Structure-Function: Central vestibular syndromes
|
|
|
- Roger Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure-Function: Central vestibular syndromes Skews Nystagmus Tilts
2 Objectives An introduction to the basic principles of eye movement control An introduction to the types of central vestibular clinical syndromes. Examples of bringing basic physiology to the bedside. Examples of basic science investigations using clinical disorders as the experimental model.
3 The dominance of the fovea G Westheimer Courtesy, Chris Kennard
4 Function of eye movements Serve the needs of vision, and specifically those of the fovea where spatial acuity is best. Bring images onto the fovea (saccades and vergence) Keep images still on the fovea, for best spatial resolution (vestibular, pursuit and vergence)
5 Oculomotor exam
6 Dominant mechanical orbital forces Elastic restoring forces to eye position If not overcome -- defective eccentric gaze holding Viscous restraining forces to eye velocity If not overcome -- slow movements Therefore to compensate for these orbital forces we must develop a phasic-tonic, or velocity-position, or pulse-step change in innervation
7 Innervation to overcome mechanical orbital forces R = oculomotor neuron or nerve discharge rate (or ocular EMG activity) E = eye position
8 David A Robinson Single-unit activity in the oculomotor nucleus (inferior rectus motoneuron)
9 E =Eye Position R = Discharge Rate Pulse Slide Step
10 Premotor commands for saccades Pulse-step Pulse from burst signal (B) neurons Step from tonic signal (T) neuron (neural integrator)
11 Ocular motor integrators Steady gaze-holding requires a tonic level of innervation to hold the eye in eccentric positions of gaze against elastic restoring forces. Ocular motor integrators take velocity commands from the conjugate systems and mathematically integrate them to produce the necessary position commands, e.g. at the end of a saccade the eye is held steadily by the position command.
12 Ocular motor integrators Horizontal integrator -- medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) and nucleus prepositus hypoglossus (NPH). Vertical integrator -- MVN (SVN), NPH, and interstitial nucleus of Cajal (INC) (via medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)). Cerebellar flocculus is necessary for optimal performance of both integrators.
13 Gaze-holding networks in medulla MVN (medial vestibular nucleus) and NPH (nucleus prepositus hypoglossus)
14 Gaze-holding networks in the midbrain Interstitial Nucleus of Cajal INC
15 Cerebellar flocculus and paraflocculus (tonsils) Flocculus Paraflocculus
16 Downbeat, gaze-evoked and rebound nystagmus in cerebellar atrophy
17 Downbeat, gaze-evoked and rebound nystagmus in cerebellar atrophy Gaze-evoked nystagmus Rebound nystagmus Remember: As eccentric gaze is maintained: Gaze-evoked nystagmus (GEN) gets Less with cerebellar disease More with myasthenia gravis Stays about the same with congenital nystagmus
18 Central labyrinthine projections SCC rostral vestibular complex VESTIBULOCEREBELLUM OTOLITH caudal vestibular complex SCC / Otolith
19 Central projections from the labyrinth SCC projections are primarily to the rostral portions of the vestibular complex. Otolith projections are primarily to the caudal portions of the vestibular complex. SCC and otoliths also project directly to the cerebellum.
20 The cerebellum and vestibular disorders Flocculus/paraflocculus Nodulus VESTIBULOCEREBELLUM SCC / Otolith
21 Cerebellar flocculus and paraflocculus (tonsils) Flocculus Paraflocculus
22 Pursuit and VOR cancellation abnormalities in cerebellar atrophy
23 Anatomy of cerebellar atrophy
24 Anatomy of cerebellar atrophy Cerebellar atrophy: SCA6
25 Structural cerebellar syndromes Cranial-cervical junction: Chiari
26 Middle aged woman with a few months of rapidly progressive ataxia
27 Velocity-increasing slow phase Blink
28 A simple control systems model of control of vertical gaze-holding by the flocculus Inherently poor brain stem neural gazeholding network (MVN,NPH). Flocculus improves its function by a positive feedback loop ( k ). Too little feedback, poor gaze holding. Too much feedback, instability and runaway slow phases.
29 Abnormal VOR in cerebellar disease: Increased gain
30 Increased VOR GAIN in Cerebellar Disease 15 Horizontal position (deg) HEAD EYE-in-HEAD (inv) Backup Saccades Time (sec)
31 Abnormal VOR in cerebellar disease Abnormal direction
32 Abnormal VOR Direction X-couple into vertical
33 The VOR is a 3D reflex Almost all rotations stimulate (excite or inhibit) all the canals (e.g., vertical canals during yaw) There is no horizontal VOR
34 The 3D VOR (Robinson 1982) E H E = [ M ] [ B] [ C] C canal orientation matrix H - angular head velocity - angular eye velocity M eye muscle orientation matrix B brainstem matrix of connections between canal pairs and eye muscle pairs
35 The brainstem matrix is likely calibrated by the cerebellum Vestibulocerebellar lesions abolish cross-axis adaptation (Schultheis and Robinson, 1981) What is the effect of cerebellar disease on the 3D calibration of the VOR?
36 Abnormal VOR direction Horizontal eye movement exceeds head movement The eyes move up even though there is almost no vertical head movement (negative is up)
37 In the normal subject, there is no vertical eye movement
38 Functional consequence: Foveal stability is impaired in patients Larger gaze position errors at the end of the rotation (fovea taken off target) Larger gaze velocities during the rotation (more retinal slip)
39 Yaw impulses Summary Inappropriate upward eye velocity, greater in the abducting eye, leading to: Larger gaze errors Vertical retinal slip RVOR disconjugacy This is the response one might expect from excitation of the AC contralateral to the direction of rotation (e.g. left AC for rightward yaw)
40 AC excitation Rotation to the right excites the left anterior canal, leading to contraction of the left SR and right IO The SR has a greater vertical pulling direction; thus, the left (abducting) eye would go up more
41 Some old physiology
42 Some old physiology Implications: Upward and convergence bias revealed with floccular lesions
43 Rhesus Monkey Flocculus/Paraflocculus CN VIII Flocculus Paraflocculus Gundez Gucer
44 Downbeat, gaze-evoked, rebound nystagmus in monkey with removal of flocculus and paraflocculus
45 Impaired smooth pursuit in monkey with removal of flocculus and paraflocculus Pre Post
46 Flocculi
47 Paraflocculi (tonsils)
48 VOR learning and the cerebellum Different VOR gains or directions for the two eyes for different corrections for the two eyes (anisometropia) Magnification effects associated with habitual wearing of spectacles require a change in the amplitude or direction of the VOR for stabilization of images during head movements THREE different VOR gains are required (presbyopia (bifocal), hyperopia (far-sighted) and no-glasses OR contacts). Change in VOR direction may be required for astigmatism
49 Loss of VOR gain adaptation after floccular/parafloccular lesions Pre-lesion Increase 4 hrs of training with increasing or decreasing spectacles Pre-lesion Decrease Post-lesion No learning Lisberger, 1984
50 VOR learning in Purkinje Cells Vestib input (head) Visual input (image slip) Ito, NatureNS
51 Periodic Alternating Nystagmus (PAN)
52 Periodic Alternating Nystagmus (PAN) Null every two minutes
53 Anatomical Locus of PAN Nodulus
54 Rotation at a constant speed in darkness Pathophysiology of PAN: Normal vestibular responses gone awry Cupula decay Velocity Storage Mechanism Nystagmus outlasts the displacement of the cupula. Velocity storage perseverates peripheral canal signals and so improves the low-frequency response of the VOR. Increases VOR duration. POTENTIAL FOR INSTABILITY
55 Pathophysiology of PAN: Normal vestibular responses gone awry Onset head rotation Reversal Phase adaptation to sustained nystagmus. POTENTIAL FOR REVERSING NYSTAGMUS
56 PAN: Pathogenesis and Treatment In PAN, instability in central vestibular velocity storage is produced by loss of inhibition from the Purkinje cells of the nodulus onto the vestibular nuclei. Short-term adaptation causes reversals of nystagmus leading to sustained oscillation. How to treat?? Baclofen (GABA-b) provides the missing inhibition and stops the nystagmus.
57 Vestibuloocular abnormalities in cerebellar atrophy Sparing of basic rotational VOR, absent translational VOR
58 Quantification of t-vor: Head sled
59 Vestibular responses on the head sled Normal subject Cerebellar patient
60 The translational VOR and the cerebellar nodulus The role of the cerebellum in generating vestibular responses to linear acceleration (with static otolith-ocular reflexes such as counterroll in response to head tilt or with dynamic otolith-ocular reflexes such as the translational VOR) is unclear. Patients with diffuse cerebellar disease have striking deficits in the translational VOR (and pursuit) The cerebellar nodulus has been implicated in some aspects of the influence of gravity on the sustained (velocity-storage) component of the rotational VOR NO information is known about the specific role of the cerebellum in pure otolith-ocular reflexes (static or dynamic).
61 The paradigm Two monkeys Uvulo-nodulectomy Measured translational VOR
62 Translational VOR After the uvula-nodulus lesion there is a clear loss of the ability to generate a sustained response in the dark. The response in the light was less affected.
63 Fitting the eye velocity response to a combination of head acceleration and head velocity signals Major change is loss of the velocity coefficient
64 What is missing after the lesion? The raw records and the fits to the response suggest that an acceleration to velocity integration is impaired after the lesion. The uvula-nodulus appears to play a key role in integrating raw otolith acceleration signals to velocity signals to permit a sustained response to a translational stimulus. This is a third role of the cerebellum in neural integration for eye movements Velocity-position integrator for all conjugate eye movements. Control of the time constant (and spatial orientation) of the velocity storage integrator for the (low-frequency) rotational VOR. Integration of acceleration to velocity signals for the translational VOR.
65 Nodulus lesion
66 Wallenberg s Syndrome PICA distribution infarct involving the dorsolateral medulla Restiform body (ICP)
67 Wallenberg s Syndrome Skew
68 Otolith-ocular imbalance in the OTR
69 Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) Counterroll Skew (vertical ocular misalignment) Head Tilt Thomas Brandt, Lancet 1999
70
71 Evaluation of Skew Deviation Maddox Rod LE RE
72 Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) OTR (head tilt, skew deviation, ocular counterroll) is an extremely common finding -- when looked for -- with vestibular and especially central vestibular lesions. It represents an imbalance in otolith-ocular and otolith-collic reflexes, which normally are part of an ocular and head righting response to lateral body tilt. The counterroll acts to maintain the horizontal meridians of the retinas aligned with the horizon, and the skew is a reflection in pathology of a phylogenetically-old reflex that is easily appreciated in lateral-eyed animals, in which a lateral head tilt normally elicits a physiological skew deviation, again to maintain eye alignment along the horizon.
73 A few key references Zee, DS, and Walker, M, Cerebellum and oculomotor control, in Squire, LR (ed), Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, third edition, vol. 2, pp , Elsevier, Press, Leigh and Zee, Neurology of Eye Movements, Edition 4, Chapters 2 and 11, 2006
Clinical aspects of vestibular and ocular motor physiology: bringing physiology and anatomy to the bedside. Skews Nystagmus Tilts
 Clinical aspects of vestibular and ocular motor physiology: bringing physiology and anatomy to the bedside Skews Nystagmus Tilts dzee@dizzy.med.jhu.edu Outline of the presentation Physiological principal
Clinical aspects of vestibular and ocular motor physiology: bringing physiology and anatomy to the bedside Skews Nystagmus Tilts dzee@dizzy.med.jhu.edu Outline of the presentation Physiological principal
Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements
 Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements Linda K. McLoon PhD mcloo001@umn.edu Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Neurosciences Your Eyes Are Constantly Moving. Yarbus, 1967 Eye
Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements Linda K. McLoon PhD mcloo001@umn.edu Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Neurosciences Your Eyes Are Constantly Moving. Yarbus, 1967 Eye
Vision Science III Handout 15
 Vision Science III Handout 15 NYSTAGMUS Nystagmus describes a pattern of eye movements in which the eyes move to and fro, usually with alternating Slow and Fast phases. Nystagmus occurs normally in some
Vision Science III Handout 15 NYSTAGMUS Nystagmus describes a pattern of eye movements in which the eyes move to and fro, usually with alternating Slow and Fast phases. Nystagmus occurs normally in some
Ocular Tilt Reaction: Vestibular Disorder in Roll Plane
 대한안신경의학회지 : 제 8 권 Supplement 1 ISSN: 2234-0971 Ocular Tilt Reaction: Vestibular Disorder in Roll Plane Ji-Yun Park Department of Neurology, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea Ocular tilt reaction
대한안신경의학회지 : 제 8 권 Supplement 1 ISSN: 2234-0971 Ocular Tilt Reaction: Vestibular Disorder in Roll Plane Ji-Yun Park Department of Neurology, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea Ocular tilt reaction
Afternystagmus and Headshaking Nystagmus. David S. Zee
 442 `447, 1993 Afternystagmus and Headshaking Nystagmus David S. Zee Departments of Neurology, Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Recent advances in vestibular
442 `447, 1993 Afternystagmus and Headshaking Nystagmus David S. Zee Departments of Neurology, Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Recent advances in vestibular
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates from the labyrinth... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates from the labyrinth... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
The Origin of Downbeat Nystagmus
 The Origin of Downbeat Nystagmus An Asymmetry in the Distribution of On-Directions of Vertical Gaze-Velocity Purkinje Cells SARAH MARTI, a DOMINIK STRAUMANN, a AND STEFAN GLASAUER b a Neurology Department,
The Origin of Downbeat Nystagmus An Asymmetry in the Distribution of On-Directions of Vertical Gaze-Velocity Purkinje Cells SARAH MARTI, a DOMINIK STRAUMANN, a AND STEFAN GLASAUER b a Neurology Department,
Ocular Motor Disorders of the Cerebellum and
 Ocular Motor Disorders of the Cerebellum and Vestibular System David Zee, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore, MD Learning Objectives 1. To better evaluate the patient at the bedside with the complaint
Ocular Motor Disorders of the Cerebellum and Vestibular System David Zee, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore, MD Learning Objectives 1. To better evaluate the patient at the bedside with the complaint
Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Define different types of eye movement and their underlying neural
Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Define different types of eye movement and their underlying neural
The Vestibular System
 The Vestibular System Vestibular and Auditory Sensory Organs Bill Yates, Ph.D. Depts. Otolaryngology & Neuroscience University of Pittsburgh Organization of Sensory Epithelium Displacement of Stereocilia
The Vestibular System Vestibular and Auditory Sensory Organs Bill Yates, Ph.D. Depts. Otolaryngology & Neuroscience University of Pittsburgh Organization of Sensory Epithelium Displacement of Stereocilia
EYE POSITION FEEDBACK IN A MODEL OF THE VESTIBULO-OCULAR REFLEX FOR SPINO-CEREBELLAR ATAXIA 6
 EYE POSITION FEEDBACK IN A MODEL OF THE VESTIBULO-OCULAR REFLEX FOR SPINO-CEREBELLAR ATAXIA 6 J. H. Anderson 1, M. C. Yavuz 2, B. M. Kazar 3, P. Christova 1, C. M. Gomez 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
EYE POSITION FEEDBACK IN A MODEL OF THE VESTIBULO-OCULAR REFLEX FOR SPINO-CEREBELLAR ATAXIA 6 J. H. Anderson 1, M. C. Yavuz 2, B. M. Kazar 3, P. Christova 1, C. M. Gomez 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
latest development in advanced testing the vestibular function
 latest development in advanced testing the vestibular function how to explore the vestibular function in detail Herman Kingma ENT Department Maastricht University Medical Centre The Netherlands how I do
latest development in advanced testing the vestibular function how to explore the vestibular function in detail Herman Kingma ENT Department Maastricht University Medical Centre The Netherlands how I do
Characters of nystagmus
 Characters of nystagmus Special types of nystagmus Ocular bobbing Ocular flutter Ocular myoclonus Characters of nystagmus Special types of nystagmus Disconjugate Nystagmus Circumduction Nystagmus Nystagmus
Characters of nystagmus Special types of nystagmus Ocular bobbing Ocular flutter Ocular myoclonus Characters of nystagmus Special types of nystagmus Disconjugate Nystagmus Circumduction Nystagmus Nystagmus
Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III.
 Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III. Measurement of Vergence:- Objective & Subjective phoria
Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III. Measurement of Vergence:- Objective & Subjective phoria
University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Systems Neuroscience Meds Vestibular System
 University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Systems Neuroscience Meds 371 2007-08 Vestibular System S. Kuwada Reading: Purves et al. (2008, 4 th edition), Neuroscience, Chapter 14.
University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Systems Neuroscience Meds 371 2007-08 Vestibular System S. Kuwada Reading: Purves et al. (2008, 4 th edition), Neuroscience, Chapter 14.
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The vestibular system has two parts.... 3 The Anatomy
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The vestibular system has two parts.... 3 The Anatomy
BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST
 BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST Steven L. Galetta, MD NYU Langone Medical Center New York, NY I. Anatomical Considerations The brain stem is about the size of a fat forefinger and
BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST Steven L. Galetta, MD NYU Langone Medical Center New York, NY I. Anatomical Considerations The brain stem is about the size of a fat forefinger and
Vestibular System Dr. Bill Yates Depts. Otolaryngology and Neuroscience 110 Eye and Ear Institute
 Vestibular System Dr. Bill Yates Depts. Otolaryngology and Neuroscience 110 Eye and Ear Institute 412-647-9614 byates@pitt.edu What is the Vestibular System? The vestibular system is the sensory system,
Vestibular System Dr. Bill Yates Depts. Otolaryngology and Neuroscience 110 Eye and Ear Institute 412-647-9614 byates@pitt.edu What is the Vestibular System? The vestibular system is the sensory system,
Cervical reflex Giovanni Ralli. Dipartimento di Organi di Senso, Università di Roma La Sapienza
 Cervical reflex Giovanni Ralli Dipartimento di Organi di Senso, Università di Roma La Sapienza The development of the neck in vertebrates allows the individual to rotate the head independently of the trunk
Cervical reflex Giovanni Ralli Dipartimento di Organi di Senso, Università di Roma La Sapienza The development of the neck in vertebrates allows the individual to rotate the head independently of the trunk
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of the vestibular organs.
Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of the vestibular organs.
LA CLINICA E LA DIAGNOSI DELLA VERTIGINE VASCOLARE
 LA CLINICA E LA DIAGNOSI DELLA VERTIGINE VASCOLARE M. Mandalà Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Senese WHY ARE WE SCARED? NEED TO BETTER UNDERSTAND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY WHAT IS KNOWN WHAT IS EFFECTIVE and SIMPLE
LA CLINICA E LA DIAGNOSI DELLA VERTIGINE VASCOLARE M. Mandalà Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Senese WHY ARE WE SCARED? NEED TO BETTER UNDERSTAND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY WHAT IS KNOWN WHAT IS EFFECTIVE and SIMPLE
Katrina Williams 2017 Specialist Neurological Physiotherapist FACP
 Your stroke patient is dizzy challenges of assessment and treatment. Katrina Williams Specialist Neurological Physiotherapist FACP 2008 Clinical Academic University of Queensland Senior Neurological Ageing
Your stroke patient is dizzy challenges of assessment and treatment. Katrina Williams Specialist Neurological Physiotherapist FACP 2008 Clinical Academic University of Queensland Senior Neurological Ageing
Vestibular System. Dian Yu, class of 2016
 Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
Treatment for Nystagmus
 ISSN: 2234-0971 Treatment for Nystagmus Seong-Hae Jeong Department of Neurology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea Treatment for Nystagmus Seong-Hae Jeong Chungnam National University
ISSN: 2234-0971 Treatment for Nystagmus Seong-Hae Jeong Department of Neurology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea Treatment for Nystagmus Seong-Hae Jeong Chungnam National University
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination
 Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination Head Impulse (right- and leftward) Nystagmus type Test of Skew (cover test for skew deviation) Stroke findings: I.N.F.A.R.C.T.
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination Head Impulse (right- and leftward) Nystagmus type Test of Skew (cover test for skew deviation) Stroke findings: I.N.F.A.R.C.T.
OBJECTIVES BALANCE EVALUATION COMMON CAUSES OF BALANCE DEFICITS POST TBI BRAIN INJURY BALANCE RELATIONSHIP
 OBJECTIVES Understand variables that contribute to balance deficits Understand the relationship between a brain injury and balance Become familiar with the components of a vestibular/balance assessment
OBJECTIVES Understand variables that contribute to balance deficits Understand the relationship between a brain injury and balance Become familiar with the components of a vestibular/balance assessment
Current Concepts in the Management of Patients With Vestibular Dysfunction
 Current Concepts in the Management of Patients With Vestibular Dysfunction Kathleen M Gill-Body, PT, MS, NCS Objectives After reading this continuing education (CE) article, you should be able to: Describe
Current Concepts in the Management of Patients With Vestibular Dysfunction Kathleen M Gill-Body, PT, MS, NCS Objectives After reading this continuing education (CE) article, you should be able to: Describe
Abducens nucleus (VI) Baclofen, nystagmus treatment 202, 203,
 ... Abducens nucleus (VI) Baclofen, nystagmus treatment 202, 203, afferent and efferent connections 10 205, 206, 209, 212, 220 structure and function 9, 10 Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo transmitters
... Abducens nucleus (VI) Baclofen, nystagmus treatment 202, 203, afferent and efferent connections 10 205, 206, 209, 212, 220 structure and function 9, 10 Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo transmitters
Differential Diagnosis and Management of Brainstem and Cerebellar Infarctions Combined Sections Meeting, February 7, 2015 Indianapolis, IN
 3 Differential Diagnosis and Management of Brainstem and Cerebellar Infarctions Combined Sections Meeting, February 7, 2015 Indianapolis, IN Janet O. Helminski, PT, PhD Professor, Midwestern University
3 Differential Diagnosis and Management of Brainstem and Cerebellar Infarctions Combined Sections Meeting, February 7, 2015 Indianapolis, IN Janet O. Helminski, PT, PhD Professor, Midwestern University
INCIDENCE OF SUSPECTED OTOLITHIC ABNORMALITIES IN MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURED VETERANS OBSERVATIONS FROM A LARGE VA POLYTRAUMA NETWORK SITE
 INCIDENCE OF SUSPECTED OTOLITHIC ABNORMALITIES IN MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURED VETERANS OBSERVATIONS FROM A LARGE VA POLYTRAUMA NETWORK SITE David Domoracki Ph.D. Cleveland VAMC Audiology Service Jennifer
INCIDENCE OF SUSPECTED OTOLITHIC ABNORMALITIES IN MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURED VETERANS OBSERVATIONS FROM A LARGE VA POLYTRAUMA NETWORK SITE David Domoracki Ph.D. Cleveland VAMC Audiology Service Jennifer
Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders :
 Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders : I. Supranuclear Pathway 1 H y u ng-jin Kim, M.D. 1, 2, Byung Hoon Lim, M.D. 3, Jae Bum Na, M.D. Jae Hyoung Kim, M.D., Sung Hoon Chung, M.D. The supranuclear
Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders : I. Supranuclear Pathway 1 H y u ng-jin Kim, M.D. 1, 2, Byung Hoon Lim, M.D. 3, Jae Bum Na, M.D. Jae Hyoung Kim, M.D., Sung Hoon Chung, M.D. The supranuclear
The relationship between optokinetic nystagmus and caloric weakness
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 The relationship between optokinetic nystagmus and caloric weakness D'Arcy D. Cyr University of South
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 The relationship between optokinetic nystagmus and caloric weakness D'Arcy D. Cyr University of South
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM. Deficits cause: Vertigo. Falling Tilting Nystagmus Nausea, vomiting
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM Objectives: Understand the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? Describe the vestibular apparatus, the 2
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM Objectives: Understand the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? Describe the vestibular apparatus, the 2
Course: PG- Pathshala Paper number: 13 Physiological Biophysics Module number M23: Posture and Movement Regulation by Ear.
 Course: PG- Pathshala Paper number: 13 Physiological Biophysics Module number M23: Posture and Movement Regulation by Ear Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Course: PG- Pathshala Paper number: 13 Physiological Biophysics Module number M23: Posture and Movement Regulation by Ear Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer:
Adaptation of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Amblyopia
 Adaptation of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Amblyopia Carol A. Wesfall and Clifton M. Schor Adaptation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is demonstrated by changes in gain in response to discrepancies
Adaptation of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Amblyopia Carol A. Wesfall and Clifton M. Schor Adaptation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is demonstrated by changes in gain in response to discrepancies
TEMPLATES FOR COMPREHENSIVE BALANCE EVALUATION REPORTS. David Domoracki PhD Cleveland Louis Stokes VA Medical Center
 TEMPLATES FOR COMPREHENSIVE BALANCE EVALUATION REPORTS David Domoracki PhD Cleveland Louis Stokes VA Medical Center The following templates are in outline form. I designed them so that the IRM local network
TEMPLATES FOR COMPREHENSIVE BALANCE EVALUATION REPORTS David Domoracki PhD Cleveland Louis Stokes VA Medical Center The following templates are in outline form. I designed them so that the IRM local network
THE VESTIBULAR APPRATUS AND PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy February 23, 2012 Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. Reading: Waxman Chapter 17 Also pp 105-108 on control of eye movments Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch. 8 Vestibulospinal Pathway Quiz http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/animations/hyperbrain/pathways/
Dental Neuroanatomy February 23, 2012 Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. Reading: Waxman Chapter 17 Also pp 105-108 on control of eye movments Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch. 8 Vestibulospinal Pathway Quiz http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/animations/hyperbrain/pathways/
Optokinetic nystagmus
 Sponsored by Optokinetic nystagmus Professor Chris Harris, PhD Nystagmus is an oscillation of one or both eyes. Nystagmus can be a physiological phenomenon such as optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) or induced
Sponsored by Optokinetic nystagmus Professor Chris Harris, PhD Nystagmus is an oscillation of one or both eyes. Nystagmus can be a physiological phenomenon such as optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) or induced
Vestibular and Visual Systems
 15 Vestibular and Visual Systems Laurie Lundy-Ekman, PhD, PT INTRODUCTION Vestibular receptors and cranial nerve axons in the periphery, vestibular nuclei in the brainstem, and an area of the cerebral
15 Vestibular and Visual Systems Laurie Lundy-Ekman, PhD, PT INTRODUCTION Vestibular receptors and cranial nerve axons in the periphery, vestibular nuclei in the brainstem, and an area of the cerebral
met het oog op evenwicht
 met het oog op evenwicht Herman Kingma, Department of ORL, Maastricht University Medical Centre Faculty of Biomedical Technology, Technical University Eindhoven problems in patients with dizziness and
met het oog op evenwicht Herman Kingma, Department of ORL, Maastricht University Medical Centre Faculty of Biomedical Technology, Technical University Eindhoven problems in patients with dizziness and
A Case of Vestibular and Oculomotor. Pathology from Bilateral AICA Watershed. Infarcts Treated with Basilar Artery Stenting
 Bilateral AICA Strokes. Kattah J, et al 1 A Case of Vestibular and Oculomotor Pathology from Bilateral AICA Watershed Infarcts Treated with Basilar Artery Stenting Jorge C Kattah, M.D * Deepak Nair M.D,
Bilateral AICA Strokes. Kattah J, et al 1 A Case of Vestibular and Oculomotor Pathology from Bilateral AICA Watershed Infarcts Treated with Basilar Artery Stenting Jorge C Kattah, M.D * Deepak Nair M.D,
Vestibular Evaluation
 Chris Carpino, MPT Vestibular Evaluation 1. History Most important aspect of evaluation (see DHI) 2. Vital Signs Check blood pressure in supine and sitting 3. Eye Exam 4. Positional Testing 5. Balance
Chris Carpino, MPT Vestibular Evaluation 1. History Most important aspect of evaluation (see DHI) 2. Vital Signs Check blood pressure in supine and sitting 3. Eye Exam 4. Positional Testing 5. Balance
Eye Movements. Geometry of the Orbit. Extraocular Muscles
 Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Saccades. Assess volitional horizontal saccades with special attention to. Dysfunction indicative of central involvement (pons or cerebellum)
 Saccades Assess volitional horizontal saccades with special attention to Amplitude? Duration? Synchrony? Dysfunction indicative of central involvement (pons or cerebellum) Dynamic Visual Acuity Compare
Saccades Assess volitional horizontal saccades with special attention to Amplitude? Duration? Synchrony? Dysfunction indicative of central involvement (pons or cerebellum) Dynamic Visual Acuity Compare
Visual Suppression is Impaired in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 6 but Preserved in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
 Diagnostics 2012, 2, 52-56; doi:10.3390/diagnostics2040052 Communication OPEN ACCESS diagnostics ISSN 2075-4418 www.mdpi.com/journal/diagnostics/ Visual Suppression is Impaired in Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Diagnostics 2012, 2, 52-56; doi:10.3390/diagnostics2040052 Communication OPEN ACCESS diagnostics ISSN 2075-4418 www.mdpi.com/journal/diagnostics/ Visual Suppression is Impaired in Spinocerebellar Ataxia
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: vestibular_function_testing 5/2017 N/A 10/2017 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Dizziness, vertigo,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: vestibular_function_testing 5/2017 N/A 10/2017 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Dizziness, vertigo,
Vestibular/Auditory Systems
 Vestibular/Auditory Systems Jay Zenner on February 3, 2012 Dental Neuroanatomy Scott Rogers Office: SOM 2C132 Boney Labyrinth Vestibular Apparatus Two Major Divisions Cochlea (anterior) VIII VII Semicircular
Vestibular/Auditory Systems Jay Zenner on February 3, 2012 Dental Neuroanatomy Scott Rogers Office: SOM 2C132 Boney Labyrinth Vestibular Apparatus Two Major Divisions Cochlea (anterior) VIII VII Semicircular
Neural Learning Rules for the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 1, 1998, 18(21):9112 9129 Neural Learning Rules for the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Jennifer L. Raymond and Stephen G. Lisberger Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
The Journal of Neuroscience, November 1, 1998, 18(21):9112 9129 Neural Learning Rules for the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Jennifer L. Raymond and Stephen G. Lisberger Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
VESTIBULAR LABYRINTHS comprising of 3 semicircular canals, saccule, utricle VESTIBULAR NERVE with the sup. & inf. vestibular nerves VESTIBULAR
 VESTIBULAR LABYRINTHS comprising of 3 semicircular canals, saccule, utricle VESTIBULAR NERVE with the sup. & inf. vestibular nerves VESTIBULAR NUCLEUS BRAINSTEM CEREBELLUM VESTIBULAR CORTEX EYES SPINAL
VESTIBULAR LABYRINTHS comprising of 3 semicircular canals, saccule, utricle VESTIBULAR NERVE with the sup. & inf. vestibular nerves VESTIBULAR NUCLEUS BRAINSTEM CEREBELLUM VESTIBULAR CORTEX EYES SPINAL
Control of eye movement
 Control of eye movement Third Nerve Palsy Eye down and out Trochlear Nerve Palsy Note: Right eye Instead of intorsion and depression action of superior oblique See extorsion and elevation Observe how
Control of eye movement Third Nerve Palsy Eye down and out Trochlear Nerve Palsy Note: Right eye Instead of intorsion and depression action of superior oblique See extorsion and elevation Observe how
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO.,
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
Brain-Gut Autonomic Connection How did my guts end up in my brain!?
 Jeremy Schmoe DC DACNB FACFN FABBIR Midwest Functional Neurology Center Brain-Gut Autonomic Connection How did my guts end up in my brain!? Special Thanks Dr. Ryan Cedermark DC DACNB! A good picture of
Jeremy Schmoe DC DACNB FACFN FABBIR Midwest Functional Neurology Center Brain-Gut Autonomic Connection How did my guts end up in my brain!? Special Thanks Dr. Ryan Cedermark DC DACNB! A good picture of
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
3/2/2017. Vestibular and Visual Systems, and Considerations for Hippotherapy. Carol A. Huegel, PT, HPCS
 Vestibular and Visual Systems, and Considerations for Hippotherapy Carol A. Huegel, PT, HPCS Objectives The participant will: Have an understanding of the anatomy of the vestibular system and related neuroanatomy
Vestibular and Visual Systems, and Considerations for Hippotherapy Carol A. Huegel, PT, HPCS Objectives The participant will: Have an understanding of the anatomy of the vestibular system and related neuroanatomy
How Neurons Do Integrals. Mark Goldman
 How Neurons Do Integrals Mark Goldman Outline 1. What is the neural basis of short-term memory? 2. A model system: the Oculomotor Neural Integrator 3. Neural mechanisms of integration: Linear network theory
How Neurons Do Integrals Mark Goldman Outline 1. What is the neural basis of short-term memory? 2. A model system: the Oculomotor Neural Integrator 3. Neural mechanisms of integration: Linear network theory
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS.
 ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS. Alan M. Wing Sensory Motor Neuroscience Centre, The University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK. a.m.wing@bham.ac.uk J. Randall Flanagan
ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS. Alan M. Wing Sensory Motor Neuroscience Centre, The University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK. a.m.wing@bham.ac.uk J. Randall Flanagan
Three-Dimensional Eye-Movement Responses to Surface Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation in Normal Subjects and in Patients
 Three-Dimensional Eye-Movement Responses to Surface Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation in Normal Subjects and in Patients A Comparison H.G. MACDOUGALL, a A.E. BRIZUELA, a I.S. CURTHOYS, a AND G.M. HALMAGYI
Three-Dimensional Eye-Movement Responses to Surface Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation in Normal Subjects and in Patients A Comparison H.G. MACDOUGALL, a A.E. BRIZUELA, a I.S. CURTHOYS, a AND G.M. HALMAGYI
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (AVS) 12/5/2017
 Sharon Hartman Polensek, MD, PhD Dept of Neurology, Emory University Atlanta VA Medical Center DIAGNOSTIC GROUPS FOR PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH DIZZINESS TO EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS Infectious 2.9% Genitourinary
Sharon Hartman Polensek, MD, PhD Dept of Neurology, Emory University Atlanta VA Medical Center DIAGNOSTIC GROUPS FOR PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH DIZZINESS TO EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS Infectious 2.9% Genitourinary
Dizziness is a Health Concern. Vestibular Disorders and Rehabilitation. ReZlexes. ReZlex (cont.) Functions of Vestibular System. Dysfunction 2/24/13
 Vestibular Disorders and Rehabilitation Week 8: Dr. E Dizziness is a Health Concern From 2001-2004, 35.4% of US adults age 40 y/o and > had vestibular dysfunction. People with a measured vestibular dysfunction
Vestibular Disorders and Rehabilitation Week 8: Dr. E Dizziness is a Health Concern From 2001-2004, 35.4% of US adults age 40 y/o and > had vestibular dysfunction. People with a measured vestibular dysfunction
Update '08: Vestibular and Balance Rehabilitation Therapy
 Update '08: Vestibular and Balance Rehabilitation Therapy In Context with Surgery Medicine & Diet Symptoms of Dizziness Dizziness non-specific term; encompasses any and all of the specific symptoms: Vertigo
Update '08: Vestibular and Balance Rehabilitation Therapy In Context with Surgery Medicine & Diet Symptoms of Dizziness Dizziness non-specific term; encompasses any and all of the specific symptoms: Vertigo
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
A Case of Acute Vestibular Neuritis with Periodic Alternating Nystagmus
 Case Report Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 218;61(3):151-5 / pissn 292-5859 / eissn 292-6529 https://doi.org/1.3342/kjorl-hns.216.1713 A Case of Acute Vestibular Neuritis with Periodic Alternating
Case Report Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 218;61(3):151-5 / pissn 292-5859 / eissn 292-6529 https://doi.org/1.3342/kjorl-hns.216.1713 A Case of Acute Vestibular Neuritis with Periodic Alternating
Random Saccade Test. Update '08: Dizziness and Balance Disorder Evaluation. Localization within the central system.
 Update '08: Dizziness and Balance Disorder Evaluation Random Saccade Test Computer Analysis Latency Accuracy Velocity Abnormalities relate to brain stem and / or cerebellar involvement Localization within
Update '08: Dizziness and Balance Disorder Evaluation Random Saccade Test Computer Analysis Latency Accuracy Velocity Abnormalities relate to brain stem and / or cerebellar involvement Localization within
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Jam Ghajar MD PhD Director, Stanford Concussion and Brain Performance Center Founder, SyncThink President, Brain Trauma Foundation
 The Concussion Conundrum: an opportunity to explore the last frontier, TIME Jam Ghajar MD PhD Director, Stanford Concussion and Brain Performance Center Founder, SyncThink President, Brain Trauma Foundation
The Concussion Conundrum: an opportunity to explore the last frontier, TIME Jam Ghajar MD PhD Director, Stanford Concussion and Brain Performance Center Founder, SyncThink President, Brain Trauma Foundation
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Video Head Impulse Testing
 Authored by: David J. Coffin, Au.D. e3 Gordon Stowe Chicago Chicago, Illinois The video Head Impulse Test (vhit) is a relatively new test that provides diagnostic and functional information about the vestibular
Authored by: David J. Coffin, Au.D. e3 Gordon Stowe Chicago Chicago, Illinois The video Head Impulse Test (vhit) is a relatively new test that provides diagnostic and functional information about the vestibular
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Head Shaking and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex in Congenital Nystagmus
 August 1965 Vol. 26/8 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science A Journal of Basic and Clinical Research Articles Shaking and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex in Congenital Nystagmus Jomes R. Carl,* Lance M.
August 1965 Vol. 26/8 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science A Journal of Basic and Clinical Research Articles Shaking and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex in Congenital Nystagmus Jomes R. Carl,* Lance M.
Magnetic Vestibular Stimulation (MVS): An Update
 Magnetic Vestibular Stimulation (MVS): An Update My collaborators Neurology: DALE ROBERTS, JORGE OTERO-MILLAN, PREM JAREONSETTASIN Otolaryngology: BRYAN WARD, JOHN CAREY, CHARLES DELLA SANTINA, GRACE TAN,
Magnetic Vestibular Stimulation (MVS): An Update My collaborators Neurology: DALE ROBERTS, JORGE OTERO-MILLAN, PREM JAREONSETTASIN Otolaryngology: BRYAN WARD, JOHN CAREY, CHARLES DELLA SANTINA, GRACE TAN,
OCULAR MOTILITY DISORDERS DUE TO BRAINSTEM DISEASE
 OCULAR MOTILITY DISORDERS DUE TO BRAINSTEM DISEASE Eric R. Eggenberger, DO, MSEpi Michigan State University Lansing, MI LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Review brainstem anatomy and its relevance to clinical presentations
OCULAR MOTILITY DISORDERS DUE TO BRAINSTEM DISEASE Eric R. Eggenberger, DO, MSEpi Michigan State University Lansing, MI LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Review brainstem anatomy and its relevance to clinical presentations
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo
 Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Gaze-evoked nystagmus: A case report and literature review
 Optometry (2007) 78, 460-464 Gaze-evoked nystagmus: A case report and literature review Doug Rett, O.D. Boston Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts KEYWORDS Gaze-evoked nystagmus; Nystagmus;
Optometry (2007) 78, 460-464 Gaze-evoked nystagmus: A case report and literature review Doug Rett, O.D. Boston Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts KEYWORDS Gaze-evoked nystagmus; Nystagmus;
Muscimol inactivation caudal to the interstitial nucleus of Cajal induces hemi-seesaw nystagmus
 DOI 10.1007/s00221-010-2376-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Muscimol inactivation caudal to the interstitial nucleus of Cajal induces hemi-seesaw nystagmus Vallabh E. Das R. John Leigh Michelle Swann Matthew J. Thurtell
DOI 10.1007/s00221-010-2376-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Muscimol inactivation caudal to the interstitial nucleus of Cajal induces hemi-seesaw nystagmus Vallabh E. Das R. John Leigh Michelle Swann Matthew J. Thurtell
CNS MCQ 2 nd term. Select the best answer:
 Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Defining Dizziness: An Acute Approach to Vestibular Dysfunction in the Hospital Setting Friday, February 17, :00 AM-10:00 AM
 Defining Dizziness: An Acute Approach to Vestibular Dysfunction in the Hospital Setting Friday, February 17, 2017 8:00 AM-10:00 AM Kerry Lammers, PT, DPT Gabrielle Steinhorn, PT, DPT, NCS Vestibular dysfunction
Defining Dizziness: An Acute Approach to Vestibular Dysfunction in the Hospital Setting Friday, February 17, 2017 8:00 AM-10:00 AM Kerry Lammers, PT, DPT Gabrielle Steinhorn, PT, DPT, NCS Vestibular dysfunction
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
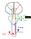 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
How to Vestibularly Make Optometric Vision Therapy More Effective COPE # Pending COVD 44 th Annual Meeting October 23, 2014
 What Kinds of Patients Might Benefit? How to Vestibularly Make Optometric Vision Therapy More Effective COPE # Pending COVD 44 th Annual Meeting October 23, 2014! Screaming child in reception area! Patient
What Kinds of Patients Might Benefit? How to Vestibularly Make Optometric Vision Therapy More Effective COPE # Pending COVD 44 th Annual Meeting October 23, 2014! Screaming child in reception area! Patient
Role of neural integrators in oculomotor systems: A systematic narrative. 2 Department of Health Services Research, University of Liverpool, UK
 Role of neural integrators in oculomotor systems: A systematic narrative literature review. Katherine Sanchez, BSc(Hons) 1, Fiona J Rowe, PhD 2 1 Department of Orthoptics, Royal Preston Hospital, Preston,
Role of neural integrators in oculomotor systems: A systematic narrative literature review. Katherine Sanchez, BSc(Hons) 1, Fiona J Rowe, PhD 2 1 Department of Orthoptics, Royal Preston Hospital, Preston,
Current Perspectives in Balance Assessment. Topics for Today. How are we doing? 3/5/2010. Scott K. Griffiths, Ph.D. March 26, 2010
 Current Perspectives in Balance Assessment Scott K. Griffiths, Ph.D. March 26, 2010 Topics for Today Evaluating the Dizzy Patient looking back, looking ahead The (Not So) New Kids on the Block: VEMPs,
Current Perspectives in Balance Assessment Scott K. Griffiths, Ph.D. March 26, 2010 Topics for Today Evaluating the Dizzy Patient looking back, looking ahead The (Not So) New Kids on the Block: VEMPs,
Acute Vertical Ophthalmoplegia Secondary to Unilateral Thalamic Stroke
 Acute Vertical Ophthalmoplegia Secondary to Unilateral Thalamic Stroke Shane Stevens, OD Richard Frick OD, FAAO, ABCMO Andrea Murphy, OD, FAAO White River Junction, VT VAMC Patient & Chief Complaint 64
Acute Vertical Ophthalmoplegia Secondary to Unilateral Thalamic Stroke Shane Stevens, OD Richard Frick OD, FAAO, ABCMO Andrea Murphy, OD, FAAO White River Junction, VT VAMC Patient & Chief Complaint 64
Relationships Among Oscillopsia, the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex, and Nystagmus
 The Vestibulo-OclIlar Reflex and Vertigo. edited by James A. Sharpe and Hugh O. Barber. Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1993. 19 Relationships Among Oscillopsia, the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex, and Nystagmus
The Vestibulo-OclIlar Reflex and Vertigo. edited by James A. Sharpe and Hugh O. Barber. Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1993. 19 Relationships Among Oscillopsia, the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex, and Nystagmus
Cold Thermal Irrigation Decreases the Ipsilateral Gain of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex
 Cold Thermal Irrigation Decreases the Ipsilateral Gain of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Laszlo T. Tamás, 1 Konrad P. Weber, 2,3 Christopher J. Bockisch, 2,3,4 Dominik Straumann, 2 David M. Lasker, 5 Béla
Cold Thermal Irrigation Decreases the Ipsilateral Gain of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Laszlo T. Tamás, 1 Konrad P. Weber, 2,3 Christopher J. Bockisch, 2,3,4 Dominik Straumann, 2 David M. Lasker, 5 Béla
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Signal Processing by Vestibular Nuclei Neurons Is Dependent on the Current Behavioral Goal
 Signal Processing by Vestibular Nuclei Neurons Is Dependent on the Current Behavioral Goal KATHLEEN E. CULLEN, JEFFERSON E. ROY, AND PIERRE A. SYLVESTRE Aerospace Medical Research Unit, Department of Physiology,
Signal Processing by Vestibular Nuclei Neurons Is Dependent on the Current Behavioral Goal KATHLEEN E. CULLEN, JEFFERSON E. ROY, AND PIERRE A. SYLVESTRE Aerospace Medical Research Unit, Department of Physiology,
From the Laboratory of Neurophysiology, University of Mons, Faculty of Medicine,
 Journal of Physiology (1993), 469, pp. 549-570 549 With 11 figure8 Printed in Great Britain TESTING THE COMMON NEURAL INTEGRATOR HYPOTHESIS AT THE LEVEL OF THE INDIVIDUAL ABDUCENS MOTONEURONES IN THE ALERT
Journal of Physiology (1993), 469, pp. 549-570 549 With 11 figure8 Printed in Great Britain TESTING THE COMMON NEURAL INTEGRATOR HYPOTHESIS AT THE LEVEL OF THE INDIVIDUAL ABDUCENS MOTONEURONES IN THE ALERT
Vestibuloocular Reflex Signal Modulation During Voluntary and Passive Head Movements
 J Neurophysiol 87: 2337 2357, 2002; 10.1152/jn.00625.2001. Vestibuloocular Reflex Signal Modulation During Voluntary and Passive Head Movements JEFFERSON E. ROY AND KATHLEEN E. CULLEN Aerospace Medical
J Neurophysiol 87: 2337 2357, 2002; 10.1152/jn.00625.2001. Vestibuloocular Reflex Signal Modulation During Voluntary and Passive Head Movements JEFFERSON E. ROY AND KATHLEEN E. CULLEN Aerospace Medical
Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010
 Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010 Asymmetry in learning in the reverse direction Full recovery from UP using DOWN: initial return to naïve values within 10 minutes,
Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010 Asymmetry in learning in the reverse direction Full recovery from UP using DOWN: initial return to naïve values within 10 minutes,
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 PARINAUD'S SYNDROME A CASE REPORT Basker K Shubha Raguram K Stanley Medical College Introduction: Gaze palsies are a group
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 PARINAUD'S SYNDROME A CASE REPORT Basker K Shubha Raguram K Stanley Medical College Introduction: Gaze palsies are a group
