(PFGE) Clostridium di$cile
|
|
|
- Dominick Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
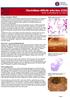
1 (PFGE) Clostridium di$cile 1) 3) 2) 2) 2) 2, 4) 5) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Clostridium di$cile (C. di$cile) A /B 141 (56.9) A /B 26 (10.5) A /B 81 (32.7) 136 (PFGE) PFGE A L (62.5) (34.6) 35 (25.7) A bu#er 200 mm C A /B A B J PFGE 5 C. di$cile Key words: Clostridium di$cile, PFGE Clostridium di$cile 7.6 1) , 3) C. di$cile b- C. di$cile ( ) 65 TEL: FAX: t-ookura@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp (CDI) 1) C. di$cile A B A B binary toxin 4, 5) (PFGE) 6) C. di$cile DNA PFGE 79) PFGE Vol. 19 No
2 206 PCR PFGE 10) PFGE 5 C. di$cile PFGE CCMA 4 11) PCR C. di$cile CCMA PFGE 2. (1) A 1 13,500 rpm ml 30 (2) PCR C. di$cile PCR C. di$cile A B C. di$cile Gumerlock PG 48 (5 - CTCTTGAAACTGGGAGACTTGA- 3 ) PG 49(5-ACTGAGAGTAGCTTTA-3) 12) A B Kato NK2(5-CCCAATAGAAGATT- CAATATTAAGCTT- 3 ) NK3(5-GGAA- GAAAACAACTTCTGGCTCACTCAGCT- 3 ) 13) A B NK9(5-CCACCAGCTGCAGCCA TA-3 ), NK 11 (5-TGATGCTAATAATGAATCT AAAATGGTAAC-3) NKV011(5-TTTTGA 14, 15) TCCTATAGAATCTAACTTAGTAAC-[S 2] 3) A B HK 2 TE (ph 8.0) McFarland ,000 rpm EXTaq 1 20 ml PCR 0.2 mm, EXTaq 0.4 unit 2 ml PCR PG48 PG49 NK2 NK NK9, NK11 NKV PCR TAE V 30 PCR C. di$cile A B (3) PFGE PFGE Alonso 10) CCMA 1 (BHI) BHI 3,000 rpm 20 Washing Solution (0.15 M NaCl, 0.01 M EDTA) 3 Pett IV (10 mm Tris HCl, 1 M NaCl) McFarland ml ml 2 mg/ml Lysis 10 mm TrisHCl, 1 M NaCl, 100 mm EDTA, 0.5 sodium N-dodecanolsalcosinate (SDS) 0.2 deoxycholate, 0.5 Brij ml 37 2 K 75 U/ml (ES solution: 0.25 M EDTA, 1 SDS) 500 ml mm 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) K TE 3 SmaI 30 1 DNA 200 mm 0.9 SmaI lladder 8 Vol. 19 No
3 Clostridium di$cile PFGE , , A 110 (8.8) 164 (13.2) 274 (22.0) 99 (7.9) 873 (70.1) 972 (78.0) 209 (16.8) 1,037 (83.2) 1,246 (100) 3. A /B 67 (34.2) 53 (27.0) 120 A /B 4 (2.0) 16 (8.2) 20 A /B 17 (8.7) 39 (19.9) (Bio-Rad) (CHEF-DR II: BIO-RAD) 200 mm 0.5TBE PFGE Alonso 10) TBE 200 mm K (5) PFGE Finger Printing II (BIO-RAD) 80 PFGE A S 1 PFGE (1) 5 A A 78.9 Vol. 19 No
4 PFGE M: lambda ladder marker, 1 NL 5090, 2 NL5092, 3 NL5094, 4 NL5122 A (2) 1 5 C. di$cile A /B 141 (56.9), A /B 25 (10.1), A /B 81 (32.7), binary toxin PCR A /B 4 A /B 17 (3) PFGE DNA 4 PFGE 1 9) DNA 45 2 Alonso 10) 2. Clostridium di$cile132 PFGE AL: PFGE 80 PFGE PFGE 340 PFGE Vol. 19 No
5 Clostridium di$cile PFGE PFGE PFGE (62.5) 47 (34.6) 4 (2.9) A A /B 35 (23) 1 (1) 5 (5) 19 (10) a 10 (8) a B A /B 14 (14) 3 (3) 6 (6) 1 (1) 4 (4) C A /B 12 (8) 1 (1) 3 (2) 4 (3) b 4 (3) b D A /B 6 (4) 4 (2) 1 (1) 1 (1) E A /B 3 (3) 1 (1) 2 (2) F A /B 3 (3) 1 (1) 1 (1) 1 (1) G A /B 3 (3) 1 (1) 1 (1) H A /B 2 (2) 2 (2) I A /B 2 (2) 1 (1) 1 (1) J A /B 2 (2) 2 (2) K A /B 2 (2) 2 (2) L A /B 2 (2) 1 (1) 1 (1) MS P A /B 12 (6) 3 (2) 3 (2) c 6 (3) c P A /B 2 (1) 2 (1) A /B 33 (30) 2 (2) 10 (10) 7 (7) 14 (11) NT A /B 4 (4) 1 (1) 2 (2) 1 (1) 136 (108) 6 (4) 8 (8) 32 (30) 44 (32) 46 (37) : PFGE ac: PFGE PFGE A L A 35 (25.7) B 14 (10.3) C 12 (8.9) 4 PFGE M S PFGE A C. di$cile 10 PFGE 11 PFGE 4 PFGE 108 PFGE C 12 P 2 A /B A /B (4) PFGE 4 PFGE PFGE A L (62.5) M S 47 (34.6) H J K 2 5 A B 141 (56.9) PCR A /B 3 A /B A /B A /B 21 Vol. 19 No
6 210 PCR (47.4) C. di$cile B CDI C. di$cile 32.7 A CDI PFGE 6) C. di$cile PFGE MRSA DNA 45 A 35 B 1 R 2 7 A 35 Kato C. di$cile (73) 7) Sawabe C. di$cile DNA 55 PFGE 33 8) Sawabe 8) PFGE Bidet 9), Corkill 16) PCR 1 G PCR PFGE PCR 8, 10, 17, 18) DNA 3 PFGE PFGE A 35 (25.7) B 14 (10.3) 2008 PFGE C 12 (8.8) A /B A /B 19) A /B A B PFGE 3 20) PFGE PFGE Vol. 19 No
7 Clostridium di$cile PFGE 211 PFGE K 2 1 PFGE 2 PFGE PCR 1) Kato, H., H. Kita, T. Karasawa, et al Colonisation and transmission of Clostridium di$cile in healthy individuals examined by PCR ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Med. Microbiol. 50: ) Bartlett, J. G The new epidemic of Clostridiumdi$cile-associated enteric diseases. Ann. Intern. Med. 145(10): ) Cookson, B Hypervirulent strains of Clostridium di$cile. Postgrad. Med. J. 83(979): ) Martin, H., B. Willey, D. E. Low, et al Characterization of Clostridium di$cile strains isolated from patients in Ontario, Canada, from 2004 to J. Clin. Microbio. 46: ) Fenner, L., R. Frei, M. Gregory, et al Epidemiology of Clostredium di$cile-associated disease at University Hospital Basel including molecular characterisation of the isolates Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 27: ) Tenovor, F. C., R. D. Arbeit, R. V. Goering, et al Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33: ) Kato, H., N. Kato, K. Watanabe, et al Analysis of Clostridium di$cile isolates from nosocomial outbreaks at three hospitals in diverse areas of Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39: ) Sawabe, E., H. Kato, K. Osawa, et al Molecular analysis of Clostridium di$cile at a university teaching hospital in Japan: A shift in predominant type over a five-year period. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 26(10): ) Bidet, P., V. Lalande, B. Salauze, et al Comparison of PCR-ribotyping, arbiratory primed PCR, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium di$cile. J. Clin. Microbial. 38: ) Alonso, R., A. Martin, T. P. Martin, et al An improved protocol for pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of Clostridium di$cile. J. Med. Microbiol. 54: ) Clostridium di$cile 12: ) Gumerlock, P. H., Y. J. Tang, F. J. Meyers, et al Use of the polymerase chain reaction for the specific and direct detection of Clostridium di$cile in human feces. Rev. Infect. Dis. 13: ) Kato, N., C.Y. Ou, H. Kato, et al Identification of toxigenic Clostridium di$cile by the polymerase chain reaction: J. Clin. Microbiol. 29: ) Kato, H., N. Kato, K. Watanabe, et al Identification of toxin A-negative, toxin B- positive Clostridium di$cile by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36: ) Kato, H., N. Kato, S. Katow, et al Detections in the repeating sequences of toxin A gene of toxin A-negative, toxin B-positive Clostridium di$cile strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 175: ) Corkill, J. E., R. Graham, C. A. Hart Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of degradationsensiteve DNAs from Clostridium di$cile PCR ribotype 1 strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38: ) Corne, H., W. Klaassen, A. Hanneke, et al Molecular fingerprinting of Clostridium di$cile isolates: Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis versus amplified fragment length polymorphism. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40: ) Killgore, G., T. Angela, S. Jhonson, et al Comparison of seven techniques for typing international epidemic strains of Clostridium di$cile: Restriction endonuclease analysis, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, PCR-ribotyping, multilocus sequence typing, multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis, amplified fragment length polymorphism, and surface layer protein A gene sequence typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46: ) toxin A toxin B Clostridium di$cile 78: ) Fawley, W. N., P. Paunell, P. Verity, et al Vol. 19 No
8 212 Molecular epidemiology of Clostridium di$cile infection and the significance of subtypes of the United Kingdom epidemic strain (PCR Ribotype 1). J. Clin. Microbiol. 43: Analysis of Clostridium di$cile Strains Isolated in a Hospital Using an Improved Procedure of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Toshi Nada 1), Masahiro Suzuki 2), Teruko Ohkura 1), Yukiko Nakanishi 1), Mariko Mochizuki 1), Hisashi Baba 1, 3), Tetsuya Yagi 4) 1) Department of Clinical Laboratory, Nagoya University Hospital 2) Department of Microbiology and Medical Zoology, Aichi Prefecture Institute of Public Health 3) Department of Infectious Diseases, Nagoya University Hospital 4) Center of National University Hospital for Infection Control, Nagoya University Hospital From January 2004 to December 2008, we isolated 340 Clostridium di$cile strains from fecal sample, and we tested for toxin type of 248 strains using PCR method. The isolates comprise of 141 toxin type A / B (56.9), and 25 A /B (10.5), A /B (32.7), and one binary toxin type. One hundred thirty six Clostridium di$cile isolates recovered from feces of 97 patients, were analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). They were classified into 51 PFGE types using the identity criteria of 80 similarity in the dendrogram analysis. Eighty-five strains (62.5), which were isolated from di#erent patients, were deviced into 12 PFGE types (from type A to type L), and the other 47 strains showed unique 40 PFGE types. Although PFGE type A (35 strains) were the most predominant genotype, these strains showed non-typable DNA degradation until the addition of 200 mm thiourea into 0.9 agarose gel and TBE running bu#er. 12 strains of PFGE type C and 2 strains of PFGE type P were toxin A /B, which showed false negative results for rapid toxin detection test. As strains of PFGE type A, B, and J were isolated from the same ward in a year, these strains might spread via nosocomial transmission. Some strains with same PFGE types were isolated consistently for 25 years, suggesting that they are surviving in the hospital environment or in the human gastrointestinal tract for such a long time. 14 Vol. 19 No
Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008*
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008* S. M. Kotila 1, A. Virolainen 1, M. Snellman 1, S. Ibrahem 1, J. Jalava 2 and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008* S. M. Kotila 1, A. Virolainen 1, M. Snellman 1, S. Ibrahem 1, J. Jalava 2 and
Whole genome sequencing & new strain typing methods in IPC. Lyn Gilbert ACIPC conference Hobart, November 2015
 Whole genome sequencing & new strain typing methods in IPC Lyn Gilbert ACIPC conference Hobart, November 2015 Why do strain typing? Evolution, population genetics, geographic distribution 2 Why strain
Whole genome sequencing & new strain typing methods in IPC Lyn Gilbert ACIPC conference Hobart, November 2015 Why do strain typing? Evolution, population genetics, geographic distribution 2 Why strain
Typing of ônh ôstaphylococcus epidermidis ôns ô Colonizing in Human Nares by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
 Microbiol. Immunol., 39(5), 315-319, 1995 Typing of ônh ôstaphylococcus epidermidis ôns ô Colonizing in Human Nares by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Lan Hu*, Akiko Umeda, and Kazunobu Amako Department
Microbiol. Immunol., 39(5), 315-319, 1995 Typing of ônh ôstaphylococcus epidermidis ôns ô Colonizing in Human Nares by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Lan Hu*, Akiko Umeda, and Kazunobu Amako Department
A Norazah, S M Liew, A G M Kamel, Y T Koh, V K E Lim. O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e
 Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(1) : 015-019 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e DNA Fingerprinting of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE): Comparison of Strains
Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(1) : 015-019 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e DNA Fingerprinting of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE): Comparison of Strains
Molecular epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection in British Columbia, Canada
 Molecular epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection in British Columbia, Canada Agatha Jassem, PhD Senior Scientist, BCCDC Public Health Laboratory Objectives Molecular typing methods for C. difficile
Molecular epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection in British Columbia, Canada Agatha Jassem, PhD Senior Scientist, BCCDC Public Health Laboratory Objectives Molecular typing methods for C. difficile
New genomic typing method MLST
 New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
Clostridium difficile colonization in healthy adults: transient colonization and correlation with enterococcal colonization
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 167 172 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.05376-0 Clostridium difficile colonization in healthy adults: transient colonization and correlation with enterococcal colonization
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 167 172 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.05376-0 Clostridium difficile colonization in healthy adults: transient colonization and correlation with enterococcal colonization
1) 1) 1) 2) 2) (ICU) Key words: (ICU), ( ) 1 30 TEL: FAX: Vol. 17 No
 2007 277 1) 1) 1) 2) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 18 10 17 19 8 20 16 7 1 (ICU) 20 2x 1.6 2.2 2SD 14 1 4 1 10 7 3 2 9 7.6; 95 2.37 24.62 6 4 5 1 DNA SpeI 9 2 A 7 B 2 A 3 B 1 ICU ICU 7 20 10 5 Key words:
2007 277 1) 1) 1) 2) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 18 10 17 19 8 20 16 7 1 (ICU) 20 2x 1.6 2.2 2SD 14 1 4 1 10 7 3 2 9 7.6; 95 2.37 24.62 6 4 5 1 DNA SpeI 9 2 A 7 B 2 A 3 B 1 ICU ICU 7 20 10 5 Key words:
Study of Bordetella pertussis in a Whooping Cough Outbreak
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1994, p. 398-402 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 2 Use of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis for Epidemiological
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1994, p. 398-402 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 2 Use of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis for Epidemiological
Polyclonality of Staphylococcus epidermidis residing on the healthy ocular surface
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2007), 56, 77 82 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46810-0 Polyclonality of Staphylococcus epidermidis residing on the healthy ocular surface Mayumi Ueta, 1 Tetsuya Iida, 2 Masako Sakamoto,
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2007), 56, 77 82 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46810-0 Polyclonality of Staphylococcus epidermidis residing on the healthy ocular surface Mayumi Ueta, 1 Tetsuya Iida, 2 Masako Sakamoto,
Lineages within Campylobacter jejuni defined by numerical.analysis of pulsed-field gel electrophoretic DNA profiles
 J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 46 (1997), 157-163 0 1997 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland E PI DE M I0 LOGICAL TYPING Lineages within Campylobacter jejuni defined by numerical.analysis
J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 46 (1997), 157-163 0 1997 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland E PI DE M I0 LOGICAL TYPING Lineages within Campylobacter jejuni defined by numerical.analysis
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
Characterization of community and hospital Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Southampton, UK
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2010), 59, 1084 1088 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.018986-0 Characterization of community and hospital Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Southampton, UK S. M. Green, 1 P. Marsh, 1
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2010), 59, 1084 1088 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.018986-0 Characterization of community and hospital Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Southampton, UK S. M. Green, 1 P. Marsh, 1
Jen KOK*, Qinning WANG, Lee C THOMAS, Gwendolyn L GILBERT. Centre for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology Laboratory Services, Institute of
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 17 August 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00752-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 17 August 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00752-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
A Guideline for the Molecular Typing of Canadian Epidemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using spa Typing.
 A Guideline for the Molecular Typing of Canadian Epidemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using spa Typing. George R. Golding National Microbiology Laboratory Winnipeg, Manitoba AMMI-CACMID
A Guideline for the Molecular Typing of Canadian Epidemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using spa Typing. George R. Golding National Microbiology Laboratory Winnipeg, Manitoba AMMI-CACMID
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017)
 Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
Genotype Variation in H. Pylori Isolates from Iranian Patients by RAPD-PCR
 Genotype Variation in H. Pylori Isolates by RAPD-PCR Genotype Variation in H. Pylori Isolates from Iranian Patients by RAPD-PCR Siavoshi F Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Tehran University
Genotype Variation in H. Pylori Isolates by RAPD-PCR Genotype Variation in H. Pylori Isolates from Iranian Patients by RAPD-PCR Siavoshi F Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Tehran University
Genomic variability among isolates of Campylobacter jejuni from broiler flocks in the Czech Republic
 Genomic variability among isolates of Campylobacter jejuni from broiler flocks in the Czech Republic M. NEBOLA* and I. STEINHAUSEROVA University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences Brno, Department
Genomic variability among isolates of Campylobacter jejuni from broiler flocks in the Czech Republic M. NEBOLA* and I. STEINHAUSEROVA University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences Brno, Department
Molecular Subtyping Scheme for Serotypes HS1 and HS4 of Campylobacter jejuni
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1995, p. 872 877 Vol. 33, No. 4 0095-1137/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Molecular Subtyping Scheme for Serotypes HS1 and HS4 of Campylobacter
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1995, p. 872 877 Vol. 33, No. 4 0095-1137/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Molecular Subtyping Scheme for Serotypes HS1 and HS4 of Campylobacter
ABSTRACT PURPOSE METHODS
 ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
Chapter 2.1. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology and transmission in a Dutch hospital
 Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology and transmission in a Dutch hospital MML van Rijen 1, T Bosch 2, MEOC Heck 2, JAJW Kluytmans 1,3 1 Laboratory for Microbiology and Infection Control,
Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology and transmission in a Dutch hospital MML van Rijen 1, T Bosch 2, MEOC Heck 2, JAJW Kluytmans 1,3 1 Laboratory for Microbiology and Infection Control,
Persistence of Skin Contamination and Environmental Shedding of Clostridium difficile during and after Treatment of C. difficile Infection
 infection control and hospital epidemiology january 2010, vol. 31, no. 1 original article Persistence of Skin Contamination and Environmental Shedding of Clostridium difficile during and after Treatment
infection control and hospital epidemiology january 2010, vol. 31, no. 1 original article Persistence of Skin Contamination and Environmental Shedding of Clostridium difficile during and after Treatment
COMPARISON OF THE PREVALENCE AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE IN A CLOSED AND INTEGRATED HUMAN AND SWINE POPULATION IN TEXAS
 COMPARISON OF THE PREVALENCE AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE IN A CLOSED AND INTEGRATED HUMAN AND SWINE POPULATION IN TEXAS A Dissertation by KERI NOELLE NORMAN Submitted to the
COMPARISON OF THE PREVALENCE AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE IN A CLOSED AND INTEGRATED HUMAN AND SWINE POPULATION IN TEXAS A Dissertation by KERI NOELLE NORMAN Submitted to the
BOTULISM. Shunji KOZAKI ), Tomoko KOHDA )
 h h h h BOTULISM Shunji KOZAKI ), Tomoko KOHDA ) and Kaoru UMEDA ) ) Department of Veterinary Science, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University, 1h58 Rinku-Orai-Kita,
h h h h BOTULISM Shunji KOZAKI ), Tomoko KOHDA ) and Kaoru UMEDA ) ) Department of Veterinary Science, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University, 1h58 Rinku-Orai-Kita,
Chromosomal analysis of group B streptococcal clinical strains; bac gene-positive strains are genetically homogenous
 FEMS Microbiology Letters 208 (2001) 93^98 www.fems-microbiology.org Chromosomal analysis of group B streptococcal clinical strains; bac gene-positive strains are genetically homogenous Abstract b A. Dmitriev
FEMS Microbiology Letters 208 (2001) 93^98 www.fems-microbiology.org Chromosomal analysis of group B streptococcal clinical strains; bac gene-positive strains are genetically homogenous Abstract b A. Dmitriev
Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:868 873 Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting JEFFREY CLOUD,* LAURA NODDIN, AMANDA PRESSMAN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:868 873 Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting JEFFREY CLOUD,* LAURA NODDIN, AMANDA PRESSMAN,
Characterization and proposed nomenclature of epidemic strains of MRSA in Canada
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization and proposed nomenclature of epidemic strains of MRSA in Canada AE Simor MD FRCPC 1,3, D Boyd MSc 4, L Louie ART 1, A McGeer MD FRCPC 2,3, M Mulvey PhD 4, BM Willey ART
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization and proposed nomenclature of epidemic strains of MRSA in Canada AE Simor MD FRCPC 1,3, D Boyd MSc 4, L Louie ART 1, A McGeer MD FRCPC 2,3, M Mulvey PhD 4, BM Willey ART
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
PULSED FIELD GEL ELECTROPHORESIS ANALYSIS OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE ISOLATES IN SOUTHERN THAILAND
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH PULSED FIELD GEL ELECTROPHORESIS ANALYSIS OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE ISOLATES IN SOUTHERN THAILAND Sumalee Kondo 1, Suwanna Trakoolsomboon 2, Nat Smittipat 3, Tada Juthayothin
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH PULSED FIELD GEL ELECTROPHORESIS ANALYSIS OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE ISOLATES IN SOUTHERN THAILAND Sumalee Kondo 1, Suwanna Trakoolsomboon 2, Nat Smittipat 3, Tada Juthayothin
I n c r e a s e d n u m b e r o f C lostridium difficile i n f e c t i o n s
 Research articles I n c r e a s e d n u m b e r o f C lostridium difficile i n f e c t i o n s a n d p r e va l e n c e o f C lostridium difficile PCR r i b o t y p e 1 in s o u t h e r n Ge r m a n y
Research articles I n c r e a s e d n u m b e r o f C lostridium difficile i n f e c t i o n s a n d p r e va l e n c e o f C lostridium difficile PCR r i b o t y p e 1 in s o u t h e r n Ge r m a n y
Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin
 2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
Molecular Epidemiology and Clinical Implications of Metallo-β- Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Urine
 Acta Med. Okayama, Vol., No., pp. Molecular Epidemiology and Clinical Implications of Metallo-β- Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Urine Shinichi Sako a, Reiko Kariyama a*, Ritsuko
Acta Med. Okayama, Vol., No., pp. Molecular Epidemiology and Clinical Implications of Metallo-β- Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Urine Shinichi Sako a, Reiko Kariyama a*, Ritsuko
Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom
 BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
Clostridium difficile in Food and Domestic Animals: ANewFoodbornePathogen?
 INVITED ARTICLE FOOD SAFETY Frederick J. Angulo, Section Editor Clostridium difficile in Food and Domestic Animals: ANewFoodbornePathogen? L. Hannah Gould and Brandi Limbago Centers for Disease Control
INVITED ARTICLE FOOD SAFETY Frederick J. Angulo, Section Editor Clostridium difficile in Food and Domestic Animals: ANewFoodbornePathogen? L. Hannah Gould and Brandi Limbago Centers for Disease Control
The New England Journal of Medicine. Case Ascertainment
 SURVEILLANCE FOR ESCHERICHIA COLI O157:H7 INFECTIONS IN MINNESOTA BY MOLECULAR SUBTYPING JEFFREY B. BENDER, D.V.M., M.S., CRAIG W. HEDBERG, PH.D., JOHN M. BESSER, M.S., DAVID J. BOXRUD, B.S., KRISTINE
SURVEILLANCE FOR ESCHERICHIA COLI O157:H7 INFECTIONS IN MINNESOTA BY MOLECULAR SUBTYPING JEFFREY B. BENDER, D.V.M., M.S., CRAIG W. HEDBERG, PH.D., JOHN M. BESSER, M.S., DAVID J. BOXRUD, B.S., KRISTINE
Molecular typing insight on diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni from Belgian chicken meat
 Molecular typing insight on diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni from Belgian chicken meat Ihab Habib Ghent University Department of Public Health and Food Safety. Contents: Molecular
Molecular typing insight on diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni from Belgian chicken meat Ihab Habib Ghent University Department of Public Health and Food Safety. Contents: Molecular
Campylobacter: the actual status and control options
 Campylobacter: the actual status and control options Prof. Jaap A. Wagenaar, DVM, PhD Dept. Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Campylobacter: the actual status and control options Prof. Jaap A. Wagenaar, DVM, PhD Dept. Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Macrorestriction analysis of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) isolates from Malaysia
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (004), 5, 99 997 DOI 0.099/jmm.0.0584-0 Macrorestriction analysis of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) isolates from Malaysia Kwai-Lin Thong, Goh Yee Ling,
Journal of Medical Microbiology (004), 5, 99 997 DOI 0.099/jmm.0.0584-0 Macrorestriction analysis of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) isolates from Malaysia Kwai-Lin Thong, Goh Yee Ling,
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 ECDIS-NET: Update on Clostridium difficile epidemiology in Europe 1 E d J. K u i j p e r, S o f i e v a n D o r p a n d D a a n N o t e r m a n s. D e p a r t m e n t o f M e d i c a l M i c r o b i o
ECDIS-NET: Update on Clostridium difficile epidemiology in Europe 1 E d J. K u i j p e r, S o f i e v a n D o r p a n d D a a n N o t e r m a n s. D e p a r t m e n t o f M e d i c a l M i c r o b i o
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
C. difficile infection
 C. difficile infection Most common cause of infectious diarrhoea in hospital patients 2 major virulence factors: PaLoc toxin A (an enterotoxin) toxin B (a cytotoxin) 3 rd binary toxin Bartlett JG Clin
C. difficile infection Most common cause of infectious diarrhoea in hospital patients 2 major virulence factors: PaLoc toxin A (an enterotoxin) toxin B (a cytotoxin) 3 rd binary toxin Bartlett JG Clin
What is the risk of persistent and evolving bacteria in an era of high diphtheria vaccination coverage?
 What is the risk of persistent and evolving bacteria in an era of high diphtheria vaccination coverage? Dr. Natasha S. Crowcroft Chief, Infectious Diseases, Public Health Ontario, Canada, Associate Professor,
What is the risk of persistent and evolving bacteria in an era of high diphtheria vaccination coverage? Dr. Natasha S. Crowcroft Chief, Infectious Diseases, Public Health Ontario, Canada, Associate Professor,
Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR
 2011 11 TEM-132 ESBL Klebsiella pneumoniae 1) 2) 1) 1) 3) 2) 1) 2) 3) 19 6 27 22 10 20 2003 4 2004 11 95 ceftazidime (CAZ) Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR b- (ESBL) PCR (PFGE) PCR bla TEM-132 PFGE 19 TEM-132
2011 11 TEM-132 ESBL Klebsiella pneumoniae 1) 2) 1) 1) 3) 2) 1) 2) 3) 19 6 27 22 10 20 2003 4 2004 11 95 ceftazidime (CAZ) Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR b- (ESBL) PCR (PFGE) PCR bla TEM-132 PFGE 19 TEM-132
Clostridium difficile Asymptomatic Carriers The Hidden Part of the Iceberg?
 Clostridium difficile Asymptomatic Carriers The Hidden Part of the Iceberg? Disclosures Merck Canada, BD Diagnostics, AMD Medical, Canadian Institute for Health Research Merck Canada, Pfizer OBJECTIVES
Clostridium difficile Asymptomatic Carriers The Hidden Part of the Iceberg? Disclosures Merck Canada, BD Diagnostics, AMD Medical, Canadian Institute for Health Research Merck Canada, Pfizer OBJECTIVES
Clinical Failure of Vancomycin Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infection in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southern Brazil
 224 BJID 2003; 7 (June) Clinical Failure of Vancomycin Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infection in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southern Brazil Larissa Lutz, Adão Machado, Nadia Kuplich and Afonso Luís
224 BJID 2003; 7 (June) Clinical Failure of Vancomycin Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infection in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southern Brazil Larissa Lutz, Adão Machado, Nadia Kuplich and Afonso Luís
HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS
 HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1 st, 2007 TO DECEMBER 31 st, 2012 TO PROMOTE AND PROTECT THE HEALTH OF CANADIANS THROUGH
HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1 st, 2007 TO DECEMBER 31 st, 2012 TO PROMOTE AND PROTECT THE HEALTH OF CANADIANS THROUGH
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines. Discontinue all unnecessary antibiotics
 Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Analysis of phenotypic variants of the serogroup C ET-15 clone of Neisseria meningitidis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 May 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00908-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 May 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00908-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Evaluation of Automated Ribotyping System for Characterization and Identification of Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated in Japan
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 56, 200-204, 2003 Original Article Evaluation of Automated Ribotyping System for Characterization and Identification of Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated in Japan
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 56, 200-204, 2003 Original Article Evaluation of Automated Ribotyping System for Characterization and Identification of Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated in Japan
Pathogens in the twilight zone: Update on emerging disease issues with implications for the pork industry
 Pathogens in the twilight zone: Update on emerging disease issues with implications for the pork industry Peter Davies BVSc, PhD University of Minnesota Introduction For an industry under increasing public
Pathogens in the twilight zone: Update on emerging disease issues with implications for the pork industry Peter Davies BVSc, PhD University of Minnesota Introduction For an industry under increasing public
Molecular Epidemiology of Hospital-Associated and Community-Acquired Clostridium difficile Infection in a Swedish County
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 2004, p. 3635 3643 Vol. 42, No. 8 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3635 3643.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 2004, p. 3635 3643 Vol. 42, No. 8 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3635 3643.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1993, p. 2724-2728 0095-1137/93/102724-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 10 DNA Fingerprinting of Streptococcus pneumoniae
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1993, p. 2724-2728 0095-1137/93/102724-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 10 DNA Fingerprinting of Streptococcus pneumoniae
T he use of central venous catheters as a means of access for
 824 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DNA fingerprinting analysis of coagulase negative staphylococci implicated in catheter related bloodstream infections B M Dobbins, P Kite, A Kindon, M J McMahon, M H Wilcox... J Clin
824 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DNA fingerprinting analysis of coagulase negative staphylococci implicated in catheter related bloodstream infections B M Dobbins, P Kite, A Kindon, M J McMahon, M H Wilcox... J Clin
Diphtheria infections caused by the different toxigenic biotypes of Corynebacterium diphtheriae
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 5 December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:0.8/jcm.054-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 5 December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:0.8/jcm.054-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Recurrent Clostridium difficile Disease: Association of Relapse with BI/NAP1/027. Scott R. Curry 1, Lee H. Harrison 1
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 10 October 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02291-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Recurrent Clostridium
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 10 October 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02291-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Recurrent Clostridium
Emerging Food Safety Issues: J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM
 Emerging Food Safety Issues: Clostridium difficile and MRSA J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM Clostridium difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first isolated in early 1900 s Cause of
Emerging Food Safety Issues: Clostridium difficile and MRSA J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM Clostridium difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first isolated in early 1900 s Cause of
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
The Role of Flagella in Clostridium difficile Pathogenesis: Comparison between a Non-Epidemic and an Epidemic Strain
 The Role of Flagella in Clostridium difficile Pathogenesis: Comparison between a Non-Epidemic and an Epidemic Strain Soza T. Baban, Sarah A. Kuehne, Amira Barketi-Klai, Stephen T. Cartman, Michelle Kelly,
The Role of Flagella in Clostridium difficile Pathogenesis: Comparison between a Non-Epidemic and an Epidemic Strain Soza T. Baban, Sarah A. Kuehne, Amira Barketi-Klai, Stephen T. Cartman, Michelle Kelly,
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review
 Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
on November 8, 2018 by guest
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:./jcm.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:./jcm.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Course Title Form Hours subject
 Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS
 Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS 1000x Ampicillin (sodium salt) 100mg/ml recipe 1. Measure out 1 g of Ampicillin tri hydrate 2. Add Milli-Q H2O to 10 ml 3. Add ~.1 g of NaOH pellets (half pellet or more
Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS 1000x Ampicillin (sodium salt) 100mg/ml recipe 1. Measure out 1 g of Ampicillin tri hydrate 2. Add Milli-Q H2O to 10 ml 3. Add ~.1 g of NaOH pellets (half pellet or more
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Evaluation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization in pigs and people that work with pigs in Ontario Veterinary College
 Evaluation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization in pigs and people that work with pigs in Ontario Veterinary College Final Report September 2007 This research has been possible
Evaluation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization in pigs and people that work with pigs in Ontario Veterinary College Final Report September 2007 This research has been possible
Surveillance of Enterococci in Belgium. M. Ieven, K. Loens, B. Jans and H. Goossens
 Surveillance of Enterococci in Belgium M. Ieven, K. Loens, B. Jans and H. Goossens Surveillance of Enterococci in Belgium Overview Introduction and epidemiological surveillance Results of isolates received
Surveillance of Enterococci in Belgium M. Ieven, K. Loens, B. Jans and H. Goossens Surveillance of Enterococci in Belgium Overview Introduction and epidemiological surveillance Results of isolates received
Update on infections with and clinical lab guidelines for Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) in the United States
 Update on infections with and clinical lab guidelines for Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) in the United States Patricia M. Griffin, MD Enteric Diseases Epidemiology Branch Centers for Disease Control
Update on infections with and clinical lab guidelines for Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) in the United States Patricia M. Griffin, MD Enteric Diseases Epidemiology Branch Centers for Disease Control
Case 1. Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea?
 Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS
 Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
L. BEVANGER, K. BERGH, G. GISNAS*, D. A. CAUGANT-F and L. 0. FR0HOLM-f
 J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 47 (998), 993-998 (~ 998 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS AND TYPI Identification of nasopharyngeal carriage of an outbreak strain of
J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 47 (998), 993-998 (~ 998 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS AND TYPI Identification of nasopharyngeal carriage of an outbreak strain of
Clinical Application of Polymerase Chain Reaction to Diagnose Clostridium difficile in Hospitalized Patients With Diarrhea
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:669 674 Clinical Application of Polymerase Chain Reaction to Diagnose Clostridium difficile in Hospitalized Patients With Diarrhea MICHAEL S. MORELLI, SUSAN
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:669 674 Clinical Application of Polymerase Chain Reaction to Diagnose Clostridium difficile in Hospitalized Patients With Diarrhea MICHAEL S. MORELLI, SUSAN
Six-Year Molecular Analysis of Burkholderia cepacia Complex Isolates among Cystic Fibrosis Patients at a Referral Center for Lung Transplantation
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 1188 1193 Vol. 40, No. 4 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1188 1193.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 1188 1193 Vol. 40, No. 4 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1188 1193.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Toxin production by an emerging strain of Clostridium difficile associated with outbreaks of severe disease in North America and Europe
 Toxin production by an emerging strain of Clostridium difficile associated with outbreaks of severe disease in North America and Europe Michel Warny, Jacques Pepin, Aiqi Fang, George Killgore, Angela Thompson,
Toxin production by an emerging strain of Clostridium difficile associated with outbreaks of severe disease in North America and Europe Michel Warny, Jacques Pepin, Aiqi Fang, George Killgore, Angela Thompson,
Detection of NDM-1, VIM-1, KPC, OXA-48, and OXA-162 carbapenemases by MALDI- TOF mass spectrometry
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01002-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01002-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Enhancing animal health security and food safety in organic livestock production
 Enhancing animal health security and food safety in organic livestock production Proceedings of the 3 rd SAFO Workshop 16-18 September 2004, Falenty, Poland Edited by M. Hovi, J. Zastawny and S. Padel
Enhancing animal health security and food safety in organic livestock production Proceedings of the 3 rd SAFO Workshop 16-18 September 2004, Falenty, Poland Edited by M. Hovi, J. Zastawny and S. Padel
The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community. J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM
 The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM C. difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first
The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM C. difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first
S. Wesley Long, MD, PhD
 Basic Molecular Microbiology: A Practical Case-Based Approach S. Wesley Long, MD, PhD Center for Molecular and Translational Human Infectious Diseases Research Houston Methodist Research Institute September
Basic Molecular Microbiology: A Practical Case-Based Approach S. Wesley Long, MD, PhD Center for Molecular and Translational Human Infectious Diseases Research Houston Methodist Research Institute September
"QUIK CHEK"[tw])) NOT ((therapy[ti] OR treatment[ti] OR treat*[ti]) NOT (diagnosis[ti] OR
![QUIK CHEK[tw])) NOT ((therapy[ti] OR treatment[ti] OR treat*[ti]) NOT (diagnosis[ti] OR QUIK CHEK[tw])) NOT ((therapy[ti] OR treatment[ti] OR treat*[ti]) NOT (diagnosis[ti] OR](/thumbs/81/84207658.jpg) Supporting information Appendix 1: Search strategy Pubmed (("Clostridium Infections/diagnosis"[majr] AND "Clostridium difficile"[majr]) OR (((("Clostridium difficile"[majr] OR "Clostridium Difficile"[ti])
Supporting information Appendix 1: Search strategy Pubmed (("Clostridium Infections/diagnosis"[majr] AND "Clostridium difficile"[majr]) OR (((("Clostridium difficile"[majr] OR "Clostridium Difficile"[ti])
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH
 The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH Some history first Clostridium difficile, a spore-forming gram-positive (i.e., thick
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH Some history first Clostridium difficile, a spore-forming gram-positive (i.e., thick
A Pharmacist Perspective
 Leveraging Technology to Reduce CDI A Pharmacist Perspective Ed Eiland, Pharm.D., MBA, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Practice and Business Supervisor Huntsville Hospital System Huntsville Hospital 881 licensed
Leveraging Technology to Reduce CDI A Pharmacist Perspective Ed Eiland, Pharm.D., MBA, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Practice and Business Supervisor Huntsville Hospital System Huntsville Hospital 881 licensed
Product # Kit Components
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
DUKE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP OUTREACH NETWORK (DASON) Antimicrobial Stewardship News. Volume 3, Number 6, June 2015
 DUKE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP OUTREACH NETWORK (DASON) Antimicrobial Stewardship News Volume 3, Number 6, June 2015 Diagnostic Testing for Clostridium difficile Infection Background Clostridium difficile
DUKE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP OUTREACH NETWORK (DASON) Antimicrobial Stewardship News Volume 3, Number 6, June 2015 Diagnostic Testing for Clostridium difficile Infection Background Clostridium difficile
Received 21 December 2004/Accepted 14 May 2005
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2005, p. 6216 6227 Vol. 71, No. 10 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.10.6216 6227.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2005, p. 6216 6227 Vol. 71, No. 10 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.10.6216 6227.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Is C. difficile a Foodborne Disease?
 Is C. difficile a Foodborne Disease? Brandi Limbago, Ph.D. Deputy Chief Clinical and Environmental Microbiology Branch IAFP 24 July 2012 Disclaimer: The findings and conclusions in this presentation are
Is C. difficile a Foodborne Disease? Brandi Limbago, Ph.D. Deputy Chief Clinical and Environmental Microbiology Branch IAFP 24 July 2012 Disclaimer: The findings and conclusions in this presentation are
Sustainable cleaning of the health care environment.
 Sustainable cleaning of the health care environment. Has the current practice of cleaning the health care environment relying on the use of disinfectants and their label claims and instructions for use
Sustainable cleaning of the health care environment. Has the current practice of cleaning the health care environment relying on the use of disinfectants and their label claims and instructions for use
Listeria monocytogenes transmission at retail
 Listeria monocytogenes transmission at retail Martin Wiedmann Department of Food Science Cornell University Ithaca, NY Collaborative effort between Cornell and New York State Department of Agriculture
Listeria monocytogenes transmission at retail Martin Wiedmann Department of Food Science Cornell University Ithaca, NY Collaborative effort between Cornell and New York State Department of Agriculture
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
DATA SHEET. Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter calf thymus DNA.
 Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
by the DiversiLab System and Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Epidemiology, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia 30329; 3 Bacterial Barcodes, Inc.
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on June 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:./jcm.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 1
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on June 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:./jcm.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 1
ESCMID Online Lecture by author
 Molecular typing as a tool for the control of MDR and XDR organisms. Whole genome sequencing - already here? Martin Llewelyn Reader, Consultant Brighton and Sussex Medical School, UK m.j.llewelyn@bsms.ac.uk
Molecular typing as a tool for the control of MDR and XDR organisms. Whole genome sequencing - already here? Martin Llewelyn Reader, Consultant Brighton and Sussex Medical School, UK m.j.llewelyn@bsms.ac.uk
Detection of Campylobacter jejuni by Multiplex PCR and Patterns of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
 Campylobacter jejuni Detection of Campylobacter jejuni by Multiplex PCR and Patterns of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Jae-Kyoo Lee*, **, Kwang-Yup Kim**, Myoung-Sook Koo***, Dong-Eun Yong****, and Eui-Chong
Campylobacter jejuni Detection of Campylobacter jejuni by Multiplex PCR and Patterns of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Jae-Kyoo Lee*, **, Kwang-Yup Kim**, Myoung-Sook Koo***, Dong-Eun Yong****, and Eui-Chong
A first molecular characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates circulating in humans from 2009 to 2014 in the Italian Veneto region
 Short communication A first molecular characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates circulating in humans from 2009 to 2014 in the Italian Veneto region Cristiano Salata 1,2, Paola Lisotto 1, Caterina
Short communication A first molecular characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates circulating in humans from 2009 to 2014 in the Italian Veneto region Cristiano Salata 1,2, Paola Lisotto 1, Caterina
DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL THE EVENT LEADER TELLS YOU TO!
 DISEASE DETECTIVES DIRECTIONS DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST!! All answers must be written on your response sheet. This test is long. You may wish to divide the test between you. If you take the pages out of
DISEASE DETECTIVES DIRECTIONS DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST!! All answers must be written on your response sheet. This test is long. You may wish to divide the test between you. If you take the pages out of
