Management of Musculoskeletal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis
|
|
|
- Calvin Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Curr Treat Options in Rheum (2016) 2:61 68 DOI /s Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Management of Musculoskeletal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Philip Clements, MD, MPH Address Professor Emeritus, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, 200 Medical Plaza, Rm 365-C, Los Angeles, CA, 90095, USA Published online: 2 February 2016 * Springer International Publishing AG 2016 This article is part of the Topical Collection on Scleroderma Keywords Systemic sclerosis I Scleroderma I Arthritis I Tendon friction rubs I Synovitis I Tender joint counts I Swollen joint counts I Bursitis I Fibromyalgia I Triple therapy for RA I Rituximab I Methotrexate Opinion statement Musculoskeletal (MSK) pain is a frequent complaint (between % of SSc patients) of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and is most problematic in patients with early diffuse SSc. There are several MSK pain syndromes that can be seen in SSc: seronegative polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, tendonitis, fibromyalgia and other MSK pain syndromes. There are, however, few systemically performed studies that show us the best ways to evaluate or to treat these syndromes. This article presents an expert s opinion about how to evaluate these pain syndromes and how best to treat them, given the limited amount of scientific data that are available. Introduction Musculoskeletal (MSK) pain is a frequent complaint of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) (between % of SSc patients) and is most problematic in patients with early diffuse SSc [1 ]. Unfortunately there are virtually no systematic studies of the causes or the management of MSK involvements in SSc and with few exceptions there have been no controlled trials to determine what are and should be the best strategies for managing MSK pain and synovitis in patients with SSc. A number of cross-sectional studies have been reported over the last few decades which give us a rough idea of how extensive the problem is. Richards reported patients perceptions: stiff joints were noted in 79 % of SSc patients, joint pain in 75 %, and generalized fatigue in 75 % [2]. In a second study, hand dexterity was reduced to % and grip force to % compared to normals [3], while in a third study impairment of hand function (as assessed by the Cochin Hand
2 62 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Function Scale) was higher than in RA or OA [4]. Although the pain may not localize well enough to attribute it to a particular anatomic location, there are several MSK pain syndromes that can be seen in SSc: 1. Tendonitis [5, 6] 2. Rheumatoid arthritis [7] 3. Polyarthritis (not RA) [8] 4. Fibromyalgia [9] 5. Other MSK syndromes Descriptions of the types of MSK pain syndromes seen in SSc Tendonitis: Although tendonitis in the generic sense occurs in many locations in SSc, the more unique form is characterized by the term tendon friction rubs. These rubs may go unnoticed by the patient but more frequently the patients are aware of pain in that area and may even acknowledge a sense of scraping or rubbing when the joint moves [5, 6]. The friction rub s underlying pathology is related to inflammatory fibrinous deposits on the surface of tendon sheaths and around the tendon. The areas that are most typically involved are the triceps, extensor, and flexor tendons of the wrist, patellar tendons, and the posterior and anterior tendons of the ankles. Other areas in which rubs can be found include subscapular, lateral trochanter, and paraspinal areas. Rheumatoid arthritis: These are SSc persons with inflammatory polyarthritis who have RF and/or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (x-ccp ab) in addition to the clinical appearance of RA. Some of these patients develop erosive, destructive joint disease and a few develop a resorptive polyarthropathy resembling arthritis mutilans. The exact prevalence of these patients is estimated to be between 5 10 % in the first 5 years of SSc disease. Polyarthritis (non-ra): These are SSc persons with a polyarthralagia/polyarthritis who do not have RF or anti-ccp antibodies but still have polyarthritic complaints. Some may develop erosive destructive joint changes (particularly in the hands) while smaller numbers may develop resorptive arthropathy and arthritis mutilans [8, 10]. Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a syndrome not a disease. It is characterized as a myofascial pain syndrome that involves many areas of the body (3 of 4 quadrants: above and below the waist and right and left of the spine) along with 11 of 18 FMS points [9]. Although there are few published data on the prevalence of FMS in SS, a post hoc analysis of apreviouslypublisheddataset[11], Malcarne (unpublished observations) revealed that 18.6 % of the 102 SSc patients examined met the 1990 classification criteria for FMS (predominantly patients with early diffuse SSC). Other MSK syndromes: These other miscellaneous pain syndromes include carpal tunnel syndrome, de Quervain s tendonitis, trochanteric and gluteus medius bursitis (lateral hip), anserine bursitis (medial knee), olecranon bursitis, epicondylitis (lateral more than medial), and rotator cuff tendonitis to name a few.
3 Musculoskeletal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Clements 63 Measurement of outcomes that can be used in the clinic to assess disease activity Clinical measures The available literature regarding outcomes and evaluations of therapy in the musculoskeletal involvement by SSc is non-uniform [1 ]. One might think that the seven core arthritis measures [12] used in assessing the response in Rheumatoid Arthritis could be borrowed directly for use in the examination of SSc patients with polyarthritis. However of the seven, only the function assessments have undergone validation in SSc, using the OMERACT filter criteria. These validated function assessments include the Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ-DI), the Cochin Hand Function Scale and the Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) assessment, all of which address function: 1. The 20-item patient self-assessed HAQ-DI is the most widely employed and reported measure for assessing overall function in SSc. In addition nearly half of the 20 questions relate to hand function [13, 14]. 2. Cochin Hand Function Scale: This is a patient selfreport questionnaire that assesses hand function in SSc [4, 14](Table 1 displays the full questionnaire). 3. HAMIS: This is a performance-based (trained physical and/or occupational therapist is usually required although clinical metricians or physicians can be trained to perform the measure) evaluation of patient sfunction[15, 16]. The instrument assesses function in the hand in SSc patients. Validation aside, the other six RA core variables might have some utility in assessing the remaining six RA core measures, although none of them have been validated for use in SSc: tender joint count and swollen joint counts (28 joints particularly), indices of inflammation (ESR, CRP), the 10-cm Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for pain, and the 10-cm visual analogue scale (VAS) for patient global arthritis activity and the 10-cm VAS for physician global arthritis activity scales. Radiographs Plain X-ray films may be of some utility for evaluating the propensity to bone destruction of the patient s arthritic complaints: for example, erosive bone disease, resorptive arthropathy, and arthritis mutilans. The technique is not, however, good for picking up soft-tissue disease. Ultrasound (MSUS) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) The literature supporting the use of these imaging techniques in SSc is in its infancy; but already it is clear that either or both imaging techniques are much better at picking up synovitis, tendonitis, tenosynovitis and other soft-tissue disease than the clinical exam in SSc [1 ]. In one study [17], for example, the baseline MSUS identified tenosynovitis in 8 (47 %) and synovitis in 1 (6 %) of the 17 SSc patients who were examined for complaints of arthralgia and in 6 (46 %) and 3 (23 %) of the 12 SSc patients who returned for a second MSUS. In the same study [17], all eight patients who were examined by MRI showed evidence of synovial inflammation in the form of synovitis in eight (100 %) of the eight and tenosynovitis in seven (88 %) of the eight patients. Bone edema was seen in five (63 %) of the eight and erosions in six (75 %) of the eight patients. Even with the few studies published of MSUS and MRI in SSc-arthritis, performed either at baseline or over time, these imaging studies will likely provide much more detail of the MSK involvement by SSc that can employed to improve the clinical management of these patients. Summary of the most reasonable outcome measures that can be used in the clinical management of SSc patients with polyarthritis 1. At baseline, examine the patient. Consider X-rays, ultrasound/mri assessments of the fingers, hands and wrist joints and especially their surrounding soft tissues. Draw rheumatoid factor, anti-ccp antibodies, ESR, and CRP. 2. At periodic times assess: (a) Joint tenderness counts (28 joints, as in RA). (b) Joint swelling counts (28 joints, as in RA); also realize that thickened skin on the hands and fingers may make this assessment difficult. (c) 10-cm visual activity scales (VAS) to assess patient s pain, the patient s 10-cmVASfor global assessment of how their arthritis is doing, and the doctor s 10-cm global assessment of how the patient s arthritis is doing.
4 64 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Table 1. Cochin Hand Function Scale. For each of the following statements, please circle the response that is most correct for you. Please use the following scale Consider your difficulties with the following in the last month Yes, without difficulty Yes, with little difficulty Yes, with some difficulty Possiblewith much difficulty Nearly impossible to do Section 1: in the kitchen 1. Can you hold a bowl? Can you seize a full bottle and raise it? Can you hold a plate full of food? Can you pour liquid from a bottle into aglass? 5. Can you unscrew the lid from a jar opened before? 6. Can you cut meat with a knife? Can you prick things well with a fork? Can you peel fruits? Section 2: dressing 9. Can you button your shirt? Can you open and close a zipper? Section 3: hygiene 11. Can you squeeze a new tube of toothpaste? 12. Can you hold a toothbrush efficiently? Section 4: at the office 13. Can you write a short sentence with an ordinary pen? 14. Can you write a letter with an ordinary pen? Section 5: other 15. Can you turn a round door knob? Can you cut a piece of paper with scissors? 17. Can you pick up coins from a table top? 18. Can you turn a key in a lock? Impossible to do Modified with permission from [19].
5 Musculoskeletal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Clements 65 (d) The Cochin Hand Function Scale (Table 1)is particularly useful here as a measure of function because it is focused on hand function and how that function may change over time. It is patientderived; its questions are readily understood and can be completed in less than 5 min. It may, however, be confounded by the fibrotic associated finger contractures that are part of SSc. (e) It is less clear how the ESR and CRP may change in meaningful ways in SSc-arthritis but it may be worth following in given individuals. Management of individual MSK syndromes Seronegative Polyarthritis Walker et al [18 ] canvassed 117 SSc experts in a 3-part internet exercise about how they would treat the entity of inflammatory polyarthritis in SSc. There was no written definition of inflammatory polyarthritis provided to the participants, and as such the participants were allowed to use their own criteria for making that diagnosis. 59 experts (43 % of the initial 117) completed all three parts of the survey. In the survey the first line treatments reported by participants included methotrexate in 60 %, corticosteroids in 30 %, and hydroxychloroquine in 28 %. If the patient was not improved enough with the initial treatments, 75 % of the participants reported that they would add a second agent while 25 % reported they would switch to a second, different agent. The second line treatments chosen by the participants included methotrexate in 54 %, corticosteroids in 37 %, hydroxychloroquine in 31 %, and biologics (including TNF-inhibitors [TNFi]) in 20 %. A second approach to treatment (Fig. 1) has been suggested that divides SSc patients with inflammatory polyarthritis by phenotype into those who look more like: 1. Erosive polyarthritis that is seronegative (rheumatoid factor [RF] and cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody [anti-ccp] tests negative) that can look like destructive RA, psoriatic arthritis and/or arthritis mutilans. In many respects they can be treated like rheumatoids even though efficacy in SSc has not been established. 2. Non-erosive polyarthritis (rheumatoid factor [RF] and cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody [anti- CCP] tests negative) that can be treated much as a lupus-like arthritis. In this scheme, all polyarthritis could/should be treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (as tolerated by the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract), low-dose corticosteroids (with the exception of early diffuse SSc [ 5 years from SSc onset] who may be at increased risk of renal crisis if managed on corticosteroids at any dose), local corticosteroid injections, and hand therapy to stretch contractured joints, improve range of motion, and potentially minimize future contractures and functional disability. As far as treatment of the polyarthritic phenotypes is concerned, we should keep in mind that the following treatment strategies have not been scientifically tested in SSc per se even though scientifically they have been found effective in RA. At this point we are forced to accept expert opinion for the following recommendations: The erosive patients (even if they are RF and/or anti-ccp negative) might be started on methotrexate (MTX). If MTX is not effective enough, leflunomide, triple therapy or a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) might be added. If these strategies fail then moving on to other biologics might be reasonable. The drugs listed in the figure have by and large been shown in RA to be bone preservers, and that can be the rationale for using them in this situation. Again we should keep in mind that thereislittlescienceintheuseoftheseagents in SSc. The same caveat holds true about the lack of scientific basis for the management of the nonerosive lupus-like polyarthritis in SSc as well. Potential treatments are listed in Fig. 1. Byand large the drugs listed in the non-erosive pathway have failed to show convincing evidence that they are significant bone preservers in RA. They can be used separately or in combinations as they often are in practice. Seropositive Polyarthritis or RA (RF and Anti-CCP Antibody Positive) The presence of seropositive RA (+ anti-ccp antibody) in association with SSc suggests a true overlap syndrome. Its management should
6 66 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) General treatment: NSAIDs, low-dose steroids, injectable corticosteroids Hand-therapy: Range of motion, splinting Erosive (Like RA, PsA, mutilans) Non-erosive (Lupus-like) Methotrexate Leflunomide Triple therapy Other DMARDs TNF inhibitors Other biologics Corticosteroids Anti-malarials Methotrexate Azathioprine Mycophenolate Rituximab Other biologics Fig. 1. Suggested algorithm for treatment of SSc-arthritis by erosive versus non-erosive polyarthritis. be driven by the scientific precepts that have developed for the management of RA. I will not discuss this entity further. Fibromyalgia As noted earlier in the introduction, about a fifth of SSc patients may have a fibromyalgia-like pain disorder at some point in their course. One useful treatment strategy is to decide who does and who does not respond to steroids: 1. Those who respond well to small doses of prednisone (5 7.5 mg daily or less) or other shortacting corticosteroid in equivalent doses. Caution: avoid the use of prednisone in patients with diffuse SSc of less than 5 years of SSc. 2. Those who do not respond to small doses of prednisone. My recommendations here are to introduce to thepatienttheconceptthat about 20 % of SSc patients have this myofascial pain syndrome called FMS and that we need to address the pain and fatigue concerns that plague these patients, almost as a separate overlapping disorder. Essentially I treat FMS as a separate entity within the larger context of SSc. The patient should be reassured that when the pain and fatigue flair, it is usually not that the SSc is getting worse only that their FMS has flared. My management principles for SSc-associated FMS are those of many experienced practitioners who see and treat FMS. I do, however, often employ a short trial (2 4 weeks)oflowdose prednisone to determine if the FMS-like disorder is really an inflammatory process that just looks like FMS. If the patient responds, then I will try to extend the time for using steroids and try to taper the prednisone to the lowest effective dose. Whether the patient does or does not respond to steroids, I otherwise treat them as if they had FMS on a noninflammatory basis. Miscellaneous Soft-Tissue Involvements Including Tendonitis, Tenosynovitis, and Bursitides MSUS/MRI appear to be useful tools for detecting the presence of inflammatory and structural abnormalities involving both joints and soft tissues [1 ]. The swollen and inflamed soft tissues that are part of SSc are often more obvious and better defined by MSUS/MRI than are apparent by clinical examination. If the health provider has any question
7 Musculoskeletal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Clements 67 about how involved seemingly simple soft tissues are, then MSUS and MRI may be helpful in demonstrating the involvements that can be managed appropriately. Many of the soft tissue involvements that are uncovered by MSUS/MRI are as treatable as they might be in the general rheumatic disease population: NSAIDS, softtissue steroid injections, physical and occupational therapy, splinting, etc. Summary Although the science of assessing and treating MSK involvements in SSc is in its infancy, there are strategies that many experts feel can help the symptomatic SSc patient with arthritic complaints. The present treatments, largely based on expert opinion, have been presented in the discussion above. The diagnostic criteria and the outcomes to therapy need to be evaluated and validated in prospective controlled trials. Compliance with Ethical Standards Funding This work was supported by grants from the NHLBI/NIH: R01 HL and R01 HL Conflict of Interest Philip Clements declares that he has no conflicts of interest. Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author. References Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: Of importance 1. Clements PJ, Allanore Y, Khanna D, Singh M, Furst DE. Arthritis in systemic sclerosis: systematic review of the literature and suggestions for the performance of future clinical trials in systemic sclerosis arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41: This systematic literature review revealed that there was very little in the way of systematically performed studies of outcomes or of therapies that could impact polyarthritis or other musculoskeletal manifestation of systemic sclerosis. 2. Richards HL, Herrick AL, Griffin K, Gwilliam PDH, Loukes J, Fortune DG. Systemic sclerosis: patients perceptions of their condition. Arthritis Care Res. 2003;49: Sandqvist G, Eklund M, Akesson A, Nordenskiöld U. Daily activities and hand function in women with scleroderma. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33: Brower LM, Poole JL. Reliability and validity of the Duruoz Hand Index in persons with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 2004;51: Steen VD, Medsger Jr TA. The palpable tendon friction rub: an important physical examination finding in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40: Khanna PP, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Maranian P, Indulkar L, Khanna D. D-Penicillamine investigators. Tendon friction rubs in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: prevalence, characteristics and longitudinal changes in a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49: Morita Y, Muro Y, Sugiura K, Tomita Y. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26:542 7.
8 68 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) 8. Avouac J, Guerini H, Wipff J, Assous N, Chevrot A, Kahan A, et al. Radiological hand involvement in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65: Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia: report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33: Bassett LW, Blocka KL, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Gold RH. Skeletal findings in progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981;136: Malcarne VL, Hansdottir I, McKinney A, Upchurch R, Greenbergs HL, Henstorf GH, et al. Medical signs and symptoms associated with disability, pain, and psychosocial adjustment in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2007;34: Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Chernoff M, Fried B, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36: Steen VD, Medsger Jr TA. The value of the health assessment questionnaire and special patient-generated scales to demonstrate change in systemic sclerosis patients over time. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40: Clements PJ, Wong WK, Hurwitz EL, Furst DE, Mayes M, White B, et al. Correlates of the disability index of the health assessment questionnaire: a measure of functional impairment in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;42: Sandqvist G, Eklund M. Validity of HAMIS: a test of hand mobility in scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res. 2000;13: Sandqvist G, Eklund M. Hand mobility in scleroderma (HAMIS) test: the reliability of a novel hand function test. Arthritis Care Res. 2000;13: Chitale S, Ciapetti A, Hodgson R, Grainger A, O Connor P, Goodson NJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and musculoskeletal ultrasonography detect and characterize covert inflammatory arthropathy in systemic sclerosis patients with arthralgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49: WalkerKM,PopeJ.Participatingmembersofthe scleroderma clinical trials consortium DSCTC], Canadian scleroderma research group. Treatment of systemic sclerosis complications: what to use when first-line treatment fails a consensus of systemic sclerosis experts. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;42: This was not a scientific study of the practices of scleroderma experts from around the world. Rather, it was questioning of physicians of what the physicians themselves thought about how they treated polyarthritis and other musculoskeletal manifestations as they occur in systemic sclerosis. 19. Duruöz MT, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, Menkes CJ, Amor B, Dougados M, et al. Development and validation of a rheumatoid hand functional disability scale that assesses functional handicap. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS. Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Early Detection of Inflammatory Arthropathy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Early Detection of Inflammatory Arthropathy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Lobna AM Habib 1, Reem A. Habeeb 2 Departments
Original Article Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Early Detection of Inflammatory Arthropathy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Lobna AM Habib 1, Reem A. Habeeb 2 Departments
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management. Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics
 + The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
+ The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Mr. OA: Case Presentation
 CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine COPYRIGHT. Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
 Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Sclérodermie systémique: Manifestations musculosquelettiques
 Sclérodermie systémique: Manifestations musculosquelettiques Benjamin Chaigne Service de Médecine Interne, hôpital Cochin, Centre de Référence Vascularites nécrosantes et sclérodermie systémique Assistance
Sclérodermie systémique: Manifestations musculosquelettiques Benjamin Chaigne Service de Médecine Interne, hôpital Cochin, Centre de Référence Vascularites nécrosantes et sclérodermie systémique Assistance
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies
 A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies T. Pincus Division of Rheumatology and Immunology,
A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies T. Pincus Division of Rheumatology and Immunology,
Objectives. Joint Pain. Case 1. Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) 12/4/2010
 Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Horizon Scanning Centre November Secukinumab for active and progressive psoriatic arthritis. SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 5330
 Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Secukinumab for active and progressive psoriatic arthritis. SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 5330 Secukinumab is a high-affinity fully human monoclonal antibody that antagonises
Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Secukinumab for active and progressive psoriatic arthritis. SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 5330 Secukinumab is a high-affinity fully human monoclonal antibody that antagonises
Aches and Pains in Rheumatology: Is it Fibromyalgia, Osteoarthritis, or Rheumatoid Disease?
 Aches and Pains in Rheumatology: Is it Fibromyalgia, Osteoarthritis, or Rheumatoid Disease? SCOTT T ANDERSON, MD, PHD, FACR, CCHP-P CLINICAL PROFESSOR Menu(rotating) DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY, ALLERGY,
Aches and Pains in Rheumatology: Is it Fibromyalgia, Osteoarthritis, or Rheumatoid Disease? SCOTT T ANDERSON, MD, PHD, FACR, CCHP-P CLINICAL PROFESSOR Menu(rotating) DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY, ALLERGY,
Early synovitis clinics
 Early synovitis clinics Jeremy Jones MD FRACP FAFRM Consultant Rheumatologist, Llandudno General Hospital Honorary Research Fellow School of Sport, Health and Exercise Sciences Bangor University RA medication
Early synovitis clinics Jeremy Jones MD FRACP FAFRM Consultant Rheumatologist, Llandudno General Hospital Honorary Research Fellow School of Sport, Health and Exercise Sciences Bangor University RA medication
Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2010 Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2010 presentations
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2010 Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2010 presentations
Rheumatology & Immunology. Regional pain syndromes to be covered today. Some definitions. Tendinitis. Bursitis. History. History. Exam.
 Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 1 What is spondyloarthritis? Spondyloarthritis is a general term that describes a number of types of inflammatory arthritis which share many articular and extra-articular features. Conditions which fall
1 What is spondyloarthritis? Spondyloarthritis is a general term that describes a number of types of inflammatory arthritis which share many articular and extra-articular features. Conditions which fall
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Soft Tissue Rheumatism. Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group
 Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
New Evidence reports on presentations given at ACR Improving Radiographic, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes with Rituximab
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at ACR 2009 Improving Radiographic, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes with Rituximab From ACR 2009: Rituximab Rituximab in combination with methotrexate
New Evidence reports on presentations given at ACR 2009 Improving Radiographic, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes with Rituximab From ACR 2009: Rituximab Rituximab in combination with methotrexate
APPLICATION FOR SUBSIDY BY SPECIAL AUTHORITY
 APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1620 Etanercept INITIAL APPLICATION - juvenile idiopathic arthritis Applications only from a named specialist rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months.
APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1620 Etanercept INITIAL APPLICATION - juvenile idiopathic arthritis Applications only from a named specialist rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist
 Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Imaging of polymyalgia rheumatica: what the radiologist should know
 Imaging of polymyalgia rheumatica: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: P-0117 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E. L. Bizetto, M. F. Correa, M.
Imaging of polymyalgia rheumatica: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: P-0117 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E. L. Bizetto, M. F. Correa, M.
Pragmatic ultrasound in the diagnosis of soft tissue rheumatic pain. Plamen Todorov
 Pragmatic ultrasound in the diagnosis of soft tissue rheumatic pain Plamen Todorov INTRODUCTION Soft tissue rheumatism: nonsystemic, focal pathological syndromes involving the periarticular structures.
Pragmatic ultrasound in the diagnosis of soft tissue rheumatic pain Plamen Todorov INTRODUCTION Soft tissue rheumatism: nonsystemic, focal pathological syndromes involving the periarticular structures.
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) INJECTION FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION
 UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Benefit Drug Policy ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) INJECTION FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION Policy Number: CS2018D0039J Effective Date: March 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS
UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Benefit Drug Policy ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) INJECTION FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION Policy Number: CS2018D0039J Effective Date: March 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Rheumatoid arthritis 2010: Treatment and monitoring
 October 12, 2010 By Yusuf Yazici, MD [1] The significant changes in the way rheumatoid arthritis has been managed include earlier, more aggressive treatment with combination therapy. Significant changes
October 12, 2010 By Yusuf Yazici, MD [1] The significant changes in the way rheumatoid arthritis has been managed include earlier, more aggressive treatment with combination therapy. Significant changes
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March. (minutes for web publishing)
 Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
Measuring Patient Outcomes:
 Measuring Patient Outcomes: Interplay of science, policy and marketing Chapel Hill, November 22, 22 Dr. Claire Bombardier Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Senior Scientist, Institute for Work
Measuring Patient Outcomes: Interplay of science, policy and marketing Chapel Hill, November 22, 22 Dr. Claire Bombardier Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Senior Scientist, Institute for Work
James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center
 Not everyone in the world needs a biologic: Lessons from TEAR and RACAT James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center Disclosure Declaration James O Dell, MD Advisory Board for Crescendo,
Not everyone in the world needs a biologic: Lessons from TEAR and RACAT James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center Disclosure Declaration James O Dell, MD Advisory Board for Crescendo,
Reliability and validity of the delta finger-to-palm (FTP), a new measure of finger range of motion in systemic sclerosis
 Reliability and validity of the delta finger-to-palm (FTP), a new measure of finger range of motion in systemic sclerosis K.S. Torok 1, N.A. Baker 2, M. Lucas 3, R.T. Domsic 3, R. Boudreau 4, T.A. Medsger
Reliability and validity of the delta finger-to-palm (FTP), a new measure of finger range of motion in systemic sclerosis K.S. Torok 1, N.A. Baker 2, M. Lucas 3, R.T. Domsic 3, R. Boudreau 4, T.A. Medsger
Inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 Learning objectives Inflammatory rheumatic diseases Bruce Kidd Barts & The London, Queen Mary, University of London To understand: 1. prevalence and range of the rheumatological s 2. clinical features
Learning objectives Inflammatory rheumatic diseases Bruce Kidd Barts & The London, Queen Mary, University of London To understand: 1. prevalence and range of the rheumatological s 2. clinical features
APPLICATION FOR SUBSIDY BY SPECIAL AUTHORITY
 APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1621 Adalimumab INITIAL APPLICATION - rheumatoid arthritis Applications only from a rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months. The patient has had an initial
APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1621 Adalimumab INITIAL APPLICATION - rheumatoid arthritis Applications only from a rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months. The patient has had an initial
Arthritis. that affects the joints.
 Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
De Quervain s Tenosynovitis
 De Quervain s Tenosynovitis What Is De Quervain s? De Quervain s tenosynovitis (ten-oh-sin-oh-vy-tis) is an inflammation of tissue on the thumb side of the wrist. Tendons (cordlike fibers that attach muscle
De Quervain s Tenosynovitis What Is De Quervain s? De Quervain s tenosynovitis (ten-oh-sin-oh-vy-tis) is an inflammation of tissue on the thumb side of the wrist. Tendons (cordlike fibers that attach muscle
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education
 Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Regional Pain Syndromes Introduction: At some time in the course of life, virtually everyone will experience pain in a tendon, muscle, or
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Regional Pain Syndromes Introduction: At some time in the course of life, virtually everyone will experience pain in a tendon, muscle, or
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future
 Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW. Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center
 RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
APPLICATION FOR SPECIAL AUTHORITY. Subsidy for Tocilizumab
 APPLICATION FOR SPECIAL AUTHORITY Fm SA1781 Subsidy f Tocilizumab Application Categy Page Cytokine release syndrome - Initial application... 2 Previous use - Initial application... 2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
APPLICATION FOR SPECIAL AUTHORITY Fm SA1781 Subsidy f Tocilizumab Application Categy Page Cytokine release syndrome - Initial application... 2 Previous use - Initial application... 2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis. August 2009
 Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Remicade (Infliximab)
 Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Professor Lisa Stamp
 Professor Lisa Stamp Rheumatologist University of Otago, Christchurch 8:30-9:25 WS #65: Joint Injection Techniques 9:35-10:30 WS #75: Joint Injection Techniques (Repeated) Joint/soft tissue corticosteroid
Professor Lisa Stamp Rheumatologist University of Otago, Christchurch 8:30-9:25 WS #65: Joint Injection Techniques 9:35-10:30 WS #75: Joint Injection Techniques (Repeated) Joint/soft tissue corticosteroid
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings
 Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Codes
 Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Dx Diagnosis Description Codes Codes 327.52 Sleep related leg cramps 717 Old bucket handle tear of medial 333.84
Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Dx Diagnosis Description Codes Codes 327.52 Sleep related leg cramps 717 Old bucket handle tear of medial 333.84
Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making
 Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making Disease Modifying Drug Therapy DMARDs Therapy El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com
Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making Disease Modifying Drug Therapy DMARDs Therapy El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com
I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide
 I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide Pierluigi Macchioni Struttura Complessa di Reumatologia, Ospedale di Reggio Emilia Topics 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA
I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide Pierluigi Macchioni Struttura Complessa di Reumatologia, Ospedale di Reggio Emilia Topics 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Manifestations and Presentations of Collagen Vascular Diseases. Joseph LaConti, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases Miami, FL
 Manifestations and Presentations of Collagen Vascular Diseases Joseph LaConti, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases Miami, FL June 29, 2018 Disclosures Joseph LaConti, M.D., Ph.D., has
Manifestations and Presentations of Collagen Vascular Diseases Joseph LaConti, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases Miami, FL June 29, 2018 Disclosures Joseph LaConti, M.D., Ph.D., has
The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint
 i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
Mary Derlacki, FNP. No financial relationships to disclose. Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner. Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner Mary Derlacki, FNP Drs. Cassell and Boren Eugene, OR 541-687-0816 mderlacki@comcast.net No financial relationships to disclose Rheumatoid Arthritis 1% of
Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner Mary Derlacki, FNP Drs. Cassell and Boren Eugene, OR 541-687-0816 mderlacki@comcast.net No financial relationships to disclose Rheumatoid Arthritis 1% of
DocSpot what patients want to know
 DocSpot what patients want to know Professor Chris Denton Royal Free Hospital London, UK Madrid, February 2012 Copyright 2011 Raynaud's & Scleroderma Association. Charity Reg. No. 326306 DocSpot Live!
DocSpot what patients want to know Professor Chris Denton Royal Free Hospital London, UK Madrid, February 2012 Copyright 2011 Raynaud's & Scleroderma Association. Charity Reg. No. 326306 DocSpot Live!
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for psoriatic arthritis second line
 Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for psoriatic arthritis second line This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for psoriatic arthritis second line This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Rheumatology Residency Rotation University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
 2010 Rheumatology Residency Rotation University of Colorado Health Sciences Center This paragraph only applies if you are rotating at the University of Colorado Hospital. Please review the rest of the
2010 Rheumatology Residency Rotation University of Colorado Health Sciences Center This paragraph only applies if you are rotating at the University of Colorado Hospital. Please review the rest of the
When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer
 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Nancy A. Brown, DO Spring 2015 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Learning objectives To review the definition and epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Nancy A. Brown, DO Spring 2015 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Learning objectives To review the definition and epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding Arthritis. Training
 Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY
 Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Rheumatoid Arthritis. By: Hadi Esmaily (PharmD., BCCP, MBA) Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti Medical University
 Rheumatoid Arthritis By: Hadi Esmaily (PharmD., BCCP, MBA) Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti Medical University Introduction RA is a Chronic, Systemic, Inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis By: Hadi Esmaily (PharmD., BCCP, MBA) Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti Medical University Introduction RA is a Chronic, Systemic, Inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology
2018 ReachMD Page 1 of 10
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2011 Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2011 presentations Benefit of continuing
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2011 Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2011 presentations Benefit of continuing
Bringing the clinical experience with anakinra to the patient
 Rheumatology 2003;42(Suppl. 2):ii36 ii40 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg331, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Bringing the clinical experience with anakinra to the patient S. B. Cohen
Rheumatology 2003;42(Suppl. 2):ii36 ii40 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg331, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Bringing the clinical experience with anakinra to the patient S. B. Cohen
Medical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
 Medical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Dr Lee-Suan Teh Rheumatologist Royal Blackburn Hospital Educational objectives ABC Appreciate the epidemiology of RA Be able to diagnosis of RA Competent
Medical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Dr Lee-Suan Teh Rheumatologist Royal Blackburn Hospital Educational objectives ABC Appreciate the epidemiology of RA Be able to diagnosis of RA Competent
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General
 Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
Inflammatory arthritis Shared Decision Making
 Inflammatory arthritis Shared Decision Making DMARDs El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com Copyrights reserved Contents 1 2 3
Inflammatory arthritis Shared Decision Making DMARDs El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com Copyrights reserved Contents 1 2 3
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Palindromic rheumatism
 1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
A Patient s Guide to. Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis Who should read this guide? This guide is aimed at people with psoriatic arthritis (abbreviated as PsA), or those who care for a person with this
A Patient s Guide to Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis Who should read this guide? This guide is aimed at people with psoriatic arthritis (abbreviated as PsA), or those who care for a person with this
Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies
 Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies Comparative Effectiveness Studies of Biologics Learning Objectives Understand the motivation for comparative effectiveness research
Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies Comparative Effectiveness Studies of Biologics Learning Objectives Understand the motivation for comparative effectiveness research
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma
 Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Rheumatology
 Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Rheumatology Faculty representative: Chris Kovacs, MD, MPH Resident representative: Diane Hislop, MD Revision date: February 1, 2006 Overview
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Rheumatology Faculty representative: Chris Kovacs, MD, MPH Resident representative: Diane Hislop, MD Revision date: February 1, 2006 Overview
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Anti-CCP antibodies and rheumatoid factor in systemic sclerosis: Prevalence and relationships with joint manifestations
 Original papers Anti-CCP antibodies and rheumatoid factor in systemic sclerosis: Prevalence and relationships with joint manifestations Ewa Wielosz A F, Maria Majdan A,C,E,F, Magdalena Dryglewska B,C,
Original papers Anti-CCP antibodies and rheumatoid factor in systemic sclerosis: Prevalence and relationships with joint manifestations Ewa Wielosz A F, Maria Majdan A,C,E,F, Magdalena Dryglewska B,C,
Management of Widespread Skin Thickening in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis
 Curr Treat Options in Rheum (2016) 2:49 60 DOI 10.1007/s40674-016-0040-0 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Management of Widespread Skin Thickening in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis Suzanne Kafaja, MD
Curr Treat Options in Rheum (2016) 2:49 60 DOI 10.1007/s40674-016-0040-0 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Management of Widespread Skin Thickening in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis Suzanne Kafaja, MD
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes. Mark S. Box, MD
 Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes Mark S. Box, MD Overlap Syndromes As many as 25% of patients with rheumatic diseases with systemic symptoms cannot be definitely diagnosed
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and Overlap Syndromes Mark S. Box, MD Overlap Syndromes As many as 25% of patients with rheumatic diseases with systemic symptoms cannot be definitely diagnosed
COSENTYX (secukinumab)
 COSENTYX (secukinumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
COSENTYX (secukinumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Trigger Finger Release
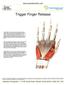 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
 Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
