The Immune and Lymphatic Systems and Cancer
|
|
|
- Clemence Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Immune and Lymphatic Systems and Cancer 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the immune and lymphatic systems 3. Discuss changes in the immune and lymphatic systems due to aging 4. Describe a common disorder of the immune system 5. Discuss infection prevention guidelines for a resident with HIV/AIDS 6. Discuss care guidelines for a resident with HIV/AIDS 7. Describe cancer 8. Discuss care guidelines for a resident with cancer Supplemental Tools transparency 24-1 the lymphatic system handout 24-1 myths about hiv and aids chapter 24: exam Assignments textbook reading, pp workbook exercises, pp Overview of Teaching Strategies This chapter describes the immune and lymphatic systems and how they work together to protect the body from disease. Different types of immunity are described, as well as normal changes of aging for these systems. There is detailed information about HIV/AIDS, including activities that do and do not spread HIV/AIDS. Infection prevention guidelines are described, with emphasis on the fact that if Standard Precautions are consistently followed, care for a resident with HIV/AIDS is no different from care for any other resident. This chapter also contains information about cancer, including risk factors, treatment, and care guidelines. 1. Define important words in this chapter textbook p. 429 workbook p. 131 Pronounce and define each of the key terms listed in the Learning Objective on page Explain the structure and function of the immune and lymphatic systems textbook pp workbook p. 131 Review the following points about the immune system: Protects the body from harmful substances Non-specific immunity is present at birth and protects the body from disease in general. Specific immunity is acquired by the body and manufactures antibodies as a response to an antigen in the body. With active immunity, vaccines cause the body to produce antibodies to protect against a particular disease. With passive immunity, a person is given the antibodies needed to defend against the antigen. Display Transparency 24-1 the lymphatic system Lymph Review the following points about the lymphatic system: Removes excess fluids and waste products from the tissues Helps the immune system fight infection
2 163 Thymus gland makes T-cells, which attack and destroy specific types of pathogens. Review the functions of the immune and lymphatic systems: Protect against the invasion of foreign substances and pathogens Return extra fluid to the circulatory system 3. Discuss changes in the immune and lymphatic systems due to aging textbook p. 431 workbook p. 131 Review normal changes of aging: Immune system weakens, causing increased risk of all types of infections. Antibody response slows. T-cells decrease in number. Response to vaccine decreases. 4. Describe a common disorder of the immune system textbook pp workbook pp Pronounce and define the following key terms: Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Review the following points about HIV and AIDS: HIV attacks the body s immune system and damages or destroys cells. Cause: HIV virus acquired through blood or body fluids from an infected person AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection. Review the most common methods of transmission of HIV: Unprotected or poorly-protected oral, vaginal, or anal sex with an infected person Sharing drug needles or syringes Transmission from infected mother to newborn during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding Explain to students that in the healthcare setting, infections can be spread through accidental contact with contaminated body fluids, needles or other sharp objects, or contaminated supplies or equipment. Distribute Handout 24-1 myths about hiv and aids Review the following common activities that do not spread HIV: Hugging another person Shaking hands Sitting on a toilet seat Drinking water from a drinking fountain Touching a doorknob, telephone, table, or chair Using drinking glasses or dishes of infected person Being bitten by mosquitoes Review ways to protect against the spread of HIV/ AIDS: Practice Standard Precautions on every person in your care. Be careful with handling and disposing of sharps. Cover any cuts, sores, tears, breaks, or rashes before caring for residents. Never share needles or syringes. Do not have unprotected sex. Stay in a monogamous relationship. Practice abstinence. Get tested for HIV and re-tested if necessary. Review the signs and symptoms of HIV infections and AIDS: Flu-like symptoms Headaches Loss of appetite Weight loss Night sweats Shaking, chills Dry cough Shortness of breath
3 164 Swollen lymph nodes Sore throat Cold sores or fever blisters on lips Mouth sores White patches on the mouth or tongue Cauliflower-like warts on the skin or in mouth Bleeding, inflamed gums Yeast infections Skin rashes or sores Bruising that does not go away Dry skin Nausea and vomiting Blurred vision Memory loss Opportunistic infection Explain to students that people with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS may get diseases that a healthy person would be able to fight off. Emphasize that lack of treatment for HIV/AIDS increases the risk of serious complications and death from the disease. Autoimmune disease Review the following points about autoimmune diseases: The body is unable to recognize its own tissue and attacks it. Examples: systemic lupus erythematosis and rheumatoid arthritis Cause: unknown, but may be genetic links, microorganisms or medications that act as triggers Signs and symptoms: fever, fatigue, dizziness Treatment: hormone supplements, medications, blood transfusions, insulin 5. Discuss infection prevention guidelines for a resident with HIV/AIDS textbook pp workbook p. 132 Remind students that it is very important to follow Standard Precautions with every single resident in their care. Explain that if they do that, there should be no difference in the care given to residents with HIV/AIDS and care given to any other resident. Review infection prevention guidelines for HIV/AIDS: Follow proper infection prevention procedures and Standard Precautions with all residents. Wear appropriate PPE. Cover all broken skin with appropriate bandages before giving care. Wash hands and other areas of body immediately after contact with blood or body fluids. Handle and dispose of sharps carefully. Remind residents and visitors to wash their hands often. Do not share residents personal items. Properly disinfect surfaces. 6. Discuss care guidelines for a resident with HIV/AIDS textbook pp workbook pp. 133 Homophobia Review the guidelines for HIV/AIDS: Wash hands often and help residents wash hands. Disinfect surfaces often. Protect resident from people having known contagious diseases. Change linen whenever it is soiled. Observe for skin breakdown. Change positions every two hours, or as directed. Give back rubs for comfort. Monitor vital signs often. Allow rest and recognize limitations. Ambulate carefully. Allow time for ADLs.
4 165 Perform ROM exercises as ordered. Give quality mouth care frequently. Use soft toothbrushes or swabs for oral care. Report if resident is not eating or not enjoying food. Encourage residents to follow their special diets. Encourage fluids. Give small meals throughout day or BRAT, BRATY, or BRATT diet for nausea and diarrhea. Carefully measure weight and I&O. Offer a trip to the bathroom or bedpan as often as needed. Encourage independence. Give emotional support. Be aware of other support systems. Review symptoms to report to the nurse for HIV/ AIDS: Loss of appetite, vomiting, or diarrhea Weight loss Reduced intake of fluids Mouth sores or discomfort Dysphagia Bleeding from anywhere on the body Bruising of skin Pressure ulcers Cracks, breaks, rashes, lumps, or sores on the skin Blood in stool Changes in vital signs Nervousness, withdrawal, severe mood swings, depression Behavior that puts resident or others at risk, suicidal thoughts or comments 7. Describe cancer textbook pp workbook pp Pronounce and define the following key terms: Cancer Tumor Benign Malignant Metastasize Review risk factors for Age Race Gender Family history Tobacco use Alcohol use Poor diet/obesity Lack of exercise Chemicals and food additives Radiation Sun exposure Review the American Cancer Society s signs of Fever Fatigue Unexplained weight loss Pain Skin changes New mole or change in appearance of existing mole or wart Change in bowel/bladder function Sore that does not heal Unusual bleeding/discharge Any thickening in breast, scrotum, or other areas Indigestion, difficulty swallowing Nagging cough or hoarseness Biopsy Briefly describe each of the following treatments for Surgery Radiation therapy Chemotherapy Hormone therapy Immunotherapy Explain that these treatments are often used in combination.
5 Discuss care guidelines for a resident with cancer textbook pp workbook p. 134 Review skin care guidelines for residents with Observe skin to prevent pressure ulcers. Change position every two hours or as directed. Follow special skin care orders exactly. Use special mattresses or pads in beds and chairs to reduce risk of pressure ulcers. Keep skin clean and dry. Apply lotion to dry skin. Do not use lotion on areas having radiation therapy. Do not remove any markings used with radiation therapy. Report signs of infection. Review guidelines for supporting good self-image in residents with Help residents stay clean and well-groomed. Offer wigs, scarves, or hats for hair loss. Assist with application of makeup, as requested. Review oral care guidelines for residents with Give oral care often. Be gentle. Use soft brushes or special swabs. Use mild mouth rinses to reduce bad taste from medication or vomiting. Review guidelines for pain in residents with Be alert for signs of pain and report immediately. Provide comfort measures, such as back rubs and repositioning. Play soft music, read, or talk quietly with residents. Notify nurse of side effects of pain medication. Report irritation around transdermal patches or resident having more than one patch on the body. Observe for redness, swelling, or warmth around the insertion site of PCA pump. Report signs of breakthrough pain. Review vital signs guidelines for residents with Monitor all vital signs, especially temperature. Report changes in vital signs to nurse. Review guidelines for mobility for residents with Allow plenty of time for rest. Recognize limitations. Assist with ambulation. Review nutrition guidelines for residents with Provide small, frequent meals to reduce nausea and prevent weight loss. Serve favorite foods and nutritious snacks. Provide food when hunger occurs. Try cool or cold foods. Cut foods into small pieces. Use plastic utensils. Weigh residents as ordered and report loss or gain. Encourage fluids. Monitor I&O and report changes. Review guidelines for bladder and bowel changes for residents with Assist residents with toileting often. Give catheter care as needed. Carefully measure output. Test stool for occult blood as ordered. Review guidelines for mental status and emotional needs of residents with Be sensitive to residents wishes. Listen if residents want to express feelings. Spend as much time with residents as possible. Encourage activities. Ask social worker about support groups. Do not use clichés. Provide support during painful episodes and difficult times.
6 167 Remind residents that there can be good days ahead. Observe and report signs of depression or comments about suicide. Review symptoms to observe and report: Pain or increased pain Changes in vital signs Signs of new bumps or lumps or changes in skin Rashes, cracks, sores, breaks, or reddened areas on the skin Odors Burns or skin irritation Bruising of the skin Difficulty with ambulation Fainting Increased fatigue or weakness Chest pain or tightness Shortness of breath Appetite changes or weight loss Difficulty chewing or swallowing Dry, sore mouth and mouth or lip sores Inflammation or irritation of the mucous membranes in the mouth Bleeding from inside the mouth Nausea or vomiting Flatus, diarrhea, or constipation Blood in the stool Change in output Any change in urine or blood in urine Urinary tract infection Change in mental status or confusion Anxiety, fear, or angry feelings Signs of depression Chapter Review Exam distribute chapter 24: exam (appendix c, pp ) Answers to Chapter Review in Textbook 1. Nonspecific immunity is present at birth and protects the body from disease in general. Specific immunity is a type of immunity acquired by the body. 2. Examples of active immunity body manufacturing antibodies as a response to an antigen, vaccine; examples of passive immunity mother passing antibodies to child, injection of antibodies 3. Lymph carries disease-fighting cells called lymphocytes. 4. Answers include: Immune system weakens, causing increased risk of all types of infections. Antibody response slows. T-cells decrease in number. Response to vaccine decreases. 5. Through blood or body fluids from an infected person 6. Answers include: unprotected or poorly-protected oral, vaginal or anal sex with an infected person; sharing drug needles or syringes; transmission from infected mother to newborn during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding; in the healthcare setting, infections can be spread through accidental contact with contaminated body fluids, needles or other sharp objects, or contaminated supplies or equipment 7. Answers include: through air or water; by insects, including mosquitoes; in saliva, tears, or sweat; through casual contact, such as hugging, shaking hands, or sharing dishes; and through closed-mouth or social kissing, such as kissing someone s cheek 8. No 9. With an autoimmune disease, the body is unable to recognize its own tissue. The immune mechanism sees the normal body tissues as foreign and begins to attack the tissues. Allow students enough time to finish the test. See Appendix D for answers to the chapter exams.
7 Answers include: Follow proper infection prevention procedures and Standard Precautions with all residents. Wear appropriate PPE. Cover all broken skin with appropriate bandages before giving care. Wash hands and other areas of body immediately after contact with blood or body fluids. Handle and dispose of sharps carefully. Remind residents and visitors to wash their hands often. Do not share residents personal items. Properly disinfect surfaces. 11. No 12. No 13. Answers include: Wash hands often and help residents wash hands. Disinfect surfaces often. Protect resident from people having known contagious diseases. Change linen whenever it is soiled. Observe for skin breakdown. Change positions every two hours, or as directed. Give back rubs for comfort. Monitor vital signs often. Allow rest and recognize limitations. Ambulate carefully. Allow time for ADLs. Perform ROM exercises as ordered. Give quality mouth care frequently. Use soft toothbrushes or swabs for oral care. Report if resident is not eating or not enjoying food. Encourage residents to follow their special diets. Encourage fluids. Give small meals throughout day or BRAT, BRATY, or BRATT diet for nausea and diarrhea. Carefully measure weight and I&O. Offer a trip to the bathroom or bedpan as often as needed. Encourage independence. Give emotional support. Be aware of other support systems. 14. Benign tumors grow slowly and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors grow rapidly and invade surrounding tissue. 15. Answers include: fever; fatigue; unexplained weight loss; pain; skin changes; new mole or change in appearance of existing mole or wart; change in bowel/bladder function; sore that does not heal; unusual bleeding/discharge; any thickening in breast, scrotum or other areas; indigestion, difficulty swallowing; or nagging cough or hoarseness 16. Answers include: The goal of surgery is to try to remove as much of the cancer as possible. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to attempt to destroy cancer cells in a specific area. Chemotherapy involves chemical agents or medications being administered, usually intravenously, to kill malignant cells and tissues. Hormone therapy uses medications to alter the hormones in the body. Immunotherapy uses the body s immune system to fight the malignant tumors. 17. Answers include: Skin care: Observe skin to prevent pressure ulcers. Change position every two hours or as directed. Follow special skin care orders exactly. Use special mattresses or pads in beds and chairs to reduce risk of pressure ulcers. Keep skin clean and dry. Apply lotion to dry skin. Do not use lotion on areas having radiation therapy. Do not remove any markings used with radiation therapy. Report signs of infection. Self-image: Help residents stay clean and wellgroomed. Offer wigs, scarves, or hats for hair loss. Assist with application of makeup, as requested. Oral care: Give oral care often. Be gentle. Use soft brushes or special swabs. Use mild mouth rinses to reduce bad taste from medication or vomiting. Pain: Be alert for signs of pain and report immediately. Provide comfort measures, such as back rubs and repositioning. Play soft music, read, or talk quietly with residents. Notify nurse of side effects of pain medication. Report irritation around transdermal patches or resident having more than one patch on the body. Observe for redness, swelling, or warmth around the insertion site of PCA pump. Report signs of breakthrough pain. Vital signs: Monitor all vital signs, especially temperature. Report changes in vital signs to nurse. Mobility: Allow plenty of time for rest. Recognize limitations. Assist with ambulation. Nutrition: Provide small, frequent meals to reduce nausea and prevent weight loss. Serve favorite foods and nutritious snacks. Provide food when hunger occurs. Try cool or cold foods. Cut foods into small pieces. Use plastic utensils. Weigh residents as ordered and report loss or gain. Encourage fluids. Monitor I&O and report changes.
8 169 Bladder and bowel changes: Assist residents with toileting often. Give catheter care as needed. Carefully measure output. Test stool for occult blood as ordered. Mental status and emotional needs: Be sensitive to residents wishes. Listen if residents want to express feelings. Spend as much time with residents as possible. Encourage activities. Ask social worker about support groups. Do not use clichés. Provide support during painful episodes and difficult times. Remind residents that there can be good days ahead. Observe and report signs of depression or comments about suicide.
HIV/AIDS. Communication and Prevention. Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018
 HIV/AIDS Communication and Prevention Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018 Discussing Sensitive Matters with Your Parents Parents: A child s first and most important teacher Parent s role is to
HIV/AIDS Communication and Prevention Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018 Discussing Sensitive Matters with Your Parents Parents: A child s first and most important teacher Parent s role is to
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA
 For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V.
 For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V. Cyclosporine (sye kloe spor een) is a drug that may be used to treat certain types of cancer. It may also be used to suppress your immune
For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V. Cyclosporine (sye kloe spor een) is a drug that may be used to treat certain types of cancer. It may also be used to suppress your immune
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Docetaxel (Taxotere )
 Page 1 of 5 Docetaxel (Taxotere ) About This Drug Docetaxel is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white
Page 1 of 5 Docetaxel (Taxotere ) About This Drug Docetaxel is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. PCV Treatment Chemotherapy for brain tumors DRAFT. PCV is a type of chemotherapy (chemo) treatment for brain
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What are these drugs used for? Docetaxel is an anticancer drug used to treat cancers in the area of the neck and throat.
 For the Patient: HNAVDOC Treatment of Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck with docetaxel HN=Head and Neck AV=Advanced DOC=Docetaxel ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What are these drugs
For the Patient: HNAVDOC Treatment of Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck with docetaxel HN=Head and Neck AV=Advanced DOC=Docetaxel ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What are these drugs
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA
 For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD
 For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD Amsacrine (AM-sa-krin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear orange-red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
For the Patient: Amsacrine Other names: AMSA PD Amsacrine (AM-sa-krin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear orange-red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know
 Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know P R E S E N T E D B Y Dee Smith WHAT YOU LL LEARN What are the 3 BBVs? S&S of each of the BBVs Transmission of BBVs What infection prevention & control
Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know P R E S E N T E D B Y Dee Smith WHAT YOU LL LEARN What are the 3 BBVs? S&S of each of the BBVs Transmission of BBVs What infection prevention & control
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
For the Patient: Ponatinib Other names: ICLUSIG
 For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
Sunitinib. Other Names: Sutent. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Sunitinib Other Names: Sutent About This Drug Sunitnib is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Headache Tiredness and weakness Soreness of the mouth and throat. You
Sunitinib Other Names: Sutent About This Drug Sunitnib is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Headache Tiredness and weakness Soreness of the mouth and throat. You
For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN
 For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN Eribulin (er'' i bue' lin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Eribulin Other names: HALAVEN Eribulin (er'' i bue' lin) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
Methotrexate. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
HIV Infection/AIDS: Care of the Child
 HIV Infection/AIDS: Care of the Child HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that causes a number of different health problems including AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome). The HIV virus
HIV Infection/AIDS: Care of the Child HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that causes a number of different health problems including AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome). The HIV virus
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth.
 For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA
 For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
Trastuzumab (Herceptin )
 Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) About This Drug Trastuzumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV) Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of white blood
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR
 For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
20. HIV and AIDS. Objectives. How is HIV transmitted?
 20. HIV and AIDS Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Explain what HIV and AIDS are. Describe how HIV is transmitted. Explain the difference between HIV and AIDS. List
20. HIV and AIDS Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Explain what HIV and AIDS are. Describe how HIV is transmitted. Explain the difference between HIV and AIDS. List
5 Fluorouracil. Other Names: Adrucil. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Fluorouracil is used to treat cancer.it is given in the vein (IV).
 5 Fluorouracil Other Names: Adrucil About This Drug Fluorouracil is used to treat cancer.it is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Hair loss. Hair loss is often temporary, although with certain
5 Fluorouracil Other Names: Adrucil About This Drug Fluorouracil is used to treat cancer.it is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Hair loss. Hair loss is often temporary, although with certain
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT. Fourth Grade Boys
 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Fourth Grade Boys PUBERTY Stage of growth and development that marks the beginning of the change from childhood to adulthood Usually starts between the ages of 11 and 17 Starts earlier
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Fourth Grade Boys PUBERTY Stage of growth and development that marks the beginning of the change from childhood to adulthood Usually starts between the ages of 11 and 17 Starts earlier
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177 What is a neuroendocrine tumor? Neuroendocrine cells are mainly found in your bowel, pancreas and lungs.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177 What is a neuroendocrine tumor? Neuroendocrine cells are mainly found in your bowel, pancreas and lungs.
TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Capecitabine. Other Names: Xeloda. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
For the Patient: CAP. Capecitabine. Uses:
 For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING
 Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING Are the two diseases specifically addressed by the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard (Be aware of Hepatitis C as it is becoming more and more
Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING Are the two diseases specifically addressed by the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard (Be aware of Hepatitis C as it is becoming more and more
For the Patient: Mitoxantrone Other names:
 For the Patient: Mitoxantrone Other names: Mitoxantrone (mite-oh-zan-trone) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a blue liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Mitoxantrone Other names: Mitoxantrone (mite-oh-zan-trone) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a blue liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if you
21. Getting Tested for HIV
 21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
For the Patient: ACTW Other names: BRAJACTW
 For the Patient: ACTW Other names: BRAJACTW A Doxorubicin (ADRIAMYCIN ) C Cyclophosphamide T Paclitaxel (TAXOL ) weekly Uses: BRAJACTW is a drug treatment given after breast cancer surgery (called adjuvant
For the Patient: ACTW Other names: BRAJACTW A Doxorubicin (ADRIAMYCIN ) C Cyclophosphamide T Paclitaxel (TAXOL ) weekly Uses: BRAJACTW is a drug treatment given after breast cancer surgery (called adjuvant
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
For the Patient: Rituximab injection Other names: RITUXAN
 For the Patient: Rituximab injection Other names: RITUXAN Rituximab (ri tux' i mab) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a monoclonal antibody, a type of protein designed to target
For the Patient: Rituximab injection Other names: RITUXAN Rituximab (ri tux' i mab) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a monoclonal antibody, a type of protein designed to target
For the Patient: USMAVFIPI
 For the Patient: USMAVFIPI Other Names: First-Line Treatment of Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma Using Ipilimumab U = Undesignated (requires special request) SM = Skin and Melanoma AV = Advanced F =
For the Patient: USMAVFIPI Other Names: First-Line Treatment of Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma Using Ipilimumab U = Undesignated (requires special request) SM = Skin and Melanoma AV = Advanced F =
For the Patient: Alemtuzumab SC injection Other names: MABCAMPATH, CAMPATH
 For the Patient: Alemtuzumab SC injection Other names: MABCAMPATH, CAMPATH Alemtuzumab (uh-lem-tooz-uh-mab) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a monoclonal antibody, a type of
For the Patient: Alemtuzumab SC injection Other names: MABCAMPATH, CAMPATH Alemtuzumab (uh-lem-tooz-uh-mab) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a monoclonal antibody, a type of
For the Patient: Epirubicin Other names: PHARMORUBICIN
 For the Patient: Epirubicin Other names: PHARMORUBICIN Epirubicin (eppy-roo-biss-in) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
For the Patient: Epirubicin Other names: PHARMORUBICIN Epirubicin (eppy-roo-biss-in) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a red liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor
Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL
 In-Home Aides Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL 2016-1 Infection Control and the In-home Aide s Role Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or
In-Home Aides Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL 2016-1 Infection Control and the In-home Aide s Role Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or
X-Plain Chemotherapy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy Reference Summary Introduction Chemotherapy is a common treatment for a variety of cancers. It has been proven to be both safe and effective. Patients should, however, learn about
X-Plain Chemotherapy Reference Summary Introduction Chemotherapy is a common treatment for a variety of cancers. It has been proven to be both safe and effective. Patients should, however, learn about
For the Patient: Adjuvant therapy for breast cancer using weekly paclitaxel and trastuzumab (Herceptin)
 For the Patient: Adjuvant therapy for breast cancer using weekly paclitaxel and trastuzumab (Herceptin) Other names: UBRAJTTW U Undesignated BR Breast AJ Adjuvant T Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN ) TW Paclitaxel
For the Patient: Adjuvant therapy for breast cancer using weekly paclitaxel and trastuzumab (Herceptin) Other names: UBRAJTTW U Undesignated BR Breast AJ Adjuvant T Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN ) TW Paclitaxel
Lymphatic System and Immunity
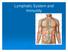 Lymphatic System and Immunity Structure of the Lymphatic System Lymph - Straw-colored, similar to plasma - Interstitial fluid in spaces between cells - Composed of water, lymphocytes. Oxygen, digested
Lymphatic System and Immunity Structure of the Lymphatic System Lymph - Straw-colored, similar to plasma - Interstitial fluid in spaces between cells - Composed of water, lymphocytes. Oxygen, digested
Discussing TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) with your healthcare team Talking to Your Doctor
 Discussing TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) with your healthcare team Talking to Your Doctor TECENTRIQ DISCUSSION SUPPORT What is TECENTRIQ? TECENTRIQ is a prescription medicine used to treat: A type of bladder
Discussing TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) with your healthcare team Talking to Your Doctor TECENTRIQ DISCUSSION SUPPORT What is TECENTRIQ? TECENTRIQ is a prescription medicine used to treat: A type of bladder
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN????
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN???? YES THIS YEAR AND EVERY YEAR HEREAFTER REMEMBER: A REVIEW IS NEVER A BAD IDEA YOUR JOBS PUT YOU AT RISK THE DAY YOU KNOW EVERYTHING AND
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: OR: DO WE REALLY HAVE TO DO THIS AGAIN???? YES THIS YEAR AND EVERY YEAR HEREAFTER REMEMBER: A REVIEW IS NEVER A BAD IDEA YOUR JOBS PUT YOU AT RISK THE DAY YOU KNOW EVERYTHING AND
For the Patient: LUSCTOP
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUSCTOP Other Names: Treatment of Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) with Topotecan LU = LUng SC = Small Cell TOP = TOPotecan What is this treatment used for?
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUSCTOP Other Names: Treatment of Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) with Topotecan LU = LUng SC = Small Cell TOP = TOPotecan What is this treatment used for?
Communicable Diseases. Detection and Prevention
 Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
JUST FOR KIDS SELECTED IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
 JUST FOR KIDS For children ages 6-17 with moderately to severely active Crohn s disease or ulcerative colitis (UC) who haven t responded well to other therapies SELECTED IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION REMICADE
JUST FOR KIDS For children ages 6-17 with moderately to severely active Crohn s disease or ulcerative colitis (UC) who haven t responded well to other therapies SELECTED IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION REMICADE
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another?
 Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Integrative Consult Patient Background Form
 Let Us Know More - So We Can Help Thank you for choosing to schedule an integrative medicine consultation with UC Health. To help us meet your needs during your visit, please take some time to sit in a
Let Us Know More - So We Can Help Thank you for choosing to schedule an integrative medicine consultation with UC Health. To help us meet your needs during your visit, please take some time to sit in a
For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option)
 For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Gemcitabine LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PG = CarboPlatin, Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS
For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Gemcitabine LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PG = CarboPlatin, Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS
What is the most important information I should know about bortezomib? What should I discuss with my healthcare provider before receiving bortezomib?
 1 of 5 6/10/2016 3:46 PM Generic Name: bortezomib (bor TEZ oh mib) Brand Name: Velcade What is bortezomib? Bortezomib interferes with the growth of some cancer cells and keeps them from spreading in your
1 of 5 6/10/2016 3:46 PM Generic Name: bortezomib (bor TEZ oh mib) Brand Name: Velcade What is bortezomib? Bortezomib interferes with the growth of some cancer cells and keeps them from spreading in your
Universal Precautions
 Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
AIDS and hepatitis B are primarily spread by three types of body fluids: Blood Vaginal secretions Semen
 Bloodborne Pathogens Introduction In an educational environment, it s very important to know how to protect yourself and students from bloodborne diseases like AIDS and hepatitis B. At the same time it
Bloodborne Pathogens Introduction In an educational environment, it s very important to know how to protect yourself and students from bloodborne diseases like AIDS and hepatitis B. At the same time it
For the Patient: LUAVPEM
 For the Patient: LUAVPEM Other Names: Second-Line Treatment Of Advanced Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PEM = PEMetrexed ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What is this drug
For the Patient: LUAVPEM Other Names: Second-Line Treatment Of Advanced Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PEM = PEMetrexed ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What is this drug
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
For the Patient: Methotrexate Other names: MTX
 For the Patient: Methotrexate Other names: MTX Methotrexate (meth oh trex ate) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a clear yellow liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Methotrexate Other names: MTX Methotrexate (meth oh trex ate) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. It is a clear yellow liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
Bridges Family Wellness PC. New Patient Intake. Bridges Family Wellness Intake Form SE Lake Rd, Suite 102 Milwaukie, OR
 New Patient Intake Bridges Family Wellness Intake Form Full Name: * What is your birthdate? MM/DD/YYYY * What is your gender identity? * Home address: * Cell Phone * Other Phone number(s): Emergency Contact
New Patient Intake Bridges Family Wellness Intake Form Full Name: * What is your birthdate? MM/DD/YYYY * What is your gender identity? * Home address: * Cell Phone * Other Phone number(s): Emergency Contact
For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF
 For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF Afatinib (a fa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose.
For the Patient: Afatinib Other names: GIOTRIF, GILOTRIF Afatinib (a fa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose.
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
 Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
For the Patient: Doxorubicin pegylated liposomal Other names: CAELYX, DOXIL, PLD
 For the Patient: Doxorubicin pegylated liposomal Other names: CAELYX, DOXIL, PLD Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (dox-oh-roo-biss-in) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. Pegylated liposomal
For the Patient: Doxorubicin pegylated liposomal Other names: CAELYX, DOXIL, PLD Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (dox-oh-roo-biss-in) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancers. Pegylated liposomal
For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
For the Patient: Cobimetinib tablets Other names: COTELLIC
 For the Patient: Cobimetinib tablets Other names: COTELLIC Cobimetinib (koe" bi me' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains
For the Patient: Cobimetinib tablets Other names: COTELLIC Cobimetinib (koe" bi me' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains
For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option)
 For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Cancer of Unknown Primary Involving the Thorax with Carboplatin and Etoposide LU = LUng PU = Primary Unknown PE = CarboPlatin, Etoposide
For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Cancer of Unknown Primary Involving the Thorax with Carboplatin and Etoposide LU = LUng PU = Primary Unknown PE = CarboPlatin, Etoposide
Trastuzumab and Lapatinib
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Trastuzumab (tras-too-zoo-mab) and how does it work? Trastuzumab is a type of targeted cancer therapy called a monoclonal antibody. Another name for
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Trastuzumab (tras-too-zoo-mab) and how does it work? Trastuzumab is a type of targeted cancer therapy called a monoclonal antibody. Another name for
(pack li TAX ell) For treating breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma or other cancers
 Medication Information Sheet (pack li TAX ell) This document provides general information about your medication. It does not replace the advice of your health care professional. Always discuss your therapy
Medication Information Sheet (pack li TAX ell) This document provides general information about your medication. It does not replace the advice of your health care professional. Always discuss your therapy
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Best Practice: Infection Control in the Home Care Setting. Page 1
 Best Practice: Infection Control in the Home Care Setting Page 1 Infection Control Many of the clients that you will work with as a caregiver will be vulnerable to catching diseases. Working in the home
Best Practice: Infection Control in the Home Care Setting Page 1 Infection Control Many of the clients that you will work with as a caregiver will be vulnerable to catching diseases. Working in the home
Regorafenib (Stivarga )
 Page 1 of 5 Regorafenib (Stivarga ) About This Drug Regorafenib is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of
Page 1 of 5 Regorafenib (Stivarga ) About This Drug Regorafenib is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number of
Contraindication: CinnoVex is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to interferon beta, or
 Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking CinnoVex.Since the information is regularly updated, make sure you read the information each time. For more information, contact your doctor or
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking CinnoVex.Since the information is regularly updated, make sure you read the information each time. For more information, contact your doctor or
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name abiraterone acetate (A-bih-RA-the-rone A-seh-tayt) Brand name Zytiga (zye-tee-ga) Approved uses Abiraterone acetate is used in combination with prednisone to treat
Name of your medication Generic name abiraterone acetate (A-bih-RA-the-rone A-seh-tayt) Brand name Zytiga (zye-tee-ga) Approved uses Abiraterone acetate is used in combination with prednisone to treat
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
For the Patient: GIPGEM Other Names: Metastatic cancer of the pancreas, gallbladder or bile duct.
 For the Patient: GIPGEM Other Names: Metastatic cancer of the pancreas, gallbladder or bile duct. GI = GastroIntestinal P = Pancreas GEM = Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS MEDIATION What is this drug used for? Gemcitabine
For the Patient: GIPGEM Other Names: Metastatic cancer of the pancreas, gallbladder or bile duct. GI = GastroIntestinal P = Pancreas GEM = Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS MEDIATION What is this drug used for? Gemcitabine
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
Noncommunicable Diseases:
 Noncommunicable Diseases: Chapter 14 Lesson 1 What Are Noncommunicable Diseases? An allergy is an example of a noncommunicable disease. noncommunicable disease A disease that cannot be spread from person
Noncommunicable Diseases: Chapter 14 Lesson 1 What Are Noncommunicable Diseases? An allergy is an example of a noncommunicable disease. noncommunicable disease A disease that cannot be spread from person
For the Patient: LUAVPP (Carboplatin Option)
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUAVPP (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PP = CarboPlatin,
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUAVPP (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Pemetrexed LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PP = CarboPlatin,
For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide
 For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide SM = Melanoma AV = Advanced TMZ = Temozolomide ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What
For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide SM = Melanoma AV = Advanced TMZ = Temozolomide ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What
Health History. Tests and Procedures: Test: Date: Location: Provider: Abnormal: Results/Notes: Monthly self breast exam. Last mammogram (female)
 Comprehensive Cancer Center A Cancer Center Designated by the National Cancer Institute Please answer the following questions and bring this form to your first appointment at Rutgers Cancer Institute of
Comprehensive Cancer Center A Cancer Center Designated by the National Cancer Institute Please answer the following questions and bring this form to your first appointment at Rutgers Cancer Institute of
What is Capecitabine (ka-pe-site-a-been) and how does it work?
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is (ka-pe-site-a-been) and how does it work? is an oral chemotherapy drug known as an antimetabolite. Another name for this drug is Xeloda. can be given
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is (ka-pe-site-a-been) and how does it work? is an oral chemotherapy drug known as an antimetabolite. Another name for this drug is Xeloda. can be given
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General
 Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
New Patient Medical History Intake Form
 New Patient Medical History Intake Form Name: Todays Date: / / Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: M / F Marital Status: S M D W Address: City: State: Zip Code Primary Ph.# (cell, hm, wk) Email Address 2nd
New Patient Medical History Intake Form Name: Todays Date: / / Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: M / F Marital Status: S M D W Address: City: State: Zip Code Primary Ph.# (cell, hm, wk) Email Address 2nd
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
TC: Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
FACT SHEET. H1N1 Influenza phone
 www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
For the Patient: LUAJPC
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUAJPC Other Names: Treatment of Resected n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant PC = Paclitaxel, Carboplatin What are these
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: LUAJPC Other Names: Treatment of Resected n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant PC = Paclitaxel, Carboplatin What are these
How to Prevent Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens. Pines Behavioral Health
 Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
