Asthma due to aluminium soldering flux
|
|
|
- Sara Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Asthma due to aluminium soldering flux G. M. STERLING From the Respiratory Department, St. George's Hospital, Lonidonl, S.W.] Thorax (1967), 22, 533. Two patients have been studied who complained of dyspnoea after the inhalation of fumes from a new soldering flux recently developed for use in jointing aluminium which has been replacing copper as a material for electric cables. A previous survey of respiratory complaints after the use of this particular flux had failed to show any objective change in lung function, and the present cases are the first to be reported. Both subjects have been investigated by means of serial spirometry, peak flow rates, and body plethysmography following inhalation of small amounts of flux fumes; delayed and prolonged bronchoconstriction has been demonstrated. Similar results have been obtained after the inhalation of one of the main constituents of the flux, namely amino-ethyl ethanolamine, which is presumably the active allergic agent. The bronchial response is unusual in being delayed in onset but otherwise resembles pollen-sensitivity asthma rather than the infiltrative process seen in farmer's lung. The type of immune mechanism involved is speculative, but it is possible that some alteration of the amino-ethyl ethanolamine is needed before it can react with reaginic antibody fixed in the bronchial tissues. Bronchial hypersensitivity to inhaled allergens has been known for a long time to be the cause of asthma in typical pollen-sensitive subjects and is thought to represent an anaphylactic type of reaction between antigen and fixed reaginic antibody which produces almost immediate bronchoconstriction. In the last few years a different, nonobstructive pattern of bronchopulmonary hypersensitivity has been described, in which pulmonary infiltrations occur in association with fever and malaise. The best-known example is the condition of farmer's lung, probably caused by the inhalation of the spores of Thermopolyspora polyspora and other thermophilic fungi (Pepys and Jenkins, 1965). Two subjects have recently been seen with an unusual delayed asthmatic response to fumes of a particular soldering flux: it has been possible to reproduce typical attacks in the laboratory and to identify the causative simple organic compound. CASE HISTORIES CASE 1 Mr. J. B., aged 29, previously well with no history of asthma or other allergy, had worked as a cable jointer's mate for about three years. At the end of 1965 he was promoted to cable jointer and his exposure to flux fumes was increased to about 2 minutes every day. In January 1966 he first developed wheezing dyspnoea, with a productive cough, and was thought to have infective bronchitis with asthma. However, after returning to work his symptoms recurred and this cycle was repeated several times before his admission for investigation in July It was notable that the dyspnoea did not develop until some hours after the exposure to flux fumes, that it was precipitated by increasingly short exposure, and that it lasted for several days. At the time of investigation he was free from symptoms, and on examination no abnormality was found in the respiratory or cardiovascular systems. A chest radiograph, haemoglobin, and white blood count were normal, and respiratory function tests showed no serious airway obstruction, though his F.E.V.1.o/V.C. ratio was rather low at 62%. CASE 2 Mr. E. C., aged 42, also previously well, had been exposed to flux fumes on only two or three occasions before he developed wheezing dyspnoea, again starting a few hours after exposure and lasting several days. He gave a past history of hay-fever and of one previous attack of asthma, possibly associated with the use of another soldering flux, but there was no history of seasonal asthma or other allergy. He was symptom-free at the time of examination, when he was found to be obese but to have no abnormality of the respiratory or cardiovascular systems. His chest radiograph, haemoglobin, and white count were normal, and there was no evidence of airway obstruction on spirometry. MATERIAL AND METHODS ALUMINIUM SOLDERING FLux Aluminium is being used increasingly as a material for electric cables on account of its lightness and cheapness, but it has the disadvantage of forming a tenaceous film 533
2 534 of oxide when heated in the process of soldering, which is the usual way in which underground cables are jointed. Fluxes used in copper jointing have proved unsuitable for use with aluminium, and new ones have been developed. The particular one investigated consists of a mixture of aminoethyl ethanolamine, zinc oxide, and fluoroborate. The exact nature of the chemical reactions that occur when the flux is heated during soldering is not known, but the' fumes contain ammonia, amine vapour, and fluoride and are alkaline in reaction, which makes it unlikely that hydrofluoric acid is present in the free state. It has been shown that the bulk of the fluoride in the fumes is particulate, not gaseous, as it is filterable, and that the main component of the fumes is a mist of unchanged amine (McCann, 1964). In view of this, attention has been directed to amino-ethyl ethanolamine as the most likely constituent of the flux to be the cause of asthma, and the effect of pure amine fumes, as well as of whole flux fumes, has been studied. investigations In view of their suggestive 'histories, the subjects were admitted to hospital for further investigation of their response to the inhalation of flux fumes. An attempt to re-produce working conditions was made by dropping a small quantity of the flux or of pure amino-ethyl ethanolamine on to a heated sheet of aluminium. The subjects then took one to three breaths of the resulting fumes, which they thought were representative of the dose taken during the jointing of a single cable. Similar inhalations were also taken by one normai subject, who acted as a control. Changes in pulmonary function were followed at frequent intervals by three different methods: (1) Peak expiratory flow rate (P.E.F.R.) was measured with a Wright peak flowmeter. (2) Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, vital capacity, and inspiratory capacity (F.E.V.1., V.C., I.C.) were measured with a conventional lightweight spirometer. (3) Airway resistance and functional residual capacity (F.R.C.) were measured with a body plethysmograph. The latter was a constant volume machine of 44 litres capacity similar to that described by DuBois, Botelho, Bedell, Marshall, and Comroe (1956) and DuBois, Botelho, and Comroe (1956). After warming up for two or three minutes, the subjects performed shallow panting at about two breaths per second through a Fleisch pneumotachograph and then continued to make shallow movements against a closed shutter incorporated G. M. Sterling into the mouthpiece and remotely controlled. The F.R.C. was measured by closing the shutter at theend of a normal slow expiration and then instructing the subject to start making shallow panting movements. The vector loops produced by these' manceuvres were displayed on an oscilloscope screen and their slopes were obtained from alignment with parallel lines ruled on a Perspex disc which rotated within a fixed protractor scale in front of the screen. Six successive measurements of airway resistance and panting lung volume (hereafter referred to as thoracic gas volume or TGV) were made, and the mean of the last five was used in calculation. After subtraction of -45 cm. H2/l./sec. for the resistance of the flowmeter and mouthpiece, airway resistance was converted'' to its reciprocal, airway conductance (CA), and divided by the lung volume to give the expression CA/ TGV. In this way a correction was made for the normal effect of lung volume on airway resistance (Nadel and Comroe, '1961). With a little training both subjects were able to produce clear and reproducible slopes, and changes in resistance and lung volume were easy to follow. The use of the body plethysmograph enabled absolute changes in airway resistance to be followed and to be compared with changes in P.E.F.R. and F.E.V., which are less precise but more convenient ways of assessing bronchial obstruction. It was also possible to follow changes in lung volume during asthma (Woolcock and Read, 1965, 1966), and it is hoped to report these results separately. In addition to the inhalation tests, skin, scratch, and prick tests were performed with dilutions of flux and amino-ethyl ethanolamine. RESULTS Peak flow, F.E.V.1 V and CA/TGV were all measured at frequent intervals to start with and the results were compared. It was found (Fig. 1) that they agreed well, and, in particular, P.E.F.R. was vindicated as a means of following changes in airway resistance. In view of the simplicity of the method it was the one used most frequently, though the others were also used when specifically wanted. Case 1 was tested by the inhalation of flux fumes on three occasions and showed a consistent response of delayed bronchoconstriction, which started two to three hours after exposure to the fumes and lasted for several days. Typical acute and long-term responses are illustrated in Figs 2
3 E F.E.V.1., FluxI Amino- ethyl Ethanolamine I Isoprenaline Asthma due to aluminium soldering flux renaline and 3, where changes in peak flow have been followed after the inhalation of flux fumes. Symptomatically he developed severe asthma with a troublesome cough but little sputum. On a fourth occasion he was tested with fumes of pure 1. amino-ethyl ethanolamine and again showed a delayed asthmatic response with a similar time 8 course to that seen after the inhalation of whole Nx flux fumes. Examination revealed widespread \ \ ~ Ob 6 wheezing but no crepitations, and he did not o 4 c) develop a fever or malaise. His chest radiograph < remained normal throughout, and his white blood x count showed a slight eosinophilia, which reached o-2 a maximum of 6% of 7,7 (462/mm.3). ~X L. -o Skin testing with standard allergens was negaloam I1 12 Ipm tive, and scratch and prick tests with dilutions of Ti me flux and amino-ethyl ethanolamine caused no FIG. 1. Case 1. Comparative changes in CA/TG V, immediate, intermediate, or delayed reactions. and P.E.F.R. after inhakcation offlux fumes. Case 2 was studied on two occasions, first with.e Lj c: 4... whole flux fumes and secondly with pure aminoethyl ethanolamine fumes. Before inhalation his resting lung function tests were normal and repeatable, and after inhalation he showed a j response very similar to that of Case 1 with a latent period of about three hours followed by a severe bronchoconstriction lasting several days. This was temporarily reversible with isoprenaline aerosol, and to a lesser extent with atropine, and o / again the effect of pure amino-ethyl ethanolamine "_,o mimicked that of whole flux (Figs 4 and 5). Scratch and prick tests with flux and amine give no immediate or delayed responses, and the chest radiograph showed no change. Carbon monoxide -2 -I b 7 uptake was measured by the 'steady-state' method Hours after inhalation at the height of the asthma and was normal. A FIG. 2. Case 1. Changes in P.E.F.R. after inhalation of moderate blood eosinophilia developed (Table) whole flux fumes (closed circles) an, rd amino-ethyl ethanol- and 8% of the leucocytes in the sputum were amine fumes (open circles). eosinophils. C- EI Iw~" lw TABLE Total Eosinophils E.S.R. (Win- (mm./hr) / E miiimc rrun.3 s ~~~~~trobe) W.B.C./ mm.b per Before inhalation 8, Days after amine fumes: 1 8, ,8 14 1, , r ). Inhalation of these fumes by one normal subo~j~l,, ject caused minimal immediate bronchoconstric- I tion, detectable only with the body plethysmo- Days graph, and no delayed response. Skin tests with FIG. 3. Case 1. Changes in P.E.F.R. over four days after dilute solutions of flux and amino-ethyl ethanolinhalation offlux fumes. amine were all negative. 2U 535
4 536 U- LaI 2 1 inhalation G. M. Sterling Both thee subjects investigated here regularly slight, brief, immediate bronchoconstriction could develope( d severe asthma some hours after the be detected by the body plethysmograph (a more inhalatio, n of fumes of whole soldering flux or sensitive instrument than the peak flowmeter), but pure amiino-ethyl ethanolamine. Since aluminium it is probable that this was a non-specific reaction is 6b 4 3* 1. FIG. 4. C becon material, hazard, McCann unlikely gated abi awhen aluminium was used in roughly Whatever the mechanism of flux asthma, the I of jointing operations and found only active agent seems to be the organic constituent, )ious case of bronchial sensitivity to amino-ethyl ethanolamine, inhalation of which soldering flux fumes. By now, many more men provoked attacks very similar to those which must be; at risk, but the present two cases are the followed whole-flux fumes. The bronchoconstricto be described. tion could be largely reversed by the inhalation first ones of at a time one-third one dub Flux Isoprenaline The mechanism of the asthma is presumably allergic rather than toxic, since it is so rare and. -ooo~o\ can be provoked by very small doses of fume. \ \ t The reaction resembles pollen-sensitivity asthma in consisting of bronchoconstriction and eosino- philia without radiographic changes or impair- "6 o _ ment of gas transfer, but it is unusual in its late t t o onset, several hours after the inhalation of the Amino-ethyl Isoprenaline provoking material. Usually allergic asthma is Ethanolamine thought to be an anaphylactic type of reaction due to a combination of the challenging antigen with O i b 7 8 fixed reaginic antibodies in the bronchial tissues Hours after inhalation (Coombs and Gell, 1963) and comes on within a few minutes. However, a biphasic response may- 'ase 2. Changes in P.E.F.R. after inhalation of occur, consisting of mild immediate broncho- white flux fumes (closed circles) and amino-ethyl ethanol- constriction, which becomes more severe after a aminie fumo!es (open circles). few hours, and it is just possible that mild pure delayed asthma may have been missed in the past if patients have not been followed for several E U- U~ CL Flux Isoprenaline hours after a test inhalation. Typical delayed pulmonary hypersensitivity of Days the type seen in farmer's lung or bird-breeder's lung (Hargreave, Pepys, Longbottom, and Wraith, 1966) differs from allergic asthma in presenting with fever, malaise, and pulmonary infiltrations, but not bronchoconstriction, and is usually associated with precipitating antibodies and a positive Arthus-type skin reaction. Thus the response described in the present, cases was most like pollen asthma, but unusual features were the delay in onset and the absence of any immediate skin reactions, though the latter do not always correlate well with bronchial base 2. Changes in P.E.F.R. over four days after reactivity even in established pollen sensitivity. offlux fumes. The cause for the delay is quite speculative, but possibly some alteration of the amino-ethyl ethanolamine is necessary before it acts as an DISCUSSION antigen and can combine with antibody fixed on the bronchial cells. In fact, in Case 2 a very ning increasingly popular as a cable to an inhaled irritant since it resembled that seen this represents a potential industrial after the inhalation of carbon particles (Widdibut a previous large-scale study by combe, Kent, and Nadel, 1962) or cigarette smoke (1964) suggested that the problem was (Nadel and Comroe, 1961), and also occurred in to be numerically serious. She investi- one normal control who developed no delayed out 3, cable jointers and their mates reaction.
5 isoprenaline in the early stages of an attack, but atropine was considerably less effective: this suggests that the constriction is mainly due to direct action rather than to a vagal reflex initiated by irritation of tracheobronchial receptors. I wish to thank Dr. J. C. Batten for his interest and encouragement, Dr. J. Pepys, of the Brompton Hospital, who referred the second subject for investigation and advised on allergic responses, and Miss F. A. Boother for her help in carrying out many of the tests. This study was supported by a research grant from the Board of Governors, St. George's Hospital, London, S.W.I. REFERENCES Coombs, R. R. A., and Gell, P. G. H. (1963). In Clinical Aspects of Immunology, ed. P. G. H. Gell and R. R. A. Coombs, p Blackwell, Oxford. Asthma due to aluminium soldering flux 537 DuBois, A. B., Botelho, S. Y., Bedell, G. N.. Marshall, R., and Comroe, J. H., Jr. (1956). A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume. J. clin. Invest., 35, 322. and Comroe, J. H., Jr. (1956). A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph. Ibid., 35, 327. Hargreave, F. E., Pepys, J., Longbottom, J. L., and Wraith, D. G. (1966). Bird breeder's (fancier's) lung. Lancet, 1, 445. McCann, Joan K. (1964). Health hazard from flux used in joining aluminium electricity cables. Ann. occup. Hyg., 7, 261. Nadel, J. A., and Comroe, J. H., Jr. (1961). Acute effects of inhalation of cigarette smoke on airway conductance. J. appl. Physiol., 16, 713. Pepys, J., and Jenkins, P. A. (1965). Precipitin (F.L.H.) test in farmer's lung. Thorax, 2, 21. Widdicombe, J. G., Kent, D. C., and Nadel, J. A. (1962). Mechanism ofbronchoconstriction during inhalation of dust. J. appl. Physiol., 17, 613. Woolcock, Ann J., and Read, J. (1965). Improvement in bronchial asthma not reflected in forced expiratory volume. Lancet, 2, (1966). Lung volumes in exacerbations of asthma. Amer. J. Med., 41, 259. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 November Downloaded from on 7 November 218 by guest. Protected by
FEVI before (5% predicted) 62 (49-77) 59 (44-77) FEV, after (% predicted) 92 (84-108) 89 (69-107) to the entire group received aerosol isoprenaline.
 Tl.orax, 1980, 35, 298-302 Lung elastic recoil and reduced airflow in clinically stable asthma D S McCARTHY AND M SIGURDSON From the Department of Medicine, University ofmanitoba, Respiratory Division,
Tl.orax, 1980, 35, 298-302 Lung elastic recoil and reduced airflow in clinically stable asthma D S McCARTHY AND M SIGURDSON From the Department of Medicine, University ofmanitoba, Respiratory Division,
Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 401-405 Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows P. W. LORD AND J. M. EDWARDS From the MRC Toxicology Unit, Clinical Section, St. Bartholomew's Hlospital
Thorax, 1978, 33, 401-405 Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows P. W. LORD AND J. M. EDWARDS From the MRC Toxicology Unit, Clinical Section, St. Bartholomew's Hlospital
controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction.
 Thorax (1974), 29, 401. A controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction J. A. EVANS', I. M. MORRISON2, and K. B. SAUNDERS3 Departments of Medicine and of Thoracic
Thorax (1974), 29, 401. A controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction J. A. EVANS', I. M. MORRISON2, and K. B. SAUNDERS3 Departments of Medicine and of Thoracic
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
Bronchoconstriction in potroom workers
 British Journal of Inidustrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 211-215 M. SARIC, E. ZUSKIN*, AND M. GOMZI From the Institute for Meclical Research and Occupational Health, Zagreb and the *Andrija Stampar School of
British Journal of Inidustrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 211-215 M. SARIC, E. ZUSKIN*, AND M. GOMZI From the Institute for Meclical Research and Occupational Health, Zagreb and the *Andrija Stampar School of
Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung
 Thorax (1969X, 24, 374. Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung P. DINDA, S. S. CHATTERJEE, AND W. D. RIDING From Baguley Hospital, Manchester Pulmonary function studies were performed at the
Thorax (1969X, 24, 374. Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung P. DINDA, S. S. CHATTERJEE, AND W. D. RIDING From Baguley Hospital, Manchester Pulmonary function studies were performed at the
PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 698. PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS THE MECHANISMS of industrial pulmonary disease due to the inhalation of organic dusts are not well
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 698. PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS THE MECHANISMS of industrial pulmonary disease due to the inhalation of organic dusts are not well
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Influences of Suggestion on Airway Reactivity in Asthmatic Subjects
 Influences of Suggestion on Airway Reactivity in Asthmatic Subjects THOMAS LUPARELLO, M.D., HAROLD A. LYONS, M.D., EUGENE R. BLEECKER, B.A., and E. R. McFADDEN, Jn., M.D. The effect of suggestion on bronchomotor
Influences of Suggestion on Airway Reactivity in Asthmatic Subjects THOMAS LUPARELLO, M.D., HAROLD A. LYONS, M.D., EUGENE R. BLEECKER, B.A., and E. R. McFADDEN, Jn., M.D. The effect of suggestion on bronchomotor
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma
 Thorax (1976), 31, 428. Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma D. P. JONES, S. A. O'CONNOR, J. V. COLLINS, and B. W. WATSON Departments of Medicine and Medical Electronics,
Thorax (1976), 31, 428. Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma D. P. JONES, S. A. O'CONNOR, J. V. COLLINS, and B. W. WATSON Departments of Medicine and Medical Electronics,
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Mushroom worker's lung
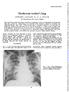 Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 355. Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis GILLIAN DAY* and MARGARET B. MEARNS From Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London Day, G., and Mearns, M. (1973).
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 355. Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis GILLIAN DAY* and MARGARET B. MEARNS From Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London Day, G., and Mearns, M. (1973).
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PomPom SHOOTER. Activity Background: Common Obstructive Lung Disorders:
 CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma
 Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD
 COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. Purposes of Pulmonary Tests. General Categories of Lung Diseases. Types of PF Tests
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
THE FORCED EXPIRATORY VOLUME AFTER EXERCISE,
 Thorax (1959), 14, 161. THE FORCED EXPIRATORY VOLUME AFTER EXERCISE, FORCED INSPIRATION, AND THE VALSALVA AND MULLER MAN(EUVRES BY L. H. CAPEL AND J. SMART From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR
Thorax (1959), 14, 161. THE FORCED EXPIRATORY VOLUME AFTER EXERCISE, FORCED INSPIRATION, AND THE VALSALVA AND MULLER MAN(EUVRES BY L. H. CAPEL AND J. SMART From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA
 ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
normal and asthmatic males
 Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
Schlueter et al., 1969). The object of this study. was to investigate by measurements of lung. mechanics the nature of airflow obstruction in
 Mechanical properties of the lung in extrinsic allergic alveolitis1 C. P. W. WARREN, K. S. TSE, AND R. M. CHERNIACK Thorax, 1978, 33, 315-321 From the Departments of Medicine and Immunology, University
Mechanical properties of the lung in extrinsic allergic alveolitis1 C. P. W. WARREN, K. S. TSE, AND R. M. CHERNIACK Thorax, 1978, 33, 315-321 From the Departments of Medicine and Immunology, University
FACTS. Health hazards by inhaling and exposure to soldering. For better workbench environment
 FACTS Health hazards by inhaling and exposure to soldering For better workbench environment FILTRONIC AB Box 2284, SE-531 02 LIDKÖPING Tel +46 510 208 10, Fax +46 510 201 40 e-mail: office@filtronic.se
FACTS Health hazards by inhaling and exposure to soldering For better workbench environment FILTRONIC AB Box 2284, SE-531 02 LIDKÖPING Tel +46 510 208 10, Fax +46 510 201 40 e-mail: office@filtronic.se
Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology
 Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing. Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum deflation. Total lung capacity at maximum inflation
 r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
polyvinylchloride dust
 Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Environmental Triggers of Asthma. Gaynor Govias BSc BEd CAI
 Environmental Triggers of Asthma Gaynor Govias BSc BEd CAI Environmental Triggers of Asthma Third Edition Gaynor Govias, B. Sc., B. Ed., CAI Gaynor D. Govias Environmental Triggers of Asthma Third edition
Environmental Triggers of Asthma Gaynor Govias BSc BEd CAI Environmental Triggers of Asthma Third Edition Gaynor Govias, B. Sc., B. Ed., CAI Gaynor D. Govias Environmental Triggers of Asthma Third edition
The Effect of Environmental Temperature on Airway Resistance in the Asthmatic Child
 Pediat. Res. 7: 627-631 (1973) Asthma nasopharynx bronchoconstriction resistance, airway cold sensitivity The Effect of Environmental Temperature on Airway Resistance in the Asthmatic Child FRANK RODRIGUEZ-MARTINEZ,
Pediat. Res. 7: 627-631 (1973) Asthma nasopharynx bronchoconstriction resistance, airway cold sensitivity The Effect of Environmental Temperature on Airway Resistance in the Asthmatic Child FRANK RODRIGUEZ-MARTINEZ,
Coexistence of confirmed obstruction in spirometry and restriction in body plethysmography, e.g.: COPD + pulmonary fibrosis
 Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids
 Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY. A. Definition of Spirometry
 UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
Pulmo-Park Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D
 Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
Enzyme Safety Management: Thanks for joining us today!
 Enzyme Safety Management: Thanks for joining us today!.the webinar will begin shortly. The webinar will be recorded. Please make sure to be on mute so that we can ensure a good quality of the audio. 1
Enzyme Safety Management: Thanks for joining us today!.the webinar will begin shortly. The webinar will be recorded. Please make sure to be on mute so that we can ensure a good quality of the audio. 1
Evaluation of two techniques for measurement of respiratory resistance by forced oscillation A study in young subjects with obstructive lung disease
 Thorax (1973), 28, 136. Evaluation of two techniques for measurement of respiratory resistance by forced oscillation study in young subjects with obstructive lung disease L. I. LNDU and P. D. PHELN Clinical
Thorax (1973), 28, 136. Evaluation of two techniques for measurement of respiratory resistance by forced oscillation study in young subjects with obstructive lung disease L. I. LNDU and P. D. PHELN Clinical
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Respiratory Health L O O K, F E E L A N D L I V E B E T T E R
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1978, 53, 873-877 Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability M. SILVERMAN, F. D. R. HOBBS, I. R. S. GORDON, AND F. CARSWELL From the Departments of Child Health and
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1978, 53, 873-877 Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability M. SILVERMAN, F. D. R. HOBBS, I. R. S. GORDON, AND F. CARSWELL From the Departments of Child Health and
Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 762-766 Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate M G HARRIES, P SHERWOOD BURGE, M SAMSON, A J NEWMAN TAYLOR, AND J PEPYS From the Brompton Hospital,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 762-766 Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate M G HARRIES, P SHERWOOD BURGE, M SAMSON, A J NEWMAN TAYLOR, AND J PEPYS From the Brompton Hospital,
A New Look At Asthma
 nhsmanagers.net Briefing 23 May 2016 Medicine for Managers Dr Paul Lambden BSc MB BS BDS FDSRCSEng MRCS LRCP DRCOG MHSM FRSH A New Look At Asthma Probably everyone knows that asthma is an increasingly
nhsmanagers.net Briefing 23 May 2016 Medicine for Managers Dr Paul Lambden BSc MB BS BDS FDSRCSEng MRCS LRCP DRCOG MHSM FRSH A New Look At Asthma Probably everyone knows that asthma is an increasingly
Basic approach to PFT interpretation. Dr. Giulio Dominelli BSc, MD, FRCPC Kelowna Respiratory and Allergy Clinic
 Basic approach to PFT interpretation Dr. Giulio Dominelli BSc, MD, FRCPC Kelowna Respiratory and Allergy Clinic Disclosures Received honorarium from Astra Zeneca for education presentations Tasked Asked
Basic approach to PFT interpretation Dr. Giulio Dominelli BSc, MD, FRCPC Kelowna Respiratory and Allergy Clinic Disclosures Received honorarium from Astra Zeneca for education presentations Tasked Asked
responsiveness in asthmatic patients and smokers
 63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
Chapter 3. Pulmonary Function Study Assessments. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
People with asthma who smoke. The combination of asthma, a chronic airway disease, and smoking increases the risk of COPD even more.
 COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement
 Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Exercise and Air Pollution
 Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans
 The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans A. Neuhaus, M.D., D. Markowitz, M.D., H. H. Rotman, M.D., and John G. Weg, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans A. Neuhaus, M.D., D. Markowitz, M.D., H. H. Rotman, M.D., and John G. Weg, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
bronchoconstriction Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced Thorax, 1978, 33,
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 700-704 Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction S G NOGRADY AND C BEVAN From the Welsh National School of Medicine
Thorax, 1978, 33, 700-704 Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction S G NOGRADY AND C BEVAN From the Welsh National School of Medicine
Pulmonary Pearls. Medical Pearls. Case 1: Case 1 (cont.): Case 1: What is the Most Likely Diagnosis? Case 1 (cont.):
 Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Inspiratory crackles-early and late
 Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
CHRONIC COUGH AS THE PRESENTING MANIFESTATION OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
 CHRONIC COUGH AS THE PRESENTING MANIFESTATION OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA T C Goh Dept of Medicine Toa Payoh Hospital Singapore 1129 T C Goh, MBBS, MRCP (UK), AM Registrar SYNOPSIS Bronchial asthma may present
CHRONIC COUGH AS THE PRESENTING MANIFESTATION OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA T C Goh Dept of Medicine Toa Payoh Hospital Singapore 1129 T C Goh, MBBS, MRCP (UK), AM Registrar SYNOPSIS Bronchial asthma may present
Time factor in the measurement of response
 Thorax (1967), 22, 538. Time factor in the measurement of response to bronchodilators G. J. MUSHIN From Pritnce Heairv's Hospital, Melbournie, A ustralia Trhe measurement of response to bronchodilators
Thorax (1967), 22, 538. Time factor in the measurement of response to bronchodilators G. J. MUSHIN From Pritnce Heairv's Hospital, Melbournie, A ustralia Trhe measurement of response to bronchodilators
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values
 PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
Hazardous Substances
 1 9 x Which strains and pollutants is the lung subject to while working? x How do possible strains and pollutants affect us? 2 9 Potential danger Aerosols are extremely fine AIRBORNE particles as solid
1 9 x Which strains and pollutants is the lung subject to while working? x How do possible strains and pollutants affect us? 2 9 Potential danger Aerosols are extremely fine AIRBORNE particles as solid
Physiology lab (RS) First : Spirometry. ** Objectives :-
 Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
THE SOUTH AFRICAN SOCIETY OF OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE
 THE SOUTH AFRICAN SOCIETY OF OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE SPIROMETRY IN INDUSTRY SASOM GUIDELINE ISBN: ISBN: 978-1-919727-72-1 2011 by SASOM All rights are reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
THE SOUTH AFRICAN SOCIETY OF OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE SPIROMETRY IN INDUSTRY SASOM GUIDELINE ISBN: ISBN: 978-1-919727-72-1 2011 by SASOM All rights are reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution?
 What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution? Dr. Judy Guernsey Department of Community Health and Epidemiology Dalhousie University Nova Scotia Department of Environment and Labour Outdoor Air Quality
What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution? Dr. Judy Guernsey Department of Community Health and Epidemiology Dalhousie University Nova Scotia Department of Environment and Labour Outdoor Air Quality
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO
 ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
Occupational asthma. Dr Gordon Parker NHS. Consultant / Honorary Lecturer in Occupational Medicine. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
 Occupational asthma Dr Gordon Parker Consultant / Honorary Lecturer in Occupational Medicine Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS The good old bad old days Coal workers pneumoconiosis
Occupational asthma Dr Gordon Parker Consultant / Honorary Lecturer in Occupational Medicine Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS The good old bad old days Coal workers pneumoconiosis
Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy
 Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers
 Thorax 1982;37:751-755 Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Cardiothoracic Centre,
Thorax 1982;37:751-755 Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Cardiothoracic Centre,
Nocturnal and morning asthma
 Thorax (1975), 30, 436. Nocturnal and morning asthma Relationship to plasma corticosteroids and response to cortisol infusion C. A. SOUTAR, J. COSTELLO, 0. IJADUOLA, and M. TURNER-WARWICK Cardiothoracic
Thorax (1975), 30, 436. Nocturnal and morning asthma Relationship to plasma corticosteroids and response to cortisol infusion C. A. SOUTAR, J. COSTELLO, 0. IJADUOLA, and M. TURNER-WARWICK Cardiothoracic
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
Revised Protocol: Criteria for Designating Substances as. Occupational Asthmagens on the AOEC List of. Exposure Codes
 Revised Protocol: Criteria for Designating Substances as Occupational Asthmagens on the AOEC List of Exposure Codes Revised September 2008 1 I. Introduction This is a project to evaluate the current AOEC
Revised Protocol: Criteria for Designating Substances as Occupational Asthmagens on the AOEC List of Exposure Codes Revised September 2008 1 I. Introduction This is a project to evaluate the current AOEC
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER. Respiratory Health
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER Respiratory Health Respiratory health: hay fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER Respiratory Health Respiratory health: hay fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A breathtaking condition
 1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
Maximal expiratory flow rates (MEFR) measured. Maximal Inspiratory Flow Rates in Patients With COPD*
 Maximal Inspiratory Flow Rates in Patients With COPD* Dan Stănescu, MD, PhD; Claude Veriter, MA; and Karel P. Van de Woestijne, MD, PhD Objectives: To assess the relevance of maximal inspiratory flow rates
Maximal Inspiratory Flow Rates in Patients With COPD* Dan Stănescu, MD, PhD; Claude Veriter, MA; and Karel P. Van de Woestijne, MD, PhD Objectives: To assess the relevance of maximal inspiratory flow rates
Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample of Children
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Allergy Volume 2011, Article ID 170989, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/170989 Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Allergy Volume 2011, Article ID 170989, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/170989 Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 882. Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children M. SILVERMAN and SANDRA D. ANDERSON with the assistance of Tina Andrea From the Department of Paediatrics,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 882. Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children M. SILVERMAN and SANDRA D. ANDERSON with the assistance of Tina Andrea From the Department of Paediatrics,
Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
 20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
Pattern of breathing during cigarette smoking
 Clinical Science (198 I) 61,85-90 85 Pattern of breathing during cigarette smoking P. J. REES AND T. J. H. CLARK Respiratory Function Unit, Guy's Hospital, London (Received I4 April115 December 1980; accepted
Clinical Science (198 I) 61,85-90 85 Pattern of breathing during cigarette smoking P. J. REES AND T. J. H. CLARK Respiratory Function Unit, Guy's Hospital, London (Received I4 April115 December 1980; accepted
spontaneously or under optimum treatment (2,3). Asthma can be classify as early onset or
 The importance of post exercise peak expiratory flow rate & plasma IgE as a diagnostic tests for Mossa M. Marbut*, Jawad Ali Salih*, Abdul- Ghani M. Al-Samarai**. * Department of physiology, College of
The importance of post exercise peak expiratory flow rate & plasma IgE as a diagnostic tests for Mossa M. Marbut*, Jawad Ali Salih*, Abdul- Ghani M. Al-Samarai**. * Department of physiology, College of
Interpreting pulmonary function tests: Recognize the pattern, and the diagnosis will follow
 REVIEW FEYROUZ AL-ASHKAR, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, The Cleveland Clinic REENA MEHRA, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University Hospitals, Cleveland PETER J. MAZZONE,
REVIEW FEYROUZ AL-ASHKAR, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, The Cleveland Clinic REENA MEHRA, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University Hospitals, Cleveland PETER J. MAZZONE,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
