This booklet was supported by an educational grant provided by: Living with Psoriatic Arthritis
|
|
|
- Dominick Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This booklet was supported by an educational grant provided by: Living with Psoriatic Arthritis
2 PERSONAL DETAILS 36 per Other 20 per annum ( 36 + donation) annum OAP
3 Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a form of arthritis that in most cases affects the skin and the joints. This booklet is designed for anyone who has Psoriatic Arthritis or suspect they might have it. In most cases people with PsA develop the condition following the onset of psoriasis. This does not mean that all people with psoriasis will develop PsA. Due to the similarities of symptoms it may sometimes be confused with other forms of arthritis. This booklet explains the condition and symptoms that may arise and helps with diagnosis and management of PsA. You will fi nd out about the different approaches to living with the condition as well useful advice on exercise, nutrition and self-management training. There is also some information on your healthcare team as well as the various benefi ts that may be available to you. 1
4
5 Contents Introducing Psoriatic Arthritis 5 What happens in PsA, what the causes are and what parts of the body are affected? Early signs and symptoms How a diagnosis is reached Managing Psoriatic Arthritis 10 How to communicate and get the best from your healthcare team Treating Psoriatic Arthritis Taking care of your Psoriatic Arthritis condition 23 Take care of your joints Exercise and rest Nutrition and supplements Complementary Therapies Taking Control 35 Coping with pain and fatigue Relaxation and coping skills Dealing with emotions and relationships Practicalities 42 How to manage at home Help with work and education Mobility and transport Finances and access to benefi ts Support from Arthritis Ireland 51 Courses Helpline 3
6 4
7 INTRODUCING PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is an autoimmune disease - a form of infl ammatory arthritis that can cause pain, swelling and sometimes damage to any joint in the body. It is a condition that strikes in two ways, requiring extra care and attention. It usually occurs in people who already have psoriasis. It is a rarer form of arthritis compared to other forms of the disease (Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis). About 1 in 50 people have psoriasis and about 1 in 14 of them will develop PsA, so having psoriasis does not automatically mean you will have PsA. In fact most people with psoriasis never develop it. Although PsA generally occurs after psoriasis develops there are cases where the arthritis develops fi rst. PsA usually begins slowly spreading to other joints over a period of a few weeks or even months. In rare instances PsA can develop quickly and can be quite severe. It is an unusual arthritis because it can look very different from person to person. At 32, I wasn t expecting a diagnosis of arthritis but it was a great relief to finally have an explanation for the pain I was feeling. 5
8 What happens? To explain what happens in PsA it helps to understand how both arthritis and psoriasis can affect the body. A healthy immune system releases antibodies agents that act as natural defences against injury or disease that heal the body in times of distress. Sometimes however an autoimmune disease occurs and turns the body against its own tissues. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the immune system becomes confused and decides to attack the skin. It leads to a condition that causes a red, scaly rash, especially on the elbows knees, back, buttocks and scalp. However some people develop PsA before the condition while others will never develop the skin condition. PsA is a type of infl ammatory arthritis and an autoimmune disease. When it occurs the joints become the target of the PsA attack. What causes PsA? At present the exact cause is not known. Research has shown that a particular combination of genes makes some people more likely to get psoriasis and PsA. However having genes that predispose you to PsA does not necessarily mean you will develop this disease. Some people think that an event has to occur to trigger it. Unfortunately we don t know what that trigger is. It could be a viral infection, trauma or something else in the environment. There may be more than one trigger. The first signs I noticed were changes in my nails and I had a lot of pain in my knees and toes. 6
9 Which parts of the body are affected? Any of the 78 joints in the body can be affected by PsA but some are more likely to be affected than others. These are outlined in the diagram below: PsA also affects the body in certain patterns. They have been categorised into 5 different groups: 1. Asymmetric Pattern This is the mildest form where PsA affects 1-3 joints on different sides of the body. 2. Symmetric Pattern PsA involves many more joints and looks very much like rheumatoid arthritis. 3. Distal pattern PsA affects the small joints in the fi ngers and toes closest to the nail. 4. Spinal Pattern PsA affects the spinal column and may cause infl ammation and stiffness in the neck, lower back, spinal vertebrae, or sacroiliac region (pelvic area), making motion diffi cult. 5. Destructive Pattern PsA is a severe, painful deforming type of arthritis. It primarily affects the small joints in the fi ngers and toes closest to the nail leading to lost function of the 7
10 involved joints. It also is frequently associated with lower back and neck pain. This pattern is very rare and is also known as arthritis mutilans. While it is most commonly associated with joints, psoriatic arthritis is a systemic condition, meaning that over time the infl ammation that characterises it can affect multiple joints and even organs. Early signs and symptoms As with other forms of arthritis, the symptoms of PsA vary among different people. Many symptoms are common to other forms of arthritis, making the disease tricky to diagnose. Here s a look at the most common symptoms and the other conditions that share them A red scaly skin rash. Thickening, discoloration and pitting of the nails. Stiff, painful, swollen joints. PsA typically affects the ankle, knees, toes and lower back. The joints at the tips of the fi ngers may also swell confusing it with gout, a form of infl ammatory arthritis that typically affects only one joint. For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Understanding Arthritis or visit Dactylitis: This is a sausagelike swelling of the fi ngers or toes.this symptom is one 8
11 that often helps differentiate PsA from RA, in which the swelling is usually confi ned to a single joint. Enthesitis: People with PsA often develop tenderness or pain where tendons or ligaments attach to bones. This commonly occurs at the heel (Achilles tendinitis) or the bottom of the foot (plantar fasciitis), but it can also occur in the elbow (tennis elbow). Each of these conditions could just as easily result from sports injuries or overuse as from PsA. Pain and swelling at the back of the heel. Eye infl ammation (less frequent). Diagnosis There is no single test for psoriatic arthritis, but the diagnosis is based on your symptoms and a physical examination. It is easier to diagnose if you have psoriasis along with red swollen fi ngers or toes. Psoriasis and PsA occur more frequently in some families than in others so your doctor may ask about your family s medical history. Sometimes the doctor may make a diagnosis by eliminating other conditions with similar symptoms. He may therefore take a sample from the joint to rule out the presence of gout crystals. Some of the symptoms of PsA are also similar to other forms of arthritis and it can sometimes be diffi cult to distinguish between psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Your doctor may therefore take a blood test for rheumatoid factor to eliminate the possibility of RA. If several joints are affected, your doctor will consider features such as the pattern of the arthritis that is, which joints are affected. Your doctor may also send you for x-rays, MRIs and blood tests to rule out these conditions. Establishing an accurate diagnosis is very important because there are many treatment options to manage the symptoms of PsA. 9
12 MANAGING PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS The importance of early intervention PsA causes infl ammation (swelling, pain and warmth) in the affected joints. PsA can cause permanent joint damage quickly when it is not treated and controlled. This damage can even occur when the pain is not severe. Once damage occurs, it is not reversible and can cause signifi cant pain and disability. Research has confi rmed that treating PsA early and aggressively often improves the long-term outcome and signifi cantly reduces damage. Early intervention and timely treatment therefore is critical to control the condition. Since there s no single test for arthritis, I had a number of tests to get an accurate diagnosis. Then at least I knew I could start treatment. 10
13 Communicating with Health professionals It is important to make the most of your appointments. Give as much information as you can, and try to be as specifi c as possible when you describe how things are going. It is important to keep notes between appointments and write down what you want to say before hand. Your appointment may not always be at a time when you are feeling at your worst, so this can really help to give the full picture. You can also make notes when you are there. If you don t understand what your doctor is telling you, ask for a more detailed explanation. Don t be put off by medical jargon. It can sometimes take time to fi nd the treatment that works best for you. There may be some periods when different treatments have to be tried and their effects monitored. Before making a decision, you should understand what you can expect from your medication, what its possible side effects are and other information. It is important to develop a good relationship with your healthcare team. Prescription medication may not be suffi cient and other treatments such as physiotherapy and topical ointments may be necessary. Over time your treatment may need to be adjusted. It is important to keep a log of your progress. You should also discuss a self-management programme with your doctor. Exercise and nutrition play an all-important role. For more information on getting the best from your health professionals, see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Let s Talk Arthritis or visit
14 Your healthcare team A number of health professionals may be involved in your treatment: General Practitioner Your GP will generally be your fi rst point of contact, and will probably be the person who refers you to a consultant rheumatologist. Your GP may also be responsible afterwards for your ongoing care and recommend one or more health professionals to contribute to your overall treatment. Rheumatologist Rheumatologists are specialists trained in diagnosing and treating arthritis and rheumatic diseases. They are mostly based in hospital rheumatology units. They will establish your diagnosis and identify a suitable treatment plan for you. You will probably see the rheumatologist regularly to monitor your disease and treatment. Nobody knows how arthritis affects me better than me. By filling in my healthcare team with all the details, they worked out how best to help me. 12
15 Rheumatology Nurse A rheumatology nurse specialises in rheumatology and has specialist experience in looking after your physical, emotional and social needs. Some rheumatology nurses can prescribe medication. Physiotherapist A physiotherapist can help you maintain the strength, movement and function of the joints and muscles affected by your arthritis. Your physiotherapist will offer you treatment and advice about an exercise programme, hydrotherapy, relaxation techniques or splinting. He or she will be closely involved in your rehabilitation after any surgery. Occupational Therapist An occupational therapist can advise you on protecting your joints from further damage, for example by using splints on your wrists or hands. He or she can advise you on altering the way you perform everyday tasks to reduce the strain on your joints. They can also give you advice about equipment to make your life easier at home or in the workplace. Podiatrist A podiatrist will help if you have problems with your feet or ankles. They try to prevent joints altering and improve their position if there are already deformities. They can provide moulded insoles to hold your foot in a better position. They will assess your foot care needs and offer advice on special footwear. Orthotist An orthotist makes splints to support and position joints. Radiographer A radiographer takes X-rays and MRI scans. 13
16 Psychologist PsA can affect your emotional well being. If you are becoming very depressed or have diffi culty adjusting to the condition you may be referred to a psychologist. Pharmacist Your pharmacist can provide lots of information on the drugs you are prescribed. They can be very helpful with over the counter medication as well as topical treatments for your psoriasis. A pharmacist is also aware of the problems some over the counter treatments cause when combined with prescription medication. They can advise you on the right course of action. Dietitian A dietitian will help you eat healthily and show you how to change what you eat if you need to lose weight. Being overweight can put extra weight on your joints, particularly the back and leg joints. Dermatologist It is equally as important to get treatment for the psoriasis. This may involve one or a combination of medication and topical treatments. The dermatologist jointly manages your care with the rest of your team. 14
17 Treating Psoriatic Arthritis Once your diagnosis is confi rmed, there are many treatments that can help decrease your pain and increase your movement. Non-medication therapies such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, education, physical activity and relaxation techniques can all be helpful in the treatment of PsA. Drugs The process of infl ammation is similar in the skin and joints, so treatment aimed at one aspect of the condition often helps the other as well. The general approach to treating PsA is to reduce joint infl ammation and prevent long-term damage to the joints. The cornerstone of therapy is Disease Modifying Anti- Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDS). They are often used in combination with Non- Steroidal Anti-Infl ammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and /or Corticosteroids (steroids). Although NSAIDs and steroids slow down the day-to-day infl ammation, they don t affect the long-term outcome of the disease. For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Drugs and Complementary Therapies or visit A newer class of medication called biologics has revolutionised the treatment of PsA. These medications, which can be used in combination with DMARDs, also suppress infl ammation and help prevent damage to the joint. Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) Disease-modifying drugs (DMARDS) are a class of medications used to treat infl ammatory types of arthritis, such as psoriatic arthritis. They help by tackling the causes of infl ammation (pain swelling and stiffness) in the joints. DMARDs are important because they help prevent damage to the joint. 15
18 Doctors know that prescribing a DMARD early on is important to slow, or even stop the progression of joint damage, but it cannot fi x joint damage that has already occurred. DMARDs will however, change the way the condition progresses and hopefully will stop your arthritis from getting worse. Most DMARDs will start to work in about six to twelve weeks; however some may take longer up to three to four months. While you are waiting for the DMARD to work, your doctor might prescribe an additional medication, such Examples of DMARDs include: Methotrexate (Maxtrex ) Sulfasalazine (Salazopyrin, Sulazine Ec ) Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ) Ciclosporin (Neoral, Sandimmun ) Lefl unomide (Arava ) Azathioprine (Imuran, Azamune, Immunoprin ) as a steroid or an NSAID, to help control the symptoms. Your doctor will recommend a therapy that is best suited to your type and stage of arthritis, other medical problems and medications. Sometimes these drugs are given by injection. Taking any medication carries some risk, which must be balanced against the potential benefi ts. It is important to recognise that the risk of joint damage and permanent disability is much greater than the risk of side effects from DMARDs to control the disease. When properly monitored, the vast majority of side effects are rare and most are reversible by adjusting the dose or switching medications. The decision to use DMARDs will depend on a number of factors, including how much effect NSAIDs have had, how active your arthritis is and how likely it is that you ll have further joint damage. Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors This newer therapy offers a treatment option for people who cannot use DMARDs or when one of these type of medicines did not work. It works by reducing the activity of an enzyme in the body called phosphodiesterase 4 which is involved in the process of inflammation. Apremilast (Otezla ) is one such medication. 16
19 Biologic Therapies Biologic therapies are a newer group of disease-modifying drugs that may be used if other DMARDs aren t working well enough. These are given either by injection or through a drip into a vein. This also includes a category of medicines called biosimilars. These drugs are follow-on versions of original biological medicines. They are independently developed after the patent protecting the original product has expired. Biosimilar medicines are intended to have the same mechanism of action as the original biological medicines, and are designed to treat the same diseases as the innovator s product. Two biosimilars are currently avalable in Ireland for PsA - Infl ectra and Remsima. Biologic therapies used for treating psoriatic arthritis include: Adalimumab (Humira ) Infl iximab (Remicade, Infl ectra, Remsima ) Etanercept (Enbrel ) Golimumab (Simponi ) Ustekinumab (Stelara ) Certolizumab Pegol (Cimzia ) 17
20 When taking almost all DMARDs you ll need to have regular blood tests which allow your doctor to monitor the effects the drug has had on your condition but also to check for possible side-effects, including problems with your liver, kidneys or blood count. Points to remember when taking biologic therapies: Prior to starting biologic treatments you may be asked to get a chest x-ray, tuberculosis (TB) test and hepatitis test. If you have an infection, or suspect you have one, contact your rheumatology team as you are at an increased risk of infection on this treatment because it can suppress the immune system. If you have an infection it is likely that your doctor will tell you to skip a dose of your medication. Do not restart your medication until you have discussed this with your doctor. Subcutaneous injections (medication received by injection under the skin) can leave injection site reactions such as redness, itchy, raised skin or tenderness around the site. This will often disappear after a few days and usually becomes less frequent over time. It is important to tell all doctors or dentists that you are taking biologic therapy. It is often recommended that you avoid live vaccines such as polio or rubella while on biologic treatment and ask your doctor about which vaccines are suitable. It is recommended that anyone on biologic treatment is immunised against the fl u every year and receive the pneumonia vaccine once every 5 years. Ensure you attend for your regular blood tests while on this treatment. 18
21 If you are planning to become pregnant speak with your rheumatologist as many of the treatments require that you stop treatment and remain drug free from 3 weeks to 1 year before you conceive. It is unknown if many of the biologic treatments are passed into breast milk and for this reason it is recommended that women stop treatment while breastfeeding or speak with their rheumatology team about potential risks. If you ve been in contact with someone who has shingles or chicken pox and you haven t had chicken pox it is advised that you contact your rheumatology team. Non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications used to treat the pain and infl ammation of arthritis. They act by blocking the infl ammation that occurs in the lining of your joints. They can be very effective in controlling pain and stiffness. Usually you ll fi nd your symptoms improve within hours of taking these drugs but the effect will only last for a few hours, so you have to take the tablets regularly. There are about 20 NSAIDs available, including: Ibuprofen (Brufen, Nurofen and others) Diclofenac (Voltarol, Diclomax, Difene ) Naproxen (Naprosyn and others). Like all drugs, NSAIDs can sometimes have side-effects, but your doctor will take precautions to reduce the risk of these, for example, by prescribing the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible period of time. 19
22 NSAIDs can cause digestive problems (stomach upsets, indigestion or damage to the lining of the stomach) so another type of drug, called a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is sometimes prescribed to help protect the stomach. NSAIDs also carry an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Although the increased risk is small, your doctor will be cautious about prescribing NSAIDs if there are other factors that may increase your overall risk, for example, smoking, circulation problems, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes. COXIBs are a newer class of NSAIDs that have been developed to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeding. Although COXIBs are safer on the stomach, they have all of the other side effects of NSAIDs and may still cause indigestion, nausea, stomach cramps and heartburn. All NSAIDs have the potential to cause fl uid retention in the body (oedema) and may raise the blood pressure or precipitate heart or kidney failure in some individuals. Speak to your doctor about whether you are at risk for these kinds of side effects. You can take NSAIDs along with DMARDs, and sometimes you might need to take more than one DMARD. Steroid injections Steroid tablets aren t generally used for psoriatic arthritis. However, your doctor might recommend steroid injections if your joints are particularly painful or your ligaments and tendons have become infl amed. 20
23 Side effects Taking drugs can be a worrying business, and you may be concerned about side effects. You will be carefully monitored for the side effects of certain drugs, with regular blood tests. Discuss possible side effects with your doctor and fi nd out what to do if you experience them. Side effects are not inevitable. Not everyone will get them and some may disappear over time. Sometimes the dose can be reduced; some side effects can be treated individually. And there may be another drug that does the same job but suits you better. Go back for advice before you stop taking any drugs unless the side effects are severe. And never stop taking steroids suddenly. You will need to take time to weigh up the risk of side effects against the benefi ts of treatment. Surgery People with PsA don t often need surgery. Very occasionally a damaged tendon may need surgical repair. Sometimes, after many years of disease, a joint that has been damaged by infl ammation is best treated with joint replacement surgery. This may help people with severe advanced PsA who have not responded to conservative pain management for their condition. Benefi ts include less pain and better movement and function. It s important to remember that surgery is not a treatment for the infl ammation of PsA. If your psoriasis is bad in the skin around the affected joint, your surgeon may recommend a course of antibiotic tablets to help prevent infection. Sometimes psoriasis can appear along the scar left by an operation, but this can be treated in the usual way. For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Surgery and Arthritis or visit
24 Skin Treatments Your skin will usually be treated with ointments. There are 5 main types: Tar-based ointments Dithranol-based ointments (it s very important not to let these come into contact with normal skin) Steroid-based creams and lotions Vitamin D-like ointments such as calcipotriol and tacalcitol Vitamin A-like (retinoid) gels such as tazarotene Properly caring for your skin will help you manage your symptoms. If you have severe psoriasis you should see a dermatologist. Other treatments If the creams and ointments don t help your psoriasis, your doctor may suggest the following: Light therapy-short spells of exposure to high-intensity ultraviolet light Retinoid tablets Note that many of the DMARDs used for psoriatic arthritis will also help your skin condition. Similarly, some of the treatments for your skin may help your arthritis. Treatments for nail psoriasis are usually less effective than the skin treatments. Many people use nail varnish to make the marks less noticeable. 22
25 TAKING CARE OF YOUR PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Flare management What is a fl are? A fl are, or acute episode of infl ammation, occurs when you have painful or swollen joints that won t settle down, and/or increased pain. How do I know if I am in a fl are? There are a number of signs that you might be in a fl are: You will be experiencing sore, infl amed or painful joints over a number of days -this can be in one or more joints. You are experiencing longer than usual morning stiffness You may be experiencing more fatigue than you normally do Your blood tests may report high levels of infl ammation 23
26 By recognising that you are experiencing a fl are early you can get a head start on managing it. What can bring on a fl are? There are a number of factors that can contribute to a fl are: Stress Another illness such as a infection Medication are you taking your medication correctly? Perhaps you may need more or different medication? Overdoing it Overusing a joint How do I manage a fl are? Here are some general tips for managing a fl are: Keep a diary of your symptoms, this will help your healthcare team to see if there are any triggers. Take painkillers if needed. Try to keep stress free- remember this will pass. Apply hot or cold packs to joints. Do gentle range of motion stretches. Use breathing techniques. Try to get a good night s sleep. Use an electric blanket to alleviate morning stiffness. Don t be afraid to ask for help. Balance rest and activity. 24
27 Plan and prioritise your daily activities, you will be less likely to get carried away and over do things. Break bigger tasks into small more manageable tasks. Speak to your healthcare team Take care of your joints It is important to start looking after your joints as soon as you know you have arthritis. You may have to re-learn the way you do things, and become aware of what you are doing all the time, not just when your joints are stiff or hurt. The following tips could help you use your body more effectively: Spread the load - use both hands to lift and hold, for example. Use less effort and shift rather than lift - slide heavy pans along a kitchen top. Use larger, stronger joints - protect the fragile joints in your fi ngers and wrists by using larger ones. So rather than pushing a door open with your hand and wrist, use your shoulder or hip. Don t grip things too tightly - with pens, for example, choose a fatter one, hold it as loosely as possible or expand the grip with padding. Change positions often - shift position or stretch every half an hour to help you avoid joint stiffness, fatigue and pain. Watch your posture - if you slouch, the weight of your body falls forward, putting added strain on muscles and joints. 25
28 Exercise and Rest Get the balance right Exercise can be the furthest thing from people s minds when they live with pain on a daily basis. However, for people with arthritis, the benefi ts of exercise are enormous. Exercise protects joints by keeping the muscles strong and keeping you mobile. It is also good for pain and stress and can help you lose any extra weight that puts strain on joints. Infl ammation can lead to muscle weakness and stiffness in the joints. Exercise is important to prevent this and to keep your joints working properly. However, infl ammation can also make you feel unusually tired so you may fi nd you need to take more rests than usual. Rest is important, especially when your joints are infl amed or your arthritis fl ares up badly. Resting infl amed joints makes them more comfortable, but too much rest will make them stiff. Therefore it is important to strike a balance between rest and activity. Your doctor or physiotherapist will be able to advise on suitable forms of exercise depending on which joints are most affected. However, you ll need to fi nd out for yourself the right balance between rest and exercise. 26
29 Plan an exercise programme that is right for you Strong muscles and tissues support those joints that have been weakened and damaged by arthritis. Exercise won t make your arthritis worse as long as it is the right sort. The wrong sort of exercise could put strain on your joints and damage them further. A properly designed programme of physical activity reduces pain and fatigue, improves mobility and overall fi tness and alleviates depression. It allows someone with arthritis to have a more productive, enjoyable life. Your GP can refer you to a physiotherapist who can help you work out a programme combining fl exibility (range of movement), strengthening or aerobic exercises: Range of Movement Range of movement (ROM) exercises form the backbone of every exercise programme. Everyone should do these as they help maintain fl exibility and are important for good posture and strength. The exercises involve taking joints through their full range of movement and then easing them a little further. ROM exercises are done smoothly and gently so they can be done even when in pain. To achieve the most benefi t, these exercises should be done daily. Strengthening Strengthening exercises are especially benefi cial, because they help to strengthen the muscles, which move, protect and support your joints. Many people become less active when they For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Physical Activity and Arthritis or visit develop arthritis because of the pain and fear of causing damage. This can lead to muscle wastage and weaker joints. By developing strong muscles, joints become more stable and activities such as walking and climbing stairs are 27
30 easier. Start slowly, gradually building up the repetitions. As the muscles get used to doing more, they become stronger. The type of exercises you do will depend on which joints are affected and how severe your condition is. Always check with a doctor or physiotherapist before starting a regime. Aerobic Aerobic exercise is any exercise that raises your heart rate. This type of exercise burns off calories, speeds up the body s metabolism, helps maintain a strong heart and helps muscles work more effectively. It also helps control and reduce weight, improves sleep, strengthens bones, reduces depression and builds up stamina. The best forms of aerobic exercise for people with arthritis are walking, cycling and swimming. Begin any exercise by stretching to warm up. To get any benefi t, aerobic exercise must be done for a prolonged period (30-60 minutes) building up to two or three times a week. You are at a good level if you start to sweat and can still hold a conversation at the same time. Check with a doctor before beginning any regime. These exercises done correctly and consistently will provide some relief from the pain of arthritis, help with good posture, and increase your energy and vitality. 28 Check out Arthritis Ireland s Take Control with Exercise DVD and book, a tried and tested exercise programme for people with arthritis. For more information visit
31 Tips for exercise Begin gently and build up gradually. Do a little every day, rather than a lot every now and then. Find something you enjoy. Try walking, swimming, dancing or cycling - but avoid high-impact activities like squash or other sports that will jar. Exercise when you are least in pain, stiff or tired and your medication is most effective. Do your range of movement exercises at least once a day. First thing, they ll help ease morning stiffness, last thing at night they ll help it stop developing. Listen to your body and don t overdo it. If you feel more pain two hours after exercising than you did before, do less next time. Don t continue with an exercise or activity that causes severe pain, stiffness or fatigue. If you have a fl are-up, only do range of movement exercises. Healthy Eating Your body needs a range of nutrients, so make sure you eat a healthy, balanced diet. Include lots of fruit, vegetables, pasta, pulses (such as beans and lentils), fi sh and white meat. Try to also cut down on sugary and fatty foods. Although no specifi c diets have been found to be very effective for PsA, studies on essential fatty acids (found in oily fi sh) show that they can ease joint pain and stiffness. Try to include more of these in your diet and consider taking a fi sh oil supplement. Some people claim that some foods seem to make their infl ammation or pain worse. If you can work out which food is the trigger, talk to your doctor for advice. It is important you don t miss out on essential nutrients. Research in this area is complicated and much more needs to be done. 29
32 The most important link between your diet and arthritis is your weight. Being overweight puts an extra burden on your weight bearing joints (back, hips, knees, ankles and feet). Maintaining an appropriate weight will help you more than any food supplements. If you are overweight and have arthritis consider a balanced diet as a way to help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight. For others, healthy eating may give you the energy to complete your daily activities. Proper nutrition is vital to controlling body weight and managing arthritis symptoms. If you are considering a diet talk it over with your doctor or dietician fi rst. Beware of diets that claim to cure arthritis, and never begin a diet that involves stopping medication without discussing it with your doctor fi rst. For more information read Arthritis Ireland s booklet Healthy Eating and Arthritis or visit Supplements People with arthritis often take various supplements including herbal remedies, homeopathic medicines, vitamins, minerals and dietary supplements. If you decide to try therapies or supplements you should be critical of what they re doing for you, and base your decision to continue on whether you notice any improvement. 30
33 Never stop taking prescribed drugs without talking to your doctor fi rst. Before you start taking supplements: Find out as much as you can. Remember that supplements will not cure arthritis. Check with your doctor or pharmacist for interaction with your prescription drugs. Tell your doctor if you are taking any supplements and report any side effects immediately. Keep a record of how you feel so you can see if they are having an effect. Buy brands from reputable manufacturers. Consider the cost - taking supplements can be expensive. Sleep Getting a good night s sleep plays an important role when living with PsA. When we sleep, our bodies secrete hormones that repair the wear and tear we ve done throughout the day. If you are experiencing broken sleep it s important to talk to your healthcare team as it may be something medication- related e.g. taking steroids late at night can keep you wide awake. It could also be pain that is causing you to wake so this is also a signal to discuss it with your doctor. A poor night s sleep can make managing your arthritis more diffi cult. Here are some tips to improve your sleep routine: Relax before bed, take some time to wind down. Have a routine go to bed and get up at the same time each day. 31
34 Take a warm bath or shower before bed, this may help if you are in pain. Reduce your caffeine intake and avoid alcohol before bed. Avoid using electrical gadgets in the bedroom or before sleep e.g. TV, phone, computer. Use a good quality pillow to support you neck and shoulders. If you are unable to sleep after 20/30 minutes, get up but avoid anything that stimulates the brain e.g. watching TV. Exercise regularly to help with getting a good night s sleep. Try to avoid worrying in bed. Try stress management strategies. Ensure muscles are as relaxed as they can be- deep breathing/ relaxation techniques may help with this. Complementary Therapies A popular option for many people with arthritis is complementary and alternative therapies, which are treatments that fall outside the scope of traditional medicine. Examples include: Naturopathic medicine Special herbs Acupuncture Massage Aromatherapy 32
35 Alexander Technique Refl exology Meditation There is no scientifi c evidence that suggests any form of complementary medicine will cure you, though in some cases certain techniques may ease pain, stiffness and some of the side effects of taking drugs, as well as helping you relax. Some points to consider when thinking about complementary therapies: Always discuss it with your doctor fi rst Always attend a legally registered therapist, or one who has a set ethical code and is fully insured Be critical of what it is doing for you and base your decision to continue on whether you notice any improvement Never stop taking your prescribed medication without talking to your doctor fi rst For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Drugs and Complementary Therapies or visit Tell your therapist about any drugs you are taking 33
36 Regard any practitioner who advises you to stop conventional medication with extreme caution Ask how much a treatment will cost, and how many sessions you will need to feel a benefi t Smoking and arthritis Cigarette smoking, whether you have PsA or not, has no positive effects on any aspects of your health. People living with PsA are strongly discouraged from smoking as it makes symptoms worse. Studies have demonstrated that smoking is associated with poor long-term outcomes. Research has also shown that it increases the risk of heart disease putting people living with PsA at a higher level of risk. If you are smoker, one of the best things that you can do for your overall health is to quit smoking. If you need help or advice to stop smoking you can contact the National Smokers Quit Line on or Many local hospitals also run clinics to help you quit. Being diagnosed with arthritis had a huge impact on my self-esteem and confidence. I felt I wasn t capable of leading the life I had previously. Eventually I opened up about it to my family and they helped me to realise that arthritis does not change who I am. 34
37 TAKING CONTROL Any long-term condition can affect your moods, emotions, and confi dence, and it can have an impact on your work, social life and relationships. Talk things over with a friend, relative or your doctor if you do fi nd your condition is getting you down. You can also contact support groups if you want to meet other people with PsA. Emotions Everyone s experience of arthritis is different. Not all people experience the same symptoms, level of pain, or fatigue or the same feelings. Don t be surprised if you feel frustrated one day and perhaps angry the next. It is good to let your emotions out. Bottling them up can make things worse. Pain can usually be controlled, stiffness and infl ammation relieved, and there are ways to overcome the loss of strength, grip and mobility. Some people fi nd that their lives do not change that much and that they can more or less carry on as normal. Some people become stronger and more determined as a result of having to adapt their lives to fi t in with their arthritis everyone is different. For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Coping with Emotions or visit
38 Your own reactions to arthritis will differ from week to week, but it is perfectly natural to feel out of sorts sometimes. Relationships Sharing information about your condition with family and friends can really help them to understand what you re going through. They may really want to help, but do not know how. You may be worried about letting them down or about depending on them too much. Talking and listening is the key. Explain how your arthritis affects you and be as clear as you an about how you are feeling. Relations may come under a bit of strain. If you have a partner, talk to them about how you feel, both physically and emotionally an encourage them to asks questions. Sex can sometimes be painful, but experimenting with different positions will usually provide a solution. If you are feeling stiff or having trouble moving around it is hard to be spontaneous; even a hug can be diffi cult if you are in pain. There will be times when you are just too tired of painful to get close to your other half, but there are alternatives. Try different positions of supporting your body with pillows and cushions to make lovemaking more comfortable Have a warm bath beforehand to loosen up your joints Ask your partner for a gentle massage Talk to your healthcare team Pregnancy 36
39 PsA won t affect your chances of having children or a successful pregnancy. The arthritis often improves during pregnancy, although your symptoms may return after the baby is born. Some drug treatments given for PsA should be avoided when trying to start a family. For instance, sulfasalazine can cause low sperm count (this isn t permanent) and you shouldn t try for a baby if you or your partner are on methotrexate or have been using it in recent months. If you re thinking about starting a family, you should discuss your drug treatment with your doctor well in advance so that your medications can be changed if necessary. Both psoriasis and PsA do tend to run in families to some extent. It there s a history of psoriasis or PsA in your family, then your children may be more likely than most to get PsA, but the risk of passing it on directly is still low. 37
40 Relaxing and Coping Skills Developing good relaxation and coping skills can help you maintain balance in your life, giving you a greater feeling of control over your arthritis and a more positive outlook. Relaxing the muscles around a sore joint reduces pain. There are many ways to relax. Try deep breathing exercises. Listen to music or relaxation tapes. Imagine or visualise a pleasant activity, such as lying on a beach. Coping with Pain Pain is one of the biggest problems you are likely to face, and learning to cope with it can be a real challenge. It can be caused by infl ammation, loss of movement, damaged joints or muscle strain. Sometimes having PsA can feel like a never-ending cycle. Pain makes you tense your muscles and put you under stress. For more information see Arthritis Ireland s booklet Coping with Pain or visit Pain is very personal it can range from a dull ache to short stabs; and for some it comes and goes, while others have persistent daily pain. One of the hardest things is that other people can t see you pain and you may feel lost for words to describe it. 38
41 Changes, uncertainty and everyday diffi culties can knock your confi dence and leave you frustrated, depressed and angry. Depression wears you out and makes pain feel worse - and so it goes on. There is a lot you can do to develop the tools, skills and resources that will help you start to break this cycle and help you to learn how to self-manage your arthritis. Distraction The more time you spend thinking about your pain, the more pain you will feel. Try to distract yourself by doing or thinking about something you really enjoy or fi nd absorbing, and turn your focus away from the pain. This can work to get you through short activities as well as longer-lasting pain. Heat and Cold Heat: Taking a warm shower and using warm packs are great ways to help reduce pain and stiffness. Always use a protective barrier, such as a towel, between the warm pack and the skin. Heat is ideal for: Relieving pain Relieving muscle spasms and tightness Relieving range of motion To avoid making symptoms worse, heat should not be applied to an already infl amed joint. Cold: Using a commercial cold pack or a home-made one (from crushed ice, ice cubes or a bag of frozen vegetables) can be helpful. Always use a protective barrier, such as a towel, between the cold pack and the skin, Cold is ideal for: Decreasing swelling Decreasing pain Constructing blood fl ow to an infl amed joint 39
42 For further details on using heat and cold to manage your arthritis, speak with your healthcare team. Managing Fatigue Most people feel tired after a hard day, but the fatigue that comes with PsA is altogether different. It tends to be worse during fl are-up, but varies from a stubborn, ongoing tiredness to a sudden drop in energy that leaves you completely wiped out. It may mean that you are too tired for even simple tasks, and can be extremely frustrating. Like pain, fatigue can vary a lot and may have a number of causes. But several things may be worth trying, to help you make the most of your energy: Decide on your priorities and pace yourself what do you really need to do? Can you rearrange your time so that you can do important tasks when you are at your best? Is there anything you can drop or do less frequently? Rest when you need to listen to your body and don t tough it out. Take a short nap or relax once or twice a day. Keep active when you are exhausted it is tempting to cut down on exercise, but muscles in a poor condition will tire sooner than the strong ones.try to get enough sleep only you know how much sleep your body needs. 40
43 Eat a healthy, balanced diet food is your body s fuel and you need it to keep going. Deal with feelings and relationships by talking openly about them. From time to time, your arthritis is going to get on top of you. Anger, frustration, uncertainty, depression, fears about whether you can cope or what the future holds - all of these feelings are very understandable and very common. Several things may help: Gather information. Talk to your health team or other people who are or know about PsA. You may fi nd that your fears don t match the facts. Ask for help and support from others if you need it. Accept your limitations try not to get too tangled up in wishing that things were different. Focus on the here and now, and remind yourself about what you can do and enjoy. Keep going even if it feels that nothing is working. Don t give up. Get out and about keeping up with friends can be tricky if you have problems with PsA but try and make space and time for a social life. 41
44 PRACTICALITIES Adjusting to PsA may not be easy, but there are plenty of sources of help. The fi rst step is fi nding out what is on offer and what your rights are. At Home There are many ways you can set things up at home to make sure your environment is as stress-free as possible. Equipment and adaptations There are lots of handy gadgets and tools and useful changes or adaptations that can help around the home. In the kitchen, for instance, they might include: rearranging cupboards and drawers so the things you use the most are nearby lightweight pans, mugs or kettle equipment with easy-to-use buttons and switches an electric tin opener, a cap gripper, or knives and peelers with padded handles a stool to sit on while you are preparing food, or a trolley for moving heavy items across the room devices for turning taps more easily It makes sense to try out a gadget before you buy it you could save a lot of money in the long run. Alternatively, make a list of criteria that the gadget must meet to avoid a bad purchase. If you fi nd you are doing a lot of work around the home, what about getting someone to help? Friends and family may be able to lend a hand. You could also think about paying a cleaner, or getting a handyperson in for bigger tasks. Local organisations 42
45 may be able to put you in touch with volunteers to help you with jobs around the house. Ask your local authority, citizen s information centre or library if they know of any such volunteers. Help with costs You may be able to get help with equipment or adaptations to your home. The Housing Adaptation Grant for People with a Disability, the Mobility Aids Grant Scheme and the Housing Aid for Older People Scheme are administered by your local authority. For further information on these schemes and to see whether you are eligible for help, contact the Housing Department of your local authority. There is no hard and fast rule on what you will get: following assessment you will be told what you are entitled to receive and you may have to contribute towards the cost. You may also have to wait a long time for an assessment to get equipment. If your needs change, contact your local authority so they can move you up on the waiting list. 43
46 Work and arthritis Most people diagnosed with PsA are of working age so you may well be settled in a career already. Only you can decide how much you want to tell people at work about your PsA. It may not affect your work at all other than time off for hospital appointments or surgery but hiding it and struggling on if you have diffi culties could make your arthritis worse. The best policy is to be positive, honest and clear about your needs, and help people understand what PsA means for you. For a while after diagnosis, you might fi nd it tough to go to work, but things should improve once your medication starts to take effect. Some people choose to work reduced hours or change to part-time while they are getting their disease under control. With advances in treatment for PsA, it is possible for most people to remain working. For more information and support on working with arthritis check out Arthritis Ireland s dedicated web site Managing your arthritis in the workplace 44
47 Smarter ways of working will help protect your joints and conserve energy. They can include: Organise your workspace most organisations can provide an ergonomic assessment of your workplace and workplace furniture. You could also ask an Occupational Therapist (OT) to advise you. An ergonomic assessment examines how suitable and comfortable your work area is. Take regular movement breaks for example, walking to the photocopier. Pace yourself don t overdo it. Get in touch with your Occupational Therapist for advice on a wide range of work-related issues. Be fl exible be prepared to change your working hours or work from home if it helps. Legislation As an employee with PsA, it is important that you know what support and advice you are entitled to. Under the law, employers must make reasonable accommodation for employees who have a disability. This means an employer is obliged to take appropriate measures to enable a person who has a disability to work unless those measures would impose an unreasonable burden on the employer. As an employee with a disability, you are entitled: to have access to employment to participate or advance in employment to undertake training Employers are not obliged to provide special treatment or facilities if it would place an unreasonable burden on them. 45
48 The Department of Social Protection website has information on services for employees with a disability, including the Workplace Equipment and Adaptation Grant, Employee Retention Grant and a Disability Awareness Training Support Scheme. Depending on how your PsA affects you, the time may come when you need to consider changing jobs. Some people do have to stop working altogether this is never an easy decision and it is important to get professional advice about your rights and options. Remember that giving up work does not mean that you are giving up life: retraining, further education and voluntary work may all open new doors. Education There is a lot of support and help available for people living with arthritis who are in higher education. A disability or access offi cer can help with a range of support services to ensure that students with arthritis have full access to the same facilities for study and recreation as the rest of the college community. Some people with arthritis may require extra time for exams, a scribe for exams, movement breaks, a laptop, or online notes. If you are going into higher education, you may be eligible for the Back to Education Allowance, paid by the Department of Social Protection. Various other education and training schemes exist. AHEAD (Association for Higher Education Access and Disability) have published a relevant booklet Accessing Third-level Education in Ireland A Guide for Students with Disabilities. 46
49 SOLAS is the Further Education and Training Authority in Ireland. It is responsible for funding, planning and coordinating training and further education programmes. For more details on schemes and training opportunities check out their website: Getting Around People with PsA often fi nd getting out and about diffi cult. Many rely on cars either driving themselves or getting lifts or public transport to get around. There are a few things you can try to make driving easier. An automatic gearbox and power steering will reduce strain. Minor adjustments, such as padded steering wheel, a headrest, extra side-mirrors or a wide-angled mirror may make driving easier. There are various means tested supports available including grants for adapting a vehicle, the Disabled Person s Parking Card and tax relief for necessary adaptations to vehicles. The Irish Wheelchair Association (Tel: or provide advice and information on all aspects of motoring. If you would like to learn to drive or have lost confi dence in your driving skills the Motoring Advice and Tuition Service in the Irish Wheelchair Association can provide assistance to you. If you are relying on public transport some forms of social welfare disability payments may entitle you to a Free Travel Pass, which allows you to travel for free on all public transports and selected private services. Benefi ts The Citizens Information Board offers a comprehensive booklet that outlines all entitlements for people with a disability, including rights relating to work education and training. You can get this booklet, Entitlements for People with Disabilities, by visiting your local Citizens Information Centre or contacting them on LoCall or You may be able to apply for state benefi ts to help with 47
50 the extra costs of having arthritis or if you are unable to work. Some of the main disability-related payments are: Social Insurance Payments Illness Benefit: This was previously called Disability Benefi t and is a short-term payment made to people who are under 66 and unable to work due to illness. It can be paid in the long-term. Your PRSI contributions or credits must be up to date. Invalidity Pension: Invalidity Pension is payable for as long as you are unable to work. At the age of 65, the personal rate of payment increases to the same rate as the State Pension (Transition). At age 66 you transfer to the State Pension (Contributory). Other Benefits: A Living Alone Increase is payable regardless of age if you live alone. You may also qualify for free travel and the Household Benefi ts Package, which includes allowances towards household bills. Rehabilitative work: You may be allowed to do rehabilitative or therapeutic work (maximum 20 hours a week) and retain your Invalidity Pension. You must get prior written approval from the Department of Social Protection before you start work. The Treatment Benefit Scheme: This is a scheme run by the Department of Social Protection that provides dental, optical and aural services to people with the required number of PRSI contributions. 48
51 Means-Tested Payments Disability Allowance: This is a long-term means-tested payment made to people with a disability. The disability must be expected to last at least a year. You must be aged between 16 and 66, satisfy both a means test and a habitual residence test, and have a specifi ed disability which results in your being substantially restricted in undertaking suitable employment. Your means and that of your spouse or partner are taken into account. Your parents means are not considered. You may qualify for a Living Alone Increase and the Household Benefi ts Package, which includes allowances towards household bills. If you are awarded Disability Allowance, you get a Free Travel Pass automatically. This allows you to travel for free and your spouse or partner to travel free in your company. If you are medically assessed as being unable to travel alone you may be entitled to a Companion Free Travel Pass. Health Service Medical Cards: Most medical cards are granted on the basis of a means test and / or medical need. Each case is decided on its merits but you may qualify if your income is not much above the guideline fi gure and your medical costs are exceptionally high. It may be possible for one or more members of a family (who would not otherwise qualify) to get a medical card in their own right if they have high medical expenses or needs. GP Visit Cards: The purpose of the card is to help people who are not eligible for medical cards with the costs of visiting a doctor. The card covers you for GP visits but nothing else. Drugs Payment Scheme: With a Drugs Payment Scheme (DPS) card, an individual or family in Ireland only has to pay a maximum amount monthly for approved prescribed drugs, medicines and certain appliances. Everyone in Ireland who doesn t have a medical card should apply for the DPS card. Everyone living in Ireland and certain visitors to Ireland are entitled to a range of health services either 49
52 free of charge or at reduced cost. If you need to attend a public hospital or stay overnight in hospital as a public patient, you may be liable for Hospital Charges. Medical card holders and certain other groups do not have to pay hospital charges. Tax Relief: You may get tax relief on certain health expenses, including prescription medication, which you have incurred and for which you have not been reimbursed. This claim should be made on a Med1 form, available from your local tax offi ce or online at Claiming benefi ts can be complicated and time-consuming, so it s worth getting expert help and advice from: a social worker from your local Health Offi ce a housing welfare offi cer from your local authority your citizens information service LoCall your local social welfare offi ce the Leafl et Request Line in the Department of Social Protection: LoCall online at 50
Keep moving. Self-help and daily living Keep moving. and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis.
 Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Psoriatic arthritis FACTSHEET
 1 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a disease where joints around the body become inflamed and sore. It can make moving about difficult and painful. People who have PsA also have
1 What is psoriatic arthritis? Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a disease where joints around the body become inflamed and sore. It can make moving about difficult and painful. People who have PsA also have
Managing your pain
 Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
Why is this important for you? Types of arthritis. Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk
 Spondyloarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk Spondyloarthritis: the care you should expect This information explains the care
Spondyloarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk Spondyloarthritis: the care you should expect This information explains the care
What sort of problems can arthritis cause?
 Here we ll identify some of the tasks that commonly cause pain, explain the principles of joint protection and give some examples of how to put them into practice. We can t cover every situation, but you
Here we ll identify some of the tasks that commonly cause pain, explain the principles of joint protection and give some examples of how to put them into practice. We can t cover every situation, but you
FACTSHEET F18 COPING WITH TIREDNESS
 COPING WITH TIREDNESS Many people with chest, heart and stroke conditions experience tiredness or fatigue. This factsheet explains some of the reasons why you might feel so tired. It also offers advice
COPING WITH TIREDNESS Many people with chest, heart and stroke conditions experience tiredness or fatigue. This factsheet explains some of the reasons why you might feel so tired. It also offers advice
Recovering at home. How will I feel when I get home? How should I look after my wound?
 How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
Psoriatic Arthritis- Secondary Care
 Psoriatic Arthritis- Secondary Care Our Psoriatic Arthritis: First Line Treatments information sheet gives information on the treatments that can be prescribed by a GP, or that might be prescribed if the
Psoriatic Arthritis- Secondary Care Our Psoriatic Arthritis: First Line Treatments information sheet gives information on the treatments that can be prescribed by a GP, or that might be prescribed if the
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
ARTHRITIS ACTION FACTSHEETS
 LAST REVIEW: MARCH 2017 COPYRIGHT OF ARTHRITIS ACTION PAIN MANAGEMENT Sometimes the cause of pain such as a broken bone is obvious. Other times the cause is less clear, especially if pain is in areas that
LAST REVIEW: MARCH 2017 COPYRIGHT OF ARTHRITIS ACTION PAIN MANAGEMENT Sometimes the cause of pain such as a broken bone is obvious. Other times the cause is less clear, especially if pain is in areas that
Drug information. Apremilast APREMILAST. is used to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Apremilast APREMILAST is used to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Apremilast is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage
Drug information Apremilast APREMILAST is used to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Apremilast is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage
Drug information. Sarilumab SARILUMAB. is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Sarilumab SARILUMAB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Sarilumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body. You
Drug information Sarilumab SARILUMAB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Sarilumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body. You
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis
 How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis Preparing for your Doctor s Appointment Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that often occurs with psoriasis of the skin, a condition that features
How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis Preparing for your Doctor s Appointment Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that often occurs with psoriasis of the skin, a condition that features
Palindromic rheumatism
 1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
Living Life with Persistent Pain. A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain
 Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Psoriatic Arthritis- Second Line Treatments
 Psoriatic Arthritis- Second Line Treatments Second line treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) are usually prescribed by a Rheumatologist, Dermatologist, or in a combined clinic where both the Dermatologist
Psoriatic Arthritis- Second Line Treatments Second line treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) are usually prescribed by a Rheumatologist, Dermatologist, or in a combined clinic where both the Dermatologist
Total ankle replacement. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
THE CIMZIA PATIENT GUIDE. what you need to know to get started. For internal use only. CZP-PRM :GPSRC Patient Starter Kit
 THE CIMZIA PATIENT GUIDE what you need to know to get started For internal use only. CZP-PRM-005483:GPSRC Patient Starter Kit What this booklet is for You re reading this booklet because you have been
THE CIMZIA PATIENT GUIDE what you need to know to get started For internal use only. CZP-PRM-005483:GPSRC Patient Starter Kit What this booklet is for You re reading this booklet because you have been
Dr. Berkson offers a list of some of the most common exercise-related injuries:
 AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco
 Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Sacroiliac joint Injection
 Sacroiliac joint Injection 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your sacroiliac injections, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need sacroiliac injections, what
Sacroiliac joint Injection 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your sacroiliac injections, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need sacroiliac injections, what
The best way to deal with back pain
 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
Drug information. Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB. is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Tofacitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing
Drug information Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Tofacitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing
Understanding bone metastases and XGEVA
 Understanding bone metastases and XGEVA Contents About bone metastases 3 About XGEVA 5 Dealing with common side effects of XGEVA 8 FAs about living with bone metastases 9 Notes 10 About bone metastases
Understanding bone metastases and XGEVA Contents About bone metastases 3 About XGEVA 5 Dealing with common side effects of XGEVA 8 FAs about living with bone metastases 9 Notes 10 About bone metastases
BACK PAIN. Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain
 BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
Ankylosing Spondylitis. Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy
 Trafford Hospitals Therapy Services Information for Patients Ankylosing Spondylitis Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy The primary aim of our service at Trafford General Hospital is to help you to
Trafford Hospitals Therapy Services Information for Patients Ankylosing Spondylitis Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy The primary aim of our service at Trafford General Hospital is to help you to
INTRODUCTION THE SPINE WHAT HAPPENS
 INTRODUCTION Ankylosing spondylitis or AS, is a form of arthritis that affects the spine, and can also affect other joints. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe,
INTRODUCTION Ankylosing spondylitis or AS, is a form of arthritis that affects the spine, and can also affect other joints. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe,
Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast
 Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast The aim of this leaflet is to give you some understanding of the problems you have with your condition and to provide some advice on how to manage this. It
Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast The aim of this leaflet is to give you some understanding of the problems you have with your condition and to provide some advice on how to manage this. It
The best way to deal with back pain
 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
Osteoarthritis of the neck
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
Drug information. Baricitinib BARICITINIB. is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Baricitinib BARICITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Baricitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body.
Drug information Baricitinib BARICITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Baricitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body.
PERSONAL DETAILS. 36 per Other 20 per annum ( 36 + donation)
 PERSONAL DETAILS 36 per Other 20 per annum ( 36 + donation) annum OAP Arthritis is a very common condition in Ireland affecting people of all ages and from all walks of life. Its symptoms often have a
PERSONAL DETAILS 36 per Other 20 per annum ( 36 + donation) annum OAP Arthritis is a very common condition in Ireland affecting people of all ages and from all walks of life. Its symptoms often have a
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
 What is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the joint tissue causing inflammation, stiffness, pain and extreme fatigue. If left
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the joint tissue causing inflammation, stiffness, pain and extreme fatigue. If left
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists
 Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists This fact sheet has been written for people whose hands, fingers and/or wrists are affected by osteoarthritis (OA). It provides general information about
Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists This fact sheet has been written for people whose hands, fingers and/or wrists are affected by osteoarthritis (OA). It provides general information about
Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond
 Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction to this booklet Receiving
Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction to this booklet Receiving
Your Journey to Living Well with Pain
 Ten Footsteps Your Journey to Living Well with Pain Learning how to manage your pain is a journey. Like any journey, it takes time and everyone s experience is different. We know from people living with
Ten Footsteps Your Journey to Living Well with Pain Learning how to manage your pain is a journey. Like any journey, it takes time and everyone s experience is different. We know from people living with
Your Guide to a Smoke Free Future
 Your Guide to a Smoke Free Future If you smoke, or if you have quit within the past 2 months, then ask for our detailed handout which provides information on how to begin and maintain a smoke-free lifestyle.
Your Guide to a Smoke Free Future If you smoke, or if you have quit within the past 2 months, then ask for our detailed handout which provides information on how to begin and maintain a smoke-free lifestyle.
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Exercising with Persistent Pain
 Exercising with Persistent Pain Why You Feel Pain When you are injured, your mind and body react. They protect the weak part of your body, and you feel pain when you try to use it. This protection is important
Exercising with Persistent Pain Why You Feel Pain When you are injured, your mind and body react. They protect the weak part of your body, and you feel pain when you try to use it. This protection is important
axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 1 What is spondyloarthritis? Spondyloarthritis is a general term that describes a number of types of inflammatory arthritis which share many articular and extra-articular features. Conditions which fall
1 What is spondyloarthritis? Spondyloarthritis is a general term that describes a number of types of inflammatory arthritis which share many articular and extra-articular features. Conditions which fall
Osteoarthritis of the hip
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the hip? The hip joint is formed by the top of the thigh bone and the pelvis. Its primary functions are to support the weight of the body and enable the legs to move. The hip
1 What is osteoarthritis of the hip? The hip joint is formed by the top of the thigh bone and the pelvis. Its primary functions are to support the weight of the body and enable the legs to move. The hip
Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know
 Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know This leaflet aims to answer your questions about taking methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). If you have any questions or
Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know This leaflet aims to answer your questions about taking methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). If you have any questions or
Fatigue after stroke. What is post-stroke fatigue? Who is affected by post-stroke fatigue?
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Fatigue after stroke Fatigue affects half of all stroke survivors, but the signs of fatigue are not always obvious to other people and
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Fatigue after stroke Fatigue affects half of all stroke survivors, but the signs of fatigue are not always obvious to other people and
Beyond Cancer Moving On
 Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Pelvic girdle pain is the name given to pain in any of the three pelvic joints (see below), lumbar spine and into the thighs. Symphysis pubis joint
 Pelvic girdle pain This leaflet offers more information about pelvic girdle pain (PGP). If you have any further questions or concerns, please speak to the staff member in charge of your care. What is pelvic
Pelvic girdle pain This leaflet offers more information about pelvic girdle pain (PGP). If you have any further questions or concerns, please speak to the staff member in charge of your care. What is pelvic
Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent
 Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
Coccygeal Denervation
 Coccygeal Denervation 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your coccygeal denervation, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need coccygeal denervation, what the
Coccygeal Denervation 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your coccygeal denervation, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need coccygeal denervation, what the
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Drug information. Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB. is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Helpline
 Drug information Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Secukinumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition
Drug information Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Secukinumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition
Chronic Low Back Pain
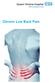 Chronic Low Back Pain This leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at the Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. It has been designed to give you accurate up-to-date knowledge
Chronic Low Back Pain This leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at the Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. It has been designed to give you accurate up-to-date knowledge
Foot and Ankle Surgery
 Information about Foot and Ankle Surgery Statement of Use The information in this leaflet is intended solely for the person to whom it was given by the health care team and is provided as a general information
Information about Foot and Ankle Surgery Statement of Use The information in this leaflet is intended solely for the person to whom it was given by the health care team and is provided as a general information
Managing Inflammatory Arthritis. What to Discuss with Your Health Care Team
 Managing Inflammatory Arthritis What to Discuss with Your Health Care Team Section 1 Introduction What to Discuss with Your Health Care Team This tool has been created with input from patients to provide
Managing Inflammatory Arthritis What to Discuss with Your Health Care Team Section 1 Introduction What to Discuss with Your Health Care Team This tool has been created with input from patients to provide
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment
 After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
Bunion Surgery. Patient information Leaflet
 Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
Patient Information for Consent
 Patient Information for Consent ER OS01 Total Hip Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of February 2017 Issued June 2016 Local information If you need any more information please contact your BMI
Patient Information for Consent ER OS01 Total Hip Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of February 2017 Issued June 2016 Local information If you need any more information please contact your BMI
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions
 Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Appendix Surgery. (Appendectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
DRAFT. The best way to deal with back pain
 Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic
 Department of Rheumatology Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Specialist Support This leaflet can be made
Department of Rheumatology Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Specialist Support This leaflet can be made
Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term
 Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term How to keep your treatment working... and why you don t want it to fail Regardless of the particular drugs you re taking, your drugs will only work when you take them.
Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term How to keep your treatment working... and why you don t want it to fail Regardless of the particular drugs you re taking, your drugs will only work when you take them.
Your home exercise and activity diary. Information for thoracic patients having lung resection surgery
 Your home exercise and activity diary Information for thoracic patients having lung resection surgery Contents Introduction 3 Physiotherapy at home before your operation General advice regarding exercises
Your home exercise and activity diary Information for thoracic patients having lung resection surgery Contents Introduction 3 Physiotherapy at home before your operation General advice regarding exercises
Sis for. smoking and pregnancy. Don t give up giving up. textphone
 Don t give up giving up. For friendly, practical advice on giving up smoking and where you can find help close to home, call the NHS Pregnancy Smoking Helpline 0800 169 9 169 textphone 0800 169 0 171 Sis
Don t give up giving up. For friendly, practical advice on giving up smoking and where you can find help close to home, call the NHS Pregnancy Smoking Helpline 0800 169 9 169 textphone 0800 169 0 171 Sis
Vibration (i.e., driving a Lack of exercise
 What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
Pain: You Can Get Help
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Pain: You Can Get Help Phyllis loves playing with her grandchildren, working in the garden, and going to bingo games twice a week. But, at age 76, the constant knee
National Institute on Aging AgePage Pain: You Can Get Help Phyllis loves playing with her grandchildren, working in the garden, and going to bingo games twice a week. But, at age 76, the constant knee
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
April 2016 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is
 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
{loadposition nhschoices} {loadposition relatedart} Condition Legs - tired, aching, heavy. Class Circulatory system. Description
 - Condition - Class - Description - Causes - Symptoms - Treatment - When to see your pharmacist - When to see your doctor - Living with tired, aching legs - Useful Tips {loadposition nhschoices} {loadposition
- Condition - Class - Description - Causes - Symptoms - Treatment - When to see your pharmacist - When to see your doctor - Living with tired, aching legs - Useful Tips {loadposition nhschoices} {loadposition
This booklet has been developed to help guide you through your post-operative rehabilitation.
 Patient Information Physiotherapy following Breast Surgery Physiotherapy Directorate Keep this booklet as a reminder with your exercises long term. If you start to develop stiffness, pain, weakness, or
Patient Information Physiotherapy following Breast Surgery Physiotherapy Directorate Keep this booklet as a reminder with your exercises long term. If you start to develop stiffness, pain, weakness, or
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies
 Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #9 Heart Failure (date) Course Objectives:
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #9 Heart Failure (date) Course Objectives:
Stiff Shoulder Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement
 Patient Education Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement Your stiff shoulder may be painful and limit your movement. There are many causes of shoulder stiffness. Most times stretching exercises
Patient Education Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement Your stiff shoulder may be painful and limit your movement. There are many causes of shoulder stiffness. Most times stretching exercises
Support for Kidney Cancer
 Page 1 Fact sheet Introduction Our series of kidney cancer fact sheets have been developed to help you understand more about kidney cancer. This fact sheet provides support information for people affected
Page 1 Fact sheet Introduction Our series of kidney cancer fact sheets have been developed to help you understand more about kidney cancer. This fact sheet provides support information for people affected
Axial Spondyloarthritis (axial SpA) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Fatigue. The National Ankylosing Spondylitis NATIONAL ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS SOCIETY
 Axial Spondyloarthritis (axial SpA) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) The National Ankylosing Spondylitis Fatigue Society NATIONAL ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS SOCIETY UK What is fatigue? Fatigue is common among people
Axial Spondyloarthritis (axial SpA) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) The National Ankylosing Spondylitis Fatigue Society NATIONAL ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS SOCIETY UK What is fatigue? Fatigue is common among people
Pain Notebook NAME PHONE. Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here. Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0
 Pain Notebook Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here NAME EMAIL PHONE Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0 What is pain? Pain is a bad sensation that tells you something is wrong. Pain falls into two
Pain Notebook Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here NAME EMAIL PHONE Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0 What is pain? Pain is a bad sensation that tells you something is wrong. Pain falls into two
Azathioprine. Drug information. Azathioprine is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other conditions.
 Azathioprine Drug information Azathioprine is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other conditions. Azathioprine should help treat your condition. It has been in use for many years and has helped
Azathioprine Drug information Azathioprine is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other conditions. Azathioprine should help treat your condition. It has been in use for many years and has helped
Unicompartmental knee replacement. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Unicompartmental knee replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Unicompartmental knee replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Fibromyalgia summary. Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group. What is fibromyalgia? What are the symptoms?
 Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group Fibromyalgia summary We all get aches and pains from time to time. But if you have long-term widespread pain across your whole body, you may have a condition called
Patient leaflets from the BMJ Group Fibromyalgia summary We all get aches and pains from time to time. But if you have long-term widespread pain across your whole body, you may have a condition called
X-Plain Exercising For a Healthy Life Reference Summary
 X-Plain Exercising For a Healthy Life Reference Summary Introduction By exercising and becoming more active, you can improve your health. People who are not physically active are much more likely to develop
X-Plain Exercising For a Healthy Life Reference Summary Introduction By exercising and becoming more active, you can improve your health. People who are not physically active are much more likely to develop
TOFACITINIB PATIENT INFORMATION ON. (Brand name: Xeljanz ) What is tofacitinib? Important things to remember
 PATIENT INFORMATION ON TOFACITINIB (Brand name: Xeljanz ) This information sheet has been produced by the Australian Rheumatology Association to help you understand the medicine that has been prescribed
PATIENT INFORMATION ON TOFACITINIB (Brand name: Xeljanz ) This information sheet has been produced by the Australian Rheumatology Association to help you understand the medicine that has been prescribed
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX
 EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
Helpline No:
 ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
Abatacept Drug information. Abatacept is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
 Abatacept Drug information Abatacept is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Abatacept should effectively treat your condition, and stop it causing damage to your joints. It has been tested and has helped
Abatacept Drug information Abatacept is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Abatacept should effectively treat your condition, and stop it causing damage to your joints. It has been tested and has helped
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment
 After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Happens After Treatment for Soft Tissue Sarcomas?
After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Happens After Treatment for Soft Tissue Sarcomas?
Sleep & Relaxation. Session 1 Understanding Insomnia Sleep improvement techniques Try a new technique
 Sleep & Relaxation Sleep & Relaxation Session 1 Understanding Insomnia Sleep improvement techniques Try a new technique Session 2 Dealing with unhelpful thoughts Putting these techniques together for better
Sleep & Relaxation Sleep & Relaxation Session 1 Understanding Insomnia Sleep improvement techniques Try a new technique Session 2 Dealing with unhelpful thoughts Putting these techniques together for better
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders
 Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery
 Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery This leaflet explains more about returning to your everyday activities after your peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO). It explains the exercises
Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery This leaflet explains more about returning to your everyday activities after your peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO). It explains the exercises
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis.
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Talk About Arthritis You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis. For example, you may
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Talk About Arthritis You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis. For example, you may
KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH. Little Victories
 FOR MODERATE TO SEVERE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH Little Victories Small improvements in your daily activities may be a sign that ORENCIA (abatacept) is working for you. Use this
FOR MODERATE TO SEVERE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH Little Victories Small improvements in your daily activities may be a sign that ORENCIA (abatacept) is working for you. Use this
Managing Fatigue. A guide to help you understand and manage your fatigue.
 Managing Fatigue A guide to help you understand and manage your fatigue East Cheshire Hospice Millbank Drive Macclesfield Cheshire SK10 3DR Physiotherapy / OT 01625 665689 Fax: 01625 666995 www.eastcheshirehospice.org.uk
Managing Fatigue A guide to help you understand and manage your fatigue East Cheshire Hospice Millbank Drive Macclesfield Cheshire SK10 3DR Physiotherapy / OT 01625 665689 Fax: 01625 666995 www.eastcheshirehospice.org.uk
Fatigue after stroke. A patient and carer s guide
 Fatigue after stroke A patient and carer s guide What is post-stroke fatigue? Tiredness affects everyone, and there are many reasons why you might feel tired, such as lack of sleep or a busy day. Usually
Fatigue after stroke A patient and carer s guide What is post-stroke fatigue? Tiredness affects everyone, and there are many reasons why you might feel tired, such as lack of sleep or a busy day. Usually
