Rescue therapy with adefovir in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus
|
|
|
- Gabriel Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 pissn eissn X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2014;20: Rescue therapy with adefovir in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus Hyun Young Woo 1, Jong Young Choi 2, Seung Kew Yoon 2, Dong Jin Suh 3, Seung Woon Paik 4, Kwang Hyub Han 5, Soon Ho Um 6, Byung Ik Kim 7, Heon Ju Lee 8, Mong Cho 1, Chun Kyon Lee 9, Dong Joon Kim 10, and Jae Seok Hwang 11 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Pusan, Korea; 2 Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea; 3 Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 4 Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 5 Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 6 Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 7 Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 8 Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea; 9 Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea; 10 Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea; 11 Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea Background/Aims: Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) is a nucleotide analogue that is effective against lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus (HBV). The aim of this study was to determine the long-term clinical outcomes after ADV rescue therapy in decompensated patients infected with lamivudine-resistant HBV. Methods: In total, 128 patients with a decompensated state and lamivudine-resistant HBV were treated with ADV at a dosage of 10 mg/day for a median of 33 months in this multicenter cohort study. Results: Following ADV treatment, 86 (72.3%) of 119 patients experienced a decrease in Child-Pugh score of at least 2 points, and the overall end-stage liver disease score decreased from 16±5 to 14±10 (mean ± SD, P<0.001) during the follow-up period. With ADV treatment, 67 patients (56.3%) had undetectable serum HBV DNA (detection limit, 0.5 pg/ ml). Virologic breakthrough occurred in 38 patients (36.1%) and 9 patients had a suboptimal ADV response. The overall survival rate was 89.9% (107/119), and a suboptimal response to ADV treatment was associated with both no improvement in Child-Pugh score ( 2 points; P=0.001) and high mortality following ADV rescue therapy (P=0.012). Conclusions: Three years of ADV treatment was effective and safe in decompensated patients with lamivudineresistant HBV. (Clin Mol Hepatol 2014;20: ) Keywords: Adefovir dipivoxil; Lamivudine-resistant; Decompensation; Hepatitis B virus Abbreviations: ADV, adefovir dipivoxil; CP, Child-Pugh; HBV, hepatitis B virus; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, model for end stage liver disease Corresponding author : Jong Young Choi Division of Hepatology, Liver Transplantation Center, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, #505 Banpodong, Seocho-gu, Seoul , Korea Tel , Fax ; jychoi@catholic.ac.kr Received : May. 21, 2014 / Revised : May. 30, 2014 / Accepted : Jun. 5, 2014 Copyright 2014 by The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
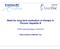
2 Hyun Young Woo, et al. Adefovir in decompensated cirrhosis INTRODUCTION About 350 million people worldwide have chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, 1 and these individuals are at increased risk of developing hepatic complications, such as cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 2 The ultimate goals of HBV treatment are to induce remission and to prevent such complications by sustained suppression of HBV replication. 3 Interferons, including pegylated interferons, and nucleotide analogues are regarded as standard treatment for patients with chronic hepatitis B, and nucleotide analogues have been shown effective and safe in chronically infected patients with decompensated cirrhosis Treatment with the nucleotide analogue lamivudine has been shown to improve liver function (Child-Pugh class) and to prolong survival in patients with decompensation. 4,5,7-9,11 In addition, earlier administration of antiviral drugs (that is, to patients with Child-Pugh B) leads to better prognosis than later administration to patients with poor liver function (that is, Child- Pugh C). 11 Over time, however, most patients experience resistance to long-term lamivudine therapy. 12,13 Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) is another orally bioavailable nucleotide analogue, effective against wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV in vitro and in the clinic Now, the outcome of ADV rescue therapy in chronic hepatitis patients with lamivudine resistance can be seen in practice guideline for hepatitis B through many clinical studies. 3,20 In addition, short-term treatment with 10 mg/day ADV of patients with decompensated cirrhosis and lamivudine resistance have been associated with favorable virologic and biochemical responses Less is known, however, about the long-term outcomes associated with ADV rescue therapy in decompensated patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV. 19 We have therefore assessed long-term clinical outcomes after ADV rescue therapy in decompensated patients infected with lamivudine-resistant HBV. hepatic function (n=18), baseline HCC (n=17), post-liver transplantation state (n=16), refusal of informed consent (n=6), and death before ADV treatment (n=17) (Fig. 1). At the time of this study, no antiviral therapy other than ADV was available in Korea for treatment of lamivudine-resistant HBV. The presence of lamivudine-resistant HBV was confirmed by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. 21 Patients remained in the study until ADV became available commercially. Decompensation was defined as a Child-Pugh (CP) score 7, together with a history of cirrhotic complications, including ascites, variceal hemorrhage, hepatic encephalopathy or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. 17,22 Concomitant lamivudine treatment was allowed and was discontinued at the discretion of the investigator. Patients with reduced renal function were managed by adjusting the dosing interval of ADV, based on creatinine clearance measurements. Factors assessed at baseline included complete blood chemistry; serum electrolyte concentrations; serum ALT, bilirubin, and albumin concentrations; international normalized ratio (INR) for prothrombin time; presence of cirrhotic complications, including hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, variceal hemorrhage or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; and hepatitis B serology, including HBsAg, anti-hbs, HBeAg, anti-hbe, and serum HBV DNA concentrations (Digene Hybrid Capture II assay, detection limit, 0.5 pg/ml). HBV serology, including HBV DNA concentration, and serum electrolytes, including serum creatinine and phosphorus concentrations, were measured regularly. Resistance surveillance for ADV was not routinely performed. All laboratory data were based on local references and assessed centrally. All patients in the study signed the informed consent form be- Exclusion (n=74) Compensation (n=18), HCC (n=17), Post LT (n=16), Refuse Tx (n=6), Death before Tx (n=17) Total patients (n=202) METHODS AND PATIENTS Decompensation, total (n=128) Decompensation without LT (n=119) -Median follow-up: 33 months- Liver transplantation (n=9) This retrospective, multi-center cohort study assessed 128 decompensated liver cirrhosis patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus who were treated with ADV 10 mg/day through the Adefovir depivoxil Compassionate Access Program (ACAP), starting in May Between May 2003 and March 2004, total 202 patients were screened at 11 hospitals in Korea. Of these, 74 patients were excluded from the analysis owing to compensated ADV treatment 6 months (n=10) Death (n=7) Unknown cause (n=3) Treatment continuation (n=95) ADV treatment >6 months (n=109) Treatment discontinuation (n=14) Undetectable HBV DNA (n=3) Non-compliance (n=8) Virologic breakthrough (n=3) Figure 1. Flow chart of patients. n, number; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma, LT, liver transplantation; Tx, treatment; ADV, adefovir dipivoxil; HBV, hepatitis B virus. 169
3 Clin Mol Hepatol Volume_20 Number_2 June 2014 fore enrollment. The study protocol was in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by each Institutional Review Board. Study endpoint The end of follow-up was patient death, time of liver transplantation or last visit. Following outcomes were analyzed: changes in CP scores and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD); the proportion of patients with normalized ALT, serum bilirubin and albumin concentrations, and prothrombin time (INR); the proportion of patients with undetectable serum HBV DNA during ADV treatment; the frequency of liver transplantation and overall patient survival. Antiviral responses, including virologic breakthrough, suboptimal response, and virologic relapse, were also evaluated. Virologic breakthrough was defined as a detectable serum HBV DNA during treatment after achieving serum HBV DNA undetectability; suboptimal response was defined as sustained detectable HBV DNA after at least 6 months of continued treatment; and virologic relapse was defined as an reappearance of detectable serum HBV DNA after discontinuation of treatment. 3,8,23 Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics were reported as mean ± standard deviation or median (range) unless indicated otherwise. Cumulative rate of patient s events was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Changes in biochemical variables from baseline were tested using a 1-sample t-test and differences between subgroups were compared using the chi-square test, or one way ANOVA test as appropriate. Factors associated with clinical outcomes were investigated using Cox proportional regression analysis. Any variables identified as significant (P<0.1) in univariate analysis were included in multivariate analysis. Two-sided tests with P<0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 14.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). RESULTS Patient characteristics The baseline characteristics of the 128 patients at the start of ADV treatment are shown in Table 1. Their mean age was 49.7±8.2 years and 97 patients (76%) were males. One hundred Table 1. Baseline characteristics at the time of ADV treatment Total patients (n=128) Age (years) 50 (23-71) Male gender, n (%) 97 (76) Duration of LAM (months) 37 (6-109) 1 year, n (%) 11 (8.6) 1 year<, 2 year, n (%) 24 (18.7) 2 year<, 3 year, n (%) 28 (21.9) 3 year<, n (%) 65 (50.8) LAM+ADF overlap (months) (n=75) 7.0 (1-25) Concomitant LAM Tx., n (%) Switch without overlapping 53 (41.4) Switch with overlapping 68 (53.1) Add-on 7 (5.5) Serum HBV DNA (pg/ml) 236 ( ) HBeAg positivity, n (%) 100 (78) ALT (U/L) 120 ( ) Prothrombin time (INR) 1.5 ( ) Total bilirubin (mg/dl) 3.0 ( ) Albumin (g/l) 2.9 ( ) Serum Creatinine (mg/dl) 0.9 ( ) MELD 15 (9-39) Child-Pugh score (A/B/C), n (%) 0/76/52 (0/59/41) History of cirrhotic complication, n (%) 64 (50) Ascites 24 (19) Variceal bleeding 18 (14) Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis 9 (7) Hepatic encephalopathy 13 (10) Data are given as median (range) or as number of cases (%). LAM, lamivudine; ADV, adefovir dipivoxil; Tx, treatment; HBV, hepatitis B virus; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, model for end stage liver disease. patients (78%) were positive for HBeAg at baseline and their mean HBV DNA concentration was 597±1039 pg/ml. None of the patients had HIV or hepatitis C virus co-infection. The mean duration of lamivudine treatment prior to ADV treatment was 36.2±17.6 months. Out of total patients (n=128), lamivudine was stopped after initiation of ADV therapy in 53 patients (41.4%). In the other 75 patients (58.6%), lamivudine was switched to ADV therapy with a mean 7.6±5.2 months of overlapping period. Of these 75 patients, 7 patients maintained lamivudine with concomitant ADV until the end of follow-up. Baseline hepatic function was CP class B in 59% and CP class C in 41%, and their mean 170
4 Hyun Young Woo, et al. Adefovir in decompensated cirrhosis MELD score was 16.6±5.6 (Table 1). Clinical efficacy of ADV rescue treatment Median follow-up period in the 128 patients was 33 months (range 1 41 months). The analysis of clinical efficacy was analyzed after excluding patients who received liver transplantation (n=9) before ADV therapy and who discontinued ADV early (n=10). Following treatment, CP score decreased by 2 points in 86 patients (78.9%), was unchanged in 16 patients (14.7%), and increased by 2 points in 7 patients (6.4%). Of the 67 patients with CP score B at baseline, 57 (85%) improved to CP score A, 6 (9%) remained at CP score B, and 4 (6%) deteriorated to CP score C. Of the 42 patients with CP score C at baseline, 29 (69%) improved to CP scores A (23, 55%) and B (6, 14%), while 13 (31%) remained at CP score C (P=0.001) (Fig. 2). Overall mean MELD score decreased from 16±5 to 14±10 (P<0.001). ALT was normalized in 74%, albumin in 67%, bilirubin in 70% and prothrombin time (INR) in 67.5%. Virologic response of ADV rescue treatment At baseline, all patients had HBV DNA concentrations >0.5 pg/ ml. Throughout ADV treatment period, undetectable HBV DNA (<0.5 pg/ml) was achieved and maintained in 67 (56.3%). During the ADV treatment, 38 of 119 (31.9%) showed virologic breakthrough during a median follow-up of 33 months; the cumulative incidence of virologic breakthrough was 6.5%, 15%, and 32.5% at 12, 24, and 36 months, respectively. Nine of 119 (7.6%) patients showed a suboptimal response to ADV treatment, as shown by sustained detectable HBV DNA ( 0.5 pg/ml) during a median 33 months (range 1-41 months). Among various clinical factors, virologic response to ADV (HBV DNA undetectability and virologic breakthrough vs. suboptimal response, 90.2%, 82.9% vs. 25%; P=0.001 Odds ratio (95% confidence interval (C.I.) ) was shown to be independently associated with improvement of CP score ( 2 points) by multivariate analysis (Table 2). The virologic response to ADV treatment (HBV DNA undetectability, virologic breakthrough, suboptimal response) was not associated with concomitant lamivudine treatment (switch without overlapping vs. switch with overlapping vs. add-on, P=0.852) or with the duration of previous lamivudine treatment (P=0.664) and other baseline characteristics were not different among patients with different virologic response except ALT level (Table 3). Of 7 patients with add-on ADV-lamivudine treatment, two patient di- 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% A 0% agnosed with HCC later had detectable HBV DNA at 6, 14 months of treatment (1 virologic breakthrough, 1 suboptimal response), respectively. Survival 42 (38%) 67 (62%) Before ADV Tx. After ADV Tx. Figure 2. Change in Child-Pugh class with ADV rescue therapy. (A) Pretreatment Child-Pugh class B; (B) pretreatment Child-Pugh class C. During the study period, nine patients underwent liver transplantation. Among the remaining 119 patients, 12 (10.1%) patients died. The cumulative 6-month, 1-year and 2-year survival rates were 95.8%, 94.1% and 89.6% (Fig. 3). Of the 12 patients who died, all patients except two patients were in CP class C at their enrollment. Five patients who died within 1-2 months of treatment without improvement in liver function had baseline MELD score 25 (Table 4). Two patients with CP class B (MELD score, 15 and 10, respectively) died at 6 months and 23 months after treatment, both due to HCC and liver failure. The remaining five patients died at a median of 17 months (range 6-23 months) after the start of treatment. These five patients showed unfavorable virologic responses; two patients had suboptimal response, two had virologic breakthrough and one had virologic relapse. Survival rate following ADV rescue therapy was different according to the virologic response to ADV treatment; patient with suboptimal response to ADV treatment showed significantly lower overall survival rate than with sustained virologic suppression or with virologic breakthrough (66.7% vs. 98%, 94.7%, respectively, P=0.012) (Fig. 4). Adverse events 6% 9% 85% Child C Child B Child A 42 (38%) 67 (62%) 31% 14% 55% Before ADV Tx. After ADV Tx. ADV was well tolerated in all 128 patients throughout the treatment period, with no serious side effects. During follow-up, the B 171
5 Clin Mol Hepatol Volume_20 Number_2 June 2014 Table 2. Factors associated with Child-Pugh score improvement ( 2 points) following ADV treatment Baseline Variables CP improvement (n=86) Age (years) 50 (23-71) 51 (38-65) Without CP Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis improvement (n=23) * P value P value OR (95% Confidence interval) LAM duration (months) 32 (6-67) 40 (8-109) ( ) Overlap period (months) 1 (0-25) 2 (0-19) Concomitant LAM Tx., n (%) Switch without overlapping 40 (46.5) 8 (34.8) Switch with overlapping 0 (0) 4 (17.4) Add-on 46 (53.5) 11 (47.8) Serum HBV DNA (pg/ml) ( ) 90.8 ( ) ALT (IU/L) 145 ( ) 99 (28-820) ( ) Total bilirubin (mg/dl) 3 ( ) 3.3 ( ) Albumin (g/l) 3.0 ( ) 2.6 ( ) ( ) Serum creatinine (mg/dl) 0.9 ( ) 0.8 ( ) ( ) Prothrombin time (INR) 1.48 ( ) 1.62 ( ) ( ) MELD 15 (9-28) 17 (9-37) ( ) Child-Pugh score 9 (7-13) 10 (7-13) ( ) Virologic response, n (%) ( ) Sustained virologic suppression 55 (63.9) 6 (26.1) Virologic breakthrough 29 (33.7) 9 (39.1) Suboptimal response 2 (2.4) 6 (26.1) Data are given as median (range) or as number of cases (%). CP, Child-Pugh score; OR, odds ratio; LAM, lamivudine; Tx, treatment; HBV, hepatitis B virus; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, model for end stage liver disease. * Virologic data was missing in two patients. P value was calculated using Cox proportional regression analysis. mean change in serum creatinine from baseline was 0.04±1.51 mg/dl (P=0.242). Ten of 98 patients (10.2%) showed 0.5 mg/dl increases in serum creatinine, with 6 patients discontinuing treatment due to death from liver failure. All six of these patients had baseline CP class C scores and their median MELD score was 22 (range 16-36). In the remaining four patients, the serum creatinine level did not exceed 1.5 mg/dl and all continued treatment until the end of follow-up. Serum phosphorus level did not decrease to less than 2 mg/dl during treatment. DISCUSSION This multicenter long-term cohort study assessed the effects of ADV treatment in 128 decompensated patients with lamivudineresistant HBV in an area in which HBV infections are highly endemic. Our findings strongly support previous results, showing that ADV rescue therapy was associated with virological, serological, and CP improvement, as well as with survival benefit in decompensated patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV In the previous studies, however, the follow-up period was relatively short (<12 months), and they involved a small number of recruited patients. In contrast, our patients had more severe liver dysfunction, all of CP class B (59%) and C (41%), and we used a longer follow-up period (median, 33 months; range 1-41 months), even when compared with a recent study of 226 patients, 25% with CP class A, who were followed for a mean of 37 weeks while awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. 19 To our knowledge, this study is the first to report long-term (approximately 3 years) results of ADV rescue treatment for decompensated patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV infection. Antiviral treatment has been found to improve CP score in decompensated patients with HBV-infection. 4,5,9,11 We found that 172
6 Hyun Young Woo, et al. Adefovir in decompensated cirrhosis Table 3. Comparison of baseline characteristics according to the virologic response to ADV treatment Sustained virologic suppression (n=67) Virologic breakthrough (n=38) Suboptimal response (n=9) P value Age (years) 50 (23-66) 50 (27-71) 51 (38-55) LAM duration (months) 37 (8-67) 29 (6-109) 37 (8-52) Overlap period (months) 1 (0-25) 2 (0-19) 10 (0-17) Concomitant LAM Tx., n (%) Switch without overlapping 28 (41.8) 16 (42.1) 3 (33.3) Switch with overlapping 36 (53.7) 21 (55.3) 5 (55.6) Add-on 3 (4.5) 1 (2.6) 1 (11.1) Serum HBV DNA (pg/ml) 236 ( ) ( ) 495 ( ) ALT (IU/L) 117 ( ) 240 ( ) 64 (52-126) Total bilirubin (mg/dl) 2.7 ( ) 3.4 ( ) 2.5 ( ) Albumin (g/l) 3.1 ( ) 2.9 ( ) 2.8 ( ) Serum creatinine (mg/dl) 0.90 ( ) 0.9 ( ) 0.8 ( ) Prothrombin time (INR) 1.48 ( ) 1.47 ( ) 1.49 ( ) MELD 14.5 (9-27) 17 (10-28) 14 (10-25) Child-Pugh score, n (%) 8 (7-13) 9 (7-13) 10 (7-12) Class B 49 (73.1) 21 (55.3) 4 (44.4) Class C 18 (26.9) 17 (44.7) 5 (55.6) Data are given as median (range) or as number of cases (%). LAM, lamivudine; Tx, treatment; HBV, hepatitis B virus; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, model for end stage liver disease. P value was calculated using one way ANOVA test. ADV treatment decreased CP score by at least 2 points in 78.9% of patients, had no effect in 14.7%, and increased CP score by at least 2 points in 6.4%. We found that 85% of patients with CP class B at baseline improved to CP class A, whereas 69% patients with CP class C improved to CP classes A and B, further suggesting that CP class C liver function at baseline is associated with poor clinical response to antiviral therapy in patients with HBV-related decompensation. Therefore, similar to baseline liver function at the start of lamivudine therapy, 11 baseline function at the initiation of ADV may predict response to treatment. In this study, the virologic response to ADV treatment was associated not only CP improvement but also survival rate following ADV treatment (HBV DNA undetectability, virologic breakthrough vs. suboptimal response). Previous study showed that antiviral therapy has been shown to slow disease progression only in patients with maintained viral suppression. 24 In contrast, failure of antiviral treatment had no impact on survival of HBV patients awaiting orthotropic liver transplantation. 23 The baseline liver function of patients enrolled in that study, however, was better: 68% of patients had low MELD scores. Interestingly, in the result, patients with virologic breakthrough following ADV treatment did not show poor clinical outcome as with suboptimal response. It may be because the observed duration following virologic breakthrough was not long enough to see the clinical consequences. Out of 12 ADV-treated patients who died during the study period, 5 patients died within 1-2 months of treatment had baseline MELD score 25. This finding is consistent with those of previous studies showing that the pretreatment severity of decompensated liver cirrhosis is the most important predictor of early mortality. 8,25-27 Clinical improvement would not be expected in these patients because they already had severe decompensation before ADV treatment. However, other antiviral agent such as tenofovir, known as more potent antiviral agent in lamivudine resistant HBV than ADV, 28,29 might suppress viral replication more rapidly and completely and would result in different outcome in these decompensated patients. A major concern during antiviral treatment in patients with decompensation is the appearance of drug-resistant HBV. In lamivu- 173
7 Clin Mol Hepatol Volume_20 Number_2 June 2014 Table 4. Causes of death in 12 patients who died during ADV treatment Patients Baseline CP score /Final CP score Baseline MELD score /Final MELD score Follow-up (months) Cause Antiviral response /15 35/35 1 Variceal bleeding NA /13 25/45 2 Liver failure NA /15 30/47 1 Hepatorenal syndrome NA /13 30/36 2 Liver failure NA /14 37/41 1 Liver failure NA 197 9/11 15/19 6 HCC and liver failure Undetectable HBV DNA 59 12/13 17/30 6 Hepatic encephalopathy Virologic breakthrough 45 12/13 25/29 12 Hepatorenal syndrome Suboptimal response 42 12/13 22/26 17 Liver failure Virologic breakthrough 14 10/13 16/51 21 Liver failure Suboptimal response 80 9/14 10/21 23 HCC and liver failure Suboptimal response 75 12/13 17/NA 17 Liver failure Virologic relapse CP score, Child-Pugh score; MELD, model for end stage liver disease; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NA, not available. Cumulative survival rate (%) Antiviral treatment (year) Patient at risk Figure 3. Cumulative survival curve of the 119 decompensated patients infected with lamivudine-resistant HBV who received ADV rescue treatment (median treatment duration, 33 months). dine-resistant patients, the cumulative incidence of ADV mutations 24 months after switching from lamivudine to ADV was more than 25%, whereas the 2-year incidence in naïve patients receiving ADV therapy was 3%. 16, Of 67 lamivudine-resistant Korean patients treated with ADV for 2 years, 9 (25.4%) showed ADV mutations. 30 Eight of these nine patients had liver cirrhosis at baseline, including four with decompensated cirrhosis. Meanwhile, given that the recent data, most would agree that the standard of care for lamivudine resistance in HBV would be the addition of a nucleotide (ex. lamivudine plus ADV or emtricitabine plus tenofovir) rather than the substitution of a nucleotide, particularly in a decompensated patient in light of recent consensus recommendations. 3 In recent study, ADV resistant rate at 3 years in patients with ADV added to lamivudine was 0% compared to 20% in patients switching to ADV monotherapy. 33 However, this is retrospective study and the consensus was not solid in that time. In this study, 38 of 119 (31.9%) patients showed viral breakthrough during a median 33 months of ADV treatment, although genotypic ADV resistance was not tested in all patients. The viral breakthrough rate was relatively high because follow-up period was long (33 months) and concomitant lamivudine treatment was discontinued in most cases. In addition, even in patients with continued lamivudine treatment, the duration of combination treatment was too short for the proper evaluation of virologic outcome. This study had some limitations. Its retrospective, observational design may lead to possible bias. Moreover, there was few with combination therapy in which patients were treated with both ADV and lamivudine. In addition, genotypic mutations conferring resistance to ADV were not analyzed. Despite these limitations, our study population clearly reflects the population of patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV receiving ADV rescue therapy for decompensation in South Korea, an area highly endemic for HBV. Although the clinical outcomes of HBV-related decompensated were serious, there was no evidence to support an alternative treatment strategy in decompensated patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV. In addition, this cohort study was large number, longterm follow up study compared to previous studies for decompensated patients with lamivudine resistant HBV. 18,19 In conclusion, long term ADV treatment was effective and safe in decompensated patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV with resulted of 2-point decrease in CP score in 72.3% and a virological 174
8 Hyun Young Woo, et al. Adefovir in decompensated cirrhosis Cumulative survival rate (%) P=0.011 Sustained virologic suppression Virologic breakthrough Suboptimal response Antiviral treatment (year) Sustained virologic suppression Virologic breakthrough Suboptimal response Figure 4. Cumulative survival curves of patients with sustained virologic suppression (n=67), virologic breakthrough (n=38), and suboptimal response (n=9) who received ADV rescue therapy. Patients with a suboptimal response to ADV treatment exhibited a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with sustained virologic suppression or with virologic breakthrough (66.7% vs. 98% and 94.7%, respectively; P=0.012). response rate of 56.3%. However, considering relatively high rates of early mortality and poor clinical outcome in suboptimal responder as well as viral breakthrough rate of 31.9% over a median follow-up period of 33 months, combination treatment with more potent, less resistant nucleos(t)ide would be better strategy in these patients. This needs to be validated in further prospective studies with longer-term follow-up periods. Acknowledgements This work was supported by clinical research grant from Pusan National University Hospital Conflicts of Interest The authors have no conflicts to disclose. REFERENCES 1. Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat 2004;11: Beasley RP. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 1988;61: Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007;45: Villeneuve JP, Condreay LD, Willems B, Pomier-Layrargues G, Fenyves D, Bilodeau M, et al. Lamivudine treatment for decompensated cirrhosis resulting from chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2000;31: Kapoor D, Guptan RC, Wakil SM, Kazim SN, Kaul R, Agarwal SR, et al. Beneficial effects of lamivudine in hepatitis B virus-related decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2000;33: Perrillo R, Tamburro C, Regenstein F, Balart L, Bodenheimer H, Silva M, et al. Low-dose, titratable interferon alfa in decompensated liver disease caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 1995;109: Perrillo RP, Wright T, Rakela J, Levy G, Schiff E, Gish R, et al. A multicenter United States-Canadian trial to assess lamivudine monotherapy before and after liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2001;33: Fontana RJ, Hann HW, Perrillo RP, Vierling JM, Wright T, Rakela J, et al. Determinants of early mortality in patients with decompensated chronic hepatitis B treated with antiviral therapy. Gastroenterology 2002;123: Yao FY, Bass NM. Lamivudine treatment in patients with severely decompensated cirrhosis due to replicating hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol 2000;33: Bain VG, Kneteman NM, Ma MM, Gutfreund K, Shapiro JA, Fischer K, et al. Efficacy of lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with 175
9 Clin Mol Hepatol Volume_20 Number_2 June 2014 active viral replication and decompensated cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation 1996;62: Bae SH, Yoon SK, Choi JY, Jang JW, Cho SH, Yang JM, et al. Timing of lamivudine administration according to Child class in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;20: Liaw YF, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, et al. Effects of extended lamivudine therapy in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. Gastroenterology 2000;119: Locarnini S. Molecular virology and the development of resistant mutants: implications for therapy. Semin Liver Dis 2005;25(Suppl 1): Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigenpositive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003;348: Peters MG, Hann Hw Hw, Martin P, Heathcote EJ, Buggisch P, Rubin R, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil alone or in combination with lamivudine in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2004;126: Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003;348: Perrillo R, Hann HW, Mutimer D, Willems B, Leung N, Lee WM, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil added to ongoing lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B with YMDD mutant hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 2004;126: Schiff ER, Lai CL, Hadziyannis S, Neuhaus P, Terrault N, Colombo M, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil therapy for lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B in pre- and post-liver transplantation patients. Hepatology 2003;38: Schiff E, Lai CL, Hadziyannis S, Neuhaus P, Terrault N, Colombo M, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for wait-listed and post-liver transplantation patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B: final long-term results. Liver Transpl 2007;13: Keeffe EB, Dieterich DT, Han SH, Jacobson IM, Martin P, Schiff ER, et al. A treatment algorithm for the management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: an update. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4: Allen MI, Gauthier J, DesLauriers M, Bourne EJ, Carrick KM, Baldanti F, et al. Two sensitive PCR-based methods for detection of hepatitis B virus variants associated with reduced susceptibility to lamivudine. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37: de Jongh FE, Janssen HL, de Man RA, Hop WC, Schalm SW, van Blankenstein M. Survival and prognostic indicators in hepatitis B surface antigen-positive cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology 1992;103: Osborn MK, Han SH, Regev A, Bzowej NH, Ishitani MB, Tran TT, et al. Outcomes of patients with hepatitis B who developed antiviral resistance while on the liver transplant waiting list. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5: Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med 2004;351: Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 2000;31: Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with endstage liver disease. Hepatology 2001;33: Tseng PL, Lu SN, Tung HD, Wang JH, Changchien CS, Lee CM. Determinants of early mortality and benefits of lamivudine therapy in patients with hepatitis B virus-related decompensated liver cirrhosis. J Viral Hepat 2005;12: van Bömmel F, Wünsche T, Mauss S, Reinke P, Bergk A, Schürmann D, et al. Comparison of adefovir and tenofovir in the treatment of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2004;40: van Bömmel F, Zöllner B, Sarrazin C, Spengler U, Hüppe D, Möller B, et al. Tenofovir for patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and high HBV DNA level during adefovir therapy. Hepatology 2006;44: Yeon JE, Yoo W, Hong SP, Chang YJ, Yu SK, Kim JH, et al. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil in lamivudine resistant chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil. Gut 2006;55: Lee YS, Suh DJ, Lim YS, Jung SW, Kim KM, Lee HC, et al. Increased risk of adefovir resistance in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B after 48 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy. Hepatology 2006;43: Fung SK, Chae HB, Fontana RJ, Conjeevaram H, Marrero J, Oberhelman K, et al. Virologic response and resistance to adefovir in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2006;44: Rapti I, Dimou E, Mitsoula P, Hadziyannis SJ. Adding-on versus switching-to adefovir therapy in lamivudine-resistant HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007;45:
Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development
 Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute of Digestive Disease Director, Center for Liver Health Assistant Dean,
Does Viral Cure Prevent HCC Development Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute of Digestive Disease Director, Center for Liver Health Assistant Dean,
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17: (doi: /IMP1945)
 Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B
 Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B Dr James YY Fung, FRACP, MD Department of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Liver Transplant Center Queen Mary Hospital State Key Laboratory for Liver
Management of Decompensated Chronic Hepatitis B Dr James YY Fung, FRACP, MD Department of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Liver Transplant Center Queen Mary Hospital State Key Laboratory for Liver
HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis
 HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
HBV Therapy in Special Populations: Liver Cirrhosis Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:261-267 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.4.261 Original Article Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:261-267 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.4.261 Original Article Virologic response is not durable after adefovir discontinuation in lamivudine-resistant
Management of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance
 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:32-41 Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients Hyo Jin Kim,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:32-41 Long-term efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy after multiple nucleos(t)ide analogue failure in chronic hepatitis B patients Hyo Jin Kim,
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting
 29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
SERUM CYSTATIN C CONCENTRATION IS A POWERFUL PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOTIC ASCITES
 SERUM CYSTATIN C CONCENTRATION IS A POWERFUL PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOTIC ASCITES YEON SEOK SEO, 1 SOO YOUNG PARK, 2 MOON YOUNG KIM, 3 SANG GYUNE KIM, 4 JUN YONG PARK, 5 HYUNG JOON YIM,
SERUM CYSTATIN C CONCENTRATION IS A POWERFUL PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOTIC ASCITES YEON SEOK SEO, 1 SOO YOUNG PARK, 2 MOON YOUNG KIM, 3 SANG GYUNE KIM, 4 JUN YONG PARK, 5 HYUNG JOON YIM,
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major public health
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Compensated Cirrhosis Patients With Low Viral Load Dong Hyun Sinn, 1 Junggyu Lee, 1 Juna Goo, 2 Kyunga Kim, 2 Geum-Youn Gwak, 1 Yong-Han
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Compensated Cirrhosis Patients With Low Viral Load Dong Hyun Sinn, 1 Junggyu Lee, 1 Juna Goo, 2 Kyunga Kim, 2 Geum-Youn Gwak, 1 Yong-Han
Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B
 Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:469 477 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1772) Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon 1, Seung Up Kim
Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:469 477 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1772) Original article Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon 1, Seung Up Kim
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 2013
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance
 Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future
 Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
 The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
Disclaimer. Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only
 Disclaimer Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only Any unsolicited request from HCP must be forwarded to Medical Information Housekeeping
Disclaimer Presenter Release are for reactive use by Medical Information only internal learning/educational use only Any unsolicited request from HCP must be forwarded to Medical Information Housekeeping
Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment. New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p
 Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy. Thomas Berg
 Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV)
 Adding-on Versus Switching-to Adefovir Therapy in Lamivudine-Resistant HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Irene Rapti, 1 Evangelini Dimou, 1,2 Panayota Mitsoula, 2 and Stephanos J. Hadziyannis 1,2 We studied
Adding-on Versus Switching-to Adefovir Therapy in Lamivudine-Resistant HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Irene Rapti, 1 Evangelini Dimou, 1,2 Panayota Mitsoula, 2 and Stephanos J. Hadziyannis 1,2 We studied
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea -
 Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1207 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1207-1212 The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score-Based System Predicts Short
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1207 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1207-1212 The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score-Based System Predicts Short
CURRENT TREATMENT. Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
Pegasys Hepatitis B. Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.02 Subject: Pegasys Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Pegasys Hepatitis
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.02 Subject: Pegasys Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Pegasys Hepatitis
Who to Treat? Consider biopsy Treat. > 2 ULN Treat Treat Treat Treat CIRRHOTIC PATIENTS Compensated Treat HBV DNA detectable treat
 Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B. Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona.
 NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of, and/or, received speaker fee from
NUCs for Chronic Hepatitis B Rafael Esteban Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Instituto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of, and/or, received speaker fee from
Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B
 ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2007) 25: 183-188 CASE REPORT Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative
ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2007) 25: 183-188 CASE REPORT Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative
Jong Young Choi, M.D.
 The Liver Week 2014 Jong Young Choi, M.D. Dept. of Internal Medicine The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine The clinical study for natural history of LC is not many. Most of them was done
The Liver Week 2014 Jong Young Choi, M.D. Dept. of Internal Medicine The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine The clinical study for natural history of LC is not many. Most of them was done
Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis B by nucleosides and nucleotides. K. Zhdanov
 EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
The presence of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) is
 Assessment of Current Criteria for Primary Nonresponse in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Entecavir Therapy Young-Joo Yang, 1 Ju Hyun Shim, 2 Kang Mo Kim, 2 Young-Suk Lim, 2 and Han Chu Lee 2 A
Assessment of Current Criteria for Primary Nonresponse in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Entecavir Therapy Young-Joo Yang, 1 Ju Hyun Shim, 2 Kang Mo Kim, 2 Young-Suk Lim, 2 and Han Chu Lee 2 A
Chronic HBV Management in 2013
 Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But
 HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Insttuto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of,
HBeAg-positve chronic hepatts B: Why do I treat my patent with a NA? Maria But Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron and Ciberehd del Insttuto Carlos III. Barcelona. Spain Disclosures Advisory board of,
HBV (AASLD) CHB, HBV, CHB , ( < 5% ) 11 ( immune tolerant phase) : 21 ( immune clearance phase ) : 31 ( inactive phase) : HBeAg - HBe HBV DNA ALT
 2010262 125 R51216 + 2 C 1001-5256 (2010) 02-0125 - 06 2005 12 [ 1 ], (HBV ) (APASL) ( EASL ) (AASLD) (CHB) [ 2 4 ], ( ) ( ), CHB,, CHB CHB,, CHB,, 2 1 HBV hepatitis B virus CHB chronic hepatitis B HB
2010262 125 R51216 + 2 C 1001-5256 (2010) 02-0125 - 06 2005 12 [ 1 ], (HBV ) (APASL) ( EASL ) (AASLD) (CHB) [ 2 4 ], ( ) ( ), CHB,, CHB CHB,, CHB,, 2 1 HBV hepatitis B virus CHB chronic hepatitis B HB
Antiviral Therapy 14:
 Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Yun Jung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Eun Soo Kim, Kyung Sik Park, Kwang Bum Cho, Woo Jin Chung, and Jae Seok Hwang
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:41-47 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.41 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article Rapid normalization of alanine aminotransferase predicts viral
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:41-47 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.41 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article Rapid normalization of alanine aminotransferase predicts viral
Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
Current Status of HBV and Liver Transplant
 Current Status of HBV and Liver HBV as Indication for Liver ation in U.S. Significant decrease in rate of wait listing for decompensated cirrhosis since 2003 (since s) No change in rate of wait listing
Current Status of HBV and Liver HBV as Indication for Liver ation in U.S. Significant decrease in rate of wait listing for decompensated cirrhosis since 2003 (since s) No change in rate of wait listing
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update.
 Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
Emerging Drug List ADEFOVIR DIPIVOXIL FOR HEPATITIS B VIRUS INFECTION NO. 48 SEPTEMBER Generic (Trade Name): Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM )
 Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM ) Gilead Sciences, Inc. NO. 48 SEPTEMBER 2003 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: For the treatment of adults showing evidence of active
Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM ) Gilead Sciences, Inc. NO. 48 SEPTEMBER 2003 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: For the treatment of adults showing evidence of active
High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy in patients with nucleoside-refractory hepatitis B
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:75-83 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.75 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2012;18:75-83 http://dx.doi.org/10.3350/kjhep.2012.18.1.75 pissn: 1738-222X eissn: 2093-8047 Original Article High efficacy of adefovir and entecavir combination therapy
Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term 2015
 THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
Our better understanding of the natural
 TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy. Watcharasak Chotiyaputta
 Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy Watcharasak Chotiyaputta Progression of Liver Disease Goal of HBV Treatment: prevention the development of cirrhosis
Optimized HBV Treatment Through Baseline and on-treatment Predictor Oral Antiviral Therapy Watcharasak Chotiyaputta Progression of Liver Disease Goal of HBV Treatment: prevention the development of cirrhosis
Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated Cirrhosis
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 6, November 2017, pp. 828-834 ORiginal Article Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 6, November 2017, pp. 828-834 ORiginal Article Effects of Entecavir and Tenofovir on Renal Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Compensated and Decompensated
Pegasys Pegintron Ribavirin
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.47 Subsection: Anti-infective nts Original Policy Date: January 1, 2019 Subject: Pegasys Pegintron
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.47 Subsection: Anti-infective nts Original Policy Date: January 1, 2019 Subject: Pegasys Pegintron
MedInform. HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Original Article
 DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease
 Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus
 Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Hussien Elsiesy, MD, and Douglas Dieterich, MD Corresponding author Douglas Dieterich, MD Division of Liver Diseases, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, One Gustave
Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Hussien Elsiesy, MD, and Douglas Dieterich, MD Corresponding author Douglas Dieterich, MD Division of Liver Diseases, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, One Gustave
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: nucleot(s)ide analogues vs. pegylated interferon
 Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
C hronic hepatitis B (CHB) virus infection affects more
 161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
Low Resistance to Adefovir Combined With Lamivudine: A 3-Year Study of 145 Lamivudine-Resistant Hepatitis B Patients
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:1445 1451 Low Resistance to Adefovir Combined With Lamivudine: A 3-Year Study of 145 Lamivudine-Resistant Hepatitis B Patients PIETRO LAMPERTICO,* MAURO VIGANÒ,* ELENA MANENTI,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:1445 1451 Low Resistance to Adefovir Combined With Lamivudine: A 3-Year Study of 145 Lamivudine-Resistant Hepatitis B Patients PIETRO LAMPERTICO,* MAURO VIGANÒ,* ELENA MANENTI,*
Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Efficacy and safety of entecavir and/or tenofovir in hepatitis B compensated and decompensated cirrhotic patients in clinical practice
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antiviral treatment in hepatitis B-related cirrhosis., 2013; 12 (2): 205-212 March-April, Vol. 12 No.2, 2013: 205-212 205 Efficacy and safety of entecavir and/or tenofovir in hepatitis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antiviral treatment in hepatitis B-related cirrhosis., 2013; 12 (2): 205-212 March-April, Vol. 12 No.2, 2013: 205-212 205 Efficacy and safety of entecavir and/or tenofovir in hepatitis
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B
 Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. with a nucleos(t)ide analogue?
 4 th PARIS HEPATITIS CONFERENCE HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my chronic hepatitis B patients with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? George V. Papatheodoridis, MD 2nd Department of Internal
4 th PARIS HEPATITIS CONFERENCE HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my chronic hepatitis B patients with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? George V. Papatheodoridis, MD 2nd Department of Internal
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a
 Clinical Improvement in Patients With Decompensated Liver Disease Caused by Hepatitis B After Treatment With Lamivudine Craig A. Sponseller, Bruce R. Bacon, and Adrian M. Di Bisceglie Lamivudine is effective
Clinical Improvement in Patients With Decompensated Liver Disease Caused by Hepatitis B After Treatment With Lamivudine Craig A. Sponseller, Bruce R. Bacon, and Adrian M. Di Bisceglie Lamivudine is effective
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a major
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:541 545 Hepatitis B Virus DNA Level Predicts Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B WEN JUEI JENG, I SHYAN SHEEN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:541 545 Hepatitis B Virus DNA Level Predicts Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B WEN JUEI JENG, I SHYAN SHEEN,
An estimated 350 million individuals are chronically
 Long-Term Effect of Antiviral Therapy on Disease Course After Decompensation in Patients With Hepatitis B Virus Related Cirrhosis Jeong Won Jang, 1,9 Jong Young Choi, 1,9 Young Seok Kim, 2,9 Hyun Young
Long-Term Effect of Antiviral Therapy on Disease Course After Decompensation in Patients With Hepatitis B Virus Related Cirrhosis Jeong Won Jang, 1,9 Jong Young Choi, 1,9 Young Seok Kim, 2,9 Hyun Young
Low-Level Viremia and the Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Receiving Entecavir Treatment
 HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 66, NO. 2, 2017 VIRAL HEPATITIS Low-Level Viremia and the Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Receiving Entecavir Treatment Jung Hee Kim,* Dong Hyun Sinn,* Wonseok Kang,
HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 66, NO. 2, 2017 VIRAL HEPATITIS Low-Level Viremia and the Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Receiving Entecavir Treatment Jung Hee Kim,* Dong Hyun Sinn,* Wonseok Kang,
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status Asokananda Konar
 Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
Lamivudine Therapy for Korean Children with Chronic Hepatitis B
 Yonsei Med J 48(6):927-933, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.927 Original Article Lamivudine Therapy for Korean Children with Chronic Hepatitis B Hong Koh, Seoung Yon Baek, and Ki Sup Chung Department of
Yonsei Med J 48(6):927-933, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.927 Original Article Lamivudine Therapy for Korean Children with Chronic Hepatitis B Hong Koh, Seoung Yon Baek, and Ki Sup Chung Department of
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease is
 Antiviral Activity and Safety of LB80380 in Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Lamivudine-Resistant Disease Man-Fung Yuen, 1 * Kwang-Hyub Han, 2 * Soon-Ho Um, 3 Seung Kew
Antiviral Activity and Safety of LB80380 in Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Lamivudine-Resistant Disease Man-Fung Yuen, 1 * Kwang-Hyub Han, 2 * Soon-Ho Um, 3 Seung Kew
Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy
 Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy Wonseok Kang Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Establishment of Individual Prediction Model for Treatment Response in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients on Lamivudine Monotherapy Wonseok Kang Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Chronic Hepatitis B Drug: Baraclude (entecavir), Epivir (lamivudine), Hepsera (adefovir), Intron A (interferon alfa- 2b), Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a), Tyzeka (telbivudine),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Chronic Hepatitis B Drug: Baraclude (entecavir), Epivir (lamivudine), Hepsera (adefovir), Intron A (interferon alfa- 2b), Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a), Tyzeka (telbivudine),
Is there a need for combination therapy? No. Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain
 Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Intron A HEPATITIS B. Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Intron A HEPATITIS
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Intron A HEPATITIS
The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B
 REVIEW The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B Evangelini Dimou Vasilios Papadimitropoulos Stephanos J Hadziyannis Department of Medicine and Liver Unit, Henry Dunant Hospital, Athens,
REVIEW The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B Evangelini Dimou Vasilios Papadimitropoulos Stephanos J Hadziyannis Department of Medicine and Liver Unit, Henry Dunant Hospital, Athens,
Slides are the property of the author and AASLD. Permission is required from both AASLD and the author for reuse.
 Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy
 Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature,
Hepatitis B Prior Authorization Policy Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature,
Complications Requiring Hospital Admission and Causes of In-Hospital Death over Time in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Cirrhosis Patients
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2016, pp. 95-100 ORiginal Article Complications Requiring Hospital Admission and Causes of In-Hospital Death over Time in and Cirrhosis Patients Hee Yeon Kim, Chang
Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2016, pp. 95-100 ORiginal Article Complications Requiring Hospital Admission and Causes of In-Hospital Death over Time in and Cirrhosis Patients Hee Yeon Kim, Chang
Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B
 Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Partial virological response
Partial virological response to entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B Young Eun Chon Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University Partial virological response
J.C. WANG, L.L. HE, Q. CHEN 1. Introduction. Abstract. BACKGROUND: Either combination. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes!
 18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine and entecavir
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2017;23:230-238 Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2017;23:230-238 Efficacy of tenofovir-based rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to lamivudine
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_
 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06545.x REVIEW Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_6545 138..143 Man-Fung Yuen and Ching-Lung Lai Department of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong,
doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06545.x REVIEW Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_6545 138..143 Man-Fung Yuen and Ching-Lung Lai Department of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong,
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics. Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology
 Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation
 BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
Landmarks for Prevention and Treatment
 HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my patient with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? Dr. Nancy Leung BSc(Lon) MSc(Lon) MBBS(Lon) MD(Lon), FRCP(Lon) FRCP(Edin) FHKCP FHKAM Consultant Physician, Alice
HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my patient with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? Dr. Nancy Leung BSc(Lon) MSc(Lon) MBBS(Lon) MD(Lon), FRCP(Lon) FRCP(Edin) FHKCP FHKAM Consultant Physician, Alice
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls. Agenda
 Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection
 Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
Hepatitis B virus infection (HBV) is global epidemic. Current Treatment Strategies for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B CHRONIC HEPATITIS B
 CHRONIC HEPATITIS B Current Treatment Strategies for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Case Study and Commentary, Robert J. Wong, MD, and Walid S. Ayoub, MD ABSTRACT Objective: To review current treatment
CHRONIC HEPATITIS B Current Treatment Strategies for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Case Study and Commentary, Robert J. Wong, MD, and Walid S. Ayoub, MD ABSTRACT Objective: To review current treatment
Natural History of HBV Infection
 Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir
 Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Therapeutic Guidelines on Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asia
 SPECIAL FEATURE Vol.6 No.2 (April 2001) Therapeutic Guidelines on Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asia Abstract Dr. Nancy Leung Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Prince of Wales Hospital, The
SPECIAL FEATURE Vol.6 No.2 (April 2001) Therapeutic Guidelines on Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asia Abstract Dr. Nancy Leung Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Prince of Wales Hospital, The
Original article Entecavir versus lamivudine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatic decompensation
 Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:605 612 (doi: 10.3851/IMP2027) Original article Entecavir versus lamivudine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatic decompensation Yao-Chun Hsu 1, Lein-Ray
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:605 612 (doi: 10.3851/IMP2027) Original article Entecavir versus lamivudine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatic decompensation Yao-Chun Hsu 1, Lein-Ray
Challenges in therapy of chronic hepatitis B
 Journal of Hepatology 39 (2003) S230 S235 www.elsevier.com/locate/jhep Challenges in therapy of chronic hepatitis B Jay H. Hoofnagle* Division of Digestive Diseases and Nutrition, National Institute of
Journal of Hepatology 39 (2003) S230 S235 www.elsevier.com/locate/jhep Challenges in therapy of chronic hepatitis B Jay H. Hoofnagle* Division of Digestive Diseases and Nutrition, National Institute of
It is estimated that there are 1.25 million individuals
 Treatment Recommendations for Chronic Hepatitis B: An Evaluation of Current Guidelines Based on a Natural History Study in the United States Myron John Tong, 1,2 Carlos Hsien, 2 Leeyen Hsu, 2 Hai-En Sun,
Treatment Recommendations for Chronic Hepatitis B: An Evaluation of Current Guidelines Based on a Natural History Study in the United States Myron John Tong, 1,2 Carlos Hsien, 2 Leeyen Hsu, 2 Hai-En Sun,
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona
 Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
A Preliminary Study on the Safety and Efficacy of HD-03/ES Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
 C linical S tudy Janardan Singh* Anupam Chakraborty* Mukul Chandra Dhar* Sudhakaran C** Mitra SK** A Preliminary Study on the Safety and Efficacy of HD-03/ES Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis
C linical S tudy Janardan Singh* Anupam Chakraborty* Mukul Chandra Dhar* Sudhakaran C** Mitra SK** A Preliminary Study on the Safety and Efficacy of HD-03/ES Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 2015
 How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:505 512 Predictive Factors for Early HBeAg Seroconversion in Acute Exacerbation of Patients With HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B HYOUNG SU KIM,* HA JUNG KIM, WOON GEON SHIN,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:505 512 Predictive Factors for Early HBeAg Seroconversion in Acute Exacerbation of Patients With HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B HYOUNG SU KIM,* HA JUNG KIM, WOON GEON SHIN,*
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 2013 update
 22 February 213 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 213 update Pietro Lampertico 1st Gastroenterology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Cà Granda - Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università di Milano EASL 212 Clinical
22 February 213 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 213 update Pietro Lampertico 1st Gastroenterology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Cà Granda - Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università di Milano EASL 212 Clinical
Hepatitis B: Future treatment developments
 Hepatitis B: Future treatment developments VIII International Update Workshop in Hepatology Curitiba, 27.08.2016 Christoph Sarrazin St. Josefs-Hospital Wiesbaden and Goethe-University, Frankfurt am Main
Hepatitis B: Future treatment developments VIII International Update Workshop in Hepatology Curitiba, 27.08.2016 Christoph Sarrazin St. Josefs-Hospital Wiesbaden and Goethe-University, Frankfurt am Main
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia
 Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Intron A Hepatitis B. Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
Management of hepatitis B virus
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published May 14, 2008 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkn188 Management of hepatitis B virus Nidhi A. Singh and Nancy Reau* Section
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published May 14, 2008 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkn188 Management of hepatitis B virus Nidhi A. Singh and Nancy Reau* Section
HBV NATURAL HISTORY. Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is the leading cause of
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2013;144:933 944 CLINICAL LIVER Accuracy of Risk Scores for Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Entecavir Treatment GRACE LAI HUNG WONG, 1,2 HENRY LIK YUEN CHAN, 1,2 HOI YUN CHAN,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2013;144:933 944 CLINICAL LIVER Accuracy of Risk Scores for Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Entecavir Treatment GRACE LAI HUNG WONG, 1,2 HENRY LIK YUEN CHAN, 1,2 HOI YUN CHAN,
