Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
|
|
|
- Dinah Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin b (CTb) was injected in the rostral VTA and red retrobeads (RB-R) in the caudal VTA to identify the topography of the projections from the PPN and LDT. (b) ChAT-immunopositive neurons contained CTb and/or RB-R in both PPN and LDT (arrows; the PPN neuron is triple-labeled and the LDT neuron in doublelabeled). (c) Pattern of retrograde labeling in relation to the expression of ChAT at three mediolateral levels of the PPN/LDT in a representative animal. (d) Similar numbers of VTA-projecting cholinergic neurons were detected at different mediolateral levels. A larger proportion of non-cholinergic VTA-projecting neurons was observed in the most lateral sections of the PPN. (e) The number of cholinergic neurons containing one of the tracers was normalized against the total number of cholinergic neurons and expressed as a percentage of the total. This was quantified at three rostrocaudal 900 μm-segments of the PPN and in the LDT. The number of cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA is higher in the caudal PPN segments and the LDT. This contrasts with the low number of ChAT+/RB-R+ neurons projecting to the caudal VTA located in the rostral PPN. Bars represent SEM (n = 4 rats).
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Specificity of transduction for cholinergic neurons in different brain areas. We tested the specificity of the transduction by injecting AAV2-EF1a-DIO-YFP in other brain regions in a different set of animals (n=3 rats), including the cerebellum, ventromedial thalamus, superior colliculus and striatum as well as the PPN and LDT (n = 5 rats). Positive (i.e. YFP-expressing) somata were only observed in the striatum, the PPN and LDT, and no retrograde transduction of cholinergic neurons was detected. The presence of two fluorescent markers in the cholinergic neurons of the PPN (AAV2-EF1a-DIO- YFP) and LDT (AAV5-EF1a-DIO-mCherry) of ChAT::Cre+ rats was used to evaluate the specificity for the transduction, in combination with immunofluorescent detection of ChAT. See Supplementary Table 2 for values.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 Lack of forebrain cholinergic innervation of the VTA. Coronal (a-e) or sagittal (f) sections showing the VTA following injections of AAV2-DIO-EF1a-eYFP into the medial septum (a), vertical limb of the diagonal band of Broca (b), horizontal limb of the diagonal band of Broca (c), nucleus basalis of Meynert (d), medial habenula (e) and the parabigeminal nucleus (f) (n = 3 per group). None of the transductions in these areas produced cholinergic axonal labeling in the VTA. The borders of the VTA were delimited by TH immunostaining (in red). Scale bar: 500 µm.
5 Supplementary Figure 4 Mediolateral distribution of cholinergic axons in the VTA. (a) The axons used in the analyses in Fig. 1c and 2c were traced and digitized, as shown in this representative sections (n = 3 rats each). (b) The axonal density was normalized to detect areas of preferential innervation from either the PPN or the LDT. Whereas in the lateral and middle VTA we observed a similar pattern, in the medial VTA some differences were observed: PPN tends to innervate the most rostral regions of the VTA, where LDT innervation is low, but then drops in the most caudal regions, where LDT innervation is higher. This coincides with the low numbers of retrogradely labeled cholinergic neurons in the PPN when the injection was located in the caudal VTA. (c) Quantification of the total length cholinergic axons in the PPN and the LDT (t = 1.29, two-tailed t-test, P = 0.266). Bars represent SEM. * P < 0.05.
6 Supplementary Figure 5 Analysis of the response of a representative neuron to the laser stimulation. (a) Three responses to the laser were obtained for this neuron. Spike events were extracted and merged into a single spike train (black trace). (b) Cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the three individual spike trains together with that of the merged spike train (black dots) were computed by increasing the CDF one unit each time a spike occurred (note that in order to maintain the same scale, the CDF of the merged spike train must be divided by the number of spike trains merged). Regression slope of the CDF was computed at each spike time by using a local (18 neighboring spikes) linear regression analysis (see grey dots on the black trace and dashed red lines for an example at three different time points, red dots). (c) Estimated instantaneous firing rate (regression slope) for the three
7 individual trains and for the merged spike train where red dots correspond to the regression points marked in panel b. (d) Smoothed version and z-scored version of the instantaneous firing rate shown in panel c (for merged trace only). Horizontal lines correspond to the mean (full) and 5 th and 95 th percentile (dashed) values of the firing rate during pre-stimulus period (-10 to 0 s). Red trace demarks the response period of the neuron (i.e., a significant P < 0.05 increase in the firing rate).
8 Supplementary Figure 6 Controls for stimulation of cholinergic axons in the VTA. (a) Following injection of AAV2-DIO-EF1a-eYFP into the PPN/LDT in ChAT::cre rats, individual TH+ neurons (n = 5 neurons) were recorded in vivo during blue light delivery and subsequently labeled with neurobiotin (b). The same protocol was followed as that used in figures 1 and 2. No change in firing was observed in neurons transduced with YFP only. Scale bar: 20 µm.
9 Supplementary Figure 7 Electrical stimulation of the PPN produces short-latency responses in DA neurons. (a) A neuron that was recorded and labeled by the juxtacellular method and identified as dopaminergic by the expression of immunoreactivity for TH. (b) Raster plot and peri-stimulus time histogram (PSTH) of the neuron shown in a, following electrical stimulation of the PPN (bin size 1 ms). (b ) A representative spike following the stimulus (s; 0.5 ms duration, ma, 0.5 Hz). Consistent with previous reports, short-latency action potentials were elicited in the DA neurons within a few milliseconds of the stimulus
10 being delivered in the PPN; this contrasts with the slow modulatory effect of the optogenetic activation of PPN cholinergic afferents. (c) Short-latency responses were consistent across the DA neuronal population (n = 12 neurons in 5 rats). (d, e, e ) Non-DA neurons (i.e. TH-immunonegative, d) were also sampled (n = 4 neurons in 5 rats). PSTH (bin size 2 ms) showing a long-lasting inhibition (average time of inhibition: 30ms +/- 8.6ms, e). Responses in non-da neurons were more heterogeneous.
11 Supplementary Figure 8 Nicotinic modulation of VTA neurons. (a) Effect of carbachol puffing on VTA DA neurons (n = 9 neurons) that were labeled and identified as TH+. (b) Example of VTA neurons showing classical dopaminergic features with low spontaneous firing and/or presence of Ih current. (c) Carbachol puffs (200 µm) provoke excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) that are blocked by mecamylamine (n = 9 neurons; 5 µm) but not by DhβE (1 µm) or methylcaconitine (500 nm). (d) Carbachol-induced EPSPs were not blocked by bicuculline (10 µm), CNQX (10 µm) or APV (10 µm) (n = 4 neurons). (e) The mecamylamine effect on EPSP size was significantly different to the control condition (t = 7.281, two-tailed t-test, P = ). (f) Effect of carbachol puffing on a VTA non-da neuron, confirmed as TH- by immunofluorescence, and showing
12 classical non-da neuron features such as higher firing rate and lack of Ih current. (g) Carbachol puffing provokes robust EPSPs that are blocked by bath application of MLA (500 nm) but not by DHβE (1 µm) or mecamylamine (5 µm). Scale bar in fluorescent images: 20 µm. Acetylcholine has been reported to induce strong somatic excitation of dopamine neurons in the VTA (Eddine, R., et al. (2015) Sci Rep 5, 8184) and its effects consist of a presynaptic component, modulating glutamate release (Schilstrom, B., et al. (1998) Neuroscience 82, ), and a postsynaptic component, involving nicotinic and muscarinic mechanisms (Gronier, B., et al. (2000) Psychopharmacology 147, ; Mameli-Engvall, M., et al. (2006) Neuron 50, ; Mansvelder, H.D., et al. (2002) Neuron 33, ). Furthermore, muscarinic agonists increase the frequency of spontaneous action potentials in DA neurons (Lacey, M.G., et al. (1990) Pharmacol Exp Ther 253, ; Scroggs, R.S., et al. (2001) J Neurophysiol 86, ) and induce glutamate release concomitantly with a decrease in GABA release in the VTA (Grillner, P., et al. (2000) Neuroscience 96, ; Mansvelder, H.D., et al. (2000) Neuron 27, ). Our results are in agreement with other studies showing that mecamylamine was able to abolish the effects mediated by cholinergic agonists in DA neurons (Zhang, L., et al. (2005) J Physiol 586, ) or following place preference associated with carbachol injections in the VTA (Ikemoto, S. & Wise R.A., et al. (2002) J Neurosci 22, ). While our experiments seem to indicate an effect predominantly mediated by nicotinic receptors, muscarinic receptors are highly expressed in the VTA and are also likely to contribute to the modulation of DA neurons, as shown previously (Forster, G.L. and Blaha C.D. (2000) Eur J Neurosci 12, ).
13 Supplementary Figure 9 Expression of vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) in YFP-labeled axons. Axons expressing YFP in the VTA from both PPN- and LDT-transduced animals were tested for the presence of vesicular transporters by immunofluorescence. VAChT immunofluorescence was detected in the majority of axonal varicosities expressing YFP (arrowheads), as has also been reported in the striatum (Dautan et al (2014) J Neurosci 34, ). In contrast, the vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGluT2) was never observed to co-localize with YFP in axonal varicosities, even though we detected large numbers of VGluT2-positive varicosities within the VTA. Thus, in agreement with in situ hybridization data (Wang and Morales (2009) Eur J Neurosci 29, ) the axons of cholinergic neurons from the brainstem lack VGluT2.
14 Supplementary Figure 10 Individual response of DA neurons to aversive (pinch) and laser stimulation. Representative traces of two TH+ neurons recorded in vivo during a hind-paw pinch (red square) and laser stimulation (blue square) of PPN (a) or LDT (b) cholinergic axons in the VTA. Scale bar: 50µm.
15 Supplementary Figure 11 Behavioral responses to the optogenetic activation of PPN and LDT axons are blocked by cholinergic receptor antagonists. (a) Optogenetic activation of cholinergic axons in the VTA of PPN (n = 12 rats), LDT (n = 6 rats) or wild-type groups (n = 8 rats) failed to produce stimulation-locked effects on locomotor activity in the presence of cholinergic antagonists (i.p. 0.3 ml final volume, MLA: 6 mg/kg; DHβE: 3 mg/kg; atropine: 0.5 mg/kg and mecamylamine: 1.0 mg/kg). Locomotor activity in all groups was similar (2-way ANOVA; stimulation effect: F (2,19) = 0.589, P = 0.565; group effect: F (2,19) = 0.140, P = 0.871). (b) Cumulative distance travelled during laser stimulation (10 Hz, 50 ms, 8 s duration, every 2 min) of cholinergic axons in wild-type (green), PPN (gray) or LDT (red) groups following a systemic injection of a cocktail of cholinergic antagonists (1-way ANOVA: F (2, 21) = 1.722, P = 0.205). (c) Number of lever presses per minute during acquisition of the operant task for wild-type (green, n = 10), PPN (gray, n = 12) and LDT (red, n = 10) animals. No significant differences were observed (2-way ANOVA; day effect F (4,26) = 4.336, P = 0.08; group effect: F (2,29) = 0.174, P = 0.842; interaction F (8,54) = 1.038, P = 0.426).
16 PPN LDT VTA-projecting ChAT(+) neurons VTA-projecting ChAT(-) neurons % ChAT(+) neurons retrogradely labeled CTb/ChAT(+) RB-R/ChAT(+) Table S1. Retrograde cell count in PPN and LDT. Two retrograde tracers were injected in the VTA, cholera toxin b (CTb) in its rostral portion and red retrobeads (RB- R) in its caudal portion (n = 4). The total number of retrogradely labeled neurons for each tracer was quantified in sagittal sections at three mediolateral levels. Immunohistochemistry for ChAT was combined with tracer detection to identify the cholinergic projection neurons. With the exception of the percentage of cholinergic neurons labeled, all numbers represent sums of neurons in all animals.
17 PPN (n = 5) LDT (n = 4) % cholinergic neurons transduced within the injection diameter % of transduced neurons immunopositive for ChAT 66 ± ± ± ± 0.31 Table S2. Analysis of the transduction specificity of the viral vector (Means ± SEM).
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Segregated cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area
 Segregated cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area Daniel Dautan 1, 2, 6, Albert Souza 1, Icnelia Huerta-Ocampo 1,6, Miguel Valencia 3, 6, Maxime Assous 6, Ilana B. Witten 4, Karl Deisseroth
Segregated cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area Daniel Dautan 1, 2, 6, Albert Souza 1, Icnelia Huerta-Ocampo 1,6, Miguel Valencia 3, 6, Maxime Assous 6, Ilana B. Witten 4, Karl Deisseroth
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplemental Information. Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body. Output Synapses Are Cholinergic
 Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters. motor- and cue- dependent behaviors
 Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Nucleus Accumbens Subnuclei Regulate Motivated Behavior via Direct Inhibition and Disinhibition of VTA Dopamine Subpopulations
 Article Nucleus Accumbens Subnuclei Regulate Motivated Behavior via Direct Inhibition and Disinhibition of VTA Dopamine Subpopulations Highlights d Mesolimbic DA subpopulations are embedded within different
Article Nucleus Accumbens Subnuclei Regulate Motivated Behavior via Direct Inhibition and Disinhibition of VTA Dopamine Subpopulations Highlights d Mesolimbic DA subpopulations are embedded within different
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response
 A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity
 An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit. Supplementary Information. Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M.
 Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
A Unique Population of Ventral Tegmental Area Neurons Inhibits the Lateral Habenula to Promote Reward
 Article A Unique Population of Ventral Tegmental Area Neurons Inhibits the Lateral Habenula to Promote Reward Alice M. Stamatakis, 1,2,3 Joshua H. Jennings, 1,2,3 Randall L. Ung, 2 Grace A. Blair, 2 Richard
Article A Unique Population of Ventral Tegmental Area Neurons Inhibits the Lateral Habenula to Promote Reward Alice M. Stamatakis, 1,2,3 Joshua H. Jennings, 1,2,3 Randall L. Ung, 2 Grace A. Blair, 2 Richard
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Modeling Excitatory and Inhibitory Chemical Synapses
 In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
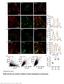 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainresrev Review Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems J. Mena-Segovia a,, P. Winn b, J.P. Bolam a a MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainresrev Review Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems J. Mena-Segovia a,, P. Winn b, J.P. Bolam a a MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus
 Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus Miklos Antal., Claudio Acuna-Goycolea., R. Todd Pressler, Dawn M. Blitz, Wade
Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus Miklos Antal., Claudio Acuna-Goycolea., R. Todd Pressler, Dawn M. Blitz, Wade
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus
 Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
The Central Auditory System
 THE AUDITORY SYSTEM Each auditory nerve sends information to the cochlear nucleus. The Central Auditory System From there, projections diverge to many different pathways. The Central Auditory System There
THE AUDITORY SYSTEM Each auditory nerve sends information to the cochlear nucleus. The Central Auditory System From there, projections diverge to many different pathways. The Central Auditory System There
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Neural Recording Methods
 Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
A toolbox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing
 A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
Supplemental Information. A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit. for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice
 Neuron, Volume Supplemental Information A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice Kentaro K. Ishii, Takuya Osakada, Hiromi Mori, Nobuhiko Miyasaka, Yoshihiro Yoshihara,
Neuron, Volume Supplemental Information A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice Kentaro K. Ishii, Takuya Osakada, Hiromi Mori, Nobuhiko Miyasaka, Yoshihiro Yoshihara,
What do you notice? Edited from
 What do you notice? Edited from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ffayobzdtc8&t=83s How can a one brain region increase the likelihood of eliciting a spike in another brain region? Communication through
What do you notice? Edited from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ffayobzdtc8&t=83s How can a one brain region increase the likelihood of eliciting a spike in another brain region? Communication through
BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects.
 Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Active Control of Spike-Timing Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in an Electrosensory System
 Active Control of Spike-Timing Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in an Electrosensory System Patrick D. Roberts and Curtis C. Bell Neurological Sciences Institute, OHSU 505 N.W. 185 th Avenue, Beaverton, OR
Active Control of Spike-Timing Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in an Electrosensory System Patrick D. Roberts and Curtis C. Bell Neurological Sciences Institute, OHSU 505 N.W. 185 th Avenue, Beaverton, OR
Supplementary Figure 1. Microdialysis measurements of extracellular dopamine in ventral and dorsal striatum.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Microdialysis measurements of extracellular dopamine in ventral and dorsal striatum. A. Behavioural preparation. Mice are placed in an operant box where a spout containing the artificial
Supplementary Figure 1 Microdialysis measurements of extracellular dopamine in ventral and dorsal striatum. A. Behavioural preparation. Mice are placed in an operant box where a spout containing the artificial
habenulointerpeduncular pathway have been studied using a rat brain slice
 J. Phyeioi. (1984), 353, pp. 101-109 101 With 5 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF CHOLINOMIMETIC SUBSTANCES ON IMPULSE CONDUCTION IN THE HABENULOINTERPEDUNCULAR PATHWAY OF THE RAT IN
J. Phyeioi. (1984), 353, pp. 101-109 101 With 5 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF CHOLINOMIMETIC SUBSTANCES ON IMPULSE CONDUCTION IN THE HABENULOINTERPEDUNCULAR PATHWAY OF THE RAT IN
Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous inhibitory networks
 Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
-80 Figure 1. Identification of dopaminergic neurons in. VTA slices (a) Micrographs demonstrate the location of the VTA with
 Potential (mv) A B C Potential (mv) D E F Biocytin TH Merge R 12 12 1 1 8 G 6 4 8 6 4 H 2 2-2 -2-4 -4-6 -6 Supplemental -8-8 Figure 1. Identification of dopaminergic neurons in -1 VTA slices. -1 (a) Micrographs
Potential (mv) A B C Potential (mv) D E F Biocytin TH Merge R 12 12 1 1 8 G 6 4 8 6 4 H 2 2-2 -2-4 -4-6 -6 Supplemental -8-8 Figure 1. Identification of dopaminergic neurons in -1 VTA slices. -1 (a) Micrographs
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60
 Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Contribution of different classes of glutamate receptors in the corticostriatal polysynaptic responses from striatal direct
Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Contribution of different classes of glutamate receptors in the corticostriatal polysynaptic responses from striatal direct
SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
Cellular Neurobiology / BIPN 140
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Neuroscience 201A (2016) - Problems in Synaptic Physiology
 Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION OF CRAYFISH TONIC FLEXOR MOTOR NEURONES BY ESCAPE COMMANDS
 J. exp. Biol. (1980), 85, 343-347 343 With a figures Printed in Great Britain POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION OF CRAYFISH TONIC FLEXOR MOTOR NEURONES BY ESCAPE COMMANDS BY J. Y. KUWADA, G. HAGIWARA AND J. J. WINE
J. exp. Biol. (1980), 85, 343-347 343 With a figures Printed in Great Britain POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION OF CRAYFISH TONIC FLEXOR MOTOR NEURONES BY ESCAPE COMMANDS BY J. Y. KUWADA, G. HAGIWARA AND J. J. WINE
