TUBERCULOSIS TODAY WORLD-WIDE, UNITED STATES, TEXAS J O R D A N C O U L S O N, R. N. S N S C O O R D I N A T O R, P H E P / H S R 1
|
|
|
- Thomasina Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TUBERCULOSIS TODAY WORLD-WIDE, UNITED STATES, TEXAS J O R D A N C O U L S O N, R. N. S N S C O O R D I N A T O R, P H E P / H S R 1
2 WHAT IS TB? TB is a disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but can attack any part of the body such as lymph nodes, bones and joints, the brain and other organs. If TB is treated properly, most people can be cured of TB If TB is NOT treated properly, people can die from TB or develop drug-resistant forms of TB
3 TRANSMISSION OF M. TUBERCULOSIS M. tuberculosis spread via airborne particles called droplet nuclei Expelled when person with infectious TB coughs, sneezes, shouts, or sings Transmission occurs when droplet nuclei inhaled and reach the alveoli of the lungs, via nasal passages, respiratory tract, and bronchi
4 TB HISTORY Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Found in Egyptian mummies, circa 2400 BC Around 460 BC, Hippocrates termed the disease phthisis or consumption almost always fatal most widespread disease of the time
5 PUBLIC HEALTH THREAT IDENTIFIED An edict issued by the Republic of Lucca (central Italian peninsula), 1699: Henceforth, human health should no longer be endangered by objects remaining after the death of a consumptive. The names of the deceased should be reported to the authorities, and measures undertaken for disinfection
6 PERSON TO PERSON TRANSMISSION Benjamin Marten theorized the TB could be caused by Wonderfully minute living creatures..it may be therefore very likely that by an habitual lying in the same bed with a consumptive patient, constantly eating and drinking with him, or by very frequently conversing so nearly as to draw in part of the breath he emits from the lungs, a consumption may be caught by a sound person
7 FIRST STEP TOWARD A TB CURE. Dr. Herman Brehmer Developed TB, was told to find a healthier climate, so he traveled to the Himalayan mountains, where he became cured of TB submitted his doctoral dissertation- Tuberculosis is a Curable Disease Codified the concept of the Sanatoria in 1863 Exposed to continuous fresh air and good nutrition
8 AND THE BALL SLOWLY STARTED ROLLING French Military doctor (Jean-Antoine Villemin) found that consumption could be passed from humans to cattle and from cattle to rabbits.. Previous to this, it was believed that consumption arose spontaneously in each affected organism Robert Koch- stained M. Tuberculosis
9 HOWEVER, Treatment still centered around the sanatoria, where rest and proper nutrition was the main tool used to combat the infection Isolated the sick Circa early 1900s, other cures included lung collapsing, artificial pneumothorax, surgical limiting of the lung, and radiation
10 S- STREPTOMYCIN, AND OTHER DRUGS Previously, other drugs had been available, but were too toxic to use on animals or humans Streptomycin became THE front line drug in the fight against TB Quickly, TB became streptomycin resistant, but it was found that two or more drugs would overcome this problem
11 GLOBAL THREAT Although TB is preventable and treatable, it is not just a disease of the past. It is still one of the world s deadliest diseases. An estimated 2 billion people, or one third of the world's population, are infected with M. tuberculosis. Each year, approximately 9 million people develop TB disease 1.4 million people die of TB disease
12 GLOBAL RESURGENCE Contributing factors: Inadequate funding for TB control programs HIV epidemic Increased immigration from countries where TB is common Spread in homeless shelters and correctional facilities Increase and spread of multidrug-resistant TB
13 HIGH-RISK GROUPS FOR TB INFECTION FOREIGN-BORN/IMMIGRANTS In the U.S., LTBI and TB disease often occur among people born in areas of the world where TB is common: Asia Africa Russia Eastern Europe Latin America
14 UNITED STATES TB disease was once the leading cause of death in the United States. After the discovery of drugs that could treat TB in the 1950s, death rates began to drop dramatically. TB is still a problem in the United States Approximately 9 to 14 million people are infected with M. tuberculosis In 2010, over 11,000 people developed TB disease
15 TB REPORTING IN U.S.
16
17 TEXAS In Texas: 51.3 percent of reported TB cases in 2010 were among Hispanics 18.4 percent were among African Americans, 14.8 percent were among Whites, 14.8 percent were among Asians 0.7 percent were among persons of unknown ethnicity TB rates are higher along the Texas-Mexico border.
18 TEXAS COUNTIES County 2007 Cases 2008 Cases 2009 Cases 2010 Cases 2011 Cases Bexar Cameron Collingsworth Dallas Deaf Smith El Paso Garza Harris Lubbock Tarrant Terry Travis
19 RISK FACTORS* AMONG TB CASES AGES 18+, TEXAS 2010 Risk Factor State Foreign born 58% Excess alcohol use 21% Diabetes 16% Prison/Jail Inmate 11% Non-injection drug use 9% HIV positive 9% Homeless 6% Health Care Worker 3% Injection drug use 2% Migrant Farm Worker <1% *Note: Individuals can have more than one risk factor.
20 TARGETED TESTING Used to identify and treat persons who are at high risk of developing TB, once infected with M. Tuberculosis HIV/AIDS Persons recently infected with M. Tuberculosis Cigarette smokers ETOH/Drug abusers
21 MEDICAL EVALUATION FOR TB Medical History Symptoms of pulmonary TB: Prolonged cough (3 weeks or longer), hemoptysis Chest pain Loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss Night sweats, fever Fatigue
22 MEDICAL EVALUATION Done anytime a pt. has a (+) Mantoux or IGRA test Consists of five parts Medical history Physical exam HIV test/counseling Test for TB infection (TST or IGRA) CXR Bacteriological exam NAA test
23 BACTERIOLOGICAL EXAM, CONT. AKA- how do we kill this thing? Mono- resistant Resistant to one TB treatment drug Poly-resistant Resistant to at least two TB treatment drugs (but not both isoniazid and rifampin) MDRTB Resistant to both isoniazid and rifampin XDR-TB Resistant to both of the above, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least on of three injectable second line drugs
24 TB S/S Fatigue Malaise Weight loss/loss of appetite Coughing Enlarged lymph nodes Night Sweats
25 MEDICAL EVALUATION FOR TB Test for M. tuberculosis Infection Two methods for detecting M. tb infection: TST and IGRAs TST and IGRAs help differentiate persons with M. tb infection from those not infected Negative reaction to either does not exclude diagnosis of TB or LTBI
26 IGRA Interferon-gamma release assays QuantiFERON-TB Gold in Tube (QFT-GIT) T-SPOT Obtain a blood sample, send to lab If pt. is infected with M Tuberculosis, the blood cells will release interferon-gamma in response to the test
27 CHEST X-RAY With active TB, classic cloudy CXR Not conclusive, due to other disease processes that damage the lungs If immunocomprimised, CXR may appear normal
28 ADMINISTERING THE TST Inject 0.1 ml of PPD (5 tuberculin units) into forearm between skin layers Produce wheal (raised area) 6 10 mm in diameter Follow universal precautions for infection control
29 READING THE TST Trained health care worker assesses reaction hours after injection Palpate (feel) injection site to find raised area Measure diameter of induration across forearm; only measure induration, not redness Record size of induration in millimeters; record 0 if no induration found
30 MANTOUX SKIN TEST Given SQ, between skin layers Wait 24 hours, observe reaction (if any) DO NOT care about or measure the red area DO care about the swelling (Induration) DO measure the induration (and the induration ONLY, not the red area) Did the non-compliant patient miss the reading? -Must repeat the test NOT effective with those who have taken the BCG vaccinegives false positives.
31 WHAT CONSTITUTES A POSITIVE MANTOUX SKIN TEST? THAT DEPENDS.. CDC classification of tuberculin reaction : An induration (palpable raised hardened area of skin) of more than 5 15 mm (depending upon the person's risk factors) to 10 Mantoux units is considered a positive result, indicating TB infection. 5 mm or more is positive in HIV-positive person Recent contacts of TB case Persons with nodular or fibrotic changes on CXR consistent with old healed TB Patients with organ transplants and other immunosuppressed patients -A tuberculin test conversion is defined as an increase of 10 mm or more within a 2-year period, regardless of age.
32 WHAT CONSTITUTES A POSITIVE MANTOUX SKIN TEST? THAT DEPENDS.. 10 mm or more is considered positive for: People who have come into the US within the last 5 years from areas of the world where TB is common Injection drug users Residents and employees of high risk congregate settings Mycobacteria laboratory personnel Persons with conditions that increase risk for progressing to TB disease Infants, children and adolescents to adults in high-risk categories
33 WHAT CONSTITUTES A POSITIVE MANTOUX SKIN TEST? THAT DEPENDS.. 15 mm or more is considered positive in anyone, including persons with no risk factors
34 LTBI VS. TB DISEASE Person with LTBI (Infected) Has a small amount of TB bacteria in his/her body that are alive, but inactive Cannot spread TB bacteria to others Does not feel sick, but may become sick if the bacteria become active in his/her body Usually has a TB skin test or TB blood test reaction indicating TB infection Radiograph is typically normal Sputum smears and cultures are negative Should consider treatment for LTBI to prevent TB disease Does not require respiratory isolation Not a TB case Person with TB Disease (Infectious) Has a large amount of active TB bacteria in his/her body May spread TB bacteria to others May feel sick and may have symptoms such as a cough, fever, and/or weight loss Usually has a TB skin test or TB blood test reaction indicating TB infection Radiograph may be abnormal Sputum smears and cultures may be positive Needs treatment for TB disease May require respiratory isolation A TB case
35 LATENT TB INFECTION (LTBI) Granulomas may persist (LTBI), or may break down to produce TB disease 2 to 8 weeks after infection, LTBI can be detected via TST or interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) The immune system is usually able to stop the multiplication of bacilli Persons with LTBI are not infectious and do not spread organisms to others
36 LTBI TREATMENT REGIMENS Isoniazid (INH) 9-month daily regimen is preferred: 270 doses within 12 months Effective for HIV-infected as well as HIV-uninfected persons Can be given twice weekly via DOT: 76 doses within 12 months Children should always receive 9 months of therapy
37 LTBI TREATMENT REGIMENS Isoniazid (INH) (cont.) 6-month regimen also generally acceptable: 180 doses within 9 months Can be given twice weekly via DOT: 52 doses within 9 months Not recommended for children, HIV infected, persons whose x-rays suggest previous TB
38 TB DISEASE In some, the granulomas break down, bacilli escape and multiply, resulting in TB disease Can occur soon after infection, or years later Persons with TB disease are usually infectious and can spread bacteria to others Positive M. tb culture confirms TB diagnosis
39 HIGH-RISK GROUPS FOR TB INFECTION CLOSE CONTACTS Close contacts are people who spend time with someone who has infectious TB disease May include: Family members Coworkers Friends On average, 20 30% of close contacts become infected with TB
40 PUBLIC HEALTH According to CDC, The responsibility for successful TB treatment is clearly assigned to the public health program or the private provider, not to the patient
41 CARE To develop treatment plan where patient is assessed, interviewed and treated Implement appropriate and continuous therapy
42 MAJOR GOALS OF TB TREATMENT Cure patient, minimize risk of death/disability, prevent transmission to others Provide safest, most effective therapy in shortest time Prescribe multiple drugs to which the organisms are susceptible Never treat with a single drug or add single drug to failing regimen Ensure adherence and completion of therapy
43 DEVELOP TREATMENT AND MONITORING PLAN Plan should include Description of treatment regimen Methods for assessing/ensuring adherence Monitoring methods for treatment response and adverse events
44 ADHERENCE Nonadherence results in inadequate treatment Can lead to treatment failure, relapse, ongoing transmission, and drug resistance Clinician responsible for completion of therapy To ensure adherence, provide education, case management, DOT, incentives and enablers, and combination pills If these fail, take more restrictive action
45 CASE MANAGEMENT Strategy to ensure patients complete treatment; includes Assigning responsibility to case manager Conducting regular systematic review Developing plans to address barriers to adherence Case managers must ensure patients are educated about TB, therapy is continuous, and contacts are evaluated properly
46 DIRECTLY OBSERVED THERAPY (DOT) Health care worker watches patient swallow each dose DOT is preferred management strategy for all patients Can reduce acquired drug resistance, treatment failure, and relapse Nearly all regimens can be intermittent if given as DOT DOT reduces total number of doses and encounters For drug-resistant TB, use daily regimen and DOT
47 CURRENT ANTI-TB DRUGS 10 drugs FDA-approved for treatment of TB Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin (RIF) Pyrazinamide (PZA) Ethambutol (EMB) Rifapentine (RPT) Streptomycin (SM) Cycloserine Capreomycin ρ-aminosalicylic acid Ethionamide
48 CURRENT ANTI-TB DRUGS (CONT.) Four first-line drugs considered standard treatment: Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin (RIF) Pyrazinamide (PZA) Ethambutol (EMB) Rifabutin and rifapentine also considered first-line drugs in some circumstances Streptomycin (SM) formerly first-line drug, but now less useful owing to increased SM resistance
49 WHY ARE WE HERE Monitor response to treatment Educate each patient about TB, treatment and infection control. Evaluate each contact
50 PROVIDE TRAINING AND EDUCATION Staff Health-Care Providers and Members Medical/nursing schools Community-based organizations Professional societies Minority advocacy groups
51 PROVIDE TRAINING AND EDUCATION CONT. Infection Control Environmental Control Administrative Control Regular intervals for up-to-date and accurate knowledge
52 ACKNOWLEDGMENT Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
53 TUBERCULOSIS TODAY HEALTH SERVICE REGION 1 Rick Tull, Program Specialist PHEP/HSR1
54 REQUEST FOR RESPONSE
55 TB RESPONSE Health Service Region 1 --PHEP Based on the ICS Structure The primary goal is to decrease the number of individuals who may become ill. The role of Public Health is to provide the vaccine and/or medication
56 THE ROLE OF PUBLIC HEALTH Public Health will provide the vaccine and/or medication resources.
57 INCIDENT COMMAND STRUCTURE
58 INCIDENT ACTION PLAN
59 INCIDENT OBJECTIVES
60
61 CLINIC FLOW Assessment Waiting PLACEMENT PLACEMENT DATA ENTRY FORMS ASSESSMENT PLACEMENT EXIT EDUCATION FORMS ASSESSMENT PLACEMENT PLACEMENT EXIT TRANSPORT WAITING AREA ENTER CHECK IN HERE (GREETER) Forms Waiting FOLDER RECEIVED Placement Waiting TRIAGE/EDUCATION
62 CLINIC ENTRANCE Due to the potential risk of exposure to others, no one is allowed into the POD until they have either been cleared through initial screening or the Triage Station. Healthy Entrance
63 TRIAGE The Triage staff will ask questions and gather information from incoming clients to determine whether they have been exposed and could present a risk to others. POD Entrance
64 TRIAGE FORM
65 CLIENT EDUCATION
66 CLIENT EDUCATION
67 SYMPTOMATIC If at any point the client is notably symptomatic, they are masked and are immediately escorted to the acute room. Further assessment/screening are completed along with a TST and Chest X-ray referral. HIV and STD testing is also offered
68 3 TYPES OF CLIENTS There are three (3) types of clients that could be present at a Clinic Healthy Sick Pre-existing
69 SCREENING/ASSESSMENT Clients who have drug allergies, or pre-existing health conditions are directed to the Medical Screening Station for the assessment of the appropriate drug/dosage. Counseling Screening
70 SCREENING/ASSESSMENT The client discusses a symptom review and medical history with health care provider.
71 TESTING/PLACEMENT Clients leave Forms Review or Medical Screening/Assessment (if appropriate) and are directed to Testing/Placement. The Testing/Placement Station is where the client receives their TST skin test
72 EXIT EDUCATION Exit Education and Form Collection is where the client is provided additional information in regard to the vaccine or medication that they have just received. This will include directions on taking any medication and other relevant information.
73 HSR1 CLINIC RESULTS EXAMPLE 61 DECLINED 1418 PLACED 1491 SCREENED 2278 EXPECTED
74 HSR1 CLINIC EXAMPLES Total TB Clinic Numbers CLINIC 1 CLINIC 2 CLINIC 3 CLINIC 4 SCREENED PLACED DECLINED
75 READING RESULTS 48 to 72 hours after testing results need to be read. Ideally 48 hours If not read within the hour window, their TST will need to be retested
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010
 Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
TUBERCULOSIS. Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County
 TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States
 Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States The purpose of this primer is to provide instructors who have no prior background in TB research or clinical care with basic knowledge that they may find
Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States The purpose of this primer is to provide instructors who have no prior background in TB research or clinical care with basic knowledge that they may find
Tuberculosis 6/7/2018. Objectives. What is Tuberculosis?
 Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know
 Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014
 TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014 Catalina Navarro, BSN, RN has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant financial relationships with
TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014 Catalina Navarro, BSN, RN has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant financial relationships with
Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1
 Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1 Tuberculosis Erin Burdi Ferris State University TUBERCULOSIS 2 Abstract Tuberculosis is one of the world s oldest infectious diseases. It is a disease that continues to affect
Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1 Tuberculosis Erin Burdi Ferris State University TUBERCULOSIS 2 Abstract Tuberculosis is one of the world s oldest infectious diseases. It is a disease that continues to affect
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB)
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
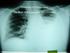 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014
 What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014 The Critical First Step Consider TB in the Differential 1. Risks
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014 The Critical First Step Consider TB in the Differential 1. Risks
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012
 TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Why need to havetb Clearance. To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis
 Why need to havetb Clearance To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis How to ID Tuberculosis There are two kinds of tests that are used to determine if a person has been infected with TB bacteria: the tuberculin
Why need to havetb Clearance To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis How to ID Tuberculosis There are two kinds of tests that are used to determine if a person has been infected with TB bacteria: the tuberculin
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
LATENT TUBERCULOSIS. Robert F. Tyree, MD
 LATENT TUBERCULOSIS Robert F. Tyree, MD 1 YK TB OFFICERS Ron Bowerman Elizabeth Roll Mien Chyi (Pediatrics) Cindi Mondesir (Pediatrics) The new guys: Philip Johnson Robert Tyree 2009 CDC TB CASE DEFINITION
LATENT TUBERCULOSIS Robert F. Tyree, MD 1 YK TB OFFICERS Ron Bowerman Elizabeth Roll Mien Chyi (Pediatrics) Cindi Mondesir (Pediatrics) The new guys: Philip Johnson Robert Tyree 2009 CDC TB CASE DEFINITION
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk
 Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Facts. TB is not spread by: Sharing food and drink Shaking someone s hand Touching bed lines or toilet seats
 Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Tuberculosis. Impact of TB. Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH)
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011
 Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
TB the basics. (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ)
 TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
Stop TB Poster (laminated copies are available from TB Control: )
 Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Northwestern Polytechnic University
 Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona
 TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona March 24, 2011 Treatment of Latent TB Infection Renuka Khurana MD, MPH March 24, 2011 Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona March 24, 2011 Treatment of Latent TB Infection Renuka Khurana MD, MPH March 24, 2011 Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
Evaluation and Management of the Patient with Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)
 Evaluation and Management of the Patient with Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) CURTIS FOWLER MPT,PA C ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF THE PACIFIC Learning objectives Recognize the appropriate
Evaluation and Management of the Patient with Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) CURTIS FOWLER MPT,PA C ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF THE PACIFIC Learning objectives Recognize the appropriate
TB and Respiratory Protection
 Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection
 Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 109 Introduction.... 111 Candidates for the Treatment of LTBI... 112 LTBI Treatment Regimens.... 118 LTBI
Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 109 Introduction.... 111 Candidates for the Treatment of LTBI... 112 LTBI Treatment Regimens.... 118 LTBI
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization.
 HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
Case Management of the TB/HIV Infected Patient
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 Case Management of the TB/HIV Infected Patient Sarah Hoffman, MPH, MSN, ACRN December 9, 2009 TB/HIV: Considerations in the Care of the Coinfected
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 Case Management of the TB/HIV Infected Patient Sarah Hoffman, MPH, MSN, ACRN December 9, 2009 TB/HIV: Considerations in the Care of the Coinfected
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
TUBERCULOSIS. Pathogenesis and Transmission
 TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Proposed Regs.pdf
 Kansas Wesleyan University TB testing Policy In Compliance with Kansas Statue KSA 2009 Supp. 65-129, all Kansas Wesleyan University students who have traveled, resided in for more than three months, or
Kansas Wesleyan University TB testing Policy In Compliance with Kansas Statue KSA 2009 Supp. 65-129, all Kansas Wesleyan University students who have traveled, resided in for more than three months, or
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the. United States. MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology. Summer A 2014
 Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control
 The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targe te d Te s ting and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targe te d Te s ting and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control
Tuberculosis Screening and Targeted Testing of College and University Students: Developing a Best Practice Approach:
 Tuberculosis Screening and Targeted Testing of College and University Students: Developing a Best Practice Approach: Lori A. Soos MA, BSN, RN, Niagara University Deborah Penoyer, MS, RN, SUNY Geneseo Learning
Tuberculosis Screening and Targeted Testing of College and University Students: Developing a Best Practice Approach: Lori A. Soos MA, BSN, RN, Niagara University Deborah Penoyer, MS, RN, SUNY Geneseo Learning
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department
 Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers. Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program
 Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Topics of Discussion TB Overview Epidemiology of TB in Oregon Annual Facility
Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Topics of Discussion TB Overview Epidemiology of TB in Oregon Annual Facility
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey
 Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 7 References Related ACA Standards 4 th Edition Standards for Adult Correctional Institutions 4-4350, 4-4355 These guidelines are based on the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society
PAGE 1 of 7 References Related ACA Standards 4 th Edition Standards for Adult Correctional Institutions 4-4350, 4-4355 These guidelines are based on the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society
#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]
![#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]](/thumbs/96/128750142.jpg) Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis?
 What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers
 Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers Who Should Be Screened for Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)?... 2 What tests are used to screen for LTBI?... 2 How
Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers Who Should Be Screened for Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)?... 2 What tests are used to screen for LTBI?... 2 How
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia
 Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
These recommendations will remain in effect until the national shortage of PPD solution has abated.
 Maryland Recommendations Regarding the National Shortage of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) Solution; Attachment to Health Officer Memorandum National Shortages of Tubersol and Aplisol for TB Skin Testing;
Maryland Recommendations Regarding the National Shortage of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) Solution; Attachment to Health Officer Memorandum National Shortages of Tubersol and Aplisol for TB Skin Testing;
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016
 Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
10/3/2017. Updates in Tuberculosis. Global Tuberculosis, WHO 2015 report. Objectives. Disclosures. I have nothing to disclose
 Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS. Dr Amitesh Aggarwal
 PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS Dr Amitesh Aggarwal 25 to 50 % of persons exposed to intimate contact with active PTB - latent infection with TB. Exposure to index case for 12 hours - high risk of infection.
PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS Dr Amitesh Aggarwal 25 to 50 % of persons exposed to intimate contact with active PTB - latent infection with TB. Exposure to index case for 12 hours - high risk of infection.
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2013
 What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2013 Case 1: 52 y/o male Born in the Pacific Islands; some travel in
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2013 Case 1: 52 y/o male Born in the Pacific Islands; some travel in
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of
 TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
Therapy for Latent Tuberculosis Infection
 Screening and Treatment of LTBI in TB Control in the US Margarita Elsa Villarino MD MPH Division of TB Elimination, CDC April 14, 2004 TB Prevention and Control in the United States The fundamental strategies
Screening and Treatment of LTBI in TB Control in the US Margarita Elsa Villarino MD MPH Division of TB Elimination, CDC April 14, 2004 TB Prevention and Control in the United States The fundamental strategies
Tuberculosis Reporting, Waco-McLennan County Public Health District TB Control WMCPHD (254)
 Tuberculosis Reporting, Waco-McLennan County Public Health District TB Control WMCPHD (254)-750-5496 Local health care providers, including physicians offices, labs and hospitals, are required by law to
Tuberculosis Reporting, Waco-McLennan County Public Health District TB Control WMCPHD (254)-750-5496 Local health care providers, including physicians offices, labs and hospitals, are required by law to
Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices
 Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices Last Updated September 7, 2016 LTBI Demographics in the US o 13million people in the US with LTBI (estimate) o In 2014, approximately 66% of TB cases in the United States
Latent Tuberculosis Best Practices Last Updated September 7, 2016 LTBI Demographics in the US o 13million people in the US with LTBI (estimate) o In 2014, approximately 66% of TB cases in the United States
2017/2018 Annual Volunteer Tuberculosis Notice
 Lewis Center for Educational Research Academy for Academic Excellence Norton Science and Language Academy Business Offices 17500 Mana Road Apple Valley, CA 92307 E-mail: hr@lcer.org 760-946-5414 Fax 760-946-9193
Lewis Center for Educational Research Academy for Academic Excellence Norton Science and Language Academy Business Offices 17500 Mana Road Apple Valley, CA 92307 E-mail: hr@lcer.org 760-946-5414 Fax 760-946-9193
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]
![CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]](/thumbs/89/99628771.jpg) CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
Asking the Right Questions. A Visual Guide to Tuberculosis Case Management for Nurses. Reference Guide
 Asking the Right Questions A Visual Guide to Tuberculosis Case Management for Nurses Reference Guide The Francis J. Curry National Tuberculosis Center is a joint project of the San Francisco Department
Asking the Right Questions A Visual Guide to Tuberculosis Case Management for Nurses Reference Guide The Francis J. Curry National Tuberculosis Center is a joint project of the San Francisco Department
Tuberculosis. WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED
 Tuberculosis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments COL Paul Keiser LTC James E. Moon LTC Jaime Mancuso LTC Anjali Kunz MAJ Kristopher Paolino MAJ Leyi
Tuberculosis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments COL Paul Keiser LTC James E. Moon LTC Jaime Mancuso LTC Anjali Kunz MAJ Kristopher Paolino MAJ Leyi
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES
 FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES Superintendent Signature Designated Health Authority Signature Effective Date: November 1, 2016 Subject: TUBERCULOSIS
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES Superintendent Signature Designated Health Authority Signature Effective Date: November 1, 2016 Subject: TUBERCULOSIS
Managing Complex TB Cases Diana M. Nilsen, MD, RN
 Managing Complex TB Cases Diana M. Nilsen, MD, RN Director of Medical Affairs NYC Department of Health & Mental Hygiene Bureau of TB Control Case #1 You are managing a patient who was seen at a private
Managing Complex TB Cases Diana M. Nilsen, MD, RN Director of Medical Affairs NYC Department of Health & Mental Hygiene Bureau of TB Control Case #1 You are managing a patient who was seen at a private
Symptoms Latent TB Active TB
 1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas May 7-10, 2013
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas May 7-10, 2013 TB in the HIV Patient Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD May 09, 2013 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas May 7-10, 2013 TB in the HIV Patient Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD May 09, 2013 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2017
 Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2017 Charles L. Daley, MD National Jewish Health University of Colorado Health Sciences Center Treatment of Tuberculosis Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson,
Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2017 Charles L. Daley, MD National Jewish Health University of Colorado Health Sciences Center Treatment of Tuberculosis Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson,
TB is Global. Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Sharing the Care: Working Together. September 24, 2014
 Sharing the Care: Working Together to Meet the Challenge of TB Presented by: Barbara Cole, RN, PHN, MSN Director, Disease Control County of Riverside Department of Public Health Curry International TB
Sharing the Care: Working Together to Meet the Challenge of TB Presented by: Barbara Cole, RN, PHN, MSN Director, Disease Control County of Riverside Department of Public Health Curry International TB
Tuberculosis in Chicago 2007
 City of Chicago Communicable Disease Information Department of Public Health Richard M. Daley, Mayor May 2008 Terry Mason, MD, FACS, Commissioner www.cityofchicago.org/health/ West Side Center For Disease
City of Chicago Communicable Disease Information Department of Public Health Richard M. Daley, Mayor May 2008 Terry Mason, MD, FACS, Commissioner www.cityofchicago.org/health/ West Side Center For Disease
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014
 TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014 AIR TRAVEL & TB CONTROL With respect to non-ambulance air travel of patients diagnosed with or suspected as having active Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014 AIR TRAVEL & TB CONTROL With respect to non-ambulance air travel of patients diagnosed with or suspected as having active Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease. Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015
 Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks
 1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
TB in the Patient with HIV
 TB in the Patient with HIV Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 11, 2017 TB Intensive May 9 12, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD, has the following disclosures to
TB in the Patient with HIV Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 11, 2017 TB Intensive May 9 12, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD, has the following disclosures to
4/25/2012. The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB
 Sindy M. Paul, MD, MPH, FACPM May 1, 2012 The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB morbidity, including resistance Identifying people
Sindy M. Paul, MD, MPH, FACPM May 1, 2012 The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB morbidity, including resistance Identifying people
Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis. Disclosures. Case
 Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis Neha Shah MD MPH Field Medical Officer Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention September 2016 1 Disclosures
Diagnosis Latent Tuberculosis Neha Shah MD MPH Field Medical Officer Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention September 2016 1 Disclosures
A Mobile Health Intervention Utilizing Community Partnership to Improve Access to Latent Tuberculosis Infection Treatment
 A Mobile Health Intervention Utilizing Community Partnership to Improve Access to Latent Tuberculosis Infection Treatment Cassandra Garcia, MSN, RN, FNP-BC Mobile Clinic Provider Texas Children s Mobile
A Mobile Health Intervention Utilizing Community Partnership to Improve Access to Latent Tuberculosis Infection Treatment Cassandra Garcia, MSN, RN, FNP-BC Mobile Clinic Provider Texas Children s Mobile
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
All you need to know about Tuberculosis
 All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
Community pharmacy-based tuberculosis skin testing
 Community pharmacy-based tuberculosis skin testing Shanna K. O Connor, PharmD ISU KDHS Spring CE Seminar 2018 In support of improving patient care, Idaho State University Kasiska Division of Health Sciences
Community pharmacy-based tuberculosis skin testing Shanna K. O Connor, PharmD ISU KDHS Spring CE Seminar 2018 In support of improving patient care, Idaho State University Kasiska Division of Health Sciences
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis
 What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
Tuberculosis: A Provider s Guide to
 Tuberculosis: A Provider s Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Active Tuberculosis (TB) Disease and Screening and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Alameda County Health Care Services Agency
Tuberculosis: A Provider s Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Active Tuberculosis (TB) Disease and Screening and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Alameda County Health Care Services Agency
Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now?
 Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now? Amee Patrawalla MD MPH Rutgers - NJ Medical School Global TB Institute Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey Learning Objectives Understand the current epidemiologic
Tuberculosis: Where Are We Now? Amee Patrawalla MD MPH Rutgers - NJ Medical School Global TB Institute Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey Learning Objectives Understand the current epidemiologic
5. HIV-positive individuals treated with INH should receive Pyridoxine (B6) 25 mg daily or 50 mg twice/thrice weekly on the same schedule as INH
 V. TB and HIV/AIDS A. Standards of Treatment and Management The majority of TB treatment principles apply to persons with HIV/AIDS who require treatment for TB disease. The following points are either
V. TB and HIV/AIDS A. Standards of Treatment and Management The majority of TB treatment principles apply to persons with HIV/AIDS who require treatment for TB disease. The following points are either
Diagnosis and Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 27, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Diagnosis and Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 27, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make:
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Diagnosis and Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 27, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make:
Santa Clara County Tuberculosis Screening Requirement for School Entrance Effective June 1, 2014
 Guidelines to Revisions to the School Mandate and Requirements 1) What are the tuberculosis (TB) screening requirements for school entrance in Santa Clara County? Students must undergo a TB risk assessment
Guidelines to Revisions to the School Mandate and Requirements 1) What are the tuberculosis (TB) screening requirements for school entrance in Santa Clara County? Students must undergo a TB risk assessment
2016 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County
 206 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County Cases Rate per 00,000 people 206 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health (FCDPH) Tuberculosis Control Program Tuberculosis
206 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County Cases Rate per 00,000 people 206 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health (FCDPH) Tuberculosis Control Program Tuberculosis
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA
 Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA George D. McSherry, MD Division of Infectious Disease Penn State Children s Hospital Pediatric Section TB Center of Excellence Rutgers Global Tuberculosis
Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA George D. McSherry, MD Division of Infectious Disease Penn State Children s Hospital Pediatric Section TB Center of Excellence Rutgers Global Tuberculosis
Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer
 Tuberculosis in the 21 st Century Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer Feedback Poll In my opinion, the recent media coverage of
Tuberculosis in the 21 st Century Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer Feedback Poll In my opinion, the recent media coverage of
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control
 TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
Drug Interactions Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 17, 2010
 Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Oklahoma City, Oklahoma November 17, 2010 Drug Interactions Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 17, 2010 Drug Interactions Lisa Y. Armitige, M.D., Ph.D. Medical Consultant
Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Oklahoma City, Oklahoma November 17, 2010 Drug Interactions Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 17, 2010 Drug Interactions Lisa Y. Armitige, M.D., Ph.D. Medical Consultant
