Chapter 5 Skin! Chapter 5! The Integumentary System!
|
|
|
- Annabella Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5! The Integumentary System! 2 1!
2 The Integumentary System Consists of:! 1. A cutaneous membrane! Epidermis! Dermis! 2. Accessory structures! E.g. hair, glands, nails! 3. Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis)! 3 Integumentary System Functions 1! Protection of underlying tissues from:! Abrasion, chemicals, UV radiation, infection, etc.! Excretion! Salts, wastes, water! Production of melanin! UV protection! Production of keratin! Resists abrasion, waterproofs skin! Synthesis of vitamin D 3! Aids in Ca 2+ absorption! 4 2!
3 ! Chapter 5 Skin! Integumentary System Functions 2! Lipid storage! Detection of touch, pressure, pain, temperature! Body temperature regulation! Insulation, evaporation, vasomotion! Blood storage! Blood is diverted from skin to skeletal muscles during emergency situations.! 5 Integumentary System Figure 5-1! 6 3!
4 SECTION 5-1! The epidermis is composed of strata (layers) with various functions! 7 Thin Skin and Thick Skin Figure 5-3! Epidermis is dominated by layers of keratinocytes! Thin skin: four layers (strata)! Thick skin: a) five strata on palms, soles of feet! b) stratum corneum very thick! c) contains stratum lucidum! 8 4!
5 Layers of the Epidermis! From deepest to most superficial! Stratum germinativum (basale)! Stratum spinosum! Stratum granulosum! Stratum lucidum (thick skin only)! Stratum corneum! 9 Structure of the Epidermis Figure 5-3! Thick Skin 10 5!
6 Epidermal Cell Types! Keratinocytes! Langerhans (dendritic) cells! Merkel cells! Melanocytes! 11 Keratinocytes (1 of 2)! 90% of epidermal cells are this type! A. Produce keratin (intermediate filaments)! Resists abrasion! Decreases water loss! B. Produce keratohyalin! Dehydrates cell! Cross-links keratin fibers! C. Cells have desmosomes ( spot welds )! Intermediate filaments (keratin) hold cells together! 12 6!
7 Keratinocytes (2 of 2)! D. Stratum germinativum (basale) cells have hemidesmosomes! Anchor epidermis to basal lamina! E. Produce lamellar granules! Found primarily in stratum granulosum! Lipid-rich secretion! Released from cells! Waterproofing function! 13 Dendritic (Langerhans) Cells! Immune function:! Migrate to skin from bone marrow! Function as antigen-presenting cells in lymph nodes! Interact with T lymphocytes! Very important immune system cells (Ch. 22)! University of Washington Dept. of Bioengineering 14 7!
8 !! Chapter 5 Skin! Merkel Cells! Found in stratum basale of hairless skin! Attached to keratinocytes by desmosomes! Produce receptor potentials, release neurotransmitter! Activate Merkel discs (neuron cell processes)! Function in light touch and pressure reception! 15 Melanocytes! Cell body is part of stratum germinativum! Contain enzyme tyrosinase Tyrosine (amino acid) tyrosinase melanin (pigment) Pigment packaged in melanosomes Colors = Black brown yellow! Keratinocytes engulf melanosomes! Melanin protects DNA from UV radiation! Vitiligo Treatment Clinics 16 8!
9 Melanocytes Figure 5-4! 17 SECTION 5-2! Factors influencing skin color are epidermal pigmentation and dermal circulation! 18 9!
10 Skin Color Variation (1 of 3)! Melanin is major factor:! All races have about same number of melanocytes! Melanin protects DNA in epidermal and dermal! cells from UV radiation! Color differences depend upon:! Melanin type (color)! Amount of melanin produced! Degree of dispersal and persistence of pigment! 19 Skin Color Variation (2 of 3)! Importance of melanin dispersal/persistence:! Lighter-skinned races! Melanosomes dispersed in:! S. basale and s. spinosum! Melanin destroyed rapidly by lysosomes! Darker-skinned races! Melanosomes dispersed in:! S. basale, s. spinosum and s. granulosum! Melanin not as rapidly destroyed by lysosomes! 20 10!
11 Skin Color Variation (3 of 3)! Other factors:! A. Hemoglobin in blood vessels (dermal blood flow pattern)! B. Carotene (Vitamin A precursor)! Yellow-orange pigment from diet! Accumulates in s. corneum and in fat! C. Albinism! Genetic absence of tyrosinase! D. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (abnormal)! 21 SECTION 5-3! Sunlight causes epidermal cells to convert a steroid into vitamin D 3! 22 11!
12 !! Chapter 5 Skin! Epidermal Cells - Vitamin D! Epidermal cells synthesize vitamin D 3 (cholecalciferol) when exposed to UV! S. germinativum and spinosum! Conversion to active form involves liver and kidneys!! D 3 blood LIVER blood KIDNEYS! Vitamin D (Calcitriol - hormone from kidneys) required for Ca 2+ absorption from gut! 23 Vitamin D Synthesis! Skin Vitamin D 3 inactive form Liver Kidney Calcitriol, active form !
13 Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)! A peptide released by:! Salivary glands! Duodenal glands! Effects:! mitosis in s. basale and spinosum! keratin production rate! epidermal repair rate! activity by epithelial glands! 25 SECTION 5-5! The dermis is the tissue layer that supports the epidermis! 26 13!
14 Dermal Organization, Strength, Elasticity! Contains blood vessels, lymphatics, sensory nerves! Papillary layer! (dermal papillae)! Nearest epidermis! Loose CT! Reticular layer! Papillary layer Dense irregular CT ( leather)! Collagen fibers for strength! Elastic fibers for elasticity! Figure 5-3a Reticular layer 27 Dermal Circulation Figure 5-10! Back to slide 65! 28 14!
15 Dermal Circulation! Cutaneous plexus in reticular layer! Subpapillary plexus in papillary layer! Plexus = network! Blood vessels are within CT, maintain avascular epidermis! Thermoregulation (via vasomotion)! Stores blood! 29 SECTION 5-6! The hypodermis is tissue beneath the dermis that connects it to underlying tissues 30 15!
16 Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)! Not technically part of cutaneous membrane (skin)! A.K.A. hypodermis, superficial fascia! Contains loose (areolar) CT and adipose tissue! Functions:! Anchors skin to underlying structures! Acts as a cushion (fat)! Acts as thermal insulation (fat)! Stores energy (fat)! 31 SECTION 5-7! Hair is composed of keratinized dead cells that have been pushed to the surface 32 16!
17 ! Chapter 5 Skin! Hair Functions! A. Shields scalp from UV! B. Cushions a light blow to the head! C. Senses external environment! e.g. Root hair plexus - early warning system! D. Protection from particles! e.g. Eyelashes, nose hairs! E. Insulates cranium! More important in other animal species:! Piloerection insulating layer of dead air! 33 Hairs and Hair Follicles! Hair is produced by hair follicles (epithelial structures)! Are keratinized invaginations of epidermis! Associated with:! Sebaceous gland (epithelial)! Arrector pili (smooth muscle)! Root hair plexus (nervous)! We will skip the microanatomy of hairs.! 34 17!
18 ! Chapter 5 Skin! Hair Types! Lanugo! Fine, unpigmented - usually shed before birth! Vellus hairs ( peach fuzz, translucent)! Covers much of body surface! Terminal hairs! Heavy, pigmented, perhaps curly! Club hairs (cessation of growth)! Shed and grow according to hair growth cycle! 35 Hair Color! Melanin type and amount determines normal color! Aging:! tyrosinase activity melanin production! gray color! Air bubbles also accumulate in medulla white! 36 18!
19 SECTION 5-8! Sebaceous glands and sweat glands are exocrine glands found in the skin Recall that glands are epithelial derivatives.!! The first four slides about glands are from Chapter 4.! 37 Glandular Epithelia from Chapter 4, pp ! Exocrine glands! Secrete into ducts that empty onto an epithelial surface - E.g. sweat (sudoriferous) glands, oil (sebaceous)glands! Endocrine glands! Release hormones into extracellular fluid blood - E.g. pituitary gland, thyroid gland! Heterocrine glands! Do both - E.g. pancreas, ovaries, testes! 38 19!
20 Modes of Secretion! Merocrine (eccrine)! Product released through exocytosis! E.g. merocrine sweat glands, sublingual salivary gland! Apocrine! Involves the loss of both product and cytoplasm! E.g. mammary glands! E.g. sweat glands in armpits, groin are called this*! Holocrine! Cell fills with product, dies, releases product! E.g. oil (sebaceous) glands in skin! 39 Mechanisms of Glandular Secretion Figure 4-6! 40 20!
21 Secretions by Exocrine Glands! Serous glands! Secrete watery solution containing enzymes! E.g. parotid salivary glands, sweat glands! Mucous glands! Secrete mucins (proteoglycans)! Mucin + water = mucus! E.g. sublingual salivary glands, Brunner s glands in duodenum! Mixed glands! Secrete both - submaxillary salivary gland! 41 Sebaceous (Oil) Glands (back to Chapter 5)! Holocrine secretion type! Most connected to hair follicles! Others = sebaceous follicles! e.g. on face, back, glans penis, labium minus, tarsal glands (eyelids)! Secretion = sebum! Accumulated sebum = blackhead (comedo)! Black = melanin + oil oxidized (bananas)! Bacteria feed on sebum comedo! 42 21!
22 Zits FYI! Bacterium (Propionibacterium acnes) is part of normal (commensal) bacteria on skin! Becomes trapped in airless (plugged) hair follicle! Converts sebum into fatty acids that deactivate histone deacetylases. These normally inhibit inflammation.! Inhibition removed à inflammation occurs in keratinocytes ( zits )! Puberty: sex hormones à increased production of sebum à more chance for acne! 43 Functions of Sebum! Composed of triglycerides, cholesterol, proteins, electrolytes! Secretion mechanism = holocrine! Moisturizes hair! Prevents keratin from becoming brittle! Moisturizes skin! Helps waterproof skin! Softens skin! Inhibits bacterial growth! 44 22!
23 ! Chapter 5 Skin! Sebaceous Glands and Follicles Figure 5-13! 45 Sudoriferous (Sweat) Glands! Sudoriferous = to bear sweat! Types! Apocrine! Merocrine (eccrine)! Do not blame me for the ridiculously confusing terminology! 46 23!
24 1. Apocrine Sweat Glands! Method of secretion is actually merocrine (controversial) Produce secretion that becomes odorous! Sticky, viscous sweat! Secreted onto hair follicle! Secretion begins at puberty! Axilla, pubic region, areola of breast! Bacterial growth odor! Myoepithelial cells contract, promote discharge! Merocrine (Eccrine) Sweat Glands! Most sweat glands are merocrine! Most dense on palms, soles! Serous (watery) secretion = sensible perspiration! Functions:! Excretion! Salts, urea, uric acid, amino acids, sugars, lactate! Thermoregulation! Protection! Flush chemicals, bacteria from surface! Contains antibiotic = dermacidin! 48 24!
25 Sweat (Sudoriferous) Glands Figure 5-14! 49 Other Glands! 1. Mammary glands! Structurally related to apocrine sweat glands! Discussed in Chapter 28! 2. Ceruminous glands! Modified sweat glands! In external ear canal! Mix with sebaceous secretions cerumen! 60% keratin, 12-20% fatty acids, alcohols, oils, <10% cholesterol! Traps foreign particles! 50 25!
26 Control of Glandular Secretion! Sebaceous glands and apocrine glands! Regional control not possible! All on or all off! Merocrine sweat glands! Regional control possible! Thermoregulation! 51 Nails! Functions! Protect ends of digits! Facilitate manipulation with fingers! Structure! Epithelial derivatives!! We will not be covering the microanatomy of nails.! 52 26!
27 Sensory Structures Figure 15-4! Receptor! Location! Function(s)! Free nerve endings! Between epidermal cells! Pain, touch, pressure, temperature! Root hair plexus! Around hair root! Movement of hair! Merkel cells and Merkel (tactile) discs! Meissner s (tactile) corpuscles! Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles! Ruffini corpuscle! S. basale of epidermis! Papillary layer of dermis! Throughout dermis, hypodermis, joint capsules! Reticular layer of dermis! Fine touch and pressure! Fine touch and pressure! Deep pressure, distortion! Deep pressure, distortion! No short-answer questions on this 53 Sensory Structures Figure 15-4! 54 27!
28 SECTION 5-10! Several steps are involved in repairing the integument following an injury Repair is possible because skin contains stem cells.! Epidermis - stratum basale (germinativum)! Dermis - mesenchyme cells Epidermal Wound Healing! Wound is to epidermis only! S. basale cells leave basement membrane! Cells enlarge! Cells migrate across wound to center! Stop when surrounded by similar cells! (Contact inhibition)! Replace upper layers by mitosis! 56 28!
29 2. Deep Wound Healing! Wound extends into dermis! Repair may leave a scar! Four general phases:! Inflammation phase! Migratory phase! Proliferative phase! Maturation phase! 57 Integumentary Repair - 1 of 2 Figure 5-16! Inflammation Phase! (Mast cells, basophils) Migratory Phase 58 29!
30 Integumentary Repair - 2 of 2 Figure 5-16! Proliferative Phase Maturation (Scarring) Phase Inflammation Phase! Area is red, swollen, hot, painful (Why?)! A. Blood clot (scab) forming! Unites edges of wound (fibrin)! Stop bleeding! bacterial invasion! B. vasodilation and vessel permeability! Histamine from mast cells, basophils! Cytokines attract WBCs to wound! C. Mesenchyme cells begin differentiating into fibroblasts! 60 30!
31 2. Migratory Phase! Scab has formed from fibrin! Epithelial cells migrating under scab! Fibroblasts migrating in, making collagen! WBCs still migrating in! Blood vessels growing into site! Clot + fibroblasts + blood vessels = granulation tissue! Proliferative Phase! Growth and proliferation of epithelial cells under scab! Fibroblasts producing collagen fibers in random patterns! More vessel growth occurring! 62 31!
32 ! Chapter 5 Skin! 4. Maturation Phase! Scab falls off! Epithelium regains proper thickness! Collagen fibers become more organized! Fibroblast population returns to normal number! Scar! CT grows faster than EPI! More than normal amount of CT growth! Collagen arranged in more regular pattern! Myofibroblasts! 63 SECTION 5-11! Effects of aging include dermal thinning, wrinkling, and reduced melanocyte activity 64 32!
33 Changes with Aging (1 of 3)! 1. S. basale activity thickness of epidermis! More injuries, more and recurring infections! 2. Langerhans cell activity! More and recurring infections! 3. Vitamin D 3 production Ca 2+ and PO 4 2- uptake! Bone loss, muscular weakness! 4. Glandular activity! sebum dry, scaly skin! merocrine secretion overheating! 65 Changes with Aging (2 of 3)! 5. Blood supply to dermis (see slide 28)! Skin cool inappropriate sensation of cold! Less able to release heat when appropriate! 6. Melanocyte activity! paler skin, sunburn, gray hair! 7. Number and thickness of collagen/elastin fibers! strength of dermis! elasticity of dermis, sagging skin! 66 33!
34 Changes with Aging (3 of 3)! 8. hair follicle function hair loss! 9. Changes in sex hormones hair and fat distribution! Effects of Weightlessness on Skin Preliminary results from astronauts:! Collagen production in dermis stimulated (antiaging?)! Epidermis gets thinner! Being investigated. Would be important on long space flights like to Mars.! !
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
The Integumentary System
 C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
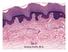 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Cell Types in Epidermis
 Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Chapter 4. The Integumentary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Objectives. To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis.
 Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
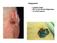 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
The Integumentary System
 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Anatomy of the Skin Learning Outcomes 5.1 Describe the tissue structure of the integument and the functions of the
5 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Anatomy of the Skin Learning Outcomes 5.1 Describe the tissue structure of the integument and the functions of the
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
-Skin- -Integumentary-
 BIO 225: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 06 -Skin- -Integumentary- Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Illustrations courtesy of McGraw-Hill. 2 GENERAL FUNCTIONS Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis
BIO 225: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 06 -Skin- -Integumentary- Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Illustrations courtesy of McGraw-Hill. 2 GENERAL FUNCTIONS Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
2.2 Integumentary System. Chapter 5
 2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. General Anatomy. Overview. Skin and its accessory structures
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Skin and its accessory structures structure function growth and repair development aging disorders 5-1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Skin and its accessory structures structure function growth and repair development aging disorders 5-1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Objectives: 1- Describe the functions of the integumentary system. 2- Identify the major structures found in the three layers of the skin. 3. Describe the anatomy and physiology of
Integumentary System Objectives: 1- Describe the functions of the integumentary system. 2- Identify the major structures found in the three layers of the skin. 3. Describe the anatomy and physiology of
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Contents: The skin and its derivatives: hair, nails and glands. Functions: 1. Regulaiton of body temperature -sweating
 The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
28a A&P - Integumentary System
 28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 4. Skin and Body Membranes. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Chapter 5.1. Integumentary System
 Chapter 5.1 Integumentary System resistance to trauma and infection /// keratin /// acid mantle Functions of the Skin provide other barrier functions /// waterproofing - UV radiation - harmful chemicals
Chapter 5.1 Integumentary System resistance to trauma and infection /// keratin /// acid mantle Functions of the Skin provide other barrier functions /// waterproofing - UV radiation - harmful chemicals
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
The Integumentary System. Health & Anatomy
 The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
