Category Description / Key Findings Publication
|
|
|
- Amos Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PUBLICATIONS Selected T-SPOT.TB test publications, by area of interest, up to 31 th August Category Description / Key Findings Publication Background A useful primer on the evolution, administration and interpretation of the tuberculin skin test and its limitations. A useful summary describing the evolution, principle and methodology of the T-SPOT.TB test and its advantages over the TST. A useful primer on the history and current state of tuberculosis as an infectious disease. T-SPOT.TB test sensitivity was 98% (57/58) in subjects with culture confirmed TB. T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 91% (30/33) in subjects with active TB. T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 94.1% (254/270) in subjects with culture confirmed TB. Huebner RE, et al. The tuberculin skin test. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17(6): Lalvani A. Diagnosing tuberculosis infection in the 21st century: new tools to tackle an old enemy. Chest. 2007;131(6): doi: /chest Pai M,et al. Tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016;16076(6) doi: /nrdp Janssens JP,et al. Quantitative scoring of an interferon-gamma assay for differentiating active from latent tuberculosis. Eur Respir J. 2007;30(4): doi: / Dominguez J, et al. Comparison of Two Commercially Available Gamma Interferon Blood Tests for Immunodiagnosis of Tuberculosis. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology. 2008;15(1): Chee CB, et al. Comparison of sensitivities of two commercial gamma interferon release assays for pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(6): doi: /jcm Utility in active disease / sensitivity T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 94% (33/35) in immunocompetent subjects and 95% (20/21) in immunosuppressed subjects with confirmed extrapulmonary TB. the ELISPOT assay is a useful adjunct test for excluding active tuberculosis in patients with suspected extrapulmonary tuberculosis regardless of immunosuppressive condition. T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 94.2% (81/86) in subjects with confirmed or probable osteoarticular TB. the results of our study suggest that the IGRA assay is a useful adjunctive tool for diagnosing osteoarticular TB. T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 93% (40/43) in subjects with miliary TB. The T-SPOT.TB test may be a helpful adjunct test for miliary tuberculosis. Kim SH, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of a T-cellbased assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis in immunocompromised patients. Am J Med. 2009;122(2): doi: /j.amjmed Jia H, et al. Evaluation of interferon-gamma release assay in the diagnosis of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;76(3): doi: /j.diagmicrobio Lee Y-M, et al. Diagnostic Usefulness of a T-Cell Based Assay in Patients With Miliary Tuberculosis Compared With Those With Lymph Node Tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(2):e26-e29. T-SPOT.TB sensitivity was 90% (91/101) for patients with disseminated or military TB. In a subgroup analysis of the 58 patients in whom both QFT-GIT and the T-SPOT.TB results were available, the sensitivity of T-SPOT.TB was 95% (55/58) compared to 67% (39/58) for QFT-GIT. Patients confirmed for active TB (culture or a positive TB PCR) were tested by QFT-GIT (192 patients) or T-SPOT.TB (212 patients). Considering all age groups, the overall sensitivity was 80.2% (154/192) for QFT-GIT and 91.0% (193/212) for T-SPOT.TB. The sensitivities of QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB according to age group were as follows: <29 years, 93.3% (28/30) and 96.7% (29/30); years, 86.5% (45/52) and 94.7% (72/76); years, 76.8% (53/69) and 87.5% (56/64); and >70 Yu SN, et al. Diagnostic Usefulness of IFN- Gamma Releasing Assays Compared With Conventional Tests in Patients With Disseminated Tuberculosis: Medicine. 2015;94(28):e1094. doi: /md Bae W, et al. Comparison of the Sensitivity of QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and T-SPOT.TB According to Patient Age. Shams H, ed. PLOS ONE. 2016;11(6):e doi: /journal.pone
2 Specificity years, 68.3% (28/41) and 85.7% (36/42), respectively. While the trend of age-related changes in sensitivity was significant for both QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB, a multivariate analysis indicated that only QFT-GIT was significantly affected by age The specificity of T-SPOT.TB test in 326 Naval recruits in the USA was 98% (275/278). The specificity of T-SPOT.TB test in individuals from Ohio State University and the Nationwide Children s Hospital was 99% (107/108) The specificity of T-SPOT.TB test in low risk military recruits in the USA was 98.7% (1336/1354). The specificity of T-SPOT.TB test in low risk controls in Japan was 99% (110/111). T-SPOT.TB observed specificity was at least 98.6% during serial screening programs of healthcare workers in 19 US hospitals. In the largest study of its kind, 42,155 T-SPOT.TB test results from healthcare workers were analyzed and the rates of positivity, reversion, and conversion were 2.3%, 0.8% and 17.6% respectively, correlating with known TB risk factors. The findings suggest that the T-SPOT.TB test is an accurate and reliable way to screen healthcare workers. Bienek DR, Chang CK. Evaluation of an interferon-gamma release assay, T-SPOT.TB, in a population with a low prevalence of tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13(11): Wang SH, et al. Evaluation of a modified interferon-gamma release assay for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in adult and paediatric populations that enables delayed processing. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010;42(11-12): doi: / Mancuso JD, et al. Discordance among commercially available diagnostics for latent tuberculosis infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;185(4): doi: /rccm oc. Higuchi K, et al. Comparison of specificities between two interferon-gamma release assays in Japan. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16(9): doi: /ijtld King TC, et al. T-SPOT.TB Interferon-γ Release Assay Performance in Healthcare Worker Screening at Nineteen U.S. Hospitals. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192(3): doi: /rccm oc. 312 patients awaiting kidney transplant from Seoul were tested with the TST and the T-SPOT.TB test. Patients were followed up prospectively for the subsequent development of active TB disease to demonstrate the positive and negative predictive value of the tests. 4/71 (5.6%) patients with positive T-SPOT.TB test but negative TST developed active TB after kidney transplant, whereas none of the 231 patients with negative or indeterminate T-SPOT.TB test developed TB after kidney transplant. Kim SH, et al. A prospective longitudinal study evaluating the usefulness of a T-cell-based assay for latent tuberculosis infection in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(9): doi: /j x. Positive/negative predictive value for development of active TB disease 50/520 HIV infected subjects attending an out patients clinic in London were positive by the T-SPOT.TB test. Follow-up of these patients identified 3 with subclinical active TB. No patient with a negative T-SPOT.TB test result has developed TB in 3 years of follow-up. 583 household contacts were tested with the T-SPOT.TB test and followed-up every 6 months for 3 years. 6.3% (9/144) T-SPOT.TB positive contacts who did not receive preventive therapy converted to active disease. None of the 407 household contacts who were T-SPOT.TB negative or the 32 who received TB therapy developed active TB. Kall MM, et al. Latent and subclinical tuberculosis in HIV infected patients: a cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:107. doi: / Wang JY, et al. Interferon-gamma release assay and Rifampicin therapy for household contacts of tuberculosis. J Infect. 2012;64(3): doi: /j.jinf asymptomatic household contacts of smear-positive patients were tested with T-SPOT.TB test and TST. T-SPOT.TB gave a significantly higher positive rate (32.7% vs 22.1%) and better association with exposure time than TST at the 15 mm cut-off. Using a TST cut-off of 15 mm, 56% of future TB cases and 62.5% of bacteriologically confirmed cases were missed. Lowering the TST cut-off to 10 mm or 5 mm could achieve sensitivity comparable with that of T-SPOT.TB, but at the expense of lower specificities, with more positive tests (thus requiring treatment) per case of TB predicted. T-SPOT.TB outperformed TST in predicting TB among household contacts in a high-income area with widespread BCG vaccination coverage. Leung CC, et al. T-Spot.TB outperforms tuberculin skin test in predicting development of active tuberculosis among household contacts. Respirology. 2015;20(3): doi: /resp Immunosuppressed 138 patients with various hematology disorders had been in contact with an infectious TB case. Subjects were split into a cohort with normal WBC count and a cohort with abnormal WBC count. T-SPOT.TB positivity was 44.6% and 44.3% respectively. TST s positivity declined from 26% to 15% respectively in the same cohorts Piana F, et al. Use of a T-cell-based test for detection of tuberculosis infection among immunocompromised patients. Eur Respir J. 2006;28(1): doi: /
3 50/201 HIV positive subjects were T-SPOT.TB test positive, of which 33 (66%) had a CD4 count < 300 and 9 (18%) had a CD4 count <100. The T-SPOT.TB test s responses were shown to be unaffected by CD4 count. Clark SA, et al. Tuberculosis antigen-specific immune responses can be detected using enzyme-linked immunospot technology in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 patients with advanced disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;150(2): doi: /j x. 197 immunosuppressed, hematological patients who were contacts of 2 infectious TB cases were tested with TST and T-SPOT.TB test. A control group of 324 community contacts of infectious TB cases was also tested. In the control cohort, TST and T-SPOT.TB results were positive in 84.9% (275/324) and 51.5% (167/324) of the contacts respectively. In the immunosuppressed cohort, positivity for TST and T-SPOT.TB was 17.3% (34/197) and 35.5% (70/197) respectively. Our findings highlight that TST is 10-fold more affected immunosuppression than T-SPOT.TB, and confirm that T-SPOT.TB is a better marker for LTBI. Piana F,et al. Use of T-SPOT.TB in latent tuberculosis infection diagnosis in general and immunosuppressed populations. The new microbiologica. 2007;30(3): In subjects with chronic renal infection undergoing hemodialysis T-SPOT.TB positivity was associated with TB risk factors, whereas the TST did not and was shown to only be associated with prior BCG vaccination. The TST is insensitive in hemodialysis patients and is not recommended to be used in isolation to diagnose latent tuberculosis infection. Passalent L, et al. Detecting latent tuberculosis infection in hemodialysis patients: a head-to-head comparison of the T-SPOT.TB test, tuberculin skin test, and an expert physician panel. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2(1): doi: /cjn Rheumatic disease patients were tested with T-SPOT.TB assay and TST. A history of BCG was associated with TST positive /T-SPOT.TB test negative discordance. Steroid use was associated with TST negative/ T-SPOT.TB test positive discordance. Elispot assay is a useful test for diagnosis of LTBI in rheumatic patients scheduled for anti-tnf therapy and identification of patients with false-positive TST results due to previous BCG vaccination. T-SPOT.TB test results were not affected in subjects with silicosis or old age. Psoriasis patients were tested with the T-SPOT.TB test and TST. The T-SPOT.TB test was correlated with risk factors for LTBI whereas the TST was not Patients from 62 German rheumatology centres were evaluated for LTBI using the TST, the T-SPOT.TB assay and the Cellestis In Tube assay. Only the TST and T-SPOT.TB test results significantly correlated to clinical risk factors for TB in the 852 subjects diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Vassilopoulos D, et al. Usefulness of enzymelinked immunospot assay (Elispot) compared to tuberculin skin testing for latent tuberculosis screening in rheumatic patients scheduled for antitumor necrosis factor treatment. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(7): Leung CC, et al. Comparison of T-Spot.TB and tuberculin skin test among silicotic patients. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(2): doi: / Laffitte E, et al. Tuberculosis screening in patients with psoriasis before antitumour necrosis factor therapy: comparison of an interferon-gamma release assay vs. tuberculin skin test. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(4): doi: /j x. Kleinert S, et al. Screening for latent tuberculosis infection: performance of tuberculin skin test and interferon-gamma release assays under real-life conditions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(11): Immunosuppressed (cont.) 1343 children from 6 months to < 15 years of age from high TB/HIV burden setting were evaluated for LTBI using TST and IGRAs; associations with child characteristics were measured. Contact tracing detected TB in 8% of child contacts within 3 months of exposure and IGRAs correlated better with contact than TSTs. QFT indeterminate rates were more frequent in children infected with HIV (4.7%) while the T-SPOT.TB test invalid rates were rare (0.2%) and not affected by HIV status. In children with no documented contact, TST and QFT had greater positivity rates than T-SPOT.TB test and would result in treating a higher proportion of children of children with little to no documented TB exposure. 108 pediatric patients with rheumatic disease were evaluated for LTBI using T-SPOT.TB and QFT. The study identified overall a 9.9% indeterminate rate for QFT, with an 87.5% rate for patients on prednisolone (>0.5mg/kg). No other treatments (biologics, immunosuppressant) affected QFT. None of the treatments affected T-SPOT.TB test as the invalid rate was 0%. The T-SPOT.TB test was suitable for evaluating latent tuberculosis infection even under immunosuppression, when TB tests are generally hard to perform. Mandalakas AM, et al. Optimizing the Detection of Recent Tuberculosis Infection in Children in a High Tuberculosis-HIV Burden Setting. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191(7): doi: /rccm oc. Nozawa T, et al. Usefulness of two IFN-γ release assays for patients with rheumatic disease. Pediatr Int. December doi: /ped
4 Results from contact tracing clinic obtained over a one year period were used to determine the most cost-effective TB screening strategy. Costs of a T-SPOT.TB test only strategy were much less than a TST only strategy. Costs were lowest in the strategy where TST was used first followed by T-SPOT.TB test in those that were +ve, however the study did not take into account false +ve who would be missed by TST. Wrighton-Smith P, et al. Direct costs of three models for the screening of latent tuberculosis infection. Eur Respir J. 2006;28(1): doi: / A 2 year screening model directed at screening 1,000 contacts in the UK was used to perform a cost-effectiveness comparison of TST, T-SPOT.TB test and QFT In Tube test using either a single (TST or IGRA) or dual (TST followed by IGRA) strategy. The cost per active case of TB prevented was lowest when the T-SPOT.TB test was used alone followed by 2 step testing using the TST followed by the T-SPOT.TB test. Pooran A, et al. Different screening strategies (single or dual) for the diagnosis of suspected latent tuberculosis: a cost effectiveness analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2010;10:7. doi: / Cost effectiveness The SWITCH study a comprehensive study of the costs of running an employee health TB screening program at a large urban hospital (Johns Hopkins) using either the TST or an IGRA. The cost of the TST-based screening program was calculated to be $73.20 per person. The results of the study showed that switching to an IGRA would be cost saving versus the TST if the T-SPOT.TB cost is $54.83 or less per test. In new hires, switching to an IGRA would be cost saving at $81.16 or less per test. Wrighton-Smith P, et al. Screening health care workers with interferon-gamma release assay versus tuberculin skin test: impact on costs and adherence to testing (the SWITCH study). J Occup Environ Med. 2012;54(7): doi: /jom.0b013e f. A single-centre, retrospective review and economic evaluation of 125 adult IBD patients (109 of which were BCG vaccinated) tested for LTBI using the T-SPOT.TB test. 98% (122/125) of subjects had a negative T-SPOT.TB result, 2% (2/125) had a positive result, and 1% (1/125) had an invalid. A strategy using IGRA to guide TB preventative treatment produced cost savings of per person compared to the BTS guidance. Greveson K, et al. Yield and cost effectiveness of mycobacterial infection detection using a simple IGRA-based protocol in UK subjects with inflammatory bowel disease suitable for anti- TNFalpha therapy. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(5): doi: /j.crohns Abbreviations: TB tuberculosis TST Tuberculin Skin Test LTBI - Latent Tuberculosis Infection
5 IGRA Comparisons in Sensitivity Studies All studies below are head to head comparisons between the T-SPOT.TB test and QFT-GIT in confirmed TB patients Publication Sensitivity % (n/n) T-SPOT.TB Test Indeterminate % (n) Sensitivity % (n/n) QFT-GIT Indeterminate % (n) Detjen Clin Infect Dis, (26/28) 0 (0) 92.9 (26/28) 0 (0) Chee J Clin Microbiol, (254/274) 1.5 (4) 81.8 (224/274) 10 (3.6) Domínguez Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, (32/38) 5.3 (2) 71.1 (27/38) 2.6 (1) Kampmann Eur Respir J, (14/24) 0 (0) 80.0 (20/25) 8.0 (2) Latorre. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, (37/39) NR 85.0 (34/40) NR Markova Biotechnol. & Biotechnol. Eq, (8/13) 30.8 (4) 92.3 (12/13) 0 (0) Lai Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, (86/98) 0 (0) 65.3 (64/98) 6.1 (6) Ling Eur Respir J, (116/138) 0.7 (1) 76.1 (105/138) 11.6 (16) Kobashi Intern Med, (21/22) 0 (0) 86.4 (19/22) 4.5 (1) Theron Eur Respir J, (91/107) excluded 84.9 (90/106) excluded Chiappini Pediatr Infect Dis J, (21/28) 0 (0) 89.3 (25/28) 0 (0) Kobashi OJRD, (11/12) 0 (0.) 83.3 (10/12) 8.3 (1) Young Eur Respir J, (13/21) 28.6 (6) 61.9 (13/21) 33.3 (7) Yu Medicine, (46/48) NR 70.8 (34/48) NR Notes: - TB confirmed through direct detection of MTB via culture or PCR - Updated 08/03/ Analysis based on peer-reviewed articles published between 01/01/2007 and update date - Indeterminate results excluded prior to sensitivity calculation, but not quantified within the article are listed as excluded T-SPOT is a registered trademark of Oxford Immunotec Ltd. The Oxford Immunotec logo is a registered trademark of Oxford Immunotec Ltd. QFT is a registered trademarks of the QIAGEN Group 2016 Oxford Immunotec, Inc. All rights reserved. CTS-TB-UK-V22
Testing for TB. Bart Van Berckelaer Territory Manager Benelux. Subtitle
 Testing for TB Bart Van Berckelaer Territory Manager Benelux Subtitle Agenda TB infection pathway TB immunisation Testing options Pre lab considerations of the whole blood ELISA test The T-SPOT.TB test
Testing for TB Bart Van Berckelaer Territory Manager Benelux Subtitle Agenda TB infection pathway TB immunisation Testing options Pre lab considerations of the whole blood ELISA test The T-SPOT.TB test
TB Prevention Who and How to Screen
 TB Prevention Who and How to Screen 4.8.07. IUATLD 1st Asia Pacific Region Conference 2007 Dr Cynthia Chee Dept of Respiratory Medicine / TB Control Unit Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Cycle of Infection
TB Prevention Who and How to Screen 4.8.07. IUATLD 1st Asia Pacific Region Conference 2007 Dr Cynthia Chee Dept of Respiratory Medicine / TB Control Unit Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Cycle of Infection
Peggy Leslie-Smith, RN
 Peggy Leslie-Smith, RN EMPLOYEE HEALTH DIRECTOR - AVERA TRAINING CONTENT 1. South Dakota Regulations 2. Iowa Regulations 3. Minnesota Regulations 4. Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA)Testing 1 SOUTH
Peggy Leslie-Smith, RN EMPLOYEE HEALTH DIRECTOR - AVERA TRAINING CONTENT 1. South Dakota Regulations 2. Iowa Regulations 3. Minnesota Regulations 4. Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA)Testing 1 SOUTH
Interferon Gamma Release Assay Testing for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Physician Guidelines
 Interferon Gamma Release Assay Testing for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Physician Guidelines Historically, Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) diagnosis was based on risk assessment, chest x-ray (CXR)
Interferon Gamma Release Assay Testing for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Physician Guidelines Historically, Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) diagnosis was based on risk assessment, chest x-ray (CXR)
Use of Interferon-γ Release Assays (IGRAs) in TB control in low and middle-income settings - EXPERT GROUP MEETING -
 Use of Interferon-γ Release Assays (IGRAs) in TB control in low and middle-income settings - EXPERT GROUP MEETING - Date and time: 20-21 July 2010, 09:00 18:00 Venue: Salle B, WHO-HQ, Geneva, Switzerland
Use of Interferon-γ Release Assays (IGRAs) in TB control in low and middle-income settings - EXPERT GROUP MEETING - Date and time: 20-21 July 2010, 09:00 18:00 Venue: Salle B, WHO-HQ, Geneva, Switzerland
Evidence-based use of the new diagnostic tools for TB-infection
 Evidence-based use of the new diagnostic tools for TB-infection Roland Diel, MD, MPH German Central Committee against Tuberculosis, Germany 20. Tuberkulose-Symposium in Münchenwiler, 24 th March 2011 1
Evidence-based use of the new diagnostic tools for TB-infection Roland Diel, MD, MPH German Central Committee against Tuberculosis, Germany 20. Tuberkulose-Symposium in Münchenwiler, 24 th March 2011 1
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas December 2-4, 2008
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas December 2-4, 2008 Interferon Gamma Releasing Assays: Diagnosing TB in the 21 st Century Peter Barnes, MD December 2, 2008 TOPICS Use of interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs)
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas December 2-4, 2008 Interferon Gamma Releasing Assays: Diagnosing TB in the 21 st Century Peter Barnes, MD December 2, 2008 TOPICS Use of interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs)
Evaluation and Treatment of TB Contacts Tyler, Texas April 11, 2014
 Evaluation and Treatment of TB Contacts Tyler, Texas April 11, 2014 Interferon Gamma Release Assays: Understanding the Test David Griffith, BA, MD April 11, 2014 David Griffith, BA, MD has the following
Evaluation and Treatment of TB Contacts Tyler, Texas April 11, 2014 Interferon Gamma Release Assays: Understanding the Test David Griffith, BA, MD April 11, 2014 David Griffith, BA, MD has the following
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013 Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRA s) Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 16, 2013 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013 Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRA s) Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 16, 2013 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
Barbara J Seaworth MD Medical Director, Heartland National TB Center Professor, Internal Medicine and Infectious Disease UT Health Northeast
 Practical Aspects for Using the Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) Test Live Webinar July 14, 2017 Barbara J Seaworth MD Medical Director, Heartland National TB Center Professor, Internal Medicine and
Practical Aspects for Using the Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) Test Live Webinar July 14, 2017 Barbara J Seaworth MD Medical Director, Heartland National TB Center Professor, Internal Medicine and
Nguyen Van Hung (NTP, Viet Nam)
 Technical Consultation Meeting on the Programmatic Management of Latent Tuberculosis Infection 31 August-1 September 2017, Seoul, Republic Korea Adopting new LTBI diagnostics at country level: perspective
Technical Consultation Meeting on the Programmatic Management of Latent Tuberculosis Infection 31 August-1 September 2017, Seoul, Republic Korea Adopting new LTBI diagnostics at country level: perspective
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
Approaches to LTBI Diagnosis
 Approaches to LTBI Diagnosis Focus on LTBI October 8 th, 2018 Michelle Haas, M.D. Associate Director Denver Metro Tuberculosis Program Denver Public Health DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures or conflicts
Approaches to LTBI Diagnosis Focus on LTBI October 8 th, 2018 Michelle Haas, M.D. Associate Director Denver Metro Tuberculosis Program Denver Public Health DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures or conflicts
Dimitrios Vassilopoulos,* Stamatoula Tsikrika, Chrisoula Hatzara, Varvara Podia, Anna Kandili, Nikolaos Stamoulis, and Emilia Hadziyannis
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 2102 2108 Vol. 18, No. 12 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.05299-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparison
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 2102 2108 Vol. 18, No. 12 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.05299-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparison
Richard O Brien, Consultant, FIND 3 rd Global Symposium on IGRAs Waikoloa, Hawaii, 13 January 2012
 Global l Applications of IGRAs Richard O Brien, Consultant, FIND 3 rd Global Symposium on IGRAs Waikoloa, Hawaii, 13 January 2012 Disclosure I have no personal financial conflicts of I have no personal
Global l Applications of IGRAs Richard O Brien, Consultant, FIND 3 rd Global Symposium on IGRAs Waikoloa, Hawaii, 13 January 2012 Disclosure I have no personal financial conflicts of I have no personal
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014 Interferon Gamma Release Assays Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 12, 2014 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014 Interferon Gamma Release Assays Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 12, 2014 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of
Validity of interferon-c-release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in haemodialysis patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Validity of interferon-c-release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in haemodialysis patients W. K. Chung 1,2, Z. L. Zheng 1, J. Y. Sung 1, S. Kim 1,H.H.Lee 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Validity of interferon-c-release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in haemodialysis patients W. K. Chung 1,2, Z. L. Zheng 1, J. Y. Sung 1, S. Kim 1,H.H.Lee 1,
Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis. Disclosures. Case
 Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis Neha Shah MD MPH Field Medical Officer Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention September 2016 1 Disclosures
Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis Neha Shah MD MPH Field Medical Officer Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention September 2016 1 Disclosures
Qualitative and quantitative results of interferon-γ release assays for monitoring the response to anti-tuberculosis treatment
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 217;32:32-38 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.216.199 Qualitative and quantitative results of interferon-γ release assays for monitoring the response to anti-tuberculosis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 217;32:32-38 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.216.199 Qualitative and quantitative results of interferon-γ release assays for monitoring the response to anti-tuberculosis
Detecting latent tuberculosis using interferon gamma release assays (IGRA)
 Detecting latent tuberculosis using interferon gamma release assays (IGRA) American Society for Microbiology June 2017 Edward Desmond, Ph.D., D (ABMM) San Lorenzo, CA Edward Desmond has no financial connections
Detecting latent tuberculosis using interferon gamma release assays (IGRA) American Society for Microbiology June 2017 Edward Desmond, Ph.D., D (ABMM) San Lorenzo, CA Edward Desmond has no financial connections
The Challenges and Pitfalls in Diagnosing or Misdiagnosing Tuberculosis: Are the Days of TB Skin Tests Over?
 The Challenges and Pitfalls in Diagnosing or Misdiagnosing Tuberculosis: Are the Days of TB Skin Tests Over? ROY F. CHEMALY, MD, MPH, FIDSA, FACP PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIRECTOR, INFECTION CONTROL SECTION
The Challenges and Pitfalls in Diagnosing or Misdiagnosing Tuberculosis: Are the Days of TB Skin Tests Over? ROY F. CHEMALY, MD, MPH, FIDSA, FACP PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIRECTOR, INFECTION CONTROL SECTION
These recommendations will remain in effect until the national shortage of PPD solution has abated.
 Maryland Recommendations Regarding the National Shortage of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) Solution; Attachment to Health Officer Memorandum National Shortages of Tubersol and Aplisol for TB Skin Testing;
Maryland Recommendations Regarding the National Shortage of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) Solution; Attachment to Health Officer Memorandum National Shortages of Tubersol and Aplisol for TB Skin Testing;
Interferon-gamma release assay for treatment monitoring of active tuberculosis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02278-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Interferon-gamma
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02278-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Interferon-gamma
DENOMINATOR: All patients aged 18 and older with a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease
 Measure #274: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Testing for Latent Tuberculosis (TB) Before Initiating Anti-TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
Measure #274: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Testing for Latent Tuberculosis (TB) Before Initiating Anti-TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
Update on IGRA Predictive Value
 Update on IGRA Predictive Value Sandra Kik, PhD Molebogeng Rangaka, MD, PhD Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD McGill International TB Centre, McGill University University of Cape Town & London School of Hygiene and
Update on IGRA Predictive Value Sandra Kik, PhD Molebogeng Rangaka, MD, PhD Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD McGill International TB Centre, McGill University University of Cape Town & London School of Hygiene and
Diagnostic challenges of active childhood TB in Tanzania. Michala Vaaben Rose, MD, Ph.D Department of Infectious Diseases, Hvidovre
 Diagnostic challenges of active childhood TB in Tanzania Michala Vaaben Rose, MD, Ph.D Department of Infectious Diseases, Hvidovre 1 Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis Muheza hospital, TZ Hilleroedhospital.dk
Diagnostic challenges of active childhood TB in Tanzania Michala Vaaben Rose, MD, Ph.D Department of Infectious Diseases, Hvidovre 1 Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis Muheza hospital, TZ Hilleroedhospital.dk
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 IGRA s and Their Use in TB Nurse NCM Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD July 18, 2012 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 IGRA s and Their Use in TB Nurse NCM Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD July 18, 2012 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
Identifying TB co-infection : new approaches?
 Identifying TB co-infection : new approaches? Charoen Chuchottaworn MD. Senior Medical Advisor, Central Chest Institute of Thailand, Department of Medical Services, MoPH Primary tuberculosis Natural history
Identifying TB co-infection : new approaches? Charoen Chuchottaworn MD. Senior Medical Advisor, Central Chest Institute of Thailand, Department of Medical Services, MoPH Primary tuberculosis Natural history
Juzar Ali, MD, FRCP(C) FCCP has the following disclosures to make:
 Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRA) Juzar Ali, MD, FRCP(C) FCCP June 27, 2018 TB Intensive June 26-29, 2018 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Juzar Ali, MD, FRCP(C) FCCP has the following
Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRA) Juzar Ali, MD, FRCP(C) FCCP June 27, 2018 TB Intensive June 26-29, 2018 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Juzar Ali, MD, FRCP(C) FCCP has the following
Thorax Online First, published on December 8, 2009 as /thx
 Thorax Online First, published on December 8, 2009 as 10.1136/thx.2009.119677 Title Page Cost effectiveness of the NICE guidelines for screening for latent tuberculosis infection: the Quantiferon-TB gold
Thorax Online First, published on December 8, 2009 as 10.1136/thx.2009.119677 Title Page Cost effectiveness of the NICE guidelines for screening for latent tuberculosis infection: the Quantiferon-TB gold
Using Interferon Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of TB Infection
 Learning Objectives Using Interferon Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of TB Infection 1. Describe available Interferon Gamma Release Assay tests for TB infection and how they work. 2. Understand interpretation
Learning Objectives Using Interferon Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of TB Infection 1. Describe available Interferon Gamma Release Assay tests for TB infection and how they work. 2. Understand interpretation
Report on WHO Policy Statements
 Report on WHO Policy Statements Christopher Gilpin TB Diagnostics and Laboratory Strengthening Unit Secretariat, Global Laboratory Initiative Stop TB Department, WHO Geneva New Diagnostics Working Group
Report on WHO Policy Statements Christopher Gilpin TB Diagnostics and Laboratory Strengthening Unit Secretariat, Global Laboratory Initiative Stop TB Department, WHO Geneva New Diagnostics Working Group
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients
 ERJ Express. Published on July 25, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00040007 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients Yoshihiro Kobashi, Keiji Mouri, Yasushi
ERJ Express. Published on July 25, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00040007 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients Yoshihiro Kobashi, Keiji Mouri, Yasushi
Interferon gamma release assays and the NICE 2011 guidelines on the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis
 CLINICAL AUDIT Clinical Medicine 2013, Vol 13, No 4: 362 6 Interferon gamma release assays and the NICE 2011 guidelines on the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis Helen R Mujakperuo, Richard D Thompson and
CLINICAL AUDIT Clinical Medicine 2013, Vol 13, No 4: 362 6 Interferon gamma release assays and the NICE 2011 guidelines on the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis Helen R Mujakperuo, Richard D Thompson and
LTBI-Tuberculin skin test. T-Spot.TB Technology. QuantiFERON -TB Gold In Tube T-SPOT.TB ELISA ELISA
 LTBI-Tuberculin skin test QuantiFERON -TB Gold In Tube ELISA PPD ~200 antigens 3 ml blood ESAT-6 TB 7.7 16-24 hour incubation Nil Negative control PHA Positive control Andersen et al Lancet 2000;356:1099-1104
LTBI-Tuberculin skin test QuantiFERON -TB Gold In Tube ELISA PPD ~200 antigens 3 ml blood ESAT-6 TB 7.7 16-24 hour incubation Nil Negative control PHA Positive control Andersen et al Lancet 2000;356:1099-1104
Conflict of Interest Disclosures:
 Mady Slater, M.D. Stanford University Medical Center Division of Infectious Diseases 04/23/14 WOEMA webinar Conflict of Interest Disclosures: I have no financial relationships with commercial entities
Mady Slater, M.D. Stanford University Medical Center Division of Infectious Diseases 04/23/14 WOEMA webinar Conflict of Interest Disclosures: I have no financial relationships with commercial entities
(2) 83.3% b/w TST and T-SPOT, (2) 77.4% b/w TST and T-SPOT. 77.7% b/w TST and QFT-GIT. QFT-GIT, 22.2% in T-SPOT. TSPOT vs. TST (> 5 mm) vs.
 Supplementary Table 1. Study characteristics of the included literature Low to moderate TB endemic region Shovman et al. (2009) [21] Minguez et al. (2012) [16], type 35 RA 35 RA 53 Patients with s (RA
Supplementary Table 1. Study characteristics of the included literature Low to moderate TB endemic region Shovman et al. (2009) [21] Minguez et al. (2012) [16], type 35 RA 35 RA 53 Patients with s (RA
Latent tuberculosis (TB) infection (LTBI), a
 COMMENTARY Time for a change? Updated guidelines using interferon gamma release assays for detection of latent tuberculosis infection in the office setting Marisa Kardos, BS, and Alexa Boer Kimball, MD,
COMMENTARY Time for a change? Updated guidelines using interferon gamma release assays for detection of latent tuberculosis infection in the office setting Marisa Kardos, BS, and Alexa Boer Kimball, MD,
Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012
 Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Targeted Tuberculin Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Lloyd Friedman, M.D. Milford Hospital Yale University
 Targeted Tuberculin Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Lloyd Friedman, M.D. Milford Hospital Yale University Tuberculosis Estimates USA World Infection 15,000,000 2,000,000,000
Targeted Tuberculin Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Lloyd Friedman, M.D. Milford Hospital Yale University Tuberculosis Estimates USA World Infection 15,000,000 2,000,000,000
New Standards for an Old Disease:
 New Standards for an Old Disease: Practical Implications of the TB Standards TB Prevention and Control Saskatchewan September 16, 2015 Practical Implications of the TB Standards Learning Objectives At
New Standards for an Old Disease: Practical Implications of the TB Standards TB Prevention and Control Saskatchewan September 16, 2015 Practical Implications of the TB Standards Learning Objectives At
Investigation of false-positive results by the QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 July 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00730-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Investigation of false-positive
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 July 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00730-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Investigation of false-positive
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Life Cycle of M. tuberculosis
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
Indeterminate test results of T-SPOT TM.TB performed under routine field conditions
 Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 842 846 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00117207 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Indeterminate test results of T-SPOT TM.TB performed under routine field conditions P. Beffa*, A. Zellweger
Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 842 846 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00117207 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Indeterminate test results of T-SPOT TM.TB performed under routine field conditions P. Beffa*, A. Zellweger
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 TB Partial Update Appendix 1 - Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial
TB Partial Update Appendix 1 - Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial
The Direct Comparison of Two Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Tuberculosis Screening of Japanese Healthcare Workers
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Direct Comparison of Two Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Tuberculosis Screening of Japanese Healthcare Workers Masaki Tanabe 1, Akiko Nakamura 1, Akie Arai 1, Daisuke Yamasaki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Direct Comparison of Two Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Tuberculosis Screening of Japanese Healthcare Workers Masaki Tanabe 1, Akiko Nakamura 1, Akie Arai 1, Daisuke Yamasaki
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
A look at medical factors that increase the risk for TB disease
 A look at medical factors that increase the risk for TB disease Mark Lobato, MD New England TB Consultant Division of Tuberculosis Elimination CDC Overview The spectrum of M. tuberculosis infection Immune
A look at medical factors that increase the risk for TB disease Mark Lobato, MD New England TB Consultant Division of Tuberculosis Elimination CDC Overview The spectrum of M. tuberculosis infection Immune
Literature Overview. Health Economics. Experience with QuantiFERON -TB Gold. Cellestis Clinical Guide series
 Literature Overview Experience with QuantiFERON -TB Gold Health Economics Cellestis Clinical Guide series 2008 www.cellestis.com This literature overview is intended to provide healthcare professionals
Literature Overview Experience with QuantiFERON -TB Gold Health Economics Cellestis Clinical Guide series 2008 www.cellestis.com This literature overview is intended to provide healthcare professionals
Use of an Interferon- Release Assay To Diagnose Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Foreign-Born Patients*
 Original Research MYCOBACTERIAL DISEASE Use of an Interferon- Release Assay To Diagnose Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Foreign-Born Patients* Daniel Brodie, MD; David J. Lederer, MD, MS; Jade S. Gallardo,
Original Research MYCOBACTERIAL DISEASE Use of an Interferon- Release Assay To Diagnose Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Foreign-Born Patients* Daniel Brodie, MD; David J. Lederer, MD, MS; Jade S. Gallardo,
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
A Clinician s Perspective: Improving Rheumatology Patient Care Using the T-SPOT.TB Test
 A Clinician s Perspective: Improving Rheumatology Patient Care Using the T-SPOT.TB Test Solomon Forouzesh, MD, FACD, FACR Medical Director Arthritis Care & Treatment Center Clinical Associate Professor
A Clinician s Perspective: Improving Rheumatology Patient Care Using the T-SPOT.TB Test Solomon Forouzesh, MD, FACD, FACR Medical Director Arthritis Care & Treatment Center Clinical Associate Professor
IGRAs for Diagnosis of Tuberculosis: 2010 Update
 IGRAs for Diagnosis of Tuberculosis: 2010 Update Nira Pollock, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA May 1, 2010 Problems with the PPD False positives
IGRAs for Diagnosis of Tuberculosis: 2010 Update Nira Pollock, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA May 1, 2010 Problems with the PPD False positives
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial update) 1.1 Short title Tuberculosis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial update) 1.1 Short title Tuberculosis
QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube Test for Tuberculosis Prevention in HIV-Infected Patients
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 70, 502 506, 2017 Original Article QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube Test for Tuberculosis Prevention in HIV-Infected Patients Thana Khawcharoenporn 1 *, Benjawan Phetsuksiri 2, Janisara
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 70, 502 506, 2017 Original Article QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube Test for Tuberculosis Prevention in HIV-Infected Patients Thana Khawcharoenporn 1 *, Benjawan Phetsuksiri 2, Janisara
Interferon-gamma release assays versus tuberculin skin testing for detection of latent tuberculosis in chronic haemodialysis patients
 NDT Advance Access published January 22, 2009 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 1 of 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn748 Original Article Interferon-gamma release assays versus tuberculin skin testing for detection
NDT Advance Access published January 22, 2009 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 1 of 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn748 Original Article Interferon-gamma release assays versus tuberculin skin testing for detection
Effect of prolonged incubation time on the results of the QuantiFERON TB Gold In-Tube assay for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 July 2013 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00290-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Effect of prolonged
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 July 2013 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00290-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Effect of prolonged
New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents
 New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine [With great thanks to Andrea
New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine [With great thanks to Andrea
AT HIGH RISK OF PROGRESSING TO ACTIVE TB? Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician University Hospitals of Leicester UK
 HOW WELL DO IGRAS PERFORM IN THE IDENTIFICATION OF PERSONS WHO ARE AT HIGH RISK OF PROGRESSING TO ACTIVE TB? Dr Pranab Haldar MD MRCP Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician University Hospitals of Leicester
HOW WELL DO IGRAS PERFORM IN THE IDENTIFICATION OF PERSONS WHO ARE AT HIGH RISK OF PROGRESSING TO ACTIVE TB? Dr Pranab Haldar MD MRCP Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician University Hospitals of Leicester
Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening
 Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.06 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: November 20, 2013 Most Recent Review
Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.06 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: November 20, 2013 Most Recent Review
Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients
 Eur Respir J 2007; 30: 945 950 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00040007 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients Y. Kobashi, K. Mouri, Y. Obase,
Eur Respir J 2007; 30: 945 950 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00040007 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Clinical evaluation of QuantiFERON TB-2G test for immunocompromised patients Y. Kobashi, K. Mouri, Y. Obase,
결핵노출접촉자감염관리 서울아산병원감염내과 김성한
 결핵노출접촉자감염관리 서울아산병원감염내과 김성한 TB incidence (2012) TB incidence South Korea 108 China 73 Taiwan 68 Portucal 26 Japan 19 Spain 14 US 3.6 * unit- per 100,000 population Adapted from WHO Adapted from WHO Emerg
결핵노출접촉자감염관리 서울아산병원감염내과 김성한 TB incidence (2012) TB incidence South Korea 108 China 73 Taiwan 68 Portucal 26 Japan 19 Spain 14 US 3.6 * unit- per 100,000 population Adapted from WHO Adapted from WHO Emerg
Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management
 Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management Patrick T. Dowling MD,MPH Professor and Chair Dept of Family Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pri-Med March 29 2014 Pdowling@mednet.ucla.edu
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management Patrick T. Dowling MD,MPH Professor and Chair Dept of Family Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pri-Med March 29 2014 Pdowling@mednet.ucla.edu
Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices
 Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices Last Updated September 7, 2016 LTBI Demographics in the US o 13million people in the US with LTBI (estimate) o In 2014, approximately 66% of TB cases in the United States
Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices Last Updated September 7, 2016 LTBI Demographics in the US o 13million people in the US with LTBI (estimate) o In 2014, approximately 66% of TB cases in the United States
T-CELL RESPONSES ASSESSED USING IGRA AND TST ARE NOT CORRELATED WITH AFB GRADE AND CHEST RADIOGRAPH IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS
 T-CELL RESPONSES ASSESSED USING IGRA AND TST ARE NOT CORRELATED WITH AFB GRADE AND CHEST RADIOGRAPH IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS Kiatichai Faksri 1, 4, Wipa Reechaipichitkul 2, 4, Wilailuk Pimrin
T-CELL RESPONSES ASSESSED USING IGRA AND TST ARE NOT CORRELATED WITH AFB GRADE AND CHEST RADIOGRAPH IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS Kiatichai Faksri 1, 4, Wipa Reechaipichitkul 2, 4, Wilailuk Pimrin
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Interpretation of TST & IGRA results. Objectives
 Interpretation of TST & IGRA results Randall Reves, MD, MSc Volunteer Clinician Denver Metro TB Program and Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine University of Colorado Denver Objectives
Interpretation of TST & IGRA results Randall Reves, MD, MSc Volunteer Clinician Denver Metro TB Program and Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine University of Colorado Denver Objectives
Technical Bulletin No. 172
 CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory QuantiFERON -TB Gold Plus Assay Contact: J Matthew Groeller, MPA(HCM), MT(ASCP), 717-851-4516 Operations Manager, Clinical Pathology, CPAL Jennifer Thebo,
CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory QuantiFERON -TB Gold Plus Assay Contact: J Matthew Groeller, MPA(HCM), MT(ASCP), 717-851-4516 Operations Manager, Clinical Pathology, CPAL Jennifer Thebo,
Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now?
 Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now? Amee Patrawalla MD MPH Rutgers - NJ Medical School Global TB Institute Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey Learning Objectives Understand the current epidemiologic
Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now? Amee Patrawalla MD MPH Rutgers - NJ Medical School Global TB Institute Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey Learning Objectives Understand the current epidemiologic
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016
 Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
Kinetics of T-cell-based assays on cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with tuberculous meningitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 214;29:793-799 http://dx.doi.org/1.394/kjim.214.29.6.793 Kinetics of T-cell-based assays on cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 214;29:793-799 http://dx.doi.org/1.394/kjim.214.29.6.793 Kinetics of T-cell-based assays on cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with
Guidance for Identifying Risk Factors for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) During Evaluation of Potential Living Kidney Donors
 Summary and Goals On November 13, 2012, the OPTN/UNOS Board of Directors approved a requirement that all potential living kidney donors undergo evaluation for infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Summary and Goals On November 13, 2012, the OPTN/UNOS Board of Directors approved a requirement that all potential living kidney donors undergo evaluation for infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
LATENT TUBERCULOSIS. Robert F. Tyree, MD
 LATENT TUBERCULOSIS Robert F. Tyree, MD 1 YK TB OFFICERS Ron Bowerman Elizabeth Roll Mien Chyi (Pediatrics) Cindi Mondesir (Pediatrics) The new guys: Philip Johnson Robert Tyree 2009 CDC TB CASE DEFINITION
LATENT TUBERCULOSIS Robert F. Tyree, MD 1 YK TB OFFICERS Ron Bowerman Elizabeth Roll Mien Chyi (Pediatrics) Cindi Mondesir (Pediatrics) The new guys: Philip Johnson Robert Tyree 2009 CDC TB CASE DEFINITION
Screening for Tuberculosis Infection. Harlingen, TX. Linda Dooley, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 TB Infection Diagnosis Recommendations Talk Developed by Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD Medical Consultant, Heartland National TB Center Associate Professor Internal Medicine/Pediatrics/Infectious Disease UT
TB Infection Diagnosis Recommendations Talk Developed by Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD Medical Consultant, Heartland National TB Center Associate Professor Internal Medicine/Pediatrics/Infectious Disease UT
Diagnosis of tuberculosis
 Diagnosis of tuberculosis Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Epidemiology McGill University, Montreal, Canada madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca Global TB Case Detection A major concern 2.6 million new smear
Diagnosis of tuberculosis Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Epidemiology McGill University, Montreal, Canada madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca Global TB Case Detection A major concern 2.6 million new smear
Tuberculosis Update. Topics to be Addressed
 Tuberculosis Update Robert M. Jasmer, M.D. University of California, San Francisco TB Control Section, San Francisco Department of Public Health Topics to be Addressed TB in the USA Screening recommendations
Tuberculosis Update Robert M. Jasmer, M.D. University of California, San Francisco TB Control Section, San Francisco Department of Public Health Topics to be Addressed TB in the USA Screening recommendations
Didactic Series. Latent TB Infection in HIV Infection
 Didactic Series Latent TB Infection in HIV Infection Jacqueline Peterson Tulsky, MD UCSF Positive Health Program at SFGH Medical Director, SF and North Coast AETC March 13, 2014 ACCREDITATION STATEMENT:
Didactic Series Latent TB Infection in HIV Infection Jacqueline Peterson Tulsky, MD UCSF Positive Health Program at SFGH Medical Director, SF and North Coast AETC March 13, 2014 ACCREDITATION STATEMENT:
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Global Impact of TB
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of
 TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
Northwestern Polytechnic University
 Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening
 Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.06 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: November 20, 2013 Most Recent Review
Clinical Policy Title: Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.06 Effective Date: March 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: November 20, 2013 Most Recent Review
Clinical Utility of the QuantiFERON TB-2G Test for Elderly Patients With Active Tuberculosis*
 CHEST Clinical Utility of the QuantiFERON -2G Test for Elderly Patients With Active Tuberculosis* Yoshihiro Kobashi, MD, PhD; Keiji Mouri, MD; Shinich Yagi, MD; Yasushi Obase, MD, PhD; Naoyuki Miyashita,
CHEST Clinical Utility of the QuantiFERON -2G Test for Elderly Patients With Active Tuberculosis* Yoshihiro Kobashi, MD, PhD; Keiji Mouri, MD; Shinich Yagi, MD; Yasushi Obase, MD, PhD; Naoyuki Miyashita,
Diagnosis and Medical Case Management of Latent TB. Bryan Rock, MD April 27, 2010
 TB Nurse Case Management Lisle, Illinois April 27-28, 28 2010 Diagnosis and Medical Case Management of Latent TB Infection Bryan Rock, MD April 27, 2010 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LATENT TUBERCULOSIS
TB Nurse Case Management Lisle, Illinois April 27-28, 28 2010 Diagnosis and Medical Case Management of Latent TB Infection Bryan Rock, MD April 27, 2010 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LATENT TUBERCULOSIS
Laboratory Updates on IGRA Testing
 Laboratory Updates on IGRA Testing Edward A. Graviss, PhD, MPH, FIDSA August 18, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Edward A. Graviss, PhD, MPH, FIDSA, has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
Laboratory Updates on IGRA Testing Edward A. Graviss, PhD, MPH, FIDSA August 18, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Edward A. Graviss, PhD, MPH, FIDSA, has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
Diagnostic Usefulness of a T-cell-based Assay for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompromised Patients
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Diagnostic Usefulness of a T-cell-based Assay for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompromised Patients Sung-Han Kim, MD, a,b,c Kyoung-Ho Song, MD, a Su-Jin Choi, MS, b Hong-Bin
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Diagnostic Usefulness of a T-cell-based Assay for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompromised Patients Sung-Han Kim, MD, a,b,c Kyoung-Ho Song, MD, a Su-Jin Choi, MS, b Hong-Bin
Diagnosis & Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis & Management of Latent TB Infection Prof. Ashok Rattan, MD, MAMS, INSA DFG, WHO Lab Director Academics, Industry: Research, Diagnosis, Public Health, Academics Adviser: Laboratory Operations,
Diagnosis & Management of Latent TB Infection Prof. Ashok Rattan, MD, MAMS, INSA DFG, WHO Lab Director Academics, Industry: Research, Diagnosis, Public Health, Academics Adviser: Laboratory Operations,
2016 OPAM Mid-Year Educational Conference, Sponsored by AOCOPM Sunday, March 13, 2016
 Learning Objectives Tuberculosis Case Discussions: Evaluation for Tuberculosis Infection Melissa C. Overman, DO, MPH, CHES, FAOCOPM Describe appropriate technique for TST placement, reading and interpretation
Learning Objectives Tuberculosis Case Discussions: Evaluation for Tuberculosis Infection Melissa C. Overman, DO, MPH, CHES, FAOCOPM Describe appropriate technique for TST placement, reading and interpretation
TB Intensive Houston, Texas. Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith. November 12, 2009
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus
 QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus A New Interferon-γ Release Assay (IGRA) for the Indirect Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Elitza S. Theel, PhD, D(ABMM) Director of Infectious
QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus A New Interferon-γ Release Assay (IGRA) for the Indirect Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Elitza S. Theel, PhD, D(ABMM) Director of Infectious
Diagnosis of tuberculosis: principles and practice of using interferon- release assays (IGRAs)
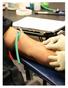 Diagnosis of tuberculosis: principles and practice of using interferon- release assays (IGRAs) Educational aims To provide an overview of interferon- release assays (IGRAs) used for detection of tuberculosis
Diagnosis of tuberculosis: principles and practice of using interferon- release assays (IGRAs) Educational aims To provide an overview of interferon- release assays (IGRAs) used for detection of tuberculosis
RESEARCH NOTE QUANTIFERON -TB GOLD IN-TUBE TEST FOR DIAGNOSING LATENT TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION AMONG CLINICAL-YEAR THAI MEDICAL STUDENTS
 Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health RESEARCH NOTE QUANTIFERON -TB GOLD IN-TUBE TEST FOR DIAGNOSING LATENT TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION AMONG CLINICAL-YEAR THAI MEDICAL STUDENTS Benjawan Phetsuksiri 1, Somchai
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health RESEARCH NOTE QUANTIFERON -TB GOLD IN-TUBE TEST FOR DIAGNOSING LATENT TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION AMONG CLINICAL-YEAR THAI MEDICAL STUDENTS Benjawan Phetsuksiri 1, Somchai
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) and Interferon-gamma Release Assays (IGRA)
 Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) and Interferon-gamma Release Assays (IGRA) April 2019 Bob Belknap M.D. Director, Denver Metro TB Program Disclosures No relevant financial relationships Objectives Be able to
Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) and Interferon-gamma Release Assays (IGRA) April 2019 Bob Belknap M.D. Director, Denver Metro TB Program Disclosures No relevant financial relationships Objectives Be able to
Evidence on IGRAs in Low & Middle Income Countries. Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD McGill University, Montreal
 Evidence on IGRAs in Low & Middle Income Countries Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD McGill University, Montreal Madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca Disclosure No industry/financial conflicts I co-chair the Stop TB Partnership
Evidence on IGRAs in Low & Middle Income Countries Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD McGill University, Montreal Madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca Disclosure No industry/financial conflicts I co-chair the Stop TB Partnership
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey
 Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
