, normal free T4 79
THYROID AWARENESS. By: Karen Carbone. January is thyroid awareness month. At least 30 million Americans
 THYROID AWARENESS By: Karen Carbone January is thyroid awareness month. At least 30 million Americans have a thyroid disorder and half-15 million-are silent sufferers who are undiagnosed, according to
THYROID AWARENESS By: Karen Carbone January is thyroid awareness month. At least 30 million Americans have a thyroid disorder and half-15 million-are silent sufferers who are undiagnosed, according to
DRUGS. 4- Two molecules of DIT combine within the thyroglobulinto form L-thyroxine (T4)' One molecule of MIT & one molecule of DIT combine to form T3
 THYROID HORMONEs & ANTITHYROID The thyroid secretes 2 types of hormones: DRUGS 1- Iodine containing amino acids (are important for growth, development and metabolism) and these are: triodothyronine, tetraiodothyronine,(
THYROID HORMONEs & ANTITHYROID The thyroid secretes 2 types of hormones: DRUGS 1- Iodine containing amino acids (are important for growth, development and metabolism) and these are: triodothyronine, tetraiodothyronine,(
25/10/56. Hypothyroidism Myxedema in adults Cretinism congenital deficiency of thyroid hormone Hashimoto thyroiditis. Simple goiter (nontoxic goiter)
 THERAPEUTIC USES OF THYROID HORMONE Supeecha Wittayalertpunya Wannarasmi Ketchart Nov 2013 Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) Grave s disease (diffuse toxic goiter) Toxic uninodular & Toxic multinodular
THERAPEUTIC USES OF THYROID HORMONE Supeecha Wittayalertpunya Wannarasmi Ketchart Nov 2013 Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) Grave s disease (diffuse toxic goiter) Toxic uninodular & Toxic multinodular
HYPOTHYROIDISM AND HYPERTHYROIDISM
 HYPOTHYROIDISM AND HYPERTHYROIDISM SHAHIDA PERVEEN, AMBREEN Post RN BSCN Semester II FACULTY SIR RAJA April 13, 016 Objectives: State the functions of thyroid hormone. Understand the pathologic mechanism
HYPOTHYROIDISM AND HYPERTHYROIDISM SHAHIDA PERVEEN, AMBREEN Post RN BSCN Semester II FACULTY SIR RAJA April 13, 016 Objectives: State the functions of thyroid hormone. Understand the pathologic mechanism
Graves Disease. What is Graves disease?
 Graves Disease What is Graves disease? The thyroid gland s production of thyroid hormones (T 3 and T 4 ) is triggered by thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), which is made by the pituitary gland. Graves disease,
Graves Disease What is Graves disease? The thyroid gland s production of thyroid hormones (T 3 and T 4 ) is triggered by thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), which is made by the pituitary gland. Graves disease,
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Hyperthyroidism
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyperthyroidism Purpose of Guideline The management and referral criteria of patients with newly diagnosed hyperthyroidism. Background Hyperthyroidism
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyperthyroidism Purpose of Guideline The management and referral criteria of patients with newly diagnosed hyperthyroidism. Background Hyperthyroidism
5/3/2017. Ahn et al N Engl J Med 2014; 371
 Alan Failor, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition University of Washington April 20, 2017 No disclosures to report 1. Appropriately evaluate s in adult
Alan Failor, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition University of Washington April 20, 2017 No disclosures to report 1. Appropriately evaluate s in adult
Managing thyrotoxicosis in the acute medical setting
 44 Review Article Managing thyrotoxicosis in the acute medical setting C Napier MBBS MRCP (UK) Endocrine Unit, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Queen Victoria Road, Newcastle Upon Tyne, NE1 4LP UK Email: c.napier2@newcastle.
44 Review Article Managing thyrotoxicosis in the acute medical setting C Napier MBBS MRCP (UK) Endocrine Unit, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Queen Victoria Road, Newcastle Upon Tyne, NE1 4LP UK Email: c.napier2@newcastle.
THYROID DISEASES. CASE BASED WORKSHOP Z. Henry He, MD, PhD. Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard Medical School
 THYROID DISEASES CASE BASED WORKSHOP Z. Henry He, MD, PhD Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard Medical School DISCLOSURE I have no relevant financial disclosure OBJECTIVES
THYROID DISEASES CASE BASED WORKSHOP Z. Henry He, MD, PhD Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard Medical School DISCLOSURE I have no relevant financial disclosure OBJECTIVES
Thyroid Disorders. January 2019
 Thyroid Disorders January 2019 What is the Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland inside the neck, located in front of the trachea (windpipe) and below the larynx (voicebox). It produces
Thyroid Disorders January 2019 What is the Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland inside the neck, located in front of the trachea (windpipe) and below the larynx (voicebox). It produces
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACC. See Adrenal cortical carcinoma. Acromegaly and the pituitary gland, 551 Acute suppurative thyroiditis, 405, 406 Addison, Thomas and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACC. See Adrenal cortical carcinoma. Acromegaly and the pituitary gland, 551 Acute suppurative thyroiditis, 405, 406 Addison, Thomas and
Graves Disease in Pediatrics
 Graves Disease in Pediatrics Graves disease is a common cause of an overactive thyroid. It occurs in about 1 in 5000 children and teens. It occurs more often in females than males. This booklet is designed
Graves Disease in Pediatrics Graves disease is a common cause of an overactive thyroid. It occurs in about 1 in 5000 children and teens. It occurs more often in females than males. This booklet is designed
HYPO- AND HYPERTHYROIDISM. Esztella Mikolás MD Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Medicine
 HYPO- AND HYPERTHYROIDISM Esztella Mikolás MD Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Medicine Anatomy https://healthjade.com Histology http://www.proteinatlas.org Thyroxin synthesis and excretion Häggström,
HYPO- AND HYPERTHYROIDISM Esztella Mikolás MD Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Medicine Anatomy https://healthjade.com Histology http://www.proteinatlas.org Thyroxin synthesis and excretion Häggström,
Hyperthyroidism. concepts. Graves Disease. Etiology 4/22/12
 concepts Hyperthyroidism Dr. B. Paudel Thyroid overactivity F:M = 5:1 2.5% of all females at sometimes; get affected 20-40 years: peak 90% of cases are intrinsic thyroid disease, pituitary causes extremely
concepts Hyperthyroidism Dr. B. Paudel Thyroid overactivity F:M = 5:1 2.5% of all females at sometimes; get affected 20-40 years: peak 90% of cases are intrinsic thyroid disease, pituitary causes extremely
Common Causes of Hypothyroidism
 Common Causes of Hypothyroidism Autoimmune thyroidi4s Surgical removal of thyroid gland Medica4on Therapy Iodine and iodine containing medica4ons Neck radia4on Post Partum thyroidi4s Prevalence of Hypothyroidism
Common Causes of Hypothyroidism Autoimmune thyroidi4s Surgical removal of thyroid gland Medica4on Therapy Iodine and iodine containing medica4ons Neck radia4on Post Partum thyroidi4s Prevalence of Hypothyroidism
HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY
 HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY In contrast to the hormones of the anterior lobe of the pituitary, those of the posterior lobe, vasopressin and oxytocin, are not
HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY In contrast to the hormones of the anterior lobe of the pituitary, those of the posterior lobe, vasopressin and oxytocin, are not
The Use of Iodine as First Line Therapy in Graves' Disease Complicated with Neutropenia at First Presentation in a Paediatric Patient
 British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(2): 324-328, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Use of Iodine as First Line Therapy in Graves' Disease Complicated with Neutropenia
British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(2): 324-328, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Use of Iodine as First Line Therapy in Graves' Disease Complicated with Neutropenia
Thyroid in the elderly. Akbar Soltani M.D. Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center (EMRC) Shariati Hospital
 Thyroid in the elderly Akbar Soltani M.D. Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center (EMRC) Shariati Hospital soltania@tuma.ac.ir Case 1 A 79 year old female is seen because of a 6 month history of fatigue,
Thyroid in the elderly Akbar Soltani M.D. Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center (EMRC) Shariati Hospital soltania@tuma.ac.ir Case 1 A 79 year old female is seen because of a 6 month history of fatigue,
Grave s autoimmune Graves and Hashimotos: antithyroglobulin and antimicrosomal antibodies T3 X 10d should decrease TSH 50%
 Vesalius SCALpel : Thyroid (see also: head and neck folios) Anatomic lingual thyroid most common ectopic location normal thyroid tissue patients may have no thyroid in neck manifest as teenager, may enlarge
Vesalius SCALpel : Thyroid (see also: head and neck folios) Anatomic lingual thyroid most common ectopic location normal thyroid tissue patients may have no thyroid in neck manifest as teenager, may enlarge
THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY
 THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY https://www.wddty.com/magazine/2016/june/depression-its-not-your-brain-its-your-thyroid.html Grand Rounds December 5, 2018 Maria Kolojeski, DO (PGY3) REVIEW OF THYROID HORMONES
THYROID DISEASE IN PREGNANCY https://www.wddty.com/magazine/2016/june/depression-its-not-your-brain-its-your-thyroid.html Grand Rounds December 5, 2018 Maria Kolojeski, DO (PGY3) REVIEW OF THYROID HORMONES
THE THYROID BOOK. Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems
 THE THYROID BOOK Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems Trouble with Your Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland in your neck that plays a big role in how your body functions. It impacts
THE THYROID BOOK Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems Trouble with Your Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland in your neck that plays a big role in how your body functions. It impacts
B-Resistance to the action of hormones, Hormone resistance characterized by receptor mediated, postreceptor.
 Disorders of the endocrine system 38 Disorders of endocrine system mainly are caused by: A-Deficiency or an excess of a single hormone or several hormones: - deficiency :can be congenital or acquired.
Disorders of the endocrine system 38 Disorders of endocrine system mainly are caused by: A-Deficiency or an excess of a single hormone or several hormones: - deficiency :can be congenital or acquired.
2014 NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) CPT CODE(S): 84436, 84439, 84443, THYROID TESTING DESCRIPTION
 017.50-017.56 Tuberculosis of the thyroid gland 183.0 Malignant neoplasm of ovary 193 Malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland 194.8 Malignant neoplasm of other endocrine glands and related structures 198.89
017.50-017.56 Tuberculosis of the thyroid gland 183.0 Malignant neoplasm of ovary 193 Malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland 194.8 Malignant neoplasm of other endocrine glands and related structures 198.89
Tapazole Methimazole Tablets, USP DESCRIPTION
 Tapazole Methimazole Tablets, USP DESCRIPTION TAPAZOLE (Methimazole Tablets, USP) (1-methylimidazole-2-thiol) is a white, crystalline substance that is freely soluble in water. It differs chemically from
Tapazole Methimazole Tablets, USP DESCRIPTION TAPAZOLE (Methimazole Tablets, USP) (1-methylimidazole-2-thiol) is a white, crystalline substance that is freely soluble in water. It differs chemically from
Oh, I get it, the TSH goes up and down
 Evaluation and Management of the Thyroid Nodule Oh, I get it, the TSH goes up and down UCSF Head and Neck Conference October 24, 2008 Peter A. Singer, M.D. Professor and Chief Clinical Endocrinology University
Evaluation and Management of the Thyroid Nodule Oh, I get it, the TSH goes up and down UCSF Head and Neck Conference October 24, 2008 Peter A. Singer, M.D. Professor and Chief Clinical Endocrinology University
Management of Common Thyroid Disorders
 Management of Common Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine No Disclosures Cases 68 yr old woman with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04,
Management of Common Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine No Disclosures Cases 68 yr old woman with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1.
Thyroid Storm: Uncommon Presentation. Noora M. Butti, MBBcH*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 3, September 2014 Thyroid Storm: Uncommon Presentation Noora M. Butti, MBBcH* Thyroid storm could lead to mortality; it is rare and characterized by severe clinical
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 3, September 2014 Thyroid Storm: Uncommon Presentation Noora M. Butti, MBBcH* Thyroid storm could lead to mortality; it is rare and characterized by severe clinical
Management of Common Thyroid Disorders
 Cases Management of Common Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine No Disclosures 68 yr old female with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04,
Cases Management of Common Thyroid Disorders Douglas C. Bauer, MD UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine No Disclosures 68 yr old female with new atrial fibrillation and no other findings except TSH=0.04,
