Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version)
|
|
|
- Ellen West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital, you should be able to answer these 3 questions about your illness or condition. Please ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist for help! 1. What is the main problem? 2. What should I do? 3. Why should I do this?
2 Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, Gastrostomy Tubes (G Tubes) and Jejunostomy Tubes (J Tubes) (TJUH) Introduction Good nutrition is an important part of your treatment, recovery, and well being. When you are not able to eat enough, it becomes necessary to use a tube feeding. Your tube feeding was chosen for you with your unique nutritional and medical needs in mind. Your healthcare team will teach you and your caregivers what you need to know to manage your tube feeding at home. Types of Feeding Tubes There are many ways to do tube feedings. Depending on the circumstances, tube feedings may go into the stomach or the small intestine. Some feeding tubes pass through the nose, while others go directly into the stomach or small intestine through the abdomen. Feeding tubes that go into the stomach directly through the abdomen are called PEG tubes, Gastrostomy tubes or G tubes. If your feeding tube goes through your abdomen into your small intestine, it is called a Jejunostomy tube or J tube.
3 Your Feeding Tube Your feeding tube is called a tube. The tip of the tube is in your. The feeding tube was placed on (date). The brand name and size of the tube are.
4 Care of Your Abdomen Tube G tubes and J tubes are usually covered with a bandage to protect the insertion site. For the first week or two after the tube is placed, your doctor may give you specific instructions for cleaning around the tube. After the site heals completely, wash around the tube with warm soap and water and dry your skin thoroughly. If your doctor has prescribed ointment, apply a small amount around your tube, before covering the area with a gauze pad. Tape the gauze pad in place. Wash around the tube and change the bandage every day. Watch for redness of the skin, tenderness, swelling, drainage, or leaking around the tube. Report any of these signs to your doctor or nurse. Keeping Abdomen Tubes in Position It is important to prevent the tube from moving. If the tube is not held in place, it will move slightly in and out of the opening in your abdomen. Over time, this motion could cause the opening to leak. If there is a lot of movement in the tube, it could fall out completely. There are several ways that tubes may be held in place. Many tubes are held in place with stitches when they are put in. Some tubes have specially designed bumpers that prevent excess tube movement. There are also anchoring devices available for tubes that need to be held in place more securely.
5 You should make a mark on the tube with permanent ink near your abdomen. You will know right away if the tube is moving in or out by noting the position of the mark on the tube. You should also tape the tube to your abdomen to prevent it from accidentally coming out. Sometimes a feeding tube will fall out. This is not a serious problem but you should contact your doctor right away to have the tube replaced so that you do not miss any of the fluid or formula that you need. A delay in having the tube replaced could give the opening a chance to shrink, making it difficult to put in a new tube. Your Tube Feeding Formula Your tube feeding formula has been selected by your healthcare team with your nutritional needs in mind. Tube feeding formulas come in ready to use containers or as powders that you must mix with water. For the most part, tube feeding formulas contain all the calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals that you need. Some formulas contain less water than others. The instructions for the feeding will tell you if you need to add water. Your Formula: Guidelines for Handling and Storage 1. Always wash your hands with soap and water before touching the formula or tube feeding equipment. 2. Shake the container well and wipe or rinse the top of the container before you open it. 3. If you do not use all of the formula, cover the opened container and store it in the refrigerator. Throw away any opened formula that you have not used in 24 hours. 4. When using a powdered formula, mix of the powder with of water, according to the instructions on the package. Pour the formula into a clean container labeled with the date and time the formula was mixed. Store the container in the refrigerator. If the formula is not used in 24 hours, throw it away. 5. While you are giving the feeding, you may keep the formula at room temperature for up to 12 hours. 6. You should wash the containers, syringes and other equipment used to mix, store and give the tube feeding in hot, soapy water after each use. You can also put these items on the top rack of the dishwasher. 7. The administration bag and tubing that you use to give your feeding should also be washed after each time you use it. Your nurse will tell you how often you should replace this bag.
6 Your Formula: How Much to Take The name of your tube feeding formula: The number of cans (or ounces) you need each day: Suggested schedule for feedings: The amount of additional water you need each day: Giving the Tube Feeding If the tip of your feeding tube is in your stomach, your doctor may want you to check to be sure your stomach is empty and ready for more formula. This is called checking the residual. If your doctor wants you to check for residual, please see the steps below. Before you begin tube feeding, gather the equipment you will need. Check the position of your tube and the residual, if this is necessary. If you don t feel full or nauseated, you are ready to begin the feeding. You should be relaxed and in a comfortable position during tube feeding. However, don t lie flat during the feeding since the formula could back up into your throat while you are in this position. It is best to sit in a chair or to prop up your head in bed during the feeding and for 30 to 60 minutes afterward. You may also stand and walk during your feeding if your doctor has not restricted your activity. Checking Your Stomach Residual (for stomach tubes only) If your doctor has instructed you to check your stomach residual please follow these steps: 1. Wash your hands. 2. Gather the equipment you need: A 50 60cc syringe A clean container Fresh, clean water
7 3. Remove the cap from the end of your feeding tube (or if you are on continuous feedings, stop the feeding and disconnect the tubing). 4. Place the tip of a 50 60cc syringe into the end of your feeding tube and open the clamp on your tube if you have one. 5. Gently draw back on the plunger of the syringe to remove the fluid in your stomach. Place this fluid in a clean container if you get more than one full syringe. Check the amount in the syringe by looking at the numbers on the side. 6. Once you have measured all of the residual in your stomach, you should use the syringe to return it back to the stomach through the feeding tube. 7. After you have returned any residual to your stomach, you should use the syringe to flush 20 30cc of water into your feeding tube. 8. If your stomach residual is more than 250cc or 8oz, or you feel unusually full or nauseated, wait one hour and do another residual check. If the residual is still more than 250cc or 8oz, do not give the feeding. Contact your nurse or doctor for instructions so that the feeding may be restarted as soon as possible. Flushing Your Feeding Tube: 1. Use this much water. 2. When to flush your tube: Always flush the tube before and after checking residuals, before and after giving formula, and before and after each medication. 3. Follow these steps: Attach a 50 60cc syringe (with water) to your feeding tube. Open any clamps on your tube and push the water through the tube. Close the clamp or cap on your tube.
8 Giving Tube Feeding with a Syringe When giving tube feeding with a syringe, you pour the formula through a syringe directly into your feeding tube. The formula flows through the tube in just a few minutes. 1. Gather this equipment: A 50 60cc syringe with the plunger removed from the barrel of the syringe Formula Water for flushing the tube 2. Attach the syringe barrel (with the plunger removed) to your feeding tube. 3. Flush your tube with water. 4. Pour the formula through the feeding tube until you have received the right amount of formula. 5. Flush your tube with water and cap the tube.
9 Giving Tube Feeding by Gravity To give tube feedings by gravity, you must pour your formula into a container that connects to your feeding tube. You will then allow the formula to drip slowly through your feeding tube, usually over 30 minutes to 1 hour. 1. Gather this equipment: A feeding bag and tubing Formula A pole or wall hook Water for flushing your feeding tube A 50 60cc syringe 2. Close the clamp on the feeding bag. 3. Pour the formula into the feeding bag. 4. Hang the bag on a pole or hook. 5. Open the clamp to allow the formula to fill the tubing; close the clamp. 6. Flush your tube with water. 7. Attach the feeding bag to your feeding tube. 8. Open the clamp and adjust the flow so the formula runs in over 30 minutes. 9. Flush your tube with water and cap the tube.
10 Giving Tube Feeding With a Pump Using a feeding pump to give your feeding allows you to control how fast the formula flows through the tube. This way of giving feeding works best for certain kinds of tubes. Using a pump can also let you give your feeding at night while you sleep. 1. Gather this equipment: Feeding bag with tubing Pole Feeding pump Formula 50 60cc syringe Water for flushing 2. Close the clamp on the feeding bag. 3. Pour your formula into the bag. (No more than 12 hours of formula.) Fill the tubing with formula. 4. Hang the feeding bag on the pole. 5. Attach the feeding bag to the pump using the directions that are on the pump. 6. Set the pump to the correct rate. 7. Flush the tube with water. 8. Insert the tip of the pump tubing into your feeding tube. 9. Open all clamps. 10. Turn the pump on. 11. Allow the formula to run for the number of hours your doctor has prescribed. 12. Disconnect the pump tubing from the feeding tube. 13. Flush and cap the feeding tube.
11 Giving Medication Through a Feeding Tube It is best to take medication by mouth, if possible. However, if you cannot take medicine by mouth, it is okay to give medicine through your feeding tube. When giving medicine through a feeding tube, it is important to take steps to keep the medicine from reacting with other drugs or with your formula. These reactions could change the action of your medicine or clog the feeding tube. Here are some tips for giving medicine through your feeding tube: 1. Use a liquid medicine whenever possible. Check with your pharmacist to see which of your medicines come in liquid form. Since many over the counter liquid medicines are for children, the pharmacist can also help you figure out the correct dose. 2. Do not mix medicines together. Give each medicine separately, flushing with water before and after each medicine. 3. Avoid thick liquid medications that could clog your feeding tube, such as bulk forming laxatives (Metamucil). 4. If you must crush a solid medication, check with a pharmacist to be sure it is safe to crush. Some long acting medications should not be crushed. 5. When crushing a pill or tablet, be sure to grind it into a fine powder and mix it with 15 30cc of water to dissolve the powder. Pill fragments are a common cause of blocked feeding tubes. 6. Some kinds of medicine may not be effective if they bypass your stomach. For example, antacids will not work if you give them through a jejunostomy tube. When you are started on a new medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist if it can be given through the kind of feeding tube you have.
12 7. It is best to give some medicine with food; others should be given on an empty stomach. Ask your pharmacist to set up a schedule for giving your medicine. Follow these steps for giving medicine through your feeding tube: 1. Gather this equipment: The right medicine A syringe (the size depends on the amount of medicine) Water for flushing your tube and a cc syringe 2. Flush your feeding tube with 10 to 20cc of water. 3. Draw up the correct amount of medicine into the syringe. 4. Attach the syringe to the end of your feeding tube and flush the medicine through the tube. 5. Flush the tube again with water to be sure no medicine is left in the feeding tube. Personal Care Mouth Care Even though you may not be eating or drinking normally, it is as important as ever to floss and brush your teeth. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a regular tooth brush and toothpaste. You can also use mouth wash to freshen your breath. Try not to lick your lips since this could make them chapped. You can use a lip balm to moisturize your lips. Watching Your Weight You should weigh yourself a few times a week while you are receiving tube feeding. Get on the scale at the same time each day, wearing the same amount of clothing. Your weight gives you important information not only about your nutrition but also about whether or not you are getting enough fluid. Everyone s weight varies a little from day to day. It is the trends that you see in your weight over time that give you the best information. If your goal is to gain weight, you should expect to see your weight go up by 1 to 1½ pounds a week. If you gain weight faster, it could mean that you are retaining (holding on to) fluid. On the other hand, if your weight drops by 1 or more pounds in a week, it could mean that you are not getting enough fluid. Bowel Habits During tube feeding, bowel movements are less frequent than usual. In time you should see a new bowel movement schedule that is normal for you. Keep track of your bowel habits so that you can note changes before problems occur.
13 Activity Before you go home, your doctor will give you instructions about how much physical activity you are allowed. With so much to think about, it is easy to overlook this important part of your care. Exercise will improve your strength and endurance, keep your bowels regular, and help you feel better in general. Set simple goals for yourself and gradually increase your activity as you have been instructed. Preparing for the Unexpected Problem Cause Solution Upset Stomach: A feeling of nausea, fullness, cramping, or vomiting. Giving the formula too fast Give the feeding more slowly. Incorrect body position Sit up or raise your head at least 30 during the feeding. Do not lie flat for one hour after you have finished a feeding. Spoiled formula Wash your hands and equipment well, store open cans of formula in the refrigerator, do not use formula that has passed the expiration date. If you are taking a concentrated formula or if you need a large amount at one time, changing the formula (with the help of the healthcare team) may help to relieve your symptoms.
14 Type of formula Do not give your feeding if you feel full or nauseated. Call your doctor if you have an upset stomach for more than one day. If you vomit, stop the feeding and call your doctor. General points Problem Cause Solution Dehydration: Not enough water. Symptoms include: weight loss, thirst, dizziness, dark urine, small amounts of urine. A sudden drop in weight may mean that you are not getting enough water. Not enough water in tube feeding formula Diarrhea, vomiting Fever Water pills Increased activity, especially in warm weather Excessive sweating The best solution is to prevent dehydration in the first place: Call your doctor or nurse. You may need to change your formula or add more water. Watch your weight. Inform your doctor or nurse of changes in your activity level or medical condition that may raise your fluid needs.
15 Aspiration: Formula enters the breathing passages. Feeding tube in incorrect position Check the position of the tube before each feeding. Symptoms include: fever, coughing, shortness of breath, noisy breathing. Giving feedings while lying flat Keep your head raised during the feedings. Tube Slipping Out: The markings on your feeding tube have moved or the tube has fallen out completely. Vomiting during feeding Tube is not held in place properly If you have these symptoms, stop your feeding and call your doctor. Tape your feeding tube to hold it in place. Be careful when you are changing your clothing or moving about during feeding. Blocked Feeding Tube: Formula will not flow through the tube. Kinked feeding tube Clamp on feeding tube Call your doctor if you think your tube has moved out of place. Check the tube for clamps or kinks. Build up of formula in the feeding tube. Pill fragments Flushing the tube before and after each medication, before and after each feeding, and before and after checking residuals. Use liquid medications if possible. Crush tablets to a fine powder and dissolve in water before giving them through a feeding tube.
16 Call your doctor or nurse if formula will not flow through the tube. Problem Cause Solution Leaking Feeding Tube: Formula or other fluid leaks around the feeding tube. (abdominal tubes only) Excess motion of the feeding tube. Anchor tube to stop tube from moving in and out of the opening. Tube may be replaced with a larger one. Diarrhea: Improperly washed equipment: blenders, mixing bottles, storage containers, administration bag, etc. Wash hands and equipment thoroughly. Store opened cans of formula in the refrigerator. Do not use formula that has passed the expiration date. Call your doctor if diarrhea lasts more than one day. Medications Check with your doctor before you take over the counter medicines for diarrhea. Other solutions depend on the reason for loose stools. Rate or type of formula
17 Infection Constipation: Infrequent or hard stools. Spoiled formula Formula without fiber Low water intake Pain medicine Call your doctor. Some things that may help include fiber enriched formulas, stool softeners, laxatives, more water intake, and more activity. Failure to meet weight goals: Unexpected weight loss or gain or weight that does not change Calorie intake does not match needs Incorrect fluid intake Call your doctor or nurse to see if your formula, feeding schedule, or fluid intake should be adjusted. Change in level of activity Change in medical condition Reasons to Contact Your Nurse or Doctor Upset stomach or vomiting Fullness, bloating, abdominal cramps Dizziness, thirst, weakness Blocked tube Tube site (nose or abdomen) becomes red, swollen, painful, or begins draining Body temperature of 101 F Diarrhea/Constipation
18 A weight gain or loss of more than 2 pounds in one week Tube falls out or appears longer than usual Cough, shortness of breath, particularly after receiving tube feeding Change in eating habits Important Phone Numbers Doctor: Nurse: Dietitian: Pharmacist: Home Health Agency: Supplies Provider: Words You May Hear Aspiration Any fluid (could be tube feeding) that enters the lungs. Signs of aspiration are fever, coughing and difficulty breathing. Bolus CC Constipation Diarrhea Duodenum Formula A dose of medicine or feeding formula given all at once. 30cc = 1 ounce Infrequent bowel movements often with stool that are hard and painful. Frequent loose watery bowel movements. First part of the small intestine (also called small bowel). A liquid nutrition preparation. G.I. tract The gastrointestinal tract. The body system used to digest and absorb nutrients. Includes mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines or bowels. Gastric Having to do with the stomach.
19 Irrigation Jejunum Pylorus Residual Saline Flushing or cleansing a tube or device usually with water or salt water (saline). Second part of the small intestine (small bowel). A muscle that separates the stomach from the small intestine. The amount of fluid measured after a period of time. Salt water Notes and Questions Original date: June 2009 Revised: November 7, Truven Health Analytics Inc. This patient education document was created using the MICROMEDEX(R) System and may contain MICROMEDEX proprietary information. All illustrations and images included in CareNotes are the copyrighted property of A.D.A.M., Inc. or Truven Health Analytics.
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding
 Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Enteral Nutrition. Introduction. Brooks Health Care, Inc. Patient Instruction 1
 Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS
 YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
Tube Feeding at Home. Your Nutrition Partner. Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit
 Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults. Clinical Nutrition Services
 Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
Tube Feeding At Home. A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers
 A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube
 Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Gastrostomy Tube Management
 Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression
 Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport
 Nutrition and Dietetics Department Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport Please bring this booklet with you for all tube changes Patient Information If you need this information in another format or language
Nutrition and Dietetics Department Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport Please bring this booklet with you for all tube changes Patient Information If you need this information in another format or language
Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System
 HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica )
 Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Guide to ADULT TUBE FEEDING. Parents Practical Guide to Pediatric Tube Feeding XX
 Guide to ADULT TUBE FEEDING Parents Practical Guide to Pediatric Tube Feeding XX Contents Introduction 3 Finding Community Support 4 Understanding the Tube Feeding System 6 Monitoring Your Response to
Guide to ADULT TUBE FEEDING Parents Practical Guide to Pediatric Tube Feeding XX Contents Introduction 3 Finding Community Support 4 Understanding the Tube Feeding System 6 Monitoring Your Response to
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
What is a catheter? What do I need to learn about catheter care?
 Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
DEPARTMENT NAME GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT
 GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION. Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID
 STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the g ravity method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the g ravity method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
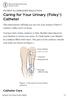 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Help Your Body Heal. Clinic Visits. After weight loss surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
Chapter 20. Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids
 Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE. Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage. Physician Contact Information. Dr. Phone:
 Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
For the Patient: Ponatinib Other names: ICLUSIG
 For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Going home after breast surgery without drains
 Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home.
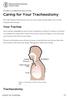 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Appendix Surgery. (Appendectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Medications. Managing and Administering Medication
 Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Steps for Giving an Enema
 Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. PCV Treatment Chemotherapy for brain tumors DRAFT. PCV is a type of chemotherapy (chemo) treatment for brain
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA
 For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Information
 1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: LUAVPEM
 For the Patient: LUAVPEM Other Names: Second-Line Treatment Of Advanced Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PEM = PEMetrexed ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What is this drug
For the Patient: LUAVPEM Other Names: Second-Line Treatment Of Advanced Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PEM = PEMetrexed ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What is this drug
Chapter 23. Nutrition Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level
 If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Instructions for Use. Welcome!
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
SAMPLE. Check your child s skin with each pouch change. Size the stoma and cut the barrier to fit the stoma.
 Problem Solving Irritated and Red Skin The skin around your child s stoma can become irritated and red. This is the most common problem for new ostomy patients. It is most often due to stool or urine on
Problem Solving Irritated and Red Skin The skin around your child s stoma can become irritated and red. This is the most common problem for new ostomy patients. It is most often due to stool or urine on
It is used to treat or prevent upset stomach and throwing up. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
Eltrombopag (Promacta )
 Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Medicare Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Medicare Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA
 For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR
 For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Post Operative Instructions: Wisdom Teeth
 The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Do Not Reproduce. Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider
 Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
The Johns Hopkins Hospital Patient Information Home Instructions After REVERSE Total Shoulder Replacement Surgery
 Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
For the Patient: CAP. Capecitabine. Uses:
 For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide
 Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide Your safety and wellbeing are our priority. Issues can occur during your treatment and it is important that you recognize the symptoms. This guide will teach you how to
Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide Your safety and wellbeing are our priority. Issues can occur during your treatment and it is important that you recognize the symptoms. This guide will teach you how to
Information about Feeding Tubes
 Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Colon Cancer Surgery
 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Capecitabine. Other Names: Xeloda. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
Trastuzumab (Herceptin )
 Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery
 Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop.
 Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
Royal Columbian Hospital. We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully.
 Adrenal Surgery (Adrenalectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully. Bring
Adrenal Surgery (Adrenalectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully. Bring
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions
 Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions Your sutures or staples need to stay in place for at least 10 days after surgery. To have them removed you can: Call your surgeon s office (the number is on your discharge
Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions Your sutures or staples need to stay in place for at least 10 days after surgery. To have them removed you can: Call your surgeon s office (the number is on your discharge
Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth.
 For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
ARE YOUR LEVODOPA PILLS WORKING LIKE THEY USED TO?
 ARE YOUR LEVODOPA PILLS WORKING LIKE THEY USED TO? You may have noticed a change... Levodopa is a common treatment for Parkinson s, and doctors have relied on it for decades. Over time as Parkinson s progresses,
ARE YOUR LEVODOPA PILLS WORKING LIKE THEY USED TO? You may have noticed a change... Levodopa is a common treatment for Parkinson s, and doctors have relied on it for decades. Over time as Parkinson s progresses,
For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF
 For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF Afatinib (a fa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose.
For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF Afatinib (a fa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose.
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method
 How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml)
 Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
MICAFUNGIN MIXING
 1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Gallbladder Surgery. (Cholecystectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Gallbladder Surgery (Cholecystectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read
Gallbladder Surgery (Cholecystectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read
Esophagectomy Surgery
 Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
What is the most important information I should know about Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution?
 Medication Guide MORPHINE SULFATE (mor-pheen) (CII) Oral Solution IMPORTANT: Keep Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution in a safe place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
Medication Guide MORPHINE SULFATE (mor-pheen) (CII) Oral Solution IMPORTANT: Keep Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution in a safe place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN
 For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN Eribulin (er'' i bue' lin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN Eribulin (er'' i bue' lin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Methotrexate. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD
 For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD Amsacrine (AM-sa-krin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear orange-red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD Amsacrine (AM-sa-krin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear orange-red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
Total Thyroidectomy. Post-Surgery Instructions for: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW:
 Post-Surgery Instructions for: Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Total Thyroidectomy Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R. Smith,
Post-Surgery Instructions for: Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Total Thyroidectomy Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R. Smith,
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA
 For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
