Update on imaging in rheumatic diseases: cartilage
|
|
|
- Ralph Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Update on imaging in rheumatic diseases: cartilage P. Sewerin 1, C. Schleich 2, S. Vordenbäumen 1, B. Ostendorf 1 1 Department and Hiller Research Unit of Rheumatology, 2 Department of Diagnostic and Interventional, Radiology, Heinrich-Heine University Dusseldorf, Germany. Philipp Sewerin, MD* Christoph Schleich,* Stefan Vordenbäumen, Benedikt Ostendorf, *These authors contributed equally. Please address correspondence to: Dr Philipp Sewerin, Department and Hiller Research Unit of Rheumatology, Heinrich-Heine University Dusseldorf, Moorenstraße 5, Dusseldorf, Germany. philipp.sewerin@med.uni-duesseldorf.de Received on August 21, 2018; accepted in revised form on August 30, Clin Exp Rheumatol 2018; 36 (Suppl. 114): S Copyright Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology Key words: ultrasound, cartilage, rheumatic diseases Competing interests: none declared. ABSTRACT In recent years, the role of articular cartilage for understanding pathogenesis as well as for clinical research has become increasingly important. Whereas previously cartilage could only be assessed invasively, various imaging procedures are available for its evaluation now. Although still widely used, conventional radiography bears significant limitations since it assesses cartilage indirectly by joint space width. Today, the cartilage thickness and structure can be reliably evaluated using ultrasound, although the molecular structure cannot be determined, yet. Besides ultrasound, MRI offers the possibility to image morphological changes with a very high resolution. In addition, the quality and composition of joint cartilage can already be measured due to a constant technical improvement and new MRI sequences such as dgemric even in small joints (e.g. MCP or MTP joints). Despite the advantages of contrast agents for the detection of inflammation, its use is reevaluated today. Regarding that contrast agent-free imaging techniques for the assessment of joint cartilage are developed with great effort to depict its quality and changes over time. These novel MRI methods such as T2/T2*- and T1ρ-mapping, gagcest, and sodium imaging provide promising quantitative imaging biomarkers that can detect early cartilage changes before morphological alterations occur. Hence, US and MRI will likely be of paramount importance in future clinical trials and clinical assessment of inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases not only for understanding pathogenesis but also for using its possible value in daily practice. Introduction Alterations in the composition of articular cartilage are a common feature in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases. Cartilage is a key component of synovial joints and consists of chondrocytes, which are the exclusive cell type embedded within a dense and highly organised extracellular matrix (ECM). Cartilage ECM is synthesised by these chondrocytes and is composed of a collagenous network that contains primarily type II collagen along with glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as hyaluronan, and a variety of proteoglycans, e.g. GAGcontaining proteins that are linked to the collagen network. The exact composition of cartilage ECM, its physiology, and the interactions of its individual components, are described in detail elsewhere (1). Cartilage loss is a hallmark of osteoarthritis (OA). Indeed, chondrocyte and dysfunctional ECM production is likely paramount for the development of this widespread disorder (2). Patients experience considerable loss of joint function, pain and impaired quality of life. Unfortunately, there is currently no effective pharmacological treatment available, which significantly alters the course of the disease. An important obstacle to the development of pharmacological agents is the slowly progressive course of OA, requiring long and costly clinical trials (3). Reliable non- or minimal invasive imaging techniques of cartilage therefore have the potential to facilitate significantly the search for effective treatments options Treatment goals for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as defined by both American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) are directed to include a treat to target strategy with a goal of low disease activity or remission according to an index derived from an RA core data set (4, 5). Therefore, it is recommended to initiate conventional synthetic disease modifying drugs (cs- DMARDs) immediately after the diagnosis, ideally before erosive disease of the bone is detected. For decades, imaging has played an important role for diagnosis and therapy Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018 S-139
2 control in patients with inflammatory joint diseases. It is well known that bone erosions in conventional radiographs are associated with a high likelihood for a progressive course of the disease (6, 7). Moreover, it has been shown that joint space narrowing, representing cartilage loss, is predictive for new bone erosions in follow-up and that it is independently associated with functional impairment and decreased work ability (8, 9). Joint space narrowing is observed when cartilage degradation has already occurred. Hence, more sophisticated methods to detect early cartilage injury were sought. Ultrasound (US) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are increasingly used in both research and clinical routine to inform diagnostic algorithms and guide therapy, especially in RA (10, 11). This review introduces the current possibilities of ultrasound and MRI for the detection of early cartilage damage and loss of cartilage integrity using molecular imaging techniques in arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ultrasound Conventional radiographs permit indirect recognition of cartilage damage depicted as joint space narrowing. In contrast, ultrasound (US) allows a detailed visualisation of the hyaline cartilage: Small cartilage abnormalities in patients with RA can be identified sonographically from loss of the hyperechoic superficial margin of articular cartilage with reverberation artifacts (grade 1 defect) up to osteochondral defects appearing as a complete loss of the cartilage substance and a contour defect of subchondral bone, with loss of uniformity of the strongly hyperechoic subchondral bone interface (grade 4 defect) (12). US now can be considered a reliable and valid technique for cartilage assessment even at small finger joints, with excellent sensitivity compared to x-rays (13). Moreover, there is a good interobserver reproducibility when analysing the morphological changes of the cartilage at MCP joint in patients with RA (14). Hence, there is evidence showing that ultrasound can depict cartilage defects in inflammatory joint disease. Abe et al. compared synovial histology (from 215 joints undergoing synovectomy and reconstructive surgery) with US on 177 patients with RA. Power Doppler signal grade reflected histological scores in both large and small joints, and was correlated significantly with DAS28, C-reactive protein and matrixmetalloproteinase-3, while there is no specific data for cartilage assessment up until now (15). Moreover, ultrasound is used regularly in clinical practice to detect crystal arthropathies such as gout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPDD) showing a typical hyperechoic spots within the hyaline cartilage layer (16, 17). Due to these opportunities ultrasound is now part of the current classifications criteria in gout (18). In osteoarthritis (OA), current studies attempt to clarify the association between US pathologies and symptoms of patients with OA. In a recent published meta-analysis, US signs of OA including synovial hypertrophy and positive power Doppler (PD) signal were associated with knee pain and OA. These aspects were significantly less common in general population or among asymptomatic controls and were more related to structural changes of the cartilage itself than to pain (19). Furthermore, US imaging including grey-scale synovitis and PD signals could predict future risk of radiographic progression of hand OA. However, only morphological cartilage changes (not on a molecular level) were taken into consideration (20). However, no study to date has shown that US measures permit prediction of future cartilage loss. In addition, US does not depict changes of the cartilage integrity or composition; US can capture morphological damage of the cartilage, but molecular assessment is not possible yet. Magnetic resonance imaging Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a well evaluated imaging technique in RA clinical trials and is used more frequently in daily practice for early diagnosis and therapy control in RA patients (21-23). Modern MRI techniques can depict inflammatory smooth tissue (such as synovitis, enthesitis and tenovsynovitis) and bony changes and lesions (such as bone marrow oedema, erosions, and joint space narrowing) with a high level of sensitivity (24). Moreover, MRI can detect erosive joint damage much earlier than conventional x-rays (25). In addition, validated scoring systems such as Outcome Measures in RA Clinical Trials (OMERACT) RA MRI Score (RAMRIS) and simplified versions facilitate comparison of MRI readings due to standardisation (26, 27). The RAMRIS is a highly reliable sum-score based on the semi-quantitative rating of the severity of synovitis, bone marrow oedema and erosions in hand and wrist joints that has been applied in therapy-response trials in RA (22, 24). More recently, a score of joint space narrowing/cartilage thinning was added to RAMRIS (28-30). This is all the more relevant in view of the study of Aletaha et al. who demonstrated that physical disability in RA is associated with cartilage damage rather than bone destruction (9). Morphological imaging of cartilage is possible mainly in proton density, proton density with fat saturation/spectral attenuated inversion recovery (SPAIR), T2-weighted, T2-weighted with fat saturation, T1 volume isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition (VISTA) 3D, and 3D fast spoiled gradient echo (FSPGR) sequences (31). In some centres, the modified Outerbridge system (grading scale) that originally was based on arthroscopic findings, is used to classify changes in hyaline cartilage on MRI. This system is based on a grading of the depth, location, and severity of chondral injuries as follows: grade 0 normal cartilage, grade 1 signal intensity alterations with an intact surface of the articular cartilage compared with the surrounding normal cartilage, grade 2 partial thickness defect of the cartilage, grade 3 fissuring of the cartilage to the level of the subchondral bone and grade 4 exposed subchondral bone (32). Another morphological technique is the double-echo steady state (DESS) MR sequence with water excitation that offers high-resolution, three-dimensional (3D) imaging and multiplanar reformatting. Its strong fluid signal creates an ar- S-140 Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018
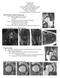
3 Fig. 1. DESS (double-echo steady state) sequence of the sacroiliac joint of a healthy control (left picture) and a patient with sacroiliitis (right image). In addition to the typical signs of sacroiliitis like erosion, ankylosis and joint space narrowing, it is possible to detect morphological alterations of the cartilage visible by signal loss of cartilage. throgram-like effect within the joint that may increase the diagnostic possibilities in finding cartilage alterations. The radial imaging approach will further improve the visualisation the cartilage and provides information on the localisation and extent of that is essential if surgical treatment is intended. The good reliability of the DESS technique with radial imaging for evaluation of cartilage was shown by comparative analysis with intraoperative data (33) (Fig. 1). Regarding the high impact of assessing cartilage thickness and integrity, high resolution morphological and biochemical imaging came more and more in focus of scientific research. Delayed gadolinium-enhanced MRI of the cartilage (dgemric) is a high reliable, histologically controlled MRI feature to visualise proteoglycan loss in cartilage composition (34, 35). With dgemric, it is possible to detect proteoglycan loss after the intravenous application of negatively charged contrast agent (gadolinium diethylenetriamine pentaacetate anion - Gd-DTPA). The negatively charged Gd-DTPA penetrates cartilage in an inverse relationship to the concentration of negatively charged glycosaminoglycan side chains of proteoglycan. A depletion of proteoglycan content in degenerated cartilage results in accumulation of the paramagnetic gadolinium ions. This progressively accelerates T1 relaxation time (36) (Fig. 2). dgemric has been performed in several joints of patients suffering from RA or OA. For example, Tiderius et al. demonstrated that cartilage damage in biochemical MRI continues irrespective of disease activity following therapy escalation with TNF-alpha-blockers in RA (37). Schleich et al. showed the capability of dgemric as an additional feature in the preoperative assessment of degenerated cervical intervertebral discs (IVDs). IVDs scheduled for discectomy demonstrated significantly lower dgemric values compared to IVDs who were not scheduled for surgical intervention (38). OA is the most frequent condition associated with cartilage degeneration and dgemric has been used to assess cartilage degeneration in the knee joint and hip joint with secondary osteoarthritis due to hip dysplasia (39, 40). Joint space narrowing and the development of osteophytes at the knee joints as indicators for knee OA have been reported to be associated with lower dgemric values at baseline making dgemric a predictor of radiologically manifest knee OA following partial meniscectomy. The first study to assess small joints proved the feasibility of dgemric in the first metacarpophalangeal joint in an OA case. Follow-up dgemric measurements have been used to assess the effect of cartilage repair procedures of the knee, suggesting varying degree of proteoglycan replenishment. Cartilage repair tissue after Matrixinduced Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (MACI) in the knee joint has been demonstrated to have a reduced zonal variation of dgemric values and a decrease in the relaxation rate of the deep zone of the transplant in the 1 year follow-up was interpreted as a slow increase in GAG (41). In RA, early cartilage damage prior to macroscopic cartilage loss has been assumed based on decreased dgemric in the metacarpophalangeal joints of RA patients prior to the initiation of therapy with disease modifying drugs (35). For dgemric, the application of intravenous contrast agent is obligatory. However, recent studies have brought potential adverse effects of gadolinium to international attention. Due to potential gadolinium depositions in the brain, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) banned several linear gadolinium-based contrast agents. Even though macrocyclic contrast agents have not been suspended, they should be used with care and a strict indication (42). Hence, future research should focus more on gadolinium-free molecular MR imaging of cartilage such as glycosaminoglycan chemical exchange saturation transfer (gagcest), sodium MRI and T1 rho mapping to visualise the GAG content, T2/T2* mapping to evaluate the water content and collagen network integrity or diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI)(43 45) (Fig. 3). In clinical studies, especially T2 and T2* mapping have been used mostly at the knee and the hip showing promising results in assessing early diseases stages Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018 S-141
4 Fig. 2. Colour-coded dgemric map with low dgemric index in red and high dgemric index in green in ms. The left picture shows a patient with low grade synovitis, while the right picture illustrates a patient with high grade synovitis, both patients suffering from RA. The right picture demonstrates significantly lower dgemric index compared to the left picture, indicating higher cartilage alteration of the patient with higher synovitis. Fig. 3. Colour-coded gagcest map of the lumbar spine (L1 - S1), with high GAG content in blue and low GAG content in red. This patient with radiculopathy presented significantly lower GAG content compared to controls, especially at the affected segment L5/S1. and in monitoring cartilage changes. Kijowski et al. found improved sensitivity in the detection of cartilage lesions of the knee and for the identification of early cartilage degeneration(46). Ellermann et al. have focused on T2 and T2* mapping of the hip, showing that T2* relaxation times in normal cartilage were significantly higher than those of cartilage with early and more advanced degeneration (47). T2 maps have also been obtained from the ankle, proximal interphalangeal joint and wrist. The association of physical activity with cartilage degeneration remains controversial and only a few studies have assessed the relationship using T2 mapping. T2-mapping has also been applied for quantitative assessment of fibrocartilage, in particular IVDs and menisci. In IVDs, T2 relaxation times are dependent on the quantity of water and the integrity of the proteoglycan (PG)-collagen matrix. During early disc degeneration, T2 mapping shows a decrease in water and collagen matrix (48). Even in early RA (era), molecular cartilage damage could be found in this early stage of the disease while morphological alterations (for example joint space narrowing) are not visible (49). Herz et al. investigated the relation between inflammation of synovitis and cartilage degradation measured with biochemical and morphological MRI (50). They demonstrated an association with high synovitis and proteoglycan loss measured by dgemric. It is known that structural bony destructions develop mostly at bare area, an area without cartilage coat. This protection is at stake in progressive disease and may lead to severe joint destruction. Additionally, McGonagle et al. found erosions in sites lined by cartilage (51). These authors described lesser bone destruction at these areas, so they concluded that cartilage coat minimises bone damage. S-142 Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018
5 Future directions US is increasingly explored as a bedside tool for early diagnosis, and quantification of OA progression as well as RA cartilage damage. Conventional US techniques including PD and duplex techniques do not yet permit analysis of chemical cartilage or ECM composition. MRI has constantly been improved to obtain higher resolution images and detect cartilage injury on a molecular level, even without the need for potentially hazardous contrast agents. Both techniques are well tolerated by the patient and serious adverse events are rare, with the exception of potential side effects from contrast agents. Therefore, US and MRI will likely be of increasing importance in future clinical trials and clinical assessment of RA and OA. References 1. PAP T, KORB-PAP A: Cartilage damage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis two unequal siblings. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2015; 11: GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, WU C-L, MEU- LENBELT I: Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol 2018 May 22 [Epub ahead of print]. 3. NELSON AE: Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018; 26: ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ et al.: 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/ European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BIJLSMA JWJ et al.: Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: DARAWANKUL B, CHAIAMNUAY S, PAK- CHOTANON R, ASAVATANABODEE P, NARONGROEKNAWIN P: The good EULAR response at the first year is strongly predictive of clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis: results from the TARAC cohort. Clin Rheumatol 2015; 34: FUNCK-BRENTANO T, GANDJBAKHCH F, ETCHEPARE F et al.: Prediction of radiographic damage in early arthritis by sonographic erosions and power Doppler signal: a longitudinal observational study. Arthritis Care Res 2013; 65: van der HEIJDE D: Erosions versus joint space narrowing in rheumatoid arthritis: what do we know? Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70 (Suppl. 1): i ALETAHA D, FUNOVITS J, SMOLEN JS: Physical disability in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with cartilage damage rather than bone destruction. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: BLIDDAL H, BOESEN M, CHRISTENSEN R, KUBASSOVA O, TORP-PEDERSEN S: Imaging as a follow-up tool in clinical trials and clinical practice. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2008; 22: American College of Rheumatology Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials Task Force Imaging Group and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Magnetic Resonance Imaging Inflammatory Arthritis Working Group. Review: The utility of magnetic resonance imaging for assessing structural damage in randomized controlled trials in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65: DISLER DG, RAYMOND E, MAY DA, WAYNE JS, McCAULEY TR: Articular cartilage defects: in vitro evaluation of accuracy and interobserver reliability for detection and grading with US. Radiology 2000; 215: MÖLLER B, BONEL H, ROTZETTER M, VIL- LIGER PM, ZISWILER H-R: Measuring finger joint cartilage by ultrasound as a promising alternative to conventional radiograph imaging. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 61: FILIPPUCCI E, DA LUZ KR, DI GESO L et al.: Interobserver reliability of ultrasonography in the assessment of cartilage damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: ABE A, ISHIKAWA H, NAKAZONO K, MURA- SAWA A, WAKAKI K: A comparison of the ultrasonography images of the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the corresponding synovial histological findings. Mod Rheumatol 2016; 26: GUTIERREZ M, DI GESO L, SALAFFI F et al.: Ultrasound detection of cartilage calcification at knee level in calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease: ultrasound in calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease. Arthritis Care Res 2014; 66: TERSLEV L, GUTIERREZ M, SCHMIDT WA et al.: Ultrasound as an outcome measure in gout. A validation process by the OMER- ACT Ultrasound Working Group. J Rheumatol 2015; 42: NEOGI T, JANSEN TLTA, DALBETH N et al.: 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74: SARMANOVA A, HALL M, MOSES J, DOHERTY M, ZHANG W: Synovial changes detected by ultrasound in people with knee osteoarthritis - a meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2016; 24: MATHIESSEN A, SLATKOWSKY-CHRISTENS- EN B, KVIEN TK, HAMMER HB, HAUGEN IK: Ultrasound-detected inflammation predicts radiographic progression in hand osteoarthritis after 5 years. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: CONAGHAN P, LASSERE M, ØSTERGAARD M et al.: OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 4: an international multicenter longitudinal study using the RA-MRI Score. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: HETLAND ML, STENGAARD-PEDERSEN K, JUNKER P et al.: Radiographic progression and remission rates in early rheumatoid arthritis - MRI bone oedema and anti-ccp predicted radiographic progression in the 5-year extension of the double-blind randomised CIMESTRA trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: FREESTON JE, BIRD P, CONAGHAN PG: The role of MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: research and clinical issues. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2009; 21: BAKER JF, OSTERGAARD M, EMERY P et al.: Early MRI measures independently predict 1-year and 2-year radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: secondary analysis from a large clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73: HAAVARDSHOLM EA, BØYESEN P, ØSTER- GAARD M, SCHILDVOLD A, KVIEN TK: Magnetic resonance imaging findings in 84 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: bone marrow oedema predicts erosive progression. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67: ØSTERGAARD M, PETERFY C, CONAGHAN P et al.: OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: ØSTERGAARD M, EMERY P, CONAGHAN PG et al.: Significant improvement in synovitis, osteitis, and bone erosion following golimumab and methotrexate combination therapy as compared with methotrexate alone: a magnetic resonance imaging study of 318 methotrexate-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: OSTERGAARD M, BØYESEN P, ESHED I et al.: Development and preliminary validation of a magnetic resonance imaging joint space narrowing score for use in rheumatoid arthritis: potential adjunct to the OMERACT RA MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 2011; 38: GLINATSI D, BIRD P, GANDJBAKHCH F et al.: Validation of the OMERACT Psoriatic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Score (PsAMRIS) for the hand and foot in a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Rheumatol 2015; 42: ØSTERGAARD M, PETERFY CG, BIRD P et al.: The OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scoring System: updated recommendations by the OMERACT MRI in Arthritis Working Group. J Rheumatol 2017; 44: OSTROWSKA M, MAŚLIŃSKI W, PROCHO- REC-SOBIESZEK M, NIECIECKI M, SUDOŁ- SZOPIŃSKA I: Cartilage and bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatologia 2018; 56: OEI EHG, van TIEL J, ROBINSON WH, GOLD GE: Quantitative radiological imaging techniques for articular cartilage composition: Towards early diagnosis and development of disease-modifying therapeutics for osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2014; n/a-n/a. 33. SCHLEICH C, HESPER T, HOSALKAR HS et al.: 3D double-echo steady-state sequence assessment of hip joint cartilage and labrum at 3 Tesla: comparative analysis of magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative data. Eur Radiol 2017; 27: BURSTEIN D, VELYVIS J, SCOTT KT et al.: Protocol issues for delayed Gd(DTPA) (2-)-enhanced MRI (dgemric) for clinical Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018 S-143
6 evaluation of articular cartilage. Magn Reson Med 2001; 45: MIESE F, BUCHBENDER C, SCHERER A et al.: Molecular imaging of cartilage damage of finger joints in early rheumatoid arthritis with delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: CREMA MD, ROEMER FW, MARRA MD et al.: Articular cartilage in the knee: current MR imaging techniques and applications in clinical practice and research. Radiographics 2011; 31: TIDERIUS CJ, SANDIN J, SVENSSON J, DAHL- BERG LE, JACOBSSON L: Knee cartilage quality assessed with dgemric in rheumatoid arthritis patients before and after treatment with a TNF inhibitor. Acta Radiol 2010; 51: SCHLEICH C, MIESE F, MÜLLER-LUTZ A et al.: Value of delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage for the pre-operative assessment of cervical intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res 2017; 35: KIM Y-J, JARAMILLO D, MILLIS MB, GRAY ML, BURSTEIN D: Assessment of early osteoarthritis in hip dysplasia with delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003; 85-A: TIDERIUS CJ, OLSSON LE, LEANDER P, EK- BERG O, DAHLBERG L: Delayed gadoliniumenhanced MRI of cartilage (dgemric) in early knee osteoarthritis. Magn Reson Med 2003; 49: PINKER K, SZOMOLANYI P, WELSCH GC et al.: Longitudinal evaluation of cartilage composition of matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte transplants with 3-T delayed gadolinium-enhanced MRI of cartilage. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008; 191: GULANI V, CALAMANTE F, SHELLOCK FG, KANAL E, REEDER SB, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: Gadolinium deposition in the brain: summary of evidence and recommendations. Lancet Neurol 2017; 16: REHNITZ C, KUPFER J, STREICH NA et al.: Comparison of biochemical cartilage imaging techniques at 3 T MRI. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2014; 22: WELSCH GH, TRATTNIG S, PATERNOSTRO- SLUGA T et al.: Parametric T2 and T2* mapping techniques to visualize intervertebral disc degeneration in patients with low back pain: initial results on the clinical use of 3.0 Tesla MRI. Skeletal Radiol 2011; 40: SCHLEICH C, MÜLLER-LUTZ A, BLUM K et al.: Facet tropism and facet joint orientation: risk factors for the development of early biochemical alterations of lumbar intervertebral discs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2016; 24: KIJOWSKI R, BLANKENBAKER DG, MUNOZ DEL RIO A, BAER GS, GRAF BK: Evaluation of the articular cartilage of the knee joint: value of adding a T2 mapping sequence to a routine MR imaging protocol. Radiology 2013; 267: ELLERMANN J, ZIEGLER C, NISSI MJ et al.: Acetabular cartilage assessment in patients with femoroacetabular impingement by using T2* mapping with arthroscopic verification. Radiology 2014; 271: ZHANG Y, HU J, DUAN C, HU P, LU H, PENG X: Correlation study between facet joint cartilage and intervertebral discs in early lumbar vertebral degeneration using T2, T2* and T1ρ mapping. PLoS One 2017; 12: e SCHLEICH C, MÜLLER-LUTZ A, SEWERIN P et al.: Intra-individual assessment of inflammatory severity and cartilage composition of finger joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Skeletal Radiol 2015; 44: HERZ B, ALBRECHT A, ENGLBRECHT M et al.: Osteitis and synovitis, but not bone erosion, is associated with proteoglycan loss and microstructure damage in the cartilage of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73: McGONAGLE D, TAN AL, MØLLER DØHN U, OSTERGAARD M, BENJAMIN M: Microanatomic studies to define predictive factors for the topography of periarticular erosion formation in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: S-144 Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2018
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint
 i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Optimal use of MRI in clinical trials, clinical care and clinical registries of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Optimal use of MRI in clinical trials, clinical care and clinical registries of patients with rheumatoid arthritis M. Østergaard 1,2, S. Møller-Bisgaard 1,3 1 Copenhagen Center for Arthritis Research,
Optimal use of MRI in clinical trials, clinical care and clinical registries of patients with rheumatoid arthritis M. Østergaard 1,2, S. Møller-Bisgaard 1,3 1 Copenhagen Center for Arthritis Research,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Immanuel Krankenhaus Berlin, Medical Centre for Rheumatology Berlin - Buch; 2
 Low-field MRI versus ultrasound: which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis? W.A. Schmidt 1, B. Schicke 2, B. Ostendorf
Low-field MRI versus ultrasound: which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis? W.A. Schmidt 1, B. Schicke 2, B. Ostendorf
An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System
 Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
S tructural joint damage, a major outcome in
 i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
Cartilage Repair Options
 Imaging of Cartilage Repair Carl S. Winalski, MD Imaging Institute Department of Biomedical Engineering Cleveland Clinic Cartilage Repair Options Direct repair Marrow stimulation Autologous transplantation
Imaging of Cartilage Repair Carl S. Winalski, MD Imaging Institute Department of Biomedical Engineering Cleveland Clinic Cartilage Repair Options Direct repair Marrow stimulation Autologous transplantation
MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians
 MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians I. Eshed 1, K.G.A. Hermann 2 1 Department of Radiology, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel; 2 Department of Radiology, Charité -
MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians I. Eshed 1, K.G.A. Hermann 2 1 Department of Radiology, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel; 2 Department of Radiology, Charité -
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Numerous studies have demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive for detection of
 Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
Aoyagi, Kiyoshi; Eguchi, Katsumi; K
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Combination of MRI-detected bone ma arthritis classification criteria i rheumatoid arthritis Tamai, Mami; Kita, Junko; Nakashima Horai, Yoshiro; Okada,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Combination of MRI-detected bone ma arthritis classification criteria i rheumatoid arthritis Tamai, Mami; Kita, Junko; Nakashima Horai, Yoshiro; Okada,
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
The use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSKUS) as a. Musculoskeletal Ultrasound as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Tool in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 215 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Tool in Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Jain, M.D., and Jonathan Samuels, M.D. Abstract The use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSKUS) has increased
215 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Tool in Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Jain, M.D., and Jonathan Samuels, M.D. Abstract The use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSKUS) has increased
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Imaging is essential in the diagnosis
 Review Article Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Articular Cartilage Laith M. Jazrawi, MD Michael J. Alaia, MD Gregory Chang, MD Erin F. FitzGerald, MD Michael P. Recht, MD From the Department
Review Article Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Articular Cartilage Laith M. Jazrawi, MD Michael J. Alaia, MD Gregory Chang, MD Erin F. FitzGerald, MD Michael P. Recht, MD From the Department
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the Knee
 doi: 10.5505/actamedica.2016.81905 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 4 Issue 3 2016 Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the
doi: 10.5505/actamedica.2016.81905 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 4 Issue 3 2016 Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the
Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy
 Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy Surgically Induced canine OA models: Anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament transection model Pond MJ, Nuki G. Ann Rheum Dis 1973 (and > 100 others) Meniscal disruption
Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy Surgically Induced canine OA models: Anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament transection model Pond MJ, Nuki G. Ann Rheum Dis 1973 (and > 100 others) Meniscal disruption
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
The value of the simplified RAMRIS-5 in early RA patients under methotrexate therapy using high-field MRI
 Frenken et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1789-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The value of the simplified RAMRIS-5 in early RA patients under methotrexate
Frenken et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1789-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The value of the simplified RAMRIS-5 in early RA patients under methotrexate
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
When (How) MRI Became the Gold Standard Hollis G. Potter, MD
 When (How) MRI Became the Gold Standard Hollis G. Potter, MD potterh@hss.edu Target audience: Radiologists and imaging scientists interested in assessing MRI of cartilage Outcome/Objectives: 1. To become
When (How) MRI Became the Gold Standard Hollis G. Potter, MD potterh@hss.edu Target audience: Radiologists and imaging scientists interested in assessing MRI of cartilage Outcome/Objectives: 1. To become
ARD Online First, published on December 15, 2014 as /annrheumdis Clinical and epidemiological research
 ARD Online First, published on December 15, 2014 as 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206359 Clinical and epidemiological research Handling editor Tore K Kvien For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence
ARD Online First, published on December 15, 2014 as 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206359 Clinical and epidemiological research Handling editor Tore K Kvien For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence
SSSR. 1. Nov Ankle. Postoperative Imaging of Cartilage Repair. and Lateral Ligament Reconstruction
 Ankle Postoperative Imaging of Cartilage Repair and Lateral Ligament Reconstruction Andrea B. Rosskopf, MD University Hospital Balgrist Imaging of Cartilage Repair Why? To assess the technical success
Ankle Postoperative Imaging of Cartilage Repair and Lateral Ligament Reconstruction Andrea B. Rosskopf, MD University Hospital Balgrist Imaging of Cartilage Repair Why? To assess the technical success
Clinical Practice Guideline. Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings. Version
 Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: Version: Accepted Version
 This is a repository copy of The OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scoring System: Updated Recommendations by the OMERACT MRI in Arthritis Working Group. White Rose Research
This is a repository copy of The OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scoring System: Updated Recommendations by the OMERACT MRI in Arthritis Working Group. White Rose Research
Key Indexing Terms: PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OMERACT
 The OMERACT Psoriatic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (PsAMRIS): Definitions of Key Pathologies, Suggested MRI Sequences, and Preliminary Scoring System for PsA Hands MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
The OMERACT Psoriatic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (PsAMRIS): Definitions of Key Pathologies, Suggested MRI Sequences, and Preliminary Scoring System for PsA Hands MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
Disclosures. Ultrasonography. Conventional radiography (XR) Magnetic resonance imaging. Conventional CT 10/27/2013
 What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Concise report RHEUMATOLOGY
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2012;51:2034 2038 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes124 Advance Access publication 30 July 2012 Concise report Head-to-head comparison of quantitative and semi-quantitative ultrasound
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2012;51:2034 2038 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes124 Advance Access publication 30 July 2012 Concise report Head-to-head comparison of quantitative and semi-quantitative ultrasound
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Is synovial hypertrophy without Doppler activity sensitive to change? Post-hoc analysis from a rheumatoid arthritis ultrasound study
 Terslev et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:224 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1709-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is synovial hypertrophy without Doppler activity sensitive to change? Post-hoc
Terslev et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:224 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1709-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is synovial hypertrophy without Doppler activity sensitive to change? Post-hoc
Overview of musculoskeletal ultrasound for the clinical rheumatologist
 Overview of musculoskeletal ultrasound for the clinical rheumatologist S. Hassan Rheumatology Division, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, USA. Sobia Hassan, MD, MRCP, RhMSUS Please address correspondence
Overview of musculoskeletal ultrasound for the clinical rheumatologist S. Hassan Rheumatology Division, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, USA. Sobia Hassan, MD, MRCP, RhMSUS Please address correspondence
MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: a useful tool for the clinician?
 Review Editor s choice Scan to access more free content Correspondence to Professor Fiona McQueen, Department of Molecular Medicine and Pathology, University of Auckland, 85 Park Road, Grafton, Auckland
Review Editor s choice Scan to access more free content Correspondence to Professor Fiona McQueen, Department of Molecular Medicine and Pathology, University of Auckland, 85 Park Road, Grafton, Auckland
Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104
 Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Advantages of a combined rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) for hand and feet: does the
Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Advantages of a combined rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) for hand and feet: does the
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Magnetic resonance imaging in juvenile idiopathic arthritis diagnosis and follow-up, beyond imagination Hemke, R.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Magnetic resonance imaging in juvenile idiopathic arthritis diagnosis and follow-up, beyond imagination Hemke, R. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Magnetic resonance imaging in juvenile idiopathic arthritis diagnosis and follow-up, beyond imagination Hemke, R. Link to publication Citation for published version
"EULAR endorsed course"
 MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE InterMediate Level 15 17 September, 2017 Dubai, UAE Organizing Office: Compass Conferences "EULAR endorsed course" Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer) Esperanza
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE InterMediate Level 15 17 September, 2017 Dubai, UAE Organizing Office: Compass Conferences "EULAR endorsed course" Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer) Esperanza
David Bong (Spain), MD Faculty member of the EULAR MSUS courses since 2011.
 MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Intermediate Level Sept 30 & Oct 1 & 2, 2016 Dubai, United Arab Emirates Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer)
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Intermediate Level Sept 30 & Oct 1 & 2, 2016 Dubai, United Arab Emirates Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer)
Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Comparative Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, September: 615-620, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, September: 615-620, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients,
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
The Role of Ultrasonography in the Assessment of Rheumatic Diseases. Current and Potential Role of Ultrasonography in Rheumatology
 The Role of Ultrasonography in the Assessment of Rheumatic Diseases Karina D. Torralba, MD, MACM, CCD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California Objective:
The Role of Ultrasonography in the Assessment of Rheumatic Diseases Karina D. Torralba, MD, MACM, CCD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California Objective:
Early diagnosis of Rheumatoid
 26 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Detection of Destructive Changes in Small Joints of Hands in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
26 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Detection of Destructive Changes in Small Joints of Hands in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison between Pre-Contrast and Post-Contrast Images
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping
 TR_002 Technical Reports Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping Min A Yoon 1,*, Suk-Joo Hong 1, Chang Ho Kang 2, Baek Hyun Kim 3 1 Korea University
TR_002 Technical Reports Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping Min A Yoon 1,*, Suk-Joo Hong 1, Chang Ho Kang 2, Baek Hyun Kim 3 1 Korea University
A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies
 A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies T. Pincus Division of Rheumatology and Immunology,
A 3-page standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA): Efficient capture of essential data for clinical trials and observational studies T. Pincus Division of Rheumatology and Immunology,
Saltzherr et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:55 DOI /s
 Saltzherr et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:55 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1262-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging to detect cartilage loss in severe osteoarthritis
Saltzherr et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:55 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1262-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging to detect cartilage loss in severe osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions. Claudio Mella, MD
 Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis to predict rheumatoid arthritis development?
 Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
 Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
REVIEW ARTICLE EDWIN H. G. OEI, 1 JASPER VAN TIEL, 2 WILLIAM H. ROBINSON, 3 AND GARRY E. GOLD 4
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 66, No. 8, August 2014, pp 1129 1141 DOI 10.1002/acr.22316 2014, American College of Rheumatology REVIEW ARTICLE Quantitative Radiologic Imaging Techniques for Articular
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 66, No. 8, August 2014, pp 1129 1141 DOI 10.1002/acr.22316 2014, American College of Rheumatology REVIEW ARTICLE Quantitative Radiologic Imaging Techniques for Articular
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
MRI osteitis predicts cartilage damage at the wrist in RA: a three-year prospective 3T MRI study examining cartilage damage
 McQueen et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R33 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access MRI osteitis predicts cartilage damage at the wrist in RA: a three-year prospective 3T MRI study examining cartilage
McQueen et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R33 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access MRI osteitis predicts cartilage damage at the wrist in RA: a three-year prospective 3T MRI study examining cartilage
Radiologic manifestations of gout in MRI
 Radiologic manifestations of gout in MRI Poster No.: C-1053 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit D. Gorostiza Laborda, A. Urresola Olabarrieta, B. Canteli Padilla, F. Perez-Ruiz,
Radiologic manifestations of gout in MRI Poster No.: C-1053 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit D. Gorostiza Laborda, A. Urresola Olabarrieta, B. Canteli Padilla, F. Perez-Ruiz,
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
June 26 th 28 th, 2014 Innsbruck, Austria
 MUSCULOSKELETAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE FOR RHEUMATOLOGISTS - INTERMEDIATE LEVEL - June 26 th 28 th, 2014 Innsbruck, Austria This course is scientifically endorsed by: GENERAL INFORMATION Course opening: Thursday,
MUSCULOSKELETAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE FOR RHEUMATOLOGISTS - INTERMEDIATE LEVEL - June 26 th 28 th, 2014 Innsbruck, Austria This course is scientifically endorsed by: GENERAL INFORMATION Course opening: Thursday,
The Evidence for Magnetic Resonance Imaging as an Outcome Measure in Proof-of-Concept Rheumatoid Arthritis Studies
 OMERACT 7 Special Interest Group The Evidence for Magnetic Resonance Imaging as an Outcome Measure in Proof-of-Concept Rheumatoid Arthritis Studies PHILIP G. CONAGHAN, FIONA M. McQUEEN, CHARLES G. PETERFY,
OMERACT 7 Special Interest Group The Evidence for Magnetic Resonance Imaging as an Outcome Measure in Proof-of-Concept Rheumatoid Arthritis Studies PHILIP G. CONAGHAN, FIONA M. McQUEEN, CHARLES G. PETERFY,
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor
 Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Extremity Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Updated Literature Review
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 63, No. 5, May 2011, pp 660 665 DOI 10.1002/acr.20413 2011, American College of Rheumatology REVIEW ARTICLE Extremity Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 63, No. 5, May 2011, pp 660 665 DOI 10.1002/acr.20413 2011, American College of Rheumatology REVIEW ARTICLE Extremity Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Review. Structural progression in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Frederique Gandjbakhch*1 & Violaine Foltz1
 Structural in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Remission has become an achievable goal in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thanks to a large choice of drug therapies and improvement of treatment
Structural in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Remission has become an achievable goal in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thanks to a large choice of drug therapies and improvement of treatment
Graz, October 3 rd 5 th, 2013
 MUSCULOSKELETAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE IN RHEUMATOLOGY INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Graz, October 3 rd 5 th, 2013 This course has been scientifically endorsed by: GENERAL INFORMATION Course opening: Thursday, October
MUSCULOSKELETAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE IN RHEUMATOLOGY INTERMEDIATE LEVEL Graz, October 3 rd 5 th, 2013 This course has been scientifically endorsed by: GENERAL INFORMATION Course opening: Thursday, October
Osteochondral regeneration. Getting to the core of the problem.
 Osteochondral regeneration. Getting to the core of the problem. TM TM Bio-mimetic, biointegratable and resorbable Flexible and easy to shape Straightforward one-step procedure Promotes a guided osteo-chondral
Osteochondral regeneration. Getting to the core of the problem. TM TM Bio-mimetic, biointegratable and resorbable Flexible and easy to shape Straightforward one-step procedure Promotes a guided osteo-chondral
Targeted Ultrasound of the Fifth Metatarsophalangeal Joint in an Early Inflammatory Arthritis Cohort
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 61, No. 7, July 15, 2009, pp 1004 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.24564 2009, American College of Rheumatology CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE FIELD Targeted Ultrasound
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 61, No. 7, July 15, 2009, pp 1004 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.24564 2009, American College of Rheumatology CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE FIELD Targeted Ultrasound
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as /ard Extended report
 ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as 10.1136/ard.2010.146068 Extended report An additional supplementary table is published online only. To view this fi le please visit the journal online (
ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as 10.1136/ard.2010.146068 Extended report An additional supplementary table is published online only. To view this fi le please visit the journal online (
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the
 CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Is the Doppler Ultrasound Score More Reliable than the Grey Scale Ultrasound Score in Assessing the Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient s Joints?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the Doppler Ultrasound Score More Reliable than the Grey Scale Ultrasound Score in Assessing the Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient s Joints? Copotoiu Monica 1, Georgescu Lia 1, Poór G 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the Doppler Ultrasound Score More Reliable than the Grey Scale Ultrasound Score in Assessing the Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient s Joints? Copotoiu Monica 1, Georgescu Lia 1, Poór G 2,
Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand and Wrist in Early Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 4, April 2015, pp 869 876 DOI 10.1002/art.39000 2015, American College of Rheumatology Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 4, April 2015, pp 869 876 DOI 10.1002/art.39000 2015, American College of Rheumatology Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
This is a repository copy of Iterative development and reliability of the OMERACT hand osteoarthritis MRI scoring system..
 This is a repository copy of Iterative development and reliability of the OMERACT hand osteoarthritis MRI scoring system.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/110435/
This is a repository copy of Iterative development and reliability of the OMERACT hand osteoarthritis MRI scoring system.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/110435/
Laura M. Fayad, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University
 Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Tomosynthesis of the Wrist and Hand in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Comparison With Radiography and MRI
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Aoki et al. Imaging of the Wrist and Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masami Fujii 1 Yoshiko Yamashita 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Aoki et al. Imaging of the Wrist and Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masami Fujii 1 Yoshiko Yamashita 1
CARTILAGE REPAIR INTRODUCTION. M. BERRUTO and G.M. PERETTI 1,2. Received January 6, Accepted January 8, 2013
 CARTILAGE REPAIR INTRODUCTION M. BERRUTO and G.M. PERETTI 1,2 Gaetano Pini Orthopedic Institute, Milan; 1 Department of Biomedical Sciences for Health, University of Milan, 2 IRCCS Galeazzi Orthopedic
CARTILAGE REPAIR INTRODUCTION M. BERRUTO and G.M. PERETTI 1,2 Gaetano Pini Orthopedic Institute, Milan; 1 Department of Biomedical Sciences for Health, University of Milan, 2 IRCCS Galeazzi Orthopedic
Utilizing ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of osteoarthritis
 & n- Special Report International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology Utilizing ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common rheumatic disease and the
& n- Special Report International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology Utilizing ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common rheumatic disease and the
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM04690) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis
 Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM469) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., John
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM469) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., John
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
