RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Interpretations
|
|
|
- Loreen Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
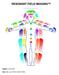
1 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Interpretations Subject: XYZ Investigator: Nishant Date: Tue Nov 20 02:28:18 IST 2012 Session Notes: Sample report RFI is designed only for use in health psychology and collaborative health care, to provide data relating client psychology to health conditions, and to alert non-medical professionals when a referral should be made. The technology is not intended for any medical diagnosis. PSYCHOLOGICAL LEVEL INTERPRETATIONS The Psychological (Emotional) Level of the human bioenergy field, radiating 4-18 inches from the physical body, is highly characterized by the emotional and psychological conditions and attributes of the subject. Left Psychological Level Analysis - Environmental Influences
2 The left side of the Psychological Level, connected to the right hemisphere of the brain, reveals how the subject experiences or perceives the world, or which energies the person is receiving from his or her social environment. Left body bioenergies generally consist of energy-information imprints from predominant energies in a person's environment, to which the person is the most strongly or frequently exposed. This may also indicate a propensity or tendency to receive and absorb the detected energies, or an inherent sensitivity to such energies. The left hand is the primary channel for inflow of electrofield energy through the ulnar and radial nerves, so it is the most significant for revealing the subject's environmental influences and perceptions. Distribution of bioenergies detected in the Left Psychological Level: Orange: 25%; Gold: 12.5%; Yellow: 12.5%; Black: 12.5%; Purple: 12.5%; Orchid: 25% Based on the bioenergy frequencies measured, the following descriptions characterize the nature of the energies you are receiving from others and the environment: Orange: You are receiving energies characterized by comfort, healing and vitality from others or the environment. Yellow: You are within an environment in which the energies are generally stable and peaceful. Such energies may be produced by people or other things around you. Purple: You are in an environment characterized by clear thoughts, beliefs or intellect, such as an academic setting. Such energies are generally stable. Gold: You are receiving an abundance of uninhibited healing energies from people or things in your environment. Black: Your ability to receive life-enhancing energies is diminished within the region(s) determined to be black. Such a condition may produce stress on the physical body. Subsequent measurements are recommended for verification of this condition. If this condition persists, it is recommended that a mental health professional be consulted, particularly one with an understanding of metaphysical sciences. Orchid: Your environment is one characterized by truth, clarity, spirituality, and higher levels of being. Such environments are conducive to psychic work and creativity. Right Psychological Level Analysis - Behavioral Patterns The right side of the body, connected to the left hemisphere of the brain, reveals how the subject interacts socially, or which bioenergies the person contributes or transmits back into their environment. Right body bioenergies generally influence the way others perceive and respond to the subject. They indicate the subject 's current reactions to present situations, and predominant habits or behaviors for interacting with his or her environment. The right hand is the primary channel for outflow of electrofield energy through the ulnar and radial nerves, so it is the most significant for revealing the subject's reactions and behavioral patterns. Distribution of bioenergies detected in the Right Psychological Level: Rose: 12.5%; Yellow: 12.5%; Green: 12.5%; Cyan: 25%; Black: 12.5%; Blue: 12.5%; Silver: 12.5% Based on the bioenergy frequencies measured, the following descriptions characterize the nature of the energies you are projecting to others and the environment: Yellow: You project thoughts of happiness and well being toward others. You also project a desire for emotional stability. You attempt to live and operate within a framework that is comfortable, and may be cautious in personal matters. Green: You are experiencing an emotional release, often in the form of love in personal relationships. You apply creativity in work and personal matters. Blue: You are a strong communicator. Others are easily influenced by your thoughts, words, and actions. You also display a heightened sensitivity to and understanding of other's needs.
3 Rose: You express desires for physical and sensual enjoyment. You project thoughts of fun and entertainment and for being in the presence of others. Cyan: You are a sensitive, empathetic person who expresses emotions as a form of communication. Black: You are experiencing an energetic blockage in the expression of thoughts or desires. This blockage may be due to a number of reasons, including repression of past events, insecurities or fears. Silver: You are conveying protective and stabile energies to others and the environment. You seek peace and emotional balance in your life. You may also be shielding yourself against emotional harm. Cerebral Bioenergy Analysis - Predominant Thoughts The regions of bioelectrical field around the head consist of electromagnetic brain waves. The left head (on right side of chart) shows left brain activity, the right head (on the left side of the chart) shows right brain activity, and the regions on the top of the head show integrated brain activity. The brain waves in these cerebral regions reveal inherent characteristics of the person, particularly their predominant thoughts and mental preoccupations. Distribution of detected bioenergies within the Cerebral Regions: Red: 20%; Orange: 40%; Yellow: 20%; Cyan: 20% Red - Material and Physical focus. Indicates mental activity related to material self-gratification, accomplishment of material goals and ambitions. Subject's thoughts may involve power and status, desire for attention and acceptance from others, indulgence or luxury items. Orange - Emotional Healing. Mental activity is related to resolving emotional issues, recovering from intense life experiences, and overcoming obstacles. Generally healthy, but psychological support and psychotherapy are highly likely to be greatly beneficial. Yellow - Happiness and well-being, with a healthy measure of balanced caution. Cyan - Emotional energy. Subject exhibits empathy and sensitivity to emotions of others, and is likely to be communicating or expressing their own emotions, either consciously or subconsciously. Chakra Bioenergy Analysis - Personal Characteristics The Chakras are bioenergy vortexes located at fixed points along the spinal column, which radiate energy-information related to the activity of corresponding endocrine glands. In accordance with the known functions of the endocrine glands, each Chakra represents a category, or sphere, of the subject's life. The color of bioenergy found in each Chakra reveals events and conditions in that category of the person's life. The color Black (related to energy voids or blockages) in the Base Chakra means that you may be experiencing an identity crisis or a void in the expression of your sexuality. The color Silver (related to protective energies) in the Sacral Chakra means that an issue concerning protection or security needs to be, or is now being, healed or resolved. The color Silver (related to protective energies) in the Solar Plexus Chakra means that the way you handle stress and your state of mind is generally a function of how well protected and secure you feel. The color Green (related to emotional energy) in the Heart Chakra means that there is a healthy flow of emotional energy, often love, moving through your system. The color Orange (related to emotional healing) in the Throat Chakra means that you have the ability to promote the emotional healing of yourself and others through your communication skills.
4 The color Orchid (related to truth and spirituality) in the Third Eye Chakra means that your mental and psychic capacities are primarily focused on the acquisition and understanding of truth in all endeavors. The color Blue (related to communication and openness) in the Crown Chakra means that your highest purpose and predominant spiritual priorities involve the experience of communication with yourself and others. HEALTH LEVEL INTERPRETATIONS Physiological Analysis The Health level of the human bioenergy field, radiating 0-4 from the physical body, consists of electromagnetic resonance from neurological activity originating in the brain, combined with electromagnetic field energy transmitted from the various areas of the body. The colors of bioenergy detected in each region of the body reveal information about conditions in the specific region where each color is found. Distribution of detected bioenergies within the Health Level: Red: 29.4%; Orange: 5.9%; Gold: 17.6%; Yellow: 5.9%; Cyan: 5.9%; Black: 5.9%; Blue: 11.8%; Navy: 17.6% Orange - Healing energy is currently acting upon the effected area. Immune system activity, and recovery. Generally unhealthy at the moment, but positive prognosis, and making progress towards becoming healthy. Gold - Healing energy is emanating from an area which is already vital and healthy. This excess of healing energy projects outward to contribute healthy and healing energy to the environment, and other people, animals, plants and objects which come in contact with this bioenergy. Yellow - Vitality, Neurological activity. Generally healthy. Cyan - Comfort and healthy biological activity in the circulatory systems, including blood circulation, respiratory, and lymphatic systems, and any fluid generating systems in the area of the bioenergy. Generally healthy. Black - Overstimulation and stress of biological systems, organs or circulatory systems. Bioenergy in effected area is being used up or demanded by an environmental, behavioral or dietary situation, or a biological condition. Generally unhealthy, especially if this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time. May be healthy in the sense of an appropriate adaptation and coping mechanism, if the presence of this bioenergy is temporary. Blue - Soothing energy or stimulus is currently acting upon the effected area. Related to physical comfort, relaxation or resting of muscles or organs. Generally healthy. Navy - Increased biological activity. Could be current functioning of metabolic systems, or certain organs or circulatory systems currently exerting extra effort. Generally healthy, unless this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time.
5 Endocrine System Analysis The Chakras are bioenergy vortexes located at fixed points along the spinal column, which radiate energy-information related to the activity of corresponding endocrine glands. Accordingly, they indicate which bioenergies are currently emanating from, influencing, or acting upon the corresponding endocrine glands. The Base Chakra, located in the genital area, is related to the bioenergy information in the Ovaries and Testes. Black - Overstimulation and stress of biological systems, organs or circulatory systems. Bioenergy in effected area is being used up or demanded by an environmental, behavioral or dietary situation, or a biological condition. Generally unhealthy, especially if this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time. May be healthy in the sense of an appropriate adaptation and coping mechanism, if the presence of this bioenergy is temporary. The Sacral Chakra, located above the genital area just below the navel, is related to bioenergy in the Adrenal Medulla, which stimulates the immune system with the adrenocorticotropic hormone. Silver - Strength, stability, and endurance in the area of the body where this bioenergy is located. Generally healthy. The Solar Plexus Chakra, located around the navel, is related to the bioenergy in the Islet of the Pancreas, which stimulates the nervous system with insulin. Silver - Strength, stability, and endurance in the area of the body where this bioenergy is located. Generally healthy. The Heart Chakra, located at the center of the chest in the heart area, is related to bioenergy in the Adrenal Cortex and the Thyroid, which stimulates biological manifestations of emotion with thyroxin, and the Anterior Pituitary, which triggers hormone secretion in the whole endocrine system. Green - The effected area is currently experiencing either a state of increased blood circulation, or a situation where healthy neurological activity is causing an increase in blood circulation from an inhibited, unhealthy level, up to a healthy level. The Throat Chakra, located at the center of the throat, is related to bioenergy in the Thyroid and Parathyroid glands. Orange - Healing energy is currently acting upon the effected area. Immune system activity, and recovery. Generally unhealthy at the moment, but positive prognosis, and making progress towards becoming healthy. The Third Eye Chakra, located on the center of the forehead between the eyebrows, is related to bioenergy in the Pineal Body of the brain, both an electromagnetic sensory organ and a gland which produces melatonin. Orchid - There is a clear and direct Mind-Body connection to the area of this bioenergy. The person has a positive and pleasant psychological association with the part of the body where this bioenergy is located. Events, actions, and therapies involving this area are highly likely to have a significant psychological impact upon the person. Also indicates that mental activity is currently influencing and controlling biological activity and physical health in this area. Generally healthy. The Crown Chakra, located directly above the head, is related to bioenergy in the Anterior Pituitary gland, which controls the endocrine system. Blue - Soothing energy or stimulus is currently acting upon the effected area. Related to physical comfort, relaxation or resting of muscles or organs. Generally healthy.
6 ENERGY FIELD SCORES Physical Health Score The Physical Health Score is derived from the use of an experimental equation that calculates a person's probable physical health based on the distribution of colors within the physiological health level of the energy field. This is not a diagnostic parameter and should not be represented as such. ITEM makes no claims as to the validity of this score and shall not be held liable for any misuse or misrepresentation. It is provided as a guide for more in-depth analyses. If in your opinion or experience the score does not represent a person's actual overall health conditions, please disregard it. Based on the frequency measurements, your Physical Health Score is 51 (out of a possible 100). You are experiencing moderate overall physical health at this time. Follow up analysis and medical attention is recommended. Mental/Emotional Health Score The Mental/Emotional Health Score is derived from the use of an experimental equation that calculates a person's probable mental and emotional health based on the difference in energy flowing in to the person's energy field and the energy being transmitted outward. This score is based on the theory that a person's ability to process incoming energies and increase their rate of energyinformation exchange can be correlated to the person's mental and emotional well-being. This is not a diagnostic parameter and should not be represented as such. ITEM makes no claim as to the validity of this score and shall not be held liable for any misuse or misrepresentation. It is provided as a guide for more in-depth analyses. If in your opinion or experience the score does not represent a person's actual overall health conditions, please disregard it. Based on the frequency measurements, your Mental/Emotional Health Score is 65 (out of a possible 100). You are experiencing good overall mental/emotional health at this time. Energy Field Stability Score The Energy Field Stability Score is an empirical indicator of how stable or how dynamic a person's energy field is. There are no "good" or "bad" scores. The score takes into account the coefficient of variation for all 40 regions measured in a full-body scan, as well as the difference in mean frequency between the left and right sides of the Psychological Level. A high stability score generally means that a person has a calm, stable demeanor or personality, and a low stability score generally means that a person has a dynamic demeanor or personality. A variable that must also be considered is the nature of the environment where measurements are taken. In a dynamic environment such as a health fair with numerous people in the area, stability scores will likely be lower than a more stable environment such as a cabin in the mountains. Based on the frequency measurements, your Energy Field Stability Score is 30 (out of a possible 100). Your energy field exhibits a moderate degree of variation at this time. This could be a function of the environment you are presently in, of your personality (dynamic), or of the way you tend to process the energies you receive and transmit them back to others and the environment.
7 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Brain Image Interpretations Subject: XYZ Investigator: Nishant Date: Tue Nov 20 02:28:18 IST 2012 Session Notes: Sample report RFI is designed only for use in health psychology and collaborative health care, to provide data relating client psychology to health conditions, and to alert non-medical professionals when a referral should be made. The technology is not intended for any medical diagnosis. INTERNAL BRAIN IMAGE The human brain is neurologically connected to all parts of the human body, receiving bioenergy information from the various biological and bioenergy systems, and often transmitting bioenergy which can influence those systems. The internal brain image generated by RFI shows and identifies the bioenergies which are currently present in specific parts of the brain. The bioenergies in the brain itself can influence the body, other parts of the brain, or aspects of the subject's psychology, through various energy-information exchange processes.
8 R1) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Lower Left Leg. R2) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Upper Left Leg. Gold - Healing energy is emanating from an area which is already vital and healthy. This excess of healing energy projects outward to contribute healthy and healing energy to the environment, and other people, animals, plants and objects which come in contact with this bioenergy. R3) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Left Torso. Black - Overstimulation and stress of biological systems, organs or circulatory systems. Bioenergy in effected area is being used up or demanded by an environmental, behavioral or dietary situation, or a biological condition. Generally unhealthy, especially if this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time. May be healthy in the sense of an appropriate adaptation and coping mechanism, if the presence of this bioenergy is temporary. R4) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Upper Left Arm. Gold - Healing energy is emanating from an area which is already vital and healthy. This excess of healing energy projects outward to contribute healthy and healing energy to the environment, and other people, animals, plants and objects which come in contact with this bioenergy. R5) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Lower Left Arm. R6) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Left Hand. R7) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Left Neck and Shoulder. Yellow - Vitality, Neurological activity. Generally healthy. R8) Prefrontal Cortex - region controlling cognitive functions and information processing, related to Dopamine which balances and controls the speed of information processing. Contains energy information which is transmitted as brain waves. L1) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Lower Right Leg. Gold - Healing energy is emanating from an area which is already vital and healthy. This excess of healing energy projects outward to contribute healthy and healing energy to the environment, and other people, animals, plants and objects which come in contact with this bioenergy. L2) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Upper Right Leg. Navy - Increased biological activity. Could be current functioning of metabolic systems, or certain organs or circulatory systems currently exerting extra effort. Generally healthy, unless this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time.
9 L3) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Right Torso. Blue - Soothing energy or stimulus is currently acting upon the effected area. Related to physical comfort, relaxation or resting of muscles or organs. Generally healthy. L4) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Upper Right Arm. Navy - Increased biological activity. Could be current functioning of metabolic systems, or certain organs or circulatory systems currently exerting extra effort. Generally healthy, unless this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time. L5) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Lower Right Arm. L6) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Right Hand. Blue - Soothing energy or stimulus is currently acting upon the effected area. Related to physical comfort, relaxation or resting of muscles or organs. Generally healthy. L7) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Right Neck and Shoulder. Navy - Increased biological activity. Could be current functioning of metabolic systems, or certain organs or circulatory systems currently exerting extra effort. Generally healthy, unless this bioenergy appears in the same area for extended periods of time. L8) Prefrontal Cortex - region controlling cognitive functions and information processing, related to Dopamine which balances and controls the speed of information processing. Contains energy information which is transmitted as brain waves. Orange - Healing energy is currently acting upon the effected area. Immune system activity, and recovery. Generally unhealthy at the moment, but positive prognosis, and making progress towards becoming healthy. I9) Cerebral Cortex - region of motor control for the Throat. Orange - Emotional Healing. Mental activity is related to resolving emotional issues, recovering from intense life experiences, and overcoming obstacles. Generally healthy, but psychological support and psychotherapy are highly likely to be greatly beneficial. I10) Visual Cortex - region of the brain which receives visual information from the optic nerves, and processes visual information, including mental imagery. Orchid - Clarity of thought, psychic activity, understanding of truth. Subject may be currently participating in energy information exchange. I11) Cerebellum - structure of the brain controlling the nervous system. Silver - Protection, shielding from destructive energies, emotional balance, peacefulness, and stability. I12) Pineal Body - organ of the brain which transmits and receives electromagnetic waves, and regulates the hormone Melatonin. Orchid - Clarity of thought, psychic activity, understanding of truth. Subject may be currently participating in energy information exchange.
10 I13) Pituitary Gland - organ of the brain related to kidney and urinary functions, reproductive systems, and regulation of hormone secretion throughout the endocrine system. Blue - Communication, perspective of reality, search for and expression of truth. Open-minded communication with good intentions. I14) Limbic System - region of the brain systems for emotional control, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, and hippocampus, regulating Serotonin and Dopamine. Green - Emotional energy, love and caring, can also be negative emotion or trauma. Subject is experiencing some emotional event or situation. I15) Parietal Lobe - region controlling memory, perception, and self-awareness, contains energy information which is transmitted as brain waves. Cyan - Comfort and healthy biological activity in the circulatory systems, including blood circulation, respiratory, and lymphatic systems, and any fluid generating systems in the area of the bioenergy. Generally healthy. BRAIN SYNCHRONIZATION The electrical activity of the left hemisphere of the brain has been characterized by a frequency measurement of 247 MHz. The electrical activity of the right hemisphere of the brain has been characterized by a frequency measurement of 214 MHz. The left hemisphere is experiencing greater electrical activity than the right hemisphere, indicating a possible imbalance.
RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Interpretations
 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Interpretations Subject: Megha Investigator: Nishant Sharma Date: Mon Dec 17 12:14:32 IST 2012 Session Notes: Practices Reiki healing daily RFI is designed
RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Interpretations Subject: Megha Investigator: Nishant Sharma Date: Mon Dec 17 12:14:32 IST 2012 Session Notes: Practices Reiki healing daily RFI is designed
RESONANT FIELD IMAGING
 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Subject: John Smith Date: Mon Jun 07 20:01:32 EST 2004 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Date: Mon Jun 07 20:01:32 EST 2004 Subject: John Smith Investigator: Mike Jones
RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Subject: John Smith Date: Mon Jun 07 20:01:32 EST 2004 RESONANT FIELD IMAGING Bioenergy Field Image Date: Mon Jun 07 20:01:32 EST 2004 Subject: John Smith Investigator: Mike Jones
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
SLHS1402 The Talking Brain
 SLHS1402 The Talking Brain What are neuroscience core concepts? Neuroscience Core Concepts offer fundamental principles that one should know about the brain and nervous system, the most complex living
SLHS1402 The Talking Brain What are neuroscience core concepts? Neuroscience Core Concepts offer fundamental principles that one should know about the brain and nervous system, the most complex living
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Class X: Biology. Chapter 2: Control and coordination.
 Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Neurology and Trauma: Impact and Treatment Implications Damien Dowd, M.A. & Jocelyn Proulx, Ph.D.
 Neurology and Trauma: Impact and Treatment Implications Damien Dowd, M.A. & Jocelyn Proulx, Ph.D. Neurological Response to a Stressor Information from the senses goes to the thalamus which sends the information
Neurology and Trauma: Impact and Treatment Implications Damien Dowd, M.A. & Jocelyn Proulx, Ph.D. Neurological Response to a Stressor Information from the senses goes to the thalamus which sends the information
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
RESEARCH FORM CLIENT #: NELSP
 RESEARCH FORM DATE: NOVEMBER 10/08 AGE: 55 FEMALE X CITY: STATE/PROVINCE: FAVORITE COLOUR: LEAST FAVORITE COLOUR: SENSITIVITIES/ALLERGIES: MEDICAL HISTORY: TIME: CLIENT #: NELSP MEDICATIONS TAKEN: ACHES/PAINS:
RESEARCH FORM DATE: NOVEMBER 10/08 AGE: 55 FEMALE X CITY: STATE/PROVINCE: FAVORITE COLOUR: LEAST FAVORITE COLOUR: SENSITIVITIES/ALLERGIES: MEDICAL HISTORY: TIME: CLIENT #: NELSP MEDICATIONS TAKEN: ACHES/PAINS:
Stress Releasing Technique Healing (Adrenal Support Healing)
 Stress Releasing Technique Healing (Adrenal Support Healing) This healing supports the system by reducing negative stress and resetting the adrenal glands from the constant state of firing and the flight/flight
Stress Releasing Technique Healing (Adrenal Support Healing) This healing supports the system by reducing negative stress and resetting the adrenal glands from the constant state of firing and the flight/flight
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Model 3-50B or 3-88 III VIII. Olfactory Nerve. Optic Nerve. Oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Trigeminal Nerve. Abducens Nerve.
 Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Sentelligent Medical Intuitive Body Scan
 Sentelligent Medical Intuitive Body Scan 1 1) Ask for presenting symptoms. Get clear channel and set sacred space. 2) Ask if any resistance or interference. 3) Ask Source to provide information only on
Sentelligent Medical Intuitive Body Scan 1 1) Ask for presenting symptoms. Get clear channel and set sacred space. 2) Ask if any resistance or interference. 3) Ask Source to provide information only on
Complete Reflexology for Life by Barbara & Kevin Kunz (2009)
 Complete Reflexology for Life by Barbara & Kevin Kunz (2009) CLASS: G540 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer,
Complete Reflexology for Life by Barbara & Kevin Kunz (2009) CLASS: G540 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer,
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
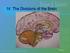 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9)
 NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
The Five Tibetan Rites: Exercises for Healing, Rejuvenation, and Longevity
 The Five Tibetan Rites: Exercises for Healing, Rejuvenation, and Longevity Potential Benefits of the Five Rites Examples of the benefits of the "Five Tibetan Rites" including the following: looking much
The Five Tibetan Rites: Exercises for Healing, Rejuvenation, and Longevity Potential Benefits of the Five Rites Examples of the benefits of the "Five Tibetan Rites" including the following: looking much
Name Group. 8. Growth 9. Insulin 10. Iodine 11. Manufactures 12. Nervous system 13. Neuron 14. Neurotransmitter
 THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name Group 0. Translate all these words 1. Adrenaline 2. Brain 3. Cerebellum 4. Cerebrum 5. Dendrite 6. Dwarfism 7. Goiter 8. Growth 9. Insulin 10. Iodine 11. Manufactures
THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name Group 0. Translate all these words 1. Adrenaline 2. Brain 3. Cerebellum 4. Cerebrum 5. Dendrite 6. Dwarfism 7. Goiter 8. Growth 9. Insulin 10. Iodine 11. Manufactures
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
by Dr. Steve G. Jones Statbrook Associates
 Radiant Health by Dr. Steve G. Jones Radiant Health Hypnosis Script By Dr. Steve G. Jones And as you continue relaxing deeper and deeper and more deeply relaxed, I would like you to imagine your body to
Radiant Health by Dr. Steve G. Jones Radiant Health Hypnosis Script By Dr. Steve G. Jones And as you continue relaxing deeper and deeper and more deeply relaxed, I would like you to imagine your body to
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. By Vinnie Partridge, Nicholas Young, and Mercedes Smith
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM By Vinnie Partridge, Nicholas Young, and Mercedes Smith WHAT IS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM? The Endocrine System, also referred to as the glandular system, is made up of multiple types of
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM By Vinnie Partridge, Nicholas Young, and Mercedes Smith WHAT IS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM? The Endocrine System, also referred to as the glandular system, is made up of multiple types of
The Emotional Nervous System
 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Corporate Wellness Program - Lunch & Learn Seminars. How to allow Positive Thinking & Optimism to Create your Life
 Corporate Wellness Program - Lunch & Learn Seminars How to allow Positive Thinking & Optimism to Create your Life Motivational Speech Awareness of our Thoughts, Words, Actions & Perceptions How we Shape
Corporate Wellness Program - Lunch & Learn Seminars How to allow Positive Thinking & Optimism to Create your Life Motivational Speech Awareness of our Thoughts, Words, Actions & Perceptions How we Shape
Quantum Education SCIO Energy Medicine
 Quantum Education SCIO Energy Medicine SCIO - Latin: To know - Acronym: Scientific Interface Operation System QUANTUM is the smallest amount of a physical quantity that can exist independently, especially
Quantum Education SCIO Energy Medicine SCIO - Latin: To know - Acronym: Scientific Interface Operation System QUANTUM is the smallest amount of a physical quantity that can exist independently, especially
Neuroscience and Consciousness. Chapter 2
 Neuroscience and Consciousness Chapter 2 Neurons Neuron cell communication is electrical Axon Dendrites Mylin sheath Terminal buttons Synapses Firing of neuron is electrical process All-or-none law Action
Neuroscience and Consciousness Chapter 2 Neurons Neuron cell communication is electrical Axon Dendrites Mylin sheath Terminal buttons Synapses Firing of neuron is electrical process All-or-none law Action
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
What does stress do to the body?
 Stress is any reaction to a physical, emotional, psychological or environmental stimulus that triggers the release of adrenal hormones. Since our bodies prioritize a stress response over all other bodily
Stress is any reaction to a physical, emotional, psychological or environmental stimulus that triggers the release of adrenal hormones. Since our bodies prioritize a stress response over all other bodily
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
STUDENT NAME. 1. Reflexology is the application of techniques to the hands and feet to affect another part of the body.
 STUDENT NAME STUDENT ID G540 Complete Reflexology for Life by Barbara & Kevin Kunz (2009) CLASS: G540 Grade /69 % Chapter 1 1. Reflexology is the application of techniques to the hands and feet to affect
STUDENT NAME STUDENT ID G540 Complete Reflexology for Life by Barbara & Kevin Kunz (2009) CLASS: G540 Grade /69 % Chapter 1 1. Reflexology is the application of techniques to the hands and feet to affect
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system
 3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Healing With Sound The Effects Of Different Notes
 Healing With Sound The Effects Of Different Notes Musical Note: Sense: Physical Aspects Emotional Aspects C Uh Red Smell Gross circulation Large/thick muscles Hormones Heart muscle Sore muscles Colon Constipation
Healing With Sound The Effects Of Different Notes Musical Note: Sense: Physical Aspects Emotional Aspects C Uh Red Smell Gross circulation Large/thick muscles Hormones Heart muscle Sore muscles Colon Constipation
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Health Psychology. Health Psychology. Health Psychology. Health Psychology. What is Health Psychology? Biobehavioural aspects of health
 Health Psychology Health Psychology Psychology 46.339 (01) Summer 2007 Instructor: Dr. Fuschia Sirois Wednesday July 4: Introduction & Lecture 1 Taylor text, 6 th ed. Lecture slides in pdf format on course
Health Psychology Health Psychology Psychology 46.339 (01) Summer 2007 Instructor: Dr. Fuschia Sirois Wednesday July 4: Introduction & Lecture 1 Taylor text, 6 th ed. Lecture slides in pdf format on course
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Releasing Self Sabotage and Addictions
 Releasing Self Sabotage and Addictions I used to offer two separate healing sessions one for releasing self sabotage and one for releasing addictions. However, there is so much energetic overlap between
Releasing Self Sabotage and Addictions I used to offer two separate healing sessions one for releasing self sabotage and one for releasing addictions. However, there is so much energetic overlap between
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
English Language Arts READING COMPREHENSION: SESSION 1
 English Language Arts READING COMPREHENSION: SESSION 1 DIRECTIONS This session contains one reading selection with seven multiple-choice questions and one open-response question. Mark your answers to these
English Language Arts READING COMPREHENSION: SESSION 1 DIRECTIONS This session contains one reading selection with seven multiple-choice questions and one open-response question. Mark your answers to these
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Control And Coordination 49
 7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Main Function: signal other cells to behave in certain. of communication.
 Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS
 THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTROLS THE BODY S ACTIVITIES IT RECEIVES AND SENDS OUT INFORMATION ABOUT ACTIVITIES WITHIN THE BODY MONITORS AND RESPONDS TO CHANGES
THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTROLS THE BODY S ACTIVITIES IT RECEIVES AND SENDS OUT INFORMATION ABOUT ACTIVITIES WITHIN THE BODY MONITORS AND RESPONDS TO CHANGES
Control and Coordination
 CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology. Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour
 NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour Question 1. How does the evolutionary perspective explain the biological basis of behaviour? Answer: Evolution refers to gradual
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour Question 1. How does the evolutionary perspective explain the biological basis of behaviour? Answer: Evolution refers to gradual
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
psychology. experience. mind when Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc.
 1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
