Percutaneous nephrostomy or double J stenting, which is better modality for obstructive uropathy-a descriptive study
|
|
|
- Della Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Mittal V et al. Int J Res Med Sci Aug;4(8): pissn eissn Research Article DOI: Percutaneous nephrostomy or double J stenting, which is better modality for obstructive uropathy-a descriptive study Vinamra Mittal, Manoj Biswas*, Shobha Lal Department of General Surgery, Himalayan Institute and Hospital Trust University, Swami Rama Nagar, Doiwala, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India Received: 18 June 2016 Revised: 30 June 2016 Accepted: 08 July 2016 *Correspondence: Dr. Manoj Biswas, manojbiswas2006@gmail.com Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: Percutaneous Nephrostomy or Ureteric Stenting is indicated in patients with Acute Renal Failure following urinary tract obstruction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the better treatment modality in terms of S. Creatinine level. Methods: Total 50 patients with Creatinine level of >2 mg/dl and hydronephrosis due to upper urinary tract obstruction were grouped into either percutaneous nephrostomy or stent insertion groups. These patients were then evaluated by overall trend of S. creatinine and urine output levels postoperatively. Results: Two comparable groups of PCN and DJS were formed with a mean age of 45.5 years and 47.9 years. Male to female ratio was 1.5:1 and 1.2:1 respectively. Pain with oliguria or anuria was the major presentation. The urine output levels showed a sudden increase postoperatively with a subsequent trend towards normal value in both the groups. Creatinine however showed a normalizing trend from a mean 6.46 mg/dl preoperatively to 1.01mg/dl postoperatively in PCN group whereas in DJS group 5.38mg/dl preoperatively to 2.75mg/dl with a rising trend from POD 15 requiring conversion to PCN in 20% of patients with subsequent normalization of creatinine levels to 0.95 mg/dl. Statistically we found no difference in the outcome when both the groups were compared in view of serum creatinine and urine output levels whereas there is a significant difference in the pre and post operative outcome of both the groups. Conclusions: Our results thus support that though there is no significant difference among both the procedures, ureteral stents are associated with intolerable lower urinary tract symptoms owing to conversion to secondary percutaneous Nephrostomy. Hence percutaneous nephrostomy is superior to ureteral stents for diversion of urine in patients with ARF due to obstructive uropathy. Keywords: Nephrostomy, Percutaneous, Ureter, Stents, Hydronephrosis, Urinary calculi, Renal failure, Acute renal failure INTRODUCTION Renal stone disease is one of the most common afflictions of modern society and has been described since antiquity. The high occurrence and substantial morbidity and mortality of Acute Renal Failure demand a logical approach to its early recognition and prevention, as well as prompt diagnosis and management of its complications. 1 Revolutionary advances in the minimally invasive and noninvasive management of stone disease over the past 2 decades have greatly facilitated the ease with which stones are removed. However, surgical treatments, although they remove the offending stone, do little to alter the course of the disease. As the limitations of ESWL were recognized, percutaneous surgery once again rose in popularity with a redefined role in stone management. The most common methods in these situations are insertion of double-j catheter or placement International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3486
2 of percutaneous nephrostomy. 2 The present study thus aims at evaluating the better mode of diversion among the two most popular modalities in management of ARF due to obstructive causes i.e. DJ Stenting and PCN. METHODS The study was conducted in the Department of Surgery, Himalayan Institute of Medical Sciences (HIMS), Swami Ram Nagar, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India from 15 th October 2011 to 15 th October patients with a primary diagnosis of Obstructive Acute Renal Failure were recruited in the study and based on the patients preference for the procedure were grouped into either Group A (patients who underwent PCN) and Group B (patients who underwent DJS). A malecots catheter or a Pig tail stent was used as a percutaneous nephrostomy tube. The Seldinger technique was used for minimally or non-dilated collecting systems and cases. Polyethylene or silicon double J (coiled at both ends) stent were used. In an operation theatre (OT) under spinal anaesthesia with C arm guidance, the ureteric orifice was visualized and guidewire inserted upto the renal pelvis over which the stent was inserted. Inclusion criteria Patient with stone induced hydronephrosis and diagnosed as acute renal failure with a serum creatinine level of greater than 2 mg/dl were included in the study. Exclusion criteria Criteria included patient with non-obstructive cause of ARF and obstruction other than in the upper urinary tract. Chronic renal failure patients having serum creatinine levels greater than 2 mg/dl even after 1 month of the procedure were excluded from the study. Evaluation parameters were related to the postoperatively serum creatinine and Urine output levels. Follow up for 15 days for Urine Output and 30 days for creatinine levels was done and findings recorded. Individual serum creatinine and urine output levels were subjected to paired Student t test was performed for statistical analyses with p>0.005 considered significant and Repeated measure ANOVA. RESULTS In the present Study, overall male to female ratio was 1.5:1. Both the groups also had a male to female ratio of 1.5:1. This is similar to the study done by Mokhmalji et al in which the patients who underwent ureteric stenting had a 9:11 male to female ratio and the patients who underwent Percutaneous nephrostomy had a 12:8 male to female ratio. 3 The sex ratio is also similar to the study conducted by Abdul Ghaffar et al which showed a 1.4:1 male to female ratio. 4 The mean age of patients included in Group A (PCN group) in our study was 45.5±15.83 years and in Group B (DJ Stenting Group) was 50.4±14.45 years. Mokhmalji et al showed a mean age of 55 years in PCN group and a mean age of 49 years in DJS Group. More than half (56%) patients in our study were in the range of years. In present study all the patients had a urinary tract obstruction due to renal lithiasis. Table 1: Age and sex ratio comparison. Present study Mokhmalji PCN DJS PCN DJS Age 45.5± ± M:F 1.5:1 1.5:1 12:8 9:11 Out of 50 patients included in the study pain in the flank region was the major symptom occurring in 90% (45) patients whereas fever was present in 52% (26) patients and hematuria in 22%. 2 This was in contrast to study by Abdul Ghaffar et al which showed the most frequent presentation was pain and oliguria and anuria in 51.5%. 4 Kenan et al however showed comparable result of presenting symptom of pain in 100%. Hematuria (94.4%) and Fever (11.1%) were in contrast to our study. 5 Oligoanuria as a presenting symptom was present in 66% of the patients in present study in contrast to 55.8% reported by Tazi k et al. 6 Past history of urinary calculi was present in 16 (32%) of the patients in our study, quite comparable to 25% in the study conducted by Kenan et al. 5 Table 2: Symptoms comparison. Symptoms Present Study Kenan Pain 90% 100% Fever 52% 11.1% Hematuria 22% 94.4% Past H/O urinary calculi 32% 25% In this study, ureteric stents were placed under analgesic sedation. Percutaneous Nephrostomy was performed as an outpatient procedure after infiltration of adequate local anaesthesia. Ureteric stenting was done in the operating theatre with the guidance of fluoroscopy and C-arm. Nephrostomy on the other hand was done under USG guidance on a dilated pelvic system. Percutaneous Nephrostomy was successfully placed in 100 % (n=25) of the patients with a single puncture. Ureteric Stenting was also successfully performed in 100% (n=25) of the patients. Mokhmalji et al showed a success rate of 100% in PCN group but only 80% rate was achieved in the DJS group. 3 Yagci et al also show a International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3487
3 similar pattern in Solely Ultrasound guided nephrostomy to have a comparable success rate and complication rate ranging from 90 to 100% and 1-4% respectively. 7 A stent insertion failure rate of approximately 20% was reported in 1999 by Van Glabecke et al who similarly detected stone location in the lumbar ureter in all failed cases. 8 In 1975 Fowler et al asserted that failure in ureteral stenting is attributed to the impacted stones. 9 Both Stables and Stanley et al reported in 1982 and 1983, respectively, a percutaneous nephrostomy success rate of about 98% in adults and children. 10,11 Total Leukocyte count was normal in 44% of the patients in our study and raised in 56%. Out of these 32% patients underwent percutaneous nephrostomy and 16% underwent ureteric stenting. Remaining 8% initially underwent ureteric stenting but was not relieved hence a secondary percutaneous nephrostomy was carried out in these patients. UTI was present in 44 (88%) of the patients in our study. In a study conducted on Diagnosis and management of ureteric stones during pregnancy, Urinary tract infection was present in 27.7% patients. 5 Out of these 44 patients, 20 (40%) underwent PCN and 24 (48%) underwent DJS. Rest patients had a normal Urinary WBC levels. In present study the main inclusion criteria was Serum Creatinine levels at the time of admission. Overall Creatinine levels ranged from 2-23mg/dl. 34 (68%) of the patients had a creatinine level between 2-7 mg/dl. Only 2 (4%) of the patients had a creatinine level >12 mg /dl. In a study conducted by Abdul Ghaffar in 2007 preoperative creatinine ranged from Minimum of 5.2 mg/dl to Maximum of 27mg/dl. Fifteen patients (45.4%) had creatinine more than 10 mg/dl. Four had range of 5-9 mg/dl and rest 14 had creatinine of <05 mg/dl. Five patients had creatinine >15 mg/dl. 4 All the patients included in the study required admission for post-operative care and for assessment of creatinine levels. Following the procedure a strict urine output charting was done in all patients. Treatment with antibiotics lasted for 7 days in 60 % of the patients who underwent Percutaneous Nephrostomy (Group A) whereas 55% (n=20) patients who underwent Ureteric Stenting needed a longer antibiotic coverage than 7 days. Although suggestive, but this finding was not significant owing to the longer use of antibiotics in patients with a higher leukocyte count and presence of WBC in urine thus was evident in those patients with fever, urinary tract infection and urosepsis. 3 Post operatively a strict urine output charting was done in all the patients on POD 1, POD 3, POD 5, POD 7, POD 9, POD 11, POD 13, POD 15. The urine output levels included the urine in the drainage bag as well as the nephrostomy bag. The urine output levels did not show a significant difference among the two procedures when compared on each post-operative day but when the urine output was compared pre and postoperatively, we found a significant change in both the groups (p value <0.005) Figure 1: Comparison between PCN and DJ Stenting in respect to urine output levels This change was more pronounced in the patients who underwent PCN (p value=0.001) when compared to patients who underwent DJ Stenting (p value=0.003) thus implying a better response in urine output levels in Group A patients to Group B patients. By repeated measure ANOVA (p<0.001) also we found a significant difference in the pre and post-operative outcome of the patients undergoing PCN. In Patients undergoing DJ stenting also repeated measure ANOVA (p <0.001) showed a significant difference in the pre and post opearive urine output characteristics. Our results are in acceptance to a study conducted by Mokhmalji et al which showed a 100% success in placement of PCN and subsequent impoving of renal functions. 3 Along with the urine output level, the patients underwent a serial serum creatinine level on each postoperative day Pre OP POD 1 POD 3 POD 15 POD 30 Group A Group A Group B Figure 2: Comparison between PCN and DJ Stenting in respect to serum creatinine levels. On POD 3 the serum creatinine levels are nearly the same in both the groups (p value = 0.376). But on POD 15 an increase in the creatinine levels is found in patients who underwent DJS whereas the patients of Group A continued to show an improving trend. The mean International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3488
4 creatinine level on POD 15 is 1.32 and 2.25 in each group respectively (p value = 0.053). On evaluating the cause for this rise in the creatinine level, it was found that five patients who underwent DJ stenting and initially showed an improving response in urine output levels as well as serum creatinine started complaining of dysuria and lower abdominal pain, flank pain and increased frequency of urine from POD 1 only. These symptoms were only found in 5 (20%) of the patients of Group B selectively. It was also noticed that these patients also showed a decrease in their urine output level along with a declining trend in their serum creatinine levels. These patients were observed thereafter till POD 30 but when their serum creatinine levels increased to 9.54 mg/dl compared to 0.96 mg / dl in rest of the group and intolerability in their symptom, these patients were taken up for an emergency Secondary percutaneous Nephrostomy and their DJ stents were removed after POD 30. Post-secondary PCN these patients dramatically improved similar to the patients who underwent primary PCN. The s. creatinine levels did not show a significant difference among the two procedures when compared on each post-operative day but when the creatinine levels were compared pre and postoperatively, we found a significant change in both the groups (p value <0.005). This change was again more pronounced in the patients who underwent PCN (p value = 0.001) when compared to patients who underwent DJ Stenting (p value=0.004) thus implying a better response in serum creatinine levels in Group A patients to Group B patients. By repeated measure ANOVA (p<0.001) also we found a significant difference in the pre and post-operative serum creatinine levels of the patients undergoing PCN. In Patients undergoing DJ stenting also repeated measure ANOVA (p <0.001) showed a significant difference in the pre and post operative serum creatinine levels DISCUSSION This is in accordance with a study conducted by Tazi et al who showed a 100 % success in PCN placement and resulting improvement in their renal functions. 6 Mokhmalji et al also showed a failure rate of 20 % in patients who underwent DJ stenting resulting in their conversion to secondary PCN. 3 Hussain et al also showed an improvement in the renal function with serum creatinine below 2 mg/dl in 72% of calculus anuria and 49.5% of calculus renal failure patients at two year follow up following percutaneous nephrostomy. 12 A Successful PCN placement with improvement in renal failure and treatment of initial infectious syndrome was also found in 93% of the patients in a study conducted by Fournier G et al. 13 Abber et al reported an obstruction of the ureteral stent resulting from the early onset of incrustation in 5% of cases with accompanying urinary tract infection and subsequent pyelonephritis. 14 Pollard and Macfarlane evaluated symptoms, including irritative bladder complaints, and suprapubic and flank pain, associated with ureteral stents in 20 patients and confirmed that the symptoms disappeared after stent removal. 15 They found no association between the degree of symptoms and stent composition, style or length. Bregg et al noted flank pain in 38%, symptoms of bladder irritation in 26% and macrohematuria in 42% of patients with stones after ureteral stenting. 16 The majority of their patients complained of frequency, dysuria and flank discomfort, especially during voiding, walking or strenuous activities. The complaints were classified as intolerable in 6% of patients. Pryor et al reported urinary dysfunction after ureteral stenting with 4 different types of stents. 17 They also found no differences among the 4 types of stents in terms of incidence and severity of irritative symptoms. In 1988 Mardis and Kroeger observed erosion and bullous edema of the bladder mucosa caused by the lower tip of the stent, which explained the development of macrohematuria and pyuria after ureteral stenting without urinary tract infection. 18 Danilovic et al evaluated the urgent ureteral decompression in patients with ureteral obstruction due to intrinsic and extrinsic pathologies and found that Retrograde double-j stenting failed in 9% (2/22) of intrinsic obstruction and in 52% (13/25) of extrinsic obstruction (p<0.001). 2 Mokhmalji et al evaluated the quality of life of patients undergoing diversion procedure and showed that retrograde ureteral stenting was more problematic and negatively affects the quality of life more than percutaneous nephrostomy. 3 Similarly Mays et al suggested that percutaneous nephrostomy only minimally affected quality of life. 5 Although there is no significant difference in the improving trends among both the groups in regard to Urine output level in our study but there is a significant difference in the post-operative patient outcome in both the groups. After removal of the diversion also the urine output levels remained the same and no variation was found among the patients before and after removal of the diversion as far as urine output was concerned. All these patients also underwent a definitive procedure for removal of the obstructing cause. Similarly there is no significant difference in the improving trends among both the groups when the postoperative creatinine levels are International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3489
5 considered. But a significant difference is found in the pre and post-operative creatinine levels of the patients. When the creatinine levels of patients undergoing PCN and ureteric stenting was compared to the patients who required conversion, the trend of PCN and DJS was shown to be similar also signifying no significant difference among the two procedures but a rising trend is seen in the patients undergoing conversion. Thus patients undergoing DJ stent may initially show improvement but may develop irritative and intolerable lower urinary tract symptoms which may hamper their renal function and cause a deteriorating effect in their outcome. These patients when underwent secondary PCN with removal of the DJ stents subsequently showed a better response. Although Joshi and colleagues accessed the impact in quality of life caused by temporary urinary diversion and reported no functional or psychosocial difference between double-j catheter and percutaneous nephrostomy in ureteral decompression and it is often presumed that diversion with the ureteral stent is the most suitable method and is more agreeable to the patient present results suggest that though both the procedures are equally efficient for diverting an obstructive urinary tract as shown by urine output and serum creatinine levels on each post-operative day and a significant improvement is seen in patients when urine output and serum creatinine levels are compared pre and postoperatively, patients undergoing PCN have comparatively shown a better outcome and tolerability than patients who underwent DJ stenting. 20 Thus in our opinion the due to the better effectiveness of percutaneous nephrostomy over DJ stenting, PCN should be given preference over ureteral stents. CONCLUSION Diverting an obstructed urinary system improves the overall renal function of the patient. Percutaneous nephrostomy and DJ stenting are the two modalities of treatment. DJ Stenting is associated with 20 % failure rate. Intolerable complications post DJ Stenting may require emergent conversion to secondary Percutaneous nephrostomy. Funding: No funding sources Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee REFERENCES 1. Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: A prospective, multicenter, communitybased study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996;50: Danilovic A, Ioannis M. Antonopoulos. Likelihood of Retrograde Double J Stenting according to ureteral obstructing pathology. International Braz J Urol. 2005;31(5): Mokhmalji H, Braun PM, Martinez Portillo FJ. Percutaneous nephrostomy versus ureteral stents for diversion of hydronephrosis caused by stones: A prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Urol. 2001;166: Fasano JM, Khan SR. Intratubular crystallization of calcium oxalate in the presence of membrane vesicles: An in vitro study. Kidney Int. 2001;59: Wei B, Xu Z, Ruan J, Zhu M, Hu Q, Wang Q, et al. Experience with the Diagnosis and Management of Symptomatic Ureteric Stones During Pregnancy. Urology 2012;79: Tazi K. Percutaneous nephrostomy: indications, techniques and results. Retrospective study of 81 cases: Ann Urol (Paris). 2000;34(6): Yagci C, Ustuner E, Atman ED, Baltaci S, Uzun C, Akyar S. Diuretic agent and normal saline infusion technique for ultrasound-guided percutaneous nephrostomies in nondilated pelvicaliceal systems. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36(2): Van Glabecke E, Conort P, Chartier-Kastler E. Treatment of complicated renal colic in patients treated with indinavir: value of double J stents. Prog Urol. 1999;9: Fowler JE Jr., Meares EM, Goldin AR. Percutaneous nephrostomy: techniques, indications, and results. Urology. 1975;6: Stables DP. Percutaneous nephrostomy: techniques, indications, and results. Urol Clin North Am. 1982;9: Nariculam A. Nephrostomy insertion for patients with bilateral ureteric obstruction caused by prostate cancer: The British Journal of Radiology. 2009;82: Hussain M, Lal M, Ali B, Ahmed S, Zafar N, Naqvi SA, et al. Management of urinary calculi associated with renal failure: Pak Med Assoc. 1995;45(8): Fournier G. Percutaneous drainiage nephrostomy in patients over 70 years of age. Apropos of 98 nephrostomies in 74 patients: Prog Urol. 1994;4(3): Abber JC, Kahn RI. Pyelonephritis from severe incrustations on silicone ureteral stents: management. J Urol. 1983;130: Pollard SG, Macfarlane R. Symptoms arising from Double-J ureteral stents. J Urol. 1988;139: Bregg K, Riehle RA. Morbidity associated with indwelling internal ureteral stents after shock wave lithotripsy. J Urol. 1989;141: Pryor JL, Langley MJ, Jenkins AD. Comparison of symptom characteristics of indwelling ureteral catheters. J Urol. 1991;145: Mardis HK, Kroeger RM. Ureteral stents. Materials. Urol Clin North Am. 1988;15: International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3490
6 19. Mays NB, Petruckevitch A, Snowdon C. Patients quality of life following extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy and percutaneous nephrolithotomy for renal calculi. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1990; 6: Joshi HB, Adams S, Obadeyi OO, Rao PN. Nephrostomy tube or JJ ureteric stent in ureteric obstruction: assessment of patient perspectives using quality-of-life survey and utility analysis. Eur Urol. 2001;39: Cite this article as: Mittal V, Biswas M, Lal S. Percutaneous nephrostomy or double J stenting, which is better modality for obstructive uropathy-a descriptive stud. Int J Res Med Sci 2016;4: International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences August 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 Page 3491
The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.26, No. 1, Mach 2004 The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study Waleed Ali, FRCS* Mohammed Al-Durazi, FRCS** Reem Al-Bareeq,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.26, No. 1, Mach 2004 The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study Waleed Ali, FRCS* Mohammed Al-Durazi, FRCS** Reem Al-Bareeq,
Objectives: To analyze various factors predicting success of retrograde ureteric stenting in managing patients with ureteric obstruction.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
Does the Size of Ureteral Stent Impact Urinary Symptoms and Quality of Life? A Prospective Randomized Study
 European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 673 678 Endourology Does the Size of Ureteral Stent Impact Urinary Symptoms and Quality of Life? A Prospective Randomized Study Rocco Damiano a, *, Riccardo
European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 673 678 Endourology Does the Size of Ureteral Stent Impact Urinary Symptoms and Quality of Life? A Prospective Randomized Study Rocco Damiano a, *, Riccardo
Complication of long indwelling urinary catheter and stent COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT
 151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 42/Sep 08, 2014 Page 10564
 MANAGING LARGE COMPLICATED BILATERAL STAGHORN, URETERIC AND VESICAL CALCULI: IMAGES AND DILEMMAS Ranjith Chaudhary 1, Kulwant Singh 2, Chirag Shanthi Dausage 3, Nidhi Jain 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ranjith
MANAGING LARGE COMPLICATED BILATERAL STAGHORN, URETERIC AND VESICAL CALCULI: IMAGES AND DILEMMAS Ranjith Chaudhary 1, Kulwant Singh 2, Chirag Shanthi Dausage 3, Nidhi Jain 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ranjith
Having a Ureteric Stent What to expect and how to manage
 Service: Urology Having a Ureteric Stent What to expect and how to manage Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction In patients who have, or might have, an obstruction (blockage) of the
Service: Urology Having a Ureteric Stent What to expect and how to manage Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction In patients who have, or might have, an obstruction (blockage) of the
CASE REVIEW. Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications
 CASE REVIEW Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications Youness Ahallal, MD, Abdelhak Khallouk, PhD, Mohammed Jamal El Fassi, PhD, Moulay Hassan Farih, PhD Department of
CASE REVIEW Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications Youness Ahallal, MD, Abdelhak Khallouk, PhD, Mohammed Jamal El Fassi, PhD, Moulay Hassan Farih, PhD Department of
Are there any predictive risk factors for failure of ureteric stent in patients with obstructive urolithiasis with sepsis?
 Original Article - Endourology/Urolithiasis pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Are there any predictive risk factors for failure of ureteric stent in patients with obstructive urolithiasis with sepsis? Siddharth
Original Article - Endourology/Urolithiasis pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Are there any predictive risk factors for failure of ureteric stent in patients with obstructive urolithiasis with sepsis? Siddharth
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 9 (58) No. 2-2016 URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY L. MAXIM 1,2 I.A. BĂNUŢĂ 2 I.
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 9 (58) No. 2-2016 URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY L. MAXIM 1,2 I.A. BĂNUŢĂ 2 I.
Clinical Study Ureteral Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy for Distal Ureteral Stones: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
 Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 892890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/892890 Clinical Study Ureteral Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy for Distal Ureteral Stones: A Randomized,
Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 892890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/892890 Clinical Study Ureteral Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy for Distal Ureteral Stones: A Randomized,
Two cases of retained ureteral stents presenting with breakage and encrustations
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 10:208-212 Two cases of retained ureteral stents presenting with breakage and
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 10:208-212 Two cases of retained ureteral stents presenting with breakage and
Urolithiasis. Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery
 Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study
 Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study J Med Assoc Thai 2017; 100 (Suppl. 3): S174-S178 Full text. e-journal:
Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study J Med Assoc Thai 2017; 100 (Suppl. 3): S174-S178 Full text. e-journal:
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 33/ Apr 23, 2015 Page 5690
 SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTOMY IN INFANTS PRESENTING WITH OBSTRUCTIVE RENAL CALCULI AND ANURIA Yugesh M 1, Pandurangarao K 2, Prasad D. V. S. R. K 3, Srinivas S 4, Sudarshan G 5, Santosh
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTOMY IN INFANTS PRESENTING WITH OBSTRUCTIVE RENAL CALCULI AND ANURIA Yugesh M 1, Pandurangarao K 2, Prasad D. V. S. R. K 3, Srinivas S 4, Sudarshan G 5, Santosh
Manual Replacement of Double J Stent Without Fluoroscopy. Osman Kose, Sacit Nuri Gorgel, Sait Ozbir, Sekan Yenigurbuz, Cengiz Kara
 Int Surg 2015;100:381 385 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00248.1 Manual Replacement of Double J Stent Without Fluoroscopy (Double j stent replacement) Osman Kose, Sacit Nuri Gorgel, Sait Ozbir, Sekan Yenigurbuz,
Int Surg 2015;100:381 385 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00248.1 Manual Replacement of Double J Stent Without Fluoroscopy (Double j stent replacement) Osman Kose, Sacit Nuri Gorgel, Sait Ozbir, Sekan Yenigurbuz,
RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES
 1110-5712 Vol. 20, No. 3, 2014 Egyptian Journal of Urology 121-125 RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES AHMED EL-FEEL, AHMED SAMIR, HESHAM FATHY, OMAR M
1110-5712 Vol. 20, No. 3, 2014 Egyptian Journal of Urology 121-125 RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES AHMED EL-FEEL, AHMED SAMIR, HESHAM FATHY, OMAR M
KIDNEY STONES. When to call for help Call these rooms if any of the following occur:
 KIDNEY STONES Background Kidney stones that move into the ureter (the narrow tube that drains each kidney) often cause a lot of pain. If the stones measure 5mm or less in diameter then most will eventually
KIDNEY STONES Background Kidney stones that move into the ureter (the narrow tube that drains each kidney) often cause a lot of pain. If the stones measure 5mm or less in diameter then most will eventually
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report
 198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
Can the complicated forgotten indwelling ureteric stents be lethal?
 International Urology and Nephrology (2005) 37:541 546 Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11255-004-4704-6 Can the complicated forgotten indwelling ureteric stents be lethal? V. Singh, A. Srinivastava, R. Kapoor
International Urology and Nephrology (2005) 37:541 546 Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11255-004-4704-6 Can the complicated forgotten indwelling ureteric stents be lethal? V. Singh, A. Srinivastava, R. Kapoor
Comparative Study between Slow Shock Wave Lithotripsy and Fast Shock Wave Lithotripsy in the Management of Renal Stone
 Original Article Comparative Study between Slow Shock Wave Lithotripsy and Fast Shock Wave Lithotripsy in the Management of Renal Stone Deb Prosad Paul 1, Debashish Das 2, A S M Zahidur Rahman 3, A K M
Original Article Comparative Study between Slow Shock Wave Lithotripsy and Fast Shock Wave Lithotripsy in the Management of Renal Stone Deb Prosad Paul 1, Debashish Das 2, A S M Zahidur Rahman 3, A K M
ANTIBIOTIC USE DURING ENDOUROLOGIC SURGERY
 ANTIBIOTIC USE DURING ENDOUROLOGIC SURGERY Comprehensive Kidney Stone Center at Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina Glenn M. Preminger LEADING EDGE UROLOGY 49th Annual Duke Urologic Assembly
ANTIBIOTIC USE DURING ENDOUROLOGIC SURGERY Comprehensive Kidney Stone Center at Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina Glenn M. Preminger LEADING EDGE UROLOGY 49th Annual Duke Urologic Assembly
Having a Ureteric Stent: What to expect and how to manage
 Having a Ureteric Stent: What to expect and how to manage This leaflet explains: In patients who have, or might have, an obstruction (blockage) of the kidney, an internal drainage tube called a stent is
Having a Ureteric Stent: What to expect and how to manage This leaflet explains: In patients who have, or might have, an obstruction (blockage) of the kidney, an internal drainage tube called a stent is
90% of bladder tumours are transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), the remaining 10% of cases are squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma and sarcoma.
 The Role of the Interventional Radiologist in Management of Post-Radical Cystectomy Ureteral Obstruction : A Case Review of Retrograde Transileal Conduit Ureteric Stents. Poster No.: C-2288 Congress: ECR
The Role of the Interventional Radiologist in Management of Post-Radical Cystectomy Ureteral Obstruction : A Case Review of Retrograde Transileal Conduit Ureteric Stents. Poster No.: C-2288 Congress: ECR
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy and Laparoscopic Management of Urinary Tract Calculi
 16 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy and Laparoscopic Management of Urinary Tract Calculi Pedro-José López, Michael J. Kellett, and Patrick G. Duffy Urinary calculus in childhood is not common. The incidence
16 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy and Laparoscopic Management of Urinary Tract Calculi Pedro-José López, Michael J. Kellett, and Patrick G. Duffy Urinary calculus in childhood is not common. The incidence
Bilateral Hydronephrosis in Adults: To Do or Not To Do Percutaneous Nephrostomy
 Bilateral Hydronephrosis in Adults: To Do or Not To Do Percutaneous Nephrostomy Poster No.: C-0802 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S.-H. You, D. J. Sung, N. Y. Han, B. J. Park, M.
Bilateral Hydronephrosis in Adults: To Do or Not To Do Percutaneous Nephrostomy Poster No.: C-0802 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S.-H. You, D. J. Sung, N. Y. Han, B. J. Park, M.
Management of Urinary Calculi Associated with Renal Failure
 Management of Urinary Calculi Associated with Renal Failure Pages with reference to book, From 205 To 208 Syed Ali Anwar Naqvi, Syed Adib-ul-Hassan Rizvi ( Sindh Institute of Urology and Transplantation,
Management of Urinary Calculi Associated with Renal Failure Pages with reference to book, From 205 To 208 Syed Ali Anwar Naqvi, Syed Adib-ul-Hassan Rizvi ( Sindh Institute of Urology and Transplantation,
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
Impact of ureteral stenting prior to ureterorenoscopy on stone-free rates and complications
 World J Urol (2013) 31:855 859 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0789-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of ureteral stenting prior to ureterorenoscopy on stone-free rates and complications P. P. Lumma P. Schneider A. Strauss
World J Urol (2013) 31:855 859 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0789-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of ureteral stenting prior to ureterorenoscopy on stone-free rates and complications P. P. Lumma P. Schneider A. Strauss
Obstructive Uropathy in Gynecologic Malignancy and Value of Percutaneous Nephrostomy
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (II) July-December 2015 Obstructive Uropathy in Gynecologic Malignancy and Value of Percutaneous Nephrostomy Pariseema S. Dave *, Bijal M. Patel**, Himanshu
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (II) July-December 2015 Obstructive Uropathy in Gynecologic Malignancy and Value of Percutaneous Nephrostomy Pariseema S. Dave *, Bijal M. Patel**, Himanshu
SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN SAS J. Surg., Volume-1; Issue-3 (Sep-Oct, 2015); p Available online at
 SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-1; Issue-3 (Sep-Oct, 2015); p-80-87 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Research Article Comparison between Double J Ureteral Stenting
SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-1; Issue-3 (Sep-Oct, 2015); p-80-87 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Research Article Comparison between Double J Ureteral Stenting
Comparison of the results of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in different age groups
 International Surgery Journal Borekoglu A et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Dec;5(12):3888-3892 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20185013
International Surgery Journal Borekoglu A et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Dec;5(12):3888-3892 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20185013
Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Bladder Stones
 Human Journals Research Article February 2018 Vol.:11, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Haider A. AbuAlmaali et al. Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Bladder Stones Keywords: Shock Wave Lithotripsy, Bladder
Human Journals Research Article February 2018 Vol.:11, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Haider A. AbuAlmaali et al. Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Bladder Stones Keywords: Shock Wave Lithotripsy, Bladder
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
URINARY TRACT DESOBSTRUCTION IN PATIENTS WITH MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE UTERINE CERVIX. Summary
 Original Article URINARY TRACT DESOBSTRUCTION IN PATIENTS WITH MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE UTERINE CERVIX Nikolay H. Kolev, Alexander Vanov, Vladislav R. Dunev, Rumen P. Kotsev, Boyan A. Stoykov, Fahd Al-Shargabi,
Original Article URINARY TRACT DESOBSTRUCTION IN PATIENTS WITH MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE UTERINE CERVIX Nikolay H. Kolev, Alexander Vanov, Vladislav R. Dunev, Rumen P. Kotsev, Boyan A. Stoykov, Fahd Al-Shargabi,
DAll that you need to know
 DAll that you need to know ouble - J Stenting D.Dalela UroHealth Education Cell UroHealth Research Centre, Lucknow What is a Double-J Stent? Double J (D.J.) Stent is a fine tube made of silicone coated
DAll that you need to know ouble - J Stenting D.Dalela UroHealth Education Cell UroHealth Research Centre, Lucknow What is a Double-J Stent? Double J (D.J.) Stent is a fine tube made of silicone coated
SciFed Journal of Public Health. Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature
 SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
Approach and Management of Obstructive Uropathy
 Approach and Management of Obstructive Uropathy INTRODUCTION One of the most urgent clinical entity need to be diagnosed 1. 10% of the causes of ARF and 4% of CRF 2. Symptoms and signs of obstruction are
Approach and Management of Obstructive Uropathy INTRODUCTION One of the most urgent clinical entity need to be diagnosed 1. 10% of the causes of ARF and 4% of CRF 2. Symptoms and signs of obstruction are
Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case
 Original case report research Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case Kristen McAlpine; Michael J. Leveridge, MD, FRCSC; Darren Beiko, MD, MBA, FRCSC Department
Original case report research Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case Kristen McAlpine; Michael J. Leveridge, MD, FRCSC; Darren Beiko, MD, MBA, FRCSC Department
Original Article Ureteroscopy During Pregnancy with Followthe-Wire ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION PATIENTS AND METHODS. E. R. Tawfiek
 African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 15, No. 4, 2009 245-249 Original Article Ureteroscopy During Pregnancy with Followthe-Wire Technique E. R. Tawfiek Department of Urology, El-Minia University,
African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 15, No. 4, 2009 245-249 Original Article Ureteroscopy During Pregnancy with Followthe-Wire Technique E. R. Tawfiek Department of Urology, El-Minia University,
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
 Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
GU Interventions. Gerant Rivera-Sanfeliz, MD Professor of Radiology
 GU Interventions Gerant Rivera-Sanfeliz, MD Professor of Radiology History of GU Interventions Percutaneous nephrostomy - 1955 Percutaneous stone removal - 1976 Ureteral stent placement late 70 s ESWL
GU Interventions Gerant Rivera-Sanfeliz, MD Professor of Radiology History of GU Interventions Percutaneous nephrostomy - 1955 Percutaneous stone removal - 1976 Ureteral stent placement late 70 s ESWL
Challenges in Stone Management of Complex Patients
 Challenges in Stone Management of Complex Patients Eugene Minevich, MD Professor, Division of Pediatric Urology Director, Stone Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital, Cincinnati, USA Financial and Other
Challenges in Stone Management of Complex Patients Eugene Minevich, MD Professor, Division of Pediatric Urology Director, Stone Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital, Cincinnati, USA Financial and Other
Continuous Bladder Irrigation
 Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
이학종분당서울대학교병원. Ultrasound in Urinary Colic
 이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
Case Presentation - Pediatric Endourology
 Case Presentation - Pediatric Endourology PA N E L : E U G ENE M I N EV I C H, U S A J O NAT H A N G L A S S, UK R OY M O R AG, I S R A E L YO R A M M O R, I S R A E L P I N C H AS L I V N E, I S R A E
Case Presentation - Pediatric Endourology PA N E L : E U G ENE M I N EV I C H, U S A J O NAT H A N G L A S S, UK R OY M O R AG, I S R A E L YO R A M M O R, I S R A E L P I N C H AS L I V N E, I S R A E
Esam M. Riad, Mamdouh Roshdy, Mohamed A. Ismail, Tarek R. El-Leithy, Samir EL. Ghoubashy, Hosam El Ganzoury, Ahmed G. El Baz and Ahmed I.
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2(3): 672-676, 2008 ISSN 1991-8178 Extracorporeal Shock wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) Versus Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in the Eradication of Persistent
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2(3): 672-676, 2008 ISSN 1991-8178 Extracorporeal Shock wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) Versus Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in the Eradication of Persistent
RATIONALE: The organs making up the urinary system consist of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
 Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Urolithiasis. Kyong Tae Moon, Hee Ju Cho, Jeong Man Cho, Jeong Yoon Kang, Tag Keun Yoo, Hong Sang Moon 1, Seung Wook Lee 1
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.10.698 Urolithiasis Comparison of an Indwelling Period Following Ureteroscopic Removal of Stones between Double-J Stents and Open-Ended Catheters:
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.10.698 Urolithiasis Comparison of an Indwelling Period Following Ureteroscopic Removal of Stones between Double-J Stents and Open-Ended Catheters:
Treatment of Kidney and Ureteral Stones
 Patient Information English 3 Treatment of Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. You have been diagnosed with a kidney or ureteral stone. This leaflet describes the
Patient Information English 3 Treatment of Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. You have been diagnosed with a kidney or ureteral stone. This leaflet describes the
Forgotten JJ stent: A rare case report
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(2):6-10 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.201529390 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Forgotten
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(2):6-10 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.201529390 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Forgotten
Information for Patients
 Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTOMY
 PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport Tel: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside Tel: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport Tel: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside Tel: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Endoscopic Versus Open Surgical Techniques in the Management of Renal and Ureteric Calculi
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 2 Ver. 5 February. (2018), PP 07-13 www.iosrjournals.org Endoscopic Versus Open Surgical Techniques
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 2 Ver. 5 February. (2018), PP 07-13 www.iosrjournals.org Endoscopic Versus Open Surgical Techniques
MA HOSSAIN. Summary: Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011
 Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011 Comparative Study of Stone Pulverization and Clearance Rate between Patients Treated by ESWL Under Spinal Anesthesia
Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011 Comparative Study of Stone Pulverization and Clearance Rate between Patients Treated by ESWL Under Spinal Anesthesia
Cystitis cystica is a rare chronic reactive inflammatory
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province
 Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province Bingqian Liu *, Yudong Wu, Jinxing Wei, Jianguang Gao Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,
Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province Bingqian Liu *, Yudong Wu, Jinxing Wei, Jianguang Gao Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1
 Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Solo Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Management of Upper Ureteral Calculi With Hydronephrosis
 Endourology and Stone Disease Solo Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Management of Upper Ureteral Calculi With Sushant Wadhera, Rajkumar K Mathur, Sudershan Odiya, Ram Sharan Raikwar, Govindaiyah
Endourology and Stone Disease Solo Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Management of Upper Ureteral Calculi With Sushant Wadhera, Rajkumar K Mathur, Sudershan Odiya, Ram Sharan Raikwar, Govindaiyah
Obstructive Nephropathy
 Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Open Stone Surgery: Is it Still a Preferable Procedure in the Management of Staghom Calculi?*
 International Urolog-v and Nephrology 26 (3). pp. 27-253 (199) Open Stone Surgery: Is it Still a Preferable Procedure in the Management of Staghom Calculi?* A. A. ESEN, Z. KIRKALI, C. GOLER Department
International Urolog-v and Nephrology 26 (3). pp. 27-253 (199) Open Stone Surgery: Is it Still a Preferable Procedure in the Management of Staghom Calculi?* A. A. ESEN, Z. KIRKALI, C. GOLER Department
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery
 Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones: our experience
 Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Setting The setting was secondary care. The economic study was carried out in the USA.
 Prospective randomized trial comparing shock wave lithotripsy and ureteroscopy for management of distal ureteral calculi Pearle M S, Nadler R, Bercowsky E, Chen C, Dunn M, Figenshau R S, Hoenig D M, McDougall
Prospective randomized trial comparing shock wave lithotripsy and ureteroscopy for management of distal ureteral calculi Pearle M S, Nadler R, Bercowsky E, Chen C, Dunn M, Figenshau R S, Hoenig D M, McDougall
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/411 Role of Non-contrast Computed Tomography - Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder in Predicting the Stone Fragility and Extracorporeal
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/411 Role of Non-contrast Computed Tomography - Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder in Predicting the Stone Fragility and Extracorporeal
Clinical Study Clinical Profile and Outcome of Conservatively Managed Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 931982, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2012/931982 Clinical Study Clinical Profile and Outcome of Conservatively Managed Emphysematous
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 931982, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2012/931982 Clinical Study Clinical Profile and Outcome of Conservatively Managed Emphysematous
Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A New Concern for Urologists?
 ARC Journal of Urology Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online):2456-060X http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-060x.0301001 www.arcjournals.org Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A
ARC Journal of Urology Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online):2456-060X http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-060x.0301001 www.arcjournals.org Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM
 DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
Lithotripsy for Kidney Stones
 Lithotripsy for Kidney Stones Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Lithotripsy for Kidney Stones Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome
 Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Treatment of Steinstrasse by Transureteral Lithotripsy
 Endourology and Stone Disease Treatment of Steinstrasse by Transureteral Lithotripsy Sayed Mohammad Reza Rabbani Keywords: urinary calculi, complications, steinstrasse, ureteroscopy, shock wave lithotripsy
Endourology and Stone Disease Treatment of Steinstrasse by Transureteral Lithotripsy Sayed Mohammad Reza Rabbani Keywords: urinary calculi, complications, steinstrasse, ureteroscopy, shock wave lithotripsy
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
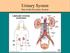 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Preface. Prasad P. Godbole. vii
 Preface Pediatric urology has rapidly developed as a separate subspeciality in the last decade. During this time, significant advances in technology and instrumentation have meant that more procedures
Preface Pediatric urology has rapidly developed as a separate subspeciality in the last decade. During this time, significant advances in technology and instrumentation have meant that more procedures
EFFICACY OF PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROSTOMY FOR MANAGEMENT OF PYONEPHROSIS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFICACY OF PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROSTOMY FOR MANAGEMENT OF PYONEPHROSIS Muhammad Naeem 1, Faiz ur Rahman 2, Anayat Ullah 3, Tariq Ahmad 4, Liaqat Ali 5, Hazrat Ullah 6 ABSTRACT Objective:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFICACY OF PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROSTOMY FOR MANAGEMENT OF PYONEPHROSIS Muhammad Naeem 1, Faiz ur Rahman 2, Anayat Ullah 3, Tariq Ahmad 4, Liaqat Ali 5, Hazrat Ullah 6 ABSTRACT Objective:
In Situ Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) and ESWL after Push Back For Upper Ureteric Calculi: A Comparative Study
 ISSN: 2091-2331 (PRINT) 2091-234X (ONLINE) Original Article Journal of Nobel Medical College Available Online: www.nepjol.info, www.nobelmedicalcollege.com.np Volume 6, Number 1, Issue 10, January-June
ISSN: 2091-2331 (PRINT) 2091-234X (ONLINE) Original Article Journal of Nobel Medical College Available Online: www.nepjol.info, www.nobelmedicalcollege.com.np Volume 6, Number 1, Issue 10, January-June
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v7i4.97 Study of Efficacy of the Conservative and Surgical Management
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v7i4.97 Study of Efficacy of the Conservative and Surgical Management
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Indications and Complications of Indwelling U reteral Stents (DJS)
 Proceedi1t[;S.Z.P.G.M.. vol: 17(1): pp. 13-17, 2003. ndications and Complications of ndwelling U reteral Stents (DJS) Khalid Jamil, Shamim Hashim, Muhammad Usman Khan Department of Urology, Shaikh Zayed
Proceedi1t[;S.Z.P.G.M.. vol: 17(1): pp. 13-17, 2003. ndications and Complications of ndwelling U reteral Stents (DJS) Khalid Jamil, Shamim Hashim, Muhammad Usman Khan Department of Urology, Shaikh Zayed
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide
 2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 20: Urology CPT Changes: Key Into Guideline Updates for Successful Procedure Coding in 2017 Plus: New coding tips also will help keep you on track.
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 20: Urology CPT Changes: Key Into Guideline Updates for Successful Procedure Coding in 2017 Plus: New coding tips also will help keep you on track.
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS. Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital
 URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist
 The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
Urological Procedure Coding
 Urological Procedure Coding AAPC Annual Conference April 6, 2011 Long Beach, California Objectives Understand anatomy and CPT procedural terminology related to urological procedures Recognize and code
Urological Procedure Coding AAPC Annual Conference April 6, 2011 Long Beach, California Objectives Understand anatomy and CPT procedural terminology related to urological procedures Recognize and code
Caring for a Nephrostomy and what is Ureteric Stenting
 Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
Effect of Tamsulosin on Stone Clearance after Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
 Orginal Article Effect of Tamsulosin on Stone Clearance after Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy M Z Hossain 1, N P Biswas 2, M S Islam 3, M Z Hossain 4, I A Shameem 5, S Kibria 6 Abstract This prospective
Orginal Article Effect of Tamsulosin on Stone Clearance after Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy M Z Hossain 1, N P Biswas 2, M S Islam 3, M Z Hossain 4, I A Shameem 5, S Kibria 6 Abstract This prospective
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Ureteroscopic and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Rather Large Renal Pelvis Calculi
 Endourology and Stone Disease Ureteroscopic and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Rather Large Renal Pelvis Calculi Kamyar Tavakkoli Tabasi, Mehri Baghban Haghighi Introduction: The aim of this
Endourology and Stone Disease Ureteroscopic and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Rather Large Renal Pelvis Calculi Kamyar Tavakkoli Tabasi, Mehri Baghban Haghighi Introduction: The aim of this
An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL. Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH)
 An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH) What is ESWL? ESWL Machine Body Stone Renal Stone Incidence rate in HK population
An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH) What is ESWL? ESWL Machine Body Stone Renal Stone Incidence rate in HK population
Nephrostomy insertion for patients with bilateral ureteric obstruction caused by prostate cancer
 The British Journal of Radiology, 82 (2009), 571 576 Nephrostomy insertion for patients with bilateral ureteric obstruction caused by prostate cancer 1 J NARICULAM, MBBS, MRCS, 2 D G MURPHY, MBBS, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 82 (2009), 571 576 Nephrostomy insertion for patients with bilateral ureteric obstruction caused by prostate cancer 1 J NARICULAM, MBBS, MRCS, 2 D G MURPHY, MBBS, MD,
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY
 INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
Prevention of Important HAIs: Principle & Case Scenario in VAP/CAUTI. CPT. Pasri Maharom MD, MPH Dec 15, 2015
 Prevention of Important HAIs: Principle & Case Scenario in VAP/CAUTI CPT. Pasri Maharom MD, MPH Dec 15, 2015 Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI CAUTI Epidemiology Key Principles of Preventing
Prevention of Important HAIs: Principle & Case Scenario in VAP/CAUTI CPT. Pasri Maharom MD, MPH Dec 15, 2015 Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI CAUTI Epidemiology Key Principles of Preventing
european urology 50 (2006)
 european urology 50 (2006) 1073 1078 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Nephrovesical Subcutaneous Ureteric Bypass: Long-term Results in
european urology 50 (2006) 1073 1078 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Nephrovesical Subcutaneous Ureteric Bypass: Long-term Results in
Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Nephrostomy, Feasibility in Lateral Position
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1580-1586 Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Nephrostomy, Feasibility in Lateral Position Ayman F. Alham, Mohamed A. Hindawy, Sayed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1580-1586 Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Nephrostomy, Feasibility in Lateral Position Ayman F. Alham, Mohamed A. Hindawy, Sayed
Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy
 CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
