Spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome. A series of eight cases
|
|
|
- Russell Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 52 University hospital J Minjoz, boulevard Fleming, Besançon Cedex, France: Department of Rheumatology E Toussirot D Wendling Department of Internal Medicine J L Dupond Correspondence to: Pr D Wendling Accepted for publication 16 September 1996 Spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome. A series of eight cases E Toussirot, J L Dupond, D Wendling Abstract Objective To determine the frequency, clinical features, and radiological and bone scintigraphic changes of spondylodiscitis in patients with SAPHO (synovitis, acne,, hyperostosis, and osteitis). Methods The study was retrospective. Data from patients with the diagnostic criteria of SAPHO syndrome were analysed for clinical features, biological data (HLA B antigen), and pelvic and spine x rays. Spine computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were also examined in some cases. Results 25 patients with a diagnosis of SAPHO were seen since Eight had spondylodiscitis. These included five with palmoplantar, one with pustular psoriasis, one with psoriasis vulgaris, and one with chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis without skin disease. The skin lesion occurred before the spondylodiscitis in four cases. Chest wall involvement was observed in four cases and sacroiliac joint lesions only in the case with osteomyelitis. HLA B27 was always negative and HLA B8 was found in four cases. Radiological findings consisted of erosive or sclerosing remodelling of endplates with a narrowed disc space; a reduced height of the vertebral body was also observed in some cases. These spinal lesions occurred in the three vertebral segments. Multiple sites of spondylodiscitis in the same patient were common. Bone scan showed mildly increased uptake and CT and MRI were useful for detecting signs of infection such as abscess. Enhanced signals on T2 weighted sequence or after injection of gadolinium were often observed. Follow up study of most of these patients suggests that the prognosis of spondylodiscitis in the SAPHO syndrome is favourable. Conclusions Despite few description in the literature, spondylodiscitis in the SAPHO syndrome is common (32% in this series). These radiological findings are similar to the discovertebral changes of spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis, thus giving support to the relations between SAPHO syndrome and spondylarthropathies. However, this does not mean that the pathogenic mechanisms are the same in these two conditions. (Ann Rheum Dis 1997;56:52 58) journal Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1997;56:52 58 Palmoplantar is associated with a wide variety of osteoarticular disorders, including inflammatory and pseudoinfectious osteitis with hyperostosis, mainly located to the anterior chest wall. 1 4 Aseptic and pseudoinfectious lesions also involve the peripheral bones and joints. 5 7 Furthermore, sacroiliitis and spine lesions are observed in palmoplantar suggesting a link to the spondylarthropathies. 156 Psoriasis and acne have also been reported to be associated with these diverent bone and joint lesions Psoriasis can be pustular and diycult to distinguish from palmoplantar. 5 For some investigators, palmoplantar and pustular psoriasis are the same skin disease, while for others they are two distinct entities. 11 These bone associated lesions have also been described in psoriasis vulgaris 9 and in chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, a condition without skin involvement most often observed in children. 12 In the French literature, it has been proposed that the syndrome of synovitis, acne,, hyperostosis, and osteitis (SAPHO) includes rheumatic disorders associated with acne, palmoplantar, pustular psoriasis, sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis, and chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. 56 Involvement of the axial skeleton in the SAPHO syndrome includes sacroiliitis and spinal abnormalities. Syndesmophytes, hyperostosis, and erosions of the vertebral bodies are commonly observed on x ray. 16 Spondylodiscitis is more rarely described. Our aim was to evaluate the frequency, radiological changes, and course of spondylodiscitis in our SAPHO patients. Methods PATIENTS A retrospective study was conducted. All the inpatients seen in our department and satisfying the previously proposed diagnostic criteria for SAPHO syndrome 13 were included: osteoarticular manifestations of acne (conglobata or fulminans), hidrosadenitis suppurativa, palmoplantar, pustular psoriasis, hyperostosis (anterior chest wall, spine, pelvis and limb), or chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis with or without skin disease. The diagnosis of palmoplantar or psoriasis required clinical confirmation by a dermatologist but not always a skin biopsy. Exclusion criteria were septic spondylodiscitis with evidence of infection, infectious palmoplantar, psoriatic arthritis, divuse
2 Spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome 53 Table 1 Clinical features and HLA B antigens Patient Sex Age (years) Cutaneous lesion Location of back pain Clinical measures Other bone and/or joint involvement HLA B antigens 1 F 67 Palmoplantar Thoracic Chest expansion: + 4 cm Sternoclavicular and B7, B35 interphalangeal joint arthritis 2 M 18 Pustular psoriasis Thoracic and Schober s score: + 1 cm Knee and sternoclavicular arthritis B8, B lumbar 3 F 56 Psoriasis vulgaris Cervical Cervical spine range of movement: None B8, B18 limited in all range of motion 4 F 64 Palmoplantar Lumbar Schober s score: + 0 cm None B5, B 5 M 64 Palmoplantar Thoracic Chest expansion: + 4 cm None B8, B12 6 F 57 None Lumbar and Schober s score: 0 cm Sacroiliac joints B39, B44 sacral 7 F 15 Palmoplantar Thoracic Chest expansion: + 4 cm Sternocosto-clavicular hyperostosis and tibial B8, B 8 F 56 Palmoplantar F, female; M, male Table 2 osteomyelitis Thoracic Schober s score: + 3 cm Sternocosto-clavicular arthritis B5, B14 idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, and fluoride or retinoid therapy. Psoriasis vulgaris, if associated with spondylodiscitis, was included in this study. Data for each patient were available on clinical features, including back pain, and the results of physical examination, including the Schober test, chest expansion, and cervical spine motion. PROCEDURES Radiological investigations Pelvic and spine x rays were examined. Spondylodiscitis was defined by destructive or sclerotic changes with or without reduction of height of the vertebral body and a narrowed disc space. A 99m technetium bone scan was performed in each patient. A computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or both, were performed in seven cases to provide better definition of the spinal lesions and to show the extent of the inflammatory process. Laboratory assessment Data from erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C reactive protein, white cell count, and HLA B antigen determination were studied. Blood and urine cultures, serological tests for infection (salmonella agglutination test; brucella agglutination or Rose Bengal test), and a tuberculin skin test were determined if the patient was febrile. Disc Radiological, bone scintigraphic, tomographic, and MRI features space and vertebral biopsies were performed for histological examination and for culture in three cases. Results CLINICAL FEATURES Between 1985 and 1996, 25 inpatients with previously defined criteria for the diagnosis of SAPHO syndrome 13 were seen in our department. Fifteen had proven palmoplantar and six had pustular psoriasis. One patient had acne conglobata, one chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, and one sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis without skin disease. One patient with psoriasis vulgaris was also included in this study. Chest wall involvement was found in 18 cases (including 11 with sternoclavicular arthritis, six with manubriosternal arthritis, and three with sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis), and 10 had peripheral joint or appendicular skeleton manifestations. Fourteen patients had lesions of the axial skeleton, including five with sacroiliitis, and there were eight patients with spondylodiscitis. These eight patients (table 1) included six females and two males (mean age 49.6 years). Five had palmoplantar (cases 1, 4, 5, 7, and 8), one had pustular psoriasis (case 2), one had psoriasis vulgaris (case 3), and one had no skin disease (case 6). In four cases, the dermatological lesions were observed before the bone involvement (mean 5.75 years) and in three cases, bone and skin lesions occurred simultaneously. Sacroiliac involvement was only observed in the patient with chronic Patient Spinal radiography Bone scintigraphy Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging 1 Spondylodiscitis T7-T8 T7-T8 Increased uptake ND T1: Decreased signal T6,T7,T8 T1 + gado: increased signal T6,T7,T8 2 Spondylodiscitis L1-L2 T9-T10 Increased uptake Erosions in T10 ND Spondylodiscitis T9-T10 3 Spondylodiscitis C6-C7-T1 then C5-C6-C7-T1 C6-C7-T1 Increased uptake ND T1: Decreased signal C7-T2: Increased signal C5,C6 + disc spaces C6-C7,C7-T1 4 Spondylodiscitis L4-L5 L4-L5 Increased uptake Erosions in L4 and L5 T1 and T2: Spondylodiscitis sequelae. No increased signal 5 Spondylodiscitis T8-T9 T8-T9 Increased uptake Erosions in T8 and T9 ND 6 Spondylitis L3,L4,L5 L3,L4,L5 Increased uptake Sclerotic remodelling in ND L3,L4,L5 7 Spondylodiscitis T9-T10 T6-T7 and T9-T10 Increased uptake ND ND 8 Spondylodiscitis T6-T7 L4-L5 T6-T7 and L4-L5 Increased uptake Erosions in L4-L5 T1 and T2: Spondylodiscitis sequelae. No enhanced signal ND, not determined; gado, gadolinium
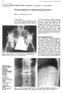
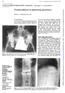
3 54 Toussirot, Dupond, Wendling Figure 1 Case 6: frontal and lateral x ray views of lumbar spine: bony sclerosis and large hyperostosis extending from the anterior and lateral margins of L3, L4, and L5. recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (case 6). Other joint and bone conditions consisted of knee arthritis in one patient (case 2), anterior chest wall involvement in four patients (cases 1, 2, 7, and 8: three with sternoclavicular arthritis and one with sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis), proximal interphalangeal joint arthritis in one patient (case 1), and tibial aseptic osteomyelitis in one patient (case 7) (proven by biopsy and negative bone culture). No familial history of inflammatory bowel disease or psoriasis was found. All these patients complained of backache, with fever occurring in only one patient (case 2, 37.8 C). A reduced spine range of movement at the level of spine involvement was observed for each patient with spondylodiscitis (table 1). BIOLOGICAL DATA (table 1) Each patient admitted for spondylodiscitis had a raised ESR (range 20 to 86 mm) or C reactive protein (10 to 85 mg litre -1 ; normal < 8). The white cell count was raised in one patient (case 2, mm -3 ; polymorphonuclear leucocytes 70%). No HLA B27 was found; one patient was HLA B27 positive and four were HLA B8 positive. No infectious cause was found in the febrile patient (case 2): blood and urine cultures remained negative and infectious serologies were also negative. Cultures of the open discovertebral biopsies (performed in cases 4, 6, and 8) for aerobic and anaerobic organisms and tuberculosis were also negative. RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS (table 2) Destructive and sclerotic changes of lumbar vertebral bodies without narrowing of disc spaces were observed in the patient with chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (case 6) and this corresponded more to a spondylitis than a spondylodiscitis (fig 1). The seven other patients presented one or more examples of spondylodiscitis on x ray (one patient in the cervical spine: case 3; five patients in the thoracic spine: cases 1, 2, 5, 7, and 8; and three patients in the lumbar spine: cases 2, 4, and 8), with narrowed disc space and erosive and sclerotic remodelling in the opposite regions of the vertebral bodies (fig 2). In two patients (cases 2 and 8), destruction of the entire vertebral junction (T9-T10 and T6-T7 respectively) was observed. No infectious lesion such as abscess was shown on Figure 2 Case 5: lateral thoracic x ray: T8 and T9 erosive lesions, sclerotic remodelling of the endplates, and disc space narrowing.
4 Spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome 55 A B A BB Figure 3 Case 1: dorsal MRI. T1 weighted sequence without (A) and after injection (B) of gadolinium: decreased signal intensity in T6, T7, and T8 enhanced after injection of gadolinium. These signal abnormalities are mainly localised to the anterior portion of the discovertebral junction. Figure 4 Case 3: cervical MRI. T1 (A) and T2 (B) weighted sequences: increased signal intensity in C5 and C6 vertebral bodies and considerable increased signal intensity in the C6-C7-T1 disc spaces in the T2 weighted sequence. radiographs, neither were syndesmophytes. Bridging osteophytes were noted in two patients (cases 1 and 5) and a large hyperostosis anteriorly and laterally to L3, L4, and L5 in one patient (case 6) (fig 1). BONE SCINTIGRAPHY (table 2) Accumulation of radionuclide activity was noted in all the sites of spondylodiscitis. This was characterised by mildly increased uptake. However, in one case increased uptake revealed a new spine lesion which was not observed on x ray (case 7: T6-T7). Increased uptake was also observed at the right sacroiliac joint in case 6. COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AND MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FINDINGS (table 2) CT was performed in five patients and revealed erosive lesions in the vertebral bodies without spinal cord compression or abscess. MRI was performed at the onset of spondylodiscitis in two patients (cases 1 and 3) and showed a decreased signal intensity on T1 weighted sequence in thoracic vertebral bodies enhanced after injection of gadolinium (case 1), while the disc spaces showed no increased signal (fig 3A and B). In the case of the cervical spondylitis (case 3), similar signal abnormalities were observed in the cervical vertebral bodies. However, an intense signal was observed in the C6-C7 and C7-T1 disc spaces, corresponding to discitis associated with contiguous spondylitis (fig 4A and B). No abscesses or epiduritis were seen. DISCOVERTEBRAL HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS Open biopsies of the disc or the vertebral body were performed in three patients (L4-L5 disc space: case 8; L4 and L5: cases 4 and 6). Neither specific lesion nor inflammatory cells were
5 56 Toussirot, Dupond, Wendling Table 3 Frequency of spondylodiscitis in the SAPHO syndrome Author Sonozaki Chamot Le Loët Kasperczyk Maugars Patients n = Cutaneous lesion or bone involvement PPP 13 Acne 44 PPP 28 SCCH PPP 13 PPP 12SCCH 3 Acne 11 PPP 5 Pustular psoriasis Frequency of spondylodiscitis 18,8% Acne: 0% PPP: 9% SCCH: 21.4% 0% PPP:41.1% SCCH:8% 15.7% PPP, palmoplantar ; SCCH, sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis observed in the disc. Biopsy of L4 in patient 4 showed infiltration of lymphocytes and plasmacytes. Biopsy of L5 in patient 8 showed replacement of bone by fibrous tissue and the Figure 5 Case 2: frontal x ray view of the lumbar spine showing L1-L2 spondylodiscitis. Note the lateral hyperostosis bridging the vertebral bodies. Figure 6 Case 3: lateral cervical x ray showing cervical spondylitis located at C5-C6, C6-C7, and C7-T1, with narrowed disc spaces, bone sclerosis, and reduced height of the vertebral bodies. A large hyperostosis extends from anterior margin of the cervical vertebral bodies (arrow). picture of chronic osteomyelitis with cellular infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. In some areas microabscesses were seen. Cultures of disc and bone tissue remained sterile. FOLLOW UP STUDY In all patients, back pain was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Seven patients (cases 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, and 8) were seen again between one and eight years later. None had recurrence of backache. In two patients, spine x rays showed the same lesions as initially, with additional constructive bone lesions: osteophytes bridging the vertebral bodies (case 4) and hyperostosis bridging the lateral margin of L1 and L2 for patient 2 (fig 5); new cervical x rays were also available one year later in patient 3 and showed progression of spondylodiscitis to C5-C6 and a large hyperostosis anterior to C5, C6, C7, and T1 (fig 6). Two patients were seen five years after the onset (cases 4 and 8) and MRI showed erosive changes but no enhanced signal in the disc or the vertebral bodies on T2 weighted image. During this follow up period, we observed correction of the initially elevated inflammatory markers. Discussion The SAPHO syndrome was proposed to group together those rheumatic conditions closely associated with dermatological disorders, mainly palmoplantar and pustular psoriasis The interval between the appearance of these two conditions could be long. 14 Evidence of similar bone and joint lesions in psoriasis vulgaris has also been reported. 9 Thus we have also included in our series a patient with psoriasis vulgaris with vertebral lesions suggestive of spondylodiscitis. Joint and bone involvement in the SAPHO syndrome is mainly located to the anterior chest wall and combines arthritis, aseptic osteitis, and hyperostosis The other sites of skeletal diseases in the SAPHO syndrome are peripheral as well as axial. Sacroiliitis is well described in 13-52% of cases. 16 Axial skeletal lesions consist of erosions, sclerotic changes, syndesmophytes, hyperostosis, and spondylodiscitis. Published data give a frequency of % for the spondylodiscitis in the SAPHO syndrome (table 3). However, Le Loët et al 15 found no spondylodiscitis in their series of 15 cases. In a recent report by the same investigators, 11 there is no comment about spondylodiscitis in 23 cases of SAPHO
6 Spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome 57 syndrome. Maugars et al 17 reported three cases of spondylodiscitis among 19 cases of the SAPHO syndrome (15.7%). In our own series, we found spondylodiscitis in 32%. These cases of spondylodiscitis are observed in the course of palmoplantar and pustular psoriasis ; reports of spondylodiscitis with acne are exceptional. As with the other rheumatological disorders, the spondylodiscitis can occur before or after the skin disease. Most of our patients had skin lesions before the onset of spondylodiscitis. The main clinical feature is inflammatory back pain with no or mild fever. No neurological complications are described. Biological investigations show an inflammatory syndrome with mildly elevated or normal white cell count. There is no association with HLA B27 or other HLA antigen. 16 However, in our series four patients were HLA B8 positive. The radiological findings are a narrowed disc space, erosions, and sclerotic changes on the opposite region of the vertebral bodies. 116 These defects are mainly localised to the central or anterior portions of the discovertebral junction. Isolated sclerotic lesions of the vertebral body are also seen 20 and are generally associated with a reduced height of the vertebral body, corresponding more to a spondylitis than to a spondylodiscitis. In our series, the spondylodiscitis was observed at different spinal levels. Two or more foci of spondylodiscitis at separate sites or at the same spinal level can occur in the same patient. The spondylodiscitis is frequently associated with constructive bone lesions such as osteophytes or hyperostosis of the vertebral body. However, adjacent syndesmophytes are not described and sacroiliitis is generally not a feature. Patient 6 of our series (L3, L4, and L5 spondylitis) presented sclerotic remodelling and erosions of the right sacroiliac joint. The apophyseal joints were intact without destructive or constructive changes. Data from bone scintigraphy, CT, and MRI are not available in published reports on the spondylodiscitis of the SAPHO syndrome. In our series we found the following: v A mild increased scintigraphic uptake in our eight patients. Of interest, areas of increased uptake may reveal an undepicted spinal lesion on x rays. v CT scans show the erosive lesions and support the likely inflammatory cause of the spondylodiscitis, as no abscesses are seen. v All the sites of spondylodiscitis are revealed by MRI, which shows enhanced signal in T2 weighted sequence (or after gadolinium injection) in the disc and vertebral bodies. Of interest in our series, some vertebrae without abnormalities on x rays or bone scintigraphy showed evidence of inflammatory involvement on MRI. Abscesses and epiduritis are also not seen on MRI. Thus MRI is useful and should be performed in cases of spondylodiscitis in the SAPHO syndrome to provide better definition of the extent of the inflammatory process. v Histopathological examination in three cases in our study showed inflammatory changes in the vertebral body but not in the disc space. This suggests that the inflammatory process starts in bone tissue and then progresses to the disc. Furthermore, these lesions are similar to those observed in ankylosing spondylitis. 21 The course of the spondylodiscitis is favourable. The patients present with back pain at onset and for many weeks, but they become progressively asymptomatic. No complications (such as neurological disturbances) are described, and recurrence at the same spinal level is not mentioned in published reports. However, total destruction of the disc space can induce vertebral kyphosis (as was observed in case 8 of our series). We observed no complications, recurrences, or new localisation of spondylodiscitis in the majority of our patients. MRI, performed five years after the initial back pain in patients 4 and 8, shows no inflammatory changes but only sequelae of the spondylodiscitis. Conversely, constructive bone lesions such as osteophytes or hyperostosis may develop and bridge the vertebral bodies. In patient 3, we observed cervical spondylitis in association with psoriasis vulgaris. Psoriasis vulgaris can be associated with the same bone and joint lesions as palmoplantar and the pustular form of psoriasis. However, we have excluded from our study the patient diagnosed as having psoriatic arthritis. Axial involvement is well known in psoriatic arthritis. 22 However, spondylodiscitis is estimated to occur in 22% of cases of psoriatic arthritis, 23 though in association with other lesions such as syndesmophytes, ligamentous ossification, apophyseal joint narrowing or fusion, and subluxation at the cervical level. Another diverential diagnosis is infectious spondylodiscitis. The radiological findings are the same in inflammatory and infectious spondylodiscitis. No abscesses or epiduritis are observed in the SAPHO syndrome; conversely, multiple foci of spondylodiscitis are uncommon in infection. Furthermore, the constructive changes occur earlier in SAPHO than in infectious spondylodiscitis. While open vertebral biopsy has sometimes been required in the past to rule out infection, such biopsies could certainly now be avoided with the advent of MRI, which shows changes diagnostic of an inflammatory process. Finally, the spondylodiscitis observed in the SAPHO syndrome and ankylosing spondylitis have clinical and radiological similarities and this supports the relation between SAPHO syndrome and spondylarthropathies. Discovertebral erosions and destructive changes are indeed well known in ankylosing spondylitis and occur in 1-10% of cases. These findings result from inflammatory lesions, discal herniation, and fractures and occur in early or late phases of the disease. Some investigators emphasise the inflammatory aetiology. 21 However, severe discovertebral lesions are relatively uncommon in ankylosing spondylitis and are mainly located in the thoracic and lumbar segments of the spine, while other changes such as syndesmophytes, Romanus osteitis,
7 58 Toussirot, Dupond, Wendling osteoporosis, apophyseal joint sclerosis, and sacroiliitis are associated with the spondylodiscitis of ankylosing spondylitis. In addition, the similar clinical and radiological features of spondylodiscitis in SAPHO syndrome and ankylosing spondylitis do not mean that these two conditions have the same pathogenic mechanisms. In fact, HLA B27 is expressed less often in the SAPHO syndrome than in ankylosing spondylitis, and hypothetical infectious agents involved in SAPHO syndrome (Proprionibacterium acnes) 45 are not the same than those in ankylosing spondylitis (Klebsiella pneumoniae). 1 Sonozaki H, Mitsui H, Miyanaga Y, Okitsu K, Igarashi M, Hayashi Y, et al. Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthro-osteitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1981;40: Sonozaki H, Kawashima M, Hongo O, Yaoita H, Ikeno M, Matsuura M, et al. Incidence of arthro-osteitis in patients with palmaris et plantaris. Ann Rheum Dis 1981;40: HradileE, Gentz CF, Matilainen T, Moller H, Sanzen L, Uden A. Skeletal involvement in palmoplantaris with special reference to the sterno-costoclavicular joints. Acta Derm Venereol 1988;68: Edlund E, Johnsson U, Lidgren L, Pettersson H, Sturfelt G, Svensson B, et al. Palmoplantar and sternocostoclavicular arthro-osteitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1988; 47: Kahn MF, Chamot AM, Benhamou CL. Syndrome synovite, acné, pustulose, hyperostose, ostéite SAPHO. Actualité rhumatologique présentée au praticien. Paris: Expansion Scientifique Française, 1988: Chamot AM, Benhamou CL, Kahn MF, Beraneck L, Kaplan G, Prost A. Le syndrome acné, pustulose, hyperostose, ostéite (SAPHO). Résultats d une enquête nationale. 85 observations. Rev Rhum 1987;54: Prier A, Koeger AC, Struz P, Boeuve C, Pointud P, Camus JP. Rhumatismes inflammatoires et pustulose palmoplantaire. A propos de trois observations. Sem Hop Paris 1985;61: Huaux JP, Pieters T, Malghem J, Maldague B, Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C. Pustulose palmo-plantaire et arthrites des membres. Analogies apparentes et réelles avec l arthropathie psoriasique. A propos d un cas. Rev Rhum 1988;55: Laxer M, Shore AD, Manson D, King S, Silverman ED, Wilmot DM. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis and psoriasis. A report of a new association and review of related disorders. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1988;17: Knitzer RH, Needleman BW. Musculoskeletal syndromes associated with acne. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1991; 20: Mejjad O, Daragon A, Louvel JP, Da Silva LF, Thomine E, Lauret P, et al. Osteoarticular manifestations of palmaris et plantaris and of psoriasis: two distinct entities. Ann Rheum Dis 1996;55: Yu L, Kasser JR, O Rourke E, Kozakewich H. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Association with vertebra plana. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989;71-A: Benhamour CL, Chamot AM, Kahn MF. Synovitis-acne-hyperostosis-osteomyelitis syndrome (SAPHO). A new syndrome among the spondylarthropathies? Clin Rheumatol 1988;6: Kahn MF, Bouvier M, Palazzo E, Tebib J, Colson F. Sternoclavicular pustulotic osteitis (SAPHO). 20 years interval between skin and bone lesions. J Rheumatol 1991; 18: Le Loet X, Bonnet B, Thomine E, Mejjad O, Lucet L, Louvel JP, et al. Manifestations ostéo-articulaires de la pustulose palmo-plantaire. Etude prospective de 15 cas. Presse Méd 1991;20: Kasperczyk A, Freyschmidt J. Pustulotic arthroosteitis: spectrum of bone lesions with palmoplantar. Radiology 1994;191: Maugars Y, Berthelot JM, Ducloux JM, Prost A. SAPHO syndrome: a follow-up study of 19 cases with special emphasis on enthesis involvement. J Rheumatol 1995; 22: Gerster JC, Lagier R, Nicod L. Case report 311. Skel Radiol 1985;14: Fallet GH, Arroyo J, Vischer TL. Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis: case report with a 31 year follow-up. Arthritis Rheum 1983;26: Hunter LY, Hensinger RN. Destructive arthritis associated with acne fulminans: a case report. Ann Rheum Dis 1980; 39: Rasker JJ, Prevo RL, Lanting PJH. Spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis, inflammation or trauma? A description of six cases. Scand J Rheumatol 1996;25: Salvarani C, Macchioni P, Cremonesi T, Mantovani W, Battistel B, Rossi F, et al. The cervical spine in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a clinical, radiological and immunogenetic study. Ann Rheum Dis 1992;51: Jenkinson T, Armas J, Evinson G, Cohen M, Lovell C, McHugh NJ. The cervical spine in psoriatic arthritis: a clinical and radiological study. Br J Rheumatol 1994; 33: Resnick D, Niwayama G. Ankylosing spondylitis. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1988: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 January Downloaded from on 21 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
SAPHO syndrome or psoriatic arthritis? A familial case study
 Rheumatology 1999;38:463 467 Case report: Paediatric Rheumatology/Series Editor: P. Woo SAPHO syndrome or psoriatic arthritis? A familial case study A. Dumolard, Ph. Gaudin, R. Juvin, M. Bost1, M. Peoc
Rheumatology 1999;38:463 467 Case report: Paediatric Rheumatology/Series Editor: P. Woo SAPHO syndrome or psoriatic arthritis? A familial case study A. Dumolard, Ph. Gaudin, R. Juvin, M. Bost1, M. Peoc
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
The SAPHO syndrome: a clinical and imaging study
 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1560-x BRIEF REPORT The SAPHO syndrome: a clinical and imaging study Meritxell Sallés & Alejandro Olivé & Ricard Perez-Andres & Susana Holgado & Lourdes Mateo & Elena Riera & Xavier
DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1560-x BRIEF REPORT The SAPHO syndrome: a clinical and imaging study Meritxell Sallés & Alejandro Olivé & Ricard Perez-Andres & Susana Holgado & Lourdes Mateo & Elena Riera & Xavier
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN. Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
SAPHO Syndrome in a Patient with Breast Cancer Mimicking Bone Metastasis: A Case Report
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(1) : 59-63, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report SAPHO Syndrome in a Patient with Breast Cancer Mimicking Bone Metastasis: A Case Report Kyungran Ko 1, Hee Jung Suh
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(1) : 59-63, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report SAPHO Syndrome in a Patient with Breast Cancer Mimicking Bone Metastasis: A Case Report Kyungran Ko 1, Hee Jung Suh
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS CRMO 1.1 What is it? Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) is
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS CRMO 1.1 What is it? Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) is
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
EVOLUTION OF CHRONIC RECURRENT MULTIFOCAL OSTEITIS TOWARD SPONDYLARTHROPATHY OVER THE LONG TERM
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 1, January 2000, pp 109 119 2000, American College of Rheumatology 109 EVOLUTION OF CHRONIC RECURRENT MULTIFOCAL OSTEITIS TOWARD SPONDYLARTHROPATHY OVER THE LONG TERM
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 1, January 2000, pp 109 119 2000, American College of Rheumatology 109 EVOLUTION OF CHRONIC RECURRENT MULTIFOCAL OSTEITIS TOWARD SPONDYLARTHROPATHY OVER THE LONG TERM
A rare case of the SAPHO syndrome with pulmonary complications. G Ngom, A Désiré, J Savadogo, M Fall, O Ndour, I Fall, M Ndoye
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 4 Number 2 A rare case of the SAPHO syndrome with pulmonary complications G Ngom, A Désiré, J Savadogo, M Fall, O Ndour, I Fall, M Ndoye Citation G
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 4 Number 2 A rare case of the SAPHO syndrome with pulmonary complications G Ngom, A Désiré, J Savadogo, M Fall, O Ndour, I Fall, M Ndoye Citation G
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Imaging of sternocostoclavicular joint in spondyloarthropaties and other rheumatic conditions
 Imaging of sternocostoclavicular joint in spondyloarthropaties and other rheumatic conditions G. Guglielmi 1,2, A. Cascavilla 1, G. Scalzo 1, F. Salaffi 3, W. Grassi 3 1 Department of Radiology, University
Imaging of sternocostoclavicular joint in spondyloarthropaties and other rheumatic conditions G. Guglielmi 1,2, A. Cascavilla 1, G. Scalzo 1, F. Salaffi 3, W. Grassi 3 1 Department of Radiology, University
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis syndrome: a single centre study of a cohort of 164 patients
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2016;55:1023 1030 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew015 Advance Access publication 25 February 2016 Original article Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis syndrome:
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2016;55:1023 1030 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew015 Advance Access publication 25 February 2016 Original article Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis syndrome:
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and the
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Since 1959, there have been
 Original Article A Study of Musculoskeletal Manifestations in 12 Patients with SAPHO Syndrome Jeff P. Steinhoff, Ana Cilursu, Gerald F. Falasca, Leonardo Guzman, Antonio J. Reginato Synovium and synovial
Original Article A Study of Musculoskeletal Manifestations in 12 Patients with SAPHO Syndrome Jeff P. Steinhoff, Ana Cilursu, Gerald F. Falasca, Leonardo Guzman, Antonio J. Reginato Synovium and synovial
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis: a review
 Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease Review Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis: a review Matthew B. Carroll Abstract: Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis (SCCH) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease Review Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis: a review Matthew B. Carroll Abstract: Sternocostoclavicular hyperostosis (SCCH) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
To review the mechanisms, characteristics and diagnostic roles of fatsuppressed water bright magnetic resonance images such as short tau
 Differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic vertebral and paravertebral disorders with increased signal intensity on short tau inversion recovery (STIR) or fat-suppressed T2weighted images Poster No.: C-1375
Differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic vertebral and paravertebral disorders with increased signal intensity on short tau inversion recovery (STIR) or fat-suppressed T2weighted images Poster No.: C-1375
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies
 A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Spondylarthropathies
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis
 SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Bone mineral density and vertebral compression fracture rates in ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 117-121 117 Rheumatology, Whipps Cross Hospital, Leytonstone, London, United S Donnelly D V Doyle A Denton I Rolfe Human Metabolism, University of Sheffield Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 117-121 117 Rheumatology, Whipps Cross Hospital, Leytonstone, London, United S Donnelly D V Doyle A Denton I Rolfe Human Metabolism, University of Sheffield Medical
A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004?
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury
 Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Osteomieliti STEOMIE
 OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy S Chandela, J Llena, J Houten Citation S Chandela, J Llena,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy S Chandela, J Llena, J Houten Citation S Chandela, J Llena,
Title: Childhood osteomyelitis-incidence and differentiation from other acute onset musculoskeletal features in a population-based study
 Author's response to reviews Title: Childhood osteomyelitis-incidence and differentiation from other acute onset musculoskeletal features in a population-based study Authors: Øystein Riise (oystein.riise@rikshospitalet.no)
Author's response to reviews Title: Childhood osteomyelitis-incidence and differentiation from other acute onset musculoskeletal features in a population-based study Authors: Øystein Riise (oystein.riise@rikshospitalet.no)
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Synovitis-acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis (SAPHO) Syndrome with Significant Bilateral Pleural Effusions
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8250-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synovitis-acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis (SAPHO) Syndrome with Significant Bilateral Pleural Effusions Shoichi Hasegawa 1,2,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8250-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synovitis-acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis (SAPHO) Syndrome with Significant Bilateral Pleural Effusions Shoichi Hasegawa 1,2,
Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Input-dms SPINE Volume 31, Number 13, pp 000 000 2006, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing
Input-dms SPINE Volume 31, Number 13, pp 000 000 2006, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Posterior Correction and Fixation Without Anterior Fusion for Pseudoarthrosis With Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Special Imaging MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION. Special Imaging. Special Imaging. 18yr old male pt What is it? Additional Imaging
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION Additional Imaging May assist in diagnosis and, possibly, treatment Help create the picture May help differentiate from neoplasia 18yr old male pt What is it? Lymphoma Ewings
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION Additional Imaging May assist in diagnosis and, possibly, treatment Help create the picture May help differentiate from neoplasia 18yr old male pt What is it? Lymphoma Ewings
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Elective Student P. H.
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Differentiating Inflammatory and Mechanical Back Pain
 This resource was organised and funded by AbbVie. It has been developed in collaboration with Claire Harris, Susan Gurden, Dr Jane Martindale, Claire Jeffries and NASS. For UK healthcare professionals
This resource was organised and funded by AbbVie. It has been developed in collaboration with Claire Harris, Susan Gurden, Dr Jane Martindale, Claire Jeffries and NASS. For UK healthcare professionals
Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging
 Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Anterior Chest Wall Joint and Bone Disorders
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
ARTHRITIS* x rays of the cervical spine from patients with. with similar films from a control population.
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
arthritis: a clinical, radiological and immunogenetic study
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors. Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA
 Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Pyogenic spondylitis as a complication of ear piercing : Differentiating between spondylitis and discitis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 128-132 CASE REPORT Pyogenic spondylitis as a complication of ear piercing : Differentiating between spondylitis and discitis Miguel SEWNATH, Tina FABER, Rene CASTELEIN From
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 128-132 CASE REPORT Pyogenic spondylitis as a complication of ear piercing : Differentiating between spondylitis and discitis Miguel SEWNATH, Tina FABER, Rene CASTELEIN From
DIFFERENTIATING INFLAMMATORY AND MECHANICAL BACK PAIN
 DIFFERENTIATING INFLAMMATORY AND MECHANICAL BACK PAIN CHALLENGE YOUR DECISION MAKING Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, The North West London Hospitals NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
DIFFERENTIATING INFLAMMATORY AND MECHANICAL BACK PAIN CHALLENGE YOUR DECISION MAKING Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, The North West London Hospitals NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no :
 Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R
 The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
Bone Disease in Adolescents with Acne Fulminans and Severe Cystic Acne: Radiologic and
 1161 Bone Disease in Adolescents with Acne Fulminans and Severe Cystic Acne: Radiologic and Scintigraphic Findings Leena S. 1 OBJECTIVE. Acne fuiminans is an uncommon form of ulcerative acne with acute
1161 Bone Disease in Adolescents with Acne Fulminans and Severe Cystic Acne: Radiologic and Scintigraphic Findings Leena S. 1 OBJECTIVE. Acne fuiminans is an uncommon form of ulcerative acne with acute
3 Sternoclavicular Joints
 3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
Spondylodiscitis Due To Histoplasma Duboisii: Report Of One Case And Review Of Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 2 Number 2 Spondylodiscitis Due To Histoplasma Duboisii: Report Of One Case And Review Of Literature I Ghfir, J Rahali, N Ben Raïs Citation I Ghfir,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 2 Number 2 Spondylodiscitis Due To Histoplasma Duboisii: Report Of One Case And Review Of Literature I Ghfir, J Rahali, N Ben Raïs Citation I Ghfir,
