The Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Geraldine Wilkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus and between optic chiasma and mamillary bodies Connected to the hypothalamus by infundibulum 2 1
2 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Pituitary Gland has a two part embryological origin One part develops from floor of the diencephalon Other part comes from the roof of the stomodeum The stomodeum a depression between the brain and pericardium and is the precursor to mouth and anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. (image : 3 week embryo (Gray s Anatomy) 3 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Around 4 th week, an epithelial pouch grows upwards from the stomodeum towards the developing brain (= Rathke s Pouch), where it meets up with a down growth (= Infundibulum) from the brain region. 4 2
3 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Around 6 th week, the connection between Rathke s pouch (RP) and stomodeum become degenerated (see C) Cells of RP proliferate to form the Pars distalis, and upwards the infundibulum to form the Pars tuberalis, while the infundibulum expands inferiorly. 5 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis In later stages, the sphenoid bone isolates the pituitary gland from the roof region, protecting it within the sella tursica. 6 3
4 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Third ventricle Median eminence Mamillary body HYPOTHALAMUS Optic chiasm Infundibulum Anterior lobe Pars tuberalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Posterior pituitary lobe Sphenoid (sella turcica) The adult form is thus made from a posterior lobe and an anterior lobe (containing Pars tuberalis, Pars distalis and Pars intermedia) 7 ANTERIOR LOBE Anterior lobe of the PG is also called the adenohypophysis (or anterior pituitary gland) Has 3 distinct regions Pars distalis Pars tuberalis Pars intermedia It is derived from epithelial tissue, differentiated into several groups with important glandular functions. There is no neural connection with the HT 8 4
5 Anterior pituitary gland 6 distinct hormones are produced in the adenohypophysis The secretion of these hormones is controlled by specific releasing and inhibiting hormones produced in the Hypothalamus ( tropic hormones) This requires an intricate network of blood vessels and capillaries to direct the hypothalamic hormones to APG cells 9 Hypophyseal Portal System Optic chiasm Capillary beds ANTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY GLAND MEDIAN EMINENCE Mamillary body Superior hypophyseal artery Infundibulum Portal vessels Inferior hypophyseal artery POSTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY GLAND Endocrine cells Hypophyseal veins There are thus two capillary beds connected via portal vessels! This system is called the hypophyseal portal system and is fed by the superior hypophyseal artery. 10 5
6 Posterior pituitary gland or PPG Contains mostly nerves The cell bodies of the nerves are located in the hypothalamus Axons extend into the PPG Hormones are directed to the axon terminals and secreted by nerve stimuli. Thus, other names for the PPG are Pars Nervosa HYPOTHALAMUS Neuro-hypophysis an inferior hypophyseal artery and vein supply and drain the posterior lobe 11 Hormones of the posterior pituitary gland Only two hormones are released by the PPG Oxytocin Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH) The hormones are produced by neuronal cell bodies, located in the Hypothalamus and directed via neurons of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract to the capillary bed of the PPG. (why is it called a tract? ) 6
7 Hormones of the posterior pituitary gland Supraoptic nuclei HYPOTHALAMUS Paraventricular nuclei Those neuronal cell bodies in the HT are : Optic chiasm Supraoptic nuclei these produce ADH Paraventricular nuclei these produce Oxytocin AntiDiuretic Hormone or ADH (Vasopressin ) Physiological effect is to decrease the urine output and urine production ADH causes the kidneys to remove water from the urine that is being formed in the nephrons of the kidneys and re-direct it into the bloodstream. Since ADH promotes water return to the blood, it regulates blood volume and the state of dehydration of our body ADH production is thus of homeostatic importance and regulation is by means of negative feedback 14 7
8 Feedback Regulation of Kidneys Hypothalamic nuclei have osmo-receptors that detect changes in blood osmolarity Increased state of Dehydration means less fluid and results in increased "particles" per volume unit = osmolarity This increased blood osmolarity is sensed by the osmoreceptors in hypothalamus and results in the release of ADH from the PPG into the blood ADH travels via the blood stream to the target organ (the kidney ), where it promotes water retention. less urine production 15 Dehydration In Kidneys 16 8
9 Feedback Regulation of Kidneys Release of ADH is directly correlated to the degree of dehydration ( blood osmolarity) normal blood osmolarity = 285 mosm) above that = indicates dehydration 17 Factors that affect ADH Release Factors that release ADH Dehydration excessive sweating not enough water intake diarrhea Low blood pressure blood loss Factors that inhibit ADH release Osmolarity below 280 Osm over-hydration Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion 18 9
10 Clinical Correlation Diabetes insipidus Results from hypo-secretion of ADH or hypo-responsiveness damage to PPG or nonfunctional ADH receptors Symptoms : excretion of large amounts of urine, dehydration, thirst Normal urine volume ~ 1 to 1.5 L / day With no ADH present : urine volume ~ 24 L / day 19 Oxytocin Major function in the female, less important in the male Enhances smooth muscle contraction in the uterus during labor It is one of the few positive feedback mechanisms stretching of cervix during delivery stimulates stretch receptors in the uterine wall receptors signal HT to release more oxytocin results in more contractions and movement of baby through the birth canal, additional stretching Additional help is provided by release of local prostaglandins
11 Oxytocin 21 Oxytocin Oxytocin also Enhances milk ejection by stimulation of smooth muscle in lacteal ducts of the mammary glands after childbirth ProLactin, an APG hormone, is responsible for milk production and secretion. (see later) 22 11
12 Oxytocin makes you wanna cuddle Research links oxytocin with socio-sexual behaviors Cuddle Hormone The Hormone Involved In Reproduction May Have a Role In The Maintenance Of Relationships! 23 Oxytocin negates fear, induces trust? The scans of oxytocin's effects on the human brain reveal that it quells the brain's fear hub, the amygdala (and its associated brainstem relay stations), in response to fearful stimuli. Research seems to indicate that oxytocin negates fear and increases trust in humans 24 12
13 The many roles of oxytocin 25 ADH and Oxytocin are Peptide Hormones Oxytocin Cys - Tyr - Ile - Gln - Asn - Cys - Pro - Leu - Gly - NH 2 S-S ADH ( vasopressin) Cys - Tyr - Phe - Gln - Asn - Cys - Pro - Arg - Gly - NH 2 S-S Knowing this, can they enter cells? How would they work at cell level? 13
14 Oxytocin for sale! 27 14
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology LECTURE NO (-) Hypothalamus. Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology
 LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Endocrine Glands. Endocrine glands
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
 Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]
![BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ] BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]](/thumbs/87/96904971.jpg) BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
 Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland
 Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
Hypothalamus. Small, central, & essential.
 Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D.
 The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Construct the relationships between
The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Construct the relationships between
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA
 RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
The Endocrine System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris
 18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
-Ahmad Rawajbeh. -Dania alkouz. -Saleem Khresha. 1 P a g e
 -2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
-2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Behavioral and Motivational mechanisms of Brain. Limbic system and the Hypothalamus
 Behavioral and Motivational mechanisms of Brain Limbic system and the Hypothalamus 1 General functions 1. Control of behavior 2. Control level of activities in different parts of brain 3. Motivational
Behavioral and Motivational mechanisms of Brain Limbic system and the Hypothalamus 1 General functions 1. Control of behavior 2. Control level of activities in different parts of brain 3. Motivational
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Pituitary Disorders. Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: /1/2019
 Pituitary Disorders Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 0915020385 31/1/2019 Objectives By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Understand basic Pituitary axis physiology State the common causes of
Pituitary Disorders Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 0915020385 31/1/2019 Objectives By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Understand basic Pituitary axis physiology State the common causes of
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Endocrine system. General principle of endocrinology. Mode of hormone delivery to target. Mode of hormone delivery to target
 Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline. Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland
 Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Antidiuretic Hormone
 1 Antidiuretic Hormone 2 Physiology of the Posterior Pituitary The posterior pituitary gland secretes two hormones which are: oxytocin, increase uterine contractions during parturition Contraction of mammary
1 Antidiuretic Hormone 2 Physiology of the Posterior Pituitary The posterior pituitary gland secretes two hormones which are: oxytocin, increase uterine contractions during parturition Contraction of mammary
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones
 Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
Homeostasis. Agenda. Preserving homeostasis requires long term co-ordination of cell activity throughout the body. Homeostasis
 Agenda Introduction & Syllabus (always exciting!) Chapter 18: Endocrine System Lab 33 Looking ahead-wed: Chapter 18 Homeostasis Homeostasis refers to a state of relative balance within the body, and the
Agenda Introduction & Syllabus (always exciting!) Chapter 18: Endocrine System Lab 33 Looking ahead-wed: Chapter 18 Homeostasis Homeostasis refers to a state of relative balance within the body, and the
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Hypothalamus. To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine secretions NTA Ch 14, pgs Key Figs: 14-3; 14-4,
 Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
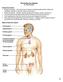 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
HIHIM 409. Endocrine system. Differences between systems. Hormone effects. Similarities. Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system
 The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
Hypothalamus. lies below the hypothalamic sulcus. includes the following ventral surface structures:
 Hypothalamus I. Overview The Hypothalamus is a division of the diencephalon. lies within the floor and ventral part of the walls of the third ventricle, functions primarily in the maintenance of homeostasis.
Hypothalamus I. Overview The Hypothalamus is a division of the diencephalon. lies within the floor and ventral part of the walls of the third ventricle, functions primarily in the maintenance of homeostasis.
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS
 Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Attribution: Department of Neurology, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Attribution: Department of Neurology, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13. The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2. PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM
 BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
54a A&P: Endocrine System
 54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Hypophysis. Organization
 Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination
 I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Laurie A. Loevner, MD
 Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System. Collection of glands that secrete hormones.
 Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Unit 9 The Endocrine System
 Unit 9 The Endocrine System Chapter 17 The Endocrine System 731 17 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Figure 17.1 A Child Catches a Falling Leaf Hormones of the endocrine system coordinate and control growth, metabolism,
Unit 9 The Endocrine System Chapter 17 The Endocrine System 731 17 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Figure 17.1 A Child Catches a Falling Leaf Hormones of the endocrine system coordinate and control growth, metabolism,
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
The Endocrine System. Hormone =
 The Endocrine System Hormone = Types: peptide or protein = at least 3 amino acids steroid = derived from cholesterol amine = derived from single amino acids (tryptophan, tyrosine) Peptide Hormones Synthesis/transport/half-life
The Endocrine System Hormone = Types: peptide or protein = at least 3 amino acids steroid = derived from cholesterol amine = derived from single amino acids (tryptophan, tyrosine) Peptide Hormones Synthesis/transport/half-life
Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Chapter 8 Human Organization
 Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3.
 Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND
 STUDY COMPONENT Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System UNIT THEME 1: UNIT THEME 2: UNIT THEME 3: UNIT THEME 4: HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND THYROID AND PARATHYROID PANCREAS; ADRENAL GLANDS
STUDY COMPONENT Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System UNIT THEME 1: UNIT THEME 2: UNIT THEME 3: UNIT THEME 4: HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND THYROID AND PARATHYROID PANCREAS; ADRENAL GLANDS
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Autocrine. Control of Lactation. Lactation. Illinois Module :
 Autocrine Control of Lactation Illinois Module : Lactation Autocrine Control of Lactation Control of lactation is clearly regulated by hormones, However local factors are also important Evidences Cows
Autocrine Control of Lactation Illinois Module : Lactation Autocrine Control of Lactation Control of lactation is clearly regulated by hormones, However local factors are also important Evidences Cows
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
