Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
|
|
|
- Harry Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body axon 2 2: Complete the following by filling in the blank spaces. Nerve pathways are our information super highways. They are made up of cells called. Both and signals are used to transmit information along a nerve pathway. S Y N A P S E S Y N A P S E Signal Transmission 3 3: Write the appropriate signal received and transmitted by the three neurons in boxes below. Neuron 1 Neuron 2 Neuron 3 Using an arrow indicate which direction the signal is travelling in from one neuron to another. 1
2 The synapse in close-up 4: Molecules called neurotransmitters carry the message across the synapse and bind to receptor molecules on the next post-synaptic neuron. Draw a line to show the path taken by a neurotransmitter across the synapse. 4 Neurotransmitters stored in vesicles at end of axon Synapse Receptors 1. Electrical impulse 5. Electrical impulse axon of pre-synaptic neurone 3.Neurotransmitters - cross the synapse Dendrite of post - synaptic neuron 2.Neurotransmitters- released from axon of pre-synaptic neuron. 4.Neurotransmitters- bind to receptors on dendrites of post-synaptic synaptic neuron. Chemical signals and receptors Just like a key needs to be a certain shape to fit a lock, the shape of the signalling molecule determines whether it can bind to its specific receptor. 5: Circle one of the following molecules to show which molecule you think will bind to the receptor below? 5 Molecule 1 Molecule 3 Molecule 2 Receptor 2
3 Congratulations! You have now acquired the basic knowledge to understand how drugs act on neurons. Now that you have worked through the introduction it is time to take a look at how drugs act on neurons. Drugs are molecules just like neurotransmitters and have a specific shape. If their shape is similar to that of a neurotransmitter they will bind to the receptor just like a key fitting into a lock. Instructions Only use the mouse to move through the program! Make sure to answer all questions as you go. Slides with corresponding questions in the workbook are indicated by the symbol. Follow the slides through by clicking on the next slide symbol in the bottom right hand corner. If you want to replay a slide click on the play again symbol in the bottom right hand corner. When completing the interactive drug section you can move back to choose a drug and also to see how drugs act by clicking on their links in the bottom right hand corner. 3
4 Drug action on neurons Click on each of the 3 links to see how various drugs can act on neurons and answer the questions. Make sure to try them all.. Mimicking neurotransmitters Drugs mimic neurotransmitters because they have a similar shape. These drugs are able to bind to the postsynaptic receptors in the same way that the brains normal chemical messengers, the neurotransmitters can. Drug binds to receptors on the post-synaptic synaptic neuron and activates the neuron. Electrical impulse Pre-synaptic neuron NOT activated. Neurotransmitters still stored in the end of axon. Drugs the same shape as the neurotransmitter can mimic the Neurotransmitters. 6: Circle which of the following drugs in the interactive choice is going to be able to mimic the neurotransmitter and activate the post-synaptic neuron? 6 Nicotine LSD Alcohol Explain your choice: 4
5 Blocking postsynaptic receptors Some drugs affect neurons by blocking the receptors that neurotransmitters normally act on. 1. Receptors- are blocked by drug Electrical impulse 2. Pre-synaptic neuronelectrical signal causes release of neurotransmitters 4. NO electrical signal in Post-synaptic neuron 3. Neurotransmitterscross synapse and try to bind to receptors- CANT! 7: Circle which of the following drugs in the interactive choice is going to be able block the postsynaptic receptor? 7 LSD Antipsychotics Scopolamine Explain your choice: 5
6 Blocking reuptake of neurotransmitters by the pre-synaptic neuron Normal reuptake of neurotransmitters Once a neuron has sent the message on to the next neuron it doesn t want to keep sending the same message. It would be like sending the same text message to your friend over and over again. To stop sending the message after a neurotransmitter has done its job it is taken back up into the neuron it came from to be stored. In this way the neuron is recycling its chemical messengers (the neurotransmitters). 2. Receptors- are no longer being activated by the neurotransmitters Pre-synaptic neuron 1. Neurotransmitters once they have done their job they are taken back up into the axon for later use via re-uptake channels. NO electrical signal in Post-synaptic neuron Drugs can block reuptake of neurotransmitters Some drugs can block the reuptake of neurotransmitters. This means that the neurotransmitters can remain in the synapse where they will continue to stimulate postsynaptic receptors and continue to activate the postsynaptic neuron. This would be like sending a text message over and over again. 3. Neurotransmitter- remains in synapse where it can bind to receptors 4. Activation- of post- synaptic neuron!! Pre-synaptic neuron 1. Drug binds to and blocks re-uptake channel. Electrical impulse!!! Post-synaptic synaptic neuron 2. Neurotransmittercan no longer be taken up for storage 8 6
7 8: Circle which of the following drugs in the interactive choice is going to be able block the reuptake channel in the choice scenario? (HINT: Be careful to check the shape of the binding site on the reuptake channel on the computer screen). Marijuana LSD Cocaine The problem with drugs Drugs alter how we think feel and act. Many drugs impair our judgement and increase the likelihood that we will do dangerous things. They can also make us do stupid things. Whilst they can sometimes make as feel good to start off with, this is short lasting and they generally end up making us feel really bad. In the long term they can also cause serious and often permanent damage to our brains. This is because the way drugs act on neurons ends up changing how the neurons work and can kill the neurons Looking at the consequences of drug use on the brain 9a: Do all drugs act on the same neurotransmitters? Circle the correct answer Yes / No 9b: What are the long term effects of all drugs on neurons? Click on the scan links to take a look at some brain scans showing how different psychoactive drugs affect brain activity and answer the questions for each drug on the following pages. 7
8 ETHANOL Plant Source Ethanol is the by product of anaerobic cellular respiration. Various plants are used in the production of ethanol including grapes, wheat, barley and potatoes. Action Ethanol is a central nervous system depressant and has significant psychoactive effects in sub-lethal doses. Ethanol acts by binding to receptors for the neurotransmitter called GABA, increasing the inhibitory effect of the neurotransmitter. Medical sse Ethanol is commonly used as a preservative and antiseptic agent. Negative effects Long-term use of alcohol in excessive quantities is capable of damaging nearly every organ and system in the body. The developing adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of alcohol. Damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system can occur from sustained alcohol consumption Compare the brain scans of an alcoholic s brain to that of a non-alcoholic s brain. 10a: Describe what has happened to the alcoholic s brain? Why has this happened? 10b: How do you think this might affect the alcoholic s memory, ability to think clearly and overall brain function? 10c: If an alcoholic stopped drinking do you think they could re-grow the neurons that have died and recover normal brain function? 8
9 OPIATES (MORPHINE, HEROIN) Plant Source Morphine and codeine come from the opium poppy. Codeine and heroin can be synthetically made from morphine. Action Mimics bodies own endorphins and binds to opioid receptors. Medical use Pain killers nervous system depressants Negative effects Constipation, highly addictive, terrible withdrawal symptoms, alters gene expression, decreases the immune response Compare the brain scans of a heroin user s brain and that of a non-user. 11a: Is blood flow increased or decreased in the heroin user s brain? 11b: What does this tell us about the level of brain activity in the heroin user s brain? Is it increased or decreased? 11c: Why do you think good blood flow is so important for the brain? 11d: What do you think the consequences of reduced blood flow in the brain might be? 9
10 COCAINE Plant Source Cocaine is obtained from the leaves of coca plant indigenous to South America. The leaf is almost universally chewed by some native communities. Cocaine is psychoactive and highly addictive. It Increases alertness, feelings of well-being, euphoria, energy, motor activity, feelings of competence and sexuality. Action Stimulates the nervous system and acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Medicinal uses It is used as an analgesic (pain killer) and in morphine addiction. Negative effects Cocaine use produces anxiety, paranoia and restlessness, tremors, convulsions and increased body temperature Compare the brain scans of a cocaine user s brain and that of a non-user. 12a: What effect does cocaine have on brain activity? 12b: Do you think a cocaine user is going to be able to think clearly and make rational decisions? Explain. 12c: Cocaine molecules block (inhibit) the re-uptake of dopamine. Would you expect the reward pathway to have more or less dopamine stimulation? 10
11 TETRAHYDROCANNABINOL (CANNIBIS, MARIJUANA) Plant Source Tetrahydrocannabinol is the main psychoactive molecule found in the cannabis plant. Action Tetrahydrocannabinol is a nervous system depressant: the molecule acts on natural cannabinoid receptors. Medical Use Cannabis has a long history of medicinal use dating back 12,000 years. It has been used for pain relief, appetite stimulation, and treatment of nausea and as an anti-inflammatory. Negative effects Prolonged use causes altered memory function, lethargy, anxiety, hallucinations, cancer and heart disease due to the drug being inhaled via smoking. Recent evidence suggests prolonged use may trigger psychosis in some users Compare the brain scans of a cannabis user s, an Alzheimer s patient s brain and that of a non-user. 13a: What do the brain scans of a cannabis user and an Alzheimer s sufferer have in common? 13b: Is the blood flow to the brain of a cannabis user increased or decreased? 13c: What symptoms would a cannabis user and Alzheimer sufferers have in common? Explain you reasoning. 11
12 NICOTINE Plant Source Nicotine is a psychoactive drug sourced from a family of plants commonly known as nightshades. The tobacco plant is the most common source of nicotine. Action Nicotine is interesting as it can act as both a stimulant (increases neuron activity) and depressant (decreases neuron activity) of the nervous system depending on how much there is. At low doses it acts as a stimulant. At high doses it acts as a depressant. Medical Use Nicotine is used to treat epilepsy. It has also been shown to reduce the risk of some cancers. Nicotine increases concentration and memory, induces calmness, suppress the appetite, aids in pain relief and decreases anxiety. Negative effects These are mostly due to the way nicotine is taken through smoking and include heart disease, lung cancer and stroke Compare the body scans of a non-smoker and that of a smoker. Nicotine also affects the activities of many important chemicals in our bodies called metabolites. These substances are important for growth and development. The scan compares the activity of an important metabolite in a non-smoker to that in a smoker. 14a: Does the body scan show an increased or decreased level of activity for the smoker? 14b: Is the brain the only organ affected by smoking? What other organs are affected? 12
13 Extension questions Each neuron can receive chemical signals in the form of neurotransmitters from a large number of other neurons. These neurotransmitters may either stimulate or depress the activity of the post synaptic neuron. For example when dopamine acts on its receptor it stimulates the generation of an electrical signal in the post- synaptic neuron by exciting it. Whilst other neurotransmitters such as GABA actually inhibit the generation of an electrical signal in the post synaptic neuron, that is they depress the activity. It is a matter of adding the stimulatory (+) and inhibitory (-) signals together to determine whether chemical signals will result in the generation of an electrical signal in the post synaptic neuron. Axon - Pre-synaptic Neuron A Pre-synaptic neuron A uses the neurotransmitter GABA Axon Pre-synaptic Neuron B Pre-synaptic neuron B uses the neurotransmitter Glycine Pre-synaptic neuron C uses the neurotransmitter Glutamine Pre-synaptic neuron D uses the neurotransmitter Aspartate Post-synaptic Neuron Glutamine and Aspartate are excitatory or stimulatory neurotransmitters Axon - Pre-synaptic Neuron C GABA and Glycine are inhibitory or depressive neurotransmitters Axon - Pre-synaptic Neuron D 13
14 Assuming that each neurotransmitter acts on the neuron with the same level of strength can you determine which of the following scenarios will result in the generation of an electrical signal in the post synaptic neuron? - Axon A + B + C send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon A + C + D send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon D + B + C send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon A + D send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon A + B send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon A + C send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No - Axon D + C send their corresponding chemical message to the post-synaptic neuron. o Would an electrical signal be generated in the post-synaptic neuron? Yes / No Neurological diseases Neurologic diseases are disorders of the brain, spinal cord and nerves throughout your body. Together they control all the workings of the body. When something goes wrong with a part of your nervous system, you can have trouble moving, speaking, swallowing, breathing or learning. You can also have problems with your memory, senses or mood. Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face Stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk Slowness of movement Poor balance and coordination As symptoms get worse, people with the disease may have trouble walking, talking or doing simple tasks. They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. 14
15 In Parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. What kind of treatment do you think might be used to treat Parkinson s Disease? Schizophrenia Many studies have investigated the possible role of brain neurotransmitters in the development of schizophrenia. Most of these studies have focused on the neurotransmitter called dopamine. The "dopamine theory of schizophrenia" states that schizophrenia is caused by an overactive dopamine system in the brain. In light of this theory what kind of treatment do you think may be effective in treating the symptoms of Schizophrenia? Specifically how would the drug target neurons? Given what has been discussed above regarding Parkinson s Disease what might be some of the negative side effects of this treatment? It should be noted that whilst there is very strong evidence for the "dopamine theory of schizophrenia" there is also evidence that does not support it and there are a wide range of other factors involved in the disorder, including changes in serotonin neurotransmission. 15
BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES
 Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
NEUROTRANSMITTERS. Contraction of muscles to move our bodies Release hormones Psychological states of thinking and emotions
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain
 Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Nervous System Notes
 Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs. CHM 108 Lab. Spring Dr. Angela King
 Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON
 UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Drugs, addiction, and the brain
 Drugs, addiction, and the brain Topics to cover: What is addiction? How is addiction studied in the lab? The neuroscience of addiction. Caffeine Cocaine Marijuana (THC) What are the properties of addiction?
Drugs, addiction, and the brain Topics to cover: What is addiction? How is addiction studied in the lab? The neuroscience of addiction. Caffeine Cocaine Marijuana (THC) What are the properties of addiction?
TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (ACH) Deals with motor movement and memory. Too much and you will. Too little and you will Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer s disease. Serotonin Involved
TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (ACH) Deals with motor movement and memory. Too much and you will. Too little and you will Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer s disease. Serotonin Involved
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Recreational Chemistry
 Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
Physical and Physiological Aspects of Drug Use and Abuse
 Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Research Paper 21/08/
 Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
Nervous System 2. Quick Video
 Nervous System 2 McMurray/Tarshish Intro Psych Quick Video https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=4gdjcd68sge 1 10/16/15 Divisions of Nervous System Nervous system divisions CNS PNS Sensory (in) Motor (out)
Nervous System 2 McMurray/Tarshish Intro Psych Quick Video https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=4gdjcd68sge 1 10/16/15 Divisions of Nervous System Nervous system divisions CNS PNS Sensory (in) Motor (out)
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission. BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
General Functions (3) 1.Sensory gathers information 2.Integrative information is brought together 3.Motor responds to signals, homeostasis
 Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs
 Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Nervous System (cont)
 Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
2Lesson. Outline 3.2. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 3.2: How do our neurons communicate with each other? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
The Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain Webquest
 The Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain Webquest Part 1: Click here to begin ( might need a laptop not ipad) Complete this chart. Focus on what you DON T REMEMBER FROM HEALTH CLASS. If you know
The Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain Webquest Part 1: Click here to begin ( might need a laptop not ipad) Complete this chart. Focus on what you DON T REMEMBER FROM HEALTH CLASS. If you know
Psychology 210. Chemical Messengers. Types of NTs. Properties of Neurotransmitters. Cholinergic Neurons. Small molecule NTs.
 Psychology 210 Lecture 3 Kevin R Smith Chemical Messengers Neurotransmitters Act on neurons locally At one synapse Neuromodulators Act on clusters of neurons May not be in the immediate vicinity of where
Psychology 210 Lecture 3 Kevin R Smith Chemical Messengers Neurotransmitters Act on neurons locally At one synapse Neuromodulators Act on clusters of neurons May not be in the immediate vicinity of where
Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP
 Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
The study of drugs. Pharmacology
 The study of drugs Pharmacology Psychopharmacology The study of psychoactive drugs Psychoactive drugs Drugs that influence psychological processes mood emotion perception cognition behavior Psychoactive
The study of drugs Pharmacology Psychopharmacology The study of psychoactive drugs Psychoactive drugs Drugs that influence psychological processes mood emotion perception cognition behavior Psychoactive
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Introduction and Background
 Introduction and Background The brain consists of several large regions, each responsible for some of the activities vital for living. These include the brainstem, cerebellum, limbic system, diencephalon,
Introduction and Background The brain consists of several large regions, each responsible for some of the activities vital for living. These include the brainstem, cerebellum, limbic system, diencephalon,
9neurotransmission: Content lessons
 Making the leap part 2 Making the leap station Cards (Laminate for re-use) Making the Leap Station 1 Neuron Structure and Function The nervous system is like an electrical network. It relays information
Making the leap part 2 Making the leap station Cards (Laminate for re-use) Making the Leap Station 1 Neuron Structure and Function The nervous system is like an electrical network. It relays information
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test
 Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work
 Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Nervous System Communication. Nervous System Communication. The First Nerve Cells 1/2/11
 Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
MIDDLE SCHOOL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE. Customized for Prevention.org
 MIDDLE SCHL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE Customized for Prevention.org LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences, Health, and Physical Education Activity Duration 1 class session (45 minutes)
MIDDLE SCHL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE Customized for Prevention.org LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences, Health, and Physical Education Activity Duration 1 class session (45 minutes)
The Science of Addiction Webquest
 1 The Science of Addiction Webquest For this assignment you will be using the website of The University of Utah s Genetic Science Learning Library (http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/). For
1 The Science of Addiction Webquest For this assignment you will be using the website of The University of Utah s Genetic Science Learning Library (http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/). For
Addiction. Counselling. Short Course STUDY GUIDE
 Addiction Counselling Short Course STUDY GUIDE HOW TO WORK THROUGH THIS COURSE Over the following pages, you will move through a logical, self-paced learning experience that can enlighten and educate you
Addiction Counselling Short Course STUDY GUIDE HOW TO WORK THROUGH THIS COURSE Over the following pages, you will move through a logical, self-paced learning experience that can enlighten and educate you
Learning Intention. Name and describe the components of a neuron
 c) Neural Pathways Learning Intention Name and describe the components of a neuron Cells of the Nervous System The nervous system consists of a complex network of nerve cells called neurons which receive
c) Neural Pathways Learning Intention Name and describe the components of a neuron Cells of the Nervous System The nervous system consists of a complex network of nerve cells called neurons which receive
Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs
 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
The Art of being Human
 Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Heroin. Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor
 Heroin Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor Heroin H, Smack, Dope, Junk Can be purchased as a white powder White China or a dark resin Black Tar Opiates Derived from the opium poppy Morphine:
Heroin Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor Heroin H, Smack, Dope, Junk Can be purchased as a white powder White China or a dark resin Black Tar Opiates Derived from the opium poppy Morphine:
Peripheral Nervous System
 Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Step 1: Go to this web address
 Name: Period Drugs Webquest Step 1: Go to this web address http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/ The New Science of Addictions: Genetics and the Brain Drug addiction is a chronic disease characterized
Name: Period Drugs Webquest Step 1: Go to this web address http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/ The New Science of Addictions: Genetics and the Brain Drug addiction is a chronic disease characterized
Synapse. 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6.
 Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION. Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre
 1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
 CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
How Addiction Affects the Brain: The Neuroscience of Compulsive Behavior
 How Addiction Affects the Brain: The Neuroscience of Compulsive Behavior Table of Contents INTRODUCTION.... 3 NEUROSCIENCE 101: NEURONS AND NEUROTRANSMITTERS.... 4 BRAIN REGIONS INVOLVED IN ADDICTION:
How Addiction Affects the Brain: The Neuroscience of Compulsive Behavior Table of Contents INTRODUCTION.... 3 NEUROSCIENCE 101: NEURONS AND NEUROTRANSMITTERS.... 4 BRAIN REGIONS INVOLVED IN ADDICTION:
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Module 10: Drugs and Consciousness. Topics to digest, to expand our consciousness 3/23/16. Altering Consciousness: Drugs
 Module 10: Drugs and Consciousness Topics to digest, to expand our consciousness When Drugs are a problem: Criteria for Tolerance and Addic:on Types of Psychoac:ve Drugs: Depressants S:mulants Hallucinogens
Module 10: Drugs and Consciousness Topics to digest, to expand our consciousness When Drugs are a problem: Criteria for Tolerance and Addic:on Types of Psychoac:ve Drugs: Depressants S:mulants Hallucinogens
Neurons have cell membranes that separate them from the environment outside the neuron.
 Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes. Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
 Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes mood, perception, memory, state of consciousness May be illegal: Heroin Cocaine Legal: Alcohol nicotine Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes mood, perception, memory, state of consciousness May be illegal: Heroin Cocaine Legal: Alcohol nicotine Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis
 Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
The Biological Perspective. Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo
 The Biological Perspective Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo The Biological Perspective What is it? More than «the» one biological
The Biological Perspective Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo The Biological Perspective What is it? More than «the» one biological
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Neuropharmacology NOTES
 Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells. Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD
 Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Why does the writer above love running so much? One of the reasons. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure. Reader s Guide. Exploring Psychology
 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What are the biological factors that affect our behavior? In this unit we are going to take a look at biological psychology,
Biological Psychology Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What are the biological factors that affect our behavior? In this unit we are going to take a look at biological psychology,
The Nervous System. Chapter 35: Biology II
 The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
Modeling Excitatory and Inhibitory Chemical Synapses
 In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
3 Basic Nerve Cells. Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON
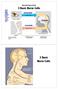 Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
18. Mind and Addiction
 18. Mind and Addiction What is Mind? Chemistry of the Brain: drugs and love 2% body weight Human Brain 20% energy expenditure 100 billion neurons 25,000 connections per neuron 100 trillion connections
18. Mind and Addiction What is Mind? Chemistry of the Brain: drugs and love 2% body weight Human Brain 20% energy expenditure 100 billion neurons 25,000 connections per neuron 100 trillion connections
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
AP Biology Unit 6. The Nervous System
 AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
Name Date Class. In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system.
 The Nervous System Reinforcement and Study Guide Section.1 The Nervous System In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system. Complete the table by filling in the missing information
The Nervous System Reinforcement and Study Guide Section.1 The Nervous System In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system. Complete the table by filling in the missing information
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
Cell Communication. Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model STO-133
 STO-133 Cell Communication Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model In this activity you will use a model to explore how cells send, receive, and respond to signals. Then you will use this model to
STO-133 Cell Communication Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model In this activity you will use a model to explore how cells send, receive, and respond to signals. Then you will use this model to
The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin
 The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin Plant Secondary Compounds The Spice of Life Cultural Use of Spices Spice Use by Region 1 Silurian Land Plants History of Insect Damage 416-447 MYA Colonization of
The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin Plant Secondary Compounds The Spice of Life Cultural Use of Spices Spice Use by Region 1 Silurian Land Plants History of Insect Damage 416-447 MYA Colonization of
The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA)
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
