RESEARCH GRANTS LAY SUMMARIES
|
|
|
- Marylou Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH GRANTS LAY SUMMARIES Name: Sheila Leah Arvikar, MD Project Title: P.gingivalis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Exploring the Mouth-Joint Connection Institution: Massachusetts General Hospital Mentor: Allen steere, MD Award Period: July 1, 2012 June 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Rheumatoid Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease, characterized by chronic joint inflammation and destruction. The cause is unknown, but it is suspected that infectious agents may trigger autoimmunity in genetically susceptible individuals. Recently, there has been increasing evidence of a connection between periodontal disease and RA. Specific bacteria in dental plaque can cause periodontitis (inflammation of the tooth-supporting structures), leading to bone and tooth loss. Numerous studies have shown that the prevalence and severity of periodontal disease is increased in RA patients. Treatment of periodontal disease in some preliminary studies has improved RA disease activity. Moreover, periodontal disease and RA share similar risk factors such as genetic predisposition and smoking. One of the major bacterial pathogens that causes periodontal disease is P. gingivalis. This organism has also been linked to RA with immune responses to P. gingivalis found in RA patients. The studies examining the connection between RA, periodontal disease, and P. gingivalis have done so only in patients with longstanding RA whom were already taking immune modulating medications. In an effort to demonstrate a causal role for P. gingivalis and periodontal disease in RA, it may be more instructive to assess patients who have early disease and who have not been treated with medications which may alter the immune responses. Furthermore, if treatment of periodontal disease could improve the outcome of RA, it would be more likely to have an impact early in the course of RA. We have established a prospective cohort study of early RA patients at Massachusetts General Hospital. We have now enrolled >60 untreated RA patients with early disease. In our cohort, antibody responses to P. gingivalis were significantly increased in untreated early RA patients compared with those in healthy controls or in patients with established RA. The experiments proposed here are designed to better characterize the relationship of periodontal disease, P. gingivalis, and RA, using immunologic and
2 microbiologic methods. These studies will be performed in both newly diagnosed, untreated early RA patients, and in more established RA patients, already undergoing treatment. P. gingivalis is a promising candidate organism as a trigger of autoimmunity in RA. Our unique study involves a high degree of clinical characterization of patients by both rheumatologists and dentists. To our knowledge, this work will be the first to evaluate the frequency of P. gingivalis immunity in a cohort of patients with early, untreated RA, and may further support a causal role for P. gingivalis in this disease. Further, we envision that this work will lead to an interventional trial of periodontal disease treatment in RA, which in addition to RA medications, may have a significant impact on disease activity and outcome for a subgroup of RA patients. Name: Jennifer Belasco, MD Project Title: Characterization of Inflammatory Pathways in Psoriatic Arthritis Institution: Rockefeller University Mentor: James Krueger, MD, PhD Award Period: September 1, 2012 August 31, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Psoriatic Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis. The earliest joint inflammation is thought to involve an area near the joint where muscle tendons and ligaments insert into bone. It also involves both abnormal bone formation and bone destruction. It is difficult to obtain tissue from this area for research purposes. For this reason having a surrogate tissue that is easier to obtain, such as skin, would be useful to show what is occurring in this area. In addition, we do not understand the link between the skin rash and joint symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. We have already started a study where we looked at patients with only psoriasis (skin rash) and patients with both psoriasis and arthritis (skin and joint symptoms). We have found many differences in the skin of patients with only psoriasis vs. patients with both psoriasis and arthritis. We believe that some of the differences we have found may indicate which patients have abnormal bone formation and destruction. Unfortunately, the patients with only psoriasis were not as carefully selected as would like and we would now like to recruit more patients that we are certain only have psoriasis or have both psoriasis and arthritis. We will also compare joint tissue from these patients to joint tissue from patients with other forms of joint inflammation and abnormal bone formation and destruction. These patients will have osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. This would be the first study to show that the skin shows signs of what is going on in and near the joint in patients with psoriatic arthritis. This may help us to identify which patients with psoriasis will go on to have psoriatic arthritis. In addition, our findings could be used to create new medications to treat these diseases. Furthermore, patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis tend to have other related conditions that affect their whole body such as heart disease and diabetes. Our findings may also help us to understand why this happens and help doctors choose better medications to treat these problems.
3 Name: Elana J. Bernstein, MD Project Title: A Submaximal Stress Test to Identify Pulmonary Hypertension in Scleroderma Institution: Trustees of Columbia University Mentor: Lisa A. Mandl, MD, MPH Award Period: October 1, 2012 September 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Research Disease Focus: Sclerodema Lay Language Summary: Systemic sclerosis (SSc), or scleroderma, is an autoimmune disease that affects many organ systems, including the heart and the lungs. Pulmonary hypertension (PH), an increase in pressure in the blood vessels that connect the heart to the lungs, is the leading cause of death in patients with SSc. Right heart catheterization (RHC), a procedure in which a thin tube is inserted into the right side of the heart to measure pressure, is the gold standard for diagnosing PH. However, this is an expensive, invasive test with significant risks. Currently, echocardiogram, a test in which a probe is placed on the chest and ultrasound pictures of the heart are taken, is the most common noninvasive way to screen for PH. However, echocardiogram is much less accurate than RHC and can sometimes give incorrect results. Given the risks of RHC, patients with SSc are often not referred for RHC until they have trouble breathing. Unfortunately, by this time, irreversible changes in the blood vessels that connect the heart to the lungs have often already occurred. Given the effective therapies now available to treat PH, it is crucial that PH be identified as early as possible, ideally before permanent changes in the blood vessels that connect the heart to the lungs have occurred. A new, noninvasive stress test called the submaximal heart and pulmonary evaluation (SHAPE) may be a better way to evaluate for PH in patients with SSc. The SHAPE test is a 5.5 inch high step that patients step up and down on for 3 minutes at their own pace while their heart rate, heart rhythm, and breathing are monitored. It has been used to identify PH in other populations, but has never been evaluated in patients with SSc. Therefore, the main purpose of this study is to determine whether the SHAPE test can accurately distinguish SSc patients with PH from SSc patients without PH. Sixty patients with SSc will be recruited for this study. Results from RHC within the prior 24 months will be used to divide these 60 patients into those with PH and those without. The primary outcome will be change in end tidal carbon dioxide after 3 minutes of step exercise. This is automatically calculated by the SHAPE test. In healthy patients, end tidal carbon dioxide increases with exercise and is an indicator of how well a patient's heart and lungs are working. It is therefore hypothesized that SSc patients with PH will have a significantly lower mean change in end tidal carbon dioxide than SSc patients without PH. Patients will also complete questionnaires that assess their physical function, health-related quality of life, and perception of breathlessness. Blood will be collected to help evaluate lung function, to test for SSc autoantibodies, and to study genetic biomarkers. If the SHAPE test can accurately distinguish between SSc patients with PH and SSc patients without PH, further studies could be undertaken to see if the SHAPE test might be useful for regular PH screening in the SSc population.
4 Name: Daria B Crittenden, MD Project Title: Effects of Colchicine on Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Gout Institution: New York University School of Medicine Mentor: Anthony Carna Award Period: August 1, 2012 July 31, 2014 Study Section: Epidemiology Disease Focus: Inflammation Lay Language Summary: Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis, affecting approximately 12 million Americans. Gout patients are at increased risk for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular (CV) disease, such as heart attacks and strokes. It is increasingly recognized that atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process, and that patients with chronic inflammatory diseases such as gout may have increased CV risk because of their systemic inflammation. On this basis, investigators have begun to ask whether agents that reduce inflammation may have a beneficial impact on cardiovascular disease. Colchicine, often used for gout treatment, is one such agent. Colchicine is generally well-tolerated, and has effects on a number of cell types that are known to play a role in the build-up of atherosclerosis and progression to heart attack. However, little is known about whether there might be a role for colchicine in treating CV disease. In a pilot study looking at gout patients at the New York Harbor Veterans Affairs (VA) Health Care System, we observed that patients taking colchicine experienced a 64% reduction in myocardial infarction (manuscript in revision, J Rheumatology). However, by its design that study had a number of limitations, leading me to now propose further investigation. I will approach the question of colchicine and MI risk taking two different, but complementary approaches. In the first approach, we will conduct a detailed chart review of more than 7,000 gout patients who were cared for between 2000 and 2010 in our local VA hospital system; the nature of the VA medical record will permit us to precisely ascertain which patients were on colchicine, and how many events they had while on the drug. We will then validate our findings using the Geisinger Health System database. Although this second study will need to use coded information, rather than careful parsing of charts, the size of the Geisinger database (more than 2 million patients), its less homogeneous patient population (compared to the VA patients), and the power of its electronic search capacities should offset any limitation. These two methodologies should therefore complement each other and let us get a solid idea of the ability of colchicine to modify MI risk. If the results support my hypothesis that colchicine use lowers CV risk they could lead to prospective trials of colchicine for CV risk lowering in gout patients, or possibly even in non-gout patients. Thus, my project could lay important groundwork for further investigation into the relationship between inflammation and cardiovascular complications, and may shed light on potential new approaches to therapy. Given the overall tolerability of colchicine, finding that its use lowers CV risk could make it a valuable addition to the treatment of CV disease in gout and/or non-gout patients.
5 Name: Trevor E. Davis, MD Project Title: Immune Cell microrna Expression in Pediatric SLE Institution: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Mentor: George Tsokos, MD Award Period: July 1, 2012 June 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Juvenille Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototypic autoimmune disease in which the immune system causes damage to multiple organs including the skin, joints, and kidneys and less often the heart, lung, liver, and brain. Antibodies are involved in the disease, however other immune cells, T cells, also play an important role. T cells directly infiltrate targeted organs and help produce autoantibodies instead of inhibiting their production. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are newly identified DNA like molecules that can effect immune cells responses by blocking expression of target genes. Altered mirnas have been identified in adult autoimmune diseases such as Rheumatoid Arthritis and SLE. These abnormalities have not been studied in response to medications used to treat SLE, correlated to arthritis in SLE patients, or examined in pediatric SLE. We hypothesize the mirna are altered in pediatric SLE similar to adult SLE. Altered mirnas will correlate to disease activity and treatments, including presence of arthritis and treatment with steroids. Methods Immune cells from pediatric SLE and healthy control subjects will be isolated and cultured. Microarrays, testing greater than a thousand mirna and genes at one time, will be used to initially identify candidates. These candidates will be validated using a second lower throughput technique. Molecular techniques will then be used to examine the consequences of these altered genes. Conclusion Although it is known adult SLE immune cells display multiple altered mirnas these findings are not yet validated in children. The proposed work will accomplish this validation but also has the potential to find novel aberrant mirnas. Identified mirnas could reveal specific targets for treatment, biomarkers of disease activity or inherent defects of pediatric SLE. This will significantly advance knowledge of both the field of mirnas and immunology of pediatric SLE. Moreover these findings may have special importance for prognosis and treatment of pediatric onset SLE and pediatric arthritis. Name: Maureen Dubreuil, MD Project Title: Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes in Ankylosing Spondylitis Institution: Boston University Mentor: Hyon Choi, MD, PhD Award Period: July 1, 2013 June 30, 2015 Study Section: Epidemiology Disease Focus: Ankylosing Spondylitis Lay Language Summary: Objective: Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) die earlier due to heart disease. This may be because AS patients are more likely to smoke and to be obese. As patients may also have greater risk due to certain medications, called NSAIDs, which are used to treat pain from the
6 disease. Studies have not addressed this yet, but experts in the field have agreed it is important. Similarly, AS patients may have diabetes more often than people without AS, though studies are unclear on this, as well. Methods: We will use medical records from 8 million patients in the United Kingdom, which were recorded by the patients' general practitioners (GPs). In this database, we will identify patients with AS, and compare the rates of heart disease and diabetes in AS patients, with the rates in people who do not have AS. We will use statistical methods to determine if higher rates of heart disease and diabetes are due to risk factors such as smoking and obesity, in AS patients, or if the risk is due to AS itself (chronic inflammation). We will also use statistical methods to determine if certain NSAIDs cause greater heart disease in AS patients than in people without AS, as the combination of risk factors may be important. Expected results: The results of this study will allow doctors of AS patients to know what risk factors are the most important in terms of AS patients developing heart disease or diabetes. Doctors can then counsel their patients and treat them better. Similarly, doctors will be able to prescribe the safest NSAID medications to AS patients. Name: Beatriz Hanaoka, MD Project Title: Muscle architecture in chronic DM and PM Institution: University of Kentucky Research Foundation Mentor: Lesie Crofford, MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Polymyositis Lay Language Summary: Dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM) are diseases that cause muscle inflammation leading to muscle damage and weakness. While some patients return to normal after being treated with medications, the large majority of patients suffer from chronic muscle weakness and disability. A better understanding of why this happens despite treatment will allow more effective and targeted therapies to be developed in the future. Muscle inflammation and/or its treatment may lead to certain changes in muscle architecture that contribute to ongoing muscle weakness in DM/PM patients. We will enroll 20 participants with DM/ PM and 10 healthy participants will be enrolled in this study over an 18 month period. Study participants will be interviewed and examined. They will also undergo a series of tests that will allow us to study their muscle strength and structure. The results of this study will allow us to determine the contributors to long-term muscle weakness and develop treatment approaches to prevent disability in DM/PM patients.
7 Name: Jonathan David Jones, MD Project Title: Rituximab modulates B cell function through shaving Institution: Dartmouth College Mentor: Willam Rigby, MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2014 Study Section: Cellular Immunology Disease Focus: Rheumatoid Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Background: Rituximab (RTX) is a medication that is used in several autoimmune diseases, especially in rheumatoid arthritis. This medication is an antibody that targets a particular immune cell, the B lymphocyte. Interestingly, though we know that this antibody binds B lymphocytes and results in a suppressed immune system with subsequent disease remission, we don't know the exact mechanism behind this effect. Historically, the major focus on RTX effect was in its ability to promote the death of B lymphocytes. However, depletion of these B cells has not correlated with clinical efficacy. The presence of B cells is determined by measuring a surface protein, CD19. We have shown that blood cells combined with RTX rapidly loose CD19, but that this is not because of cell death, but is rather due to loss of the CD19 protein from the surface through a relatively unknown process termed shaving. We hypothesize that the efficacy of rituximab treatment lies not so much in its ability to deplete B cells, but in its ability to promote loss of surface proteins from the B cells, therefore changing the function and cellular interactions of the B cells. Methods: To investigate our hypothesis we will build on the experience we already have with rituximab shaving of B cells to evaluate other surface proteins besides CD19 that are also removed with the addition of RTX. We will focus on those proteins that have a functional importance to the B cells through playing key roles in cell growth and differentiation or cell-cell interactions. We will also explore different subsets of B cells that may be more or less susceptible to RTX induced shaving. Our second emphasis will be evaluating functional changes of B cells induced by RTX-shaving by determining changes in B cell proliferation and cytokine production after RTX treatment. Additionally, we will examine the effect of RTX treatment on the B cells' ability to interact with and inform T lymphocyte function and differentiation. Anticipated Results: We expect to find several additional functionally significant surface proteins that are lost from B cells in the shaving process. We anticipate identifying changes in B cell function due to treatment with RTX related to cytokine production and T cell interactions. These findings will lead to additional clinical studies evaluating the in vivo effect of RTX in patients being treated for rheumatoid arthritis, and has the potential to opening the doors to additional therapeutic options for several autoimmune diseases.
8 Name: Suzanne Kafaja, MD Project Title: Effect of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis Institution: University of California, Los Angeles Mentor: Ram Raj Singh, MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Scleroderma Lay Language Summary: Scleroderma is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects a number of organs in the human body including the skin, intestines, lungs, and kidneys. The cause of scleroderma remains unknown. It is believed to be due to abnormalities of immune system, where different components (cells) of immune system do not coordinate properly, resulting in damage to blood vessels, and replacement of normal organ cells with fibers. This process is called fibrosis. There are different types of immune cells. One of them is called dendritic cells. This project proposes to investigate the role of a subset of dendritic cells, called plasmacytoid dendritic cells. These cells normally circulate in blood and go to various organs such as skin and lung during infection and inflammation. We have studied these cells in the blood, skin biopsy and lung lavage fluid from patients with scleroderma. We have found that these cells are reduced in the blood, but abundant in the skin and lung lavage fluid, from patients with scleroderma. Importantly, the presence of these cells in lung fluid correlates with the extent of lung fibrosis seen on imaging of the lungs (CT scan). These cells were also noted to decrease in patients treated with a medication called Imatinib. In the proposed project, I will move forward the above preliminary work and investigate the role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in modifying immune system in a way that leads to the formation of excess fibers in organs such as skin and lungs leading to scleroderma. This may in the future help us find a treatment for hardening of the skin and lungs of patients with scleroderma. Name: Kichul Ko, MD Project Title: Differential Gene Expression Analysis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Institution: University of Chicago Mentor: Timothy Niewold, MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2014 Study Section: Genetics Disease Focus: Lupus Lay Language Summary: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by a strong genetic contribution and activation of a number of immune system pathways. It manifests differently by ancestry as African American (AA) patients tend to have higher disease activity, kidney involvement and more autoantibodies compared to European American (EA) patients. Moreover, autoantibodies directed against the body s own cells (anti-rbp) are associated with different SLE
9 characteristics and activity. Our overall hypothesis is that the underlying mechanisms of SLE differ between AA and EA SLE patients, and between those with anti-rbp antibodies and those who lack these antibodies. We will explore this hypothesis by examining how genes are expressed differently in those groups and identify the key molecules for the differences. In this study, we posit that different autoantibody profiles and ancestral backgrounds in SLE are associated with different gene expression patterns. The knowledge of the relationships amongst gene expression, autoantibody profile and ancestral differences in SLE will significantly aid our understanding of the heterogeneity of pathogenesis and lay the foundation for individualized therapy. Moreover, discovering new pathways in SLE pathogenesis may identify potential therapeutic targets. Name: Dana Orange, MD Project Title: Using Dendritic Cells to Evaluate T cell Specificity in ACPA+ RA Institution: Rockefeller University Mentor: Gila Budescu, PhD Award Period: September 1, August 30, 2014 Study Section: Cellular Immunology Disease Focus: Rheumatoid Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Recent advances in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have improved the quality of life for many patients living with the disease. We now have potent drugs, which block cytokines such as TNF and IL6 inhibitors or lead to the death certain types of cells such as B cells. Still, many patients receive inadequate relief or unwanted side effects from those drugs. One major problem with cytokine inhibitors is that they do not block only arthritis-associated inflammation but all inflammation and so can lead to increased susceptibility to infection and possibly tumors. The goal of this project is to look at arthritis specific T cell responses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with the hope that one day we can turn off the immune responses that cause arthritis without increasing susceptibility to infection. There are some hints that T cells may play a pivotal role in the initiation of arthritis: T cells can be found in inflamed joints, the gene that confers the most increased risk for arthritis is involved in activating specific T cells, and the antibodies seen in RA patients are of the type that are usually thought to require a helper T cell for their generation. We now have more sensitive ways of diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis earlier but we still don t know how it starts. The ultimate goal is to figure out what causes arthritis so we can cure arthritis.
10 Name: Michelle J. Ormseth, MD Project Title: HDL Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis Institution: Vanderbilt University Medical Center Mentor: C. Michael Stein MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2015 Study Section: Clinical Research Disease Focus: Rheumatoid Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) develop hardening of the arteries, called atherosclerosis, much earlier in life than healthy people. This leads to RA patients having double the risk of heart attacks compared to the general population. However, it is much harder to predict atherosclerosis in patients with RA than in the general population. High density lipoprotein (HDL) is considered good cholesterol, protecting most people from atherosclerosis by removing cholesterol from the artery wall. However, in RA patients HDL doesn t seem to always be protective. We believe this is because HDL is made dysfunctional by inflammation and oxidative stress. For example, oxidative stress can rapidly damage proteins like HDL. This changes the protein structure, stops it working properly, and makes the protein unrecognizable to the immune system, resulting in the body making antibodies against the damaged protein. These antibodies can be an easily detectable marker that these changes have occurred or can attach to the protein and affect its function. We will determine if HDL dysfunction in patients with RA is associated with atherosclerosis, inflammation, oxidative stress and antibodies that bind to a damaged protein in HDL. To do this we will use stored blood samples from 169 RA patients and 92 non-ra controls that have been in other studies where we measured markers of inflammation, oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. We will add patient blood that is enriched with HDL to cholesterol-filled cells and measure how much cholesterol each person s HDL removes from cells. We will also measure levels of antibodies that bind to a damaged protein in HDL. For analyses we will compare HDL function between RA patients and non-ra controls and the relationship between HDL function and measures of atherosclerosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and antibodies to modified protein component of HDL. This study is important because heart disease due to atherosclerosis is the most common cause of death in RA patients. This study will give us tools to better predict which patients are at highest risk to develop atherosclerosis, and provide important information to devise new ways to reduce atherosclerosis risk in order to prolong the lives of patients with RA. Name: Julie Jisun Paik, MD Project Title: Neuropathy in Scleroderma) Institution: Johns Hopkins University Mentor: Laura K. Hummers MD Award Period: July 1, June 30, 2015 Study Section: Clinical Research Disease Focus: Scleroderma Lay Language Summary: Nerve pain can cause significant disability and pain in patients with scleroderma. Since nerve conduction studies and muscle biopsies can provide objective evidence of
11 nerve dysfunction, we decided to study scleroderma patients with muscle weakness. Twenty-seven muscle biopsies were reviewed from scleroderma patients who had muscle weakness. Esterase staining, which is a special stain that is prominent on muscle biopsy if there is nerve damage was found in over 50% of these biopsies. Furthermore, 63% of the same group of scleroderma patients also had evidence of nerve damage on the gold standard test nerve conduction study. To make sure that this was not coincidental, we also compared this group of scleroderma patients with 26 patients with another autoimmune muscle disease- dermatomyositis. There were only 15% of dermatomyositis patients who had evidence of nerve damage on biopsy and only 8% had evidence of nerve damage on the gold standard test of nerve conduction. Thus, overall 78% of scleroderma patients with muscle weakness had evidence of nerve dysfunction on muscle biopsy and or/nerve conduction study. Based on this preliminary data, the purpose of this proposal is to first determine what the rate of nerve dysfunction is in scleroderma patients since it is completely unknown. And second, once we determine which patients have neuropathy, we will determine if there is any clinical correlation between diffuse or limited scleroderma, autoantibody profile, muscle weakness, and disability. We expect to find that nerve dysfunction will be more common in patients with muscle weakness as shown in our preliminary study. This will be important because it can identify a special group of scleroderma patients who may have a different prognosis in terms of their disability and pain from not only scleroderma in of itself but also from nerve pain and dysfunction. Once identified, they may require even more tailored therapy for their disease to prevent further disability. Name: Sebastian Horacio Unizony, MD Project Title: Mechanisms of action of anti IL-6 therapy in Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) Institution: Massachusetts General Hospital Mentor: John Stone, MD, MPH Award Period: October 1, September 30, 2014 Study Section: Clinical Immunology Disease Focus: Other Lay Language Summary: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a disease that causes inflammation within the arteries of the human body with predilection for the aorta and its main branches. GCA is the most common form of vasculitis in adults, and more than 200,000 persons are affected by this disease in the United States now. Patients with this condition experience severe headaches, jaw pain, visual abnormalities, and generalized body aches, but the most feared complication is blindness, which occurs in about 1 out of 7 cases Cells of the immune system called lymphocytes "attack" the arteries in GCA. Two specific types of lymphocytes, namely Th1 and Th17 cells, orchestrate this process. Besides infiltrating (occupying) the arteries, the number of these cells is increased in the blood of GCA patients. The treatment of GCA is challenging. This condition responds to moderate doses of glucorticoids (prednisone) but most of the patients suffer disease exacerbations (flares) when trying to come off this medication. The reason for this is unknown, but might be related to the fact that the glucocorticoids only reduce the number of Th17 cells but spare the Th1 lymphocytes, that remain elevated. More over, the glucocorticoids cause undesirable side effects in the majority of the patients that use them (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, cataracts, bone fractures, stomach bleeding, and weight gain).
12 Other drugs have failed to ameliorate the disease and reduce the requirement of glucocorticoids. Therefore, there is an unmet need for new medications to control the inflammation, and reduce the use and side effects of glucocorticoids in individuals with GCA Research showed that a molecule called interleukin (IL)-6 may have an important role in causing inflammation in GCA. Tocilizumab (TCZ), a drug that blocks the actions of IL-6, has been developed. Studies using TCZ in a small number of GCA patients showed promising results, therefore, a large controlled trial is on its way. Despite these encouraging results, we do not know how TCZ works in GCA, or whether this medication is good for all the patients. We speculate that TCZ decreases the number of inflammatory lymphocytes, but we do not know if both (Th1 and Th17) lymphocyte types are targeted. To answer these questions, we will study patients with GCA treated with TCZ, and we will analyze the impact that this medication has in the lymphocytes that cause the disease. We will measure the number of Th1 and Th17 cells (and several molecules related with them) in the blood of these patients over the period of one year. If both cell types are decreased, then TCZ will prove to represent an alternative option for patients with GCA. If only one lymphocyte type is affected and the other type is spared, then we will provide a note of caution regarding the value of this medication in GCA. Name: Yujuan Zhang, MD Project Title: The role of IL-1 in sjia monocyte phenotypes Institution: Stanford University Mentor: Elizabeth Mellins, MD Award Period: July 1, 2012 June 30, 2014 Study Section: Cellular Immunology Disease Focus: Juvenille Rheumatoid Arthritis Lay Language Summary: Systemic idiopathic juvenile arthritis (SJIA) is a chronic childhood disease that causes arthritis, fever, rash and other kinds of inflammation (e.g. around the heart and lungs). It is unknown what causes this disease, or what drives one of its main complications, called macrophage activation syndrome. Notably, some patients respond to medication that inhibits IL-1, an inflammatory mediator made by the body. In conjunction with a trial of the IL-1 inhibitor Rilanocept, we propose to investigate how IL-1 affects a particular immune cell type, the monocyte, which appears to be a key cell in SJIA pathology. We also hope to identify changes in monocytes during disease that predict response to Rilanocept.
Myositis and Your Lungs
 Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
SPOTLIGHTONRESEARCH. Grant Recipients. The physical and financial ramifications of arthritis both on. From Bench to Bedside
 SPOTLIGHTONRESEARCH Grant Recipients SUMMER 2012 From Bench to Bedside These ten Arthritis Foundation grant recipients are investigating the causes of arthritis with the goals of advancing more effective
SPOTLIGHTONRESEARCH Grant Recipients SUMMER 2012 From Bench to Bedside These ten Arthritis Foundation grant recipients are investigating the causes of arthritis with the goals of advancing more effective
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
GIANT CELL ARTERITIS. Page 1 of 6 Reproduction of this material requires written permission of the Vasculitis Foundation. Copyright 2018.
 What is giant cell arteritis (GCA)? Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage
What is giant cell arteritis (GCA)? Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage
Antibiotic Therapy for Systemic Scleroderma
 Antibiotic Therapy for Systemic Scleroderma Background The concept of using antibiotics to treat scleroderma stems from research done initially by Thomas M Brown, MD at the National Institutes of Health,
Antibiotic Therapy for Systemic Scleroderma Background The concept of using antibiotics to treat scleroderma stems from research done initially by Thomas M Brown, MD at the National Institutes of Health,
Lupus. Fast facts. What is lupus? What causes lupus? Who gets lupus?
 Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
10/25/2018. Autoimmunity and how to treat it. Disclosure. Why do we get autoimmunity? James Verbsky MD/PhD Pediatric Rheumatology/Immunology
 Autoimmunity and how to treat it James Verbsky MD/PhD Pediatric Rheumatology/Immunology Disclosure None I will mention drug names and some brand names but I have no financial interest or any other ties
Autoimmunity and how to treat it James Verbsky MD/PhD Pediatric Rheumatology/Immunology Disclosure None I will mention drug names and some brand names but I have no financial interest or any other ties
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
What is Enbrel? Key features
 What is Enbrel? Enbrel (also known by its generic name etanercept) is a biologic medication approved in April 2004 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe
What is Enbrel? Enbrel (also known by its generic name etanercept) is a biologic medication approved in April 2004 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Tocilizumab for Giant cell arteritis (adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Tocilizumab for Giant cell arteritis (adults) Version Number: NHS England A13X12/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Tocilizumab for Giant cell arteritis (adults) Version Number: NHS England A13X12/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Clinician Educator. Available daily in outpatient clinics and teaches inpatient consultation in rheumatology and in Fellow s Clinic.
 Full Name with credentials Role in training program Description of involvement 1. Jose Aliling, Clinical Instructor Available daily in Thousand Oaks outpatient clinic, teaches 2. Roy Altman, Emeritus of
Full Name with credentials Role in training program Description of involvement 1. Jose Aliling, Clinical Instructor Available daily in Thousand Oaks outpatient clinic, teaches 2. Roy Altman, Emeritus of
Mechanisms of Autontibodies
 Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Staging of Type 1 Diabetes: Clinical Implications. April Deborah Hefty, MN, RN, CDE.
 Staging of Type 1 Diabetes: TT Clinical Implications April 2016 Deborah Hefty, MN, RN, CDE dhefty@benaroyaresearch.org BRI s major contributions to type 1 diabetes research Identified type 1 diabetes susceptibility
Staging of Type 1 Diabetes: TT Clinical Implications April 2016 Deborah Hefty, MN, RN, CDE dhefty@benaroyaresearch.org BRI s major contributions to type 1 diabetes research Identified type 1 diabetes susceptibility
ENFERMEDADES AUTOINMUNES SISTÉMICAS. Dr. J. María Pego Reigosa
 ENFERMEDADES AUTOINMUNES SISTÉMICAS Dr. J. María Pego Reigosa ABSTRACT NUMBER: 888 PHASE 3 TRIAL RESULTS WITH BLISIBIMOD, A SELECTIVE INHIBITOR OF B-CELL ACTIVATING FACTOR, IN SUBJECTS WITH MODERATE-TO-SEVERE
ENFERMEDADES AUTOINMUNES SISTÉMICAS Dr. J. María Pego Reigosa ABSTRACT NUMBER: 888 PHASE 3 TRIAL RESULTS WITH BLISIBIMOD, A SELECTIVE INHIBITOR OF B-CELL ACTIVATING FACTOR, IN SUBJECTS WITH MODERATE-TO-SEVERE
AD (Leave blank) PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-06-2-0038 TITLE:T Cell Lipid rafts and complement Ligands for Diagnosis and Monitoring PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George C. Tsokos, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-06-2-0038 TITLE:T Cell Lipid rafts and complement Ligands for Diagnosis and Monitoring PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George C. Tsokos, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
What will we discuss today?
 Autoimmune diseases What will we discuss today? Introduction to autoimmune diseases Some examples Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Sometimes relapsing Progressive damage Epitope spreading more
Autoimmune diseases What will we discuss today? Introduction to autoimmune diseases Some examples Introduction to autoimmune diseases Chronic Sometimes relapsing Progressive damage Epitope spreading more
Investor Update. Basel, 24 January 2017
 Investor Update Basel, 24 January 2017 FDA grants priority review for Roche s Actemra/RoActemra (tocilizumab) supplemental biologics license application for giant cell arteritis, a form of vasculitis Roche
Investor Update Basel, 24 January 2017 FDA grants priority review for Roche s Actemra/RoActemra (tocilizumab) supplemental biologics license application for giant cell arteritis, a form of vasculitis Roche
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Arthritis. Canada s most common chronic health condition. About the Arthritis Society
 About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
The Diagnosis of Lupus
 The Diagnosis of Lupus LUPUSUK 2017 This information booklet has been produced by LUPUS UK 2017 LUPUS UK LUPUS UK is the registered national charity for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and
The Diagnosis of Lupus LUPUSUK 2017 This information booklet has been produced by LUPUS UK 2017 LUPUS UK LUPUS UK is the registered national charity for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW. Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center
 RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL
 TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease. Mark Gourley, MD
 What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
What your autoantibodies tell us about your disease Mark Gourley, MD The Importance of the Immune System Defends us against foreign invaders Self (cancer) and Nonself (virus, bacteria, etc.) But, if the
The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. However, gender, race, and genetics can increase the risk of developing the condition:
 What is sarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease in which granulomas, or clumps of inflammatory cells, form in various organs. This causes organ inflammation. Sarcoidosis may be triggered by
What is sarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease in which granulomas, or clumps of inflammatory cells, form in various organs. This causes organ inflammation. Sarcoidosis may be triggered by
Addressing Vascular Plaque Ruptures
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/medical-breakthroughs-from-penn-medicine/addressing-vascularplaque-ruptures/3131/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/medical-breakthroughs-from-penn-medicine/addressing-vascularplaque-ruptures/3131/
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Q&A for the BCG Clinical Trial Program at MGH
 Q&A for the BCG Clinical Trial Program at MGH www.faustmanlab.org Where are the BCG clinical trials being conducted? The BCG clinical trials are being conducted in the Immunobiology Lab at Massachusetts
Q&A for the BCG Clinical Trial Program at MGH www.faustmanlab.org Where are the BCG clinical trials being conducted? The BCG clinical trials are being conducted in the Immunobiology Lab at Massachusetts
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis
 Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
What prescribers need to know
 HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) What prescribers need to know 2 / This is your guide to identifying HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in your Electronic Medical
HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) What prescribers need to know 2 / This is your guide to identifying HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in your Electronic Medical
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for.
 Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Editing file. Color code: Important in red Extra in blue. Autoimmune Diseases
 Editing file Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Autoimmune Diseases Objectives To know that the inflammatory processes in autoimmune diseases are mediated by hypersensitivity reactions (type II,
Editing file Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Autoimmune Diseases Objectives To know that the inflammatory processes in autoimmune diseases are mediated by hypersensitivity reactions (type II,
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Oral Disease as a Risk Factor for Acute Coronary Syndrome Single Center Experience
 1167 International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health Oral Disease as a Risk Factor for Acute Coronary Syndrome Single Center Experience Sachin Kumar Amruthlal Jain
1167 International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health Oral Disease as a Risk Factor for Acute Coronary Syndrome Single Center Experience Sachin Kumar Amruthlal Jain
Overview of Paediatric Investigation Plan (PIP) in Paediatric Rheumatology
 Overview of Paediatric Investigation Plan (PIP) in Paediatric Rheumatology Paediatric Rheumatology Expert Meeting, London 4 th December 29 Dr. Richard Veselý, Dr. Emma Sala Soriano Paediatric Investigation
Overview of Paediatric Investigation Plan (PIP) in Paediatric Rheumatology Paediatric Rheumatology Expert Meeting, London 4 th December 29 Dr. Richard Veselý, Dr. Emma Sala Soriano Paediatric Investigation
Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MSc HVD05_1.ppt Outline Review of autoimmune diseases (AID). Role of transplantation for AID Data collection:
Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MSc HVD05_1.ppt Outline Review of autoimmune diseases (AID). Role of transplantation for AID Data collection:
ADDITIONAL DOSAGE STRENGTHS OF OTREXUP (METHOTREXATE) INJECTION APPROVED BY FDA
 ADDITIONAL DOSAGE STRENGTHS OF OTREXUP (METHOTREXATE) INJECTION APPROVED BY FDA Now Available 12.5 mg/0.4 ml, 17.5 mg/0.4 ml and 22.5 mg/0.4 ml EWING, N.J., March 29, 2016 Antares Pharma, Inc. (NASDAQ:
ADDITIONAL DOSAGE STRENGTHS OF OTREXUP (METHOTREXATE) INJECTION APPROVED BY FDA Now Available 12.5 mg/0.4 ml, 17.5 mg/0.4 ml and 22.5 mg/0.4 ml EWING, N.J., March 29, 2016 Antares Pharma, Inc. (NASDAQ:
Periodontal (Gum) Disease
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015!
 Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis
 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis You may think that arthritis is a single condition, but there are many forms of arthritis. Each type can be caused by different
Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis You may think that arthritis is a single condition, but there are many forms of arthritis. Each type can be caused by different
Quality Data on Core Measures
 Quality Data on Core Measures The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) have developed several measurements to reflect the quality of care in hospitals. They include pneumonia, surgical care, heart failure
Quality Data on Core Measures The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) have developed several measurements to reflect the quality of care in hospitals. They include pneumonia, surgical care, heart failure
How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
 Fever with no known cause Red rashes, most often on the face Chest pain when taking a deep breath Hair loss Pale or purple fingers or toes Sensitivity to the sun Swelling in legs or around eyes Mouth ulcers
Fever with no known cause Red rashes, most often on the face Chest pain when taking a deep breath Hair loss Pale or purple fingers or toes Sensitivity to the sun Swelling in legs or around eyes Mouth ulcers
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY
 Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
A Patient s Guide to Understanding Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis
 A Patient s Guide to Understanding Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis Compared with the general population, patients with systemic sclerosis (also known as scleroderma) have a higher
A Patient s Guide to Understanding Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis Compared with the general population, patients with systemic sclerosis (also known as scleroderma) have a higher
Announcing HUMIRA. Psoriasis Starter Package
 Announcing HUMIRA (adalimumab) Psoriasis Starter Package HUMIRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy
Announcing HUMIRA (adalimumab) Psoriasis Starter Package HUMIRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy
RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 !! RAMOS RHEUMATOLOGY, PC RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: / / NAME: Birthdate: / / Last First M. I. Age: Sex: F M Marital status: Never married Married Divorced Separated Widowed Partnered/significant
!! RAMOS RHEUMATOLOGY, PC RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: / / NAME: Birthdate: / / Last First M. I. Age: Sex: F M Marital status: Never married Married Divorced Separated Widowed Partnered/significant
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis
 Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Writing White Papers class Bellevue Community College TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OVERVIEW...3 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS... 3 JUVENILE RHEUMATOID
Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Writing White Papers class Bellevue Community College TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OVERVIEW...3 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS... 3 JUVENILE RHEUMATOID
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes
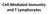 Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
CHRONIC PAIN EVALUATION. Please help us understand your pain by completing this drawing:
 JOSE G. VELIZ MD, INC. Diplomate of the American Board of Interventional Pain Management Diplomate of the American Board of Anesthesiology Diplomate of the American Board of Pain Medicine Fellow of Interventional
JOSE G. VELIZ MD, INC. Diplomate of the American Board of Interventional Pain Management Diplomate of the American Board of Anesthesiology Diplomate of the American Board of Pain Medicine Fellow of Interventional
Clinical Study Results
 Clinical Study Results 1. Study Name What does this summary cover? This summary shows the main results from one clinical study. The results are only for this study. Other studies may find different results.
Clinical Study Results 1. Study Name What does this summary cover? This summary shows the main results from one clinical study. The results are only for this study. Other studies may find different results.
IMO 3100, an antagonist of Toll like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9, demonstrates clinical activity in psoriasis patients
 IMO 3100, an antagonist of Toll like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9, demonstrates clinical activity in psoriasis patients with 4 weeks of treatment in a Phase 2a trial A. B. Kimball 1, J. Krueger 2, T. Sullivan
IMO 3100, an antagonist of Toll like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9, demonstrates clinical activity in psoriasis patients with 4 weeks of treatment in a Phase 2a trial A. B. Kimball 1, J. Krueger 2, T. Sullivan
ArLAR 2018, the Pan Arab Rheumatology Conference in conjunction with the 1st OSR meeting 23 to 25 February 2018, Muscat, Oman.
 ArLAR 2018, the Pan Arab Rheumatology Conference in conjunction with the 1st OSR meeting 23 to 25 February 2018, Muscat, Oman. to change at any time www.arlar.org info@arlar.org #ArLAR2018 Thursday, 22
ArLAR 2018, the Pan Arab Rheumatology Conference in conjunction with the 1st OSR meeting 23 to 25 February 2018, Muscat, Oman. to change at any time www.arlar.org info@arlar.org #ArLAR2018 Thursday, 22
Coronary Artery Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE
 UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE START YOUR JOURNEY TOWARD UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 4 WHAT IS CROHN S DISEASE? 6 Symptoms of Crohn s disease 6 WHAT CAUSES CROHN S DISEASE?
UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE START YOUR JOURNEY TOWARD UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 4 WHAT IS CROHN S DISEASE? 6 Symptoms of Crohn s disease 6 WHAT CAUSES CROHN S DISEASE?
MAGNESIUM: THE FORGOTTON MIRACLE NUTRIENT Part 1 of 2 Articles By Dr. Michael John Badanek, BS, DC, CNS, CTTP, DACBN, DCBCN, MSGR.
 MAGNESIUM: THE FORGOTTON MIRACLE NUTRIENT Part 1 of 2 Articles By Dr. Michael John Badanek, BS, DC, CNS, CTTP, DACBN, DCBCN, MSGR. /CHEV Magnesium Misinformation is Widespread, Untreated, and Potentially
MAGNESIUM: THE FORGOTTON MIRACLE NUTRIENT Part 1 of 2 Articles By Dr. Michael John Badanek, BS, DC, CNS, CTTP, DACBN, DCBCN, MSGR. /CHEV Magnesium Misinformation is Widespread, Untreated, and Potentially
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
 Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis
 Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective
 Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective Pamela Thorpe, MD, FACP Lupus Foundation of America, Inc. Philadelphia Tri-State Chapter Volunteer May 2014 My Own Story Is it Lupus Yet? The What What is this?
Living with Lupus: An Insider s Perspective Pamela Thorpe, MD, FACP Lupus Foundation of America, Inc. Philadelphia Tri-State Chapter Volunteer May 2014 My Own Story Is it Lupus Yet? The What What is this?
Year In Review: VasculitisPers. Disclosures. Learning Objectives. none 4/16/2018. Describe new medications for the treatment of vasculitis
 Year In Review: VasculitisPers Cailin Sibley, M.D., M.H.S. Director, Vasculitis Clinic April 27 th, 2018 NTEREST DISCLOSURE Disclosures none Learning Objectives Describe new medications for the treatment
Year In Review: VasculitisPers Cailin Sibley, M.D., M.H.S. Director, Vasculitis Clinic April 27 th, 2018 NTEREST DISCLOSURE Disclosures none Learning Objectives Describe new medications for the treatment
associated conditions a closer look at connective tissue disease and PAH
 associated conditions a closer look at connective tissue disease and PAH The link between connective tissue disease and PAH Those living with a connective tissue disease (CTD) have an increased risk of
associated conditions a closer look at connective tissue disease and PAH The link between connective tissue disease and PAH Those living with a connective tissue disease (CTD) have an increased risk of
LUPUS. and Associated Conditions LUPUSUK 2015
 11 LUPUS and Associated Conditions LUPUSUK 2015 LUPUS and Associated Conditions Although lupus most often occurs alone, in many people, other medical conditions caused by or associated with the disease
11 LUPUS and Associated Conditions LUPUSUK 2015 LUPUS and Associated Conditions Although lupus most often occurs alone, in many people, other medical conditions caused by or associated with the disease
Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases. Mark Gourley, MD
 Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases Mark Gourley, MD Newsweek January, 2003 Current Knowledge of Environment and Myositis Environment Genes Autoimmunity What Is an Environmental Exposure?
Environmental Influence in Autoimmune Diseases Mark Gourley, MD Newsweek January, 2003 Current Knowledge of Environment and Myositis Environment Genes Autoimmunity What Is an Environmental Exposure?
Carotid Ultrasound Scans for Assessing Cardiovascular Risk
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/lipid-luminations/carotid-ultrasound-scans-for-assessing-cardiovascularrisk/4004/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/lipid-luminations/carotid-ultrasound-scans-for-assessing-cardiovascularrisk/4004/
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE
 Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
Hypertension AN OVERVIEW
 AN OVERVIEW Hypertension Your doctor has determined that you have high blood pressure, or hypertension. Although high blood pressure is never really cured, it can be controlled by early detection, lifestyle
AN OVERVIEW Hypertension Your doctor has determined that you have high blood pressure, or hypertension. Although high blood pressure is never really cured, it can be controlled by early detection, lifestyle
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM VASCULITIS
 What is central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis? Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is among a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which restricts blood flow
What is central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis? Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is among a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which restricts blood flow
Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/ie/intro Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Clinical signs and investigations
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/ie/intro Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Clinical signs and investigations
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets , Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 12/15/ months or as otherwise noted by indication
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS.
 1 IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS. A NETWORK ORGANIZED BY THE EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Coordination:
1 IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS. A NETWORK ORGANIZED BY THE EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Coordination:
Jennifer Lam MPH candidate 2009 Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Preceptors: Wendy Cronin, PhD MT(ASCP), Cathy Goldsborough, RN
 Jennifer Lam MPH candidate 2009 Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Preceptors: Wendy Cronin, PhD MT(ASCP), Cathy Goldsborough, RN Phase Symposium: May 6, 2009 Background & Rationale Maryland
Jennifer Lam MPH candidate 2009 Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Preceptors: Wendy Cronin, PhD MT(ASCP), Cathy Goldsborough, RN Phase Symposium: May 6, 2009 Background & Rationale Maryland
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for the treatment of dermatomyositis and polymyositis (Adults) Reference: NHS England A13X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside
Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
Comments to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Regarding the Patient-Focused Drug Development Re: Docket No. FDA-2012-N-0967
 Comments to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Regarding the Patient-Focused Drug Development Re: Docket No. FDA-2012-N-0967 The American Lung Association welcomes the opportunity to comment on the
Comments to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Regarding the Patient-Focused Drug Development Re: Docket No. FDA-2012-N-0967 The American Lung Association welcomes the opportunity to comment on the
9/25/2013 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
13. Behçet s - In Children
 Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk 13. Behçet s - In Children How are children affected by Behçet s disease? Behçet s disease (also
Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk 13. Behçet s - In Children How are children affected by Behçet s disease? Behçet s disease (also
Diseases in which appear swelling, redness, pain and heat; aspects of the immune system (Inflammatory and immunologic conditions-imid)
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prednisolone is generally preferred amongst glucocorticoids for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive treatment. There are three
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prednisolone is generally preferred amongst glucocorticoids for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive treatment. There are three
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism
 MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders
 Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders Linda Felver, Ph.D., R.N. Associate Professor School of Nursing Oregon Health & Science University The immune system has two arms: Adaptive (Acquired) Immune
Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders Linda Felver, Ph.D., R.N. Associate Professor School of Nursing Oregon Health & Science University The immune system has two arms: Adaptive (Acquired) Immune
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure
 Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 1-1 Chapter Highlights 1. This Manual is for You 2. What is Scleroderma? 3. Who gets Scleroderma? 4. What are the Early Symptoms of Scleroderma? 5. Is All Scleroderma the
Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 1-1 Chapter Highlights 1. This Manual is for You 2. What is Scleroderma? 3. Who gets Scleroderma? 4. What are the Early Symptoms of Scleroderma? 5. Is All Scleroderma the
Evidence Review: Title. Month/ Year. Evidence Review:
 Evidence Review: Title Month/ Year Evidence Review: Rituximab for connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease October 2014 Standard Operating Procedure: NHS England Evidence Review:
Evidence Review: Title Month/ Year Evidence Review: Rituximab for connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease October 2014 Standard Operating Procedure: NHS England Evidence Review:
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
The Importance of Glutamine and Antioxidant Vitamin Supplementation in HIV
 The Importance of Glutamine and Antioxidant Vitamin Supplementation in HIV An Introduction to Glutamine Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, and plays extremely important role in
The Importance of Glutamine and Antioxidant Vitamin Supplementation in HIV An Introduction to Glutamine Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, and plays extremely important role in
Autoimmune disorders: An emerging risk factor for CV disease
 Autoimmune disorders: An emerging risk factor for CV disease DR. SHARON MULVAGH: Greetings. I'm Dr Sharon Mulvagh, professor of medicine and director of Mayo Clinic Women's Heart Clinic. During today's
Autoimmune disorders: An emerging risk factor for CV disease DR. SHARON MULVAGH: Greetings. I'm Dr Sharon Mulvagh, professor of medicine and director of Mayo Clinic Women's Heart Clinic. During today's
What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant
 Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 A Patient s Guide to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 2 kidneys. These changes make it impossible for the kidneys to function normally. The inflammation of SLE can be seen in the lining, covering, and muscles
A Patient s Guide to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 2 kidneys. These changes make it impossible for the kidneys to function normally. The inflammation of SLE can be seen in the lining, covering, and muscles
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine COPYRIGHT. Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
 Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
Immunity and Infection. Chapter 17
 Immunity and Infection Chapter 17 The Chain of Infection Transmitted through a chain of infection (six links) Pathogen: Disease causing microorganism Reservoir: Natural environment of the pathogen Portal
Immunity and Infection Chapter 17 The Chain of Infection Transmitted through a chain of infection (six links) Pathogen: Disease causing microorganism Reservoir: Natural environment of the pathogen Portal
