Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability and accuracy of a
|
|
|
- Madeleine Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reliability and accuracy of a radiographic analysis method for posterior maxillary mini-implant location Luís Carlos Sampaio DIAS 1, Yomara Barreto da Costa FERREIRA 2, Rudys Rodolfo de JESUS TAVAREZ 3, Célia Regina Maio PINZAN-VERCELINO 3, Júlio de Araújo GURGEL 4 1- DDS, MSc, Graduate student in Orthodontics, University Center of Maranhão - UNICEUMA, São Luis, MA, Brazil. 2- Undergraduate student, Dental School, University Center of Maranhão - UNICEUMA, São Luis, MA, Brazil. 3- DDS, MSc, PhD, Professor of Master s Degree Program in Dentistry, University Center of Maranhão - UNICEUMA, São Luis, MA, Brazil. 4- DDS, MSc, PhD, Professor and Coordinator of the Master s Degree Program in Dentistry, University Center of Maranhão - UNICEUMA, São Luis, MA, Brazil. Corresponding address: Dr. Júlio de Araújo Gurgel - R. Cel José Braz, Centro - Marília - SP Brazil - Phone/Fax: jagurgel@terra.com.br Received: December 02, Modification: May 10, Accepted: October 26, 2009 abstract Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability and accuracy of a radiographic analysis method for the location of mini-implants inserted in the posterior region of the maxilla. Material and Methods: Two self-drilling mini-implants were installed between the second premolar and the first molar on the right side and left side in three dry skulls. Three operators performed three occlusal radiographs, using an occlusal x-ray film holder, at three different times in each of the three skulls. Results: The interclass correlation coefficient showed a significantly high, positive correlation (p<0.05), indicating an excellent reliability between operators. The analysis of variance showed no significant differences in time and among the operators. Conclusion: Based of these findings, it may be concluded that this methodology can be used by several operators in longitudinal clinical studies on orthodontic mini-implants at the anterior-posterior and lateral-medial locations or longitudinal displacement. Key words: Dental implants. Radiographic film. Orthodontic anchorage procedures. INTRODUCTION Orthodontic anchorage is a basic procedure necessary for a successful treatment. For this reason, clinicians seek to better understand various orthodontic devices, such as headgear, transpalatal arch, lingual arch, and Nance s button. These devices allow a certain degree of movement of the anchorage unit and are dependent, to varying degrees, on patient compliance. In severe cases or in cases of non-cooperative patients, treatment could be compromised. Recently, skeletal anchorage has increased in popularity due to the benefit of direct transfer of the point of anchorage from the teeth to the skeleton 6,9,10. However, since these miniimplants have been used in orthodontics, a small displacement during treatment has been detected. The mini-implant displacement allows contact between the screw and the dental root, causing damage to the root or the periodontal ligament, potentially leading to mobility or loss of the miniimplant 3,11,12,15,16,17,18. Unfortunately, there is not much information available on the displacement or adverse effects of mini-implants. Recently, Hsieh, et al. 8 (2008) found that even endosseous titanium implants may not necessarily serve as a rigid orthodontic anchorage at all force levels. Lateral films no longer provide the best images to study such small devices. Liou, et al. 13 (2004) investigated cephalometric tracings and found a noteworthy extrusion and tipping forward of mini-implants after en-masse retraction of anterior teeth. Recently, tomographic studies have evaluated the position of mini-implants in both jaws, though without relating them to longitudinal control 1,14. To the best of our knowledge, no tomographic study had quantified mini-implant displacement in orthodontic patients. J Appl Oral Sci. 99
2 Reliability and accuracy of a radiographic analysis method for posterior maxillary mini-implant location General dentistry and orthodontics constantly use radiographs with the main purpose of assessing the validity of treatment methods. Zanda 20 (2007) described a new film holder for occlusal film that showed effective reproducibility of occlusal radiographic images in dry skulls (Figure 1), making it possible to take an occlusal radiographic sequence at different times. Gurgel, et al. 16 (2005) used dry human skulls to analyze the reliability in determining tooth position in posterior-anterior films. Using markers inserted in the bands of molars and premolars from Hyrax expanders allow identifying each one in each side on posterior-anterior films. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the reliability and accuracy of a radiographic analysis method for identifying the location of mini-implants inserted in the posterior region of the maxilla in dry human skulls. MATERIAL AND METHODS Three human skulls were obtained from the Anatomy Department of the Dental School of the University Center of Maranhão, Brazil. All skulls had preserved maxilla and mandible and sufficient teeth on the posterior area of the maxilla for the successful placement of mini-implants. The cortical bone condition and the maxillary interadicular space were evaluated using radiographic images between the second premolars and the first molars. According to the same technical criteria used for patients, six self-drilling mini-implants (1.6x1x7 mm; OSAS, DEWIMED, Tuttlingen, Germany) were placed between the second premolars and the first molars at a 45 angle relative to the tooth s long axis. Once the study began, the main purpose was to test the reliability of different operators for the proposed method in this research. Therefore, clinical operators with various levels of professional experience were invited to take the occlusal radiographs. Three operators were selected: an orthodontist, an implantodontist and an undergraduate dental student. Each operator performed three occlusal radiographs taken at three intervals of 15 days in each of the three skulls. The set of three radiographs of each skull was identified externally according to an identification number for the skull, the operator and the time. A total of 27 randomized occlusal radiographs were obtained using insight IO-41 film (size 5.7 cm x 7.6 cm; KODAK) with 1.5 s exposure time at 10 ma and 70 kv. The occlusal radiographs were taken with a correct alignment between the cylinder localizer from the x-ray machine and the ring from the occlusal radiographic position self-drilling film. Each operator took the occlusal radiograph for each of the skulls with the occlusal films inserted in the Zanda 20 (2007) film holder and fit the film in more Figure 1- Occlusal x-ray film holder and skull positioned for standardized occlusal radiograph Figure 2- Occlusal radiographs with mini-implants placed Figure 3- Occlusal radiographs and measurements J Appl Oral Sci. 100
3 DIAS LCS, FERREIRA YBC, JESUS TAVAREZ RR, PINZAN-VERCELINO CRM, GURGEL JA Table 1- Mean and standard deviation (SD) for each measurement and operator (OP) OP1 OP2 OP3 Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Skull 1 Left x y x' y' Right x y x' y' Skull 2 Left x y x' y' Right x y x' y' Skull 3 Left x y x' y' Right x y x' y' number of posterior teeth of the maxilla. All radiographs and a ruler with same lateral size were digitized using a scanner (Be@rPaw 2400TA Plus, Scanner A4) (Figure 2). The radiographs were measured using MacBiophotonics ImageJ software originally applied in biologic researches for microscopic image capture. Two ruler points were initially defined for calibration. After the mini-implant positions, the points were defined and measured using a Cartesian coordinate system (Figure 3). The Cartesian system was composed by the following measures: Line A: a straight line traced over the maximum number point of the midpalatal suture; Line B: a line perpendicular to the intersection of line A at the virtual point representative of the incisive foramen; Distance xd: for the mini-implant on the right Distance yd: for the mini-implant on the right mini-implant to line B; Distance x d: for the mini-implant on the right side, the minimum distance from the tip of the miniimplant to line A; Distance y d: for the mini-implant on the right side, the minimum distance from the tip of the miniimplant to line B; Distance xe: for the mini-implant on the left Distance ye: for the mini-implant on the left mini-implant to line B; Distance x e: for the mini-implant on the left side, the minimum distance from the tip of the Distance y e: for the mini-implant on the left side, the minimum distance from the tip of the mini-implant to line B. The means and standard deviations of the distances on each side were calculated considering the operator and the skull (Table 1). The intraoperator reliability for the measurements was estimated using the interclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the effect of different image times and different operators. RESULTS Statistical analysis indicated a significantly high, positive correlation between the maxillary occlusal radiography taken by the different operators (Table 2). These data indicate an excellent reliability between operators. The ICC test verified the measurements of each J Appl Oral Sci. 101
4 Reliability and accuracy of a radiographic analysis method for posterior maxillary mini-implant location Table 2- Intra-operator reliability for mini-implant measurements expressed as interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) (n=3) Variable r P Significance x <0.05 NS y <0.05 NS x' <0.05 NS y' <0.05 NS NS=not significant Table 3- ANOVA for measurements of x, y, x' and y' variable ANOVA ANOVA ANOVA operator p time p time and operator p x y x' y' variable made by each operator on each skull that localize the head and the tip of the mini-implant (x, y, x and y ). Intra-operator correlations were above 0.87 for all the operators and each of the skulls (Table 2). This value seems to indicate a similar variation, indicating an excellent reproducibility through a positive and high correlation. In terms of the effect of time, the operator and its interactions showed no statistically significant differences in any of the variables analyzed by ANOVA (Table 3). DISCUSSION The goal of the present study was to test the reliability and accuracy of the radiographic occlusal position developed by Zanda 20 (2007) used as a device to verify the stability of posteroanteriorly and lateromedially positioned orthodontic mini-implants. The hypothesis was that this method can be used as a replicate for maxillary occlusal radiographs for location of mini-implant placement in the posterior region of the maxilla. Since the introduction of the cephalostat as a standard for taking cephalometric radiographs, the cephalostat has been traditionally used to determine the direction and amount of skeletal and dental changes. Several devices have also been developed and improved with longitudinal research in orthodontic patients. Some studies have reported that film holders and markers of anatomic structures contribute to the improvement in radiographic images. Also creating more information about the position of structures during orthodontic treatments 5,7. Based on these presumptions, our study used a model of an occlusal x-ray film holder to obtain the most uniform radiographic series. Additionally, the selected anatomic structures used as references to determinate the measurements were chosen because they are known to be stable during treatment. This study showed that the use of the occlusal x-ray film holder is sufficiently accurate for investigations of mini-implant stability and an alternative to cephalometric analyses for determinate mini-implant displacement. Furthermore, the numerical information on the displacement of the mini-implants can be correlated with the amount of dental movement determined by the retraction. Liou, et al. 13 (2004) reported that mini-implants do not remain stable at forces higher than 400 g. These findings suggest that studies are necessary to quantify mini-implant displacement caused by treatment, especially by means of the innumerable variables related to the use of this transitional anchorage device. Our findings show that future clinical studies will be able to evaluate the direction of the displacement of the mini-implants. Also, different types of this skeletal anchorage device could be compared considering the thickness, the design and the length with the suffered displacement. Computed tomography (CT) scans are not routinely used to improve the quality of craniofacial measurements in orthodontics. The present data prove that the method presented here is valid and can be performed at a much lower cost compared to CT. This means that clinicians and researchers can better understand this innovative modality of anchorage using an easily attainable and low-cost material. Another important benefit of this method is a lower exposure of patients to radiation to detect the stability of the mini-implants. We believe that clinical studies on this topic are very important for further acknowledgment of transitory anchorage device. However, there is a great deal of responsibility in deciding to prescribe radiographs, especially CT scans; it is complicated and depends on the effects on the orthodontic therapy management 19. Human skulls were used for safety reasons due to the potential exposure of patients to ionizing radiation. The adopted model simulates similar conditions used for patients, with a reduced x-ray exposure time 4. Additionally, the anatomic structures used to obtain all measurement tracings are easily identified, as well as their presence in the same plane and height as the indicated inserted mini-implant in the posterior maxillary area. Here we used dry skulls. For future studies in patients, we believe that the selected areas are not influenced by soft tissue thickness and do not compromise the visualization of the anatomic structures used and J Appl Oral Sci. 102
5 DIAS LCS, FERREIRA YBC, JESUS TAVAREZ RR, PINZAN-VERCELINO CRM, GURGEL JA the installed mini-implants. The number of dry skulls used in this type of study has revealed variations in other studies 1,7,14,. These differences are probably due to the number of measurements analyzed. The number of skulls used in the present study was sufficient to verify the influence of individual anatomic variations in the statistical analysis. It should be noted that we opted for a research design that did not evaluate the anatomic aspects in relation to accuracy and reliability 2. The aim of the study was to analyze operator s reproducibility on separate occasions. The intraclass correlation proved that, with the skull change and, consequently, the occurrence of anatomic variations, a high and significant correlation was found among the different measurements of each skull. These data indicate an excellent reproducibility between the operators. The agreement in the operators measurements (Table 3) shows that this method is useful for research and for clinical evaluation. For clinical use, it is indicated to attach the film to the film holder (Figure 1) and after adaption inside of the mouth, ask for the patient to occlude. Only with the dental occlusion is possible to achieve stability to use this intraoral radiographic technique. Zanda 20 (2007) found variations in the reliability of measurements far from the occlusal plane, whereas the present study showed no statistically significant differences. In the present study, this reproducibility was found because the mini-implants and the anatomic structures used the same plane into the maxilla, both are at the same tall of palatal plane. Variables describing the position of the head and the tip of the mini-implant were in the same plane. Also, the midpalatal suture was chosen as a reliable reference for the determination of a measurement for each variable. It should be mentioned that the method presented here only identifies mini-implant localization on the posterior region of the maxilla. This implies that, in future studies, an additional use for this method in another site of the maxilla or mandible may be the identification of a more reliable anatomic structure for each studied region. CONCLUSIONS The results of the present study demonstrate that this radiographic method was highly reproducible among operators and accurate for the identification of measurements. Also, no differences were observed based on the time and the operator using this method. These results support the use of this standardized method for occlusal radiographs for mini-implant identification on the posterior maxilla. REFERENCES 1- Baumgaertel S, Palomo JM, Palomo L, Hans MG. Reliability and accuracy of cone-bean computed tomographiy dental measurements. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136: Berco M, Rigali PH Jr, Miner RM, DeLuca S, Anderson, NK, Will LA. Accuracy and reliability of linear cephalometric measurements from cone-beam computed tomography scans of a dry human skull. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136: Berens A, Wiechmann D, Dempf R. Mini- and micro-screws for temporary skeletal anchorage in orthodontic therapy. J Orofac Orthop. 2006;67: Brazil. Ministry of Health. National Health Surveillance Agency. Publication 453 of June 1st, Diretrizes de proteção radiológica em radiodiagnóstico médico e odontológico. Federal Official Gazette of Brazil. Brasília (1998 Jun 2). 5- Byloff FK, Mossaz CF. Skeletal and dental changes following surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Eur J Orthod. 2004,26: Cornelis MA, Scheffler NR, De Clerck HJ, Tulloch JF, Behets CN. Experimental systematic review of the uses of temporary skeletal anchorage devices in orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;131:S Gurgel JA, Sant'ana E, Ferreira Júnior O, Sant'ana LFM, Giglio FPM. O uso de marcadores para identificação de posicionamento dentário em telerradiografias frontais póster-anteriores: proposta de um método. Rev Dent Press Ort Ortop Facial. 2005;10: Hsieh YD, Su CM, Yang YH, Fu E, Chen HL, Kung S. Evaluation on the movement of endosseous titanium implants under continuous orthodontic forces: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19: Kanomi R. Mini-implant for orthodontic anchorage. J Clin Orthod. 1997;31: Kuroda S, Sugawara Y, Deguchi T, Kyung HM, Takano- Yamamoto T. Clinical use of miniscrew implants as orthodontic anchorage: success rates and postoperative discomfort. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;131: Kuroda S, Yamada K, Deguchi T, Hashimoto T, Kyung HM, Yamamoto T. Root proximity is a major factor for screw failure in orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;131:S Lee JS, Park HS, Kyung HM. Micro-implant anchorage for lingual treatment of a skeletal Class II malocclusion. J Clin Orthod. 2001;35: Liou EJ, Father BC, Lin JC. Do miniscrews remain stationary under orthodontic forces? Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004;126: Monnerat C, Restle L, Mucha JN. Tomographic mapping of mandibular interradicular spaces for placement of orthodontic miniimplants. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135:428.e1-e Park HS. The skeletal cortical anchorage using titanium microscrew implants, Kor J Orthod. 1999;29: Park HS, Bae SM, Kyung HM, Sung JH. Micro-implant anchorage for treatment of skeletal Class I bialveolar protrusion. J Clin Orthod. 2001;35: Park, HS, Jeong SH, Kwon OW. Factors affecting the clinical success of screw implants used as orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130: Romanos GE, Toh CG, Siar CH, Swaminathan D. Histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of peri-implant bone subjected to immediate loading: and experimental study with Macaca fascicularis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17: Turpin DL. British Orthodontic Society revises guidelines for clinical radiography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;134: Zanda MJ, Vidotti BA, Capelozza, ALA. Development of a film-holding instrument to obtain occlusal radiographs. Revista APCD. 2007;61: J Appl Oral Sci. 103
Bone density assessment for mini-implants position
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Bone density assessment for mini-implants position Marlon Sampaio Borges*, José Nelson Mucha** Abstract Introduction: Cortical thickness, interradicular space width and bone
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Bone density assessment for mini-implants position Marlon Sampaio Borges*, José Nelson Mucha** Abstract Introduction: Cortical thickness, interradicular space width and bone
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
Intraoral molar-distalization appliances that
 2014 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com Distalization with the Miniscrew- Supported EZ Slider Auxiliary ENIS GÜRAY, DDS, PHD FARUK IZZET UCAR, DDS, PHD NISA GUL, DDS
2014 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com Distalization with the Miniscrew- Supported EZ Slider Auxiliary ENIS GÜRAY, DDS, PHD FARUK IZZET UCAR, DDS, PHD NISA GUL, DDS
ORTHODONTIC CORRECTION Of OCCLUSAL CANT USING MINI IMPLANTS:A CASE REPORT. Gupta J*, Makhija P.G.**, Jain V***
 ORTHODONTIC CORRECTION Of OCCLUSAL CANT USING MINI IMPLANTS:A CASE REPORT Gupta J*, Makhija P.G.**, Jain V*** Abstract: The inability of orthodontists to change the cant of the maxillary occlusal plane
ORTHODONTIC CORRECTION Of OCCLUSAL CANT USING MINI IMPLANTS:A CASE REPORT Gupta J*, Makhija P.G.**, Jain V*** Abstract: The inability of orthodontists to change the cant of the maxillary occlusal plane
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
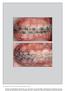 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Failure of Orthodontic Mini-implants by Age, Sex, and Arch; Number of Primary Insertions; and Frequency of Reinsertions After Failure:
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Failure of Orthodontic Mini-implants by Age, Sex, and Arch; Number of Primary Insertions; and Frequency of Reinsertions After Failure:
Non-osseointegrated. What type of mini-implants? 3/27/2008. Require a tight fit to be effective Stability depends on the quality and.
 Non-osseointegrated What type of mini-implants? Require a tight fit to be effective Stability depends on the quality and quantity of cortical and trabecular bone. Osseointegrated Non-osseointegrated AbsoAnchor
Non-osseointegrated What type of mini-implants? Require a tight fit to be effective Stability depends on the quality and quantity of cortical and trabecular bone. Osseointegrated Non-osseointegrated AbsoAnchor
3D Cortical Bone Anatomy of the Mandibular Buccal Shelf: a CBCT study to define sites for extra-alveolar bone screws to treat Class III malocclusion
 3D Cortical Bone Anatomy of the Mandibular Buccal Shelf: a CBCT study to define sites for extra-alveolar bone screws to treat Class III malocclusion Abstract Objective: Assess the feasibility of a proposed
3D Cortical Bone Anatomy of the Mandibular Buccal Shelf: a CBCT study to define sites for extra-alveolar bone screws to treat Class III malocclusion Abstract Objective: Assess the feasibility of a proposed
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Orthodontic Microimplants and Its
 CASE REPORT Orthodontic Microimplants and Its Applications Rajesh Patil 1, Girish Karandikar 2, Manish Sonawane 3 Abstract Microimplants usage has revolutionized the clinical orthodontic practice over
CASE REPORT Orthodontic Microimplants and Its Applications Rajesh Patil 1, Girish Karandikar 2, Manish Sonawane 3 Abstract Microimplants usage has revolutionized the clinical orthodontic practice over
Skeletal class III maloeclusion treated using a non-surgieal approach supplemented with mini-implants: a case report
 Journal oforthodontîcz^ol 40, 2013, 256-263! CLINICAL SECTION Skeletal class III maloeclusion treated using a non-surgieal approach supplemented with mini-implants: a case report Marcel Marchiori Farret^
Journal oforthodontîcz^ol 40, 2013, 256-263! CLINICAL SECTION Skeletal class III maloeclusion treated using a non-surgieal approach supplemented with mini-implants: a case report Marcel Marchiori Farret^
Since their introduction, the use of orthodontic
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival analysis of orthodontic mini-implants Shin-Jae Lee, a Sug-Joon Ahn, a Jae Won Lee, b Seong-Hun Kim, c and Tae-Woo Kim d Seoul and Gyeonggi-Do, Korea Introduction: Survival analysis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival analysis of orthodontic mini-implants Shin-Jae Lee, a Sug-Joon Ahn, a Jae Won Lee, b Seong-Hun Kim, c and Tae-Woo Kim d Seoul and Gyeonggi-Do, Korea Introduction: Survival analysis
6. Timing for orthodontic force
 6. Timing for orthodontic force Orthodontic force is generally less than 300gm, so early mechanical stability is enough for immediate orthodontic force. There is no actually difference in success rate
6. Timing for orthodontic force Orthodontic force is generally less than 300gm, so early mechanical stability is enough for immediate orthodontic force. There is no actually difference in success rate
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015
 AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
There is little controversy regarding whether temporary
 CLINICIAN'S CORNER Control of maxillary dentition with 2 midpalatal orthodontic miniscrews Yoon-Goo Kang, a Ji-Young Kim, b and Jong-Hyun Nam c Seoul, Korea The midpalatal area has no critical anatomic
CLINICIAN'S CORNER Control of maxillary dentition with 2 midpalatal orthodontic miniscrews Yoon-Goo Kang, a Ji-Young Kim, b and Jong-Hyun Nam c Seoul, Korea The midpalatal area has no critical anatomic
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Soft Tissue Thickness for Placement of an Orthodontic Miniscrew Using an Ultrasonic Device
 Original Article Soft Tissue Thickness for Placement of an Orthodontic Miniscrew Using an Ultrasonic Device Bong-Kuen Cha a ; Yeon-Hee Lee b ; Nam-Ki Lee c ; Dong-Soon Choi c ; Seung-Hak Baek d ABSTRACT
Original Article Soft Tissue Thickness for Placement of an Orthodontic Miniscrew Using an Ultrasonic Device Bong-Kuen Cha a ; Yeon-Hee Lee b ; Nam-Ki Lee c ; Dong-Soon Choi c ; Seung-Hak Baek d ABSTRACT
Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach
 Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Maxillary sinus perforation by orthodontic anchor screws
 95 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 57, No. 2, 95-100, 2015 Original Maxillary sinus perforation by orthodontic anchor screws Mitsuru Motoyoshi 1,2), Rina Sanuki-Suzuki 1,2), Yasuki Uchida 1,2), Akari Saiki
95 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 57, No. 2, 95-100, 2015 Original Maxillary sinus perforation by orthodontic anchor screws Mitsuru Motoyoshi 1,2), Rina Sanuki-Suzuki 1,2), Yasuki Uchida 1,2), Akari Saiki
Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage
 CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
Maxillary Molar Distalization with micro-implants:
 Predictable Maxillary Molar Distalization with Micro-implant Anchorage in the correction of class II Malocclusion Dr. Ramesh Sabhlok BDS, MDS, Cert. Ortho. (USA), FDS RCS (Edinburgh), FDS RCPS (Glasgow),
Predictable Maxillary Molar Distalization with Micro-implant Anchorage in the correction of class II Malocclusion Dr. Ramesh Sabhlok BDS, MDS, Cert. Ortho. (USA), FDS RCS (Edinburgh), FDS RCPS (Glasgow),
Periapical Radiography
 Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
KJLO. A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in. Lingual Orthodontics. Case Report INTRODUCTION DIAGNOSIS
 KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
In recent years, orthodontic mini-implants have been
 ONLINE ONLY Factors affecting the long-term stability of orthodontic mini-implants Mitsuru Motoyoshi, a Miwa Uemura, b Akiko Ono, c Kumiko Okazaki, d Toru Shigeeda, d and Noriyoshi Shimizu e Tokyo, Japan
ONLINE ONLY Factors affecting the long-term stability of orthodontic mini-implants Mitsuru Motoyoshi, a Miwa Uemura, b Akiko Ono, c Kumiko Okazaki, d Toru Shigeeda, d and Noriyoshi Shimizu e Tokyo, Japan
Molar intrusion with skeletal anchorage ; from single tooth intrusion to canting correction and skeletal open bite
 Molar intrusion with skeletal anchorage ; from single tooth intrusion to canting correction and skeletal open bite Tae-Woo Kim DDS MSD PhD Professor, Department of Orthodontics School of Dentistry, Seoul
Molar intrusion with skeletal anchorage ; from single tooth intrusion to canting correction and skeletal open bite Tae-Woo Kim DDS MSD PhD Professor, Department of Orthodontics School of Dentistry, Seoul
MOLAR DISTALIZATION WITH MODIFIED GRAZ IMPLANT SUPPORTED PENDULUM SPRINGS. A CASE REPORT.
 MOLAR DISTALIZATION WITH MODIFIED GRAZ IMPLANT SUPPORTED PENDULUM SPRINGS. A CASE REPORT. Author : Dr. Arundhati P. Tandur MDS, MDORCPS [Glasgow], IMORTHRCS [England], Diplomate of Indian Board Vice-Principal
MOLAR DISTALIZATION WITH MODIFIED GRAZ IMPLANT SUPPORTED PENDULUM SPRINGS. A CASE REPORT. Author : Dr. Arundhati P. Tandur MDS, MDORCPS [Glasgow], IMORTHRCS [England], Diplomate of Indian Board Vice-Principal
Molar distalisation with skeletal anchorage
 Molar distalisation with skeletal anchorage Antonio Gracco, Lombardo Luca and Giuseppe Siciliani Department of Orthodontics, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy Background: Distalisation of the upper
Molar distalisation with skeletal anchorage Antonio Gracco, Lombardo Luca and Giuseppe Siciliani Department of Orthodontics, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy Background: Distalisation of the upper
Mini-implants in Orthodontics: A Review
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3(1): 6-10 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Review Mini-implants in Orthodontics: A Review Singla
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3(1): 6-10 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Review Mini-implants in Orthodontics: A Review Singla
Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation
 ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.02 No.02 Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation Seyed Hossein Moslemzade 1, Yusef Kananizadeh
ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.02 No.02 Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation Seyed Hossein Moslemzade 1, Yusef Kananizadeh
Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws
 Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Palatal Bone Density in Adult Subjects: Implications for Mini-Implant Placement
 Original Article Palatal Bone Density in Adult Subjects: Implications for Mini-Implant Placement Sung Hee Moon a ; Sun Hyung Park b ; Won Hee Lim c ; Youn Sic Chun d ABSTRACT Objectives: To evaluate palatal
Original Article Palatal Bone Density in Adult Subjects: Implications for Mini-Implant Placement Sung Hee Moon a ; Sun Hyung Park b ; Won Hee Lim c ; Youn Sic Chun d ABSTRACT Objectives: To evaluate palatal
Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital,
 Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
The Clinical Success of Self-tapping and Self-drilling Orthodontic Miniscrews
 Biological Forum An International Journal 7(2): 33-37(25) ISSN No. (Print): 975-3 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 The Clinical Success of Self-tapping and Self-drilling Orthodontic Miniscrews Abbas Salehi
Biological Forum An International Journal 7(2): 33-37(25) ISSN No. (Print): 975-3 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 The Clinical Success of Self-tapping and Self-drilling Orthodontic Miniscrews Abbas Salehi
Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME)
 Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Maxillary Growth Control with High Pull Headgear- A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
Clinical indices for orthodontic mini-implants
 407 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 53, No. 4, 407-412, 2011 Review Clinical indices for orthodontic mini-implants Mitsuru Motoyoshi 1,2) 1) Department of Orthodontics, Nihon University School of Dentistry,
407 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 53, No. 4, 407-412, 2011 Review Clinical indices for orthodontic mini-implants Mitsuru Motoyoshi 1,2) 1) Department of Orthodontics, Nihon University School of Dentistry,
Combined use of digital imaging technologies: ortho-surgical treatment
 DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2018059 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2018;21:210 The authors Combined use of digital imaging technologies: ortho-surgical treatment L. Petitpas Private practice, 54700 Pont-à-Mousson Are
DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2018059 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2018;21:210 The authors Combined use of digital imaging technologies: ortho-surgical treatment L. Petitpas Private practice, 54700 Pont-à-Mousson Are
TADs Supported Tongue Crib: A New Minimalistic Design
 Clinical Pearl TADs Supported Tongue Crib: A New Minimalistic Design Patni V 1, Kolge NE 2 To cite: Patni V, Kolge NE. TADs Supported Tongue Crib: A New Minimalistic Design. Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics,
Clinical Pearl TADs Supported Tongue Crib: A New Minimalistic Design Patni V 1, Kolge NE 2 To cite: Patni V, Kolge NE. TADs Supported Tongue Crib: A New Minimalistic Design. Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics,
Research Article Success Rate of Microimplants in a University Orthodontic Clinic
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 982671, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/982671 Research Article Success Rate of Microimplants in a University Orthodontic Clinic P.
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 982671, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/982671 Research Article Success Rate of Microimplants in a University Orthodontic Clinic P.
Assessment of palatal bone thickness in adults with cone beam computerised tomography
 Assessment of palatal bone thickness in adults with cone beam computerised tomography Antonio Gracco, Lombardo Luca, Mauro Cozzani and Giuseppe Siciliani Department of Orthodontics, University of Ferrara,
Assessment of palatal bone thickness in adults with cone beam computerised tomography Antonio Gracco, Lombardo Luca, Mauro Cozzani and Giuseppe Siciliani Department of Orthodontics, University of Ferrara,
PAIN PERCEPTION DURING MINIPLATE-ASSISTED ORTHODONTIC THERAPY
 PAIN PERCEPTION DURING MINIPLATE-ASSISTED ORTHODONTIC THERAPY Yu-Chuan Tseng, 1 Chun-Ming Chen, 2 Huang-Chi Wang, 3 Chau-Hsiang Wang, 4 Huey-Er Lee, 4 and Kun-Tsung Lee 5 Departments of 1 Orthodontics,
PAIN PERCEPTION DURING MINIPLATE-ASSISTED ORTHODONTIC THERAPY Yu-Chuan Tseng, 1 Chun-Ming Chen, 2 Huang-Chi Wang, 3 Chau-Hsiang Wang, 4 Huey-Er Lee, 4 and Kun-Tsung Lee 5 Departments of 1 Orthodontics,
Sliding Mechanics with Microscrew Implant Anchorage
 Clinical Report Sliding Mechanics with Microscrew Implant Anchorage Hyo-Sang Park, DDS, MSD, PhD a ; Tae-Geon Kwon, DDS, MSD, PhD b Abstract: Three cases are illustrated. One was treated with maxillary
Clinical Report Sliding Mechanics with Microscrew Implant Anchorage Hyo-Sang Park, DDS, MSD, PhD a ; Tae-Geon Kwon, DDS, MSD, PhD b Abstract: Three cases are illustrated. One was treated with maxillary
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite
 BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
Absolute anchorage has been a long sought after,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Buccal cortical bone thickness for mini-implant placement Sebastian Baumgaertel a and Mark G. Hans b Cleveland, Ohio Introduction: The thickness of cortical bone is an important factor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Buccal cortical bone thickness for mini-implant placement Sebastian Baumgaertel a and Mark G. Hans b Cleveland, Ohio Introduction: The thickness of cortical bone is an important factor
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Journal Home Page: http://www.ijmhs.net ISSN:2277-4505 Case Report Mini Screw Implant Taking Orthodontics to New Dimensions A Case Report Deepak Victor
International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Journal Home Page: http://www.ijmhs.net ISSN:2277-4505 Case Report Mini Screw Implant Taking Orthodontics to New Dimensions A Case Report Deepak Victor
Introduction Subjects and methods
 European Journal of Orthodontics 33 (2011) 126 131 doi:10.1093/ejo/cjq047 Advance Access Publication 8 November 2010 The Author 2010. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontic
European Journal of Orthodontics 33 (2011) 126 131 doi:10.1093/ejo/cjq047 Advance Access Publication 8 November 2010 The Author 2010. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontic
Changes in Lip, Cheek, and Tongue Pressures After Rapid Maxillary Expansion Using a Diaphragm Pressure Transducer
 Original Article Changes in Lip, Cheek, and Tongue Pressures After Rapid Maxillary Expansion Using a Diaphragm Pressure Transducer Nazan Küçükkeleş, DDS, PhD a ; Cenk Ceylanoğlu, DDS b Abstract: The purpose
Original Article Changes in Lip, Cheek, and Tongue Pressures After Rapid Maxillary Expansion Using a Diaphragm Pressure Transducer Nazan Küçükkeleş, DDS, PhD a ; Cenk Ceylanoğlu, DDS b Abstract: The purpose
Anchorage control is a critical consideration when
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Soft-tissue and cortical-bone thickness at orthodontic implant sites Hee-Jin Kim, a Hee-Sun Yun, b Hyun-Do Park, c Doo-Hyung Kim, b and Young-Chel Park d Seoul, South Korea Introduction:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Soft-tissue and cortical-bone thickness at orthodontic implant sites Hee-Jin Kim, a Hee-Sun Yun, b Hyun-Do Park, c Doo-Hyung Kim, b and Young-Chel Park d Seoul, South Korea Introduction:
Lever-arm and Mini-implant System for Anterior Torque Control during Retraction in Lingual Orthodontic Treatment
 Clinical Report Lever-arm and Mini-implant System for Anterior Torque Control during Retraction in Lingual Orthodontic Treatment Ryoon-Ki Hong, DDS, PHD a ; Jung-Min Heo, DDS b ; Young-Ki Ha, DDS b Abstract:
Clinical Report Lever-arm and Mini-implant System for Anterior Torque Control during Retraction in Lingual Orthodontic Treatment Ryoon-Ki Hong, DDS, PHD a ; Jung-Min Heo, DDS b ; Young-Ki Ha, DDS b Abstract:
Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector
 15 CASE REPORT Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector Amit Prakash 1,O.P.Mehta 2, Kshitij Gupta 3 Swapnil Pandey 4 Deep Kumar Suryawanshi 4 1 Senior lecturer Bhopal - INDIA 2 Professor Bhopal
15 CASE REPORT Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector Amit Prakash 1,O.P.Mehta 2, Kshitij Gupta 3 Swapnil Pandey 4 Deep Kumar Suryawanshi 4 1 Senior lecturer Bhopal - INDIA 2 Professor Bhopal
Use of Palatal Miniscrew Anchorage and Lingual Multi-Bracket Appliances to Enhance Efficiency of Molar Scissors-Bite Correction
 Case Report Use of Palatal Miniscrew Anchorage and Lingual Multi-Bracket Appliances to Enhance Efficiency of Molar Scissors-Bite Correction Nagato Tamamura a ; Shingo Kuroda b ; Yasuyo Sugawara b ; Teruko
Case Report Use of Palatal Miniscrew Anchorage and Lingual Multi-Bracket Appliances to Enhance Efficiency of Molar Scissors-Bite Correction Nagato Tamamura a ; Shingo Kuroda b ; Yasuyo Sugawara b ; Teruko
Open Access Relationship Between the Thickness of Cortical Bone at Maxillary Mid-palatal Area and Facial Height Using CBCT
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, (Suppl 2: M6) 287-291 287 Open Access Relationship Between the Thickness of Cortical Bone at Maxillary Mid-palatal
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, (Suppl 2: M6) 287-291 287 Open Access Relationship Between the Thickness of Cortical Bone at Maxillary Mid-palatal
Tomographic mapping of the hard palate and overlying mucosa
 Orthodontics Orthodontics Tomographic mapping of the hard palate and overlying mucosa Mariana Marquezan (a) Lincoln Issamu Nojima (a) Amanda Osório Ayres de Freitas (a) Carolina Baratieri (a) Matheus Alves
Orthodontics Orthodontics Tomographic mapping of the hard palate and overlying mucosa Mariana Marquezan (a) Lincoln Issamu Nojima (a) Amanda Osório Ayres de Freitas (a) Carolina Baratieri (a) Matheus Alves
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics
 Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE , 1,2 onplant, 3,4, . 12, 13,14 , 7,8. 9, ,,. 16,17
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 8 mm 14 mm 16 mm 14 mm 16 mm 14 mm 16 mm 4 20 16 mm 14 mm 14 mm 16 mm 2006;36(4):275-83) 1 11 56 12 onplant 34 12 1314 78 910 15 5 1617 36 4 2006 Table 1 Chemical composition and mechanical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 8 mm 14 mm 16 mm 14 mm 16 mm 14 mm 16 mm 4 20 16 mm 14 mm 14 mm 16 mm 2006;36(4):275-83) 1 11 56 12 onplant 34 12 1314 78 910 15 5 1617 36 4 2006 Table 1 Chemical composition and mechanical
Microscrew implant as an orthodontic anchoring device
 Microscrew implant as an orthodontic anchoring device Mira Nurtania Supriadi, Eky Setiawan Soeria Soemantri, Ida Ayu Evangelina Department of Orthodontic Faculty of Dentistry, Universitas Padjadjaran ABSTRACT
Microscrew implant as an orthodontic anchoring device Mira Nurtania Supriadi, Eky Setiawan Soeria Soemantri, Ida Ayu Evangelina Department of Orthodontic Faculty of Dentistry, Universitas Padjadjaran ABSTRACT
Nonextraction Treatment of Upper Canine Premolar Transposition in an Adult Patient
 Case Report Nonextraction Treatment of Upper Canine Premolar Transposition in an Adult Patient Shingo Kuroda a ; Yasuko Kuroda b Abstract: This article reports the successful treatment of a unilateral
Case Report Nonextraction Treatment of Upper Canine Premolar Transposition in an Adult Patient Shingo Kuroda a ; Yasuko Kuroda b Abstract: This article reports the successful treatment of a unilateral
International Journal of Therapeutic Applications ISSN X
 International Journal of Therapeutic Applications ISSN 2320-138X HEAD GEAR EFFECT USING MINI-IMPLANT (DISTALIZATION AND INTRUSION) A CASE REPORT Mohammadi Begum 1*, Arjun Karra 2 1 DRs. Sudha and Nageswara
International Journal of Therapeutic Applications ISSN 2320-138X HEAD GEAR EFFECT USING MINI-IMPLANT (DISTALIZATION AND INTRUSION) A CASE REPORT Mohammadi Begum 1*, Arjun Karra 2 1 DRs. Sudha and Nageswara
Treatment of Class II, Division 2 Malocclusion with Miniscrew Supported En-Masse Retraction: Is Deepbite Really an Obstacle for Extraction Treatment?
 TURKISH JOURNAL of DOI: 10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2017.17034 CASE REPORT Treatment of Class II, Division 2 Malocclusion with Miniscrew Supported En-Masse Retraction: Is Deepbite Really an Obstacle for Extraction
TURKISH JOURNAL of DOI: 10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2017.17034 CASE REPORT Treatment of Class II, Division 2 Malocclusion with Miniscrew Supported En-Masse Retraction: Is Deepbite Really an Obstacle for Extraction
A SIMPLE METHOD FOR CORRECTION OF BUCCAL CROSSBITE OF MAXILLARY SECOND MOLAR
 Short Communication International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 03 A SIMPLE METHOD FOR CORRECTION OF BUCCAL CROSSBITE OF MAXILLARY SECOND MOLAR Sumit Yadav 1,Davender Kumar 2,Achla
Short Communication International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 03 A SIMPLE METHOD FOR CORRECTION OF BUCCAL CROSSBITE OF MAXILLARY SECOND MOLAR Sumit Yadav 1,Davender Kumar 2,Achla
Management of three impacted teeth detected early
 DOI: 10.1051/odfen/ 2018124 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2017;20:310 The authors C L I N I C A L C A S E Management of three impacted teeth detected early P. Guézénec Qualified Specialist in Dento facial
DOI: 10.1051/odfen/ 2018124 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2017;20:310 The authors C L I N I C A L C A S E Management of three impacted teeth detected early P. Guézénec Qualified Specialist in Dento facial
Class III malocclusion occurs in less than 5%
 CDABO CASE REPORT Orthodontic correction of a Class III malocclusion in an adolescent patient with a bonded RPE and protraction face mask Steven W. Smith, DDS, a and Jeryl D. English, DDS, MS b Dallas,
CDABO CASE REPORT Orthodontic correction of a Class III malocclusion in an adolescent patient with a bonded RPE and protraction face mask Steven W. Smith, DDS, a and Jeryl D. English, DDS, MS b Dallas,
Case Report. profile relaxed relaxed smiling. How would you treat this malocclusion?
 Pre-Treatment profile relaxed relaxed smiling How would you treat this malocclusion? Case R. C. 16 years, 9 months introduction This female adolescent with bilabial protrusion and flared upper anterior
Pre-Treatment profile relaxed relaxed smiling How would you treat this malocclusion? Case R. C. 16 years, 9 months introduction This female adolescent with bilabial protrusion and flared upper anterior
Influence of Third Molars on the Availability of Interradicular Spaces for Miniscrew Implant Placement
 Õ æ Õßøíπ Ë Ë µàõ π Õß àõß À«à ß øíπ À ªí À ÿ «π Á Influence of Third Molars on the Availability of Interradicular Spaces for Miniscrew Implant Placement «Original Article º ß µ 1, ÿ» «Ÿ Ÿ 2, Õ «å â Ÿ
Õ æ Õßøíπ Ë Ë µàõ π Õß àõß À«à ß øíπ À ªí À ÿ «π Á Influence of Third Molars on the Availability of Interradicular Spaces for Miniscrew Implant Placement «Original Article º ß µ 1, ÿ» «Ÿ Ÿ 2, Õ «å â Ÿ
Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars
 Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony
 Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony AAO Lecture May 7, 2013 Philadelphia, PA Will A. Andrews, D.D.S. Optimal oral and facial harmony implies a state of maximum health, function and appearance
Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony AAO Lecture May 7, 2013 Philadelphia, PA Will A. Andrews, D.D.S. Optimal oral and facial harmony implies a state of maximum health, function and appearance
Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report
 Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance
 2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
Objective: There is little information regarding the mesiodistal angulation of permanent teeth
 www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
Simple Mechanics to Upright Horizontally Impacted Molars with Ramus Screws
 Simple Mechanics to Upright Horizontally Impacted Molars with Ramus Screws Abstract Simplified mechanics are reported for uprighting horizontally impacted mandibular molars with ramus bone screws. A 27-year-old
Simple Mechanics to Upright Horizontally Impacted Molars with Ramus Screws Abstract Simplified mechanics are reported for uprighting horizontally impacted mandibular molars with ramus bone screws. A 27-year-old
Anchorage conservation has always been a challenge
 2011 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com En-Masse Retraction Using Skeletal Anchorage in the Tuberosity and Retromolar Regions SUNDARAM VENKATESWARAN, MDS VENKATESHWARA
2011 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com En-Masse Retraction Using Skeletal Anchorage in the Tuberosity and Retromolar Regions SUNDARAM VENKATESWARAN, MDS VENKATESHWARA
Anchorage control is a fundamental prerequisite
 ONLINE ONLY Five-year experience with orthodontic miniscrew implants: A retrospective investigation of factors influencing success rates Joanna Antoszewska, a Moschos A. Papadopoulos, b Hyo-Sang Park,
ONLINE ONLY Five-year experience with orthodontic miniscrew implants: A retrospective investigation of factors influencing success rates Joanna Antoszewska, a Moschos A. Papadopoulos, b Hyo-Sang Park,
Quantitation of transverse maxillary dimensions using computed tomography: a methodological and reproducibility study
 European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 209 215 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 2 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. Quantitation of transverse maxillary dimensions
European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 209 215 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 2 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. Quantitation of transverse maxillary dimensions
Palatal Depth and Arch Parameter in Class I Open Bite, Deep Bite and Normal Occlusion
 26 Iraqi Orthod J 1(2) 2005 Palatal Depth and Arch Parameter in Class I Open Bite, Deep Bite and Normal Occlusion Ahmad A. Abdulmawjood, a Mahmood K. Ahmed, a and Ne am R. Al-Saleem a Abstract: This study
26 Iraqi Orthod J 1(2) 2005 Palatal Depth and Arch Parameter in Class I Open Bite, Deep Bite and Normal Occlusion Ahmad A. Abdulmawjood, a Mahmood K. Ahmed, a and Ne am R. Al-Saleem a Abstract: This study
The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss
 1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
Extraoral Imaging. Chapter 42. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1
 Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
The use of mini-implants in en masse retraction for the treatment of bimaxillary dentoalveolar protrusion
 The Saudi Dental Journal (2010) 22, 35 39 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com CASE REPORT The use of mini-implants in en masse retraction for the treatment
The Saudi Dental Journal (2010) 22, 35 39 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com CASE REPORT The use of mini-implants in en masse retraction for the treatment
Influence of the thickness of cortical bone on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews
 DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2013305 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2013;16:403 Ó RODF / EDP Sciences Influence of the thickness of cortical bone on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews J. COBO PLANA, F. DE CARLOS
DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2013305 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2013;16:403 Ó RODF / EDP Sciences Influence of the thickness of cortical bone on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews J. COBO PLANA, F. DE CARLOS
CPD Article ISSUE 59. Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future
 CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
Histomorphometric evaluation of cortical bone surrounding mini-screw: Why is the insertion torque critical for primary stability?
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (14): 3028-3033 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Histomorphometric evaluation of cortical bone surrounding mini-screw: Why is the insertion torque critical for primary stability?
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (14): 3028-3033 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Histomorphometric evaluation of cortical bone surrounding mini-screw: Why is the insertion torque critical for primary stability?
New treatment paradigms have reduced the importance
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Palatal bone thickness compared with cone-beam computed tomography in adolescents and adults for mini-implant placement Jun-Ha Ryu, a Jae Hyun Park, b Trang Vu Thi Thu, c Mohamed Bayome,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Palatal bone thickness compared with cone-beam computed tomography in adolescents and adults for mini-implant placement Jun-Ha Ryu, a Jae Hyun Park, b Trang Vu Thi Thu, c Mohamed Bayome,
Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography Akira Nakajima a ; Glenn T. Sameshima b ; Yoshinori Arai c ; Yoshito Homme d ; Noriyoshi Shimizu
Original Article Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography Akira Nakajima a ; Glenn T. Sameshima b ; Yoshinori Arai c ; Yoshito Homme d ; Noriyoshi Shimizu
Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report
 Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Skeletal Anchorage for Orthodontic Correction of Severe Maxillary Protrusion after Previous Orthodontic Treatment
 The Angle Orthodontist: Vol. 78, No. 1, pp. 181 188. Skeletal Anchorage for Orthodontic Correction of Severe Maxillary Protrusion after Previous Orthodontic Treatment Eiji Tanaka; a Akiko Nishi-Sasaki;
The Angle Orthodontist: Vol. 78, No. 1, pp. 181 188. Skeletal Anchorage for Orthodontic Correction of Severe Maxillary Protrusion after Previous Orthodontic Treatment Eiji Tanaka; a Akiko Nishi-Sasaki;
The treatment options for nongrowing skeletal Class
 CASE REPORT Total distalization of the maxillary arch in a patient with skeletal Class II malocclusion Yoon Jeong Choi, a Jong-Suk Lee, b Jung-Yul Cha, c and Young-Chel Park d Seoul, Korea In nongrowing
CASE REPORT Total distalization of the maxillary arch in a patient with skeletal Class II malocclusion Yoon Jeong Choi, a Jong-Suk Lee, b Jung-Yul Cha, c and Young-Chel Park d Seoul, Korea In nongrowing
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
Surgical technique. IMF Screw Set. For temporary, peri opera tive stabilisation of the occlusion in adults.
 Surgical technique IMF Screw Set. For temporary, peri opera tive stabilisation of the occlusion in adults. Table of contents Features and benefits 2 Indications and contraindications 3 Surgical technique
Surgical technique IMF Screw Set. For temporary, peri opera tive stabilisation of the occlusion in adults. Table of contents Features and benefits 2 Indications and contraindications 3 Surgical technique
Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion
 Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Clinicians: Drs. Chris Chang, Hsin-Yin Yeh, Sophia Pei-Wen Shu, W. Eugene Roberts Patient: Miss Jhan Pre-treatment Diagnosis An
Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Clinicians: Drs. Chris Chang, Hsin-Yin Yeh, Sophia Pei-Wen Shu, W. Eugene Roberts Patient: Miss Jhan Pre-treatment Diagnosis An
ortho case report Sagittal First international magazine of orthodontics By Dr. Luis Carrière Special Reprint
 Cover image courtesy of K Line Europe GmbH (www.kline-europe.de) ortho Special Reprint international magazine of orthodontics 1 2017 case report Sagittal First By Dr. Luis Carrière Sagittal First Author:
Cover image courtesy of K Line Europe GmbH (www.kline-europe.de) ortho Special Reprint international magazine of orthodontics 1 2017 case report Sagittal First By Dr. Luis Carrière Sagittal First Author:
Influence of Surface Characteristics on Survival Rates of Mini-Implants
 Original Article Influence of Surface Characteristics on Survival Rates of Mini-Implants Karim Chaddad a ; André F.H. Ferreira b ; Nico Geurs c ; Michael S. Reddy d ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the clinical
Original Article Influence of Surface Characteristics on Survival Rates of Mini-Implants Karim Chaddad a ; André F.H. Ferreira b ; Nico Geurs c ; Michael S. Reddy d ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the clinical
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy*
 O C a s e R e p o r t ngle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy* Daniela Kimaid Schroeder** bstract This article reports the treatment of a young patient at
O C a s e R e p o r t ngle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy* Daniela Kimaid Schroeder** bstract This article reports the treatment of a young patient at
Effective Tooth Movement Using Lingual Segmented Arch Mechanics Combined With Miniscrews
 日本舌側矯正歯科学会会誌 23 原 著 Effective Tooth Movement Using Lingual Segmented Arch Mechanics Combined With Miniscrews Tae-Hyun Choi a) Kyung-Keun Shi b), Young-Chel Park c), Kee-Joon Lee d) Department of Orthodontics,
日本舌側矯正歯科学会会誌 23 原 著 Effective Tooth Movement Using Lingual Segmented Arch Mechanics Combined With Miniscrews Tae-Hyun Choi a) Kyung-Keun Shi b), Young-Chel Park c), Kee-Joon Lee d) Department of Orthodontics,
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults
 Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
