Siglec-15 Is A Potential Therapeutic Target For Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
|
|
|
- Anne Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Siglec-15 Is A Potential Therapeutic Target For Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Yusuke Kameda, Masahiko Takahata, Tomohiro Shimizu, Hiroki Hamano, Norimasa Iwasaki. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan. Disclosures: Y. Kameda: None. M. Takahata: None. T. Shimizu: None. H. Hamano: None. N. Iwasaki: None. Introduction: Sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec)-15 is a novel type of immunoreceptor that regulates osteoclast development in association with an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-harboring adaptor DAP12. Recent studies demonstrated that Siglec-15 deficient mice exhibit no growth retardation but mild osteopetrosis due to impaired development of osteoclasts, suggesting that Siglec-15 plays an important role in physiological bone remodeling [1].The role of Siglec-15 in pathological bone loss; however, remains to be elucidated. Especially, it is of great interest whether Siglec-15 is implicated in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Although Siglec-15 was shown to regulate osteoclast development by modulating RANKL signaling, it is unknown whether Siglec-15 is associated with TNFα signaling, which is one of the key molecule for postmenopausal osteoporosis [2]. Therefore, we aimed to investigate whether Siglec-15 deficient mice are resistant to ovariectomy in terms of bone loss and to examine the involvement of Siglec-15 in TNFα induced osteoclastogenesis. Methods: Mice: Both WT and Siglec-15 -/- mice were on a C57BL/6 background. Female mice were ovariectomized (OVX) or sham operated at 14 wk of age. Mice were sacrificed either at 4 weeks after ovariectomy for histology or at 8 weeks after ovariectomy for micro-computed tomography (micro-ct) analysis. Micro-CT analysis: Left tibiae and 5th lumbar vertebral bodies were scanned individually by micro-ct (CT, R_mCT2; Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) at a 10-µm isotropic resolution. Both were quantitatively analyzed using a TRI/3D-BON (Ratoc System Engineering Co. Tokyo, Japan). Histological evaluation: Proximal tibiae of either OVX or sham operated mice were fixed in paraformaldehyde (PFA), decalcified in EDTA, and embedded in paraffin. Sections were stained for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) to observe osteoclasts. In vitro osteoclastogenesis: Bone marrow macrophages (BMMs) were cultured with 30 ng/ml M-CSF and 100 ng/ml TNFα for 5 d at 37 C in a 5% humidified CO2 incubator to generate osteoclasts. Immunocytochemistry: Cells were cultured on plastic wells or on bovine bone slices, and fixed for 5 min with 4% PFA and then treated with 0.1% Triton X-100. The cells were treated with polyclonal anti-siglec-15 antibody followed by staining with Alexa Fluor-labeled secondary antibody (Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA). The cytoskeletal actin was stained using Alexa Fluor 633 phalloidin (Molecular Probes). The nuclei were visualized using 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole reagent (Dojindo Laboratories, Japan). Immunoblot analysis: Cell lysates were extracted using the PhosphoSafe Extraction Reagent (Novagen, Madison, WI). Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analyses using the appropriate antibodies. Statistical analysis: Data of two-group comparisons were analyzed using a two-tailed Student s t test. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The data are represented as mean ± SD. Results: Trabecular bone loss after ovariectomy was observed in both WT and Siglec-15 -/- mice, but the extent of bone loss in Siglec-15 -/- mice was much smaller than that in WT. The percent difference between Sham and OVX groups in proximal tibiae were 50.7% in WT and 20.2% in Siglec-15 -/-, and those in vertebral bodies were 27.4% in WT and 12.1% in Siglec-15 -/- mice, respectively (Fig. 1). Histologically, the number of TRAP positive osteoclasts in OVX mice was much higher than that in sham mice in both WT and Siglec-15 -/- mice. Osteoclasts in Siglec-15 -/- mice were small in size and did not spread on the bone surface and the number of multinuclear osteoclasts in Siglec-15 -/- mice were significantly smaller than that in WT mice (Fig. 2). In vitro experiment showed that Siglec-15 is required for the TNFα-induced development of functional osteoclasts. Under the existence M-CSF, TNFα induced differentiation of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells from WT cells, while it induced predominantly TRAP-positive mononuclear cells from Siglec-15 -/- cells. When cultured on bovine bone slices, Siglec-15 -/- osteoclasts showed impaired bone resorptive activity and could not form an actin ring (Fig. 3). On the contrary to our expectation; however, TNFα-induced intracellular signaling including ERK, Akt, PI3K, IκB, JNK and p38 was not altered in Siglec-15 deficient cells (data not shown). Discussion:
2 This study shows that Siglec-15 is a potential therapeutic target for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Although Siglec-15 deficiency did not completely block estrogen-deficiency induced bone loss, it reduced the estrogen-deficiency induced bone loss to less than half of WT mice. Early studies have shown that upregulated production of TNFα by activated T cells is a primary mechanism for estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss [2]. Although Siglec-15 deficiency does not affect known intracellular signaling downstream of TNFR1, Siglec-15 deficient osteoclasts were morphologically abnormal and showed impaired bone resorptive function, suggesting that Siglec-15 is involved in TNFα induced osteoclastogenesis. Our data suggests that blocking of Siglec-15 reduces bone resorptive activity of osteoclasts in acute estrogen deficiency and that Siglec-15 will be a potential therapeutic target for postmenopausal osteoprosis. Significance: This is the first study to show the relationship of Siglec-15 in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Although further studies are required to confirm our speculation, Siglec-15 may be a target molecule for a novel and effective strategy for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Acknowledgments: This project was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Exploratory Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (N. Iwasaki); and a Grant-in-Aid for Research Activity Start-up from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (to M. Takahata). References: [1] Kameda Y. et al., J Bone Miner Res 2013 (in printing) [2] Roggia C., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:
3
4 ORS 2014 Annual Meeting Poster No: 0563
5
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Estrogen receptor α- (ERα), but not ERβ-signaling, is crucially involved in mechanostimulation of bone fracture healing by whole-body vibration
 Estrogen receptor α- (ERα), but not ERβ-signaling, is crucially involved in mechanostimulation of bone fracture healing by whole-body vibration Melanie Haffner-Luntzer et.al. published in BONE 1 Abstract
Estrogen receptor α- (ERα), but not ERβ-signaling, is crucially involved in mechanostimulation of bone fracture healing by whole-body vibration Melanie Haffner-Luntzer et.al. published in BONE 1 Abstract
Fig. S1 A. week 4 week 6
 Fig. S1 Trabecular Number Trabecular Thickness number/mm 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 mm.45.4.35.3.25.2.15.1.5 SKG-c SKG-A mm 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4.2 Trabecular Spacing D. week 4 week 6 Figure S1. MicroCT analysis
Fig. S1 Trabecular Number Trabecular Thickness number/mm 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 mm.45.4.35.3.25.2.15.1.5 SKG-c SKG-A mm 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4.2 Trabecular Spacing D. week 4 week 6 Figure S1. MicroCT analysis
Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa, Yusuke Ozawa, Kenji
 Supplementary Information Mitochondrial superoxide in osteocytes perturbs canalicular networks in the setting of age-related osteoporosis Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa,
Supplementary Information Mitochondrial superoxide in osteocytes perturbs canalicular networks in the setting of age-related osteoporosis Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa,
Mutation in Osteoactivin Enhances RANKL-Mediated Signaling, Promoting Osteoclast Differentiation, Survival and Inhibiting Bone Resorption
 Mutation in Osteoactivin Enhances RANKL-Mediated Signaling, Promoting Osteoclast Differentiation, Survival and Inhibiting Bone Resorption Samir Abdelmagid, MD, PhD, Fouad Moussa, BS, Sondag Gregory, MS,
Mutation in Osteoactivin Enhances RANKL-Mediated Signaling, Promoting Osteoclast Differentiation, Survival and Inhibiting Bone Resorption Samir Abdelmagid, MD, PhD, Fouad Moussa, BS, Sondag Gregory, MS,
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
Citation Nagasaki University ( 長崎大学 ), 博士 ( 歯学 )
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Inhibitory effects of two ellagitan osteoclastogenesis 岩竹, 真弓 Citation Nagasaki University ( 長崎大学 ), 博士 ( 歯学 ) Issue Date 2016-09-20 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/36927
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Inhibitory effects of two ellagitan osteoclastogenesis 岩竹, 真弓 Citation Nagasaki University ( 長崎大学 ), 博士 ( 歯学 ) Issue Date 2016-09-20 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/36927
Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasma measurements Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were determined using ELISA kits according
Supplemental Data Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasma measurements Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were determined using ELISA kits according
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
RBP-J imposes a requirement for ITAM-mediated costimulation of osteoclastogenesis
 RBP-J imposes a requirement for ITAM-mediated costimulation of osteoclastogenesis Susan Li, 1 Christine H. Miller, 1 Eugenia Giannopoulou, 1,2 Xiaoyu Hu, 1,3 Lionel B. Ivashkiv, 1,3,4 and Baohong Zhao
RBP-J imposes a requirement for ITAM-mediated costimulation of osteoclastogenesis Susan Li, 1 Christine H. Miller, 1 Eugenia Giannopoulou, 1,2 Xiaoyu Hu, 1,3 Lionel B. Ivashkiv, 1,3,4 and Baohong Zhao
Species differences in histomorphometry
 Species differences in histomorphometry Reinhold G. Erben Department of Biomedical Sciences Institute of Physiology and Pathophysiology University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Purpose of histomorphometry
Species differences in histomorphometry Reinhold G. Erben Department of Biomedical Sciences Institute of Physiology and Pathophysiology University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Purpose of histomorphometry
The Regulation of Bone Formation by the Met-5-enkephalin-Opioid Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis
 The Regulation of Bone Formation by the Met-5-enkephalin-Opioid Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis Nikhil Thakur, MD, Sean D. DeBoyace, BS, Bryan S. Margulies, PhD. SUNY Upstate Medical University,
The Regulation of Bone Formation by the Met-5-enkephalin-Opioid Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis Nikhil Thakur, MD, Sean D. DeBoyace, BS, Bryan S. Margulies, PhD. SUNY Upstate Medical University,
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2006 April 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2005 July ; 11(7): 774 779. Regulation of bone mass, bone loss and osteoclast activity by cannabinoid receptors Aymen I Idris,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2005 July ; 11(7): 774 779. Regulation of bone mass, bone loss and osteoclast activity by cannabinoid receptors Aymen I Idris,
A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD)
 A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD) Adeline H. Ng 1,2, Thomas L. Willett, PhD 2,1, Benjamin A. Alman 3,1, Marc D. Grynpas 1,2. 1 University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2 Samuel Lunenfeld
A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD) Adeline H. Ng 1,2, Thomas L. Willett, PhD 2,1, Benjamin A. Alman 3,1, Marc D. Grynpas 1,2. 1 University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2 Samuel Lunenfeld
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate
 Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells?
 Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells? KOJI IWASAKI 1, Hideki Sudo 2, Katsuhisa Yamada 1, Norimasa Iwasaki 1. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate
Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells? KOJI IWASAKI 1, Hideki Sudo 2, Katsuhisa Yamada 1, Norimasa Iwasaki 1. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate
Supplemental figures and figure legends (90517-INS-RG-RV-2) Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental figures and figure legends (957-INS-RG-RV-) Supplemental Figure. A B.5.5 Interaction p=.89 Model p
Supplemental figures and figure legends (957-INS-RG-RV-) Supplemental Figure. A B.5.5 Interaction p=.89 Model p
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals. Massimo Marenzana
 CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss by enhancing T-cell production of TNF-α
 Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss by enhancing T-cell production of TNF-α Simone Cenci, 1,2 M. Neale Weitzmann, 1 Cristiana Roggia, 1 Noriyuki Namba, 3 Deborah Novack, 3 Jessica Woodring, 1 and Roberto
Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss by enhancing T-cell production of TNF-α Simone Cenci, 1,2 M. Neale Weitzmann, 1 Cristiana Roggia, 1 Noriyuki Namba, 3 Deborah Novack, 3 Jessica Woodring, 1 and Roberto
1. Supplementary Prevention Experiment Additional Results
 1. Supplementary 1. 1. Prevention Experiment Additional Results Figure 1 presents the NMR measurements of tibiae and femurs bones, which were measured 6 weeks post operation at the central zone of bone
1. Supplementary 1. 1. Prevention Experiment Additional Results Figure 1 presents the NMR measurements of tibiae and femurs bones, which were measured 6 weeks post operation at the central zone of bone
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis
 In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
Osteoclasts- What Do They Do and How Do They Do It? Prof. Steven L. Teitelbaum
 Osteoclasts; What Do They Do 1 Steven L. Teitelbaum, M.D. Wilma and Roswell Messing Professor Department of Pathology and Immunology Washington University School of Medicine OSTEOCLASTS OSTEOBLASTS 2 Osteoclasts
Osteoclasts; What Do They Do 1 Steven L. Teitelbaum, M.D. Wilma and Roswell Messing Professor Department of Pathology and Immunology Washington University School of Medicine OSTEOCLASTS OSTEOBLASTS 2 Osteoclasts
Disclosures CONSULTANT WRIGHT MEDICAL CONSULTANT ORTHO FIX
 Disclosures CONSULTANT WRIGHT MEDICAL CONSULTANT ORTHO FIX Overview Radiographic Pattern Histopathology Pathways: RANKL/OPG AGE/RAGE Treatment based on Evidence Radiographic Pattern Pattern of Diabetic
Disclosures CONSULTANT WRIGHT MEDICAL CONSULTANT ORTHO FIX Overview Radiographic Pattern Histopathology Pathways: RANKL/OPG AGE/RAGE Treatment based on Evidence Radiographic Pattern Pattern of Diabetic
Bryan D. Johnston, BSc
 The effect of 17- estradiol therapy on bone mineral density and structure of alveolar bone in the ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal osteoporosis Bryan D. Johnston, BSc Submitted in partial fulfillment
The effect of 17- estradiol therapy on bone mineral density and structure of alveolar bone in the ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal osteoporosis Bryan D. Johnston, BSc Submitted in partial fulfillment
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Immune receptors Y Y. Multiple immune responses CLR TLR NLR ITAM RLR. C-type lectin. ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif
 C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-593 TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Selvarangan Ponnazhagan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-593 TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Selvarangan Ponnazhagan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Effect Of Centralization For Extruded Meniscus Extrusion In A Rat Model
 Effect Of Centralization For Extruded Meniscus Extrusion In A Rat Model Kenichi Kawabata 1, Nobutake Ozeki 1, Hideyuki Koga 1, Yusuke Nakagawa 1, Mio Udo 1, Ryusuke Saito 1, Katsuaki Yanagisawa 1, Toshiyuki
Effect Of Centralization For Extruded Meniscus Extrusion In A Rat Model Kenichi Kawabata 1, Nobutake Ozeki 1, Hideyuki Koga 1, Yusuke Nakagawa 1, Mio Udo 1, Ryusuke Saito 1, Katsuaki Yanagisawa 1, Toshiyuki
Title oral squamous cell carcinoma. Alternative. Takano, N. Journal Oral oncology, 43(3):
 Establishment of a murine model of Title oral squamous cell carcinoma Author(s) Nomura, T; Shibahara, T; Katakura, Alternative Takano, N Journal Oral oncology, 43(3): 257-262 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/56
Establishment of a murine model of Title oral squamous cell carcinoma Author(s) Nomura, T; Shibahara, T; Katakura, Alternative Takano, N Journal Oral oncology, 43(3): 257-262 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/56
Retinoid X receptors orchestrate osteoclast differentiation and postnatal bone remodeling
 Retinoid X receptors orchestrate osteoclast differentiation and postnatal bone remodeling María P. Menéndez-Gutiérrez, 1 Tamás Rőszer, 1,2 Lucía Fuentes, 1 Vanessa Núñez, 1 Amelia Escolano, 3 Juan Miguel
Retinoid X receptors orchestrate osteoclast differentiation and postnatal bone remodeling María P. Menéndez-Gutiérrez, 1 Tamás Rőszer, 1,2 Lucía Fuentes, 1 Vanessa Núñez, 1 Amelia Escolano, 3 Juan Miguel
TITLE: Effect of a High Bone Turnover State Induced by Estrogen Deficiency on the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer Bone Metastases
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-5-1-311 TITLE: Effect of a High Bone Turnover State Induced by Estrogen Deficiency on the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer Bone Metastases PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Wende
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-5-1-311 TITLE: Effect of a High Bone Turnover State Induced by Estrogen Deficiency on the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer Bone Metastases PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Wende
Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation via the osteoclast
 Research article Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation via the osteoclast Hyun-Ju Kim, 1 Haibo Zhao, 1 Hideki Kitaura, 1 Sandip Bhattacharyya, 2 Judson A. Brewer, 2 Louis J. Muglia, 2 F. Patrick Ross,
Research article Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation via the osteoclast Hyun-Ju Kim, 1 Haibo Zhao, 1 Hideki Kitaura, 1 Sandip Bhattacharyya, 2 Judson A. Brewer, 2 Louis J. Muglia, 2 F. Patrick Ross,
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
a surface permeabilized
 a surface permeabilized RAW 64.7 P388D1 J774 b CD11b + Ly-6G - Blood Monocytes WT Supplementary Figure 1. Cell surface expression on macrophages and DCs. (a) RAW64.7, P388D1, and J774 cells were subjected
a surface permeabilized RAW 64.7 P388D1 J774 b CD11b + Ly-6G - Blood Monocytes WT Supplementary Figure 1. Cell surface expression on macrophages and DCs. (a) RAW64.7, P388D1, and J774 cells were subjected
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
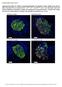 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
The ADP receptor P2RY12 regulates osteoclast function and pathologic bone remodeling
 Research article The ADP receptor P2RY12 regulates osteoclast function and pathologic bone remodeling Xinming Su, 1 Desiree H. Floyd, 1 Alun Hughes, 2 Jingyu Xiang, 1 Jochen G. Schneider, 1,3,4 Ozge Uluckan,
Research article The ADP receptor P2RY12 regulates osteoclast function and pathologic bone remodeling Xinming Su, 1 Desiree H. Floyd, 1 Alun Hughes, 2 Jingyu Xiang, 1 Jochen G. Schneider, 1,3,4 Ozge Uluckan,
Cdc42 regulates bone modeling and remodeling in mice by modulating RANKL/M-CSF signaling and osteoclast polarization
 Cdc42 regulates bone modeling and remodeling in mice by modulating RANKL/M-CSF signaling and osteoclast polarization Yuji Ito,, F. Patrick Ross, Haibo Zhao J Clin Invest. 2010;120(6):1981-1993. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci39650.
Cdc42 regulates bone modeling and remodeling in mice by modulating RANKL/M-CSF signaling and osteoclast polarization Yuji Ito,, F. Patrick Ross, Haibo Zhao J Clin Invest. 2010;120(6):1981-1993. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci39650.
PLCγ2 regulates osteoclastogenesis via its interaction with ITAM proteins and GAB2
 Research article PLCγ2 regulates osteoclastogenesis via its interaction with ITAM proteins and GAB2 Dailing Mao, 1 Holly Epple, 2 Brian Uthgenannt, 1 Deborah V. Novack, 3 and Roberta Faccio 1 1 Department
Research article PLCγ2 regulates osteoclastogenesis via its interaction with ITAM proteins and GAB2 Dailing Mao, 1 Holly Epple, 2 Brian Uthgenannt, 1 Deborah V. Novack, 3 and Roberta Faccio 1 1 Department
Terms and Conditions for Self-Archi
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Castalagin Exerts Inhibitory Effect Blocking a Broad Range of Signaling Iwatake, Mayumi; Okamoto, Kuniaki; Takayuki Phytotherapy Research, 29(6),
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Castalagin Exerts Inhibitory Effect Blocking a Broad Range of Signaling Iwatake, Mayumi; Okamoto, Kuniaki; Takayuki Phytotherapy Research, 29(6),
Joint and Epiphyseal Progenitor Cells Revitalize Tendon Graft and Form Mineralized Insertion Sites in Murine ACL Reconstruction Model
 Joint and Epiphyseal Progenitor Cells Revitalize Tendon Graft and Form Mineralized Insertion Sites in Murine ACL Reconstruction Model Yusuke Hagiwara 1,2, Nathaniel A. Dyment 3, Douglas J. Adams 3, Shinro
Joint and Epiphyseal Progenitor Cells Revitalize Tendon Graft and Form Mineralized Insertion Sites in Murine ACL Reconstruction Model Yusuke Hagiwara 1,2, Nathaniel A. Dyment 3, Douglas J. Adams 3, Shinro
Original Article Establishing a rapid animal model of osteoporosis with ovariectomy plus low calcium diet in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(8):5123-5128 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001041 Original Article Establishing a rapid animal model of osteoporosis with ovariectomy plus low calcium diet in rats Xiang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(8):5123-5128 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001041 Original Article Establishing a rapid animal model of osteoporosis with ovariectomy plus low calcium diet in rats Xiang
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/ncb1963 a wild 5.3kb 11.2kb targeting vector stop PCR primer KKpn NNhe targeted allele 5.7kb 6.8kb probe b d (g) 35 3 25 2 genomic Southern blot Kpn I digest Nhe I digest / / / / / / 11.2 kb 5.7
DOI:.38/ncb1963 a wild 5.3kb 11.2kb targeting vector stop PCR primer KKpn NNhe targeted allele 5.7kb 6.8kb probe b d (g) 35 3 25 2 genomic Southern blot Kpn I digest Nhe I digest / / / / / / 11.2 kb 5.7
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Original Article Eleutherococcus senticosus Inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation by attenuating the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathway
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4514-4521 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048305 Original Article Eleutherococcus senticosus Inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation by attenuating the NF-κB and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4514-4521 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048305 Original Article Eleutherococcus senticosus Inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation by attenuating the NF-κB and
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Interactions between bone and the central nervous system Florent Elefteriou, PhD
 Interactions between bone and the central nervous system Florent Elefteriou, PhD Department of Medicine Center for Bone Biology VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY Nashville, USA BONE REMODELING Bone marrow cells Estrogen
Interactions between bone and the central nervous system Florent Elefteriou, PhD Department of Medicine Center for Bone Biology VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY Nashville, USA BONE REMODELING Bone marrow cells Estrogen
Dihydroartemisinin, an anti-malaria drug, suppresses estrogen deficiencyinduced. osteoporosis, osteoclast formation and RANKL induced signalling
 Dihydroartemisinin, an anti-malaria drug, suppresses estrogen deficiencyinduced osteoporosis, osteoclast formation and RANKL induced signalling pathways Lin Zhou 1, Qian Liu 1, 2, Mingli Yang 1, Tao Wang
Dihydroartemisinin, an anti-malaria drug, suppresses estrogen deficiencyinduced osteoporosis, osteoclast formation and RANKL induced signalling pathways Lin Zhou 1, Qian Liu 1, 2, Mingli Yang 1, Tao Wang
Prediction Of Pathological Fracture In The Proximal Femora With Bone Lesions Using A CT Scan-based Finite Element Method
 Prediction Of Pathological Fracture In The Proximal Femora With Bone Lesions Using A CT Scan-based Finite Element Method Yusuke Kawabata 1, Kosuke Matsuo 2, Hiroyuki Ike, MD 2, Tomoyuki Saito, MD, PhD
Prediction Of Pathological Fracture In The Proximal Femora With Bone Lesions Using A CT Scan-based Finite Element Method Yusuke Kawabata 1, Kosuke Matsuo 2, Hiroyuki Ike, MD 2, Tomoyuki Saito, MD, PhD
Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function
 Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function Prof. Ralph Müller, PhD Institute for Biomechanics, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland 1 Motivation and aims Engineering endpoints have become an important
Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function Prof. Ralph Müller, PhD Institute for Biomechanics, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland 1 Motivation and aims Engineering endpoints have become an important
Dual effects of baicalin on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption
 Received: 30 December 2017 Revised: 5 June 2018 Accepted: 12 June 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13785 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dual effects of baicalin on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption Xuanyuan Lu 1
Received: 30 December 2017 Revised: 5 June 2018 Accepted: 12 June 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13785 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dual effects of baicalin on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption Xuanyuan Lu 1
Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method
 Research Article Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method Mitsugu Todo * Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University, Kasuga, Japan
Research Article Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method Mitsugu Todo * Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University, Kasuga, Japan
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB
 Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
TITLE: Enhancing Osteoclastic Resorption for the Prevention and Treatment of Heterotopic Ossification
 Award Number:W81XWH-11-2-0042 TITLE: Enhancing Osteoclastic Resorption for the Prevention and Treatment of Heterotopic Ossification PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kevin P. McHugh, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Award Number:W81XWH-11-2-0042 TITLE: Enhancing Osteoclastic Resorption for the Prevention and Treatment of Heterotopic Ossification PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kevin P. McHugh, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis. March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD
 Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD Review: normal bone formation Bone Modeling Remodeling Peak Bone Mass Maximum bone mass
Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD Review: normal bone formation Bone Modeling Remodeling Peak Bone Mass Maximum bone mass
Osteoporosis and its Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Prednisolone Therapy
 Osteoporosis and its Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Prednisolone Therapy Master s Thesis Ane Eriksen Medicine with Industrial Specialization Aalborg University Osteoporosis and its Association
Osteoporosis and its Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Prednisolone Therapy Master s Thesis Ane Eriksen Medicine with Industrial Specialization Aalborg University Osteoporosis and its Association
NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES
 NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES C.T. Lim, B.H.B. Omar and J.C.J. Goh 1 Division of Bioengineering & Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National
NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES C.T. Lim, B.H.B. Omar and J.C.J. Goh 1 Division of Bioengineering & Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National
SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis on Endothelial Progenitor Cells Regulates Bone Fracture Healing
 SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis on Endothelial Progenitor Cells Regulates Bone Fracture Healing Yohei Kawakami, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2, Masaaki Ii 3, Tomoyuki Matsumoto, M.D., Ph.D. 1, Astuhiko Kawamoto, M.D., Ph.D. 2, Yutaka
SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis on Endothelial Progenitor Cells Regulates Bone Fracture Healing Yohei Kawakami, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2, Masaaki Ii 3, Tomoyuki Matsumoto, M.D., Ph.D. 1, Astuhiko Kawamoto, M.D., Ph.D. 2, Yutaka
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA 02115
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0219 TITLE: Skeletal Complications in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: The Role of Neurofibromin Haploinsufficiency in Defective Skeletal Remodeling and Bone Healing in NF1 PRINCIPAL
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0219 TITLE: Skeletal Complications in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: The Role of Neurofibromin Haploinsufficiency in Defective Skeletal Remodeling and Bone Healing in NF1 PRINCIPAL
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae
 J Med Dent Sci 2009; 56: 107-112 Original Article Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae Niroshani Surangika Soysa 1, Neil Alles 1,2, Kazuhiro
J Med Dent Sci 2009; 56: 107-112 Original Article Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae Niroshani Surangika Soysa 1, Neil Alles 1,2, Kazuhiro
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Ampelopsis brevipedunculata Extract Prevents Bone Loss by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo
 Molecules 2014, 19, 18465-18478; doi:10.3390/molecules191118465 OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Article Ampelopsis brevipedunculata Extract Prevents Bone Loss by Inhibiting
Molecules 2014, 19, 18465-18478; doi:10.3390/molecules191118465 OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Article Ampelopsis brevipedunculata Extract Prevents Bone Loss by Inhibiting
BMP ANA Abundant in Neuroepithelium Area Cnot Schnurri-2
 CIZ BMP ANAAbundant in Neuroepithelium Area Cnot Schnurri-2 M-CSF MCP BMP E2 EP4 BMP Response ElementBRE To understand the mechanism of boneformation factors that are involved in the regulation and pathology,
CIZ BMP ANAAbundant in Neuroepithelium Area Cnot Schnurri-2 M-CSF MCP BMP E2 EP4 BMP Response ElementBRE To understand the mechanism of boneformation factors that are involved in the regulation and pathology,
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts
 Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A novel pyrazole derivative protects from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase Jung Hee Joo 1*, Jeong-Eun Huh 1*,JeeHyunLee 1,DooRiPark 1,
Supplementary Information A novel pyrazole derivative protects from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase Jung Hee Joo 1*, Jeong-Eun Huh 1*,JeeHyunLee 1,DooRiPark 1,
Hyperactivation of p21 ras and PI3K cooperate to alter murine and human neurofibromatosis type 1 haploinsufficient osteoclast functions
 Research article Hyperactivation of p21 ras and PI3K cooperate to alter murine and human neurofibromatosis type 1 haploinsufficient osteoclast functions Feng-Chun Yang, 1,2 Shi Chen, 1,2 Alexander G. Robling,
Research article Hyperactivation of p21 ras and PI3K cooperate to alter murine and human neurofibromatosis type 1 haploinsufficient osteoclast functions Feng-Chun Yang, 1,2 Shi Chen, 1,2 Alexander G. Robling,
Supplementary Figure 1: Co-localization of reconstituted L-PTC and dendritic cells
 a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
Bone Apatite Composition Of Osteonecrotic Trabecular Bone From The Femoral Head Of Immature Pigs
 Bone Apatite Composition Of Osteonecrotic Trabecular Bone From The Femoral Head Of Immature Pigs Olumide O. Aruwajoye 1,2, Harry KW Kim, MD 1, Pranesh B. Aswath, PhD 2. 1 Texas Scottish Rite Hospital,
Bone Apatite Composition Of Osteonecrotic Trabecular Bone From The Femoral Head Of Immature Pigs Olumide O. Aruwajoye 1,2, Harry KW Kim, MD 1, Pranesh B. Aswath, PhD 2. 1 Texas Scottish Rite Hospital,
Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
 Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection Victoria L. Smith, Yong Cheng, Barry R. Bryant and Jeffrey S. Schorey Supplementary Figure 1: Unprocessed
Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection Victoria L. Smith, Yong Cheng, Barry R. Bryant and Jeffrey S. Schorey Supplementary Figure 1: Unprocessed
NEW HORIZONS IN OSTEOPOROSIS THERAPY. Sundeep Khosla, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
 NEW HORIZONS IN OSTEOPOROSIS THERAPY Sundeep Khosla, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN DISCLOSURES SUNDEEP KHOSLA, M.D. Investigator-initiated grant Merck No non-fda approved recommendations RISK ASSESSMENT
NEW HORIZONS IN OSTEOPOROSIS THERAPY Sundeep Khosla, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN DISCLOSURES SUNDEEP KHOSLA, M.D. Investigator-initiated grant Merck No non-fda approved recommendations RISK ASSESSMENT
Bone Cell Biology. David W. Dempster, PhD. Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University. Bone Remodeling
 Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University Bone Remodeling The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University Bone Remodeling The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Cell Biology. The Remodeling Cycle. Bone Remodeling. Remodeling Maintains Mechanical Strength. David W. Dempster, PhD
 Bone Remodeling Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Remodeling Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Blocking antibody to the β-subunit of FSH prevents bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and stimulating bone synthesis
 Blocking antibody to the β-subunit of FSH prevents bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and stimulating bone synthesis Ling-Ling Zhu a,b, Harry Blair c,d, Jay Cao e, Tony Yuen a, Rauf Latif a, Lida
Blocking antibody to the β-subunit of FSH prevents bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and stimulating bone synthesis Ling-Ling Zhu a,b, Harry Blair c,d, Jay Cao e, Tony Yuen a, Rauf Latif a, Lida
Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond
 Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond Tim Arnett Bone Curriculum Symposium 2018 Department of Cell & Developmental Biology University College London Factors affecting bone strength Mass Architectural
Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond Tim Arnett Bone Curriculum Symposium 2018 Department of Cell & Developmental Biology University College London Factors affecting bone strength Mass Architectural
Supplementary Information. Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting
 Supplementary Information Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting suppressor of IL-5-induced eosinophil development Netali Ben Baruch-Morgenstern 1,4, Dana Shik 1,4, Itay Moshkovits
Supplementary Information Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting suppressor of IL-5-induced eosinophil development Netali Ben Baruch-Morgenstern 1,4, Dana Shik 1,4, Itay Moshkovits
Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
 Mechanical Stimuli in Bone Marrow During Physiologic Loading Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
Mechanical Stimuli in Bone Marrow During Physiologic Loading Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
Epidemiological studies link osteoporosis with hyperlipidemia
 Vascular Biology Rapid Communication Hyperlipidemia Promotes Osteoclastic Potential of Bone Marrow Cells Ex Vivo Yin Tintut, Sean Morony, Linda L. Demer Objectives Osteoporosis is associated epidemiologically
Vascular Biology Rapid Communication Hyperlipidemia Promotes Osteoclastic Potential of Bone Marrow Cells Ex Vivo Yin Tintut, Sean Morony, Linda L. Demer Objectives Osteoporosis is associated epidemiologically
The farnesoid X receptor negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis in bone remodeling and pathological bone loss
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 44), pp: 76558-76573 The farnesoid X receptor negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis in bone remodeling and pathological bone loss Ting Zheng 1,*, Ju-Hee Kang 1,*, Jung-Sun Sim 1,
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 44), pp: 76558-76573 The farnesoid X receptor negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis in bone remodeling and pathological bone loss Ting Zheng 1,*, Ju-Hee Kang 1,*, Jung-Sun Sim 1,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Opg/Rankl mrna dynamic expression in the bone tissue of ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis
 Opg/Rankl mrna dynamic expression in the bone tissue of ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis C.W. Li 1 *, B. Liang 2 *, X.L. Shi 3 and H. Wang 3 * 1 Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Opg/Rankl mrna dynamic expression in the bone tissue of ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis C.W. Li 1 *, B. Liang 2 *, X.L. Shi 3 and H. Wang 3 * 1 Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
PREDICTING PATIENT-TO-PATIENT VARIABILITY IN PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY AND BREAST CANCER PROGRESSION
 PREDICTING PATIENT-TO-PATIENT VARIABILITY IN PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY AND BREAST CANCER PROGRESSION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Keon-young Park In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
PREDICTING PATIENT-TO-PATIENT VARIABILITY IN PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY AND BREAST CANCER PROGRESSION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Keon-young Park In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Quercetin, a potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 28: 521-525, 2011 Quercetin, a potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts MASAYOSHI YAMAGUCHI 2* and M. NEALE WEITZMANN 1-3* 1 Atlanta Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 28: 521-525, 2011 Quercetin, a potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts MASAYOSHI YAMAGUCHI 2* and M. NEALE WEITZMANN 1-3* 1 Atlanta Department
Chapter 4 Inhibitory regulation of osteoclast bone resorption by SIRPα
 Inhibitory regulation of osteoclast bone resorption by SIRPα Ellen M. van Beek 1, Teun J. de Vries 2, Lars Mulder 3, Ton Schoenmaker 2, Kees A. Hoeben 4, Takashi Matozaki 5, Geerling E.J. Langenbach 6,
Inhibitory regulation of osteoclast bone resorption by SIRPα Ellen M. van Beek 1, Teun J. de Vries 2, Lars Mulder 3, Ton Schoenmaker 2, Kees A. Hoeben 4, Takashi Matozaki 5, Geerling E.J. Langenbach 6,
Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 drive a RANK-independent pathway of osteoclast activation
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2015 Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 drive a RANK-independent pathway of osteoclast
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2015 Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 drive a RANK-independent pathway of osteoclast
The Contribution Of Tie2-Lineage Cells To rhbmp-2 Induced Bone Formation
 The Contribution Of Tie2-Lineage Cells To rhbmp-2 Induced Bone Formation Mille P. Kolind, Ph.D 1, Alastair Aiken 1, Kathy Mikulec 1, Lauren Peacock 1, David Little 1,2, Aaron Schindeler, PhD 1,2. 1 Orthopaedic
The Contribution Of Tie2-Lineage Cells To rhbmp-2 Induced Bone Formation Mille P. Kolind, Ph.D 1, Alastair Aiken 1, Kathy Mikulec 1, Lauren Peacock 1, David Little 1,2, Aaron Schindeler, PhD 1,2. 1 Orthopaedic
7/5/2016. We need drugs that. Disclosures. New Osteoporosis Treatments. What we have today. Maintain or promote bone formation
 New Osteoporosis Treatments Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Advisory Board: Research funding: Merck, Eli Lilly, Radius Merck, Amgen
New Osteoporosis Treatments Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Advisory Board: Research funding: Merck, Eli Lilly, Radius Merck, Amgen
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting
 MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.
![Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9. Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.](/thumbs/90/103696086.jpg) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
Effects of Whole Body Exposure to Electromagnetic Field on Normal and Osteoporotic Bone Metabolism in Rats
 Effects of Whole Body Exposure to tromagnetic Field on Normal and Osteoporotic Bone Metabolism in Rats S. Fukuda and H. Iida National Institute of Radiological Sciences, Chiba 263-8 Japan INTRODUCTION
Effects of Whole Body Exposure to tromagnetic Field on Normal and Osteoporotic Bone Metabolism in Rats S. Fukuda and H. Iida National Institute of Radiological Sciences, Chiba 263-8 Japan INTRODUCTION
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
