Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
|
|
|
- Toby Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission one neuron to the next - Impulse may be changed from a single impulse into repetitive impulses - Impulse may be integrated with impulses from other neurons to cause highly intricate patterns of impulses Types of synapses chemical and electrical Chemical synapses Almost all synapses are chemical Neurotransmitter or transmitter substances Acts on receptor proteins to excite the neuron or inhibit it or modify its sensitivity 40 transmitter substances such as acetylcholine, norepinephrine, histamine, GABA, glycine, serotonin, and glutamate Electrical synapses Direct open fluid channels that conduct electricity Protein tubular structures called gap junctions that allow free movement of ions One-way conduction at chemical synapses Transmit the signals in one direction: presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron Principle of one-way conduction
2 Physiologic Anatomy of the Synapse Presynaptic terminals Some are excitatory: they secrete a transmitter substance that excites the postsynaptic neuron Many others are inhibitory: they secrete a transmitter substance that inhibits the postsynaptic neuron Fig Synaptic cleft Transmitter vesicles: contain transmitter substance that is released into the synaptic cleft to excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron Excites with excitatory receptors at the membrane or inhibits with inhibitory receptors Action potentials cause transmitter release from the presynaptic terminals: role of calcium ions Presynaptic membrane contains voltage-gated calcium channels When an action potential depolarize the terminal, the channels open and allow large numbers of calcium ions move into neurons. Calcium ions binds with special protein molecules at release site This binding causes transmitter vesicle to fuse with the release site and open to exterior by exocytosis
3
4
5
6 Action of the transmitter substance on the postsynaptic neuron function of receptor proteins Receptor proteins in Fig Two importance components (1) binding component: protrudes outward from the membrane into the cleft, binds with neurotransmitter (2) Ionophore* component: passes all the way through the membrane to the interior of the postsynaptic neuron. Two types (i) ion channels (ii) second messenger * An ionophore is a lipid-soluble molecule usually synthesized by microorganisms to transport ions across the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Ion Channels Allows passage of specified types of ions Two types (i) cation channels that most often allow sodium ions to pass, but allow potassium and/or calcium ions (ii) anion channels that allow mainly chloride ions Cation channels: lines with negative charges. Attract positively charged sodium ions and repel chloride ions and other anions Anion channels: chloride ions pass whereas sodium, potassium and calcium cations are blocked A transmitter that opens cation channels called excitatory transmitter since opening cation channels allow sodium ions enter which excites postsynaptic neuron Inhibitory transmitters open anion channels, allow negative ions enter which inhibits the neuron Channels open and close in millisecond. Opening and closing of ion channels provide a means of rapid control of postsynaptic neurons
7 Second messenger system in the postsynaptic neuron Prolonged neuronal action is achieved by second messenger chemical system Responsible for prolonged changes in neurons for seconds to months such as memory Uses special proteins called G-proteins Fig Four changes (read textbook for more details) (1) Opening specific ion channels (2) Activation of enzyme system in the neuron s membrane (3) Activation of intracellular enzyme system (4) Activation of gene transcription Excitatory and inhibitory receptors in the postsynaptic membrane Excitation is caused by (1) opening of sodium channels to allow positively charged ions flow into the interior of the postsynaptic cell. This raises the membrane potential in the positive direction (2) Depressed conduction through chloride or potassium channels or both (3) Various changes in the internal metabolism of the cell Inhibition is caused by (1) Opening of chloride ion channels (2) Increase in the conductance of potassium ions through the cell receptor (3) Activation of receptor enzymes that inhibit cellular metabolic functions
8
9
10 Chemical substances that function as synaptic transmitters 50 chemical substances Tables 45-1 and 45-2 Two groups (1) Small-molecule, rapidly acting transmitters cause most of the acute responses of the nervous system (2) Neuropeptides of larger molecular size cause more prolonged actions (1) Small-molecule, rapidly acting transmitters 1. Acetylcholine or Ach (excitatory) - First neurotransmitter to be identified (by Henry Hallett Dale who got the Nobel Prize in 1936) - Allows nerve cells to communicate with each other within humans 2. Norepinephrine (excitatory) - Neurotransmitter in CNS and sympathetic nervous system - As a stress hormone, it increases heart rate (rate of contractions) released from sympathetic neurons. - Also increases systolic and diastolic pressure - Clinically used for attention-deficit, depression, and vaso-constriction. 3. Dopamine (inhibitory in general, but also excitatory depending on where and which receptor) - Problems if it is too low or too high. - Released from substantia nigra and hypothalamus. - On sympathetic nervous system, it increases heart rate and blood pressure - Related Parkinson s disease. - Again Nobel prize to the founder, Arvid Carlsson in 2000.
11 Parkinson s Disease The term Parkinsonism is used for symptoms of tremor, stiffness, and slowing of movement caused by loss of dopamine. 18F PET scan shows decreased dopamine activity in the basal ganglia, a pattern which aids in diagnosing Parkinson's disease.
12
13
14 4. Glycine (inhibitory) - One of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. - Causes IPSP 5. GABA (inhibitory) - Gamma-aminobutyric acid - Chief inhibitory neuro-transmitter in CNS and in retina. 6. Glutamine (excitatory) - One of the 20 amino acids - Aids for recovery after surgery (healing aids) 7. Serotonin (inhibitory) - Found in many mushrooms, plants, fruits, and veges. - Regulator of anger, aggression, body temperature, mood, sleep, sexuality, and appetite. - If low, gets aggressive, angry, depressed. 8. Nitric Oxide (excitatory) - An important gas molecule for signaling in the mammals. 혈관확장기능. - Also toxic air pollutant produced by automobile engines and power plants. (2) Neuropeptide (1) Prolonged closure of calcium pores (2) Prolonged changes in the metabolic machinery of cells (3) Prolonged changes in activation or deactivation of specific genes (4) Prolonged alterations in numbers of excitatory and inhibitory receptors
15 Electrical events during neuronal excitation Resting membrane potential of the neuronal soma is about -65 mv, not -90mV It allows the membrane more excitable and less excitable Concentration differences of ions across the neuronal soma membrane Fig Nernst Potential for Na+ Effect of synaptic excitation on the postsynaptic membrane the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Fig B Electrical events in neuronal inhibition Effect of inhibitory synapses on the postsynaptic membrane the inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Inhibitory synapses open mainly chloride channels Nernst Potential for Cl- Fig Presynaptic inhibition: caused by discharge of inhibitory synapses. This inhibitory transmitter substances released is GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid) which has the specific effect of opening anion channels. The negative charge ions cancel excitatory effect of positively charged sodium ions
16
17 Time course of postsynaptic potentials: Fig
18 Spatial summation in neurons the threshold for firing: Fig Temporal summation in neurons
19
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3
 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
Department of medical physiology 1 st week
 Department of medical physiology 1 st week Semester: summer Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology 1 st week 1. General neurophysiology 2. Central
Department of medical physiology 1 st week Semester: summer Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology 1 st week 1. General neurophysiology 2. Central
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
Synaptic Transmission
 Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Ion Channels (Part 2)
 Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Communication within a Neuron
 Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems
 CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
What is Anatomy and Physiology?
 Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Communication Between
 Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
Neurochemistry 2. Loewi s experiment
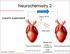 Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Notes are online at The Neuron
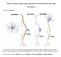 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Division Ave. High School AP Biology. cell body. signal direction
 signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review
 NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
 BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOL Week 6. Nervous System. Transmission at Synapses
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Neurons have cell membranes that separate them from the environment outside the neuron.
 Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering
 Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
Neurons: Structure and communication
 Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission.
 The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission Mitesh Shrestha Structure of the neuron the neuron consists of: the cell body, or
The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission Mitesh Shrestha Structure of the neuron the neuron consists of: the cell body, or
Neurons. Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons.
 Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
Physiology of synapses and receptors
 Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
Ameen Alsaras. Ameen Alsaras. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Overview: Lines of Communication The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve
Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Overview: Lines of Communication The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration INTRODUCTION (1:56) This sixth and final chapter deals with the summation of presynaptic currents. Glutamate and
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration INTRODUCTION (1:56) This sixth and final chapter deals with the summation of presynaptic currents. Glutamate and
Electrophysiology. General Neurophysiology. Action Potentials
 5 Electrophysiology Cochlear implants should aim to reproduce the coding of sound in the auditory system as closely as possible, for best sound perception. The cochlear implant is in part the result of
5 Electrophysiology Cochlear implants should aim to reproduce the coding of sound in the auditory system as closely as possible, for best sound perception. The cochlear implant is in part the result of
Communication Between Neurons *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Modeling Excitatory and Inhibitory Chemical Synapses
 In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
Dania Ahmad. Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad. Faisal I. Mohammed
 16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017. The Synapses
 Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017 The Synapses Conduction of a Depolarization o In dendrites: passive propagation : There is attenuation of signal transmission -Further away they
Elizabeth Biopsychology (PSY 302) The Synapses 08/29/2017 The Synapses Conduction of a Depolarization o In dendrites: passive propagation : There is attenuation of signal transmission -Further away they
The Brain & Homeostasis. The Brain & Technology. CAT, PET, and MRI Scans
 The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Neurons communicate with other cells at junctions
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Neurons communicate with other cells at junctions
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE
 1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission. BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology
 Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
Synapses. Objectives. Synaptic Relationships Between Neurons. Structure of a Chemical Synapse. Structure of a Chemical Synapse
 bjectives Synapses s Temporal & Spatial Summation EPSP & IPSP Coding Memory Synapses a nerve signal AP travels to the end of the axon triggers the release of a neurotransmitter stimulates a new wave of
bjectives Synapses s Temporal & Spatial Summation EPSP & IPSP Coding Memory Synapses a nerve signal AP travels to the end of the axon triggers the release of a neurotransmitter stimulates a new wave of
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells. Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD
 Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Overview: Lines of Communication Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Fig. 8- The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve s that transfer information within the body
Overview: Lines of Communication Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Fig. 8- The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve s that transfer information within the body
Neural Tissue. Chapter 12 Part B
 Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Human Brain and Senses
 Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
The Nervous System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine.
 The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system The Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain + Spinal Cord Peripheral
The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system The Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain + Spinal Cord Peripheral
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 3 Due: Tuesday, Oct. 27, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 3 Due: Tuesday, Oct. 27, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
