Fran D. Kendall, M.D.
|
|
|
- Gabriel Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fran D. Kendall, M.D. VMP, LLC Biochemical Genetics Metabolic, Mitochondrial & Inherited Disorders
2 To provide basic background information on Mitochondrial Disease, its clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, inheritance and to discuss its known GI complications Dr Kendall and VMP have no financial interest in any laboratory.
3 What are Mitochondria? What is Mitochondrial Disease?
4 Smallest functioning unit of our bodies Many cells together make up tissues Many sheets of tissues make up our organs
5 Located inside our body cells Composed of an inner and outer membrane The energy producing pathway is the respiratory chain The respiratory chain consists of 5 complexes (groups of chemicals) that produce ATP
6 Oxygen & phosphate used to make energy Composed of five complexes or groups of chemicals with a total of ~90 subunits Energy packets are known as ATP
7 Found in 1 in 4,000 individuals Carrier rate of common mtdna mutations may be as high as 1 in 200 Caused by an alteration in our inherited blueprint (gene mutation) or toxic affect of external factor such as medication including HIV drugs and some chemotherapeutic agents. Results in decreased energy production and localized or widespread problems
8 CNS MUSCLES CARDIAC GI SYSTEM INCLUDING LIVER KIDNEYS COMPREHENSIVE WIDESPREAD SYMPTOMS LIST CAN BE FOUND AT
9 Central Nervous system (Brain) problems such as developmental delays including autism, loss of function, seizures, hypotonia & weakness Failure to thrive Chronic fatigue Gastrointestinal issues such as chronic constipation Autonomic dysfunction such as irregular heart rate and blood pressure and temperature instability with heat intolerance.
10 There are 1,500 genes involved in coding for the various proteins and other compounds involved in OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION or mitochondrial energy production These genes are contributed by two sets of inherited genetic material; the nuclear genes located inside the nucleus of our body cells and mitochondrial genes found inside the mitochondria of our cells Nuclear genes are inherited from both parents and contribute the vast majority of the information needed for energy production Mitochondrial genes are inherited EXCLUSIVELY through mom and contribute the remaining information Inheritance patterns include autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, maternal, X-linked and sporadic.
11 Approximately 850 proteins are encoded for by the nuclear mitochondrial genes Many of these proteins are responsible for the control of electron transport chain structure and function and assembly Autosomal recessive inheritance of nuclear gene defects is the most common etiology of pediatric patients with mitochondrial disorders.
12 Inherited exclusively through the maternal line Circular molecule, a number of copies in each mitochondrium (5-10 copies typical) 16,569 bases or pieces and 37 genes Mutated mtdna may be present in varying amounts with wild type DNA (heteroplasmy)
13
14
15 Several tiers of testing are utilized to diagnose mitochondrial disease Functional testing examining the OXPHOS energy pathway. Gene testing evaluation of mtdna and nuclear mitochondrial genes Biomarker studies lactate and pyruvate levels, CSF lactate, CPK, urine organic acids, carnitine levels. Radiographic studies identification of mito related imagining abnormalities. Utilization of published Criteria such as the Bernier Criteria
16 Abnormalities in mitochondrial structure/size/shape/number on tissue biopsy Enzymatic abnormalities on testing of the energy producing system (respiratory chain or electron transport chain) Respirometry studies measures oxygen consumption in all of the complexes under conditions more reflective of in vivo functioning than isolated traditional enzyme assays Blue and Clear native gels studies help assess protein complexes and supercomplexes and can identify assembly defects
17
18 less than 2.5% of cases. And in pediatric patients histological studies are often normal. They are most often abnormal in adult patients with mtdna gene defects
19 Less invasive skin biopsy for skin fibroblast culture and OXPHOS enzyme assays Buccal swab OXHPHOS enzyme assays Approximately 80%-85% correlation between swab testing results and muscle biopsy enzyme assays Good screening tool Still under development
20 There are approximately 1,500 genes involved in mitochondrial energy production. mtdna sequencing screens 37 maternally inherited genes Nuclear gene panels vary from lab to lab and range from screening 100+ to 1,100 nuclear mito genes Baylor Courtagen GeneDx Transgenomics Of note, some gene testing can now be completed on saliva & urine samples.
21 MELAS (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy Lactic Acidosis and Stroke Like Episodes) due to trna 3243 mtdna mutation MERRF (Myoclonic Epilepsy and Ragged Red Fibers) due to trna 8344 mutation Complex I nuclear gene mutations - example NDUFV1 patients with leukodystrophy and myoclonic epilepsy Complex IV assembly gene mutations - example SURF1 mutations associated with Leigh disease
22 Increased blood and/or CSF lactate and pyruvate and/or ratio Decreased plasma carnitine Increased blood alanine Generalized aminoaciduria Increase lactate, pyruvate, Kreb cycle intermediates, tiglylglycine, and 2-oxoadipic acid on organic acid analysis
23
24 Quite variable but typically progressive over time Patients can face severe disabilities and early death Many patients stabilize or show improvements with institution of care Problems typically worsen with stressors such as illness and surgery
25 Symptomatic treat existing problems Preventative early detection of associated problems using every 6-12 month multisystem screening studies Therapeutics very limited and often include the use of Coenzyme Q10, L-carnitine, Riboflavin, Alpha lipoic acid and Creatine
26
27 GASTROINTESTINAL PROBLEMS Gastroesophageal reflux Dysphagia Pseudo-obstruction Gastroparesis and dysmotility Irritable bowel syndrome Diarrhea or constipation Exocrine pancreatic failure Pancreatitis LIVER Liver dysfunction/failure Hypoglycemia SYSTEMIC Failure to thrive Neurovisceral pain Abdominal migraines Cyclic Vomiting
28 Small, frequent meals H2 receptor antagonists example Zantac Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) example Prevacid Antireflux surgery for patients with documented chronic reflux with recalcitrant symptoms. However, surgery has complication rate (10-20%). Resumption of pre-operative medication treatment (>50%) is common and will likely increase over time.
29 To control the signs and symptoms often used are: Anti-nausea drugs (Zofran) Sedatives Acid-suppressing medications Hospitalization for intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration In many cases, the same types of medications used for migraines often help stop or even prevent episodes of cyclic vomiting. These medications include: Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline and nortriptyline (Pamelor) Triptans, such as sumatriptan (Imitrex) and zolmitriptan (Zomig) Analgesics, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others)
30 Dietary modifications: Eat smaller meals more frequently. Eat low-fiber forms of high-fiber foods, such as well-cooked fruits and vegetables rather than raw fruits and vegetables. Choose mostly low-fat foods, but if you can tolerate them, add small servings of fatty foods to your diet. Avoid fibrous fruits and vegetables, such as oranges and broccoli, that may cause bezoars. If liquids are easier for you to ingest, try soups and pureed foods. Drink water throughout each meal. Try gentle exercise after you eat, such as going for a walk. continued on next slide
31 For complete intolerance of food or liquids, placement of jejunostomy tube to by-pass the stomach. Medications to treat gastroparesis may include: Medications to control nausea and vomiting. Anti-emetic medications include prochlorperazine (Compro), diphenhydramine (Benadryl, Unisom) and lorazepam (Ativan). Medications to stimulate the stomach muscles. These medications include metoclopramide (Reglan) and erythromycin. Experimental treatments: Botox relaxes the pyloric muscle in some patients Implantation of electrical pacemaker.
32 Dietary & lifestyle changes Good hydration Ingestion of fruits and vegetables, especially uncooked Use of whole grain breads and cereals Laxatives Osmotic laxatives - work by drawing water into the colon. They are safe and perhaps are the preferred all-purpose laxatives. Examples include Milk of Magnesia and citrate of Magnesia. We also use Fiber Gummies and Sugar Free Jelly Beans which contain Sorbitol. Stimulant laxatives- work by signaling the muscles and nerves of the intestine to contract. These laxatives work relatively quickly, but tend to produce more cramping. Examples include Dulcolax and Senecott. Enemas continued on next slide
33 New Medications Amitiza - an oral treatment (capsule) approved by the FDA in It works by increasing fluid secretion in the small intestine. It helps to ease the passage of the stool. It improves symptoms associated with chronic idiopathic (of unknown cause) constipation. Surgical Interventions Placement of C-tube for fluid infusion Removal of portions of the GI tract Placement of central line for administration of TPN in cases of complete gut dysmotility and failure.
34 Abdominal migraine is a migraine attack without the headache. These most commonly occur in children from five to nine years of age. A child with an abdominal migraine will complain of stomach pain; he may also complain of nausea and might have to vomit. He will develop photophobia (sensitivity to light), be irritable, lose his appetite and have diarrhea. He may have a flushed or pale face with dark circles under his eyes. In rare instances, he may also complain of head pain. His symptoms could last any where from 1 to 72 hours.
35 Propranolol - a beta blocker is prescribed to treat or prevent migraine in children. Cyproheptadine (Periactin)- an anti-histamine that affects the level of serotonin. Amitriptyline (Elavil) precise action of tricyclic antidepressants is not fully understood, but it is believed that the most important effect is the decreased reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. Triptans - not licensed for pediatric use.
36 Neurontin Amitriptyline
37 MNGIE MELAS Pearson marrow-pancreas syndrome Mitochondrial Hepatopathies
38 Onset typically by age 20 Characterized by leukodystrophy, peripheral neuropathy, ptosis, opthalmoplegia, progressive dysphagia and severe dysmotility with extreme cachexia Caused by autosomal recessive mutations in the TYMP gene which encodes for thymidine phosporylase, a gene involved in thymidine metabolism which results in disruption of maintenance and repair of mtdna causing it to become unstable. Multi-center hemopoietic stem cell trial promising
39 Onset typically in childhood but adult onset known Neurodegenerative course with stroke like episodes, seizures and dementia, elevated lactate Pancreatitis can occur frequently in this disorder Associated with mtdna 3243 trna mutation Symptomatic treatment with use of L-arginine for strokes.
40 Onset in infancy Characterized by siderblastic anemia and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction Other clinical features include FTT, pancreatic fibrosis with IDDM, muscle involvement, hepatomegaly, cholestasis, progressive liver failure Most patients die in infancy or by several years of age but the few who survive into adulthood develop symptoms of Kearns- Sayre syndrome Caused by a deletion in mitochondrial DNA.
41 Clinical features range from hepatic steatosis, cholestasis and chronic liver disease with insidious onset to neonatal liver failure, the latter frequently associated with neuromuscular symptoms. Most mitochondrial diseases with primary involvement of the liver are caused by nuclear, rather than mtdna mutation. NO consensus on the role of liver transplantation in mitochondrial hepatopathies, largely because of the multisystem nature of the disorders. Literature review notes a survival rate in these patients of less than 50% Otherwise symptomatic treatment
42 Neonatal liver failure: Complex I deficiency (NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase) Complex IV deficiency (cytochrome c oxidase) (SCO1 mutations) Complex III deficiency (ubiquinol: cytochrome c oxidoreductase) (BCS1L mutations) Multiple Complex deficiencies Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (DGUOK, MPV17, and POLG mutations) Delayed-onset liver failure: Alpers' disease (complex I deficiency, POLG mutations) Chronic diarrhea (villous atrophy) with hepatic involvement (complex III deficiency) Navajo neurohepatopathy ( mtdna depletion; MPV17 mutations)
43 Present with acute liver failure at several weeks to months of life with death within weeks to months after onset of symptoms. Associated symptoms include lethargy, hypotonia, vomiting, poor suck and weak cry, recurrent apnea and seizures (myoclonic epilepsy). Markedly elevated plasma lactate concentration. Respiratory chain complex analysis of liver or muscle generally shows low activity of complex I, III, or IV (COX) with COX deficiency being the most common. Molecular causes include mutations in the SCO1 gene (copper chaperone of COX) and BCS1L gene (assembly protein of complex III). Of note, patients with BCS1L mutations usually have renal tubulopathy as well.
44 Patients who present with the hepatocerebral form of MDS developed hepatomegaly and progressive liver failure during the first several weeks of life with onset of death a few months later. Associated symptoms include vomiting, GERD, FTT, DD, hypotonia, nystagmus, and on occasion pyramidal signs, cardiomegaly, tubulopathy and amyotrophia (wasting of muscle tissue) Increased lactate, hypoglycemia, elevated AST/ALT, coagulopathy and elevated total and conjugated bilirubin. continued on next slide
45 Considerable overlap with neonatal liver failure form of respiratory chain disease with major difference in the demonstration in MDS of a low ratio (<10%) of the normal amount of ntdna to nuclear DNA in affected tissues with normal mtdna sequencing. Enzymology may show complex I, III and IV defects in liver. Several nuclear genes including DGUOK (maintains supply of dntps for mtdna synthesis), POLG (essential for mtdna replication)and MPR17 (essential for mtdna maintenance) are associated with MDS
46 Onset of symptoms typically between 2 months and 8 years of life but can be seen in young adults. Diagnostic triad includes 1) refractory, mixed-type seizures with a focal component; 2) episodic psychomotor regression associated with intercurrent illnesses; 3) hepatopathy with or without acute liver failure. Liver failure is preceded by the development of hypotonia, feeding difficulties, GERD, FTT, ataxia and onset of refractory partial motor epilepsy or multifocal myoclonus. continued on next slide
47 Liver symptoms include hepatomegaly, jaundice, and progressive coagulopathy and hypoglycemia. CSF and blood lactate and pyruvate can be elevated VEP may show asymmetric abnormalities In some patients complex I enzyme abnormalities are shown in liver or muscle. POLG mutations have been identified in these patients.
48 First described in two unrelatd children with severe anorexia, vomitng, chronic diarrhea and villus atrophy in the first year of life Liver involvement included increased AST/ALT, hepatomegaly, and steatosis Diarrhea, vomiting and lactic acidosis worsen with high dextrose IVF or enteral nutrition. Resolution of diarrhea by 5 years with onset of RP, ataxia, deafness and proximal muscle weakness with death in first decade of life. Complex III defect in skeletal muscle Heteroplasmic mtdna rearrangements that involved deletion and deletion duplication.
49 Sensorimotor neuropathy with progressive liver disease confined to Navajo children. Three forms with variable age of onset and prominence of liver dysfunction Typically associated with weakness, hypotonia, mutiliaton. Corneal ulceration, FTT, recurrent infections, Reye-like syndrome episodes, cholestatsis cirrhosis and liver failure. Brain MRI notable for progressive white matter lesions, +/- Lactate and pyruvate elevations. Complex I, III, IV deficiencies on enzymology. Associated with MPV17 mutations and mtdna depletion.
50 w w w. v m p g e n e t i c s. c o m i n f v m p g e n e t i c s. c o m v o i c e f a x and you can follow us on Facebook!
Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders
 Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders Carolyn J Ellaway MBBS PhD FRACP CGHGSA Genetic Metabolic Disorders Service Sydney Children s Hospital Network Disciplines of Child and Adolescent
Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders Carolyn J Ellaway MBBS PhD FRACP CGHGSA Genetic Metabolic Disorders Service Sydney Children s Hospital Network Disciplines of Child and Adolescent
MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE. Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital
 MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures & Disclaimers United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation Research Grant North American Mitochondrial
MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures & Disclaimers United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation Research Grant North American Mitochondrial
REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST BE FILLED OUT COMPLETELY FOR SAMPLE TO BE PROCESSED. Last First Last First
 #: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
#: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children
 Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
AUTISM SCIENCE DIGEST: THE JOURNAL OF AUTISMONE ISSUE 01 APRIL 2011 REPRINTED WITH PERMISSION
 FRAN KENDALL, MD, has extensive experience in the diagnosis and management of children and adults with a wide array of inborn errors of metabolism, specifically mitochondrial and metabolic disorders. She
FRAN KENDALL, MD, has extensive experience in the diagnosis and management of children and adults with a wide array of inborn errors of metabolism, specifically mitochondrial and metabolic disorders. She
An Introduction to mitochondrial disease.
 9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC
 Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
MYOCLONIC EPILEPSY WITH RAGGED RED FIBERS (MERRF) By- Promie Faruque
 MYOCLONIC EPILEPSY WITH RAGGED RED FIBERS (MERRF) By- Promie Faruque PHYSIOLOGY -MERRF is a rare panethnic mitochondrial disease which is caused by mutations in the mtdna -It mainly affects the muscle
MYOCLONIC EPILEPSY WITH RAGGED RED FIBERS (MERRF) By- Promie Faruque PHYSIOLOGY -MERRF is a rare panethnic mitochondrial disease which is caused by mutations in the mtdna -It mainly affects the muscle
Mitochondrial Cytopathies
 Mitochondrial Cytopathies Bruce H. Cohen, M.D. Neuroscience Institute Brain Tumor and Neuro-Oncology Center Pediatric Neurology Center Cleveland Clinic 2008 What Are Mitochondria? Engines within the cell
Mitochondrial Cytopathies Bruce H. Cohen, M.D. Neuroscience Institute Brain Tumor and Neuro-Oncology Center Pediatric Neurology Center Cleveland Clinic 2008 What Are Mitochondria? Engines within the cell
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract
 Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
April-May, Diabetes - the Medical Perspective. Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions
 April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
Referring Physician Information Name: (Last, First, Middle):
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Information Clinical Indication: Patient Name: (Last, First, Middle): DOB (M/D/Y): Sex: M F Guardian Name (for minor patients only): Address: City: State: ZIP: Phone: Ethnic Background
Page 1 of 5 Patient Information Clinical Indication: Patient Name: (Last, First, Middle): DOB (M/D/Y): Sex: M F Guardian Name (for minor patients only): Address: City: State: ZIP: Phone: Ethnic Background
Hypoglycemia in congenital hyperinsulinism
 How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
Biochemistry of cellular organelles
 Kontinkangas, L101A Biochemistry of cellular organelles Lectures: 1. Membrane channels; 2. Membrane transporters; 3. Soluble lipid/metabolite-transfer proteins; 4. Mitochondria as cellular organelles;
Kontinkangas, L101A Biochemistry of cellular organelles Lectures: 1. Membrane channels; 2. Membrane transporters; 3. Soluble lipid/metabolite-transfer proteins; 4. Mitochondria as cellular organelles;
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease
 Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
The Organism as a system
 The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY
 THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
Monitor patient s ability to self-administer insulin. (To evaluate safe administration of drug.)
 Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
The mitochondrion and its disorders
 100 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY H O W T O U N D E R S T A N D I T The mitochondrion and its disorders Patrick F. Chinnery Department of Neurology, Regional Neurosciences Centre, Newcastle General Hospital and
100 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY H O W T O U N D E R S T A N D I T The mitochondrion and its disorders Patrick F. Chinnery Department of Neurology, Regional Neurosciences Centre, Newcastle General Hospital and
Mitochondrial Diseases
 Mitochondrial Diseases Simon Heales SWIM Conference Taunton, November 29 th 2018 Respiratory Failure Cardiomyopathy Optic Atrophy / Retinitis Pigmentosa Seizures / Developmental delay Liver Failure Deafness
Mitochondrial Diseases Simon Heales SWIM Conference Taunton, November 29 th 2018 Respiratory Failure Cardiomyopathy Optic Atrophy / Retinitis Pigmentosa Seizures / Developmental delay Liver Failure Deafness
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia
 Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders What are functional GI disorders?
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
Chronic Hepatitis C. Risk Factors
 Chronic Hepatitis C The hepatitis C virus is one of the most important causes of chronic liver disease in the United States. Almost 4 million Americans or 1.8 percent of the U.S. population have an antibody
Chronic Hepatitis C The hepatitis C virus is one of the most important causes of chronic liver disease in the United States. Almost 4 million Americans or 1.8 percent of the U.S. population have an antibody
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
From Heave to Leave: Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome in the Adult Population
 From Heave to Leave: Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome in the Adult Population Andrea H. Thurler, DNP, FNP-BC Stephanie M. Doherty, MSN, AGNP-BC In collaboration with Dr. Braden Kuo, MD and Dr. Kyle
From Heave to Leave: Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome in the Adult Population Andrea H. Thurler, DNP, FNP-BC Stephanie M. Doherty, MSN, AGNP-BC In collaboration with Dr. Braden Kuo, MD and Dr. Kyle
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA
 Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Chapter 27 & 28. Key Terms. Digestive System. Fig. 27-1, p. 443 Also known as the Gastrointestinal System (GI system)
 Chapter 27 & 28 Nutrition & Fluids Key Terms Aspiration Dehydration Edema Dysphagia Gastrostomy tube Intravenous therapy (IV) Digestive System Fig. 27-1, p. 443 Also known as the Gastrointestinal System
Chapter 27 & 28 Nutrition & Fluids Key Terms Aspiration Dehydration Edema Dysphagia Gastrostomy tube Intravenous therapy (IV) Digestive System Fig. 27-1, p. 443 Also known as the Gastrointestinal System
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Page by: OpenStax Summary The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Page by: OpenStax Summary The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Diabetic Gastroparesis. Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017
 Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
more intense treatments are needed to get rid of the infection.
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk of getting
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk of getting
Marah Bitar. Faisal Nimri ... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh
 8 Marah Bitar Faisal Nimri... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh Summary of the 8 steps of citric acid cycle Step 1. Acetyl CoA joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the CoA group and forming a six-carbon
8 Marah Bitar Faisal Nimri... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh Summary of the 8 steps of citric acid cycle Step 1. Acetyl CoA joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the CoA group and forming a six-carbon
Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia
 Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia Linda Steinkrauss, RN, MSN, CPNP Objectives By the end of this session, attendees should be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia
Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia Linda Steinkrauss, RN, MSN, CPNP Objectives By the end of this session, attendees should be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
Robert Barski. Biochemical Genetics St James s University Hospital, Leeds. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Robert Barski Biochemical Genetics St James s University Hospital, Leeds Lactate is produced as the fate of anaerobic metabolism of pyruvate. It is an important intermediary metabolite especially with
Robert Barski Biochemical Genetics St James s University Hospital, Leeds Lactate is produced as the fate of anaerobic metabolism of pyruvate. It is an important intermediary metabolite especially with
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS IN NEUROLOGY
 MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS IN NEUROLOGY Michio Hirano, MD Columbia University Medical Center New York, NY In the opening lecture of this course, Dr. Eric Schon will describe the molecular genetic and pathogenic
MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS IN NEUROLOGY Michio Hirano, MD Columbia University Medical Center New York, NY In the opening lecture of this course, Dr. Eric Schon will describe the molecular genetic and pathogenic
CLINICAL SIGNS SUGGESTIVE OF A NEUROMETABOLIC DISEASE. Bwee Tien Poll-The Amsterdam UMC The Netherlands
 CLINICAL SIGNS SUGGESTIVE OF A NEUROMETABOLIC DISEASE Bwee Tien Poll-The Amsterdam UMC The Netherlands FRAMEWORK OF PRINCIPALS 1. Problem-oriented clinical approach 2. Biomarkers in plasma, urine, CSF
CLINICAL SIGNS SUGGESTIVE OF A NEUROMETABOLIC DISEASE Bwee Tien Poll-The Amsterdam UMC The Netherlands FRAMEWORK OF PRINCIPALS 1. Problem-oriented clinical approach 2. Biomarkers in plasma, urine, CSF
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Tips to Help Treat Diarrhea, Nausea, and Vomiting Side Effects
 Tips to Help Treat Diarrhea, Nausea, and Vomiting Side Effects If you have been prescribed OFEV (nintedanib) capsules for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) this brochure can help you
Tips to Help Treat Diarrhea, Nausea, and Vomiting Side Effects If you have been prescribed OFEV (nintedanib) capsules for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) this brochure can help you
Eosinophilic Disease. E.g.i.d. group. An Introduction written by parents
 www.egid.org.uk Our facebook group link: http://www.facebook.com/home.php?#!/group.php? gid=28072826009 Eosinophilic Disease E.G.I.D. Group E.g.i.d. group An Introduction written by parents 0 Table of
www.egid.org.uk Our facebook group link: http://www.facebook.com/home.php?#!/group.php? gid=28072826009 Eosinophilic Disease E.G.I.D. Group E.g.i.d. group An Introduction written by parents 0 Table of
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks
 A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. The energy released is trapped in the form of
Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. The energy released is trapped in the form of
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults
 Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 03
 Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy
 Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy 7.1 Mighty Mitochondria More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many of those afflicted die young
Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy 7.1 Mighty Mitochondria More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many of those afflicted die young
Symptom Management. Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director
 Symptom Management Nausea & Vomiting Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director Mr. Jones has nausea and vomiting. May I initiate Compazine from the Comfort Pak? Objectives 1. Delineate the Differential
Symptom Management Nausea & Vomiting Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director Mr. Jones has nausea and vomiting. May I initiate Compazine from the Comfort Pak? Objectives 1. Delineate the Differential
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
GASTROENTEROLOGY ESSENTIALS
 GASTROENTEROLOGY ESSENTIALS Practical Gastroenterology 8/25/2018 Jahnavi Koppala, MBBS Abdullah Abdussalam, MD A 48-year-old male was evaluated for noncardiac chest pain. Treatment with PPI twice daily
GASTROENTEROLOGY ESSENTIALS Practical Gastroenterology 8/25/2018 Jahnavi Koppala, MBBS Abdullah Abdussalam, MD A 48-year-old male was evaluated for noncardiac chest pain. Treatment with PPI twice daily
NAME KEY ID # EXAM 3a BIOC 460. Wednesday April 10, Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided!
 EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Glycogen Storage Disease
 Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
How Cells Release Chemical Energy. Chapter 8
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 8 Impacts, Issues: When Mitochondria Spin Their Wheels More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 8 Impacts, Issues: When Mitochondria Spin Their Wheels More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many
4/23/2015. Linda Steinkrauss, MSN, PNP. No conflicts of interest
 Linda Steinkrauss, MSN, PNP No conflicts of interest 1 5 year old African-American female presented to our Endocrinology Clinic with hypoglycemia Abnormal chromosomes Duplication of 11q13.5-11p14.1 affecting
Linda Steinkrauss, MSN, PNP No conflicts of interest 1 5 year old African-American female presented to our Endocrinology Clinic with hypoglycemia Abnormal chromosomes Duplication of 11q13.5-11p14.1 affecting
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Digestion. Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional
 Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Pediatric Gastroenterology Referral Guidelines
 Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017
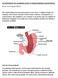 GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water
 Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]
![3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]](/thumbs/72/66350985.jpg) 3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
DYSPEPSIA Dyspepsia indigestion during or after eating Full Heat, burning or pain Note: one of every four people
 What Is Dyspepsia? Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, can have multiple symptoms. Feelings of indigestion happen during or after eating. If you have indigestion you might feel: Full during a meal. Painful
What Is Dyspepsia? Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, can have multiple symptoms. Feelings of indigestion happen during or after eating. If you have indigestion you might feel: Full during a meal. Painful
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Section 4: Exercise Physiology. Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance
 Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD
 GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure)
 Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) People who have had a Whipple procedure may have different nutritional problems. This handout will help you identify and manage common nutrition
Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) People who have had a Whipple procedure may have different nutritional problems. This handout will help you identify and manage common nutrition
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
EUCARBON 100% PLANT BASED INGREDIENTS MANAGING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROM (IBS) You are constantly complaining about
 MY IBS DIARY MANAGING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROM (IBS) EUCARBON NATURALLY REGULATES YOUR DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SINCE 1909 ALLEVIATES DIGESTIVE DISTRESS EASES CONSTIPATION REDUCES FLATULENCE 100% PLANT BASED INGREDIENTS
MY IBS DIARY MANAGING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROM (IBS) EUCARBON NATURALLY REGULATES YOUR DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SINCE 1909 ALLEVIATES DIGESTIVE DISTRESS EASES CONSTIPATION REDUCES FLATULENCE 100% PLANT BASED INGREDIENTS
The incidence of pancreatic cancer is rising in India and is higher in the urban male population in the western and northern parts of India.
 Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride mg Equivalent to metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous mg
 Name Primperan 10 mg / 2 ml Metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous Solution for I.M. or I.V. injection (Ampoules) Composition Each 2 ml ampoule contains: Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride.
Name Primperan 10 mg / 2 ml Metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous Solution for I.M. or I.V. injection (Ampoules) Composition Each 2 ml ampoule contains: Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride.
