Human African Trypanosomiasis
|
|
|
- Tamsin Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human African Trypanosomiasis
2
3
4
5
6 Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense Trypanosomoa brucei gambiense Acute -- can cause death in weeks or months Chronic --lasts years
7
8 100% Fatal if left untreated cardiac failure or from the infection itself
9 Look for presence of trypanosomes High levels of CSP protein and WBCs
10 Look for high levels of immunoglobulin protein M Anemia High levels of White blood cells
11
12
13 Taenia solium (pork tapeworm) - Cysticercus Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm) Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) Echinococcus granulosus (unilocular hydatid) Echinococcus multilocularis (alveolar hydatid) Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm) Hymenolepis diminutia Dipylidium caninum
14 Head region (scolex) : contains suckers and hooks used to attach to a host organism. Proglottids : square body segments used for reproduction.
15 Scolex - Attachment organ Zone of Proliferation - Undifferentiated area behind the scolex (neck region) Strobilia - Chain of segments (proglottids) Immature proglottids - developing reproductive Mature proglottids: mature reproductive organs. Gravid proglottids: contain eggs in the uterus.
16 note that the reproductive organs are just beginning to differentiate. (Carmine stained) Developing reproductive organs
17 Tapeworms are Hermaphroditi c
18 Worldwide, depending on dietary habits, and quality of cattle and pork farming.
19
20 Adult Worm: 2-4 m long, segments: Scolex Neck Immature segment Mature segment Gravid segment
21 The eggs of Taenia saginata and T. Solium are morphologically indistinguishable.
22 Symptoms History of eating undercooked beef or pork Recovery of proglottids and/or eggs in the stool
23 Distributed worldwide: freshwater (great lakes)
24 1 cm
25 symptoms history of eating raw fish recovery of proglottids and/or eggs in the stool
26 Praziquantel is the drug of choice Avoid uncooked fish from infested waters Freezing for 24 hours and pickling kills the tape
27
28 Lighter infections: mild abdominal disturbance Heavier infections: enteritis
29 Diagnosis rodent infestation ova in the feces Treatment and Control Praziquantel is the drug of choice rodent population control
30
31 Leishmaniasis focal distribution throughout world, especially tropics and subtropics new world: southern Texas to northern Argentina old world: Asia, Africa, middle east, Mediterranean transmitted by sand flies new world: Lutzomyia old world: Phlebotomus parasite replicates within macrophages of vertebrate host a variety of disease manifestations
32 Clinical Spectrum of Leishmaniasis Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (CL) most common form, relatively benign selfhealing skin lesions (aka, localized or simple CL) Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis (MCL) simple skin lesions that metastasize to mucosae (especially nose and mouth region) Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL) generalized infection of the reticuloendothelial system, high mortality
33 Diagnosis geographical presence of parasite demonstration of parasite in skin lesion or bone marrow delayed hypersensitivity skin test (cutaneous forms) serological tests (visceral disease) Treatment pentavalent antimonials amphotericin B (less toxic, expensive) miltefosine (phase IV, no hospitalization)
34 MALARIA causative agent = Plasmodium species 4 human Plasmodium species 40% of the world s population lives in endemic areas primarily tropical and sub-tropical million clinical cases per year million deaths (90% Africa) increasing problem (re-emerging disease) resurgence in some areas drug resistance ( mortality) P. falciparum P. vivax P. ovale P. malariae
35 ecdysozoa/nematoda.html 1 mm long nematode
36 The nematodes are quite species diverse (about 15,000 species although this is probably a huge underestimate) and the many parasitic forms have a significant impact on humans. Most nematodes are under 5cm and many are microscopic. However, some parasitic forms can be over a meter in length.
37 Nematodes use their pseudocoelom as a hydrostatic skeleton. A pseudocoelom is a fluid-filled body cavity in which mesoderm lines only the outer edge of the developing blastocoel. No peritoneal lining develops. The body has a thick cuticle (made primarily of collagen) secreted by the underlying epidermis, which resists the high hydrostatic pressure exerted by the fluid in the pseudocoelom.
38 Free-living nematode
39 Most free-living nematodes are carnivorous. However, some feed on algae and fungi and some are detritivores. Others feed on plants, especially the roots.
40 Many root feeding nematodes are major agricultural pests. These species pierce root cells and suck out their contents. Nematodes are estimated to destroy 12% of the world s cash crops annually.
41 There are a great many species of parasitic nematodes and they attack virtually all groups of animals and plants.
42 It s estimated that worldwide as many as 1.4 billion people are infected with Ascaris lumbricoides which lives in the small intestine. Females may be a foot long and produce 200,000 eggs a day. Infection occurs when parasite eggs are eaten with uncooked food or when soiled fingers are put into the mouth.
43 In the intestines the worms cause abdominal symptoms and allergic reactions and may produce an intestinal blockage.
44 Figure 15.05a 9.8 Male (top) and female Ascaris lumbricoides
45 Hookworms are named for the dorsal curve in their anterior end. Hookworms are quite small, the commonest species Necator americanus is only 11mm long. However, because they feed on blood a heavy infection can produce severe anemia.
46
47 Large plates in the hookworm s mouth are used to cut the intestinal lining of the host. The parasite then pumps blood through its gut, partially digesting it before excreting it. Because hookworms suck more blood than they use, they can cause debilitating anemia. In children a hookworm infection can stunt growth and cause a general lack of energy.
48 Figure Section through hookworm attached to dog intestine
49 Hookworms do not permanently attach in one spot, but move around the gut and reattach when they are ready to feed. Hookworms have evolved sophisticated anti-clotting factors that keep platelets from clumping and forming a clot while the hookworm is feeding.
50 Filarial worms are thread-like nematodes of which there are at least 8 species for which humans, especially in tropical regions, are the definitive host. Approximately 250 million people worldwide are infected with these worms which are spread by mosquitoes. Different species inhabit different locations in the body. Some live in the lymphatic system, others subcutaneously and others in the abdominal cavity.
51 Females can be 10cm long and they release live young microfilariae into the blood and lymphatic system. The microfilariae are picked up by mosquitoes where they develop, become infective and can infect another person.
52 In some people exposed to persistent infections with filarial parasites that live in the lymphatic system, elephantiasis may develop. This is caused by blockage of lymphatic ducts and inflammation. There may be excessive growth of connective tissue and enormous swelling of infected parts including legs, arms and scrotum.
53 Figure Elephantiasis of leg caused by filarial worms 9.12
54 Figure Diriofilaria immitis Dog heartworm 9.13
55 River blindness is also caused by filarial worms that live subcutaneously. In this case the insect that transmits the disease is a blackfly million people are infected worldwide (mainly central Africa and parts of South America) and more than 300,000 have been made blind.
56 Trichinella spiralis is a tiny nematode that causes the potentially fatal disease trichinosis. Humans typically become infected by eating undercooked pork. Trichinella lives in cysts formed in individual muscle cells of the host.
57 Trichinella when it hatches from an ingested cyst in its host s gut drills through the wall of the gut where females produce living young. These juveniles travels in the circulatory system to a muscle. The juvenile penetrates an individual muscle cell and breaks the cell down so it can be remade.
58 Trichinella, just as a virus does, manipulates the host cell s DNA. It causes the cell to recruit a blood supply to supply food to the cell and also produce collagen to form a cyst around the cell. The Trichinella juvenile awaits ingestion by another host. When ingested it emerges from its cysts enters the mucosal lining of gut, develops into an adult and continues the life cycle.
59
60 Schistosoma S. mansoni S. hematobium S. japonicum Fasciolopsis buski Fasciola hepatica Opisthorchis O. sinensis O. felineus O. viverini Paragonimus P. westermani P. kellicotti
61 It is believed that Napoleon's army in North Africa was defeated not by the enemy but by infestation of his soldiers with Schistosomal infections.
62 1 cm
63 Site Symptoms Pathogenesis Skin GI Urogenital Dermatitis (swimmers itch) abdominal pain, ascites, diarrhea, bloody stool (mansoni & japonicum chronic cystitis and urethritis parasitic toxic material, skin damage inflammatory response to eggs (mucosal fibrosis) granulomatous fibrosis due to egg-deposits
64 Cercarial Dermatitis
65
66 History Symptoms Histology Eggs in the urine or stool S. Hematobium Terminal Spine S. Mansoni Lateral Spine S. Japonicum Smaller egg Minute Spine 50 m
67 5 cm
68 Upper quadrant tenderness and pain Chills and fever Eosinophilia Hepatitis Hyperplasia and blockage of bile duct
69 Symptoms History of eating uncooked watercress from infested locale Eggs in stool 50 m
70 This species of fluke is Praziquantel resistant Triclabendazole is effective Avoid eating uncooked watercress in endemic areas Elimination of snails
71 5 mm
72 Dry cough, pleurisy Pulmonary pain Blood-stained rusty brown sputum Fluke may migrate to brain, produce eggs and cause epilepsy-like symptoms
73 Symptoms History of eating improperly cooked crabmeat in endemic areas Eggs in the sputum 50 m
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
The Nematodes (Round worms)
 The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths
 Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Protozoans and Helminthes
 Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
The Roundworms pg. 689
 The Roundworms 27-2 pg. 689 What are the defining features of roundworms Advances over Platyhelminthes (the flatworms) Body plans and body systems 2 broad types and their example animals Parasitic worms:
The Roundworms 27-2 pg. 689 What are the defining features of roundworms Advances over Platyhelminthes (the flatworms) Body plans and body systems 2 broad types and their example animals Parasitic worms:
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
L:7, L:8 Parasitology
 L:7, L:8 Parasitology 2.Fasciola hepatica Adult The adult Fasciola hepatica worm is flattened, leaf like shape, equipped with shoulders, somewhat oblong. Adult Fasciola hepatica measuring 3cm by 1cm in
L:7, L:8 Parasitology 2.Fasciola hepatica Adult The adult Fasciola hepatica worm is flattened, leaf like shape, equipped with shoulders, somewhat oblong. Adult Fasciola hepatica measuring 3cm by 1cm in
Unit 3: Phylums: Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, and Rotifera
 Invertebrate Zoology (Study Guide for Test) Unit 3: Phylums: Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, and Rotifera Objective 1: Describe the form and function of flatworms 1) Describe the characteristics of the following
Invertebrate Zoology (Study Guide for Test) Unit 3: Phylums: Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, and Rotifera Objective 1: Describe the form and function of flatworms 1) Describe the characteristics of the following
1. Parasitology Protozoa 4
 Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Platyhelminthes Flat worms
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Platyhelminthes Flat worms
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes
 Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes
 Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes - These two phylum are composed of. However, the worms we are going to look at are not common. Both of these phyla are composed of unsegmented worms. That is, these
Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes - These two phylum are composed of. However, the worms we are going to look at are not common. Both of these phyla are composed of unsegmented worms. That is, these
3 Types: I. Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms. II. Phylum Nematoda Roundworms
 Unsegmented Worms 3 Types: I. Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms II. Phylum Nematoda Roundworms Flatworms Flatworms Belong to Phylum Platyhelminthes. (Plat = flat) There are three classes: Turbellaria Trematoda
Unsegmented Worms 3 Types: I. Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms II. Phylum Nematoda Roundworms Flatworms Flatworms Belong to Phylum Platyhelminthes. (Plat = flat) There are three classes: Turbellaria Trematoda
Introduction. Causes. Roundworms. Worms. Flatworms. How Flatworms are transmitted. Fast fact. Fast fact
 Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18)
 IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
Tapeworm Infection. Tapeworm
 Tapeworm Infection Introduction Tapeworm infection is caused by ingesting food or water that is contaminated with tapeworm eggs or larvae. Larvae are newly hatched tapeworms. A tapeworm may attach itself
Tapeworm Infection Introduction Tapeworm infection is caused by ingesting food or water that is contaminated with tapeworm eggs or larvae. Larvae are newly hatched tapeworms. A tapeworm may attach itself
Introduction to Multicellular Parasites
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Multicellular Parasites Multicellular parasites are eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom Animalia (like us). Though
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Multicellular Parasites Multicellular parasites are eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom Animalia (like us). Though
Helminth infections a review
 Helminth infections a review Farrer F, BPharm Amayeza Info Centre Abstract Parasitic worms are among the most common human infections in the world. Most patients are unaware of the infection. Adherence
Helminth infections a review Farrer F, BPharm Amayeza Info Centre Abstract Parasitic worms are among the most common human infections in the world. Most patients are unaware of the infection. Adherence
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Giardia ( Giardia lamblia Coccidia ( Cryptosporidium
 Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
Human Body Systems - Parasites
 Human Body Systems - Parasites Grade Range: Middle School Key Terms Lesson Time: 40 minutes Materials and Resources Circulatory system Digestive system Immune system Malaria Nervous system Parasite Plasmodium
Human Body Systems - Parasites Grade Range: Middle School Key Terms Lesson Time: 40 minutes Materials and Resources Circulatory system Digestive system Immune system Malaria Nervous system Parasite Plasmodium
Parasite Life Cycles. Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou. Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
 Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Helminths in tropical regions
 Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
HELMINTHS CESTODES (tapeworms)
 Microbiology HELMINTHS CESTODES (tapeworms) Introduction to Parasites The eggs of cestodes as mentioned before have a striated outer covering. Inside the egg, there is a rounded embryo with six hooks.
Microbiology HELMINTHS CESTODES (tapeworms) Introduction to Parasites The eggs of cestodes as mentioned before have a striated outer covering. Inside the egg, there is a rounded embryo with six hooks.
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY. lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, hookworm. Human Parasitology (Code: ) Guideline
 HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
Amoebas are motile by means of pseudopodia cytoplasmic extensions which allow it to crawl across surfaces.
 Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions
 Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions Name: In lab this week we will work on developing an understanding of community interactions. Prior to lab answer the following questions to
Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions Name: In lab this week we will work on developing an understanding of community interactions. Prior to lab answer the following questions to
Organisms of Concern. Roundworms (nematodes) Anisakis spp., Pseudoterranova spp., Eustrongylides spp. and Gnathostoma spp.
 Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Wuchereria Morphology 10 cm 250 : m
 Wucheria bancrofti Brugia malayi Lymphatic filariasis Lymphatic Filariasis 119 million infected Elephantiasis Manifestation of lymphatic filariasis Morphology I Adult: White and thread-like. Two rings
Wucheria bancrofti Brugia malayi Lymphatic filariasis Lymphatic Filariasis 119 million infected Elephantiasis Manifestation of lymphatic filariasis Morphology I Adult: White and thread-like. Two rings
Chapter 5 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
 Chapter 5 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flat worms) One class is free living (Turbellaria) and most are parasitic, some commensals Tribloblastic bilaterally symmetrical dorsoventrally
Chapter 5 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flat worms) One class is free living (Turbellaria) and most are parasitic, some commensals Tribloblastic bilaterally symmetrical dorsoventrally
Chapter Guided Notes
 Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
Introduction to Medical Parasitology
 Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide
 Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
AGRIC SCIENCE (WEEK 5) Squatting of the bird with head tucked under the wings
 AGRIC SCIENCE (WEEK 5) PROTOZOAN DISEASES CONTINUED Symptoms of Coccidiosis 1. Closing of eyes Prevention Squatting of the bird with head tucked under the wings - Maintain good hygiene - Prevent animals
AGRIC SCIENCE (WEEK 5) PROTOZOAN DISEASES CONTINUED Symptoms of Coccidiosis 1. Closing of eyes Prevention Squatting of the bird with head tucked under the wings - Maintain good hygiene - Prevent animals
Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections
 DRUG REVIEW n Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections Allifia Abbas BSc, MRCP, Paul Wade MSc, BPharm and William Newsholme MSc, FRCP, DTM&H A number of worm infections are seen in the
DRUG REVIEW n Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections Allifia Abbas BSc, MRCP, Paul Wade MSc, BPharm and William Newsholme MSc, FRCP, DTM&H A number of worm infections are seen in the
Nematodes (roundworms)
 Intestinal human nematodes Dr Mohammed Abdulla FIBMS (general medicine), FIBMS (G&H), MRCP SCE (G&H). Medically-important nematodes Nematodes (roundworms) There are >60 species of nematodes (roundworms)
Intestinal human nematodes Dr Mohammed Abdulla FIBMS (general medicine), FIBMS (G&H), MRCP SCE (G&H). Medically-important nematodes Nematodes (roundworms) There are >60 species of nematodes (roundworms)
Blood Smears Only 6 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control 15B-K
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
16/12/2012. The Flatworms. Characteristics
 Learning Outcome G3 Learning Outcome G3 Analyze the increasing complexity of the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda and the Phylum Annelida Phylum Platyhelminthes, Nematoda and Annelida Student
Learning Outcome G3 Learning Outcome G3 Analyze the increasing complexity of the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda and the Phylum Annelida Phylum Platyhelminthes, Nematoda and Annelida Student
EDO UNIVERSITY IYAMHO
 EDO UNIVERSITY IYAMHO FACULTY OF SCIENCE SEMINAR SERIES INTESTINAL HELMINTHIASIS: SOIL TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS. PRESENTED BY Mrs. Habibat Joy, Ozemoka 3rd August, 2018 INTRODUCTION Intestinal helminthiasis
EDO UNIVERSITY IYAMHO FACULTY OF SCIENCE SEMINAR SERIES INTESTINAL HELMINTHIASIS: SOIL TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS. PRESENTED BY Mrs. Habibat Joy, Ozemoka 3rd August, 2018 INTRODUCTION Intestinal helminthiasis
Purpose: To observe the different structures of a male and female Ascaris lumbricoides.
 Biology 1 Name: Pre-lab Discussion: There are over 15,000 species in the Phylum Nematoda. They are round, unsegmented worms. Members of this phylum are free-living or parasitic. The parasitic species can
Biology 1 Name: Pre-lab Discussion: There are over 15,000 species in the Phylum Nematoda. They are round, unsegmented worms. Members of this phylum are free-living or parasitic. The parasitic species can
CHAPTER 133 Parasitic Infections
 CHAPTER 133 Parasitic Infections Bruce M. Becker and John D. Cahill PERSPECTIVE Challenge Parasitology has become increasingly important in the practice of emergency medicine. There has been a dramatic
CHAPTER 133 Parasitic Infections Bruce M. Becker and John D. Cahill PERSPECTIVE Challenge Parasitology has become increasingly important in the practice of emergency medicine. There has been a dramatic
Lab 6: Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha
 Lab 6: Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha Platyhelminthes 9 March 2016 Experiment: Planarian Regeneration (freshwater only!) As you have learned in class, these flatworms have incredible regeneration abilities.
Lab 6: Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha Platyhelminthes 9 March 2016 Experiment: Planarian Regeneration (freshwater only!) As you have learned in class, these flatworms have incredible regeneration abilities.
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases
 Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE
 INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Ascaris lumbricoides
 Case History A 4-year-old Caucasian male child of Turkish nationality was admitted to the emergency department with Abdominal pain and biliary vomiting for three days. Physical Examination revealed abdomen
Case History A 4-year-old Caucasian male child of Turkish nationality was admitted to the emergency department with Abdominal pain and biliary vomiting for three days. Physical Examination revealed abdomen
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program. Parasitology (General) 01 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
Overview IMPORTANCE CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS
 IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
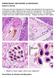 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS
 FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
Chapter 12. Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Part 2
 Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Part 2 Chapter 12 includes the fungal pathogens section from chapter 22 and Helminths from chapter 23 Fungi Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Part 2 Chapter 12 includes the fungal pathogens section from chapter 22 and Helminths from chapter 23 Fungi Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
University Of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy
 PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
HAEMOFLAGELLATES. Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine
 HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
Schistosomiasis. Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University
 Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Parasitology lab. ü interdiction
 Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
James Gaensbauer, MD MScPH October 18, 2016
 James Gaensbauer, MD MScPH October 18, 2016 Pediatric Infectious Diseases, University of Colorado School of Medicine Center for Global Health, Colorado School of Public Health Denver Health Hospital Authority
James Gaensbauer, MD MScPH October 18, 2016 Pediatric Infectious Diseases, University of Colorado School of Medicine Center for Global Health, Colorado School of Public Health Denver Health Hospital Authority
SCHISTOSOMIASIS (BILHARZIA)
 TREMATODES SCHISTOSOMIASIS (BILHARZIA) Hazem Al-Khafaji LECTURE-12- HISTORICAL FACTS... First described by German pathologist Theodore Maximilian Bilharz Bilharz performed autopsies on Egyptian patients
TREMATODES SCHISTOSOMIASIS (BILHARZIA) Hazem Al-Khafaji LECTURE-12- HISTORICAL FACTS... First described by German pathologist Theodore Maximilian Bilharz Bilharz performed autopsies on Egyptian patients
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3)
 Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Malaria. Population at Risk. Infectious Disease epidemiology BMTRY 713 (Lecture 23) Epidemiology of Malaria. April 6, Selassie AW (DPHS) 1
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby
 Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby 1 2 Onchocerca volvulus (Blinding filariasis; river blindness) Microfilaria of Onchocerca volvulus, from skin snip from a patient seen in Guatemala. Wet preparation 3 Some important
Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby 1 2 Onchocerca volvulus (Blinding filariasis; river blindness) Microfilaria of Onchocerca volvulus, from skin snip from a patient seen in Guatemala. Wet preparation 3 Some important
Lectures. Experiments. General introduction 3. Introduction to Medical Protozoa 0.5. Lobosea (amoebae) 3 3. Flagellates 3 3.
 Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Parasitic Infections Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Parasitic Infections Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
An Introduction to the Invertebrates, Part Two Platyhelminthes & Rotifers. Reference: Chapter 33.3, 33.4
 An Introduction to the Invertebrates, Part Two Platyhelminthes & Rotifers Reference: Chapter 33.3, 33.4 Quick Protist Review v Are protists monophyletic, paraphyletic, or polyphyletic? v What are protozoa?
An Introduction to the Invertebrates, Part Two Platyhelminthes & Rotifers Reference: Chapter 33.3, 33.4 Quick Protist Review v Are protists monophyletic, paraphyletic, or polyphyletic? v What are protozoa?
Trichinellosis. By Michelle Randall
 Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
NEGLECTED DISEASES. Elsa Herdiana Murhandarwati Dept. Parasitologi 2017
 NEGLECTED DISEASES Elsa Herdiana Murhandarwati Dept. Parasitologi 2017 2 3 Taeniasis 4 Survives for years Take 2 months to become adult survives for years days to months in environment Life cycle image
NEGLECTED DISEASES Elsa Herdiana Murhandarwati Dept. Parasitologi 2017 2 3 Taeniasis 4 Survives for years Take 2 months to become adult survives for years days to months in environment Life cycle image
Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest
 Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest Type of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes Trematodes Cestodes Platyhelminthes A simplified classification of flat worms Platyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest Type of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes Trematodes Cestodes Platyhelminthes A simplified classification of flat worms Platyhelminthes
Blood Smears Only 07 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control 12B A
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
Ascariasis rev Jan 2018
 rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent is caused by the soil transmitted helminths Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. Both are roundworm intestinal nematodes. Ascaris lumbricoides is found
rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent is caused by the soil transmitted helminths Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. Both are roundworm intestinal nematodes. Ascaris lumbricoides is found
Brugiamalayi, , 140 life cycle of, 137 Bubo(es), Bubonic plague, 42, 43-44, see also Plague Burma, filariasis in, 137
 Index Abscess, amebic liver, 67, 69-70 aspiration of, 73-74 Acidosis, metabolic, 29 Acute African trypanosomiases, 10 1-102, see also African trypanosomiases Acute toxoplasmosis, 94-95, see also Toxoplasmosis
Index Abscess, amebic liver, 67, 69-70 aspiration of, 73-74 Acidosis, metabolic, 29 Acute African trypanosomiases, 10 1-102, see also African trypanosomiases Acute toxoplasmosis, 94-95, see also Toxoplasmosis
Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges
 Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Welcome to Parasitic. Fall 2008
 Welcome to Parasitic Diseases Fall 2008 Dickson Despommier, Ph.D. Charles Knirsch, MPH, MD Josh Stillman, MD Parasite Any organism that takes metabolic advantage of another organism Viruses Rickettsiae
Welcome to Parasitic Diseases Fall 2008 Dickson Despommier, Ph.D. Charles Knirsch, MPH, MD Josh Stillman, MD Parasite Any organism that takes metabolic advantage of another organism Viruses Rickettsiae
I. Wuchereria bancrofti
 Parasites that affect the Musculoskeletal system (continued) Filarial Worms - Nematodes. - Tissue parasites. - Require an intermediate host, which is usually an insect. - Do not lay eggs like other worms,
Parasites that affect the Musculoskeletal system (continued) Filarial Worms - Nematodes. - Tissue parasites. - Require an intermediate host, which is usually an insect. - Do not lay eggs like other worms,
Diagnosis and management of helminth infections
 Drug review Worms Diagnosis and management of helminth infections William Newsholme MSc, MRCP, DTM&H Skyline Imaging Ltd A number of worm infections are seen in the UK, mostly acquired through foreign
Drug review Worms Diagnosis and management of helminth infections William Newsholme MSc, MRCP, DTM&H Skyline Imaging Ltd A number of worm infections are seen in the UK, mostly acquired through foreign
GI Micro Lab. B- After that the stool sample should be cultured on different types of media
 GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
Faculty and Department: Faculty of Science and Technology, Biomedical Sciences. Status: Option, BSc Biomedical Sciences, Westminster elective module
 MODULE PROFORMA Full module title: Human Parasitology Module code: 5BIOM009W Credit level: 5 Length: One semester UK credit value: 20 ECTS value: 10 Faculty and Department: Faculty of Science and Technology,
MODULE PROFORMA Full module title: Human Parasitology Module code: 5BIOM009W Credit level: 5 Length: One semester UK credit value: 20 ECTS value: 10 Faculty and Department: Faculty of Science and Technology,
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Enteric Parasites Overview ENTERIC PARASITES 101 GIARDIASIS. Description. Transmission
 Enteric Parasites Overview ENTERIC PARASITES 101 Shira Shafir, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor Department of Center for Global and Immigrant Health UCLA School of Public Health 1 Types of Parasites: Protozoa:
Enteric Parasites Overview ENTERIC PARASITES 101 Shira Shafir, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor Department of Center for Global and Immigrant Health UCLA School of Public Health 1 Types of Parasites: Protozoa:
Pop Quiz 2. Give the dominant body form for each. List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Scyphozoa anthozoa
 Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections Allifia Abbas BSc, MB ChB and William Newsholme MSc, MRCP, DTM&H
 Drug review Worms Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections Allifia Abbas BSc, MB ChB and William Newsholme MSc, MRCP, DTM&H Skyline Imaging Ltd A number of worm infections are seen in
Drug review Worms Diagnosis and recommended treatment of helminth infections Allifia Abbas BSc, MB ChB and William Newsholme MSc, MRCP, DTM&H Skyline Imaging Ltd A number of worm infections are seen in
Chapter 8 Review. 4. Scientists do not consider viruses as true living organisms because they
 Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
Entamoeba histolytica
 Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Introduction to the internal parasites. BVM&S Parasitology Tudor.W.Jones
 Introduction to the internal parasites BVM&S Parasitology Tudor.W.Jones Learning Outcomes Describe what is meant by internal parasites, where they can be found and why they are important to veterinarians.
Introduction to the internal parasites BVM&S Parasitology Tudor.W.Jones Learning Outcomes Describe what is meant by internal parasites, where they can be found and why they are important to veterinarians.
Introduction to the internal parasites
 Learning Outcomes Introduction to the internal parasites BVM&S Parasitology Tudor.W.Jones Describe what is meant by internal parasites, where they can be found and why they are important to veterinarians.
Learning Outcomes Introduction to the internal parasites BVM&S Parasitology Tudor.W.Jones Describe what is meant by internal parasites, where they can be found and why they are important to veterinarians.
Paragonimiasis added Jan 2016
 added Jan 2016 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Paragonimus species, a parasitic lung fluke (flat worm). More than 30 species of trematodes (flukes) of the genus Paragonimus have been reported which
added Jan 2016 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Paragonimus species, a parasitic lung fluke (flat worm). More than 30 species of trematodes (flukes) of the genus Paragonimus have been reported which
co URSE Medical Microbiology 3 COURSE CODE MMB310S
 @ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
@ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files
 World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files Contents Malaria Junior 1 Senior...2 Dengue Fever Junior 3 Senior.. 4 Chikungunya Junior....5 Senior. 6 Lyme disease Junior 7 Senior 8 Junior Disease Fact
World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files Contents Malaria Junior 1 Senior...2 Dengue Fever Junior 3 Senior.. 4 Chikungunya Junior....5 Senior. 6 Lyme disease Junior 7 Senior 8 Junior Disease Fact
