Pneumocystis carinii Infections in the United
|
|
|
- Philip Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1973, p Copyright 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 8, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Some Observations on the Serology of Pneumocystis carinii Infections in the United States LOIS NORMAN AND I. G. KAGAN Parasitology Branch, Center for Disease Control, Atlanta, Georgia Received for publication 12 April 1973 An indirect immunofluorescent (IF) test with antigen of partially cleaned Pneumocystis carinii cysts was evaluated for sensitivity and specificity. The test was reactive at the 1:8 and above level for 44% of the persons who had suspected and confirmed infections, for 7.3% of the healthy contacts, and for 1.4% of the general population. Results of tests with sera from people with measurable antibodies to other diseases and those on immunosuppressant therapy suggest that only titers of 1:20 and above are specific. At this level, tests with sera of 32% of the cases, 4% of the contacts, 0% of the healthy controls, and from 0% to 37% (average 5%) of individuals on long-term immunosuppressive therapy or with antibodies to other diseases were positive. The high percentage of positive reactions in cytomegalovirus and in fungal infections could represent double infections. The complement fixation test was less sensitive than the IF test. Antibodies measured by the IF test were immunoglobulin G. No differences in antigenicity were demonstrated by the IF test among the cysts from eight human infections or from induced rat infections. In epidemics of interstitial plasma cell pneumonia in Europe, both the complement fixation (CF) (1, 2, 26, 27) and the indirect immunofluorescent (IF) (4) tests have been found to be very efficient diagnostic techniques, revealing antibodies in over 75% of the suspected cases. In our laboratory in the United States, on the other hand, we have not shown comparable reactivity in sera from Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia cases (21), and thie occasional references in the North American literature indicate that serological testing has not been generally successful (6, 9, 19, 22). The cause of the low level of reactivity has usually been attributed to poor antibody response in patients who are, almost without exception, on immunosuppressant drugs or are otherwise immunodeficient. However, the roles played by other factors, such as antigenic differences and strain or species differences in the organisms (10, 12) causing the disease, should be investigated. Since the supply of heavily infected human lungs necessary for preparing antigens and serum from confirmed infections is very limited, exclusive studies cannot be performed in a single laboratory. Answers to the many problems associated with the serological diagnosis of pneumocystosis 317 must, therefore, come from compilation of data from many sources. As a contribution to this data, we are presenting the results of an evaluation of an IF test (21) which utilizes as antigen dried mounts of cysts partially separated from host tissue cells. Sera from Americans with and without P. carinii or other infections have been titrated. In addition, some aspects of the antigenicity of cysts as well as the labeled antiglobulins used in the IF test have been investigated. Results of a limited comparison of the CF and IF tests are included. MATERIALS AND METHODS Antigens. Both particulate (cyst) and soluble antigens were prepared from naturally infected human lungs and from the lungs of rats in which pneumocystis infections were induced with cortisone acetate (8). Many small lots of cyst antigen were made from eight human lungs, but most of the testing was done with the preparations from four lungs. The soluble antigen was prepared from two of the infected human lungs and from pools of the infected rat lungs. A few slides of Candida albicans were prepared for controls. Preparation of the IF antigens has been described in detail (21). In brief, it consists of processing pieces of infected lung as follows: (i) brief homogenization in Hanks balanced salt solution in Waring blender and
2 318 NORMAN AND KAGAN INFECT. IMMUNITY filtration through wet gauze to free the parasitic The CDC Laboratory Branch Complement Fixation (LBCF) microtiter test was followed without material, both the extracystic stages and the cysts, from the clumps of connective tissue; (ii) fractional modification. Optimal dilutions of lots of the Vivell centrifugation at low speeds (usually 400 x g to 500 x antigen varied from 1:8 to 1:25. Serum dilutions g), followed by passage of those fractions richest in started at 1:2, and reactions at 1:4 and above were parasites through a discontinuous sucrose gradient to considered positive. Occasional sera were positive at separate most of the host tissue from the parasite the 1:2 dilution when tested with control antigen of cells; (iii) sonic treatment for periods varying from 1 normal lung tissue. to 2 min to disintegrate the host cells; and (iv) washing of the final suspension of cysts and preparation of air-dried mounts of slides. All steps were RESULTS monitored by staining the smears with toluidine blue IF test. The IF test was easily read under (5) and Giemsa. Slides were stored at -70 C until low-power magnifications. Fluorescence was used and showed no loss of antigenicity for at least 6 usually brilliant. Some variability in the reading months. and determination of the IF titers was observed, The CF antigen, a saline extract of delipidized and but such fluctuations were kept at a minimum dehydrated infected lung, was prepared by the modification of Vivell (25) of Casals' virus antigen. The paring the degree of fluorescence with that of by using a single lot of antigen smears and com- antigen was stored either frozen at -20 C or lyophilized. Antigens for controls were also made from several standard control sera- each day. As a normal human lung and both infected and normal rat result, the titers of sera, even those frozen and lungs. thawed several times during the 3-year study, Antisera. Sera (1,100) were tested. For evaluation were very reproducible. of the IF test, the sera were selected to include The reactivity of sera from 183 healthy American adults and from 191 pneumocystis cases is samples from 58 persons with confirmed P. carinii infection, from 133 persons suspected of infection on shown in Table 1. One of 74 (1.4%) healthy the basis of clinical symptoms, and from 183 healthy controls and eight of 109 (7.3%) people in American adults, some of whom had been in contact contact with infected persons had sera that were with patients. In addition, there were 661 sera from 437 persons with other diseases. The groups included reactive at or above the 1: 8 level. Of the 191 P. many on immunosuppressant therapy. For comparisons of antigenicity of the cysts from rat and human amination, and the remainder were suspected carinii cases, 58 were confirmed by tissue ex- lungs, 104 sera from infected humans were tested. by clinical findings. Sera from 26 (45%) of the Other reagents. The fluorescein-labeled antihuman globulins included antihuman globulin Well- cases were reactive. None of the normal con- confirmed cases and 59 (44%) of the suspected come. F/P ratio [E495nm:E280nm] = 0.82, molar trols, 3.7% of the contacts, and 32.5% of the ratio 3.7. Optimally diluted for use in the test VIo to Y/20; cases showed titers of 1:20 and above. The antihuman IgG CDC (Center for Disease Control) distribution of reactors from negative titers to molar F/P ratio 7.5. Optimal dilution for test 1:15 to 1: 20; anti-human immunoglobulin (Ig) M Mann. titers of 1:320 (Table 1) is bimodal in character Optical density ratio [280/495] = 1.5. Diluted 1:5 for and suggests that IF test titers below 1:20 use could include nonspecific reactions. Titers of Ṫests. The standard IF test procedure was followed 1: 20 and above are probably specific. The with incubation periods for both the serum and results of testing 661 sera from sick people on conjugated antiglobulins of 45 min at 37 C. The sera long-term immunosuppressant therapy and were all treated with Wellcome conjugated antihuman globulin as the standard reagent, and selected (Table 2) supports the conclusion that a titer from people with antibodies to other diseases groups were also tested with anti-igg (CDC) and must be 1: 20 or higher to be diagnostic. Twenty anti-igm (Mann). Optimal dilutions of all lots of conjugate were determined as the highest concentration that, in the presence of a 1:500 or 1: 1,000 but only 5% (32) had titers of 1: 20 or over. With percent (134 sera) were reactive at the 1:8 level, dilution of Evans blue, showed no fluorescence of the sera from patients on immunosuppressants, organisms with normal control serum and no more 20% to 34% were reactive, whereas only 4% to than plus one or minus one dilution variance from the 10% were positive. In general, sera with antibodies to other diseases showed a lack of high known titers of the positive control sera. The sera were initially screened at dilutions of 1:8 and 1: 40, and all titers to pneumocystis. The exceptions, the sera reactive sera were titrated by serial dilutions starting from cytomegalovirus infection and various fungal diseases, are particularly important because at 1:5. The organisms typically appeared as rings or clumps of rings but were at times more uniformly fluoresced. Although some host cell detritis occasionally showed fluorescence, only typical cyst reactions these cases (27). It is not possible from these of the strong possibility of double infections in were considered positive. Fluorescence was read with data to determine whether the reactive sera a Leitz Ortholux scope equipped with an HBO-200 from patients with cytomegalovirus (57%) and mercury lamp and BG-12 and Leitz 510 filters. to fungal disease (27%) should be attributed to
3 VOL. 8, 1973 SEROLOGY OF P. CARINII INFECTIONS319 TABLE 1. Distribution of sera from healthy American adults and from P. Carinii cases by results of the IF test Positive at Positive at Numbers of sera at titers of: Populations No. of > 1:8 > 1:20 tested persons No. % No. % <1:8 1:8 1:10 1:20 1:40 1:80 1:160 1:320 Healthy American adults Healthy contacts Pneumocystis cases Confirmed Suspected cross-reactions or to mixed infections, and amounts of serum were inadequate for absorption studies. However, since 10% of the virus cases without specific antibodies showed above 1: 20 pneumocystis titers, it seems possible that the positive pneumocystis reactions were specific. In addition to testing the sera from patients with malignancies who were also on immunosuppressants by IF for pneumocystis, 242 sera were also tested by IF for TQxoplasma gondii antibodies by the CDC Serology Section. Forty-eight percent were positive with titers of 1:16 to 1:1,024 for toxoplasma and 21% were reactive for pneumocystis at the 1:8 level, with 5% at the 1: 20 to 1: 40 level. The distribution of the reactions is shown in Table 3. There is no evidence of cross-reactivity between the two antibodies. Although we have tested 120 serial specimens from 53 of the pneumocystis cases and 197 sera from 72 of those with malignancies, there is not enough data to show the pattern of appearance of antibodies during disease or after treatment. Such data must be cautiously interpreted, since the appearance of measurable amounts of antibody may be associated with changes in dosage of cortisone (8, 16). Antigens for the IF test. Lots of antigen prepared both with and without sonic treatment (which ruptured the extracystic bodies and host cells) from eight infected human lungs, showed no evidence that the organisms were antigenically different. Extracystic bodies also were antigenic, but they were difficult to recognize in the smears. The yield of clean cysts, ease of separation of cysts from lung tissue, and brilliance of fluorescence varied among the lots prepared from the same lung as well as among the lots from different lungs. Only one of the infected lungs contained cysts that fluoresced brilliantly without the addition of antibody. After treating a suspension of these cysts with TABLE 2. Distribution of sera and their IF test reactions from persons with diseases other than pneumocystosis Populations tested No. of % Positive % Positive sera at >1:8 at > 1: 20 On immunosuppressant drugs: Leukemias, etc Renal Transplants Malignancies Sick with other diseases: Infectious mononu cleosis Rheumatoid arthritis Fungal disease Serology positive Serology negative Cytomegalovirus Serology positive Serology negative Pneumonia Venereal disease Parasitic infections TABLE 3. Distribution of IF titers for pneumocystis and toxoplasma in 242 sera from patients with malignancies on immunosuppressant therapy Pneumocystis Toxoplasma titers titers Neg. 1:16 1:64 1:256 1:1024 ~~~~~~~~~Total no. Negative : : : citrate buffer to remove possible antibody globulin from the organisms (3), an antigen of these cysts was usable. The fluorescence of host cells, which occurred with some sera, was a consistent
4 320 NORMAN AND KAGAN INFECT. IMMUNITY serum reaction and was not associated with a particular lung. To further elucidate the role of host material and to detect possible antigenic differences between cysts from man and rat, 104 human sera were titrated with the two kinds of antigen. Results are presented in Table 4. Fluorescence with both kinds of cysts was brilliant, and the optimal dilutions of conjugate were the same for both. There was no fluorescence of cell detritis on the slides of antigen from rats which made them easier to read. No marked difference in the antigenicity of the two kinds of cysts was demonstrated. Forty-five sera were negative and 31 sera were positive with both. The three sera positive with only human cyst antigen and the three positive with only rat cysts were within one dilution of the signif'icant titer. The appearance of the tests with 14 sera reactive with human cysts and negative with rat suggests that at least part of the fluorescence seen with human cyst antigen is due to reaction with host components. Although many human sera contain antibodies to Candida albicans as evidenced by the fluorescence of these organisms on the control slides, there was no evidence of cross-reactivity with pneumocystis antibodies. Therefore, C. albicans controls were not deemed necessary for routine testing. However, since occasional yeast cells are found in all cyst antigen smears, the fluorescence of these rare organisms must not be confused with a positive pneumocystis reaction. Conjugated antiglobulins. When optimal dilutions of the conjugated antihuman and anti-igg globulins used in this study were limited to those concentrations that, with 1:500 or 1:1,000 dilution of Evans blue, gave no fluorescence with negative control serum and brilliant fluorescence to titer with the positive control sera, both conjugated antihuman globulins and conjugated anti-igg produced similar titers with the sera tested. Sera (150) were tested with the two conjugates simultaneously using the same lots of cyst antigen. Of the 76 sera from possible pneumocystis cases, 27 were positive with the antiglobulin and 28 with the TABLE 4. Distribution of the results of the IF test with 104 human sera by use of pneumocystis cysts from human and rat lungs as antigen Human P. carinii Rat P. carinii cysts Total cysts Neg. 1:8 1:20+ sera Negative ( < 1: 8) Reactive (1: 8-1:16) Positive (1: 20+) anti-igg. Of the remaining sera, from healthy people and those on immunosuppressants, six were positive with the antiglobulin and only two with the anti-igg. In addition, sera from 137 possible or confirmed infections were tested with a 1:5 dilution of labeled anti-igm (Mann). The sera, of which 75 were positive with the anti-igg conjugate, were tested in serial dilutions from 1: 2 through 1: 32. Five sera reacted: two with titers of 1: 2, two with titers of 1: 4, and one with a titer of 1: 8. All five were also positive with anti-igg. The antibodies measured by this IF test appear to be IgG. CF test. Sera from 155 persons with possible pneumocystis infections, from 40 healthy contacts and from 25 healthy adults, were tested by both IF and LBCF tests. IF titers of 1: 20 and above and CF titers of 1: 4 and above were called "positive." Comparison of the results showed that 44 (20%-o) were positive by IF, 22 (10%) were positive by CF, and 31 (14%) were anticomplementary (AC). None of the sera from healthy adults were positive by CF, while 4 (6%) were positive by IF. Of the sera from possible pneumocystis cases, 40 were positive by IF and 22 positive by CF. Fifteen sera were positive by both tests. Fourteen, positive by IF, were negative by CF, and an additional 11 were AC. Seven sera were positive by CF only. Thus, although the two tests may be measuring some of the same antibodies, the IF appears a little more sensitive. DISCUSSION P. carinii has been found in some human lungs wherever autopsy tissue has been examined specifically for its presence. In European reports, incidence of positive lungs ranged from 1% to 10% (20, 24, 28). In Texas (17), 4% of the lungs of the lungs of children with leukemias were found to harbor cysts, and Esterly (6, 7) reported 4%o of 200 of the routine autopsies of adults were positive in central United States. The presence of the organisms in animal hosts has also been noted in both Europe and North America (8, 14, 15, 23). It is realistic to assume that this opportunistic parasite is omnipresent. Nevertheless, the rates of serological reactivity measured by the IF test performed at CDC-31.5% specifically positive of possible cases, 7.3% positive of contacts, and 14% of the healthy population-are disappointingly low and considerably less than those reported during European epidemics. Although we have tested a limited number of European sera, an extensive exchange of sera is necessary before the results of serological testing can be finally interpreted.
5 VOL. 8, 1973 Antigenic differences among the organisms present in different lungs is a moot question. We could detect no qualitative differences among the cysts from 8 human lungs tested by the IF test. Meuwissen and Leenwenberg (18), in the Netherlands, found that CF antigen prepared from American lung samples was comparable to their antigens prepared from local infected tissue. We have noted a difference in the degree of fluorescence of tissue section antigen prepared from lightly and heavily infected lungs, those showing typically plugged alveoli being more reactive. However, when cysts were separated from the conglomerates and lung cells, there were no consistent differences seen in their antigenicity by IF. Although the work of Kim et al. (12) suggests possible differences between cysts from rat and human lung, our results are more compatible with the findings of Kucera and Kramar (14), Lim et al. (16), and Gentry et al. (9) and suggest that species differences, if they exist, are not detectable by the CDC-IF test. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We gratefully acknowledge the groups of sera sent us by L. 0. Gentry, Brooke Army Medical Center, Fort Sam Houston, Tex.; R. F. Betts, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, N. Y.; H. T. Wright, Children's Hospital, Los Angeles, Calif.; and E. V. Sugarbaker, Peter Bent Brigham Hospital, Boston, Mass. We also thank Leo Kaufman, Mycology Branch, Laboratory Division, CDC, for the fungal sera and the Parasitic Diseases Branch, Epidemiology Program, CDC, for their cooperation in supplying data and patients' sera. LITERATURE CITED 1. Barta, K Complement fixation test for pneumocystis. Ann. Internal. Med. 70: Barta, K., and H. Lysek Experimental pneumocystosis. I. Studies on complement fixation antibodies. Cesk. Epidem. Mikrobiol. Immunol. 11: Brozosko, W. J., K. Madaliriski, K. Krawczyriski, and A. Nowoslawski Immunohistochemistry in studies on the pathogeneses of pneumocystis pneumonia in infants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 174: Brozosko, W. J., K. Madaliniski, and A. Nowoslawski Flouorescent antibody and immunoelectrophoretic evaluation of the immune reaction in children with pneumonia induced by Pneumocystis carinii. Exp. Med. Microbiol. (Poland) 19: Chalvardjian, A. M., and L. A. Grawe A new procedure for the identification of Pneumocystis carinii cysts in tissue sections and smears. Amer. J. Clin. Pathol. 16: Esterly, J. A Pneumocystis carinii in lungs of adults at autopsy. Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis. 97: Esterly, J. A., and N. E. Warner Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Arch. Pathol. 80: SEROLOGY OF P. CARINII INFECTIONS Frenkel, J. K., J. T. Good, and J. A. Shultz Latent pneumocystis infections of rats, retapse and chemotherapy. Lab. Invest. 15: Gentry, L. O., J. Ruskin, and J. S. Remington Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Problems in diagnoses and therapy in 24 cases. Calif. Med. 116: Goetz, Serologische Befunde interstitieller Pneumonien aus den Vereinigten Staaten. Arch. Kinderheilk. 170: Goetz, Serologische Untersuchungen bei einem Sogenannten Altersfall von Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonie. Z. Kinderheilk. 95: Kim, H. K., W. T. Hughes, and S. Feldman Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 141: Kossel, A Interstitial plasma cell pneumonia in children receiving long term corticosteroid treatment. Deut. Med. Wochschr. 87: Kucera, K., and J. Kramar Die "Komplimenfairbung" zum Nachweis komplementbindender Antikorper gegen Pneumocystis carinii. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 209: Le Clair, R. A Descriptive epidemiology of interstitial pneumocystic pneumonia. Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis. 99: Lim, S. K., R. H. Jones, and W. C. Eveland Fluorescent antibody studies in experimental pneumocystis. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 136: Luna, M. A., G. P. Bodey, A. M. Goldman, and B. Lichtigen Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in cancer patients. Tex. Rep. Biol. Med. 30: Meuwissen, J. H. E., and D. E. M. Leenwenberg A microcomplement fixation test applied to infections with Pneumocystis carinii. Trop. Geogr. Med. 24: Minielly, J. A., S. P. Mills, and K. E. Holley Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Can. Med. Ass. J. 100: Moragas, A., and M. T. Vidal Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. First autopsy series in Spain. Helvetica Paed. Acta 26: Norman, L., and I. G. Kagan A preliminary report of an indirect fluorescent antibody test for detecting antibodies to cysts of Pneumocystis carinii in human sera. Amer. J. Clin. Pathol. 58: Rifkind, D., T. D. Faris, and R. B. Hill, Jr Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann. Int. Med. 65: Robbins, J. B Pneumocvstis carinii pneumonitis. A review. Pediat. Res. 1: Van de Meer, G., and S. L. Brug Infection a Pneumocystis chez l'homme et chez les animaux. Ann. Soc. Belge Med. Trop. 22: Vivell, Uber neues stabiles Antigen fur die Serodiagnose der interstitiellen plasmazellularen Pneumonie junger Sguglinge und Friugeburten. Deut. Med. Wochschr. 80: Vivell, Die Serologie der interstitiellen Pneumonie. Monatschr. Kinderheilk. 108: Wang, N. S., H. Shao, and W. M. Thurlbeck Combined Pneumocystis carinit and cytomegalovirus infection. Arch. Pathol. 90: Weisse, K., and E. Wedler Occurrence of the so called Pneumocystis carinii. Klin. Wochschr. 32:11-12,
Malignant Glial Neoplasms: Definition of a Humoral Host Response to Tumor-Associated Antigen(s)
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 50 (1977), 397-403 Malignant Glial Neoplasms: Definition of a Humoral Host Response to Tumor-Associated Antigen(s) KHALID M.A. SHEIKH, MICHAEL L.J. APUZZO, KIM
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 50 (1977), 397-403 Malignant Glial Neoplasms: Definition of a Humoral Host Response to Tumor-Associated Antigen(s) KHALID M.A. SHEIKH, MICHAEL L.J. APUZZO, KIM
pneumonitis: a serological
 Pneumocystis carinil study Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 773-777 pneumonitis: a serological VALERIE SHEPHERD', BERYL JAMESON2, AND G. K. KNOWLES3 From the 'Institute ofcancer Research and the
Pneumocystis carinil study Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 773-777 pneumonitis: a serological VALERIE SHEPHERD', BERYL JAMESON2, AND G. K. KNOWLES3 From the 'Institute ofcancer Research and the
Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Experimental Animals
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1973, p. 666-671 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Development and Evaluation of a Direct Fluorescent Antibody Method for the
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1973, p. 666-671 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Development and Evaluation of a Direct Fluorescent Antibody Method for the
Comparative Evaluation of Five Serological Methods for the Diagnosis of Sporotrichosis
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1973, p. 4-8 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Comparative Evaluation of Five Serological Methods for the Diagnosis of Sporotrichosis
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1973, p. 4-8 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Comparative Evaluation of Five Serological Methods for the Diagnosis of Sporotrichosis
Differentiation of Cytomegalovirus Antigens by Their Reactivity with Various Classes of Human Antibodies in the Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1980, p. 88-93 0095-1 137/80/01-0088/06$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No. 1 Differentiation of Cytomegalovirus Antigens by Their Reactivity with Various Classes of Human Antibodies
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1980, p. 88-93 0095-1 137/80/01-0088/06$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No. 1 Differentiation of Cytomegalovirus Antigens by Their Reactivity with Various Classes of Human Antibodies
Antibodies to Treponema pallidum
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 26- Copyright 0 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of the Qualitative and Automated Quantitative Microhemagglutination
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 26- Copyright 0 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of the Qualitative and Automated Quantitative Microhemagglutination
however, and the present communication is concerned with some of
 THE AGGLUTINATION OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES MODIFIED BY TREATMENT WITH NEWCASTLE DISEASE AND INFLUENZA VIRUS' ALFRED L. FLORMAN' Pediatric Service and Division of Bacteriology, The Mount Sinai Hospital, New
THE AGGLUTINATION OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES MODIFIED BY TREATMENT WITH NEWCASTLE DISEASE AND INFLUENZA VIRUS' ALFRED L. FLORMAN' Pediatric Service and Division of Bacteriology, The Mount Sinai Hospital, New
Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1971, p. 715-719 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized ith Visna Virus SEUNG C. KARL AND
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1971, p. 715-719 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized ith Visna Virus SEUNG C. KARL AND
Value and Interpretation of Serological Tests for the Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1968, p. 197-1912 Copyright ( 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 12 Printed in U.S.A. Value and Interpretation of Serological Tests for the Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1968, p. 197-1912 Copyright ( 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 12 Printed in U.S.A. Value and Interpretation of Serological Tests for the Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis
Serodiagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection by
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 1211-1215 Serodiagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection by the indirect fluorescent antibody test P. R. MASON From the Department of Medical Microbiology, University
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 1211-1215 Serodiagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis infection by the indirect fluorescent antibody test P. R. MASON From the Department of Medical Microbiology, University
Human Cytomegalovirus
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 332-336 Copyright ) 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Demonstration of Immunoglobulin G Receptors Induced by Human Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 332-336 Copyright ) 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Demonstration of Immunoglobulin G Receptors Induced by Human Cytomegalovirus
THE BRITISH JOURN OF VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE TRANSMISSIBLE VENEREAL TUMOUR OF THE DOG
 Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Evaluation of a New Rapid Plasma Reagin Card Test as a Screening Test for Syphilis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1982, p. 286-290 0095-1 137/82/080286-05$02.00/0 Vol. 16, No. 2 Evaluation of a New Rapid Plasma Reagin Card Test as a Screening Test for Syphilis MARY W. PERRYMAN,'*
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1982, p. 286-290 0095-1 137/82/080286-05$02.00/0 Vol. 16, No. 2 Evaluation of a New Rapid Plasma Reagin Card Test as a Screening Test for Syphilis MARY W. PERRYMAN,'*
Blood transfusion. Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD
 Blood transfusion Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD General Blood is collected from volunteer donors >90% is separated into individual components and plasma Donors should be: healthy, have
Blood transfusion Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD General Blood is collected from volunteer donors >90% is separated into individual components and plasma Donors should be: healthy, have
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections
 Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
AUTOIMMUNE RESPONSES TO HUMAN TUMOUR ANTIGENS
 510 AUTOIMMUNE RESPONSES TO HUMAN TUMOUR ANTIGENS MADELINE HODKINSON* AND G. TAYLOR From the Immunology Department, Royal Infirmary, Manchester Received for publication May 14, 1969 THE most convincing
510 AUTOIMMUNE RESPONSES TO HUMAN TUMOUR ANTIGENS MADELINE HODKINSON* AND G. TAYLOR From the Immunology Department, Royal Infirmary, Manchester Received for publication May 14, 1969 THE most convincing
Evaluation of Reagin Screen, a New Serological Test for Syphilis
 JOURNAL OF CUNICAL MICROBIOLoGY, Aug. 1976, p. 145-150 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of Reagin Screen, a New Serological Test for Syphilis
JOURNAL OF CUNICAL MICROBIOLoGY, Aug. 1976, p. 145-150 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of Reagin Screen, a New Serological Test for Syphilis
Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test
 Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1109 Pkg.Size:100T Intended use The Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test is a simple and rapid latex agglutination test for the qualitative
Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1109 Pkg.Size:100T Intended use The Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination Test is a simple and rapid latex agglutination test for the qualitative
A stable haemagglutinating antigen for detecting toxoplasma antibodies
 J. cli,,. Path., 1972, 25, 762-767 A stable haemagglutinating antigen for detecting toxoplasma antibodies H. THORBURN AND H. WLLAMS From the Microbiology Laboratory, Raigmore Hospital, nverness SYNOPSS
J. cli,,. Path., 1972, 25, 762-767 A stable haemagglutinating antigen for detecting toxoplasma antibodies H. THORBURN AND H. WLLAMS From the Microbiology Laboratory, Raigmore Hospital, nverness SYNOPSS
patient's serum is separated from other serum components by selective absorption of the IgM
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1981, p. 486-491 0095-1137/81/1 10486-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 5 Immunoglobulin M-Immunosorbent Agglutination Assay for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases: Diagnosis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1981, p. 486-491 0095-1137/81/1 10486-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 5 Immunoglobulin M-Immunosorbent Agglutination Assay for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases: Diagnosis
Detection of Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Virus Capsid Antigen
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1982, p. 69-73 95-1137/82/169-5$2./ Vol. 15, No.1 Detection of Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Virus Capsid Antigen by Immune Adherence Hemagglutination EVELYNE T. LENNETTE,t
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1982, p. 69-73 95-1137/82/169-5$2./ Vol. 15, No.1 Detection of Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Virus Capsid Antigen by Immune Adherence Hemagglutination EVELYNE T. LENNETTE,t
test. It appeared that the MHA-TP test could be
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 405-409 0095-1137/83/030405-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Reactivity of Microhemagglutination, Fluorescent
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 405-409 0095-1137/83/030405-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Reactivity of Microhemagglutination, Fluorescent
An evaluation of two new haemagglutination tests for the rapid diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 1147-115 An evaluation of two new haemagglutination tests for the rapid diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases I. CAYZER, S. R. CHALMERS, D. DONIACH', AND G.
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 1147-115 An evaluation of two new haemagglutination tests for the rapid diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases I. CAYZER, S. R. CHALMERS, D. DONIACH', AND G.
Value o f Immunodiffusion Tests in the Diagnosis o f Systemic M ycotic Diseases
 A n n a l s of C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, N o. 2 Copyright 1 9 7 3, Institute for Clinical Science Value o f Immunodiffusion Tests in the Diagnosis o f Systemic M ycotic
A n n a l s of C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, N o. 2 Copyright 1 9 7 3, Institute for Clinical Science Value o f Immunodiffusion Tests in the Diagnosis o f Systemic M ycotic
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males and Females and Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity
 Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males Females Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Phd, Sundus Fadhil Hantoosh EL-Nahi MSc Abstract Background: Antisperm
Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males Females Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Phd, Sundus Fadhil Hantoosh EL-Nahi MSc Abstract Background: Antisperm
Measuring IgG anti-a/b titres using dithiothreitol (DTT)
 Measuring IgG anti-a/b titres using dithiothreitol (DTT) R. C. KNIGHT From the Department of Haematology, St Thomas's Hospital, London SEJ Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 283-287 SUMMARY In comparing
Measuring IgG anti-a/b titres using dithiothreitol (DTT) R. C. KNIGHT From the Department of Haematology, St Thomas's Hospital, London SEJ Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 283-287 SUMMARY In comparing
Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 939-943 Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children C. R. ASHLEY, E. 0. CAUL, AND W. K. PAVER1 From the Public Health Laboratory, Myrtle Road, Bristol BS2
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 939-943 Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children C. R. ASHLEY, E. 0. CAUL, AND W. K. PAVER1 From the Public Health Laboratory, Myrtle Road, Bristol BS2
Simplex and Varicella-Zoster Virus Antigens in Vesicular
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1980, p. 651-655 0095-1137/80/11-0651/05$02.00/0 Vol. 12, No. 5 Direct Immunofluorescence Staining for Detection of Herpes Simplex and Varicella-Zoster Virus Antigens
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1980, p. 651-655 0095-1137/80/11-0651/05$02.00/0 Vol. 12, No. 5 Direct Immunofluorescence Staining for Detection of Herpes Simplex and Varicella-Zoster Virus Antigens
LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA IFA SLIDE
 1 LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA IFA SLIDE SLEPN: Slides kit for the diagnosis of Legionella pneumophila antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: More than 30 species
1 LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA IFA SLIDE SLEPN: Slides kit for the diagnosis of Legionella pneumophila antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: More than 30 species
Received 8 April 1996/Returned for modification 19 June 1996/Accepted 15 July 1996
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1996, p. 2526 2530 Vol. 34, No. 10 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Study of Abbott Toxo IMx System for Detection of Immunoglobulin
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1996, p. 2526 2530 Vol. 34, No. 10 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Study of Abbott Toxo IMx System for Detection of Immunoglobulin
Performance of Cryptococcus Antigen Latex Agglutination Kits on
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1991, p. 333-339 95-1137/91/2333-7$2./ Copyright C) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 29, No. 2 Performance of Cryptococcus Antigen Latex Agglutination
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1991, p. 333-339 95-1137/91/2333-7$2./ Copyright C) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 29, No. 2 Performance of Cryptococcus Antigen Latex Agglutination
MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IFA IgM
 1 MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IFA IgM PMYPNM: Indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA) kit for the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM antibodies in human serum. INTRODUCTION: Atypical pneumonia produced by
1 MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IFA IgM PMYPNM: Indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA) kit for the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM antibodies in human serum. INTRODUCTION: Atypical pneumonia produced by
Since ocular toxoplasmosis appears to
 Antibody tests for ocular toxoplasmosis Emily D. Maloney and Herbert E. Kaufman* The recently modified fluorescence test for antibodies to toxoplasmosis is safe and relatively simple to perform. It appears
Antibody tests for ocular toxoplasmosis Emily D. Maloney and Herbert E. Kaufman* The recently modified fluorescence test for antibodies to toxoplasmosis is safe and relatively simple to perform. It appears
Antibodies to Cytomegalovirus
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1971, p. 84-89 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Indirect Hemagglutination Test for Detection of Antibodies to Cytomegalovirus
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1971, p. 84-89 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Indirect Hemagglutination Test for Detection of Antibodies to Cytomegalovirus
C for 2 hr at 22,620 X G. The supernatant fluid. was discarded and the sediment resuspended to
 SAFETY TEST FOR Q FEVER VACCINE SANFORD BERMAN, GERALD LE, JOSEPH P. LOWENTHAL, AND RAYMOND B. GOCHENOUR Department of Biologics Research, Division of Immunology, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
SAFETY TEST FOR Q FEVER VACCINE SANFORD BERMAN, GERALD LE, JOSEPH P. LOWENTHAL, AND RAYMOND B. GOCHENOUR Department of Biologics Research, Division of Immunology, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
Immunoglobulin M from Immunoglobulin G Antibodies
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1980, p. 336-342 0095-1 137/80/09-0336/07$02.00/0 Vol. 12, No. 3 Diagnostic Significance of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii Detected After Separation
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1980, p. 336-342 0095-1 137/80/09-0336/07$02.00/0 Vol. 12, No. 3 Diagnostic Significance of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii Detected After Separation
Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS
 KING ABDULAZIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLIED MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTEMENT OF LABORATORY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS RF Latex agglutination for detection of RF INTRODUCTION
KING ABDULAZIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLIED MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTEMENT OF LABORATORY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS RF Latex agglutination for detection of RF INTRODUCTION
Method for Avoiding False-Positive Results Occurring in Immunoglobulin M Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1981, p. 73-78 0095-1 137/81/070073-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 1 Method for Avoiding False-Positive Results Occurring in Immunoglobulin M Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1981, p. 73-78 0095-1 137/81/070073-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 1 Method for Avoiding False-Positive Results Occurring in Immunoglobulin M Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit
 Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0960 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0960 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Effective Date: 09/08 Supersedes Revision/Date: Original Revision: 09/08 Date Adopted:
 Institution: Procedure No.: Page 1 of 5 Procedure: ASI RF DIRECT SLIDE TEST Doc#: 6004-700DC CLSI Effective Date: 09/08 Supersedes Revision/Date: Original Revision: 09/08 Supersedes Procedure # Prepared
Institution: Procedure No.: Page 1 of 5 Procedure: ASI RF DIRECT SLIDE TEST Doc#: 6004-700DC CLSI Effective Date: 09/08 Supersedes Revision/Date: Original Revision: 09/08 Supersedes Procedure # Prepared
Quantitative evaluation of the FTA-ABS-IgM and
 British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1977, 53, 287-291 Quantitative evaluation of the FTA-ABS-IgM and VDRL test in treated and untreated syphilis A. LUGER, B. SCHMIDT, AND I. SPENDLINGWIMMER From the
British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1977, 53, 287-291 Quantitative evaluation of the FTA-ABS-IgM and VDRL test in treated and untreated syphilis A. LUGER, B. SCHMIDT, AND I. SPENDLINGWIMMER From the
Toxoplasma gondii IgM (Toxo IgM)
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Diagnosis of California La Crosse Virus Infection by Counterimmunoelectrophoresis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 97, p. 60-60 009-7/7/0007-060$0.00/0 Copyright 97 American Society for Microbiology Diagnosis of California La Crosse Virus Infection by Counterimmunoelectrophoresis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 97, p. 60-60 009-7/7/0007-060$0.00/0 Copyright 97 American Society for Microbiology Diagnosis of California La Crosse Virus Infection by Counterimmunoelectrophoresis
[1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory
![[1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory [1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory](/thumbs/75/71961750.jpg) THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 561-565 The Antibody Response in Lyme Disease JOSEPH E. CRAFT, M.D., ROBERT L. GRODZICKI, M.S., MAHESH SHRESTHA, B.A., DUNCAN K. FISCHER, M.Phil., MARIANO
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 561-565 The Antibody Response in Lyme Disease JOSEPH E. CRAFT, M.D., ROBERT L. GRODZICKI, M.S., MAHESH SHRESTHA, B.A., DUNCAN K. FISCHER, M.Phil., MARIANO
Syphilis. syphilis. Sera from all stages of syphilis and the. to compare dilution titers with those obtained
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 238-242 0095-1137/82/020238-05$02.00/0 Vol. 15, No. 2 Unheated Serum Reagin Test as a Quantitative Test for Syphilis DEBORAH E. PETTIT, SANDRA A. LARSEN,*
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 238-242 0095-1137/82/020238-05$02.00/0 Vol. 15, No. 2 Unheated Serum Reagin Test as a Quantitative Test for Syphilis DEBORAH E. PETTIT, SANDRA A. LARSEN,*
Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN
 Policy # MI\TECH\11\v01 Page 1 of 6 Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN Latex particles coated
Policy # MI\TECH\11\v01 Page 1 of 6 Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 20, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Revision Date: July 26, 2000 CRYPTOCOCCAL ANTIGEN Latex particles coated
Part II Serology Caroline Bax BW.indd 55 Caroline Bax BW.indd : :17
 Part II Serology part II Chapter 4 Comparison of serological assays for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antibodies in different groups of obstetrical and gynaecological patients C.J. Bax J.A.E.M. Mutsaers
Part II Serology part II Chapter 4 Comparison of serological assays for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antibodies in different groups of obstetrical and gynaecological patients C.J. Bax J.A.E.M. Mutsaers
MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE ANTIBODY (IgM) TEST Product No For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES TABLE 1, PAGE 4
 ImmunoWELL MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE ANTIBODY (IgM) TEST Product No. 3130 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES TABLE 1, PAGE 4 INTENDED USE ImmunoWELL Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Antibody (IgM) Test
ImmunoWELL MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE ANTIBODY (IgM) TEST Product No. 3130 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES TABLE 1, PAGE 4 INTENDED USE ImmunoWELL Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Antibody (IgM) Test
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p very few laboratories because of inherent problems
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 243-248 0095-1137/82/020243-06$02.00/0 Vol. 15, No. 2 Improved Immunofluorescence Antigens for Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Viral
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 243-248 0095-1137/82/020243-06$02.00/0 Vol. 15, No. 2 Improved Immunofluorescence Antigens for Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Epstein-Barr Viral
EPSTEIN BARR VIRUS (VCA) IFA SLIDE
 1 STORAGE REQUIREMTS: EPSTEIN BARR VIRUS (VCA) IFA SLIDE SVCA: Slides for the diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: Antibodies
1 STORAGE REQUIREMTS: EPSTEIN BARR VIRUS (VCA) IFA SLIDE SVCA: Slides for the diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: Antibodies
Design Verification. Form:
 Design Verification SYPHILIS TPHA liquid CONTENTS 1 Function... 2 2 Sensitivity... 2 Preparation of Serum Control Panel... 2 Kit Controls Positive and Negative... 3 3 Traceability... 3 4 Specificity and
Design Verification SYPHILIS TPHA liquid CONTENTS 1 Function... 2 2 Sensitivity... 2 Preparation of Serum Control Panel... 2 Kit Controls Positive and Negative... 3 3 Traceability... 3 4 Specificity and
LEISHMANIA IFA SLIDE STORAGE REQUIREMENTS:
 1 STORAGE REQUIREMTS: SLEDO: Slides for the diagnosis of Leishmania infantum antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: Leishmania infantum is a causal agent of
1 STORAGE REQUIREMTS: SLEDO: Slides for the diagnosis of Leishmania infantum antibodies in human serum by indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA). INTRODUCTION: Leishmania infantum is a causal agent of
Indirect Fluorescent-Antibody Technique for Serological Diagnosis of La Crosse (California) Virus Infections
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 192, p. 429-434 Vol. 15, No. 3 0095-1137/2/030429-06$02.00/0 Indirect Fluorescent-Antibody Technique for Serological Diagnosis of La Crosse (California) Virus Infections
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 192, p. 429-434 Vol. 15, No. 3 0095-1137/2/030429-06$02.00/0 Indirect Fluorescent-Antibody Technique for Serological Diagnosis of La Crosse (California) Virus Infections
Yellow Fever Vaccine: Direct Challenge of Monkeys Given Graded Doses of 17D
 AppuzD MmcoaioLOGy, Apr. 1973, p. 539-544. Copyright i 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 25, No. 4 Printed in U.SA. Yellow Fever Vaccine: Direct Challenge of Monkeys Given Graded Doses of 17D
AppuzD MmcoaioLOGy, Apr. 1973, p. 539-544. Copyright i 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 25, No. 4 Printed in U.SA. Yellow Fever Vaccine: Direct Challenge of Monkeys Given Graded Doses of 17D
Serological studies on 40 cases of mumps virus
 J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 28-32 Serological studies on 40 cases of mumps virus infection R FREEMAN* AND MH HAMBLING From Leeds Regional Public Health Laboratory, Bridle Path, York Road, Leeds, UK SUMMARY
J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 28-32 Serological studies on 40 cases of mumps virus infection R FREEMAN* AND MH HAMBLING From Leeds Regional Public Health Laboratory, Bridle Path, York Road, Leeds, UK SUMMARY
Herpes Simplex Virus 2 IgM HSV 2 IgM
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Screening of Auto Antibodies using Indirect Immunofluorescence in Auto Immune Disease Patients
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 02 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.702.386
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 02 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.702.386
See external label 96 tests HSV 2 IgA. Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Mumps and
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1980, p. 319-323 0095-1137/80/04-0319/05$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No. 4 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Mumps and Parainfluenza Type 1 Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1980, p. 319-323 0095-1137/80/04-0319/05$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No. 4 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Mumps and Parainfluenza Type 1 Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit
 Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0959 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0959 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:228-232 Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation test for detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies E DUSSAIX, A SLIM, P TOURNIER From the
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:228-232 Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation test for detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies E DUSSAIX, A SLIM, P TOURNIER From the
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 42
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 42 4.1 Introduction This chapter is divided in two main sections. The first section deals with results obtained for the point-of-care tests, which encompass results of optimization final
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 42 4.1 Introduction This chapter is divided in two main sections. The first section deals with results obtained for the point-of-care tests, which encompass results of optimization final
MYCOLOGY. Candidasis. couv ASPERGILLOSIS C L I FUMOUZE CANDIDASIS FUMOUZE
 MYCOLOGY Aspergillosis C A T A L O G U E ASPERGILLOSIS C L I FUMOUZE N I C A L D I A G N O S T I C S Aspergillosis serodiagnosis by indirect hæmagglutination Shelf life: 18 months at + 2 C + 8 C couv 102
MYCOLOGY Aspergillosis C A T A L O G U E ASPERGILLOSIS C L I FUMOUZE N I C A L D I A G N O S T I C S Aspergillosis serodiagnosis by indirect hæmagglutination Shelf life: 18 months at + 2 C + 8 C couv 102
HumaTex CRP. Design Verification. Contents
 Design Verification HumaTex CRP Contents 1 Function... 2 2 Reproducibility... 2 3 Sensitivity and dynamic range... 2 Preparation of serum control panel... 2 Sensitivity test results... 2 Prozone check...
Design Verification HumaTex CRP Contents 1 Function... 2 2 Reproducibility... 2 3 Sensitivity and dynamic range... 2 Preparation of serum control panel... 2 Sensitivity test results... 2 Prozone check...
Herpes Simplex Virus 2 IgG HSV 2 IgG
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based
 APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG ELISA Kit
 Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2260 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2260 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF VIRAL INFECTIONS:
 SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF VIRAL INFECTIONS: POSSIBILITIES OF SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS TYPES OF SEROLOGICAL REACTIONS SEROLOGICAL REACTIONS Ag-Ab reactions used for the detection of unknown Ag or Ab, in vitro
SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF VIRAL INFECTIONS: POSSIBILITIES OF SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS TYPES OF SEROLOGICAL REACTIONS SEROLOGICAL REACTIONS Ag-Ab reactions used for the detection of unknown Ag or Ab, in vitro
Dengue IgG/IgM/NS1 Combo Rapid Test Device
 Dengue IgG/IgM/NS1 Combo Rapid Test Device Cat.No: DTSXY-L2 Lot. No. (See product label) Intended Use The Dengue IgG/IgM/NS1 Combo Rapid Test Device is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay for the
Dengue IgG/IgM/NS1 Combo Rapid Test Device Cat.No: DTSXY-L2 Lot. No. (See product label) Intended Use The Dengue IgG/IgM/NS1 Combo Rapid Test Device is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay for the
for Syphilis visualize the antigen-antibody reaction. Procedures
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1983, p. 1141-1145 0095-1137/83/111141-05$02.00/0 Copyright X 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 5 Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test, a Nontreponemal
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1983, p. 1141-1145 0095-1137/83/111141-05$02.00/0 Copyright X 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 5 Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test, a Nontreponemal
NEUTRALIZATION OF VISNA VIRUS BY HUMAN SERA
 THE ENTEROVIRUS DEPARTMENT, STATENS SERUMINSTITUT, COPENHAGEN, DENMARK NEUTRALIZATION OF VISNA VIRUS BY HUMAN SERA By HALLD~R THORMAR~ and HERDIS VON MACNUS Received 28.ix.62 In a previous paper (12) the
THE ENTEROVIRUS DEPARTMENT, STATENS SERUMINSTITUT, COPENHAGEN, DENMARK NEUTRALIZATION OF VISNA VIRUS BY HUMAN SERA By HALLD~R THORMAR~ and HERDIS VON MACNUS Received 28.ix.62 In a previous paper (12) the
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES
 PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
Immunofluorescence and Double-Sandwich Enzyme-Linked
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1983, p. 997-1004 0095-1137/83/060997-08$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 6 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay That Uses Labeled
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1983, p. 997-1004 0095-1137/83/060997-08$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 6 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay That Uses Labeled
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol
 IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12
 Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Rubella Latex Agglutination Test
 Rubella Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1088 Pkg.Size:30T Intended use The Rubella Latex Agglutination Test is a rapid latex particle agglutination test for the qualitative and semi-quantitative
Rubella Latex Agglutination Test Cat. No.:DLAT1088 Pkg.Size:30T Intended use The Rubella Latex Agglutination Test is a rapid latex particle agglutination test for the qualitative and semi-quantitative
Introduction.-Cytopathogenic viruses may lose their cell-destroying capacity
 AN INHIBITOR OF VIRAL ACTIVITY APPEARING IN INFECTED CELL CULTURES* BY MONTO Hot AND JOHN F. ENDERS RESEARCH DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES, THE CHILDREN'S MEDICAL CENTER, AND THE DEPARTMENT OF BACTERIOLOGY
AN INHIBITOR OF VIRAL ACTIVITY APPEARING IN INFECTED CELL CULTURES* BY MONTO Hot AND JOHN F. ENDERS RESEARCH DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES, THE CHILDREN'S MEDICAL CENTER, AND THE DEPARTMENT OF BACTERIOLOGY
Presented by DR. NUSRAT SIDDIQUA Phase B student. Department of Microbiology & Immunology, BSMMU
 Presented by DR. NUSRAT SIDDIQUA Phase B student Department of Microbiology & Immunology, BSMMU Introduction Agglutination is a laboratory diagnostic test based on the reaction between a particular antigen
Presented by DR. NUSRAT SIDDIQUA Phase B student Department of Microbiology & Immunology, BSMMU Introduction Agglutination is a laboratory diagnostic test based on the reaction between a particular antigen
Human Cytomegalovirus IgM ELISA Kit
 Human Cytomegalovirus IgM Catalog No: IRAPKT2012 ELISA Kit Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The CMV IgM ELISA is intended for use in the detection of IgM antibodies to Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in human
Human Cytomegalovirus IgM Catalog No: IRAPKT2012 ELISA Kit Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The CMV IgM ELISA is intended for use in the detection of IgM antibodies to Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in human
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS
 SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
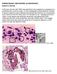 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Comparison of Standard Tube and Shell Vial Cell Culture Techniques for the Detection of Cytomegalovirus in Clinical Specimens
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1985, p. 217-221 0095-1137/85/020217-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 2 Comparison of Standard Tube and Shell Vial Cell Culture
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1985, p. 217-221 0095-1137/85/020217-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 2 Comparison of Standard Tube and Shell Vial Cell Culture
Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O
 Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: Application to Clinical Samples
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1982, p. 329-333 95-1137/82/8329-5$2./ Vol. 16, No. 2 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: Application to Clinical
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1982, p. 329-333 95-1137/82/8329-5$2./ Vol. 16, No. 2 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: Application to Clinical
patients with Lyme disease often have antibodies that bind to spirochetes isolated
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 567-572 Immunodiagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease HAZEL W. WILKINSON, Ph.D. Chief, Immunology Section, Respiratory and Special Pathogens Laboratory Branch,
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 567-572 Immunodiagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease HAZEL W. WILKINSON, Ph.D. Chief, Immunology Section, Respiratory and Special Pathogens Laboratory Branch,
HSV-1 IgM ELISA. Catalog No (96 Tests) For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures.
 For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE The GenWay, Inc. HSV-1 IgM ELISA Kit is intended for the detection of IgM antibody to HSV-1 in human serum or plasma. SUMMARY AND
For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE The GenWay, Inc. HSV-1 IgM ELISA Kit is intended for the detection of IgM antibody to HSV-1 in human serum or plasma. SUMMARY AND
Received 24 November 1997/Returned for modification 11 February 1998/Accepted 6 April 1998
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, July 1998, p. 486 490 Vol. 5, No. 4 1071-412X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Seroprevalence of Antibodies
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, July 1998, p. 486 490 Vol. 5, No. 4 1071-412X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Seroprevalence of Antibodies
(Received for publication June 3, 1946)
 A COMPARISON OF THE CEPHALIN-CHOLESTEROL FLOCCULATION AND THYMOL TURBIDITY TESTS IN PATIENTS WITH EX- PERIMENTALLY INDUCED INFECTIOUS HEPATITIS' BY W. PAUL HAVENS, JR., AND RUTH E. MARCK (From the Section
A COMPARISON OF THE CEPHALIN-CHOLESTEROL FLOCCULATION AND THYMOL TURBIDITY TESTS IN PATIENTS WITH EX- PERIMENTALLY INDUCED INFECTIOUS HEPATITIS' BY W. PAUL HAVENS, JR., AND RUTH E. MARCK (From the Section
See external label 2 C-8 C 96 tests Chemiluminescence. CMV IgM. Cat # Diluted samples, controls & calibrator 100 µl 30 minutes
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Introduction The DRG Epstein-Barr Virus (VCA) IgM Enzyme Immunoassay Kit provides materials for determination of IgM-class
This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Introduction The DRG Epstein-Barr Virus (VCA) IgM Enzyme Immunoassay Kit provides materials for determination of IgM-class
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC.
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections
 Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct Agglutination Test for Diagnosis of Toxoplasma Infection: Method for Increasing Sensitivity and Specificity
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 562-568 0095-1 137/80/06-0562/07$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No.6 Direct Agglutination Test for Diagnosis of Toxoplasma Infection: Method for Increasing Sensitivity
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 562-568 0095-1 137/80/06-0562/07$02.00/0 Vol. 11, No.6 Direct Agglutination Test for Diagnosis of Toxoplasma Infection: Method for Increasing Sensitivity
