Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2016 Subsection: Original Policy Date: March 18, 2016 Subject: Page: 1 of 9
|
|
|
- Miranda Gaines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subject: Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Page: 1 of 9 Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Summary Radiofrequency ablation of nerves has been proposed as a treatment for several different types of pain. It has been used to treat a number of clinical pain syndromes such as trigeminal neuralgia, cervical and lumbar pain, and headache syndromes. This evidence review evaluates the evidence for radiofrequency ablation in peripheral sites distant from the cranium or spine. The evidence for radiofrequency ablation of peripheral nerves in individuals who have plantar fasciitis includes case series studies and 1 randomized controlled trial (RCT). Relevant outcomes include symptoms and functional outcomes. The case series generally have small sample sizes, and many have methodologic deficiencies such as retrospective assessment of pain. The single RCT evaluated only 17 patients, and randomized outcomes could only be assessed out to 4 weeks posttreatment. Although the studies report that radiofrequency ablation reduces heel pain, the quality of the evidence is poor. The evidence is insufficient to determine the effects of the technology on health outcomes. The evidence for radiofrequency ablation of peripheral nerves in individuals who have knee osteoarthritis includes case series studies and 1 RCT. Relevant outcomes include symptoms and functional outcomes. The method of radiofrequency treatment varied between studies. Some case series showed improvement in symptoms with treatment. The single randomized trial had a small sample size of 38 and assessed outcomes out to 12 weeks. Although this trial showed improvement in pain at 12 weeks, these results are insufficient to draw conclusions about treatment efficacy. The evidence is insufficient to determine the effects of the technology on health outcomes. Related Policies None Policy *This policy statement applies to clinical review performed for pre-service (Prior Approval, Precertification, Advanced Benefit Determination, etc.) and/or post-service claims. Radiofrequency ablation of peripheral nerves to treat pain associated with plantar fasciitis or knee osteoarthritis is considered investigational.
2 Page: 2 of 9 Background Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a common cause of foot pain in adults, characterized by deep pain in the plantar aspect of the heel, particularly on arising from bed. While the pain may subside with activity, in some patients the pain may persist, impairing activities of daily living. On physical examination, firm pressure will elicit a tender spot over the medial tubercle of the calcaneus. The exact etiology of plantar fasciitis is unclear, although repetitive injury is suspected. Heel spurs are a common associated finding, although it has never been proven that heel spurs cause the pain. Asymptomatic heel spurs can be found in up to 10% of the population. Most cases of plantar fasciitis are treated with conservative therapy, including rest or minimization of running and jumping, heel cups, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Local steroid injection may also be used. Improvement may take up to 1 year in some cases. Knee Osteoarthritis Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is common, costly, and cause of substantial disability. Among U.S. adults, the most common causes of disability are arthritis and rheumatic disorders. Treatment for OA of the knee aims to alleviate pain and improve function. However, most treatments do not modify the natural history or progression of OA and are not considered curative. Nonsurgical modalities used include exercise; weight loss; various supportive devices; acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen; nutritional supplements (glucosamine, chondroitin); and intraarticular viscosupplements. Corticosteroid injection may be considered when relief from NSAIDs is insufficient or the patient is at risk from gastrointestinal adverse effects. If symptom relief is inadequate with conservative measures, invasive treatments may be considered. Operative treatments for symptomatic OA of the knee include arthroscopic lavage and cartilage débridement, osteotomy, and, ultimately, total joint arthroplasty. Surgical procedures intended to repair or restore articular cartilage in the knee (eg, abrasion arthroplasty, microfracture techniques, autologous chondrocyte implantation) are appropriate only for younger patients with focal cartilage defects secondary to injury and are not addressed in this evidence review. Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation Nerve radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive method that involves use of heat and coagulation necrosis to destroy tissue. A needle electrode is inserted through the skin and then into the tissue to be ablated. A high-frequency electrical current is applied to the target tissue. A small sphere of tissue is coagulated around the needle by the heat generated. It is theorized that the thermal lesioning of the nerve destroys peripheral sensory nerve endings, resulting in the alleviation of pain. Cooled radiofrequency (RF) treatment is a variation of nerve RFA using a special device that applies more energy at the desired location without excessive heat diffusing beyond the area, causing less tissue injury away from the nerve. The goal of ablating the nerve is the same.
3 Page: 3 of 9 For the indications assessed in this evidence review, nerve RFA should be distinguished from RF energy applied to areas other than the nerve to cause tissue damage. Some patients have been treated for plantar fasciitis with a fasciotomy procedure using a RF device. This procedure does not ablate a specific nerve. Nerve RFA is also distinguished from pulsed RF treatment, which has been investigated as a treatment for different types of pain. The mechanism of action of pulsed RF treatment is uncertain, but it is thought not to destroy the nerve.1 If it does produce some degree of nerve destruction, it is thought to cause less damage than standard RFA. Some studies refer to pulsed RF treatment as ablation. Regulatory Status A number of radiofrequency (RF) generators and probes have been cleared for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the 510(k) process. In 2005, the SInergy (Kimberly Clark/Baylis), a water-cooled single-use probe, was cleared by FDA, listing the Baylis Pain Management Probe as a predicate device. The intended use is with a RF generator to create RF lesions in nervous tissue. FDA product code: GXD. In September 2011, NeuroTherm NT 2000 (NeuroTherm) was cleared for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the 510(k) process. FDA determined that this device was substantially equivalent to existing devices for use in lesioning neural tissue. Existing predicate devices included the NeuroTherm NT 1000, Stryker Multi-Gen, and Cosman G4 RF Generator. Rationale This evidence review was created based on a search of the literature through December 10, This review includes indications for heel pain due to plantar fasciitis and knee pain due to osteoarthritis (OA). Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of other peripheral nerves is not addressed herein. Because of the variable natural history of plantar fasciitis and knee OA and the subjective nature of the outcome measures, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to determine whether outcomes are improved with interventions for pain. Trials should include a homogenous population of patients with a defined clinical condition, use standardized outcome measures when possible, and define a priori the clinically significant magnitude of response. The most clinically relevant outcome measures for pain treatments are measures of pain severity and functional limitations. Pain is a subjective, patient-reported measure. Therefore, pain outcomes require quantifiable pre- and posttreatment measures. Pain is most commonly measured with a visual analog scale (VAS). Quantifiable pre- and posttreatment measures of functional status are also used, such as 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-12) and SF-36.
4 Page: 4 of 9 Plantar Fasciitis Several case series and 1 RCT were identified that evaluated RFA for treatment of chronic heel pain. In all studies, radiofrequency (RF) treatment used constant RF application with intent to ablate the nerve endings. Some studies used a specific pretreatment test to select subjects in whom pretrial testing was hypothesized to predict trial treatment success. For example, Erken et al performed trial injections of local anesthetic at a specific location.2 Patients who responded were considered eligible for treatment. In a study by Cione et al, a sensory conduction threshold test was performed.3 Patients with abnormal results were eligible for treatment. In some studies, the procedure required the patient to be conscious and respond to the sensation of electrical stimuli to locate the proper site for ablation. In other studies, the patient was under general anesthesia and the site for ablation was determined by other means. Landsman et al reported the only randomized study of RFA.4 Seventeen patients were enrolled in a double-blind crossover trial, with crossover to the alternative treatment at 4 weeks. Patients must have failed at least 3 prior types of treatments, have had pain for more than 3 months, and rated pain at least 6 on a 0-to-10 VAS. The sham treatment consisted of all aspects of the actual RFA procedure, which included stimulation of sensory nerves in an awake patient, except for the delivery of RF energy at the final step. Outcomes assessed weekly were a pain VAS reported at the first step in the morning, average pain level, and peak pain level. In a graphic presentation of results, patient pain levels for all 3 outcomes decreased after RFA but showed minimal change after sham. At 4 weeks, change in first-step pain was 5.00 in the RF group versus 1.33 in the sham group (p=0.30), change in average pain was 4.06 in the RF group versus 0.8 in the sham group (p=0.047), and change in peak pain was 5.33 in the RF group versus 1.80 in the sham group (p=0.048). After patients crossed over from sham to RFA, there was a steep drop in all pain outcomes. The maximum follow-up assessment was at 16 weeks and appears to show similar pain levels throughout the follow-up period. The largest case series with the longest follow-up is by Cozzarelli et al. This study reported on 12-year follow-up of 82 patients who had undergone RFA for heel pain.5 Patients had undergone RFA between 1994 and 1995 and had been interviewed at 5, 10, and 12 years postprocedure. Baseline pain levels before the procedure were recalled retrospectively at the time of the follow-up interviews. Of 99 patients potentially eligible to be interviewed, the study evaluated 82 patients. The results are presented without statistical testing. It appears that 73 of 82 patients reported being pain-free at 12 years. Of the pain-free patients, they rated their preprocedure pain at a mean of 7.1 on a 0-to-10 pain VAS. Cione et al reported a retrospective case series of 75 patients treated with RFA.3 Patients who underwent RFA between 2000 and 2003 were surveyed in 2004 to assess preprocedure and current pain status. In this study, the actual number of treated patients is unknown, and preprocedure pain status was assessed only at the follow-up survey. Median preprocedure pain VAS was 9 (range, 2-10) and the postprocedure pain VAS was 1 (range, 0-8; p<0.001). Erken et al reported on 2-year follow-up of 36 feet in 29 patients who underwent RFA for heel pain.2 All patients had heel pain for at least 6 months and had failed at least 2 conservative treatments. Outcomes assessed included a pain VAS and the American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society Scale (AOFAS) scores assessed at baseline, 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years. Average VAS scores of patients
5 Page: 5 of 9 were 9.2 before treatment, 1.2 at 1 month, 1.5 at 1 year, and 1.5 at 2 years. In addition, 85.7% of the patients rated their treatment as successful or very successful at 1- and 2-year follow-ups. Mean AOFAS scores (score range, 1-100) in 20 patients were 66.9 before treatment, 95.2 at 1 month, 93 at 1 year, and 93.3 at 2 years. Discomfort after the procedure in some patients resolved within 3 months. Liden et al published a retrospective case series of 22 patients treated with RF nerve ablation.6 Patients in this study had heel pain for at least 6 months and had failed at least 2 conservative treatments. The outcome measure used was a pain VAS. Mean pain VAS decreased from 8.12 to week after treatment. At a mean follow-up duration of 8 months, pain VAS scores decreased to 1.5, 2.0, and 2.1 at 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months postprocedure. Adverse events noted were minor and transient in most cases. One adverse event was called persistent poststatic dyskinesia, which probably represents nonresponse to treatment. Section Summary: Plantar Fasciitis Case series studies and 1 randomized, double-blind trial are consistent with improvement of pain after RFA of the sensory nerves for patients with heel pain due to plantar fasciitis. However, several case series have methodologic weaknesses. In 2 of the case series, all pain assessments were performed retrospectively, including pretreatment pain assessment. The single randomized trial enrolled few subjects and, due to crossover at 4 weeks, randomized comparisons only evaluate outcomes to 4 weeks. To be more confident in the efficacy of this treatment, further studies with larger samples and longer follow-up are necessary. The safety of the procedure cannot be fully evaluated in the small samples studied so far. Knee Osteoarthritis Four studies of RFA for knee OA pain were identified. Two studies were case series, 1 study was a nonrandomized comparison to nerve block, and 1 study was a randomized double-blind trial. One of the case series used pulsed RF treatments to a broad area of the knee, and indicated that the procedure was nonablative. Treatment in this study should be considered different from treatment in the other studies. In the only RCT, Choi et al investigated RFA of the genicular nerve compared with a sham procedure in 38 patients with chronic knee pain who had not responded to other treatments.7 Before randomization into the study, patients underwent diagnostic genicular nerve blocks with local anesthetic. If patients experienced a decrease in numeric pain scale scores of at least 50% for more than 24 hours, they underwent RFA or a sham procedure. Outcome measures included a pain VAS, Oxford Knee Score, and a global assessment. The Oxford Knee Score is scaled between 12 and 60, with 12 representing the best outcome. At 1, 4, and 12 weeks, pain scores in the RF group decreased from 78 to 40 (visual estimation). The control group decreased significantly at 1 week, but then returned to baseline at 4 and 12 weeks. Ten participants in the RF group achieved at least 50% reduction in knee pain at 12 weeks versus 0 in the control group. No participants reported any adverse events during the follow-up period. Ikeuchi et al evaluated RFA compared to local nerve block in a nonrandomized study of patients with refractory anteromedial knee pain.8 Based on date of treatment, patients received either RFA of the sensory nerves to the medial knee or a nerve block using local anesthetic. Outcome measures included
6 Page: 6 of 9 the Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis index (WOMAC) score, pain VAS, and patient global assessment. WOMAC scores were lower in the RF group (worse function) throughout the trial including the baseline period, and showed no benefit of treatment. Pain VAS showed a group by time interaction consistent with a treatment benefit of RFA, but there was no statistically significant difference in pain VAS score at 6 months. There was no significant difference in patients global assessment (p=0.126). The only adverse effect mentioned was hypoesthesia, which occurred only in RF patients, and remitted within 2 to 6 weeks. The 2 case studies identified were very small. In one, Bellini et al treated 9 patients with chronic knee pain using cooled RFA of the genicular nerve.9 Patients had previously not responded to physical therapy, analgesics, hyaluronic acid, or steroid injections. They were not candidates for invasive treatments due to comorbidities. Outcome measures included a pain VAS and WOMAC scores. VAS scores improved from a baseline mean of 8 to 2, 2.3, 2.1, and 2.2 at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after treatment, respectively. WOMAC scores improved from a baseline mean of 88 to 20, 22, 21, and 20 at the same assessment intervals. All posttreatment means were statistically significant compared with baseline. No adverse effects of treatment were mentioned. Vas et al used pulsed RF treatment to 10 patients with OA.10 The authors stated that they considered their procedure nonablative, and given the type and field of treatment in this study, this treatment should be considered different from the others reviewed in this section. Treatment was applied to several nerves associated with knee sensation and motor function, including the saphenous, tibial, and common peroneal nerves. Mean WOMAC scores changed from 46 at baseline to 55 and 67 at 3 and 6 months, respectively. Pain scores during activity changed from 7.7 at baseline to 5.3 and 3.3 at 3 and 6 months, respectively. Patients underwent customized physical therapy program during the follow-up period in this study. Section Summary: Knee Osteoarthritis The evidence of RFA for knee pain consists of 2 case series, 1 nonrandomized comparison, and 1 RCT. Treatments given differ slightly across studies and may not be comparable. One study used cooled RFA, another study used pulsed RF to several nerves in the knee, and another study treated only nerves associated with anteromedial knee pain. The most rigorous study evaluated 38 patients and observed outcomes over a 12-week follow-up period. To be more confident in the efficacy of this treatment, further studies with large samples and longer follow-up are necessary. The safety of the procedure cannot be fully evaluated in the small samples studied so far. Ongoing and Unpublished Clinical Trials Some currently unpublished trials that might influence this review are listed in Table 1.
7 Page: 7 of 9 Table 1. Summary of Key Trials NCT No. Trial Name Planned Enrollment Ongoing NCT Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency for Plantar Fasciitis NCT Nerve Ablation by Cooled Radiofrequency Compared to Corticosteroid Injection for Management of Knee Pain NCT Efficacy of Cooled and Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation of the Geniculate Nerves for the Treatment of Chronic Osteoarthritic Knee Pain NCT A Controlled Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency Vs Physical Therapy on Treating Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis NCT: national clinical trial; NR: not reported. Summary of Evidence Completion Date 40 Aug Dec 2016 NR Dec Apr 2017 The evidence for radiofrequency ablation of peripheral nerves in individuals who have plantar fasciitis includes case series studies and 1 randomized controlled trial (RCT). Relevant outcomes include symptoms and functional outcomes. The case series generally have small sample sizes, and many have methodologic deficiencies such as retrospective assessment of pain. The single RCT evaluated only 17 patients, and randomized outcomes could only be assessed out to 4 weeks posttreatment. Although the studies report that radiofrequency ablation reduces heel pain, the quality of the evidence is poor. The evidence is insufficient to determine the effects of the technology on health outcomes. The evidence for radiofrequency ablation of peripheral nerves in individuals who have knee osteoarthritis includes case series studies and 1 RCT. Relevant outcomes include symptoms and functional outcomes. The method of radiofrequency treatment varied between studies. Some case series showed improvement in symptoms with treatment. The single randomized trial had a small sample size of 38 and assessed outcomes out to 12 weeks. Although this trial showed improvement in pain at 12 weeks, these results are insufficient to draw conclusions about treatment efficacy. The evidence is insufficient to determine the effects of the technology on health outcomes. Supplemental Information Practice Guidelines and Position Statements The American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons issued a guideline on the treatment of heel pain in Bipolar radiofrequency is listed as a third tier option for patients who have failed other treatments. It was given a grade C recommendation, meaning that this treatment option is supported by either conflicting or level IV (expert opinion) evidence. Not applicable. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendations
8 Page: 8 of 9 Medicare National Coverage There is no national coverage determination (NCD). In the absence of an NCD, coverage decisions are left to the discretion of local Medicare carriers. References 1. Chua NH, Vissers KC, Sluijter ME. Pulsed radiofrequency treatment in interventional pain management: mechanisms and potential indications-a review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). Apr 2011;153(4): PMID Erken HY, Ayanoglu S, Akmaz I, et al. Prospective study of percutaneous radiofrequency nerve ablation for chronic plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. Feb 2014;35(2): PMID Cione JA, Cozzarelli J, Mullin CJ. A retrospective study of radiofrequency thermal lesioning for the treatment of neuritis of the medial calcaneal nerve and its terminal branches in chronic heel pain. J Foot Ankle Surg. Mar-Apr 2009;48(2): PMID Landsman AS, Catanese DJ, Wiener SN, et al. A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study with crossover to determine the efficacy of radio-frequency nerve ablation for the treatment of heel pain. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. Jan-Feb 2013;103(1):8-15. PMID Cozzarelli J, Sollitto RJ, Thapar J, et al. A 12-year long-term retrospective analysis of the use of radiofrequency nerve ablation for the treatment of neurogenic heel pain. Foot Ankle Spec. Dec 2010;3(6): PMID Liden B, Simmons M, Landsman AS. A retrospective analysis of 22 patients treated with percutaneous radiofrequency nerve ablation for prolonged moderate to severe heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis. J Foot Ankle Surg. Nov-Dec 2009;48(6): PMID Choi WJ, Hwang SJ, Song JG, et al. Radiofrequency treatment relieves chronic knee osteoarthritis pain: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Pain. Mar 2011;152(3): PMID Ikeuchi M, Ushida T, Izumi M, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency treatment for refractory anteromedial pain of osteoarthritic knees. Pain Med. Apr 2011;12(4): PMID Bellini M, Barbieri M. Cooled radiofrequency system relieves chronic knee osteoarthritis pain: the first case-series. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2015;47(1): PMID Vas L, Pai R, Khandagale N, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency of the composite nerve supply to the knee joint as a new technique for relieving osteoarthritic pain: a preliminary report. Pain Physician. Nov-Dec 2014;17(6): PMID Thomas JL, Christensen JC, Kravitz SR, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of heel pain: a clinical practice guideline-revision J Foot Ankle Surg. May-Jun 2010;49(3 Suppl):S1-19. PMID
9 Page: 9 of 9 Policy History Date Action Reason March 2016 New Policy Add to Surgery Section Policy created with literature review through December 10, RFA of peripheral nerves to treat pain associated with plantar fasciitis or knee osteoarthritis is considered investigational. This policy was approved by the FEP Pharmacy and Medical Policy Committee on March 18, 2016 and is effective April 15, Signature on file Deborah M. Smith, MD, MPH
Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Treat Pain
 Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Treat Pain Policy Number: 7.01.154 Last Review: 09/2018 Origination: 9/2017 Next Review: 09/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Treat Pain Policy Number: 7.01.154 Last Review: 09/2018 Origination: 9/2017 Next Review: 09/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Radiofrequency Ablation of Peripheral Nerves to Treat Pain
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Related Policies None
 Medical Policy MP 7.01.154 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.154 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 12/15/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Medical Policy MP 7.01.154 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.154 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 12/15/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Ablation Procedures for Peripheral Neuromas and Peripheral Nerves File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ablation_procedures_for_peripheral_neuromas_and_peripheral_nerves
Corporate Medical Policy Ablation Procedures for Peripheral Neuromas and Peripheral Nerves File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ablation_procedures_for_peripheral_neuromas_and_peripheral_nerves
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation. Description
 Subject: Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2016 Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Description Peripheral subcutaneous field stimulation (PSFS,
Subject: Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2016 Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Description Peripheral subcutaneous field stimulation (PSFS,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: facet_joint_denervation 6/2009 4/2017 4/2018 4/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Facet joint denervation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: facet_joint_denervation 6/2009 4/2017 4/2018 4/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Facet joint denervation
Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block
 Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block Clinical Policy Number: 14.01.10 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: September 21, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2017 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block Clinical Policy Number: 14.01.10 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: September 21, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2017 Next Review
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation
 Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Facet Joint Denervation Page 1 of 22 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Facet Joint Denervation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Facet Joint Denervation Page 1 of 22 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Facet Joint Denervation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Date of Origin: April Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: April 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Date of Origin: April 2013 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: April 2014 Policy No: 188 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Date of Origin: April 2013 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: April 2014 Policy No: 188 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Facet Joint Denervation Page 1 of 20 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Facet Joint Denervation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Facet Joint Denervation Page 1 of 20 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Facet Joint Denervation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Peripheral Nerve Destruction for Pain Conditions
 Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 2/15/2018 Next Review Date... 2/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0525 Peripheral Nerve Destruction for Pain Conditions Table of Contents Related Coverage Resources
Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 2/15/2018 Next Review Date... 2/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0525 Peripheral Nerve Destruction for Pain Conditions Table of Contents Related Coverage Resources
Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
 Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% o Other studies predict up to 3.48 million TKA o 17% adults over age 45 have symptomatic OA
 NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF KNEE ARTHRITIS DAVID M SCHALL MD Knee Arthritis o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% to 1.26 million procedures per year by 2030 o Other studies predict up to 3.48
NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF KNEE ARTHRITIS DAVID M SCHALL MD Knee Arthritis o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% to 1.26 million procedures per year by 2030 o Other studies predict up to 3.48
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation
 Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Treatment of Refractory Knee Pain Steven M. Lobel, MD
 Treatment of Refractory Knee Pain Steven M. Lobel, MD Applications in the Knee Osteoarthritis Deterioration of the cartilage in the knee joint Eventual rubbing of bones One of the most common causes of
Treatment of Refractory Knee Pain Steven M. Lobel, MD Applications in the Knee Osteoarthritis Deterioration of the cartilage in the knee joint Eventual rubbing of bones One of the most common causes of
Subject: Genicular Radiofrequency Ablation and Genicular Nerve Blocks for Chronic Knee Pain. Original Effective Date: 9/13/18
 Subject: Genicular Radiofrequency Ablation and Genicular Nerve Blocks for Chronic Knee Pain Original Effective Date: 9/13/18 Policy Number: MCP-314 Revision Date(s): Review Date: MCPC Approval Date: 9/13/18
Subject: Genicular Radiofrequency Ablation and Genicular Nerve Blocks for Chronic Knee Pain Original Effective Date: 9/13/18 Policy Number: MCP-314 Revision Date(s): Review Date: MCPC Approval Date: 9/13/18
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: April 15, 2018 Related Policies: 6.01.23 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain 7.01.120 Facet Arthroplasty Facet Joint Denervation Description Percutaneous
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: April 15, 2018 Related Policies: 6.01.23 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain 7.01.120 Facet Arthroplasty Facet Joint Denervation Description Percutaneous
Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation
 Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 9/2014 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 1/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.139 Last Review: 9/2014 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 1/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2016 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Last Review Status/Date: December 2016 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2015 Subsection: Medicine Original Policy Date: September 13, 2012 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Description Page: 1 of 6 Low-frequency ultrasound (US) in the kilohertz (KHz) range may improve wound healing. Several noncontact devices have received regulatory approval
Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Description Page: 1 of 6 Low-frequency ultrasound (US) in the kilohertz (KHz) range may improve wound healing. Several noncontact devices have received regulatory approval
Interventional Pain Management
 Spinal Injections Can be beneficial for both chronic and acute pain depending on pathology Contraindications: Patient refusal Active infection Platelets less than 75 or inability to stop anticoagulation
Spinal Injections Can be beneficial for both chronic and acute pain depending on pathology Contraindications: Patient refusal Active infection Platelets less than 75 or inability to stop anticoagulation
Topic: Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain Date of Origin: April Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: December 2013
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain Date of Origin: April 2008 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: December 2013 Policy No: 156 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain Date of Origin: April 2008 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: December 2013 Policy No: 156 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine
 Dr. Michael J Walls, MD 320 Thomas More Parkway. Ste 202 Crestview Hills, KY 41017 Phone: (859) 331-0956 Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine Cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet
Dr. Michael J Walls, MD 320 Thomas More Parkway. Ste 202 Crestview Hills, KY 41017 Phone: (859) 331-0956 Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine Cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet
PERCUTANEOUS FACET JOINT DENERVATION
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-95 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-95 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: RADIOFREQUENCY JOINT ABLATION / DENERVATION
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: RADIOFREQUENCY JOINT PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: RADIOFREQUENCY JOINT PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
Surgical Interruption of Pelvic Nerve Pathways for Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea
 Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 for Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea Description Two laparoscopic surgical approaches are proposed as adjuncts to conservative surgical therapy for the
Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 for Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea Description Two laparoscopic surgical approaches are proposed as adjuncts to conservative surgical therapy for the
Neuromodulation Therapy. Description
 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Page: 1 of 11 Description Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (PENS) and percutaneous neuromodulation therapy (PNT) are therapies that combine the features
Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Page: 1 of 11 Description Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (PENS) and percutaneous neuromodulation therapy (PNT) are therapies that combine the features
Page: 1 of 6. Transtympanic Micropressure Applications as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: December 2013 as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease Description Transtympanic micropressure treatment for Meniere s disease involves use of a hand-held air pressure
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: December 2013 as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease Description Transtympanic micropressure treatment for Meniere s disease involves use of a hand-held air pressure
Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.11.04 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 13, 2014 Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.11.04 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 13, 2014 Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
Facet Joint Denervation. Description
 Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2015 Subject: Facet Joint Denervation Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Facet Joint Denervation Description Facet joint denervation is performed
Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2015 Subject: Facet Joint Denervation Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Facet Joint Denervation Description Facet joint denervation is performed
Cancer. Description. Section: Surgery Effective Date: October 15, 2016 Subsection: Original Policy Date: September 9, 2011 Subject:
 Subject: Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Last Review Status/Date: September 2016 Page: 1 of 9 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Description Saturation biopsy of the prostate, in which more cores are obtained
Subject: Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Last Review Status/Date: September 2016 Page: 1 of 9 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Description Saturation biopsy of the prostate, in which more cores are obtained
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): 3/1/2012 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 9/6/2018 Effective Date: 11/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Original Issue Date (Created): 3/1/2012 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 9/6/2018 Effective Date: 11/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Prevention Diagnosis Assessment Prescription and /or application of wide range of interventions and PRM program management
 OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
Ultrafiltration in Decompensated Heart Failure. Description
 Subject: Ultrafiltration in Decompensated Heart Failure Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2016 Ultrafiltration in Decompensated Heart Failure Description Ultrafiltration is a technique being
Subject: Ultrafiltration in Decompensated Heart Failure Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2016 Ultrafiltration in Decompensated Heart Failure Description Ultrafiltration is a technique being
A Review of Long-Term Pain Relief after Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation in Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E437-E444 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Review A Review of Long-Term Pain Relief after Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation in Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis Ferdinand Iannaccone,
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E437-E444 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Review A Review of Long-Term Pain Relief after Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation in Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis Ferdinand Iannaccone,
Expanding Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for the Treatment of Pain
 Expanding Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for the Treatment of Pain Overview Page 2 BiowavePENS Expanding the Continuum of Care www.biowave.com 1-877-BIOWAVE How Biowave Works BiowavePENS
Expanding Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for the Treatment of Pain Overview Page 2 BiowavePENS Expanding the Continuum of Care www.biowave.com 1-877-BIOWAVE How Biowave Works BiowavePENS
Facet Joint Denervation. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With suspected facet joint pain
 Protocol Facet Joint Denervation (701116) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 11/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14, 01/15, 11/15, 11/16,
Protocol Facet Joint Denervation (701116) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 11/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14, 01/15, 11/15, 11/16,
Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (PENS) and Percutaneous Neuromodulation Therapy (PNT)
 Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (PENS) and Percutaneous Neuromodulation Therapy (PNT) Policy Number: 7.01.29 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (PENS) and Percutaneous Neuromodulation Therapy (PNT) Policy Number: 7.01.29 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Osteoarthritis Pain
JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Osteoarthritis Pain
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Description. Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, Subsection: Surgery Original Policy Date: December 6, 2012 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Page: 1 of 6 Description Wireless sensors implanted in an aortic aneurysm sac after endovascular repair are being investigated to measure post procedural pressure. It
Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Page: 1 of 6 Description Wireless sensors implanted in an aortic aneurysm sac after endovascular repair are being investigated to measure post procedural pressure. It
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA THE HEEL PAIN PATIENT WHO DOES NOT HAVE PLANTAR FASCIITIS If every patient who
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA THE HEEL PAIN PATIENT WHO DOES NOT HAVE PLANTAR FASCIITIS If every patient who
Ultrasound Guided Genicular Nerve Block-A Motor Sparing Technique for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Knee Pain
 International Journal of Anesthesiology Research, 2015, 3, 37-43 37 Ultrasound Guided Genicular Nerve Block-A Motor Sparing Technique for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Knee Pain Michael Meng 1, Reid
International Journal of Anesthesiology Research, 2015, 3, 37-43 37 Ultrasound Guided Genicular Nerve Block-A Motor Sparing Technique for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Knee Pain Michael Meng 1, Reid
Coverage Guideline. BioniCare System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) DEFINITION COVERAGE CRITERIA MEDICAL BACKGROUND
 Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.75.09 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Hyaluronic
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.75.09 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Hyaluronic
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page 1 of 36 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Professional
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page 1 of 36 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Professional
Jessica Jameson MD Post Falls, ID
 Jessica Jameson MD Post Falls, ID Discuss the history of interventiona l pain Discuss previous tools to manage chronic pain Discuss current novel therapies to manage chronic pain and indications HISTORY
Jessica Jameson MD Post Falls, ID Discuss the history of interventiona l pain Discuss previous tools to manage chronic pain Discuss current novel therapies to manage chronic pain and indications HISTORY
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Policy Number: 6.01.23 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 5/2013 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Policy Number: 6.01.23 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 5/2013 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Vertebral Axial Decompression
 Vertebral Axial Decompression Policy Number: 8.03.09 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2005 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage
Vertebral Axial Decompression Policy Number: 8.03.09 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2005 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Professional
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Professional
Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery
 7.01.140 Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery Section 7.0 Surgery Subsection Description Effective Date November 26, 2014
7.01.140 Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery Section 7.0 Surgery Subsection Description Effective Date November 26, 2014
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: July 15, 2017 Related Policies: 1.01.05 Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device 7.01.07 Electrical Bone Growth Stimulation of the Appendicular Skeleton
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: July 15, 2017 Related Policies: 1.01.05 Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device 7.01.07 Electrical Bone Growth Stimulation of the Appendicular Skeleton
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain. Description
 Subject: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Description Sacroiliac joint arthrography using
Subject: Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Page: 1 of 14 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pain Description Sacroiliac joint arthrography using
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Decompression of the Intervertebral Disc Using Laser Energy (Laser File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: decompression_intervertebral_disc_using_laser_energy_or_radiofrequency_coblation
Corporate Medical Policy Decompression of the Intervertebral Disc Using Laser Energy (Laser File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: decompression_intervertebral_disc_using_laser_energy_or_radiofrequency_coblation
New Techniques for Treating Chronic Knee and Hip Pain Using Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) James Sigler, MD Katherine Travnicek, MD
 New Techniques for Treating Chronic Knee and Hip Pain Using Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) James Sigler, MD Katherine Travnicek, MD New Techniques Physics of RFA Knee (genicular) RFA Hip RFA Business Development
New Techniques for Treating Chronic Knee and Hip Pain Using Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) James Sigler, MD Katherine Travnicek, MD New Techniques Physics of RFA Knee (genicular) RFA Hip RFA Business Development
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: RADIOFREQUENCY FACET DENERVATION
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.75.09 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 20, 2015 Hyaluronic Acid
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.75.09 Subject: Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 20, 2015 Hyaluronic Acid
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery
 AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
Decompression of the Intervertebral Disc Using Laser Energy (Laser Discectomy) or Radiofrequency Coblation (Nucleoplasty)
 Last Review Status/Date: March 2017 Page: 1 of 9 Using Laser Energy (Laser Discectomy) or Description Laser energy (laser discectomy) and radiofrequency (RF) coblation (nucleoplasty) are being evaluated
Last Review Status/Date: March 2017 Page: 1 of 9 Using Laser Energy (Laser Discectomy) or Description Laser energy (laser discectomy) and radiofrequency (RF) coblation (nucleoplasty) are being evaluated
Facet Arthroplasty. Policy Number: Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2009 Next Review: 3/2019
 Facet Arthroplasty Policy Number: 7.01.120 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2009 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for total facet
Facet Arthroplasty Policy Number: 7.01.120 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2009 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for total facet
NEUROABLATION FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PAIN
 NEUROABLATION FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PAIN Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
NEUROABLATION FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PAIN Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines FACET JOINT INJECTIONS, MEDIAL BRANCH BLOCKS, AND FACET JOINT RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROTOMY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines FACET JOINT INJECTIONS, MEDIAL BRANCH BLOCKS, AND FACET JOINT RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROTOMY CPT Codes: Refer to pages 5 and 6 LCD ID Number: L35936 J K
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines FACET JOINT INJECTIONS, MEDIAL BRANCH BLOCKS, AND FACET JOINT RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROTOMY CPT Codes: Refer to pages 5 and 6 LCD ID Number: L35936 J K
Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2016 Subsection: Medicine Original Policy Date: June 7, Page: 1 of 6.
 Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2016 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Description Radiofrequency (RF) energy has been investigated as a minimally invasive treatment of fecal
Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2016 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Description Radiofrequency (RF) energy has been investigated as a minimally invasive treatment of fecal
Re: Treatment Modalities for Facetogenic Pain, Policy #141
 March 30, 2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Attn: Health Management - Medical Policy P.O. Box 995 Birmingham, AL 35298-0001 Fax: 205-220-0878 Re: Treatment Modalities for Facetogenic Pain, Policy
March 30, 2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Attn: Health Management - Medical Policy P.O. Box 995 Birmingham, AL 35298-0001 Fax: 205-220-0878 Re: Treatment Modalities for Facetogenic Pain, Policy
Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee Pain in Adults With Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Arthritis of the Knee
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS POLICY STATEMENT. Page: 1 of 5
 Page: 1 of 5 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title RADIOFREQUENCY JOINT ABLATION/DENERVATION Policy Number 7.01.42 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 10/18/01 Revised Date
Page: 1 of 5 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title RADIOFREQUENCY JOINT ABLATION/DENERVATION Policy Number 7.01.42 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 10/18/01 Revised Date
Prolotherapy. Description
 Subject: Prolotherapy Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Prolotherapy Description Prolotherapy describes a procedure intended for healing and strengthening ligaments and tendons by injecting
Subject: Prolotherapy Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Prolotherapy Description Prolotherapy describes a procedure intended for healing and strengthening ligaments and tendons by injecting
Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2017 Subsection: Medicine Original Policy Date: June 7, Page: 1 of 6.
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2017 Description Radiofrequency energy has been investigated as a minimally invasive treatment of fecal incontinence, in a procedure referred to as the Secca
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2017 Description Radiofrequency energy has been investigated as a minimally invasive treatment of fecal incontinence, in a procedure referred to as the Secca
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections
 Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
INTRA-ARTICULAR HYALURONAN INJECTIONS
 INTRA-ARTICULAR HYALURONAN INJECTIONS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
INTRA-ARTICULAR HYALURONAN INJECTIONS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: tens_(transcutaneous_electrical_nerve_stimulator) 7/1982
Corporate Medical Policy TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: tens_(transcutaneous_electrical_nerve_stimulator) 7/1982
Re: Occipital Neuralgia and Headache Treatment, Policy Number: 2018T0080Y
 May 10, 2018 United Healthcare Medical Policy Department 9500 Bren Road East Minnetonka, MN 55343 via Email: mpq@uhc.com Re: Occipital Neuralgia and Headache Treatment, Policy Number: 2018T0080Y To Whom
May 10, 2018 United Healthcare Medical Policy Department 9500 Bren Road East Minnetonka, MN 55343 via Email: mpq@uhc.com Re: Occipital Neuralgia and Headache Treatment, Policy Number: 2018T0080Y To Whom
Vertebral Axial Decompression
 Vertebral Axial Decompression Policy Number: 8.03.09 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2005 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage
Vertebral Axial Decompression Policy Number: 8.03.09 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2005 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage
Surgical Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Surgical Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Pain Policy Number: 6.01.23 Last Review: 5/2014 Origination: 5/2013 Next Review: 5/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Surgical Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Pain Policy Number: 6.01.23 Last Review: 5/2014 Origination: 5/2013 Next Review: 5/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Dornier MedTech, Inc. 1 Summary of Safety and Effectiveness
 I. General Information Data Device Generic Name: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Device Device Trade Name: Dornier Epos? Ultra Applicant s Name and Address: Dornier Medical Systems, Inc. 1155 Roberts
I. General Information Data Device Generic Name: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Device Device Trade Name: Dornier Epos? Ultra Applicant s Name and Address: Dornier Medical Systems, Inc. 1155 Roberts
Arthritis of the Shoulder
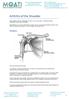 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management
 Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
Expand Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for Pain
 Expand Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for Pain How BiowavePENS Works BiowavePENS delivers therapeutic electrical signals through a patented percutaneous electrode array to block pain
Expand Your Continuum of Care Percutaneous Neurostimulation for Pain How BiowavePENS Works BiowavePENS delivers therapeutic electrical signals through a patented percutaneous electrode array to block pain
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Radiofrequency Denervation for Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review Within the Framework of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group
 Radiofrequency Denervation for Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review Within the Framework of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group 1 Spine August 15, 2003; 28(16):1877-1888 Leena Niemistö, MD;
Radiofrequency Denervation for Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review Within the Framework of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group 1 Spine August 15, 2003; 28(16):1877-1888 Leena Niemistö, MD;
Radiofrequency Ablation 101
 Radiofrequency Ablation 101 Neuroscience Summit September 10, 2016 Chris Pratt, DO Texas Health Care Pain Management 1651 West Rosedale Street, Suite #205 Fort Worth, Texas 71604 What s in a name? Radiofrequency
Radiofrequency Ablation 101 Neuroscience Summit September 10, 2016 Chris Pratt, DO Texas Health Care Pain Management 1651 West Rosedale Street, Suite #205 Fort Worth, Texas 71604 What s in a name? Radiofrequency
Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain
 Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 156 Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: February 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical
Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 156 Pulsed Radiofrequency for Chronic Spinal Pain Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: December 2017 Effective: February 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical
A70.4 Insertion of neurostimulator electrodes into peripheral nerve Z12.2 Posterior tibial nerve R15.X Faecal incontinence
 The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
Horizon Scanning Centre November Spheroids of human autologous matrix-associated chondrocytes (Chondrosphere) for articular cartilage defects
 Horizon Scanning Centre November 2014 Spheroids of human autologous matrix-associated chondrocytes (Chondrosphere) for articular cartilage defects SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 8515 This briefing is based on information
Horizon Scanning Centre November 2014 Spheroids of human autologous matrix-associated chondrocytes (Chondrosphere) for articular cartilage defects SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 8515 This briefing is based on information
Medical Policy. Description/Scope. Position Statement. Rationale
 Subject: Document#: Current Effective Date: 06/28/2017 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 05/04/2017 Description/Scope This document addresses occipital nerve stimulation (ONS), which involves delivering
Subject: Document#: Current Effective Date: 06/28/2017 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 05/04/2017 Description/Scope This document addresses occipital nerve stimulation (ONS), which involves delivering
Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test. Description
 Subject: Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test Description The Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test (ALCAT) is intended to diagnose
Subject: Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test Description The Antigen Leukocyte Antibody Test (ALCAT) is intended to diagnose
Description. Section: Therapy Effective Date: January 15, 2015 Subsection: Therapy Original Policy Date: December 6, 2012 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES), also known as cranial electrical stimulation, transcranial electrical stimulation, or electrical
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES), also known as cranial electrical stimulation, transcranial electrical stimulation, or electrical
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief?
 Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: KETAMINE INFUSION THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PAIN SYNDROMES POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally recognized by the medical community. Guidelines
Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally recognized by the medical community. Guidelines
tens_(transcutaneous_electrical_nerve_stimulator) 7/ / / /2014 This policy is NOT effective until January 13, 2015
 Corporate Medical Policy TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: tens_(transcutaneous_electrical_nerve_stimulator) 7/1982
Corporate Medical Policy TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: tens_(transcutaneous_electrical_nerve_stimulator) 7/1982
d EFFECTIVE DATE: POLICY LAST UPDATED:
 Medical Coverage Policy Epidural Injections for Pain Management d EFFECTIVE DATE: 04 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 20 2018 OVERVIEW Epidural injections are generally performed to treat pain arising from
Medical Coverage Policy Epidural Injections for Pain Management d EFFECTIVE DATE: 04 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 20 2018 OVERVIEW Epidural injections are generally performed to treat pain arising from
