Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy
|
|
|
- Polly Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgical Education Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Raimund Stein, Peter Rubenwolf, Christopher Ziesel, Mohamed M. Kamal* and Joachim W. Thüroff* Division of Paediatric Urology and *Department of Urology, University Medical Center, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER, Keywords ureteroneocystostomy, ureteric reimplantation, Boari flap, Psoas hitch Introduction In the middle of the last century, Dolff [1], Paquin [2] and Zimmermann et al. [3] developed principles for ureteroneocystostomy after gynaecological ureter injuries. Turner-Warwick and Worth [4] adopted these techniques, named it the Psoas Bladder-Hitch Procedure and applied this technique of ureteroneocystostomy for the treatment of distal ureteric obstruction, ureteric fistulas and distended duplication of the upper urinary tract. This technique includes three major advantages for a complex ureteroneocystostomy: i) Mobilisation of the bladder with fixation above the iliac vessels to guarantee a tension-free ureteric anastomosis; ii) Formation of an adequate submucosal tunnel to prevent VUR; iii) Implantation of the ureter into an immobilised part of the bladder to prevent kinking during filling and emptying of the bladder [5, 6]. In contrast to intravesical techniques for ureteric reimplantation, the psoas hitch procedure is also well suited for children with megaureters, as it can be combined with mobilisation of the ureter up to the kidney, so that secondary kinking of the ureter can be resolved. Tapering of a megaureter is rarely required, given that the diameters of the middle and proximal thirds of the ureter are usually smaller than that of the distal part, permitting creation of a submucosal tunnel for anti-refluxing ureteric implantation. The psoas (bladder) hitch technique is an almost universal approach for ureteric reimplantation whatever the problem of the distal ureter. If this technique is not possible, an additional Boari flap may be useful. At the end of the nineteenth century, Boari described a bladder flap substitution of the distal ureter [7]. The surgical technique was developed to bridge lesions of the distal ureter arising from surgical interventions (mainly gynaecological complications) or tuberculosis [8 11]. A modification by Übelhör is a deviation from the formal flap technique. Planning and Preparation Indications High-grade reflux with dilated ureter not suitable for an extravesical reimplantation. Obstructive and/or refluxive megaureter. Double system not suitable for extravesical reimplantation. Distal ureteric defects up to 5 8 cm above the ureteric orifice (for higher defects an additional Boari-flap may be used). Ureteric trauma, ureteric fistula, obstruction of the distal ureter or distal (solitary, low grade) urothelial cancer of the ureter. Specific Instruments and Materials Optical loupes ( , 50-cm focal length). Small Langenbeck retractors. 6/0 or 7/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable sutures for ureteric reimplantation (Monosyn or Monocryl ). 4/0 and 5/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable sutures (e.g. Monoplus or PDS ) for bladder closure BJU International 112, doi: /bju
2 Stein et al. 4/0 or 5/0 glyconate or polyglytone monofilament rapidly absorbable sutures for fixation of stents, cystostomy (e.g. Monosyn Quick or Caprosyn ). 3/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable sutures (e.g. Monoplus or PDS ) for bladder fixation at the psoas muscle. 4, 6 or 8 F polyurethane/polypropylene ureteric stents. 10 F pigtail cystostomy catheter. Patient Preparation Confirmation of adequate bladder capacity should be obtained preoperatively to allow a tension-free anastomosis. In patients with severe ureteric pathology, which might extend towards the middle or upper third of the ureter, bowel preparation is advisable in the event of intestinal ureter substitution becoming necessary. Acute UTI must be treated preoperatively. Patient Positioning The patient is placed supine on the table with ª15 overextension. A Foley transurethral catheter is inserted, which must provide intraoperative access for filling the bladder during the operation BJU International
3 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 1 A supra-inguinal hockey stick incision is made where the length of the cranial extension (hockey stick handle) depends on the patient's size and the expected length of the ureteric defect. In cases with an unexpected length of pathology, a primary smaller incision may be extended cranially as needed BJU International 139
4 Stein et al. Figure 2 The ureter is exposed through an extraperitoneal approach. After division of the inferior epigastric vessels and, in female patients, division of the round ligament of the uterus (in males mobilisation the spermatic cord and the spermatic vessels), the medial umbilical ligament (umbilical artery) is identified. If there is severe scarring after previous surgery or radiotherapy, the ureter is most readily identified behind the branching of the umbilical artery from the hypogastric artery (internal iliac artery) or alternatively at its crossing with the common iliac artery. The ureter is lifted up by a vessel loop to ease further preparation. Care must be taken to preserve the periureteric adventitial tissue with its inherent blood supply of the ureter BJU International
5 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 3 The ureter is mobilised towards to the bladder as far as possible, transected and its distal stump ligated. In cases with a ureteric fistula or an iatrogenic obstruction, the ureter is transected above that level. A stay suture is placed into the proximal ureteric stump at the 6 o'clock position. The ureter is carefully mobilised cranially to avoid any injury to the longitudinal ureteric vessels. In patients (mostly children) with an obstructive megaureter, the middle and/or proximal third of the ureter are usually smaller in diameter than the distal third and can be re-implanted without tailoring in most cases BJU International 141
6 Stein et al. Figure 4 Before commencing its mobilisation, the bladder is filled with 50 ml (infants) to ml (adults) of saline through the Foley catheter to ease dissection. The peritoneum is dissected from the surface of the bladder. In patients with a long ureteric defect extending higher up, bladder mobilisation is extended and both the median umbilical ligament (urachus) and the ipsilateral medial umbilical ligaments (and occasionally also the contralateral medial umbilical ligament) have to be divided. The aim is to allow a tension-free fixation of the bladder at the psoas muscle at least 2 3 cm above the common iliac vessel BJU International
7 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Psoas Hitch Figure 5 For the psoas hitch procedure, the bladder is opened using a 4 5 cm oblique incision between two stay sutures. In patients with a ureteric defect extending higher up and being too wide to bridge by this technique, a Boari flap may be developed [7] or a modified Übelhör procedure may be performed (see Figures 13 16) BJU International 143
8 Stein et al. Figure 6 With open bladder, the ipsilateral most cranial aspect of the bladder is elevated with the index finger inside the bladder to check if the raised flap easily reaches the intended point of fixation at the psoas muscle. The level of fixation at the psoas muscle is determined by the length of the proximal ureter plus additional length for creation of a submucosal tunnel. In cases where the bladder can only be brought to the psoas muscle with tension, the oblique bladder incision is extended to obtain a longer bladder flap (white arrows) BJU International
9 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 7 For fixation of the bladder at the psoas muscle, two to three 3/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable sutures (e.g. Monoplus or PDS )are placed preferentially through the tendon of the psoas muscle above the common iliac artery and the femoral branch of the nervus genitofemoralis. The sutures must encompass the whole detrusor muscle thickness without mucosa. The sutures must not be tied at this stage of the operation BJU International 145
10 Stein et al. Figure 8 For dissection of the submucosal tunnel for ureteric re-implantation, fine scissors (e.g. Metzenbaum scissors) are used; the dissection plane is between the mucosa and the detrusor muscle (submucosal tunnel) in direction of the original ureteric orifice. Two stay sutures are placed through the bladder wall at the entrance of the tunnel and a further two stay sutures at the end of the tunnel to facilitate tunnel preparation. If the assistant lifts the mucosa with two forceps this manoeuver further enhances rapid and safe preparation of the tunnel. The length of the tunnel should be about 4 5 cm. As during tunnel dissection the tissues are stretched, the resulting tunnel length after fixation of the bladder and pull-through, the ureter is usually shorter than anticipated. In case of adherence of the bladder mucosa to the bladder, e.g. from prior inflammation, radiotherapy or bladder surgery, tunnel dissection can be eased by injecting a few milliliters of saline between the detrusor and the mucosa at the intended tunnel site. The width of the tunnel is checked by opening the branches of the scissors. The end of the tunnel is opened by a transverse incision and, to avoid obstruction of the neo-orifice, an oval segment of the bladder mucosa is excised BJU International
11 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 9 With the Overholt clamp inserted retrogradely through the tunnel, the ureter is pulled on its stay suture into the tunnel. The psoas hitch sutures are tied down thereafter. After bladder fixation, the ureter should enter the bladder in a straight course without kinking at the entrance; sometimes it is necessary to widen the tunnel at the entry of the ureter by gentle dissection with scissors. Excess ureter length is excised if necessary, so that ureteric neo-orifice fits snugly BJU International 147
12 Stein et al. Figure 10 A. The ureter is spatulated at the 12 o'clock position and two anchor sutures encompassing ureteric wall, bladder mucosa and detrusor are placed at the 7 and 5 o'clock positions with 5 or 6/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable sutures for ureteric reimplantation (Monosyn or Monocryl ). B. The remainder of the ureteric orifice is completed with 6/0 or (in infants) 7/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable sutures encompassing the ureter wall and bladder mucosa only. At the entrance of the ureter into the submucosal tunnel, the adventitia of the ureter is anchored to the detrusor by one or two 5/0 to 7/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable sutures to avoid postoperative gliding of the ureter within the tunnel. After completion of the reimplantation, urine should freely ejaculate from the orifice. If this is not the case, the course of the ureter should be checked for any kinking or obstruction. Finally, the ureteric stent is placed and anchored to the bladder mucosa with 4/0 or 5/0 glyconate or polyglytone monofilament rapid absorbable sutures (e.g. Monosyn Quick or Caprosyn ). a b BJU International
13 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 11 Before closing the bladder, the ureteric stent is passed through the anterior bladder wall and a cystostomy catheter (e.g. 10 F pigtail) is placed into the bladder, both of which are anchored to the detrusor at the outside with fast-absorbing sutures. The bladder is closed in two layers by a running 5/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable suture for the mucosa and 4/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable suture for the detrusor BJU International 149
14 Stein et al. Figure 12 A and B. After the bladder has been closed, a small Overholt clamp should be used to calibrate the ureteric entrance into the tunnel for its width. Perivesically a 12 or 16-F gravity drain is placed and sutured to the skin. Both the ureteric stent and the cystostomy catheter are also brought out and sutured to the skin. a b BJU International
15 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Boari Flap Figure 13 For ureteric defects longer than 6 8 cm, which cannot be bridged by the psoas hitch technique, the Boari flap offers an option for a tension-free ureteric anastomosis. The ureter is exposed through an extraperitoneal approach in the same technique described for the psoas hitch technique. In a case of redo surgery, a transperitoneal approach may be preferable depending on the amount of scarring and fibrosis. After radiation therapy of the pelvis or after multiple previous operations, the ureter is easier identified at its crossing with the common iliac artery or higher, in a healthy area. The bladder is filled through the Foley catheter and maximum mobilisation of the bladder is performed, including division of the median umbilical ligament (urachus) and both medial umbilical ligaments (umbilical arteries). The classical rectangular Boari flap of about 3 4 cm in width is marked by stay sutures with its base at the posterior lateral bladder wall above the original ureteric orifice and its tip at the contralateral anterior bladder wall. In the Übelhör modification, the bladder is incised on the affected side slightly oblique and this incision is anteriorly and distally extended to the contralateral site. This results in a wide rhombic flap with a broad basis, which can be rotated to the psoas muscle BJU International 151
16 Stein et al. Figure 14 For fixation of the bladder flap to the psoas muscle, two to three 3/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable sutures (e.g. Monoplus or PDS ) are placed preferentially through the tendon of the psoas muscle. The sutures must encompass the entire detrusor muscle thickness without mucosa. The sutures must not be tied at this stage of the operation BJU International
17 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Figure 15 After creation of the submucosal tunnel an Overholt clamp is inserted retrogradely into the tunnel and the ureter is pulled on its stay suture into the tunnel. Thereafter the fixation sutures to the psoas muscle are tied. After bladder fixation, the ureter should enter the Boari flap in a straight course without kinking at the entrance. The ureter is re-implanted into the bladder flap using the same technique as for the psoas hitch BJU International 153
18 Stein et al. Figure 16 Before closing the bladder, the ureteric stent is passed through the anterior bladder wall and a cystostomy catheter (e.g. 10 F pigtail) is placed into the bladder, both of which are anchored to the detrusor on the outside with fast-absorbing suture. The bladder is closed in two layers. Firstly the mucosa is closed with a 4/0 or 5/0 glyconate monofilament absorbable running suture (e.g. Monosyn or Monocryl ). The detrusor is closed with another running 3/0 or 4/0 poly-p-dioxanone monofilament absorbable suture (e.g. Monoplus ). A paravesical gravity drain is placed in the vicinity of the anastomosis BJU International
19 Psoas hitch and Boari flap ureteroneocystostomy Postoperative Management Medication Antibiotics (i.e. cephalosporines) are started at the time of surgery and are continued as long as the stent is in situ. The perivesical drain is removed on day 1 or 2 and as soon as the urine is almost clear, the indwelling Foley catheter is removed. Depending on the difficulty of the procedure, the ureteric stent is removed between day 7 and 10 (in complicated cases or after Boari flap on day 10). After removal of the stent, the cystostomy is clamped and the patient starts to void. The upper tract is checked by ultrasonography on the following day (in adults upper tract imaging is achieved by IVU). The cystostomy is removed after bladder emptying without residual urine has been achieved. Surgeon to Surgeon In some patients, dilatation of the upper tract persists postoperatively. This usually resolves within 3 6 months. If there is any concern about persisting obstruction, a MAG3 clearance with furosemide should be obtained. In children antibiotic prophylaxis should be continued as long as there is increased dilatation of the upper tract as compared with preoperatively. In patients with a symptomatic postoperative ureteric obstruction a JJ catheter is placed antegradely through a percutaneous nephrostomy tract and left for 3 months. In case of persistent obstruction from implantation stenosis, redo-surgery may be performed not earlier than after 3 months. If the ureter cannot be re-implanted into the Boari flap without tension, an additional 3 5 cm of ureteral length can be gained. If ureteric reimplantation remains impossible by bladder bridging techniques, intestinal ureter substitution or kidney autotransplantation remain an option. Both procedures can be performed through the same access, should psoas hitch or Boari flap ureteric reimplantation unexpectedly be infeasible. References 1 Dolff C. [Improved results of ureterocystanastomosis by flexible bladder fixation]. Zentralbl Gynakol 1952; 74: Paquin AJ Jr. Ureterovesical anastomosis: the description and evaluation of a technique. J Urol 1959; 82: Zimmerman IJ, Precourt WE, Thompson CC. Direct uretero-cysto-neostomy with the short ureter in the cure of ureterovaginal fistula. J Urol 1960; 83: Warwick RT, Worth PH. The psoas bladder-hitch procedure for the replacement of the lower third of the ureter. BrJUrol1969; 41: Gross M, Peng B, Waterhouse K. Use of the mobilized bladder to replace the pelvic ureter. J Urol 1969; 101: Riedmiller H, Becht E, Hertle L et al. Psoas-hitch ureteroneocystostomy: experience with 181 cases. Eur Urol 1984; 10: Boari A. L urétéro-cystonostomie. Étude clinique et expérimentale. AnnMalOrgGenUrin1899; 14: Bergmeyer M. [The Boari-Casati Technic of Flap Plastic Surgery in the Treatment of Passage Disorders of the Caudal Ureter]. Urologe 1964; 14: Gil Vernet JM. [Ureterovesicoplasty under mucous membrane. (Modifications of Boari s technic)]. J Urol Medicale Chir 1959; 65: Pytel IuA. [Reconstruction of the lower third of the ureter from a bladder flap according to Boari]. Vestn KhirImIIGrek1959; 83: Kimchi D, Wiesenfeld A. Injuries to the lower third of ureter treated by bladder flap plasty: Boari-Kuss technique; report of two cases. J Urol 1963; 89: Correspondence: Raimund Stein, Division of Paediatric Urology, Department of Urology, University Medical Center, Johannes Gutenberg University, Langenbeckstrasse 1, Mainz, Germany. raimund.stein@unimedizin-mainz.de 2013 BJU International 155
FIG The inferior and posterior peritoneal reflection is easily
 PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
Surgical Atlas Politano-Leadbetter ureteric reimplantation
 Surg Ill SURGERY ILLUSTRATED STEFFENS et al. Surgical Atlas Politano-Leadbetter ureteric reimplantation JOACHIM STEFFENS, EBERHARD STARK, BJÖRN HABEN and ADRIAN TREIYER Department of Urology and Paediatric
Surg Ill SURGERY ILLUSTRATED STEFFENS et al. Surgical Atlas Politano-Leadbetter ureteric reimplantation JOACHIM STEFFENS, EBERHARD STARK, BJÖRN HABEN and ADRIAN TREIYER Department of Urology and Paediatric
Robotic distal ureterectomy with psoas hitch and ureteroneocystostomy: Surgical technique and outcomes
 Asian Journal of Urology (2015) 2, 123e127 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajur CASE REPORT Robotic distal with psoas hitch and
Asian Journal of Urology (2015) 2, 123e127 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajur CASE REPORT Robotic distal with psoas hitch and
THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone
 REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. OPERATIONS/PROCEDURES: Living related renal transplantation. HISTORY: For full details
DISCHARGE SUMMARY DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. OPERATIONS/PROCEDURES: Living related renal transplantation. HISTORY: For full details
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018
 Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
SciFed Journal of Public Health. Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature
 SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit Urinary Diversion
 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux
 Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy
 Original Article SURGERY ILLUSTRATED PANSADORO Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy VITO PANSADORO Urology, Vincenzo Pansadoro Foundation, Rome, Italy ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER, www.spitzer-illustration.com
Original Article SURGERY ILLUSTRATED PANSADORO Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy VITO PANSADORO Urology, Vincenzo Pansadoro Foundation, Rome, Italy ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER, www.spitzer-illustration.com
Surgery of urogenital trauma in condition of war or precarity
 Surgery of urogenital trauma in condition of war or precarity C. H. Rochat Multi-disciplinary Center for Robotic Surgery, Geneva (www.beaulieu.ch) Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research (www.gfmer.ch)
Surgery of urogenital trauma in condition of war or precarity C. H. Rochat Multi-disciplinary Center for Robotic Surgery, Geneva (www.beaulieu.ch) Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research (www.gfmer.ch)
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them
 Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique
 22 Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique G. Barbagli, M. Lazzeri 22.1 Introduction and Historical Background 182 22.2 Anatomical Remarks 182 22.3 Step-by-Step Surgical Details 183 22.3.1
22 Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique G. Barbagli, M. Lazzeri 22.1 Introduction and Historical Background 182 22.2 Anatomical Remarks 182 22.3 Step-by-Step Surgical Details 183 22.3.1
Urological complications in 980 consecutive patients with renal transplantation
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd2006130012711275Original ArticleUrological complications of renal transplant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd2006130012711275Original ArticleUrological complications of renal transplant
Surgical Atlas Orthotopic ileal neobladder
 Surgery Illustrated ORTHOTOPIC ILEAL NEOBLADDER U.E. STUDER ET AL. Surgical Atlas Orthotopic ileal neobladder U.E. STUDER, C. VAROL and H. DANUSER University of Bern, Department of Urology, Bern, Switzerland
Surgery Illustrated ORTHOTOPIC ILEAL NEOBLADDER U.E. STUDER ET AL. Surgical Atlas Orthotopic ileal neobladder U.E. STUDER, C. VAROL and H. DANUSER University of Bern, Department of Urology, Bern, Switzerland
Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course. Version 1.0_2018. Prepared by: Haitham Dagash. MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed)
 Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course Version 1.0_2018 Prepared by: Haitham Dagash MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed) University of Leicester and Leicester Infirmary Hospital Prof.Kokila Lakhoo PhD,FRCS(ENG+EDIN),FCS(SA),FCS(SA:PAED),MRCPCH,MBCHB
Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course Version 1.0_2018 Prepared by: Haitham Dagash MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed) University of Leicester and Leicester Infirmary Hospital Prof.Kokila Lakhoo PhD,FRCS(ENG+EDIN),FCS(SA),FCS(SA:PAED),MRCPCH,MBCHB
HOW I DO IT. Introduction and patient selection. Surgical technique, see Table 1 for key points
 HOW I DO IT Ureteric re-implant for the strictured renal allograft: How I do it Thomas McGregor, MD, 1 Tadeuz Kroczak, MD, 1 Chun Huang, MD, 1 Joshua Koulack, MD 2 1 Division of Urology, Department of
HOW I DO IT Ureteric re-implant for the strictured renal allograft: How I do it Thomas McGregor, MD, 1 Tadeuz Kroczak, MD, 1 Chun Huang, MD, 1 Joshua Koulack, MD 2 1 Division of Urology, Department of
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Li-Ming Su, MD
 Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas
 Surgery Illustrated SURGERY ILLUSTRATEDMURPHY ET AL MURPHY ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Robotically assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty Declan Murphy, Ben Challacombe,
Surgery Illustrated SURGERY ILLUSTRATEDMURPHY ET AL MURPHY ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Robotically assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty Declan Murphy, Ben Challacombe,
RECTAL INJURY IN UROLOGIC SURGERY. Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences.
 RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child
 CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child Manickam Ramalingam, MCh, Kallappan Senthil, MCh, Anandan Murugesan, MCh, Mizar Ganapathy Pai, MCh ABSTRACT Low compliance
CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child Manickam Ramalingam, MCh, Kallappan Senthil, MCh, Anandan Murugesan, MCh, Mizar Ganapathy Pai, MCh ABSTRACT Low compliance
URINARY DIVERSIONS. Susan Hilton, MD and Nicholas Papanicolaou, MD Co-Chiefs, CT Section Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
 URINARY DIVERSIONS Susan Hilton, MD and Nicholas Papanicolaou, MD Co-Chiefs, CT Section Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Neither of us has any financial relationships with commercial interests
URINARY DIVERSIONS Susan Hilton, MD and Nicholas Papanicolaou, MD Co-Chiefs, CT Section Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Neither of us has any financial relationships with commercial interests
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Prevention of Surgical Injuries in Gynecology
 in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP
 8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP The first step is to suture the labia to the thighs and cover the anus with a swab (Figure 31). Figure 31 The labia are sutured to the thighs and the anus is covered
8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP The first step is to suture the labia to the thighs and cover the anus with a swab (Figure 31). Figure 31 The labia are sutured to the thighs and the anus is covered
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 19 CBULP 2011 044 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 19 CBULP 2011 044 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Millin Retropubic Prostatectomy
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Millin Retropubic Prostatectomy John M. Fitzpatrick Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin & University College Dublin, Ireland Accepted
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Millin Retropubic Prostatectomy John M. Fitzpatrick Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin & University College Dublin, Ireland Accepted
Upper Tract Tcc. Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology)
 Upper Tract Tcc Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology) Epidemiology Peak incidence 75 to 79 years 2x more common in men 7% of all renal tumours 5% of all urothelial tumours Synchronous bilateral is rare ~ 1.6%
Upper Tract Tcc Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology) Epidemiology Peak incidence 75 to 79 years 2x more common in men 7% of all renal tumours 5% of all urothelial tumours Synchronous bilateral is rare ~ 1.6%
DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT OF URETERAL STENT: SIMPLIFICATION OF THE TECHNIQUE
 Surgical Technique International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (5): 439-445, September - October, 2002 DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT
Surgical Technique International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (5): 439-445, September - October, 2002 DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT
Renal transplant-recipient surgery
 Surgery Illustrated SURGERY ILLUSTRATED BARRY Renal transplant-recipient surgery John M. Barry Division of Urology and Renal Transplantation, The Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA INDICATIONS
Surgery Illustrated SURGERY ILLUSTRATED BARRY Renal transplant-recipient surgery John M. Barry Division of Urology and Renal Transplantation, The Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA INDICATIONS
Objectives. Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble. Disclosures. Anatomy 101. Anterior Abdominal Wall. Arcuate Line. Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C)
 Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA
 ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
Genitourinary Tract Injuries
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Chapter 18 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Introduction Genitourinary injuries constitute approximately 5% of the total injuries encountered in combat. Their treatment adheres
Genitourinary Tract Injuries Chapter 18 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Introduction Genitourinary injuries constitute approximately 5% of the total injuries encountered in combat. Their treatment adheres
Renal Transplant Surgery
 Renal Transplant Surgery Mr Somaiah Aroori MS MD EBS in HPB FRCS Consultant HPB & Renal Transplant Surgeon SWTC, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth Over next few minutes Aim to cover Details of Transplant procedure
Renal Transplant Surgery Mr Somaiah Aroori MS MD EBS in HPB FRCS Consultant HPB & Renal Transplant Surgeon SWTC, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth Over next few minutes Aim to cover Details of Transplant procedure
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Technique Guide. Bard MK Hernia Repair. Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh SOFT TISSUE REPAIR. Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE
 REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE WITH RAZ SUSPENSION 17 VAGINAL INCISION AND DISSECTION Premarin cream application to the anterior vagina daily for 1 month before cystocele repair enriches the vasculature and
REPAIR OF LARGE CYSTOCELE WITH RAZ SUSPENSION 17 VAGINAL INCISION AND DISSECTION Premarin cream application to the anterior vagina daily for 1 month before cystocele repair enriches the vasculature and
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Department of Urology, Theodor Bilharz research Institute, Cairo, Egypt
 Surgical Technique Vol. 41 (4): 796-803, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.0086 Detour technique, Dipping technique, or IIeal bladder flap technique for surgical correction of uretero-ileal
Surgical Technique Vol. 41 (4): 796-803, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.0086 Detour technique, Dipping technique, or IIeal bladder flap technique for surgical correction of uretero-ileal
RPLND: Tips and Tricks
 RPLND: Tips and Tricks Andrew J. Stephenson, MD FACS FRCS(C) Director, Center for Urologic Oncology Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH RPLND: Keys to success Knowledge
RPLND: Tips and Tricks Andrew J. Stephenson, MD FACS FRCS(C) Director, Center for Urologic Oncology Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH RPLND: Keys to success Knowledge
Urethral Stricture Management. AUA Guidelines. Michael Coburn, MD Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas
 Urethral Stricture Management AUA Guidelines Michael Coburn, MD Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas Urethral Stricture Guidelines Systematic peer-reviewed literature review
Urethral Stricture Management AUA Guidelines Michael Coburn, MD Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas Urethral Stricture Guidelines Systematic peer-reviewed literature review
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Vesicoureteral Reflux, Treatment with Periureteral Bulking Agents File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: vesicoureteral_reflux_treatment_with_periureteral_bulking_agents
Corporate Medical Policy Vesicoureteral Reflux, Treatment with Periureteral Bulking Agents File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: vesicoureteral_reflux_treatment_with_periureteral_bulking_agents
Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement
 ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
Cholecystectomy. Sarah Forsyth
 Cholecystectomy Sarah Forsyth History of Cholecystectomy First open cholecystectomy 1882 by Carl Langenbuch in Germany First lap cholecystectomy 1987, Philip Mouret (Gynaecologist) in Lyon, France 1990,
Cholecystectomy Sarah Forsyth History of Cholecystectomy First open cholecystectomy 1882 by Carl Langenbuch in Germany First lap cholecystectomy 1987, Philip Mouret (Gynaecologist) in Lyon, France 1990,
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours
 Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours A. Hașegan 1, V. Pîrvuț 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Clinical
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours A. Hașegan 1, V. Pîrvuț 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Clinical
Urinary Bladder. Prof. Imran Qureshi
 Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Citation International journal of urology (2. Right which has been published in final f
 Title Novel constant-pressure irrigation of renal pelvic tumors after ipsila Nakamura, Kenji; Terada, Naoki; Sug Author(s) Toshinori; Matsui, Yoshiyuki; Imamu Kazutoshi; Kamba, Tomomi; Yoshimura Citation
Title Novel constant-pressure irrigation of renal pelvic tumors after ipsila Nakamura, Kenji; Terada, Naoki; Sug Author(s) Toshinori; Matsui, Yoshiyuki; Imamu Kazutoshi; Kamba, Tomomi; Yoshimura Citation
SURGICAL PROCEDURES OPERATIONS ON THE UROGENITAL SYSTEM
 KIDNEYS AND PERINEPHRUM 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time of pyelolithotomy or nephrolithotomy. 2. In a routine surgical approach to the kidney and related procedures,
KIDNEYS AND PERINEPHRUM 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time of pyelolithotomy or nephrolithotomy. 2. In a routine surgical approach to the kidney and related procedures,
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Renal transplantation is the preferred treatment method of endstage
 Technical Aspects of Renal Transplantation John M. Barry Renal transplantation is the preferred treatment method of endstage renal disease (ESRD). It is more cost-effective than is maintenance dialysis
Technical Aspects of Renal Transplantation John M. Barry Renal transplantation is the preferred treatment method of endstage renal disease (ESRD). It is more cost-effective than is maintenance dialysis
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Open staghorn stone surgery. ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER,
 a c a f a d c e RIEDMILLER and SPAHN BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Open staghorn stone surgery Huertus Riedmiller and Martin Spahn Department of Urology and Pediatric Urology,
a c a f a d c e RIEDMILLER and SPAHN BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Open staghorn stone surgery Huertus Riedmiller and Martin Spahn Department of Urology and Pediatric Urology,
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Facing Surgery. for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condit ion: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters and the
Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condit ion: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters and the
Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61)
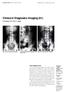 Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
Free Flap Phalloplasty For Female To Male Gender Dysphoria
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Free Flap Phalloplasty For Female To Male Gender Dysphoria Giulio Garaffa, MD, PhD, FECSM, FRCS (Eng), David J. Ralph, BSc, MS, FRCS (Urol) St Peter s Andrology and the Institute of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Free Flap Phalloplasty For Female To Male Gender Dysphoria Giulio Garaffa, MD, PhD, FECSM, FRCS (Eng), David J. Ralph, BSc, MS, FRCS (Urol) St Peter s Andrology and the Institute of
West Yorkshire Major Trauma Network Clinical Guidelines 2015
 WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Facing Surgery. for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system produces, stores, and eliminates urine. It includes
Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system produces, stores, and eliminates urine. It includes
ARTIFICIAL MESH REPAIR FOR TREATMENT OF PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
 Pelvic Floor Unit / Department of Gynaecology Ward 17, Singleton Hospital, Sketty, Swansea, SA2 8QA 01792 205666 Secretary Direct Line: 01792 285688. Fax: 01792 285874 ARTIFICIAL MESH REPAIR FOR TREATMENT
Pelvic Floor Unit / Department of Gynaecology Ward 17, Singleton Hospital, Sketty, Swansea, SA2 8QA 01792 205666 Secretary Direct Line: 01792 285688. Fax: 01792 285874 ARTIFICIAL MESH REPAIR FOR TREATMENT
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Sonography of the Bladder After Ureteral Reimplantation
 Sonography of the Bladder After Ureteral Reimplantation J. Michael Zerin, MD*, Jeffrey D. Smith, DOtt, Jill K. Sanvordenker, RNt, David A. Bloom, MDt Pre- and postoperative sonograms were reviewed in 59
Sonography of the Bladder After Ureteral Reimplantation J. Michael Zerin, MD*, Jeffrey D. Smith, DOtt, Jill K. Sanvordenker, RNt, David A. Bloom, MDt Pre- and postoperative sonograms were reviewed in 59
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report
 198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
Robot Assisted Rectopexy
 1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP. By MICHAL KRAUSS. Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP By MICHAL KRAUSS Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland RECONSTRUCTION of the nose is one of the composite procedures in
RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP By MICHAL KRAUSS Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland RECONSTRUCTION of the nose is one of the composite procedures in
The number following the procedure code is the TRICARE payment group. KIDNEY
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M JUNE 25, 1999 S POLICY CHAPTER 13 SECTION 9.1 ADDENDUM 1, SECTION 8 TRICARE-APPROVED AMBULATORY SURGERY S - URINARY SYSTEM The number following the procedure code
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M JUNE 25, 1999 S POLICY CHAPTER 13 SECTION 9.1 ADDENDUM 1, SECTION 8 TRICARE-APPROVED AMBULATORY SURGERY S - URINARY SYSTEM The number following the procedure code
Application of Yang-Monti Principle in Ileal Ureter Substitution: Is It a beneficial Modification?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 38 (6): 779-787, November - December, 2012 Application of Yang-Monti Principle in Ileal Ureter Substitution: Is It a beneficial Modification? M. Esmat, A. Abdelaal, D. Mostafa Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 38 (6): 779-787, November - December, 2012 Application of Yang-Monti Principle in Ileal Ureter Substitution: Is It a beneficial Modification? M. Esmat, A. Abdelaal, D. Mostafa Department
Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates
 Vesicoureteral Reflux Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates Yuval Bar-Yosef,* Miguel Castellan, Devandra Joshi, Andrew Labbie
Vesicoureteral Reflux Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates Yuval Bar-Yosef,* Miguel Castellan, Devandra Joshi, Andrew Labbie
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience
 Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series. Urological Trauma
 UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent Pouch with Abdominal Stoma
 Case Report Urol Int 1999;62:213 216 Received: June 19, 1998 Accepted after revision: March 8, 1999 Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent
Case Report Urol Int 1999;62:213 216 Received: June 19, 1998 Accepted after revision: March 8, 1999 Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent
JuggerLoc Bone-to-Bone System for Ankle Syndesmosis Fixation. Surgical Technique
 JuggerLoc Bone-to-Bone System for Ankle Syndesmosis Fixation Surgical Technique Table of Contents Position and Preparation... 2 Incision... 2 Fracture Reduction... 2 Drill Fibula and Tibia... 3 JuggerLoc
JuggerLoc Bone-to-Bone System for Ankle Syndesmosis Fixation Surgical Technique Table of Contents Position and Preparation... 2 Incision... 2 Fracture Reduction... 2 Drill Fibula and Tibia... 3 JuggerLoc
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis
 Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting. Kofu - Japan. September 29th - October 1st, 2010
 Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting Kofu - Japan September 29th - October 1st, 2010 Reconstruction of penile and bulbar urethra Evaluation of anterior urethral stricture Urethrography Retrograde
Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting Kofu - Japan September 29th - October 1st, 2010 Reconstruction of penile and bulbar urethra Evaluation of anterior urethral stricture Urethrography Retrograde
INTRODUCTION. MA TERJfALS AND METHODS RESULTS
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 46 No. 2 June '99 Clarence CM. Lei, FRCS(G) Md Mahi.r MS, FRCS(Ed).n.'-J'Ul'UlUWU, FRCS(G) of Urology, Institute of Urology & Nephrology, K uala '-'W,fnVW JV"'''''''''''' to the lower
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 46 No. 2 June '99 Clarence CM. Lei, FRCS(G) Md Mahi.r MS, FRCS(Ed).n.'-J'Ul'UlUWU, FRCS(G) of Urology, Institute of Urology & Nephrology, K uala '-'W,fnVW JV"'''''''''''' to the lower
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Florence robotic intracorporeal neobladder (FloRIN): a new reconfiguration strategy developed following the IDEAL guidelines
 Step-by-Step Florence robotic intracorporeal neobladder (FloRIN): a new reconfiguration strategy developed following the IDEAL guidelines Andrea Minervini*, Davide Vanacore*, Gianni Vittori*, Martina Milanesi*,
Step-by-Step Florence robotic intracorporeal neobladder (FloRIN): a new reconfiguration strategy developed following the IDEAL guidelines Andrea Minervini*, Davide Vanacore*, Gianni Vittori*, Martina Milanesi*,
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Bladder psoas hitch in hydronephrosis due to pelvic endometriosis: outcome of urodynamic parameters
 ENDOMETRIOSIS Bladder psoas hitch in hydronephrosis due to pelvic endometriosis: outcome of urodynamic parameters Luca Carmignani, M.D., a Antonella Ronchetti, M.D., b Fabio Amicarelli, M.D., b Paolo Vercellini,
ENDOMETRIOSIS Bladder psoas hitch in hydronephrosis due to pelvic endometriosis: outcome of urodynamic parameters Luca Carmignani, M.D., a Antonella Ronchetti, M.D., b Fabio Amicarelli, M.D., b Paolo Vercellini,
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System
 Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Ultrapro Hernia System Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD. dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg
 Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history:
 MP/H Quiz A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history: 9/23/06 TURB 1/12/07 TURB 4/1/07 TURB 7/12/07 TURB 11/14/07 Non-invasive papillary transitional cell carcinoma from
MP/H Quiz A patient with recurrent bladder cancer presents with the following history: 9/23/06 TURB 1/12/07 TURB 4/1/07 TURB 7/12/07 TURB 11/14/07 Non-invasive papillary transitional cell carcinoma from
Modified laparoscopic intravesical nonrefluxing ureteral reimplantation with psoas hitch using a submucosal tunneling
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2014;10(6):378-382 Modified laparoscopic intravesical nonrefluxing ureteral reimplantation with psoas hitch using a submucosal tunneling Chang-Hee Kim,
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2014;10(6):378-382 Modified laparoscopic intravesical nonrefluxing ureteral reimplantation with psoas hitch using a submucosal tunneling Chang-Hee Kim,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urethral Injuries: Realignment vs. Delayed Reconstruction
 Urethral Injuries: Realignment vs. Delayed Reconstruction E. Charles Osterberg, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery (Urology) Dell Medical School Chief of Urology and Genitourinary Reconstruction None Disclosures
Urethral Injuries: Realignment vs. Delayed Reconstruction E. Charles Osterberg, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery (Urology) Dell Medical School Chief of Urology and Genitourinary Reconstruction None Disclosures
Guido Barbagli. Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery
 Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
Vesicoureteral Reflux
 What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly
 Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
