Establishment of canine models of lunatomalacia through liquid nitrogen freezing
|
|
|
- Randell Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 880 Establishment of canine models of lunatomalacia through liquid nitrogen freezing QISHUN HUANG, QIANG FU, HUAIYUAN ZHENG, MENG GAN, YUXIONG WONG and ZHENBING CHEN Department of Hand Surgery, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei , P.R. China Received September 28, 2012; Accepted December 11, 2012 DOI: /etm Abstract. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of establishing dog models of lunatomalacia through liquid nitrogen freezing. Twelve adult crossbred dogs were divided into three groups. Unilateral lunates were peeled off the parenchyma and frozen to result in avascular necrosis. They were observed dynamically through X-ray, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Furthermore, gross and histomorphological observations of samples were performed. Disseminated punctate hyperintense images and abnormal manifestations were detected, respectively. At 12 weeks after surgery, uneven bone density of the lunate and a flattened lunate of irregular shape were detected. A large area of irregular hypointense foci and hyperintensity was observed. Gross sample observation revealed a large area of dead bone. A decrease in the density of the trabecular bones and several vacant bone lacunas were visible. Liquid nitrogen freezing is a successful and reliable method for preparing animal models of lunatomalacia. Introduction Lunatomalacia, one of the main causes of wrist pain, is a disease characterized by cystic change, fragmentation and progressive collapse of the lunate (1-3). Lunatomalacia was first reported by Peste in In 1910, Robert Kienböck formulated a classic description of its clinical and X-ray manifestations, for which it was also named Kienböck's disease (4). More than 100 years have passed since the first report on lunatomalacia; however, the origin of this disease remains unclear and no theory satisfactorily explains its original factors and pathological process. To date, a number of factors Correspondence to: Professor Qishun Huang, Department of Hand Surgery, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei , P.R. China qishunhuang@126.com Key words: animal models, liquid nitrogen freezing, lunate, lunatomalacia have been thought to correlate with the pathogenesis of lunatomalacia. These factors include vascular factors, ulnar minus variation, morphological changes of the lunate and blood hypercoagulable states due to systemic factors, a decrease in arterial perfusion and venous blood stasis, application of corticosteroids, sickle red blood cell disease, cerebral palsy and septicemic embolism (5-8). These factors require different treatment methods. For early-phase treatment of lunatomalacia, non-operative approaches and bed rest are mainly taken. For aggressive-phase treatment, various surgical procedures may be adopted, each having its own advantages and disadvantages (9-11). Although different surgical routes offer multiple choices for lunatomalacia treatment, no criteria currently exist for determination of a preferred method of treatment (2). With the exception of conservative treatments, all the methods to treat the lunatomalacia by surgical procedures are substitution therapies, in which one trauma is adopted for another. They are not specifically based on the origin of lunatomalacia or its pathological changes. To date, studies on animal models of lunatomalacia remain rare. Accordingly, this study aimed to provide an experimental basis for the clinical treatment of lunatomalacia by creating dog models of lunatomalacia through liquid nitrogen freezing. Materials and methods Animals. A total of 12 adult healthy crossbred dogs weighing kg were selected. The surgical procedures were approved by the Institute of Animal Ethics of Tongji Medical College. Sample perfusion. The blood supply sources for the lunate were identified using the emulsion perfusion method. The upper extremities were taken from fresh dog cadavers and 1 liter heparin saline (at a ratio of 12,500 units heparin to 200 ml physiological saline) was injected into the axillary artery until a colorless liquid was observed to flow out from the veins. A red emulsion (red ink and white emulsion, 1:8) was then injected into the axillary artery until a red liquid was observed to flow out from the proximal veins. The samples were placed in a refrigerator for 24 h and then taken out. Applied anatomy: constitution of carpal bones. The carpal bones of dogs are composed of two bones in the proximal
2 HUANG et al: ANIMAL MODELS OF LUNATOMALACIA 881 A B C Figure 1. X-ray images. No marked changes in sclerotin were found in weeks (A) 3 or (B) 6 after surgery. (C) In week 12 after surgery, the density of the lunate appeared uneven, the capsular space flattened and the lunate presented an irregular shape with an unsmooth articular surface. row and four in the distal row. The radial carpal bone in the proximal row is the lunate (or scapholunatum). Dogs are often used as animal models for studies on lunate or scaphoid diseases due to the similarity of their anatomical position and the biomechanic relationships in the constitution of the carpal bones to those of humans. Distribution of blood vessels. The axillary artery was traced until the elbow, where it diverged into the radial and ulnar arteries at the proximal end of the forearm. The radial and ulnar arteries spread off in branches at the wrist to form volar and dorsal nets. Tiny branches from the nets extended into the lunate. No blood vessels were observed on the articular surface of the lunate. Model preparation. Skin preparation was performed on a unilateral upper extremity. After administration of an intravenous anesthetic with 3% pentobarbital, an S-shaped incision was made on the dorsum of the radial carpal joint in a sterile condition to expose the wrist joint completely. The joint capsule was cut open and the lunate was isolated. The volar tissues were stored. A two-ply sterilized rubber tissue was used to separate the lunate from its surrounding tissues. The lunate was frozen in liquid nitrogen for 10 min and then warmed to room temperature. After three cycles of freezing and warming, the joint capsule, ligaments and skin were sutured and then fixed with plaster. The dogs were fed on normal food and the raising conditions were kept the same as those before surgery. After 3 weeks, the plaster was dismantled and the stitches were removed. The animals were observed at 3, 6 and 12 weeks after surgery. At each observation time point, four dogs were anesthetized and studied iconographically. After the dogs were sacrificed, their bilateral lunates were removed for gross and histomorphological examinations. Observational indices and methods: general conditions. The weight, mental state, coat color, gait and wound of the dogs were observed. X-ray detection. Lateral radiographs of the bilateral lunates were obtained at 3, 6 and 12 weeks after surgery. The experimental lunate was compared with the control at each observation time point to determine the changes in the density of the lunate and bone destruction following surgery. The results were also analyzed based on the Lichtman staging criteria (12). Computed tomography (CT) scanning. Bilateral lunates were scanned by CT and reconstructed three-dimensionally to observe changes in the morphology, sclerotin and density of the lunate following surgery. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detection. MRI detection was performed using an eight-channel wire coil to observe changes in the signals and morphology of the lunate following surgery. Visual observation. The shapes, sizes, articular surfaces, color and densities of the bilateral lunates were observed and compared visually. Histomorphological observation. The lunate was cut open along the coronal plane, fixed with 10% formaldehyde solution, decalcified with 5% nitric acid, dehydrated gradiently with routine ethanol and then embedded with paraffin. Sections were cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Results General observation. Following surgery, the dogs presented a negative mental state. The appetite, weight and glossiness of the coat of the dogs decreased. Furthermore, subcutaneous fat was observed. Four weeks after surgery, they began to support their weight using the forelimb on the side utilized for preparing the model. X-ray detection. No marked changes in sclerotin were identified at 3 and 6 weeks after surgery. However, abnormalities were observed at 12 weeks after surgery. The density of the lunate became uneven, the capsular space flattened and the lunate presented an irregular shape with an unsmooth articular surface (Fig. 1). CT scanning. No obvious abnormalities were detected by CT three-dimensional reconstruction at 3 or 6 weeks after surgery. Damaged articular surface and discontinuous bone cortex were apparent at 12 weeks after surgery. The structure of the trabecular bones disappeared and hypointense foci of irregular morphology appeared in the pulp chamber (Fig. 2). MRI detection. At 3 weeks after surgery, hypointense focus like images on T 1 -weighted images (T 1 WI) and disseminated punctate hyperintense images on T 2 WI were observed. At 6 weeks
3 882 A B C Figure 2. Images by computed tomography (CT) scanning. No marked abnormalities were detected by CT three-dimensional reconstruction in weeks (A) 3 or (B) 6 after surgery. (C) In week 12 after surgery, a damaged articular surface and discontinuous bone cortex were identified. The structure of the trabecular bones disappeared and hypointense foci of irregular morphology appeared in the pulp chamber. A A B B C C Figure 3. Images by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detection. (A) Images in week 3 after surgery. Hypointense foci were observed on T 1 weighted images (T 1 WI) and disseminated punctate hyperintense foci were observed on T 2 WI. (B) Images in week 6 after surgery. Changes in the hypointense images on T 1 WI and hyperintense images on T 2 WI were observed. (C) Images in week 12 after surgery. A large area of hypointensity was detected on T 1 WI and a large area of hyperintensity was detected in the lunate on T 2 WI, within which disseminated areas of punctate hypointensity (necrotic bone chips) were embedded. after surgery, changes in the hypointense and hyperintense images were detected. At 12 weeks after surgery, large areas of hypointensity and hyperintensity were captured on T 1 WI and T 2 WI, respectively. Areas of diffuse punctate hypointensity were embedded in the large area of hyperintensity (Fig. 3). Figure 4. Results of histomorphological examination. (A) Image of the un intervened lunate in week 3 after surgery. Abundant trabecular bones, full bone lacuna and plenty of capillary vessels were observed. (B) Image in week 6 after surgery. Sparseness of the trabecular bones, disappearance of the vessels, loss of calcium salt and disappearance of a large area of osteocytes were observed. (C) Image in week 12 after surgery. Fibroplasia was observed around the necrotic bones. Histomorphological observation: gross sample observation. At 6 weeks after surgery, the lunate presented destroyed sclerotin on the surface, a smaller volume compared with the control, a dull articular surface without luster and a marked decrease in the cancellous bone density. At 12 weeks after surgery, a large area of dead bones with crisp texture was detected on the coronal section of the lunate. Furthermore, a number of cancellous bones were observed under the cartilage surface, as a result of osteosclerosis.
4 HUANG et al: ANIMAL MODELS OF LUNATOMALACIA 883 Observation under a light microscope. At 3 weeks after surgery, the trabecular bones appeared thinner, a number of bone lacunas became vacant and vessel density decreased. The marrow cavity bled and neither osteoblasts nor osteoclasts were detected. At 6 weeks after surgery, the trabecular bones became sparse and fractured, calcium salt was lost and a large area of osteocytes disappeared. More than 50% of the bone lacunas became vacant and inflammatory cell infiltration was observed. At 12 weeks after surgery, the trabecular bones fractured, all bone lacunas were empty and fibroplasia was identified around the trabecular bones. By contrast, the corresponding healthy lunate presented normal bone tissues, in which abundant trabecular bones, full lacunas and abundant capillary vessels were observed (Fig. 4). Discussion The current methods used for the preparation of models of osteonecrosis include the following: i) hormone induction: Zhao et al used hormones and endotoxins to induce femur head necrosis in rabbits (13). They found that satisfactory necrosis was achieved within a short time (7). ii) Blood vessel ligation: Nishino et al prepared models with osteonecrosis through artificial dislocation of the hip joint and ligations of the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries and veins (14). These authors identified that dislocation of the joint or ligations of the blood vessels alone do not lead to osteonecrosis, and osteonecrosis only occurs when blood flow is at least 20% lower than that in the healthy control. iii) Osteotomy: Gong et al established models with femur head ischemic necrosis through osteotomy and apparent osteonecrosis was obtained two months after surgery (15). iv) Liquid nitrogen freezing: Yang et al established models with femur head necrosis via liquid nitrogen imbibition (16). These authors identified that the whole femur head presented complete necrosis with empty bone lacunas and necrotic tissue fragments filling the pulp chamber. Aside from the aforementioned techniques, methods used for the preparation of models of osteonecrosis also include local cell inactivation, the microwave method and acid base destruction. Bone absorption and formation are closely associated with the roles of blood vessels in the bone (17). During bone growth and repair, bone formation is initiated and supported by blood vessels. Osteoblasts differentiate and proliferate around the vessel, arrange along the vascular endothelium and then excrete osteoids in a direction away from the vessel. When the osteoblasts mature and develop into osteocytes, the newly formed bones deposit around the vessel. In the current study, liquid nitrogen freezing, isolation of the lunate from its surrounding tissues and destruction of the blood supply for the lunate were adopted, to prepare models of lunatomalacia. Sparseness and disruption of the trabecular bones, loss of calcium salt, disappearance of a large area of osteocytes and infiltration of inflammatory cells were found at 6 weeks after surgery. Systemic or local intravascular coagulation is the last common pathway in the pathogenetic process of osteonecrosis caused by various factors (16). Liquid nitrogen freezing instantly leads to vasospasm and embolism in the lunate due to the small volume of the lunate and extenuation of the blood vessel supply running in it. As a result, vascular permeability is enhanced, vascular endothelial cells are damaged and intravascular coagulation is disseminated, thereby causing hemorrhage and ischemic reperfusion injury after rewarming (18,19). The vascular injury in the lunate combined with the isolation of the lunate from its surrounding soft tissues inhibited the spontaneous repair reactions of the lunate. According to the improved Lichtman staging criteria formulated by Allan et al (8), Kienböck's disease is divided into four stages. At stage I, pain, loss of strength and motion limitation at the wrist may occur. No abnormality is detected by X ray in the majority of cases but a number of abnormal changes may be identified by MRI. At stage II, the bone density and fragments in the lunate increase; however, its volume, shape and anatomic associations with adjacent bones do not change. At stage III, the lunate begins to collapse. At stage IIIa, the location and correspondence of the wrist bones are normal. At stage IIIb, the joint space between the lunate and scaphoid widens. Palmar flexion of the scaphoid, an angle between the scaphoid and radius of >60 and ulnar deviation of the triangular bone are observed. Finally, at stage IV, the lunate collapses and fragments, the capitate bone shifts proximally, osteoarthritis occurs between the intercarpal joints, joint surfaces become coarse and uneven, joint spaces narrow, osteophytes are formed and the bones are hardened and degenerated cystically. In the present study, hypointense and disseminated hyperintense images were captured on T 1 WI and T 2 WI, respectively, at 3 weeks after surgery. However, such changes were not detected by X-ray or CT at the same time point. These results indicate that MRI possesses a hypersensitivity to early lunatomalacia. At 12 weeks after surgery, a hyperintense area in which areas of punctate hypointensity were embedded was observed on T 2 WI. The hyperintense area represented watery changes caused by inflammatory and repair reactions and the hypointense images in the area were necrotic bone chips. Lunatomalacia is an independent clinical disease. Thus far, little is known about the cause of this disease. Factors including nutrient artery injury of the lunate, venous embolism, ulnar variation, morphologic abnormality of the lunate, rheumatoid arthritis, sicklemia, cerebral palsy, application of non-steroidal drugs and mechanical injuries are thought to be correlated with the incidence of lunatomalacia. Lunatomalacia is currently accepted as the consequence of the combined actions of various factors and its essence is bone avascular necrosis, in which anatomical variation may be the causative factor and acute and chronic injuries and inflammation may be its primary factor (20,21). To date, studies on animal models with lunatomalacia have rarely been reported. Various methods have been used for model preparation. These methods have attempted to simulate the possible causes and pathological processes of osteonecrosis to provide an experimental basis for further studies on this disease. Sunagawa et al successfully prepared dog models with discontinuity between the scaphoid and lunate by resorting to artificial scapholunatum fractures and liquid nitrogen freezing (7). However, none of these methods reflect the pathological process of osteonecrosis completely. Therefore, the selection of proper experimental models for different purposes is of great practical significance. In this study, animal models of osteonecrosis were prepared by the
5 884 destruction of blood supply to the lunate and liquid nitrogen freezing. Compared with other methods, this method has a number of advantages. First, it achieves a high success rate with reliable osteonecrosis and a short pathological process. Second, it is easy and convenient to perform. Third, it duplicates the primary pathological process of lunatomalacia, although not completely. Finally, no residue of drugs or chemical materials is left and the basic properties of the bone are maintained. Based on the advantages of this method in model preparation, the present study is expected to provide a good platform for further remedial studies on lunatomalacia. References 1. Jones JP Jr: Fat embolism, intravascular coagulation and osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 292: , Nakamura T, Matsumoto T, Nishino M, Tomita K and Kadoya M: Early magnetic resonance imaging and histologic findings in a model of femoral head necrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 334: 68-72, Ledoux P, Lamblin D, Wuilbaut A and Schuind F: A finite element analysis of Kienbock's disease. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 33: , Kienböck R: Uber traumaische malazie des mondbeins und ihre folgezustande: Entartungs for men und kompressionsfrakturen. Fortschritte Rontgenstrahlen 16: , 1910 (In German). 5. Gelberman RH, Bauman TD, Menon J and Akeson WH: The vascularity of the lunate bone and Kienböck's disease. J Hand Surg Am 5: , Kristensen SS and Søballe K: Kienböck's disease - the influence of arthrosis on ulnar variance measurements. J Hand Surg Br 12: , Sunagawa T, Bishop AT and Muramatsu K: Role of conventional and vascularized bone grafts in scaphoid nonunion with avascular necrosis: A canine experimental study. J Hand Surg Am 25: , Allan CH, Joshi A and Lichtman DM: Kienbock's disease: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 9: , Razemon JP: Pathological study of Kienboeck's disease. Ann Chir Main 1: , 1982 (In French). 10. Mirabello SC, Rosenthal DL and Smith RJ: Correlation of clinical and radiographic findings in Kienböck's disease. J Hand Surg Am 21: , Kmano M, Koshimune M, Toyama M and Kazuki K: Palmar plating system for Colles' fractures - a preliminary report. J Hand Surg Am 30: , Lichtman DM and Degnan GG: Staging and its use in the determination of treatment modalities for Kienböck's disease. Hand Clin 9: , Zhao J, Lu S, Xue Z and Deng Q: Establish and evaluate animal models of steriod-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Chin J Bone Tumor & Bone Disease 4: , 2007 (In Chinese). 14. Nishino M, Matsumoto T, Nakamura T and Tomita K: Pathological and hemodynamic study in a new model of femoral head necrosis following traumatic dislocation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116: , Gong X and Lu L: The development of Treating of Lunatomalacia. Foreign Medical Sciences (Section of Orthopaedics) 25: , 2005 (In Chinese). 16. Yang S, Yang C, Xu W, Li J and Zhang Y: Avascular necrosisi of the Femoral Head Prouced in Rabbits by Freezing. Orthopedic J China (Chin) 8: , 2001 (In Chinese). 17. Beredjiklian PK: Kienböck's disease. J Hand Surg Am 34: , Goldfarb CA, Hsu J, Gelberman RH and Boyer MI: The Lichtman classification for Kienböck's disease: an assessment of reliability. J Hand Surg Am 28: 74-80, Bain GI and Begg M: Arthroscopic assessment and classification of Kienbock's disease. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 10: 8-13, Keith PP, Nuttall D and Trail I: Long-term outcome of nonsurgically managed Kienböck's disease. J Hand Surg Am 29: 63-67, Moran SL, Cooney WP, Berger RA, Bishop AT and Shin AY: The use of the 4+5 extensor compartmental vascularized bone graft for the treatment of Kienböck's disease. J Hand Surg Am 30: 50-58, 2005.
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Scaphoid Fractures. Mohammed Alasmari. Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University
 Scaphoid Fractures Mohammed Alasmari Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University 1 2 Scaphoid Fractures Introduction Anatomy History Clinical examination Radiographic evaluation Classification
Scaphoid Fractures Mohammed Alasmari Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University 1 2 Scaphoid Fractures Introduction Anatomy History Clinical examination Radiographic evaluation Classification
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in 99 subjects
 Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
POLSKI 2013, 85, 10,
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2013, 85, 10, 576 580 10.2478/pjs-2013-0086 Radiological investigation of relationship between lunate type and ulnar variance Ahmed Elsaftawy Department of General Surgery,
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2013, 85, 10, 576 580 10.2478/pjs-2013-0086 Radiological investigation of relationship between lunate type and ulnar variance Ahmed Elsaftawy Department of General Surgery,
Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist
 Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist Thursday, May 19, 2016 Pre-Conference Laboratory Workshop Anatomy of the Wrist & Wrist Arthroscopy 6:30 a.m. Registration and Breakfast 7:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction
Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist Thursday, May 19, 2016 Pre-Conference Laboratory Workshop Anatomy of the Wrist & Wrist Arthroscopy 6:30 a.m. Registration and Breakfast 7:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome
 Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome A. Schweizer¹( ), F. Denzler¹, G. Kohler² ¹University Children s Hospital Basel, Orthopaedic Department UKBB, Basel, Switzerland ²Kantonsspital
Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome A. Schweizer¹( ), F. Denzler¹, G. Kohler² ¹University Children s Hospital Basel, Orthopaedic Department UKBB, Basel, Switzerland ²Kantonsspital
Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options
 Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, FRCSC Director Upper Extremity Center, Peripheral Nerve Center, Cleveland Combined Hand Fellowship Cleveland Clinic Outline The Basics
Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, FRCSC Director Upper Extremity Center, Peripheral Nerve Center, Cleveland Combined Hand Fellowship Cleveland Clinic Outline The Basics
What Is the Radiographic Prevalence of Incidental Kienböck Disease?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:808 813 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4541-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Is the
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:808 813 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4541-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Is the
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Carpal rows injuries!
 Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report
 Case Report Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Valya B 2, Vishnu Vardhan M 3 1 Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics Osmania Medical
Case Report Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Valya B 2, Vishnu Vardhan M 3 1 Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics Osmania Medical
Staging of Kienböck s disease. F. Hahn
 Staging of Kienböck s disease F. Hahn Introduction Why staging? Standardisation Communication Prognosis Treatment options X-rays 1910 First description by Kienböck 1947 Ståhl(Rx) 1957 Decoulx(modif. Ståhl,
Staging of Kienböck s disease F. Hahn Introduction Why staging? Standardisation Communication Prognosis Treatment options X-rays 1910 First description by Kienböck 1947 Ståhl(Rx) 1957 Decoulx(modif. Ståhl,
SCAHPO-LUNATE DISSOCIATION
 SCAHPO-LUNATE DISSOCIATION Introduction Scapho-lunate dissociation is the most common significant ligamentous injury of the wrist. The condition is also sometimes referred to as rotary subluxation of the
SCAHPO-LUNATE DISSOCIATION Introduction Scapho-lunate dissociation is the most common significant ligamentous injury of the wrist. The condition is also sometimes referred to as rotary subluxation of the
Interesting Case Series. Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome
 Interesting Case Series Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome Saptarshi Biswas, MD, FRCS Westchester University Medical Center, Valhalla, NY Keywords: ulnar impaction, ulnar impaction syndrome, ulnar wrist pain,
Interesting Case Series Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome Saptarshi Biswas, MD, FRCS Westchester University Medical Center, Valhalla, NY Keywords: ulnar impaction, ulnar impaction syndrome, ulnar wrist pain,
Carpal Instability: Clarification of the Most Common Etiologies and Imaging Findings
 Carpal Instability: Clarification of the Most Common Etiologies and Imaging Findings Corey Matthews DO, Nicholas Strle DO, Donald von Borstel DO Oklahoma State University Medical Center, Department of
Carpal Instability: Clarification of the Most Common Etiologies and Imaging Findings Corey Matthews DO, Nicholas Strle DO, Donald von Borstel DO Oklahoma State University Medical Center, Department of
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature
 Article ID: WMC001290 2046-1690 Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature Corresponding Author: Dr. Dharm Meena, Junior Resident, Orthopaedics, PGIMER, E 402, MDH,PGIMER,Chandigarh,
Article ID: WMC001290 2046-1690 Scaphoid Fractures- Anatomy And Diagnosis: A Systemic Review Of Literature Corresponding Author: Dr. Dharm Meena, Junior Resident, Orthopaedics, PGIMER, E 402, MDH,PGIMER,Chandigarh,
3D printing lunate prosthesis for stage IIIc Kienböck s disease: a case report
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2854-0 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY 3D printing lunate prosthesis for stage IIIc Kienböck s disease: a case report Mei ming Xie 1 Kang lai Tang 1 Chen song Yuan 1 Received: 9
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2854-0 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY 3D printing lunate prosthesis for stage IIIc Kienböck s disease: a case report Mei ming Xie 1 Kang lai Tang 1 Chen song Yuan 1 Received: 9
Interesting Case Series. Perilunate Dislocation
 Interesting Case Series Perilunate Dislocation Tom Reisler, BSc (Hons), MB ChB, MRCS (Ed), Paul J. Therattil, MD, and Edward S. Lee, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Perilunate Dislocation Tom Reisler, BSc (Hons), MB ChB, MRCS (Ed), Paul J. Therattil, MD, and Edward S. Lee, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Poll the Audience 5/29/2015. Wrist Arthroplasty Where are we now?
 Wrist Arthroplasty Where are we now? Brian D Adams, MD Professor Orthopedic Surgery Baylor College of Medicine 72 y/o male, retired, no walking aides, minimal stressful activities, who has left, non-dominant
Wrist Arthroplasty Where are we now? Brian D Adams, MD Professor Orthopedic Surgery Baylor College of Medicine 72 y/o male, retired, no walking aides, minimal stressful activities, who has left, non-dominant
The Role of Lunate Morphology on Scapholunate Instability and Fracture Location in Patients Treated for Scaphoid Nonunion
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:175-180 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.175 The Role of Lunate Morphology on Scapholunate Instability and Fracture Location in Patients Treated
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:175-180 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.175 The Role of Lunate Morphology on Scapholunate Instability and Fracture Location in Patients Treated
Arthroplasty for advanced Kienböck s disease using a radial bone flap with a vascularised wrapping of pronator quadratus
 Arthroplasty for advanced Kienböck s disease using a radial bone flap with a vascularised wrapping of pronator quadratus H. S. Gong, M. S. Chung, Y. H. Lee, S. Lee, J. O. Lee, G. H. Baek From Seoul National
Arthroplasty for advanced Kienböck s disease using a radial bone flap with a vascularised wrapping of pronator quadratus H. S. Gong, M. S. Chung, Y. H. Lee, S. Lee, J. O. Lee, G. H. Baek From Seoul National
Department of Orthopaedics, Terna Medical College, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
 Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 6, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2018 TREATMENT OF STAGE II KIENBOCK S DISEASE WITH VASCULARIZED DORSAL RADIUS
Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 6, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2018 TREATMENT OF STAGE II KIENBOCK S DISEASE WITH VASCULARIZED DORSAL RADIUS
journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 texas orthopaedic journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment of Volar Tilt Measurements with Variations in X-Ray Beam Centralization Along the Longitudinal Axis of the Radius Russell A. Wagner, MD; Will Junius,
texas orthopaedic journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment of Volar Tilt Measurements with Variations in X-Ray Beam Centralization Along the Longitudinal Axis of the Radius Russell A. Wagner, MD; Will Junius,
Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 530-534 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mahmoud EL-HADIDI, Esam EL-KAREF
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 530-534 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mahmoud EL-HADIDI, Esam EL-KAREF
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE. The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus.
 TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
Wrist Arthritis & Partial Wrist Fusion
 Wrist Arthritis & Partial Wrist Fusion Mr Jason N Harvey MB.BS. FRACS (Orth) Hand,Wrist & Elbow Surgeon Clinical Symptoms Outline Physical Examination Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis Outline Non-operative
Wrist Arthritis & Partial Wrist Fusion Mr Jason N Harvey MB.BS. FRACS (Orth) Hand,Wrist & Elbow Surgeon Clinical Symptoms Outline Physical Examination Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis Outline Non-operative
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE. Temporary Scaphotrapezoidal Joint Fixation for Adolescent Kienböck s Disease
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Temporary Scaphotrapezoidal Joint Fixation for Adolescent Kienböck s Disease Yoshiyuki Ando, MD, Masataka Yasuda, MD, Kenichi Kazuki, MD, Noriaki Hidaka, MD, Yasutaka Yoshinaka, MD Purpose
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Temporary Scaphotrapezoidal Joint Fixation for Adolescent Kienböck s Disease Yoshiyuki Ando, MD, Masataka Yasuda, MD, Kenichi Kazuki, MD, Noriaki Hidaka, MD, Yasutaka Yoshinaka, MD Purpose
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid Perilunate Fracture Dislocation
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2. Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals, Apeldoorn, the Netherlands 3
 Chapter 1 F.J.P. Beeres 1 S.J. Rhemrev 1 M. Hogervorst 2 P. den Hollander 3 G.N. Jukema 4 1 Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2 Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals,
Chapter 1 F.J.P. Beeres 1 S.J. Rhemrev 1 M. Hogervorst 2 P. den Hollander 3 G.N. Jukema 4 1 Department of Surgery, Medical Centre Haaglanden, The Hague, the Netherlands 2 Department of Surgery, Gelre Hospitals,
Union rate: Union: Stable 94% All fracture 90% Union after surgery for nonunion with surgery 80% OA in healed scaphoid: 9%
 Complications Incidence of Non-union 1 cm displacement of fracture caused 55% Non-union It takes 5-20 yrs to develop SNAC. SNAC appears to be more common with waist fracture than a proximal pole. However
Complications Incidence of Non-union 1 cm displacement of fracture caused 55% Non-union It takes 5-20 yrs to develop SNAC. SNAC appears to be more common with waist fracture than a proximal pole. However
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Stress Fracture of the Capitate
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:135-139 Stress Fracture of the Capitate Hyung Joon Cho 1, Ki Taek Hong 2, Chang Ho Kang 1, Kyung-Sik Ahn 1, Yura Kim 2, Sung Tae Hwang 1 1 Department of Radiology,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:135-139 Stress Fracture of the Capitate Hyung Joon Cho 1, Ki Taek Hong 2, Chang Ho Kang 1, Kyung-Sik Ahn 1, Yura Kim 2, Sung Tae Hwang 1 1 Department of Radiology,
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Functional Orthopedic Imaging Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion. Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy.
 Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
NE Nebraska Trauma Conference Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017
 NE Nebraska Trauma Conference 2017 Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017 Traumatic arm injuries in the elderly Fractures Hand Wrist Elbow Shoulder Soft tissue injuries Definitions Elderly? old or aging
NE Nebraska Trauma Conference 2017 Tristan Hartzell, MD November 8, 2017 Traumatic arm injuries in the elderly Fractures Hand Wrist Elbow Shoulder Soft tissue injuries Definitions Elderly? old or aging
Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts. Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras
 Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras Definition AVN = massive necrosis of bone and bone marrow occurring
Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras Definition AVN = massive necrosis of bone and bone marrow occurring
Ascension. Silicone MCP surgical technique. surgical technique Ascension Silicone MCP
 Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
3. Ulno lunate, Ulno triquetral ligament. Poirier: Between RSC &LRL. 5. Dorsal intercarpal ligament
 CARPAL INSTABILITY Ligaments Intrinsic Scapho lunate ligament: Dorsal component stronger than volar ligament Luno triquetral ligament: Volar component stronger than dorsal ligament Extrinsic Palmar 1 Radio
CARPAL INSTABILITY Ligaments Intrinsic Scapho lunate ligament: Dorsal component stronger than volar ligament Luno triquetral ligament: Volar component stronger than dorsal ligament Extrinsic Palmar 1 Radio
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications
 Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Upper Limb and Sports Medicine Surgeon Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics Patras University
Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Upper Limb and Sports Medicine Surgeon Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics Patras University
Limited intercarpal fusion as a salvage procedure for advanced Kienbock disease
 HAND (2015) 10:472 476 DOI 10.1007/s11552-014-9705-z Limited intercarpal fusion as a salvage procedure for advanced Kienbock disease Matthew L. Iorio & Colin D. Kennedy & Jerry I. Huang Published online:
HAND (2015) 10:472 476 DOI 10.1007/s11552-014-9705-z Limited intercarpal fusion as a salvage procedure for advanced Kienbock disease Matthew L. Iorio & Colin D. Kennedy & Jerry I. Huang Published online:
SYMPOSIUM ON ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SCAPHOID PROBLEMS Scaphoid malunion
 Hong HKJOS Kong Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2002;6(2):104-108. SYMPOSIUM ON ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SCAPHOID PROBLEMS Scaphoid malunion Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Prince of Wales
Hong HKJOS Kong Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2002;6(2):104-108. SYMPOSIUM ON ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SCAPHOID PROBLEMS Scaphoid malunion Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Prince of Wales
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
Chapter 19. Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion. Introduction. Operative Technique. Radiocarpal and Midcarpal Exploration
 Chapter 19 Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion Introduction Scaphoid fractures are often initially missed and then diagnosed only once nonunion manifests. Because the natural history of these
Chapter 19 Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion Introduction Scaphoid fractures are often initially missed and then diagnosed only once nonunion manifests. Because the natural history of these
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
A Case Report of Kienbock s Disease in a Thirteen-Year-Old Girl
 A Case Report of Kienbock s Disease in a Thirteen-Year-Old Girl Campbell NM; Scrimshire AB; Sharpe K March 2017 Volume 13 Issue 1 Doctors Academy Publications Kienbock s disease is characterised by progressive
A Case Report of Kienbock s Disease in a Thirteen-Year-Old Girl Campbell NM; Scrimshire AB; Sharpe K March 2017 Volume 13 Issue 1 Doctors Academy Publications Kienbock s disease is characterised by progressive
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Kienbock s Disease in A 23yr Old Male: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Sasikumar K*, Venkatachalam K, Abilash Rinald GS,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Kienbock s Disease in A 23yr Old Male: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Sasikumar K*, Venkatachalam K, Abilash Rinald GS,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35777 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wijffels, Mathieu Mathilde Eugene Title: The clinical and non-clinical aspects
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35777 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wijffels, Mathieu Mathilde Eugene Title: The clinical and non-clinical aspects
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Finite Element Analysis of Osteotomy Treatment for Kienbock s Disease
 J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2016, 9, 161-170 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise ISSN Online: 1937-688X ISSN Print: 1937-6871 Finite Element Analysis of Osteotomy Treatment for Kienbock s Disease
J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2016, 9, 161-170 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise ISSN Online: 1937-688X ISSN Print: 1937-6871 Finite Element Analysis of Osteotomy Treatment for Kienbock s Disease
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane
 I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Abstract Submission Form
 Abstract Submission Form All abstracts must be submitted to the AOCR by September 15 th. All information included must be the original work of the author(s) and be in typed form. Incomplete or handwritten
Abstract Submission Form All abstracts must be submitted to the AOCR by September 15 th. All information included must be the original work of the author(s) and be in typed form. Incomplete or handwritten
COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE
 COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE The carpus Scaphoid fracture Scapholunate ligament tear
COMMON CARPAL INJURIES IN ATHLETES Nicholas A. Bontempo, MD Orthopedic Associates of Hartford I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES TO REPORT OUTLINE The carpus Scaphoid fracture Scapholunate ligament tear
Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature M Suthersan, S Chan Citation M Suthersan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature M Suthersan, S Chan Citation M Suthersan,
Management of Acute Trans Scaphoid Peri-Lunate Fracture Dislocation by Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation
 American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT) Volume 2016, 6 Pages Research Article Abstract: Management of Acute Trans Scaphoid Peri-Lunate Fracture Dislocation by Closed Reduction
American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT) Volume 2016, 6 Pages Research Article Abstract: Management of Acute Trans Scaphoid Peri-Lunate Fracture Dislocation by Closed Reduction
Brain Atrophy. Brain Atrophy
 Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Wrist movements, apart from the distal radioulnar joint, take place in two planes:
 The wrist consists of eight bones in two rows: the proximal and distal. The proximal row includes (starting from the radial bone): the scaphoid bone, the lunate bone, the triangular bone and the postulnar
The wrist consists of eight bones in two rows: the proximal and distal. The proximal row includes (starting from the radial bone): the scaphoid bone, the lunate bone, the triangular bone and the postulnar
Degrees Of Volar Angulation In Distal Radius Fracture Effects Distal Radioulnar Joint Stability:a Biomechanical Study
 Degrees Of Volar Angulation In Distal Radius Fracture Effects Distal Radioulnar Joint Stability:a Biomechanical Study Yuki Bessho, MD, Toshiyasu Nakamura, MD PhD, Takeo Nagura, MD PhD, Yoshimori Kiriyama,
Degrees Of Volar Angulation In Distal Radius Fracture Effects Distal Radioulnar Joint Stability:a Biomechanical Study Yuki Bessho, MD, Toshiyasu Nakamura, MD PhD, Takeo Nagura, MD PhD, Yoshimori Kiriyama,
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when?
 Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Neglected trans-scaphoid trans-styloid volar dislocation of the lunate
 CASE REPORT Neglected trans-scaphoid trans-styloid volar dislocation of the lunate LATE RESULT FOLLOWING OPEN REDUCTION AND K-WIRE FIXATION P. Givissis, A. Christodoulou, B. Chalidis, J. Pournaras From
CASE REPORT Neglected trans-scaphoid trans-styloid volar dislocation of the lunate LATE RESULT FOLLOWING OPEN REDUCTION AND K-WIRE FIXATION P. Givissis, A. Christodoulou, B. Chalidis, J. Pournaras From
Wrist Fusion Instrument and Implant Set.
 Wrist Fusion Instrument and Implant Set. Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0815/0479(2) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Wrist Fusion Instrument and Implant Set. Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0815/0479(2) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Interesting Case Series. Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid
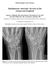 Interesting Case Series Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid Benson J. Pulikkottil, MD, Edward Ruane, MD, Michael E. Scott, DO, Alexandre Philipp Sater, BS, and Joseph E. Imbriglia,
Interesting Case Series Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid Benson J. Pulikkottil, MD, Edward Ruane, MD, Michael E. Scott, DO, Alexandre Philipp Sater, BS, and Joseph E. Imbriglia,
Speaker s Disclosure Statement. Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN. Objectives. Risk Factors
 Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
Biomechanical Comparison of Two Surgical Methods in Treating Stage IIIb Lunate Necrosis
 Clinical Report Chuan Li et al.: Surgical methods for stage IIIb lunate necrosis Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 25[2] (2016) 213-218 2016 The Hard Tissue Biology Network Association Printed in Japan, All
Clinical Report Chuan Li et al.: Surgical methods for stage IIIb lunate necrosis Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 25[2] (2016) 213-218 2016 The Hard Tissue Biology Network Association Printed in Japan, All
Osseous Anatomy. and Microanatomy of the Lunate. Chong Jin Yeo, Gregory Ian Bain, and Egon Perilli. Introduction. Gross Anatomy of the Normal Lunate
 Osseous Anatomy 2 and Microanatomy of the Lunate Chong Jin Yeo, Gregory Ian Bain, and Egon Perilli Introduction The name of the lunate bone derives from the crescent-shaped (Latin: lunatus ), from Latin
Osseous Anatomy 2 and Microanatomy of the Lunate Chong Jin Yeo, Gregory Ian Bain, and Egon Perilli Introduction The name of the lunate bone derives from the crescent-shaped (Latin: lunatus ), from Latin
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Calcium Phosphate Cement
 Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Integra. Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Description... 02 Indications... 02 Contraindications... 02 Surgical Technique... 03 Spider Introduction-Four
Integra Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Description... 02 Indications... 02 Contraindications... 02 Surgical Technique... 03 Spider Introduction-Four
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair. The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
 Michelle Brandt and Megan Passarelle Surgical Assignment Due: 11/9/14 Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair Abstract The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
Michelle Brandt and Megan Passarelle Surgical Assignment Due: 11/9/14 Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair Abstract The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Association between the capitate-triquetrum distance and carpal collapse in scaphoid nonunion
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 36-40 ORIGINAL STUDY Association between the capitate-triquetrum distance and carpal collapse in scaphoid nonunion Anastasios Dimitriadis, George Paraskevas, Panagiotis Kanavaros,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 36-40 ORIGINAL STUDY Association between the capitate-triquetrum distance and carpal collapse in scaphoid nonunion Anastasios Dimitriadis, George Paraskevas, Panagiotis Kanavaros,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
COURSE TITLE: Skeletal Anatomy and Fractures of the Lower Arm, Wrist, and Hand
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
)451( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY. Evaluation of Normal Ranges of Wrist Radiologic Indexes in Mashhad Population
 )451( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY SHORT COMMUNICATION Evaluation of Normal Ranges of Wrist Radiologic Indexes in Mashhad Population Tohid Vaezi, MD; Golnaz Ghayyem Hassankhani,
)451( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY SHORT COMMUNICATION Evaluation of Normal Ranges of Wrist Radiologic Indexes in Mashhad Population Tohid Vaezi, MD; Golnaz Ghayyem Hassankhani,
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
SCAPHOID FRACTURE. Relevant antomy
 SCAPHOID FRACTURE Relevant antomy The proximal row consists of the scaphoid, the lunate, and the triquetrum. The proximal carpal row is regarded as an intercalated segment The keystone in the coordination
SCAPHOID FRACTURE Relevant antomy The proximal row consists of the scaphoid, the lunate, and the triquetrum. The proximal carpal row is regarded as an intercalated segment The keystone in the coordination
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
