Prognostic factors for return to work and resumption of other daily activities after traumatic hand injury
|
|
|
- Kellie Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Full Length Article Prognostic factors for return to work and resumption of other daily activities after traumatic hand injury Niels Neutel 1, Peter Houpt 2 and Arnold Herman Schuurman 1 Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume) 2019, Vol. 44(2) ! The Author(s) 2018 Article reuse guidelines: sagepub.com/journals-permissions DOI: / journals.sagepub.com/home/jhs Abstract The purpose of this study was to investigate prognostic factors for the time off work, the time to resumption of activities of daily living and hobbies, and duration of complaints in patients with a traumatic hand or wrist injury. In a 10-month longitudinal prospective cohort study, 383 patients were included and interviewed in person every 2 to 3 months. Several sociodemographic, psychological and work-related prognostic factors were investigated. For the time off work, job type, diagnosis, complication, blaming someone else for the trauma and gender were all found to be individual prognostic factors in Cox regression. For the time to resumption of activities of daily living and hobbies, and duration of complaints, gender, diagnosis, treatment and complications were found to be prognostic factors in univariate analysis. Age was solely correlated with resumption of activities of daily living and the duration of complaints. Considering these prognostic factors can help predict a patient s recovery more accurately. Level of evidence: II Keywords Hand injury, prognosis, work, daily activities, trauma Date received: 26th December 2017; revised: 2nd October 2018; accepted: 22nd October 2018 Introduction Traumatic hand and wrist injuries are known to be associated with high costs and a high impact on many areas of patients lives. Previous literature has predominantly focused on the time patients need to return to work. Multiple prognostic factors have been identified, including gender, age, income, educational level, dominant hand, employment type, type of work, location of the injury, responsibility for the injury, symptoms of PTSS (post-traumatic stress syndrome), diagnosis and hand injury severity score. For many of these factors, different studies have found opposing outcomes, as outlined in the systematic review by Shi et al. (2014). Furthermore, the vast majority of previous studies have either a low level of evidence (retrospective cohort studies) or a small sample size. The high quality prospective study by Opsteegh et al. (2009) focuses solely on return to work in operatively treated patients, including elective procedures for non-traumatic hand disorders. Outcomes other than return to work, such as the time patients need to resume their activities of daily living (ADL) or hobbies, have been studied to a minimal extent. The purpose of the current study was to measure the impact of traumatic hand and wrist injury more broadly, by investigating prognostic factors for the time off work, time to return to ADL, resumption of hobbies and duration of complaints. Furthermore, the purpose was to integrate the majority of previously studied prognostic factors in one study. 1 UMC Utrecht, Department of Plastic Surgery, Utrecht, The Netherlands 2 Isala Zwolle, Department of Plastic Surgery, Zwolle, The Netherlands Corresponding Author: Niels Neutel, Department of Plastic Surgery, Heidelberglaan 100, 3584 CX Utrecht, The Netherlands. nielsneutel@hotmail.com
2 204 Journal of Hand Surgery (Eur) 44(2) Methods A prospective cohort study was carried out, including all adult patients (18 years or above) with a new traumatic hand or wrist injury who presented at the Emergency Department in a 4-month period between 1 December 2016 and 31 March 2017 at Isala Zwolle, the Netherlands. These injuries were defined as an injury caused by any form of trauma, with the location of injury including the fingers, hand or wrist (whereby the proximal border of the wrist was set at the distal one-third of the forearm). Patients Patients in whom the traumatic hand or wrist injury was not the only injury, patients with other severe illnesses and those who did not speak English or Dutch were excluded. Data was collected through structured personal interviews. Patients were first interviewed within 2 weeks after the trauma to obtain (and verify) their baseline measurements. Subsequently, they were interviewed every 1 to 2 months until patients had resumed all their activities and were free of complaints or until follow-up ended (5 to 9 months). The interviewer was blinded for all baseline measurements during all but the first interview. Demographic variables included age at the date of the trauma and gender. Clinical factors included the side of the injured hand, whether this was the patient s dominant hand and a detailed description of injury (later classified into diagnostic groups). Trauma-related factors included the circumstances of occurrence of the trauma (whether the patient holds someone else responsible for the trauma), and whether the trauma occurred during work or private time. Work-related factors included whether the patient had a job, the number of working hours per week, the type of employment (employed or selfemployed) and the type of work. A description of the job, including physical demands, was obtained and later classified into blue collar or white collar. White-collar jobs were defined as jobs that have low physical demands, such as administrative work, service jobs or light retail work. Blue-collar jobs were defined as jobs that have high physical demands, such as construction and production work or heavy retail work. Assessments Primary outcome measurements were the time to resume work fully (the same number of working hours as before the trauma) and the duration of complaints in weeks. Having complaints was defined as having pain or physical limitations to such an extent that they affected several daily activities. Secondary outcome measurements were the time to resume work partially (fewer working hours than before the trauma), the time to resume ADL and the time to resume hobbies. All times were measured in weeks. For patients who did not resume certain activities or still had complaints at the end of follow-up, the period between their trauma and the last measuring point (their last direct interview) was noted. The outcomes complication and operatively treated were recorded. A complication was defined using the definition of the Dutch federation of medical specialists (Federatie Medisch Specialisten, 2017): An unintended or unwanted outcome of treatment, resulting from the (lack of) actions from the caregiver, which is detrimental to the patients health to such extend that a change in treatment is necessary and/or that there is (irreparable) physical damage. Changes in job due to the trauma were documented. Statistical analysis Normality of the variables was assessed both by Shapiro Wilk and Kolmogorov Smirnov test. Mann Whitney U tests (two unpaired groups) or Kruskal Wallis tests (multiple unpaired groups) were used to test for differences between groups. Correlations between continuous variables were assessed using Spearman s Rho and Kendall s tau. Before Cox regression, variables were tested for multicollinearity using Pearson Chi-Square and Fisher s exact test for dichotomous variables and Spearman s Rho and Kendall s tau for continuous variables. Proportional hazards were assumed after assessing the log-minus-log plots of all variables in the model. In Cox regression, all variables were fixed covariates. Results Four hundred and eight patients were eligible for inclusion in the study. In 25 patients, consent was not obtained and another 29 patients were lost to follow-up. In 354 patients, follow-up (87% of all eligible patients) was complete. Baseline characteristics The baseline characteristics of the patients are listed in Table 1. The most common diagnoses were fractures of the distal radius, metacarpals, and distal phalanx or wrist sprain. Most trauma incidents were seen by the patient as an accident or as their
3 Neutel et al. 205 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the patients. Baseline factors Results Age in years, median (Q1 Q3) 50 (32 65) Gender (n) Male 178 Female 176 Injured hand (n) Dominant 195 Non-dominant 159 Diagnosis Distal radius fracture 78 Metacarpal fracture 47 Fingertip injury and distal phalanx fracture 35 Wrist sprain 35 Distal radius and ulnar styloid fracture 22 Laceration 21 Proximal phalanx fracture 20 Amputation a 14 MCP or PIP or DIP dislocation 13 Scaphoid fracture 12 Middle phalanx fracture 11 Mallet finger 11 Triquetrum fracture 10 Other 25 Occurrence of trauma Accident/Own fault 312 Blames someone else 42 Time of trauma Private time 287 During work 67 Working Yes 243 No 111 Of working population Working hours per week, median (Q1 Q3) 40 (32 40) Employment Employed 203 Self-employed 40 Type of work White collar worker 89 Blue collar worker 154 Total 354 a Level of amputation: MCP joint 1, proximal phalanx 4, PIP joint 1, middle phalanx 6, distal phalanx 2, one digit amputated 10, two digits amputated 4. own fault (n ¼ 312), while 42 patients blamed someone else for the occurrence of the trauma. Most patients (66%) worked 40 hours per week at the time of the trauma. Injuries occurred less often during working time than they did during private time (n ¼ 67 versus n ¼ 287), but when excluding patients without a job (n ¼ 111) this ratio changes to 67 versus 176 patients. There was no significant difference in the types of work between men and women (male 94/142 blue-collar job, female 60/101 blue-collar job). Return to work Of the 243 working patients, two did not return to work for reasons other than their hand or wrist injury. The remaining 241 patients resumed their work partially in a median time of 1 week and fully in 2 weeks. Due to the trauma, four patients did not return to work fully, 13 did not return to work at all and 17 had to change their job. When comparing the times off work for different groups (Table 2), male patients, operatively treated patients, patients with a complication and patients with a blue-collar job all took significantly longer to return to work both partially and fully. For the other variables there were no significant differences between categories for partial and full return to work. ADL and hobby resumption Four patients did not do any ADL tasks themselves before the trauma and the remaining 350 patients resumed their ADL in a median time of 4.5 weeks. Twenty-nine of 350 patients did not resume full ADL activities. Of the 343 patients who had a hobby at the time of the trauma, 40 did not resume their hobby. The median time to resume hobbies was 5 weeks. Higher age had a significant positive correlation with the time to ADL resumption, but not with hobby resumption. Female patients, patients with a complication and operatively treated patients took significantly longer to resume both their ADL and hobby. Employed patients and patients whose trauma occurred during work both resumed their ADL significantly faster. When excluding patients without a job from the analysis, this significant difference remains intact. Furthermore, self-employed patients resumed their hobby significantly faster compared with employed patients. The number of working hours per week was not correlated with either ADL or hobby resumption. Duration of complaints The median time until patients were free of complaints was 9 weeks. At the end of follow up, 108 of 354 patients still experienced complaints. Female patients, patients of higher age, operatively treated
4 206 Journal of Hand Surgery (Eur) 44(2) Table 2. Variables and median (first and third quartiles, Q1 Q3) time to event in weeks. Variable (n) patients and patients with a complication had complaints significantly longer (Table 2). Diagnosis Full return to work (n ¼ 241) Free of complaints (n ¼ 354) Gender Male (178) 2 (0 6)* 8 (4 21)* Female (176) 3.8 (0.1 8)* 10 (6 26)* Dominant hand injured Yes (195) 3 (0 8) 10 (5.5 25) No (159) 1 (0 6) 8 (5 23) Operatively treated Yes (79) 6 (2 12)* 16 (8 26)* No (275) 1 (0 4)* 8 (4 22)* Complication Yes (21) 8 (2 26)* 26 (25 33)* No (333) 2 (0 6)* 8 (5 22)* Occurrence of trauma Accident/own fault (312) 2 (0 6) 8.5 (5 23) Blames some else (42) 5 (1 10.5) 15 (4 32) Working Yes (233) 9 (4 23) No (121) 9 (6 25) Work type Blue collar (146) 5 (1 8)* 8 (4 22) White collar (87) 0.2 (0 2.5)* 9 (5.5 26) Employment Employed (190) 2.5 (0 7) 10 (5 26) Self-employed (43) 2 (0 5.8) 6 (4 20.8) Time of trauma During work (67) 2.8 (0.1 6) 6 (3 23) Private time (287) 2 (0 7) 9 (6 24) Total 2 (0 6) 9 (5 24) *p < 0.05 Mann Whitney U test. Patients with an amputation or distal radius and ulnar styloid fracture had the longest time off work, both with a median time of 7 weeks until full return to work. Those with a scaphoid or distal radius fracture both took 5 weeks to fully return to work. The fastest work resumption was seen in patients with a mallet finger or metacarpo-phalangeal, proximal interphalangeal or distal interphalangeal dislocation. They returned to work fully in a median time of zero weeks, although they were not free of complaints for median times of 10 and 6 weeks, respectively. Table 3. Return to work, Cox regression. Determinant The time needed to resume all ADL activities was the longest for patients with a scaphoid fracture (8 weeks) or proximal phalanx fracture (6.5 weeks). The time to resume hobbies was the longest for patients with an amputation (13 weeks), scaphoid fracture (11.5 weeks) or proximal phalanx fracture (8.5 weeks). The diagnoses with the longest duration of complaints were amputation (28 weeks), scaphoid fracture (25.5 weeks) and proximal phalanx fracture (24 weeks). Patients with wrist sprain or laceration had the shortest durations of complaints (3 and 4 weeks, respectively). For all outcome measures there were significant differences between diagnoses. Predictive model for return to work A predictive model using the Cox proportional hazards model was compiled, with full return to work as event of interest. The hazard ratio, which is a comparison between the probability of events (in this case: return to work) between two groups, was calculated. This ratio is adjusted for other confounding variables. A hazard ratio of two indicates that patients with that characteristic take twice as long to resume their work as patients without that characteristic. The more determinants in the model (Table 3) that apply to a patient, the longer their predicted time off work. The strongest predictor for return to work is Type of work, with a hazard ratio of 2.52 (CI ) for patients with a blue-collar job as compared with those with a white-collar job (Table 3), followed by a diagnosis other than wrist sprain, having a complication, blaming someone else for the injury and female gender. Discussion Hazard ratio (95% CI) p Blue collar job 2.52 ( ) Diagnosis other than 2.48 ( ) wrist sprain Complication 1.88 ( ) Blames someone else 1.70 ( ) for injury Female gender 1.61 ( ) For return to work, the type of work was found to be the strongest predictor. This finding is in accordance with all previous literature assessing type of work (Bruyns et al., 2003; Gustafsson and Ahlstrom,
5 Neutel et al ; Opsteegh et al., 2009; Skov et al., 1999). The second and third strongest predictors were a diagnosis other than wrist sprain and a complication. The fourth strongest predictor is the circumstances of occurrence of the trauma; patients who hold someone else responsible for their injury take longer to return to work. This finding is consistent with previous research (Grunert and Dzwierzynski, 1997; Rusch et al., 2003). The last independent predictor with the lowest hazard ratio is gender; females taking longer to return to work. This outcome is contradictory to what was reported by Chang et al. (2011), Lee et al. (2010) and Skov et al. (1999), who found gender not to be a prognostic factor. However, these were all retrospective cohort studies relying on medical records as their data source. Alongside return to work, gender was also a prognostic factor for ADL resumption, hobby resumption and the duration of complaints. Contrary to Skov et al. (1999), we did not find employment type to be a predictor for return to work. This could be due to a relatively low number of self-employed patients in the study (n ¼ 40 or 16%). Other prognostic factors for resumption of ADL and hobbies and the duration of complaints were operative treatment, complications and diagnosis (most notably, patients with wrist sprain take less time). Age is positively correlated with the time to ADL resumption and the duration of complaints. Furthermore, working patients resume their ADL significantly faster as compared with unemployed patients, although age is likely to be a confounding variable here. Next to that, patients whose trauma occurred during working time resume their ADL faster than patients whose trauma occurred during private time. This significant difference remains intact after excluding unemployed patients, making age less likely to be a confounder here. Outcome measures other than return to work have not been researched in previous literature. At the end of follow up 93% of patients had fully returned to work, 92% resumed their ADL, 86% resumed their hobby and 70% were free of complaints. Patients, who at the end follow-up had not resumed certain activities, were accounted in the analysis with the time to the last interview. This makes all the presented median times to events underestimations of the reality. Strengths of the current study are the high rate of complete follow-up (87% of all eligible patients) and the relatively large sample size. Potential prognostic factors were selected on the basis of previous literature provided they could be recorded through personal interviews. This method of data collection could induce some information bias. Although return to work is a clear event, the other outcome measures (ADL resumption, hobby resumption and duration of complaints) are more subjective. Acknowledgements The authors thank Lonneke Buijteweg (Emergency physician at Isala Zwolle, the Netherlands) and all other staff involved at the Emergency Department at Isala Zwolle for all their efforts concerning setting up the study and including patients. The authors also thank Sander Brink (Epidemiologist and statistician at Isala Zwolle, the Netherlands) for his help with the statistical analysis. Declaration of conflicting interests The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Funding The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Ethical approval details This study was approved by the medical ethics committee at Isala Zwolle, the Netherlands. Informed consent Verbal informed consent was obtained for all patients included in the study. References Bruyns CN, Jaquet JB, Schreuders TA, Kalmijn S, Kuypers PD, Hovius SE. Predictors for return to work in patients with median and ulnar nerve injuries. J Hand Surg Am. 2003, 28: Chang JH, Wu M, Lee CL, Guo YL, Chiu HY. Correlation of return to work outcomes and hand impairment measures among workers with traumatic hand injury. J Occup Rehabil. 2011, 21: Federatie Medisch Specialisten. Is het een calamiteit, complicatie of incident? Utrecht: Federatie Medisch Specilisten, (accessed 2 October 2018). Grunert BK, Dzwierzynski WW. Prognostic factors for return to work following severe hand injuries. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 1997, 1: Gustafsson M, Ahlstrom G. Problems experienced during the first year of an acute traumatic hand injury a prospective study. J Clin Nurs. 2004, 13: Lee YY, Chang JH, Shieh SJ, Lee YC, Kuo LC, Lee YL. Association between the initial anatomical severity and opportunity of return to work in occupational hand injured patients. J Trauma. 2010, 69: E Opsteegh L, Reinders-Messelink HA, Schollier D et al. Determinants of return to work in patients with hand disorders and hand injuries. J Occup Rehabil. 2009, 19: Rusch MD, Dzwierzynski WW, Sanger JR, Pruit NT, Siewert AD. Return to work outcomes after work-related hand trauma: the role of causal attributions. J Hand Surg Am. 2003, 28: Shi Q, Sinden K, MacDermid JC, Walton D, Grewal R. A systematic review of prognostic factors for return to work following workrelated traumatic hand injury. J Hand Ther. 2014, 27: Skov O, Jeune B, Lauritsen JM, Barfred T. Time off work after occupational hand injuries. J Hand Surg Br. 1999, 24:
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist. Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury
 Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Statistics as a Tool. A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations.
 Statistics as a Tool A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations. Descriptive Statistics Numerical facts or observations that are organized describe
Statistics as a Tool A set of tools for collecting, organizing, presenting and analyzing numerical facts or observations. Descriptive Statistics Numerical facts or observations that are organized describe
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
Normative thermal thresholds measured at five European test centres
 Normative thermal thresholds measured at five European test centres May 2001 Research Network on Detection and Prevention of Injuries due to Occupational Vibration Exposures EC Biomed II concerted action
Normative thermal thresholds measured at five European test centres May 2001 Research Network on Detection and Prevention of Injuries due to Occupational Vibration Exposures EC Biomed II concerted action
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Pediatric Phalanx Fractures
 Pediatric Phalanx Fractures Julie Balch Samora, MD/PhD/MPH March 1, 2019.... Disclosures Board/committee member: AOA, AAOS, ASSH, RJOS, POSNA Globus (spouse) Goals To identify the most common phalanx fractures
Pediatric Phalanx Fractures Julie Balch Samora, MD/PhD/MPH March 1, 2019.... Disclosures Board/committee member: AOA, AAOS, ASSH, RJOS, POSNA Globus (spouse) Goals To identify the most common phalanx fractures
Prognostic Factors for Return to Work, Sickness Benefits, and Transitions Between These States: A 4-year Follow-up After Work-Related Rehabilitation
 J Occup Rehabil (2014) 24:199 212 DOI 10.1007/s10926-013-9466-5 Prognostic Factors for Return to Work, Sickness Benefits, and Transitions Between These States: A 4-year Follow-up After Work-Related Rehabilitation
J Occup Rehabil (2014) 24:199 212 DOI 10.1007/s10926-013-9466-5 Prognostic Factors for Return to Work, Sickness Benefits, and Transitions Between These States: A 4-year Follow-up After Work-Related Rehabilitation
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Chapter V Depression and Women with Spinal Cord Injury
 1 Chapter V Depression and Women with Spinal Cord Injury L ike all women with disabilities, women with spinal cord injury (SCI) may be at an elevated risk for depression due to the double jeopardy of being
1 Chapter V Depression and Women with Spinal Cord Injury L ike all women with disabilities, women with spinal cord injury (SCI) may be at an elevated risk for depression due to the double jeopardy of being
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger
 PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2. Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals, Apeldoorn, the Netherlands 3
 Chapter 5 F.J.P. Beeres 1 M. Hogervorst 2 S.J. Rhemrev 1 P. den Hollander 3 G.N. Jukema 4 1 Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2 Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals,
Chapter 5 F.J.P. Beeres 1 M. Hogervorst 2 S.J. Rhemrev 1 P. den Hollander 3 G.N. Jukema 4 1 Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2 Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals,
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Epidemiology in USA: Metacarpal fractures: Page 1
 Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE
 COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE The carpus Scaphoid fracture Scapholunate ligament tear
COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE The carpus Scaphoid fracture Scapholunate ligament tear
Overview of Non-Parametric Statistics
 Overview of Non-Parametric Statistics LISA Short Course Series Mark Seiss, Dept. of Statistics April 7, 2009 Presentation Outline 1. Homework 2. Review of Parametric Statistics 3. Overview Non-Parametric
Overview of Non-Parametric Statistics LISA Short Course Series Mark Seiss, Dept. of Statistics April 7, 2009 Presentation Outline 1. Homework 2. Review of Parametric Statistics 3. Overview Non-Parametric
Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria
 Article ID: WMC00807 ISSN 2046690 Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria Corresponding Author: Dr. Ahidjo Kawu, Consultant Surgeon, Dept of Orthopaedics, UATH, Gwagwalada Abuja
Article ID: WMC00807 ISSN 2046690 Risk Factors Predicting Mortality in Spinal Cord Injury in Nigeria Corresponding Author: Dr. Ahidjo Kawu, Consultant Surgeon, Dept of Orthopaedics, UATH, Gwagwalada Abuja
Chapter 8. The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb
 Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Basic Biostatistics. Chapter 1. Content
 Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery
 Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery Natalie L. Leong 1 *, Jeremiah R. Cohen 1, Elizabeth Lord 1, Jeffrey C. Wang 2, David R. McAllister 1, and Frank A. Petrigliano 1
Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery Natalie L. Leong 1 *, Jeremiah R. Cohen 1, Elizabeth Lord 1, Jeffrey C. Wang 2, David R. McAllister 1, and Frank A. Petrigliano 1
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies
 Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang At the end of this session,
Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang At the end of this session,
Trauma Films for Upper Body. LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC
 Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases
 Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
Safety and health training model It is expected that better recognition of hazards can reduce risks to workers. Course depth and suitable teaching met
 Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008
 Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Medical Causality and Risk Assessment
 Medical Causality and Risk Assessment WORKERS COMPENSATION BASICS COURSE // MODULE 4 OF 8 Medical Causality and Risk Assessment// Page 1 Medical Causality and Risk Assessment Module 4 Objectives: Upon
Medical Causality and Risk Assessment WORKERS COMPENSATION BASICS COURSE // MODULE 4 OF 8 Medical Causality and Risk Assessment// Page 1 Medical Causality and Risk Assessment Module 4 Objectives: Upon
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology
 Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology Original Article Usage of statistical methods and study designs in publication of specialty of general medicine and its secular changes Swati Patel 1*, Vipin Naik
Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology Original Article Usage of statistical methods and study designs in publication of specialty of general medicine and its secular changes Swati Patel 1*, Vipin Naik
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Introduction ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 Cancer Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access The effect of radiation therapy in the treatment of adult soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities: a long- term community- based cancer center experience Jeffrey
Cancer Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access The effect of radiation therapy in the treatment of adult soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities: a long- term community- based cancer center experience Jeffrey
Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures
 Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions
 Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions Instructions to fill the table: When no element can be added under one or more heading, include the mention: O Not applicable when an
Template 1 for summarising studies addressing prognostic questions Instructions to fill the table: When no element can be added under one or more heading, include the mention: O Not applicable when an
11th Annual Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference June 11-12th 2015 Orlando, Florida Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference Sponsors:
 11th Annual Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference June 11-12th 2015 Orlando, Florida 2015 Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference Sponsors: Thursday, June 11th 6:15-7:00 Breakfast: (Catered/Registration
11th Annual Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference June 11-12th 2015 Orlando, Florida 2015 Teton Hand and Upper Extremity Conference Sponsors: Thursday, June 11th 6:15-7:00 Breakfast: (Catered/Registration
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Carpal and Finger Fractures. Donald S. Bae, MD Children s Hospital Boston
 Carpal and Finger Fractures Donald S. Bae, MD Children s Hospital Boston Objectives Epidemiology of hand and wrist injuries Discuss injuries requiring surgical care Common complications & strategies for
Carpal and Finger Fractures Donald S. Bae, MD Children s Hospital Boston Objectives Epidemiology of hand and wrist injuries Discuss injuries requiring surgical care Common complications & strategies for
Table of Contents. Plots. Essential Statistics for Nursing Research 1/12/2017
 Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Mallet Finger Injuries
 A Patient s Guide to Mallet Finger Injuries 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Mallet Finger Injuries 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Figure: Presentation slides:
 Joni Lakin David Shannon Margaret Ross Abbot Packard Auburn University Auburn University Auburn University University of West Georgia Figure: http://www.auburn.edu/~jml0035/eera_chart.pdf Presentation
Joni Lakin David Shannon Margaret Ross Abbot Packard Auburn University Auburn University Auburn University University of West Georgia Figure: http://www.auburn.edu/~jml0035/eera_chart.pdf Presentation
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Declaration of Conflict of Interest. No potential conflict of interest to disclose with regard to the topics of this presentations.
 Declaration of Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest to disclose with regard to the topics of this presentations. Clinical implications of smoking relapse after acute ischemic stroke Furio
Declaration of Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest to disclose with regard to the topics of this presentations. Clinical implications of smoking relapse after acute ischemic stroke Furio
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Fracture Guideline
 Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Predictors of drug sensitive tuberculosis treatment outcomes among hospitalised
 Predictors of drug sensitive tuberculosis treatment outcomes among hospitalised patients in South Africa: a multinomial logit model Abiola O. Olaleye 1,* and Andy K. Beke 1 1 School of Health Systems and
Predictors of drug sensitive tuberculosis treatment outcomes among hospitalised patients in South Africa: a multinomial logit model Abiola O. Olaleye 1,* and Andy K. Beke 1 1 School of Health Systems and
1 Emergency Medicine Academic Group, Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Leicester, UK.
 Title: A week of pain in the Emergency Department Authors: Thornton HS 1, Reynolds J 1, Coats TJ 1 1 Emergency Medicine Academic Group, Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Leicester, UK.
Title: A week of pain in the Emergency Department Authors: Thornton HS 1, Reynolds J 1, Coats TJ 1 1 Emergency Medicine Academic Group, Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Leicester, UK.
Fractures and dislocations of the fingers
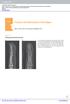 Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb AP; Lat. PA. PA; Lat.: Obls.; Elongated PA with ulnar deviation
 Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making
 MUMJ Original Research 15 ORIGINAL RESEARCH It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making Mohit Bhandari, MD, MSc Vikas Khera, BSc Jaydeep K. Moro, MD
MUMJ Original Research 15 ORIGINAL RESEARCH It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making Mohit Bhandari, MD, MSc Vikas Khera, BSc Jaydeep K. Moro, MD
Survival rates in dysvascular lower limb amputees
 International Journal of Surgery (26) 4, 217e221 journal homepage: www.int-journal-surgery.com Survival rates in dysvascular lower limb amputees J. Kulkarni*, S. Pande, J. Morris Rehabilitation Medicine,
International Journal of Surgery (26) 4, 217e221 journal homepage: www.int-journal-surgery.com Survival rates in dysvascular lower limb amputees J. Kulkarni*, S. Pande, J. Morris Rehabilitation Medicine,
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES
 HKJOT 2010;20(1):13 18 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES IN HONG KONG Hercy C.K. Li 1 and Cecilia W.P. Li-Tsang 2 Objective: This study attempted to review the incidence of sports related hand
HKJOT 2010;20(1):13 18 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPORTS RELATED HAND INJURIES IN HONG KONG Hercy C.K. Li 1 and Cecilia W.P. Li-Tsang 2 Objective: This study attempted to review the incidence of sports related hand
Gender Differences in Physical Inactivity and Cardiac Events in Men and Women with Type 2 Diabetes
 Gender Differences in Physical Inactivity and Cardiac Events in Men and Women with Type 2 Diabetes Margaret M. McCarthy 1 Lawrence Young 2 Silvio Inzucchi 2 Janice Davey 2 Frans J Th Wackers 2 Deborah
Gender Differences in Physical Inactivity and Cardiac Events in Men and Women with Type 2 Diabetes Margaret M. McCarthy 1 Lawrence Young 2 Silvio Inzucchi 2 Janice Davey 2 Frans J Th Wackers 2 Deborah
NE Nebraska Trauma Conference Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017
 NE Nebraska Trauma Conference 2017 Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017 Traumatic arm injuries in the elderly Fractures Hand Wrist Elbow Shoulder Soft tissue injuries Definitions Elderly? old or aging
NE Nebraska Trauma Conference 2017 Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017 Traumatic arm injuries in the elderly Fractures Hand Wrist Elbow Shoulder Soft tissue injuries Definitions Elderly? old or aging
Interesting Case Series. Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review
 Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
POR4ULO Assessment. Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit. Practical Guide
 POR4ULO Assessment Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit Practical Guide Pattern Making for Upper Limb, Low Temperature Thermoplastic Orthoses The use of low temperature thermoplastics
POR4ULO Assessment Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit Practical Guide Pattern Making for Upper Limb, Low Temperature Thermoplastic Orthoses The use of low temperature thermoplastics
Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Hand Service Competency Requirements
 Revised 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Hand Service Competency Requirements Patient Care Faculty will evaluate the resident s ability to obtain an H&P and appropriate radiographs and formulate
Revised 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Hand Service Competency Requirements Patient Care Faculty will evaluate the resident s ability to obtain an H&P and appropriate radiographs and formulate
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
REVIEW ARTICLE. A Review of Inferential Statistical Methods Commonly Used in Medicine
 A Review of Inferential Statistical Methods Commonly Used in Medicine JCD REVIEW ARTICLE A Review of Inferential Statistical Methods Commonly Used in Medicine Kingshuk Bhattacharjee a a Assistant Manager,
A Review of Inferential Statistical Methods Commonly Used in Medicine JCD REVIEW ARTICLE A Review of Inferential Statistical Methods Commonly Used in Medicine Kingshuk Bhattacharjee a a Assistant Manager,
Results of the 2016 Gender Equality in the Legal Profession Survey
 Results of the 2016 Gender Equality in the Legal Profession Survey October 2016 INTRODUCTION A Florida Bar Special Committee was appointed by President Bill Schifino at the beginning of the 2016-17 Bar
Results of the 2016 Gender Equality in the Legal Profession Survey October 2016 INTRODUCTION A Florida Bar Special Committee was appointed by President Bill Schifino at the beginning of the 2016-17 Bar
Audit. Public Health Monitoring Report on 2006 Data. National Breast & Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons.
 National Breast & Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Audit Public Health Monitoring Report on 2006 Data November 2009 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of
National Breast & Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Audit Public Health Monitoring Report on 2006 Data November 2009 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments. Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center
 Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
O ccupational disability due to low back pain (LBP) is
 289 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effectiveness of ergonomic interventions on return-towork after low back pain; a prospective two year cohort study in six countries on low back pain patients sicklisted for 3 4
289 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effectiveness of ergonomic interventions on return-towork after low back pain; a prospective two year cohort study in six countries on low back pain patients sicklisted for 3 4
The impact of the Belgian workers compensation system on return to work after rotator cuff surgery
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 592-597 ORIGINAL STUDY The impact of the Belgian workers compensation system on return to work after rotator cuff surgery Karolien DiDDEN, Geert LEiRs, Peter AERts From Mariaziekenhuis,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 592-597 ORIGINAL STUDY The impact of the Belgian workers compensation system on return to work after rotator cuff surgery Karolien DiDDEN, Geert LEiRs, Peter AERts From Mariaziekenhuis,
Silicone Finger Implant
 Silicone Finger Implant Manufactured from high tear resistant implant grade silicone Surgical Technique Eleven, evenly scaled sizes for comprehensive anatomical fit Simple, precise instrumentation Designed
Silicone Finger Implant Manufactured from high tear resistant implant grade silicone Surgical Technique Eleven, evenly scaled sizes for comprehensive anatomical fit Simple, precise instrumentation Designed
Louis-André Vallet (CNRS) Observatoire Sociologique du Changement (UMR CNRS & Sciences Po Paris)
 Louis-André allet (CNRS) Observatoire Sociologique du Changement (UMR 7049 - CNRS & Sciences Po Paris) louisandre.vallet@sciencespo.fr ASSESSING THE PERFORMANCE OF THE THREE ONE-DIGIT ESEG PROTOTYPES WITH
Louis-André allet (CNRS) Observatoire Sociologique du Changement (UMR 7049 - CNRS & Sciences Po Paris) louisandre.vallet@sciencespo.fr ASSESSING THE PERFORMANCE OF THE THREE ONE-DIGIT ESEG PROTOTYPES WITH
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test
 Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
Dental Earnings and Expenses: Scotland, 2011/12
 Dental Earnings and Expenses: Published 25 October 2013 We are the trusted source of authoritative data and information relating to health and care. www.hscic.gov.uk enquiries@hscic.gov.uk Author: Responsible
Dental Earnings and Expenses: Published 25 October 2013 We are the trusted source of authoritative data and information relating to health and care. www.hscic.gov.uk enquiries@hscic.gov.uk Author: Responsible
CLINICAL SCIENCE. Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre Vieira Guedes b
 CLINICS 2008;63(1):3-8 CLINICAL SCIENCE CHRONIC MULTIPLE KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES: EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MORE THAN ONE HUNDRED CASES Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre
CLINICS 2008;63(1):3-8 CLINICAL SCIENCE CHRONIC MULTIPLE KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES: EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MORE THAN ONE HUNDRED CASES Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club. A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology. August, 2013
 Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Preoperative Gleason score, percent of positive prostate biopsies and PSA in predicting biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy
 JBUON 2013; 18(4): 954-960 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason score, percent of positive prostate and PSA in predicting biochemical
JBUON 2013; 18(4): 954-960 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason score, percent of positive prostate and PSA in predicting biochemical
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
15 17 November 2018, Dubai, UAE. Event Overview
 15 17 November 2018, Dubai, UAE Event Overview Dear Friends and Colleagues, Over the last 4 years, the International Advanced Orthopaedic Congress (IAOC) has firmly established itself as the region s only
15 17 November 2018, Dubai, UAE Event Overview Dear Friends and Colleagues, Over the last 4 years, the International Advanced Orthopaedic Congress (IAOC) has firmly established itself as the region s only
Citation for published version (APA): Lammers-van der Holst, H. M. (2016). Individual differences in shift work tolerance
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Individual differences in shift work tolerance Lammers-van der Holst, H.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lammers-van der Holst, H. M.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Individual differences in shift work tolerance Lammers-van der Holst, H.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lammers-van der Holst, H. M.
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003
 NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Che Daud, A. Z., Yau, M. K., Barnett, F., Judd, J., Jones, R. E., & Muhammad Nawawi, R. F. (2016). Integration of occupation based intervention in hand injury rehabilitation:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Che Daud, A. Z., Yau, M. K., Barnett, F., Judd, J., Jones, R. E., & Muhammad Nawawi, R. F. (2016). Integration of occupation based intervention in hand injury rehabilitation:
Basic Steps in Planning Research. Dr. P.J. Brink and Dr. M.J. Wood
 Basic Steps in Planning Research Dr. P.J. Brink and Dr. M.J. Wood Research Levels Level 1: There is little or no literature available on the topic or on the population. The purpose is to describe what
Basic Steps in Planning Research Dr. P.J. Brink and Dr. M.J. Wood Research Levels Level 1: There is little or no literature available on the topic or on the population. The purpose is to describe what
How to describe bivariate data
 Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville Trauma/Fractures
 WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
TIME OFF WORK DUE TO SCAPHOID FRACTURES AND OTHER CARPAL INJURIES IN THE NETHERLANDS IN THE PERIOD 1990 TO 1993
 TIME OFF WORK DUE TO SCAPHOID FRACTURES AND OTHER CARPAL INJURIES IN THE NETHERLANDS IN THE PERIOD 1990 TO 1993 A. B. MINK VAN DER MOLEN, J. W. GROOTHOFF, G. J. P. VISSER, P. H. ROBINSON and W. H. EISMA
TIME OFF WORK DUE TO SCAPHOID FRACTURES AND OTHER CARPAL INJURIES IN THE NETHERLANDS IN THE PERIOD 1990 TO 1993 A. B. MINK VAN DER MOLEN, J. W. GROOTHOFF, G. J. P. VISSER, P. H. ROBINSON and W. H. EISMA
Trauma/Fractures WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY. TFCC Injury. Hook of Hamate Fracture. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
Mallet Baseball Finger
 Mallet Baseball Finger Introduction When you think about how much we use our hands, it's not hard to understand why injuries to the fingers are common. Most of these injuries heal without significant problems.
Mallet Baseball Finger Introduction When you think about how much we use our hands, it's not hard to understand why injuries to the fingers are common. Most of these injuries heal without significant problems.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Svens, B., Ames, E., Burford, K., & Caplash, Y. (2015). Relative active motion programs following extensor tendon repair: A pilot study using a prospective cohort and evaluating
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Svens, B., Ames, E., Burford, K., & Caplash, Y. (2015). Relative active motion programs following extensor tendon repair: A pilot study using a prospective cohort and evaluating
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Neurovascular Observations Nursing Clinical Guideline
 Reference (include title, Patel, k., & McCann, P. A. (2012). The emergent assessment of supracondylar fractures of the paediatric humerus. Hand Surgery, 17(2), 161-165. From Medline Evidence level (I-)
Reference (include title, Patel, k., & McCann, P. A. (2012). The emergent assessment of supracondylar fractures of the paediatric humerus. Hand Surgery, 17(2), 161-165. From Medline Evidence level (I-)
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 338/11
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 338/11 BEFORE: J. Noble: Vice-Chair HEARING: February 22, 2011, at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: March 2, 2011 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2011 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 338/11 BEFORE: J. Noble: Vice-Chair HEARING: February 22, 2011, at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: March 2, 2011 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2011 ONWSIAT
