Clinical pharmacology of sibutramine hydrochloride (BTS 54524), a new antidepressant, in healthy volunteers
|
|
|
- Ethel Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1988), 26, Clinical pharmacology of sibutramine hydrochloride (BTS 54524), a new antidepressant, in healthy volunteers D. J. KING & NOELEEN DEVANEY Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology, The Whitla Medical Building, The Queen's University of Belfast, Belfast BT9 7BL The cardiovascular, anticholinergic and central effects of single doses of 30, 45 and 60 mg of sibutramine hydrochloride (BTS 54524), a new potential antidepressant, were compared with amitriptyline (50 mg) and placebo given at weekly intervals in a randomised design to six healthy male volunteers. Sibutramine was associated with increases in both supine heart rate and systolic blood pressure at 1, 2 and 6 h after 60 mg (P < 0.05). Amitriptyline caused a significant 50-60% decrease in salivation compared with placebo at 2 and 6 h but there were no changes with sibutramine. No significant changes in pupil size were detected with either drug. Visual analogue rating scales (VARS) revealed significant drowsiness with amitriptyline but neither sedative nor stimulant effects with sibutramine. Impairments of simple auditory and visual reaction times, visual two-choice reaction time, finger tapping and trail making, measured using an automated test battery, occurred with amitriptyline compared with sibutramine. If sibutramine proves to be an effective antidepressant it should be devoid of anticholinergic or central depressant effects. Chronic dosage studies are indicated to evaluate the clinical significance of its cardiovascular effects. Keywords sibutramine cardiovascular anticholinergic and CNS effects volunteers Introduction Preclinical studies have shown that sibutramine hydrochloride (BTS 54524) (N-1-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclobutyl]-3-methylbutyl-N, N-dimethylamine hydrochloride monohydrate) has properties suggestive of a potent and rapidly acting potentially stimulant antidepressant drug which is free from anticholinergic and cardiovascular side-effects. It is a monoamine reuptake inhibitor active against noradrenaline and serotonin and to a lesser extent dopamine, and rapidly down-regulates both,b-adrenergic receptor binding as well as the noradrenaline-stimulated adenylate cyclase system (Buckett etal., 1987a, b). The present phase 1 study was a double-blind comparison of the cardiovascular, anticholinergic and central effects of three single doses of sibutramine (30 mg, 45 mg and 60 mg) with those of a standard antidepressant, amitriptyline (50 mg) and placebo. Methods Subjects and study design Six healthy male volunteers, aged (mean 22) years weighing (mean 72.0) kg who had given informed written consent, received single doses of 30 mg, 45 mg and 60 mg of sibutramine in ascending order as well as placebo and amitriptyline 50 mg at intervals of 1 week. Amitriptyline and placebo were given in random order on randomised occasions but full randomisation was not possible since this was the first time sibutramine was being given to man at these Correspondence: Dr D. J. King, Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology, The Whitla Medical Building, The Queen's University of Belfast, 97, Lisburn Road, Belfast BT9 7BL, Northern Ireland 607
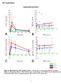
2 608 D. J. King & Noeleen Devaney dose levels. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Queen's University of Belfast. Exclusion criteria were as follows: history of cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic or renal disease; allergy or hypersensitivity to any drug; psychiatric or neurological disease; drug abuse; or drug ingestion 14 days prior to the study. The volunteers were fasted overnight from h, permitted only one cup of tea or coffee before the study and drinks containing caffeine were not permitted until after completion of the tests. No alcohol was permitted from h on the day before until h on the day after each study day. Volunteers were screened for hepatitis B (Australia antigen) and routine haematological and biochemical screening were performed at baseline and 24 h after drug ingestion. After baseline assessments the drugs were taken at h and assessments of cardiovascular, anticholinergic and central effects measured over the following 24 h. Assessment procedures Supine and standing heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) were recorded by an automated device after 8 min supine rest at baseline and at 1, 2 and 6 h. A 12-lead ECG was carried out at baseline and at 3 h. Salivary secretion was measured over 2 min using a dental roll technique (Turner, 1980) and pupil size using a pupilometer disc supplied by the Boots Company plc. Both measures were carried out at baseline and at 1, 2 and 6 h. Sixteen visual analogue rating scales (VARS) (Norris, 1971) for a variety of moods and subjective feelings were administered at 1, 2, 3, 6 and 24 h. In addition any subjective adverse effects were recorded at these times. Psychomotor effects were measured using an automated psychological assessment system (APAS) for use with an Apple IIe microcomputer devised by Elithorn and Lavander (Elithorn et al., 1982). These assessments included finger tapping, simple auditory and visual reaction times, two visual two-choice reaction time tests, trail making, trigram (recognition of 3 letter words and non-words), Necker cube and the perceptual maze test (Smith et al., 1978). The latter test yields four measures: latency, motor time, total number of correct mazes and processing time. A total of 25 measures are produced by the Elithorn APAS. Each subject had two pre-study practice sessions on the complete test battery, which took min to administer. This APAS battery was then carried out between 3.5 and 4.5 h after drug ingestion on each study day. Statistical analysis HR, BP and pupil size data were analysed using an analysis of variance of repeated measures and where a significant interaction between treatment and time was detected (P < 0.10) an analysis to compare treatments was performed at each time using one way analysis of variance and the Newman Keuls multiple range test (statistical significance: P < 0.05) (Arnitage, 1971). Salivary flow, VARS and psychomotor data were analysed by the Friedman two-way non-parametric analysis of variance (ANOVA) (statistical significance: P < 0.05) followed by the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test (statistical significance: P < 0.01). Results Cardiovascular effects Sibutramine was associated with dose-dependent increases in both supine and standing HR which were statistically significantly different from placebo for supine HR at 6 h after 45 mg, and at 1, 2 and 6 h after 60 mg (P < 0.05). Supine systolic BP was significantly elevated by the 60 mg dose at all times and by 30 mg at 2 h, compared with placebo. The effects of amitriptyline were not significantly different from placebo but the effects on supine HR and systolic BP were significantly different from those of sibutramine (60 mg) at all times after baseline. Anticholinergic effects Salivary flow was analysed by percentage change because of wide individual variations in baseline values. Highly significant decreases in salivation occurred with amitriptyline compared with placebo at 2 and 6 h (P < 0.005, Wilcoxon) but no changes with any of the doses of sibutramine (Figure 1). There were no statistically significant differences in pupil diameter with either amitriptyline or any of the doses of sibutramine compared with placebo. Central effects Three of the 16 Norris VARS which measure the main factors identified by Bond & Lader (1974) and shown to be sensitive to drug effects, viz. alertness, contentedness and calmness were analysed. Highly significant sedative effects were found with amitriptyline compared with placebo at 2 and 3 h on the alert-drowsy scale (P < 0.005). No other significant differences were found nor any subjective stimulant effects detected. The
3 Short report 609 Discussion,, S ECU30 Q-20 tio1/6 o > -30- I Time (h) Figure 1 Effects of amitriptyline (50 mg, ) and sibutramine (60 mg, - -) on salivary flow compared with placebo (----), expressed as percentage change from baseline (mean ± s.d.). 30 mg and 45 mg doses of sibutramine also did not differ from placebo and have been excluded in the interests of clarity. * P < from placebo (Wilcoxon). subjective adverse effects recorded all six volunteers reporting drowsiness (but not dry mouth) with amitriptyline. One volunteer complained of dry mouth with each dose of sibutramine. Drowsiness was reported by one volunteer after 30 mg sibutramine and by another after 45 mg, while one volunteer complained of a 'nervous feeling' after 45 mg sibutramine and another of 'tension' after 60 mg. In spite of wide inter-individual variations in response in all of the APAS tests, a general trend towards impairment was observed for amitriptyline but for none of the doses of sibutramine. The Friedman ANOVA was statistically significant for 7 of the 25 tests. These were auditory, visual and visual two-choice reaction times on the left-side and finger tapping and three trail-making tests (Table 1). The majority of these were due to significant differences in function with amitriptyline compared with one of the doses of sibutramine. No statistically significant differences were found with the tests with a larger cognitive component (perceptual maze or trigram). With the perceptual maze test there was no consistent change in the number of mazes correctly completed, mean search time was increased, and there was a mean 17.5% fall in processing speed (nodes/second) with amitriptyline compared with placebo. The clinical pharmacological profile of sibutramine was quite different from amitriptyline. Sibutramine was associated with small but statistically significant increases in supine HR and systolic BP, while amitriptyline caused a (non-significant) rise in standing HR in association with falls in both supine and standing systolic and diastolic BP. Amitriptyline was associated with an expected 30% decrease in salivation compared with a 30% increase with placebo (Longmore et al., 1985; Szabadi & Bradshaw, 1986) but there were no consistent changes with sibutramine. None of the drugs significantly altered pupil size. Amitriptyline has variously been reported to cause mydriasis, miosis and no change in resting pupil size (Szabadi & Bradshaw, 1986) the effect appearing to depend on the interaction of muscarinic, a-adrenoceptor blocking effects and the level of arousal of the subject. The lack of statistical significance of our findings with sibutramine might have been due to the relative insensitivity of our method of measurement. Neither subjective, sedative or stimulant effects of sibutramine were detected with the VARS for alertness, contentedness or calmness. Amitriptyline on the other hand was invariably associated with drowsiness and with marked and highly significant changes on the VARS alertness scale at 2 and 3 h. Both subjective and psychomotor effects of single doses of amitriptyline have been reported to persist from 90 to 300 min after dosing (Bye et al., 1978) and the peak plasma concentration occurs at 235 min (Warrington et al., 1984). Our psychomotor tests were performed between 210 and 270 min after dosing. The APAS tests which proved sensitive to acute drug effects were finger tapping, trail making and reaction times on the non-dominant side. Only one of these showed a significant placebo-drug difference (effect of amitriptyline on finger tapping), the remaining differences being between amitriptyline and one of the doses of sibutramine. This was partly because the small number of subjects reduced the statistical power of this preliminary study in which the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test was not able to evaluate differences in a number of the tests because of tied ranks. However the data suggest that the effects of sibutramine may be in the opposite direction to amitriptyline, i.e. towards improvement in psychomotor performance (Table 1). Stimulant effects on performance, however, are often more difficult to demonstrate than impairments (Loke & Meliska, 1984).
4 610 D. J. King & Noeleen Devaney Table 1 Effects of sibutramine and amitriptyline on psychomotor performance (mean ± s.d.) Sibutramine Placebo Amitriptyline 30 mg 45 mg 60 mg Reaction times (ms) Auditory (L) ± ± ± ± ± 14.64t Visual (L) ± ± ± 50.51t ± 18.41t ± Visual two-choice (L) ± ± ± ± 57.41t ± 49.23t Finger tapping (number s- 1) (Alternating L/R) 4.33 ± ± 0.69* 4.53 ± ± ± 0.73t Trail making (s/digit) Digits (1) 1.6 ± ± ± ± 0.28A 1.38 ± 0.26A Digits (2) 1.47 ± ± ± 0.16t 1.32 ± 0.23t 1.40 ± 0.20 Altemnating digits/letters 1.82 ± ± ± ± ± 0.14t * different from placebo P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon); t different from amitriptyline P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon); A different from sibutramine 30 mg P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon). The effects of practice were controlled by two pre-study sessions on the APAS which a previous, unpublished study with six volunteers suggested was adequate to reach a plateau of performance in all the tests, except for the perceptual maze. McClelland (1987) has shown that four practice sessions are adequate for most psychomotor function tests. Our inability to use a fully balanced design may, however, have reduced the sensitivity of our APAS tests due to continued learning effects particularly with the perceptual maze test. In conclusion, single doses of sibutramine had sympathomimetic effects on the cardiovascular system but lacked clinically significant anticholinergic effects and was devoid of sedative effects. However, the cardiovascular effects may limit the doses that can be safely used in clinical trials and further studies are also required to elicit possible psychostimulant properties. We thank the Boots Co plc, for the supply of the materials for this study and Dr R. D. Wynne, in particular, for his help. We are also grateful to Mr C. Patterson (Statistician, Department of Community Medicine and Medical Statistics, Queen's University of Belfast) for advice and Dr G. Henry (Senior Registrar in Psychiatry) and Dr T. Wright (Computer Centre, Queen's University of Belfast) for their help with the data analysis. References Armitage, P. (1971). Statistical methods in medical research, pp Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications. Bond, A. & Lader, M. (1974). The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br. J. med. Psychol., 47, Buckett, W. R., Hopcroft, R. H., Luscombe, G. P. & Thomas, P. C. (1987a). BTS 54524, a monoamine uptake inhibitor exhibiting potent actions in models predictive of potential antidepressant activity. Br. J. Pharmac., 90, 94P. Buckett, W. R., Luscombe, G. P. & Thomas, P. C. (1987b). The putative antidepressant BTS rapidly and potently down-regulates cortical 1- adrenoceptors in the rat. Br. J. Pharmac., 90, 261P. Bye, C., Clubley, M. & Peck, A. W. (1978). Drowsiness, impaired performance and tricyclic antidepressant drugs. Br. J. clin. Pharmac., 6, Elithorn, A., Mornington, S. & Stavrou, A. (1982). Automated psychological testing: some principles and practice. Int. J. Man-Machine Studies, 17, Loke, W. H. & Meliska, C. J. (1984). Effects of caffeine use and ingestion on a protracted visual vigilance task. Psychopharmacology, 84, Longmore, J., Szabadi, E. & Bradshaw, C. M. (1985). Comparison of the effects of binodaline and amitriptyline on peripheral autonomic functions in healthy volunteers. Br. J. clin. Pharmac., 19, McClelland, G. R. (1987). The effects of practice on measures of performance. Human Psychopharmacology, 2, Norris, H. (1971). The action of sedatives on brain stem oculomotor systems in man. Neuropharmacology, 10, Smith, J., Jones, D. & Elithorn, A. (1978). The Perceptual Maze Test. London: Medical Research Council. Szabadi, E. & Bradshaw, C. M. (1986). Antidepressant drugs and the autonomic nervous system. In The biology of depression, ed. Deakin, J. F. W., pp.
5 Short report London: Gaskell Psychiatry Series, The Royal College of Psychiatrists. Turner, P. (1980). Tests of autonomic function in assessing centrally acting drugs. Br. J. clin. Pharmac., 10, Warrington, S. J., Ankier, S. I. & Turner, P. (1984). An evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline. Br. J. clin. Pharmac., 18, (Received 5 April 1988, accepted 21 July 1988)
pupillary light reflex
 Br J clin Pharmac 1995; 39: 251-255 Effects of reboxetine and desipramine on the kinetics of the pupillary light reflex N. THEOFILOPOULOS, G. McDADE, E. SZABADI' & C. M. BRADSHAW Department of Psychiatry,
Br J clin Pharmac 1995; 39: 251-255 Effects of reboxetine and desipramine on the kinetics of the pupillary light reflex N. THEOFILOPOULOS, G. McDADE, E. SZABADI' & C. M. BRADSHAW Department of Psychiatry,
AND PROPRANOLOL IN HYPERTHYROIDISM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (78),,-7 COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF ATENOLOL AND PROPRANOLOL IN HYPERTHYROIDISM D.G. McDEVITT Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology, The Queen's University, Belfast, Northern Ireland
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (78),,-7 COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF ATENOLOL AND PROPRANOLOL IN HYPERTHYROIDISM D.G. McDEVITT Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology, The Queen's University, Belfast, Northern Ireland
DYNAMIC INTERACTION OF NOMIFENSINE
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1977), 4, 147S-15 1S DYNAMIC INTERACTION OF NOMIFENSINE WITH ALCOHOL K. TAEUBER Medical Department, Hoechst AG, Postfach 8 3 2, D-623 Frankfurt/Main 8 1 Nine healthy volunteers participated
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1977), 4, 147S-15 1S DYNAMIC INTERACTION OF NOMIFENSINE WITH ALCOHOL K. TAEUBER Medical Department, Hoechst AG, Postfach 8 3 2, D-623 Frankfurt/Main 8 1 Nine healthy volunteers participated
IMMEDIATE AND RESIDUAL EFFECTS IN MAN OF THE METABOLITES OF DIAZEPAM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1978), 6, 2-1 IMMEDIATE AND RESIDUAL EETS IN MAN O THE METABOLITES O DIAZEPAM ORAL H. LARKE & A.N. NIHOLSON Royal Air orce Institute of Aviation Medicine, arnborough, Hampshire I
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1978), 6, 2-1 IMMEDIATE AND RESIDUAL EETS IN MAN O THE METABOLITES O DIAZEPAM ORAL H. LARKE & A.N. NIHOLSON Royal Air orce Institute of Aviation Medicine, arnborough, Hampshire I
EFFECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE ON AUDITORY CORTICAL EVOKED POTENTIALS AND SUBJECTIVE THRESHOLDS
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 606-610 EFFECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE ON AUDITORY CORTICAL EVOKED POTENTIALS AND SUBJECTIVE THRESHOLDS H. G. HOUSTON, R. J. McCLELLAND AND P. B. C. FENWICK General anaesthetics are
Br. J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 606-610 EFFECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE ON AUDITORY CORTICAL EVOKED POTENTIALS AND SUBJECTIVE THRESHOLDS H. G. HOUSTON, R. J. McCLELLAND AND P. B. C. FENWICK General anaesthetics are
Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 137-142 Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prochlorperazine in healthy volunteers WENDY B. TAYLOR & D. N. BATEMAN Wolfson Unit of Clinical
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 137-142 Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prochlorperazine in healthy volunteers WENDY B. TAYLOR & D. N. BATEMAN Wolfson Unit of Clinical
CLINICAL TRIALS OF FLUVOXAMINE VS CHLORIMIPRAMINE WITH SINGLE AND THREE TIMES DAILY DOSING
 Br. J. cin. Pharmac. (1983), 15, 427S-431S CLINICAL TRIALS OF FLUVOXAMINE VS CHLORIMIPRAMINE WITH SINGLE AND THREE TIMES DAILY DOSING J.E. DE WILDE, C. MERTENS & J.S. WAKELIN' Psychiatrisch Ziekenhuis
Br. J. cin. Pharmac. (1983), 15, 427S-431S CLINICAL TRIALS OF FLUVOXAMINE VS CHLORIMIPRAMINE WITH SINGLE AND THREE TIMES DAILY DOSING J.E. DE WILDE, C. MERTENS & J.S. WAKELIN' Psychiatrisch Ziekenhuis
PRODUCT INFORMATION. SUDAFED Sinus 12 Hour Relief Tablets
 PRODUCT INFORMATION SUDAFED Sinus 12 Hour Relief Tablets NAME OF THE MEDICINE Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride CAS 2 Registry Number: 345-78-8 DESCRIPTION SUDAFED Sinus 12 Hour Relief prolonged-release tablets
PRODUCT INFORMATION SUDAFED Sinus 12 Hour Relief Tablets NAME OF THE MEDICINE Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride CAS 2 Registry Number: 345-78-8 DESCRIPTION SUDAFED Sinus 12 Hour Relief prolonged-release tablets
Pencil and paper tests- sensitivity to psychotropic drugs
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1984), 18, 15S-20S Pencil and paper tests- sensitivity to psychotropic drugs BARBARA M. STONE Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine, Farnborough, Hampshire 1 The literature
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1984), 18, 15S-20S Pencil and paper tests- sensitivity to psychotropic drugs BARBARA M. STONE Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine, Farnborough, Hampshire 1 The literature
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS
 DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Drugs Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 OTHER ANXIOLYTIC AGENTS/ A. Antidepressants Many antidepressants are effective in the treatment
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Drugs Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 OTHER ANXIOLYTIC AGENTS/ A. Antidepressants Many antidepressants are effective in the treatment
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET ACUPAN TM. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM White, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets (7 mm diameter) engraved APN on one face.
 1. PRODUCT NAME ACUPAN 30 mg tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg. For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
1. PRODUCT NAME ACUPAN 30 mg tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg. For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
CLOBAZAM AND TRIFLUBAZAM, ON SLEEP IN MAN
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1977), 4, 567-572 EFFECT OF THE 1,5-BENZODIAZEPINES, CLOBAZAM AND TRIFLUBAZAM, ON SLEEP IN MAN A.N. NICHOLSON, BARBARA M. STONE & CORAL H. CLARKE Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1977), 4, 567-572 EFFECT OF THE 1,5-BENZODIAZEPINES, CLOBAZAM AND TRIFLUBAZAM, ON SLEEP IN MAN A.N. NICHOLSON, BARBARA M. STONE & CORAL H. CLARKE Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation
TRAZODONE ENHANCES SLEEP IN SUBJECTIVE QUALITY BUT NOT IN OBJECTIVE DURATION
 Br. J. clin. Pharmnac. (1983), 16, 139-144 TRAZODONE ENHANCES SLEEP IN SUBJECTIVE QUALITY BUT NOT IN OBJECTIVE DURATION I. MONTGOMERY*, I. OSWALD, K. MORGAN & KIRSTINE ADAM University Department of Psychiatry,
Br. J. clin. Pharmnac. (1983), 16, 139-144 TRAZODONE ENHANCES SLEEP IN SUBJECTIVE QUALITY BUT NOT IN OBJECTIVE DURATION I. MONTGOMERY*, I. OSWALD, K. MORGAN & KIRSTINE ADAM University Department of Psychiatry,
Effect of acute and chronic oral administration of alfuzosin on baroreflex function and tremor in man
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1988), 25, 417-424 Effect of acute and chronic oral administration of alfuzosin on baroreflex function and tremor in man A. H. DEERING, J. G. RIDDELL, D. W. G. HARRON & R. G. SHANKS
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1988), 25, 417-424 Effect of acute and chronic oral administration of alfuzosin on baroreflex function and tremor in man A. H. DEERING, J. G. RIDDELL, D. W. G. HARRON & R. G. SHANKS
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 MUTUAL RECOGNITION PROCEDURE Page 1 of 5 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT, syrup 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of syrup contains 1 mg loratadine.
MUTUAL RECOGNITION PROCEDURE Page 1 of 5 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT, syrup 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of syrup contains 1 mg loratadine.
PERFORMANCE STUDIES WITH ANTIHISTAMINES
 Br. J. clin. Pharmnac. (1978), 6,1-5 PERFORMANCE STUDIES WITH ANTIHISTAMINES CORAL H. CLARKE & A.N. NICHOLSON Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine Farnborough, Hampshire 1 Effect of four antihistamines,
Br. J. clin. Pharmnac. (1978), 6,1-5 PERFORMANCE STUDIES WITH ANTIHISTAMINES CORAL H. CLARKE & A.N. NICHOLSON Royal Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine Farnborough, Hampshire 1 Effect of four antihistamines,
Application of Psychotropic Drugs in Primary Care
 Psychotropic Drugs Application of Psychotropic Drugs in Primary Care JMAJ 47(6): 253 258, 2004 Naoshi HORIKAWA Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract: The incidence
Psychotropic Drugs Application of Psychotropic Drugs in Primary Care JMAJ 47(6): 253 258, 2004 Naoshi HORIKAWA Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract: The incidence
Short-term difference in mood with sibutramine versus placebo in obese patients with and without depression
 Short-term difference in mood with sibutramine versus placebo in obese patients with and without depression RESEARCH ARTICLE Kristina Elfhag & Stephan Rössner Author for correspondence Karolinska University
Short-term difference in mood with sibutramine versus placebo in obese patients with and without depression RESEARCH ARTICLE Kristina Elfhag & Stephan Rössner Author for correspondence Karolinska University
Brief Report. Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived?
 Brief Report Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived? Delia C. Randall, BSc,*y Aparna Viswanath,* Punam Bharania,* Sarah M. Elsabagh, BSc,* David E.
Brief Report Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived? Delia C. Randall, BSc,*y Aparna Viswanath,* Punam Bharania,* Sarah M. Elsabagh, BSc,* David E.
EFFECTS OF ETHANOL ON PSYCHOMOTOR PERFORMANCE
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1987), 59, 961-965 EFFECTS OF ETHANOL ON PSYCHOMOTOR PERFORMANCE D. FAGAN, B. TIPLADY AND D. B. SCOTT Increasingly, psychomotor tests are being used to detect impairment of cerebral function
Br. J. Anaesth. (1987), 59, 961-965 EFFECTS OF ETHANOL ON PSYCHOMOTOR PERFORMANCE D. FAGAN, B. TIPLADY AND D. B. SCOTT Increasingly, psychomotor tests are being used to detect impairment of cerebral function
The study of drugs. Pharmacology
 The study of drugs Pharmacology Psychopharmacology The study of psychoactive drugs Psychoactive drugs Drugs that influence psychological processes mood emotion perception cognition behavior Psychoactive
The study of drugs Pharmacology Psychopharmacology The study of psychoactive drugs Psychoactive drugs Drugs that influence psychological processes mood emotion perception cognition behavior Psychoactive
auditory flutter fusion threshold (A.F.F.T.), is the auditory equivalent of the visual critical
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 30, 341-348. THE TIME COURSE OF ACTION OF SINGLE DOSES OF DIAZEPAM, CHLORPROMAZINE AND SOME BARBITURATES AS MEASURED BY AUDITORY FLUTTER FUSION AND VISUAL FLICKER FUSION
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 30, 341-348. THE TIME COURSE OF ACTION OF SINGLE DOSES OF DIAZEPAM, CHLORPROMAZINE AND SOME BARBITURATES AS MEASURED BY AUDITORY FLUTTER FUSION AND VISUAL FLICKER FUSION
Effects of oxazepam and lorazepam on implicit and explicit memory: evidence for possible influences of time course
 Psychopharmacology (1996) 128 : 139 149 Springer-Verlag 1996 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Sherry H. Stewart George F. Rioux John F. Connolly Sandra C. Dunphy Michael D. Teehan Effects of oxazepam and lorazepam
Psychopharmacology (1996) 128 : 139 149 Springer-Verlag 1996 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Sherry H. Stewart George F. Rioux John F. Connolly Sandra C. Dunphy Michael D. Teehan Effects of oxazepam and lorazepam
EFFECTS OF BENZODIAZEPINES ON SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1981), 11, 31S-3S EFFECTS OF BENZODIAZEPINES ON SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS Sleep Disorders and Research Center, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan The differential effects of short
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1981), 11, 31S-3S EFFECTS OF BENZODIAZEPINES ON SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS Sleep Disorders and Research Center, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan The differential effects of short
Elavil (amitriptyline)
 Generic name: Amitriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets; 10 mg/ml injection Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information
Generic name: Amitriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets; 10 mg/ml injection Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information
Doctors, Nurses, Pharmacists, Health Professionals Stockist of LadyCare & Mn8. LadyCare. GMC (General Medical Council) Registration Number:
 GMC (General Medical Council) Registration Number: 3586952 Doctors, Nurses, Pharmacists, Health Professionals Stockist of LadyCare & Mn8 I have been asked by LadyCare Lifetime Limited to submit my professional
GMC (General Medical Council) Registration Number: 3586952 Doctors, Nurses, Pharmacists, Health Professionals Stockist of LadyCare & Mn8 I have been asked by LadyCare Lifetime Limited to submit my professional
Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information
 Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard Adverse events should also
Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard Adverse events should also
Tianeptine Dependence: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Tianeptine Dependence: A Case Report Syed Nabil, Ng Chong Guan, Rusdi Abd Rashid Department of Psychological Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
CASE REPORT Tianeptine Dependence: A Case Report Syed Nabil, Ng Chong Guan, Rusdi Abd Rashid Department of Psychological Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Flecainide pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: the influence of urinary ph
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 20, 333-338 Flecainide pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: the influence of urinary ph A. JOHNSTON, S. WARRNGTON' & P. TURNER Department of Clinical Pharmacology, St Bartholomew's
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 20, 333-338 Flecainide pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: the influence of urinary ph A. JOHNSTON, S. WARRNGTON' & P. TURNER Department of Clinical Pharmacology, St Bartholomew's
by severe excercise, an accepted method for In addition, practolol had a proportionately larger effect on exc6rcise tachycardia than it had on
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 411-416 COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF PROPRANOLOL AND PRACTOLOL IN J.K. NELSON The Ulster Hospital, Dundonald, Belfast, N. Ireland HYPERTHYROIDISM D.G. McDEVITT Department of Therapeutics
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 411-416 COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF PROPRANOLOL AND PRACTOLOL IN J.K. NELSON The Ulster Hospital, Dundonald, Belfast, N. Ireland HYPERTHYROIDISM D.G. McDEVITT Department of Therapeutics
Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile
 Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile Posology and method of administration Elderly subjects: data do not suggest that the dose needs to be reduced in elderly subjects provided that the renal function
Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile Posology and method of administration Elderly subjects: data do not suggest that the dose needs to be reduced in elderly subjects provided that the renal function
tests of haematological, renal, hepatic and metabolic 'cheese reaction' with monoamine oxidase inhibitors
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1976), Supplement, 35-40 SCREENING PROCEDURES IN VOLUNTEERS AND PATIENTS P.J. TYRER University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Tremona Road, Southampton The chief object
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1976), Supplement, 35-40 SCREENING PROCEDURES IN VOLUNTEERS AND PATIENTS P.J. TYRER University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Tremona Road, Southampton The chief object
Effects of granisetron and haloperidol, alone and in
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1992), 34, 65-70 Effects of granisetron and haloperidol, alone and in combination, on psychometric performance and the EEG TERRY J. LEIGH, CHRISTOPHER G. G. LINK & GRAEME L. FELL
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1992), 34, 65-70 Effects of granisetron and haloperidol, alone and in combination, on psychometric performance and the EEG TERRY J. LEIGH, CHRISTOPHER G. G. LINK & GRAEME L. FELL
Post-Stroke Depression Primary Care Stroke Update: What s New in Best Practice Prevention & Care
 Post-Stroke Depression Primary Care Stroke Update: What s New in Best Practice Prevention & Care Maria Hussain MD FRCPC Dallas Seitz MD PhD(c) FRCPC Division of Geriatric Psychiatry, Queen s University
Post-Stroke Depression Primary Care Stroke Update: What s New in Best Practice Prevention & Care Maria Hussain MD FRCPC Dallas Seitz MD PhD(c) FRCPC Division of Geriatric Psychiatry, Queen s University
Optimal Use of Antidepressants: Focusing on SNRI, NDRI and SSRE
 Optimal Use of Antidepressants: Focusing on SNRI, NDRI and SSRE Chan-Hyung Kim, MD Severance Mental Health Hospital Institute of Behavioral Science in Medicine Diagnostic Criteria Pyramid Etiologic Pathophysiologic
Optimal Use of Antidepressants: Focusing on SNRI, NDRI and SSRE Chan-Hyung Kim, MD Severance Mental Health Hospital Institute of Behavioral Science in Medicine Diagnostic Criteria Pyramid Etiologic Pathophysiologic
Norpramin (desipramine)
 Generic name: Desipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Norpramin (desipramine)
Generic name: Desipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Norpramin (desipramine)
SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate)
 SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate) S N CH 3 Pizotifen. COOH CH OH CH 2 COOH MALATE DESCRIPTION Pizotifen is a cycloheptathiophene derivative structurally related to cyproheptadine and the tricyclic antidepressants.
SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate) S N CH 3 Pizotifen. COOH CH OH CH 2 COOH MALATE DESCRIPTION Pizotifen is a cycloheptathiophene derivative structurally related to cyproheptadine and the tricyclic antidepressants.
Cognitive deficits associated with chronic hepatic encephalopathy and their response to levodopa
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychliatry, 1975, 38, 794-798 Cognitive deficits associated with chronic hepatic encephalopathy and their response to levodopa ALICK ELITHORN', MICHAEL LUNZER,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychliatry, 1975, 38, 794-798 Cognitive deficits associated with chronic hepatic encephalopathy and their response to levodopa ALICK ELITHORN', MICHAEL LUNZER,
Adrafinil: A Novel Vigilance Promoting Agent
 Adrafinil: A Novel Vigilance Promoting Agent Norton W. Milgram, Heather Callahan, and Christina Siwak Division of Life Sciences, University of Toronto at Scarborough, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Introduction
Adrafinil: A Novel Vigilance Promoting Agent Norton W. Milgram, Heather Callahan, and Christina Siwak Division of Life Sciences, University of Toronto at Scarborough, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Introduction
A COMPARISON OF BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE WITH DEXAMPHETAMINE AND AMITRIPTYLINE IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 7, 469-478 A COMPARISON OF BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE WITH DEXAMPHETAMINE AND AMITRIPTYLINE IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS A.W. PECK, C.E. BYE, M. CLUBLEY, T. HENSON & C. RIDDINGTON Department
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 7, 469-478 A COMPARISON OF BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE WITH DEXAMPHETAMINE AND AMITRIPTYLINE IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS A.W. PECK, C.E. BYE, M. CLUBLEY, T. HENSON & C. RIDDINGTON Department
Guilt Suicidality. Depression Co-Occurs with Medical Illness The rate of major depression among those with medical illness is significant.
 1-800-PSYCH If you are obsessive-compulsive, dial 1 repeatedly If you are paranoid-delusional, dial 2 and wait, your call is being traced If you are schizophrenic, a little voice will tell you what number
1-800-PSYCH If you are obsessive-compulsive, dial 1 repeatedly If you are paranoid-delusional, dial 2 and wait, your call is being traced If you are schizophrenic, a little voice will tell you what number
Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych
 Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych A. Heterocyclic antidepressants: (tricyclic and tetracyclic ), e.g.amitryptaline,imipramine. B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors(m.a.o.i), e.g.phenelzine.
Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych A. Heterocyclic antidepressants: (tricyclic and tetracyclic ), e.g.amitryptaline,imipramine. B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors(m.a.o.i), e.g.phenelzine.
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1. PRODUCT NAME Sudomyl, Tablet, 60 mg 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Name and strength of the active substance Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride 60mg Excipient(s) with known effect For the full
1. PRODUCT NAME Sudomyl, Tablet, 60 mg 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Name and strength of the active substance Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride 60mg Excipient(s) with known effect For the full
The respiratory effects of oral ethyl loflazepate in volunteers
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 183-187 The respiratory effects of oral ethyl loflazepate in volunteers E. J. AZACKERLEY, N. P. C. RANDALL, B. J. PLEUVRY, I. BRADBROOK1 & G. E. MAWER Departments of Anaesthesia
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 183-187 The respiratory effects of oral ethyl loflazepate in volunteers E. J. AZACKERLEY, N. P. C. RANDALL, B. J. PLEUVRY, I. BRADBROOK1 & G. E. MAWER Departments of Anaesthesia
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve 50 mg/ml solution for injection for dogs (AT, BE, BG, CY, CZ, DE, EL, ES, HR, HU, IE, IT, LU, NL, PT, RO,
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve 50 mg/ml solution for injection for dogs (AT, BE, BG, CY, CZ, DE, EL, ES, HR, HU, IE, IT, LU, NL, PT, RO,
Novel Psychoactive Substances: Overview and Impact on Mental Health
 Novel Psychoactive Substances: Overview and Impact on Mental Health MAUREEN SWEENEY CNP ASSOCIATE MEDICAL DIRECTOR FRONTLINE SERVICE JULIE DAVIDOV CNP FRONTLINE SERVICE Disclosures Neither provider has
Novel Psychoactive Substances: Overview and Impact on Mental Health MAUREEN SWEENEY CNP ASSOCIATE MEDICAL DIRECTOR FRONTLINE SERVICE JULIE DAVIDOV CNP FRONTLINE SERVICE Disclosures Neither provider has
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
Difference in Blood Alcohol Levels Following Consumption of Whisky and Beer in Man
 Difference in Blood Alcohol Levels Following Consumption of Whisky and Beer in Man P. D u ssa u lt1 and C. I. C happel The formulation of many pharmaceutical preparations may influence the absorption of
Difference in Blood Alcohol Levels Following Consumption of Whisky and Beer in Man P. D u ssa u lt1 and C. I. C happel The formulation of many pharmaceutical preparations may influence the absorption of
Effects of felodipine on haemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with angina pectoris
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 391-396 Effects of felodipine on haemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with angina pectoris J. V. SHERIDAN, P. THOMAS, P. A. ROUTLEDGE & D. J. SHERIDAN Departments
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 391-396 Effects of felodipine on haemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with angina pectoris J. V. SHERIDAN, P. THOMAS, P. A. ROUTLEDGE & D. J. SHERIDAN Departments
European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE. Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam
 European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam 4.2 Posology and method of administration Unless otherwise prescribed by the physician, the following dosages
European PSUR Work Sharing Project CORE SAFETY PROFILE Lendormin, 0.25mg, tablets Brotizolam 4.2 Posology and method of administration Unless otherwise prescribed by the physician, the following dosages
ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
 ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 A. LABELLING 2 PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGE AND THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGE Outer carton Multi-pack 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve
ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 A. LABELLING 2 PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGE AND THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGE Outer carton Multi-pack 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ZONALON CREAM 5% GENERIC NAME DOXEPIN HYDROCHLORIDE CREAM 5% THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION TOPICAL ANTIPRURITIC
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ZONALON CREAM 5% GENERIC NAME DOXEPIN HYDROCHLORIDE CREAM 5% THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION TOPICAL ANTIPRURITIC Valeant Canada LP. Date of Preparation: Montreal, Quebec March 19, 2013 H4R
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ZONALON CREAM 5% GENERIC NAME DOXEPIN HYDROCHLORIDE CREAM 5% THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION TOPICAL ANTIPRURITIC Valeant Canada LP. Date of Preparation: Montreal, Quebec March 19, 2013 H4R
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16
 Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Guidelines MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD)
 MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD) Guidelines CH Lim, B Baizury, on behalf of Development Group Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Major Depressive Disorder A. Introduction Major depressive
MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD) Guidelines CH Lim, B Baizury, on behalf of Development Group Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Major Depressive Disorder A. Introduction Major depressive
CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF GENERALISED ANXIETY DISORDER, PANIC DISORDER AND OBSESSIVE- COMPULSIVE DISORDER
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF GENERALISED ANXIETY DISORDER, PANIC DISORDER AND OBSESSIVE- COMPULSIVE DISORDER Guideline Title Clinical Investigation of Medical Products
CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF GENERALISED ANXIETY DISORDER, PANIC DISORDER AND OBSESSIVE- COMPULSIVE DISORDER Guideline Title Clinical Investigation of Medical Products
PRODUCT INFORMATION. Sudafed* Sinus + Allergy & Pain Relief Tablets
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Sudafed* Sinus + Allergy & Pain Relief Tablets Name of the Medicine Paracetamol CAS 2 Registry Number: 103-90-2 Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride CAS 2 Registry Number: 345-78-8 Triprolidine
PRODUCT INFORMATION Sudafed* Sinus + Allergy & Pain Relief Tablets Name of the Medicine Paracetamol CAS 2 Registry Number: 103-90-2 Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride CAS 2 Registry Number: 345-78-8 Triprolidine
BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER
 BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER This document provides statistical information about non-malignant (blue table) and malignant (red table) brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers in Northern Ireland.
BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER This document provides statistical information about non-malignant (blue table) and malignant (red table) brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers in Northern Ireland.
THE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE ON HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS OVER A PERIOD OF TWO YEARS
 THE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE ON HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS OVER A PERIOD OF TWO YEARS BY ROBERT HODGKINSON From the West Middlesex Hospital, Isleworth Received November 22, 1955 To justify the use of a drug in
THE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE ON HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS OVER A PERIOD OF TWO YEARS BY ROBERT HODGKINSON From the West Middlesex Hospital, Isleworth Received November 22, 1955 To justify the use of a drug in
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
Body weight more than 30kg : 10ml (10mg) of the syrup once daily.
 1. Name of the medicinal product Clarityn Allergy 1mg/ml Syrup 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each ml of syrup contains 1mg loratadine. Excipients with known effect. The quantity of sucrose
1. Name of the medicinal product Clarityn Allergy 1mg/ml Syrup 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each ml of syrup contains 1mg loratadine. Excipients with known effect. The quantity of sucrose
ΔTHC level. ΔTHC-COOH level
 Supplemental information 12 2 11 18 1 16 THC (ng/dl) A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 Minutes 25 ΔTHC level B 14 12 1 8 6 4 2-2 -4 y = 11.92x + 42.11 R² =.1375 y =.196x + 29.63 R² =.2977 y =.1513x +.8471 R²
Supplemental information 12 2 11 18 1 16 THC (ng/dl) A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 Minutes 25 ΔTHC level B 14 12 1 8 6 4 2-2 -4 y = 11.92x + 42.11 R² =.1375 y =.196x + 29.63 R² =.2977 y =.1513x +.8471 R²
MIDAZOLAM AND OXAZEPAM IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA IN HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 145S-149S MIDAZOLAM AND OXAZEPAM IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA IN HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS 'Clinique des Maladies Infectieuses, H6pital Houphouet Boigny, Marseilles, France
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 145S-149S MIDAZOLAM AND OXAZEPAM IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA IN HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS 'Clinique des Maladies Infectieuses, H6pital Houphouet Boigny, Marseilles, France
Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a vehicle safely.
 How do we define the term drug for DRE purposes? Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a vehicle safely. Review-2 Basic Drug Statistics What
How do we define the term drug for DRE purposes? Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a vehicle safely. Review-2 Basic Drug Statistics What
Anticholinergic withdrawal and benzhexol treatment
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 936-941 Anticholinergic withdrawal and benzhexol treatment in Parkion's disease P. M. HORROCKS, D. J. VICARY, J. E. REES, J. D. PARKES, AND
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 936-941 Anticholinergic withdrawal and benzhexol treatment in Parkion's disease P. M. HORROCKS, D. J. VICARY, J. E. REES, J. D. PARKES, AND
Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology
 Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology Eb Blakely, Ph.D., BCBA-D Quest, Inc./Florida Institute of Technology Drug Facts Drug effects are dose-dependent Drugs effects are time-dependent Drugs are toxic at high
Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology Eb Blakely, Ph.D., BCBA-D Quest, Inc./Florida Institute of Technology Drug Facts Drug effects are dose-dependent Drugs effects are time-dependent Drugs are toxic at high
A substance that reduces pain and may or may not have psychoactive properties.
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS AMPHETAMINE-TYPE STIMULANTS (ATS) A group of substances, mostly synthetic, with closely related chemical structure which have, to varying degrees, a stimulating effect on the central
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AMPHETAMINE-TYPE STIMULANTS (ATS) A group of substances, mostly synthetic, with closely related chemical structure which have, to varying degrees, a stimulating effect on the central
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DOTHIEPIN (PROTMADEN) AND IMIPRAMINE IN DEPRESSION J. N. WAS 1
 ItuHm J. Psyckiat. (989), (2), 5 56 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DOTHIEPIN (PROTMADEN) AND IMIPRAMINE IN DEPRESSION J. N. WAS PRADEEP SHARMA ASHOK K. SINGHAL" SAVITA AGARWAL* SUMMARY In a single-blind, randomised,
ItuHm J. Psyckiat. (989), (2), 5 56 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DOTHIEPIN (PROTMADEN) AND IMIPRAMINE IN DEPRESSION J. N. WAS PRADEEP SHARMA ASHOK K. SINGHAL" SAVITA AGARWAL* SUMMARY In a single-blind, randomised,
Psychobiology Handout
 Nsg 85A / Psychiatric Page 1 of 7 Psychobiology Handout STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE BRAIN Psychiatric illness and the treatment of psychiatric illness alter brain functioning. Some examples of this are
Nsg 85A / Psychiatric Page 1 of 7 Psychobiology Handout STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE BRAIN Psychiatric illness and the treatment of psychiatric illness alter brain functioning. Some examples of this are
Modulation of the Acoustic Startle Response by the Level of Arousal: Comparison of Clonidine and Modafinil in Healthy Volunteers
 (2007) 32, 2405 2421 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0893-133X/07 $30.00 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Modulation of the Acoustic Startle Response by the Level of Arousal: Comparison
(2007) 32, 2405 2421 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0893-133X/07 $30.00 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Modulation of the Acoustic Startle Response by the Level of Arousal: Comparison
Diagnosis & Management of Major Depression: A Review of What s Old and New. Cerrone Cohen, MD
 Diagnosis & Management of Major Depression: A Review of What s Old and New Cerrone Cohen, MD Why You re Treating So Much Mental Health 59% of Psychiatrists Are Over the Age of 55 AAMC 2014 Physician specialty
Diagnosis & Management of Major Depression: A Review of What s Old and New Cerrone Cohen, MD Why You re Treating So Much Mental Health 59% of Psychiatrists Are Over the Age of 55 AAMC 2014 Physician specialty
(LONG ACTING FORMULATION) AND BENDROFLUAZIDE
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 727-732 COMPARATIVE PHARMACOLOGICAL AND PHARMACOKINETIC OBSERVATIONS ON PROPRANOLOL (LONG ACTING FORMULATION) AND BENDROFLUAZIDE ADMINISTERED SEPARATELY AND CONCURRENTLY
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 727-732 COMPARATIVE PHARMACOLOGICAL AND PHARMACOKINETIC OBSERVATIONS ON PROPRANOLOL (LONG ACTING FORMULATION) AND BENDROFLUAZIDE ADMINISTERED SEPARATELY AND CONCURRENTLY
Substance Abuse and Poisonings. Chapter 17
 Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
Study No Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Study Endpoints: Pharmacokinetics:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The excretion of zopiclone into breast milk
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1990), 30, 267-271 The excretion of zopiclone into breast milk I. MATHESON1, H. A. SANDE2 & J. GAILLOT3 'Department of Pharmacotherapeutics, University of Oslo, Oslo, 2Department
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1990), 30, 267-271 The excretion of zopiclone into breast milk I. MATHESON1, H. A. SANDE2 & J. GAILLOT3 'Department of Pharmacotherapeutics, University of Oslo, Oslo, 2Department
These drugs produce effects similar to the sympathetic nervous system
 Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
![PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate](/thumbs/81/82665370.jpg) NORGESIC Orphenadrine citrate and paracetamol PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: CAS number: 4682-36-4 Chemical structure: Orphenadrine citrate (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine
NORGESIC Orphenadrine citrate and paracetamol PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: CAS number: 4682-36-4 Chemical structure: Orphenadrine citrate (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine
ALCOHOL AND MARIJUANA, A LESS THAN ADDITIVE INTERACTION?
 ALCOHOL AND MARIJUANA, A LESS THAN ADDITIVE INTERACTION? Helen Dauncey, Gregory Chesher, John Crawford, Michael Adena, Kim Horne. Department of Pharmacology, University of Sydney, Australia There have
ALCOHOL AND MARIJUANA, A LESS THAN ADDITIVE INTERACTION? Helen Dauncey, Gregory Chesher, John Crawford, Michael Adena, Kim Horne. Department of Pharmacology, University of Sydney, Australia There have
I Can t Think Properly Brian Fog & POTS
 I Can t Think Properly Brian Fog & POTS Satish R Raj MD MSCI FACC FHRS Libin Cardiovascular Institute of Alberta University of Calgary Autonomic Dysfunction Center Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
I Can t Think Properly Brian Fog & POTS Satish R Raj MD MSCI FACC FHRS Libin Cardiovascular Institute of Alberta University of Calgary Autonomic Dysfunction Center Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
Haemodynamic and humoral effects of oral perindopril, an
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 159-164 Haemodynamic and humoral effects of oral perindopril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, in man K. R. LEES & J. L. RED University Department of Materia
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 159-164 Haemodynamic and humoral effects of oral perindopril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, in man K. R. LEES & J. L. RED University Department of Materia
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Optimal exploration strategies in haptic search
 Optimal exploration strategies in haptic search Vonne van Polanen, Wouter M. Bergmann Tiest, Noortje Creemers, Merel J. Verbeek, and Astrid M. L. Kappers MOVE Research Institute, Faculty of Human Movement
Optimal exploration strategies in haptic search Vonne van Polanen, Wouter M. Bergmann Tiest, Noortje Creemers, Merel J. Verbeek, and Astrid M. L. Kappers MOVE Research Institute, Faculty of Human Movement
A Pilot Study of Some Physiological and Psychological Effects of Caffeine
 A Pilot Study of Some Physiological and Psychological Effects of Caffeine Sanford Bolton, Ph.D. 1 Martin Feldman, M.D. 2, Gary Null, M.S. 3 Emanuel Revici, M.D. 3 and Linda Stumper, B.S. 1 Abstract Eleven
A Pilot Study of Some Physiological and Psychological Effects of Caffeine Sanford Bolton, Ph.D. 1 Martin Feldman, M.D. 2, Gary Null, M.S. 3 Emanuel Revici, M.D. 3 and Linda Stumper, B.S. 1 Abstract Eleven
TOULARYNX DEXTROMETHORPHAN FORTE 3 mg/ml, syrup Dextromethorphan HBr monohydrate
 TOULARYNX DEXTROMETHORPHAN FORTE 3 mg/ml, syrup Dextromethorphan HBr monohydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
TOULARYNX DEXTROMETHORPHAN FORTE 3 mg/ml, syrup Dextromethorphan HBr monohydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents
 Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
NARAMIG QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 NARAMIG Naratriptan QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Tablets containing 2.5 mg of naratriptan as naratriptan hydrochloride. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Film coated tablets. CLINICAL PARTICULARS Indications
NARAMIG Naratriptan QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Tablets containing 2.5 mg of naratriptan as naratriptan hydrochloride. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Film coated tablets. CLINICAL PARTICULARS Indications
Taking Care: Child and Youth Mental Health TREATMENT OPTIONS
 Taking Care: Child and Youth Mental Health TREATMENT OPTIONS Open Learning Agency 2004 TREATMENT OPTIONS With appropriate treatment, more than 80% of people with depression get full relief from their symptoms
Taking Care: Child and Youth Mental Health TREATMENT OPTIONS Open Learning Agency 2004 TREATMENT OPTIONS With appropriate treatment, more than 80% of people with depression get full relief from their symptoms
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Effects of a commercial product containing Guarana on psychological well-being, anxiety and mood: a single-blind, placebo-controlled study in heathy subjects Authors:
Author's response to reviews Title: Effects of a commercial product containing Guarana on psychological well-being, anxiety and mood: a single-blind, placebo-controlled study in heathy subjects Authors:
Journal of Psychopharmacology
 Journal of Psychopharmacology http://jop.sagepub.com/ The inhibition of the pupillary light reflex by the threat of an electric shock: a potential laboratory model of human anxiety P. Bitsios, E. Szabadi
Journal of Psychopharmacology http://jop.sagepub.com/ The inhibition of the pupillary light reflex by the threat of an electric shock: a potential laboratory model of human anxiety P. Bitsios, E. Szabadi
BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER
 BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER This document provides statistical information about non-malignant (purple table) and malignant (red table) brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers in Northern Ireland.
BRAIN AND NERVOUS SYSTEM CANCER This document provides statistical information about non-malignant (purple table) and malignant (red table) brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers in Northern Ireland.
Antidepressants and Sedatives. David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Antidepressants and Sedatives David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Depression A frequent problem, affecting up to 5% of the population Common presentations
Antidepressants and Sedatives David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Depression A frequent problem, affecting up to 5% of the population Common presentations
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARATERISTICS HYPERIUM. I.N.N. : Rilmenidine
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARATERISTICS HYPERIUM I.N.N. : Rilmenidine 1. DENOMINATION HYPERIUM 1 mg, tablets 2. COMPOSITION Rilmenidine (I.N.N.) dihydrogenphosphate.1.544 mg amount equivalent to rilmenidine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARATERISTICS HYPERIUM I.N.N. : Rilmenidine 1. DENOMINATION HYPERIUM 1 mg, tablets 2. COMPOSITION Rilmenidine (I.N.N.) dihydrogenphosphate.1.544 mg amount equivalent to rilmenidine
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology - continued. Chapter 7 The Science of Psychopharmacology
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 7 The Science of Psychopharmacology Psychopharmacology A primary treatment mode of psychiatric-mental health nursing care Psychopharmacology - continued
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 7 The Science of Psychopharmacology Psychopharmacology A primary treatment mode of psychiatric-mental health nursing care Psychopharmacology - continued
Pamelor (nortriptyline)
 Generic name: Nortriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg capsules; 10 mg/5 ml oral solution Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Pamelor
Generic name: Nortriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg capsules; 10 mg/5 ml oral solution Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Pamelor
PANADOL COLD & FLU RELIEF ORIGINAL FORMULA is a white, capsule-shaped tablet with flat edges, one face marked with C&F, PANADOL on the other.
 Product description PANADOL COLD & FLU RELIEF ORIGINAL FORMULA is a white, capsule-shaped tablet with flat edges, one face marked with C&F, PANADOL on the other. Ingredients Active Ingredients: Paracetamol
Product description PANADOL COLD & FLU RELIEF ORIGINAL FORMULA is a white, capsule-shaped tablet with flat edges, one face marked with C&F, PANADOL on the other. Ingredients Active Ingredients: Paracetamol
Clinical research. The value of assessing cognitive function in drug development Keith A. Wesnes, PhD
 The value of assessing cognitive function in drug development Keith A. Wesnes, PhD It is difficult to overestimate the need for the definitive evaluation of cognitive function throughout the drug development
The value of assessing cognitive function in drug development Keith A. Wesnes, PhD It is difficult to overestimate the need for the definitive evaluation of cognitive function throughout the drug development
Tofranil and Tofranil-PM (imipramine)
 Tofranil and Tofranil-PM (imipramine) Generic name: Imipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg tablets; 75 mg, 100 mg, 125 mg, 150 mg capsules (Tofranil-PM) Available in generic: Yes Drug class:
Tofranil and Tofranil-PM (imipramine) Generic name: Imipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg tablets; 75 mg, 100 mg, 125 mg, 150 mg capsules (Tofranil-PM) Available in generic: Yes Drug class:
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory. (Dahlstrom et al., 1972). Sleep status was determined
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 8, 47S-54S EFFECTS OF TEMAZEPAM, FLURAZEPAM AND QUINALBARBITONE ON SLEEP: PSYCHOMOTOR AND COGNITIVE FUNCTION T. ROTH*, P. PICCIONE*, P. SALIS*, M. KRAMERt & M. KAFFEMAN Sleep
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 8, 47S-54S EFFECTS OF TEMAZEPAM, FLURAZEPAM AND QUINALBARBITONE ON SLEEP: PSYCHOMOTOR AND COGNITIVE FUNCTION T. ROTH*, P. PICCIONE*, P. SALIS*, M. KRAMERt & M. KAFFEMAN Sleep
EMT. Chapter 19 Review
 EMT Chapter 19 Review Review 1. Which of the following questions is of LEAST pertinence for the EMT to ask a patient who intentionally overdosed on a medication? A. How much do you weigh? B. How much did
EMT Chapter 19 Review Review 1. Which of the following questions is of LEAST pertinence for the EMT to ask a patient who intentionally overdosed on a medication? A. How much do you weigh? B. How much did
